Kinetics and Solid Effect Investigations During Oil Droplet Desorption from Oil-Contaminated Soil Using the Chemical Cleaning Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Kinetics of Oil Droplet Desorption from Oil-Contaminated Soil
2.2. Deoiling from Oil-Contaminated Soil
2.2.1. Effect of CDG on De
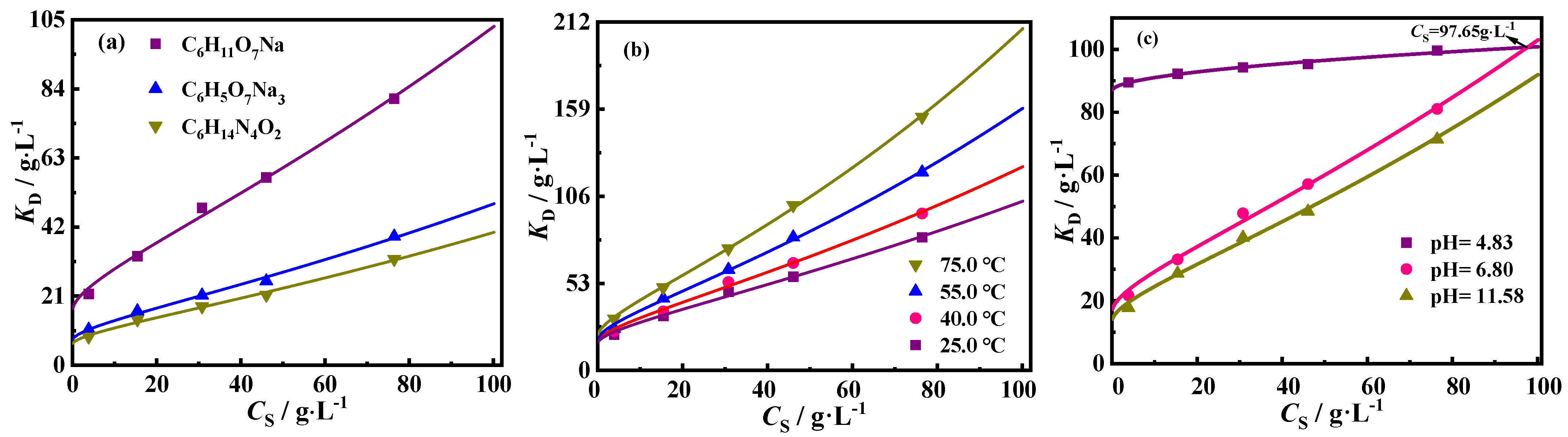
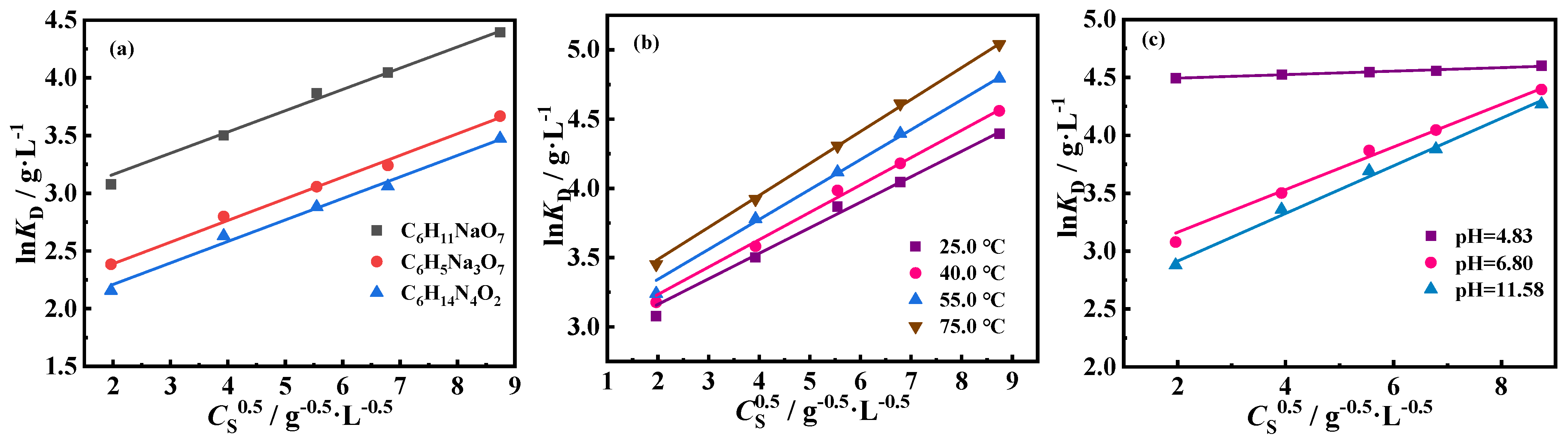
2.2.2. Effects of CS and Temperature on De
2.2.3. Effect of pH Value of Detergent Aqueous Solution on De
2.3. Deoiling Data Analysis Using the SCA Model
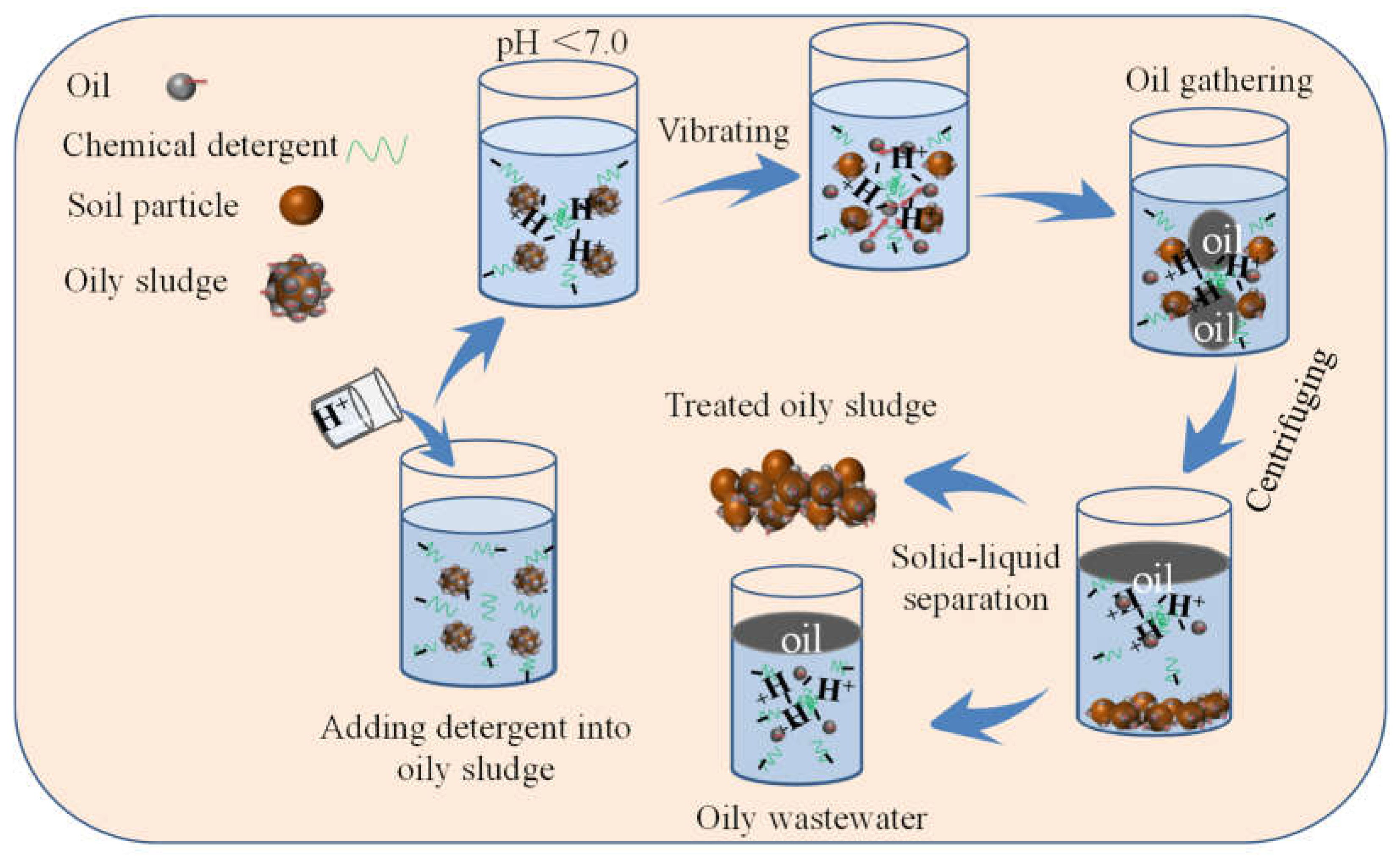
3. Experiments
3.1. Materials
3.2. Deoiling Tests
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hui, K.; Tang, J.; Lu, H.; Xi, B.; Qu, C.; Li, J. Status and prospect of oil recovery from oily sludge: A review. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 6523–6543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Zhao, L.; Hou, W. Solid effect in chemical cleaning treatment of oily sludge. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 522, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, O.A.; Affam, A.C. Petroleum sludge treatment and disposal: A review. Environ. Eng. Res. 2018, 24, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murungi, P.I.; Sulaimon, A.A. Petroleum sludge treatment and disposal techniques: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 40358–40372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Hu, X.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, P.; Guo, H.; You, Y.; Liu, Z. Response surface methodology for the optimization of the ultrasonic-assisted rhamnolipid treatment of oily sludge. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 102971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Chen, W.; Hou, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, W.; Christie, P.; Luo, Y. Hydrogen peroxide combined with surfactant leaching and microbial community recovery from oil sludge. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Sun, L.; Kang, J. Experimental study on the chemical cleaning technology of oil sludge in offshore oil tank. Fresen. Environ. Bull. 2020, 29, 544–550. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Doury, M.M.I. Treatment of oily sludge produced from Baiji oil refineries using surfactants. Petrol. Sci. Technol. 2019, 37, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, D.; Collins, C.D. Maximisation of oil recovery from an oil-water separator sludge: Influence of type, concentration, and application ratio of surfactants. Waste Manag. 2018, 82, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Zhao, L.; Du, N.; Li, H.; Hou, W. Solid effect in solvent extraction treatment of pre-treated oily sludge. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 130, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Lin, Z.; Tan, J.; Hu, L.; Zhang, T. Application of hydrophobic ionic liquid in solvent extraction for oily sludge. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 28, 2294–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; McGill, W.B.; Whitcombe, T.W.; Li, J. Ionic liquid-enhanced solvent extraction for oil recovery from oily sludge. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 3429–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Wang, X.; Liu, D.; Li, Z.; Guo, S.; Zhu, W.; Shi, N.; Wen, F.; Dong, J. Insight into essential channel effect of pore structures and hydrogen bonds on the solvent extraction of oily sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 121826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taiwo, E.A.; Otolorin, J.A. Oil recovery from petroleum sludge by solvent extraction. Petrol. Sci. Technol. 2009, 27, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubaidy, E.A.H.; Abouelnasr, D.M. Fuel recovery from waste oily sludge using solvent extraction. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2010, 88, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, B.; Zhu, W.; Zhong, J.; Chen, L.; Lin, N.; Wang, C.; Chen, S.; Li, Z. Mechanism of separation and removal of water from oily sludge using liquid dimethyl ether to dissolve hydrocarbons. Chemosphere 2021, 279, 130452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Han, X.; Huang, Q.; Ma, Z.; Chi, Y.; Yan, J. Characterization and migration of oil and solids in oily sludge during centrifugation. Environ. Technol. 2018, 39, 1350–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, S. Solid-liquid separation capacity in centrifuges. Chem. Eng. 2020, 127, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva, D.C.; Lucas, C.R.D.; Juviniano, H.B.D.; Moura, M.C.P.D.; Dantas, T.N.D.; Neto, A.A.D. Analysis of the use of microemulsion systems to treat petroleum sludge from a water flotation unit. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, C.; Yang, X.; Huang, Y.; Bai, Z.; Xu, X. Oil droplet movement and micro-flow characteristics during interaction process between gas bubble and oil droplet in flotation. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 45, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Jiang, H.; You, Y.; Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Qi, H. Mechanism of magnetic nanoparticle enhanced microwave pyrolysis for oily sludge. Energies 2022, 15, 1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Tariq, R.; Naqvi, S.R.; Khoja, A.H.; Mehran, M.T.; Naqvi, M.; Gao, N. Kinetic and thermodynamic analyses of dried oily sludge pyrolysis. J. Energy Inst. 2021, 95, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Wei, X.; Chen, S. Continuous pyrolysis technology for oily sludge treatment in the chain-slap conveyors. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Thring, R.W.; Hu, X.; Song, X. Oil recovery from refinery oily sludge via ultrasound and freeze/thaw. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 203, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean, D.S.; Lee, D.J.; Wu, J.C.S. Separation of oil from oily sludge by freezing and thawing. Water Res. 1999, 33, 1756–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; He, G. Separation of water and oil from water-in-oil emulsion by freeze/thaw method. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2003, 31, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaković, V.; Skala, D. Separation of water-in-oil emulsions by freeze/thaw method and microwave radiation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 49, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; He, G.; Li, X.; Peng, L.; Dong, C.; Gu, S.; Xiao, G. Freeze/thaw induced demulsification of water-in-oil emulsions with loosely packed droplets. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 56, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Coupland, J.N. Factors affecting the freeze-thaw stability of emulsions. Food Hydrocolloid. 2008, 22, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Gong, H.; He, Z.; Zhang, P.; He, L. Research on mechanism and characteristics of oil recovery from oily sludge in ultrasonic fields. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 399, 123137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Xu, F.; Wang, L.; Hu, L.; Zhu, L.; Tan, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, T. Characterization of oil component and solid particle of oily sludge treated by surfactant-assisted ultrasonication. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 34, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zheng, Z.; He, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, R.; Chen, Q. Oily sludge treatment in subcritical and supercritical water: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 433, 128761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.K.; Cahyadi, H.S.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, J. Efficient oil recovery from highly stable toxic oily sludge using supercritical water. Fuel 2019, 235, 460–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.L.; Tsai, C.H.; Jou, C.J.G. Energy and resource utilization of refining industry oil sludge by microwave treatment. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Song, Z.; Yu, J.; Su, Y.; Zhao, X.; Sun, J.; Mao, Y.; Wang, W. Study on the demulsification of refinery oily sludge enhanced by microwave irradiation. Fuel 2020, 279, 118417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, H.; Jiang, Z.; Song, Y.; Zhang, T.; Siyal, A.A.; Dai, J.; Bi, X.; Fu, J.; Ao, W.; et al. Microwave pyrolysis of oily sludge under different control modes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; He, L.; Zhang, K. Study on transient kinetics and parameter optimization of degradation of oily sludge by bioreactor. Biochem. Eng. J. 2020, 159, 107581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Lin, J.; Wang, Q. A clean production process on oily sludge with a novel collaborative process via integrating multiple approaches. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 322, 128983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivagami, K.; Anand, D.; Divyapriya, G.; Nambi, I. Treatment of petroleum oil spill sludge using the combined ultrasound and Fenton oxidation process. Ultrason Sonochem. 2019, 51, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Lin, J. Enhancing anaerobic degradation of oily sludge using subcritical hydrothermal pretreatment. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 130, 1582–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Duan, Y.; Li, Z.; Quan, C.; Yoshikawa, K. Hydrothermal treatment combined with in-situ mechanical compression for floated oily sludge dewatering. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 124173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Liang, J.; Li, Q.; Hao, C.; Zhang, L.; Zha, W.; Wang, L.; Ma, X.; Ma, H. Solid effect during magnetic demulsification of diluted waste cutting fluid. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 577, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Hou, W. The effect of sorbent concentration on the partition coefficient of pollutants between aqueous and particulate phases. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 396, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Song, S.; Du, N.; Hou, W. A sorbent concentration-dependent Freundlich isotherm. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2012, 291, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Toro, D.M.; Mahony, J.D.; Kirchgraber, P.R.; O’Byrne, A.L.; Pasquale, L.R.; Piccirilli, D.C. Effects of nonreversibility, particle concentration, and ionic strength on heavy-metal sorption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1986, 20, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Liss, P.S. Metastable-equilibrium adsorption theory I, theoretical. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 1998, 201, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmy, A.K.; Ferreiro, E.A.; De Bussetti, S.G. Effect of particle association on 2,2-bipyridyl adsorption onto kaolinite. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2000, 225, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.W.; Wang, M.K. Assessment of sorbent/water ratio effect on adsorption using dimensional analysis and batch experiments. Chemosphere 2002, 48, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahmasebpour, R.; Peighambardoust, S.J. Decontamination of tetracycline from aqueous solution using activated carbon/Fe3O4/ZIF-8 nanocomposite adsorbent. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 343, 127188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Austad, T. Wettability and oil recovery from carbonates: Effects of temperature and potential determining ions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2006, 279, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babadagli, T. Temperature effect on heavy-oil recovery by imbibition in fractured reservoirs. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 1996, 14, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.S.; Lai, D.M.C.; Chang, B.K.L.; Klaila, W.J. Oil recovery and waste reduction by microwave radiation. Environ. Prog. 1989, 8, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Otoom, A.; Allawzi, M.; Al-Omari, N.; Al-Hsienat, E. Bitumen recovery from Jordanian oil sand by froth flotation using petroleum cycles oil cuts. Energy 2010, 35, 4217–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
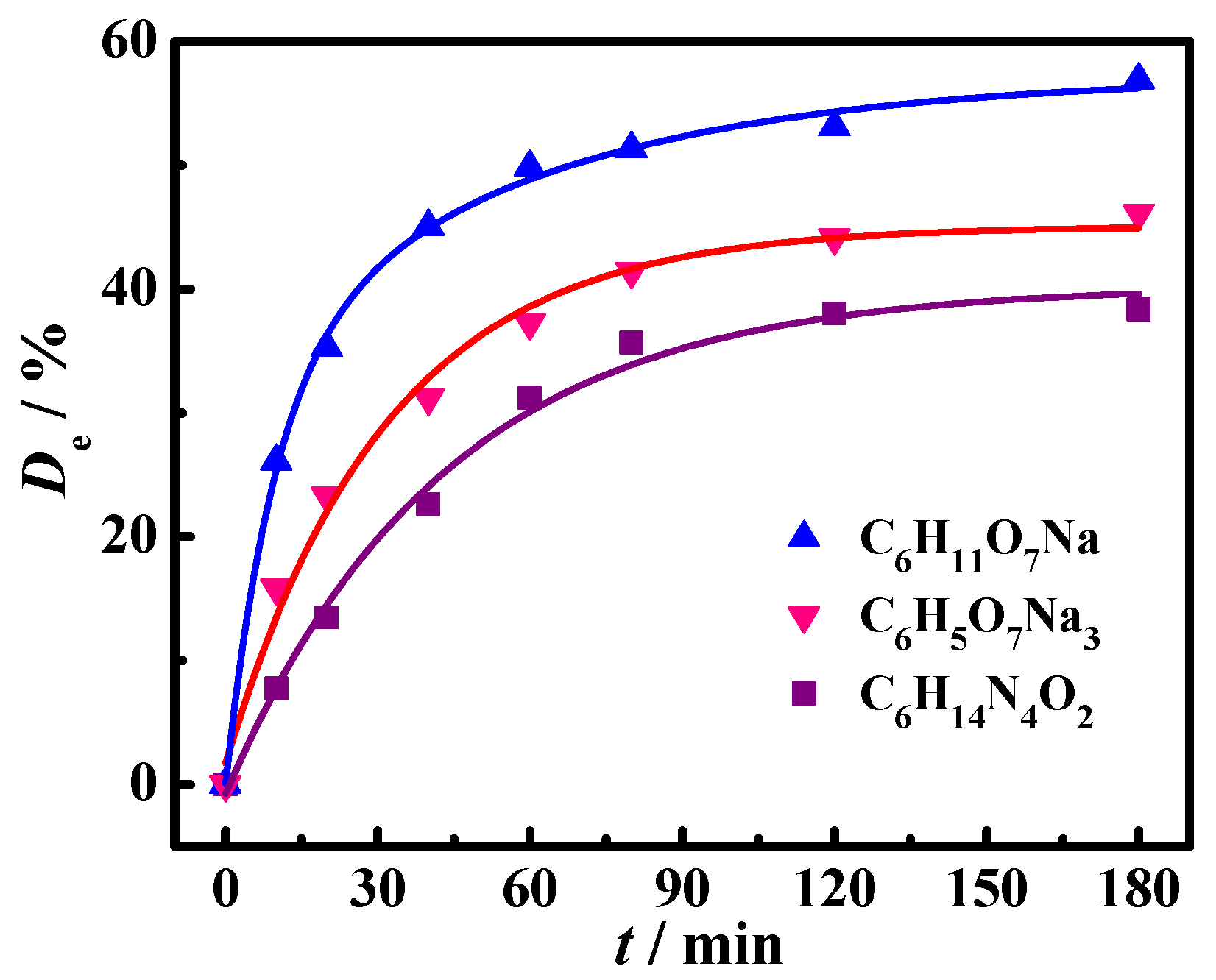
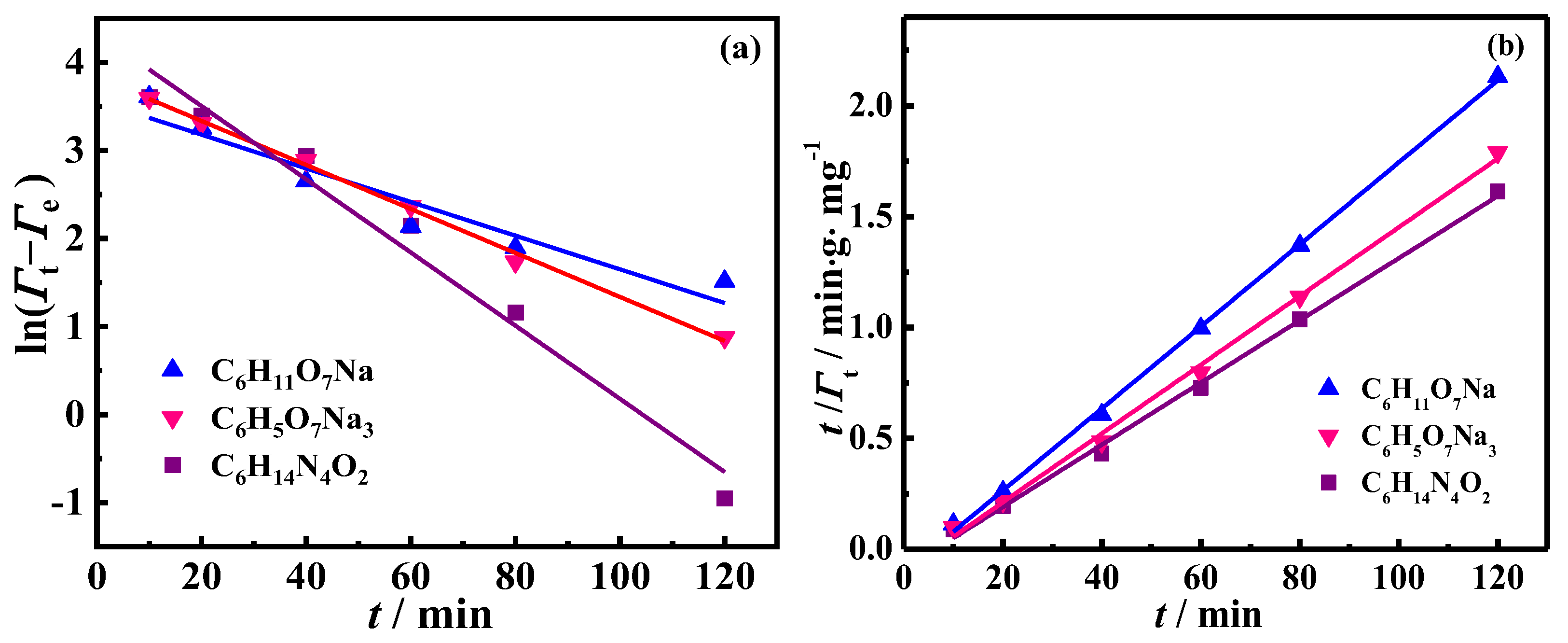




| Liquid System | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | Γe, exp (mg·g−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 (min−1) | Γe, cal (mg·g−1) | R2 | K2 (g·mg−1·min−1) | Γe (mg·g−1) | R2 | ||
| C6H14N4O2 | 0.042 | 76.40 | 0.967 | 0.00219 | 71.28 | 0.997 | 74.01 |
| C6H5O7Na3 | 0.025 | 46.33 | 0.996 | 0.00244 | 64.52 | 0.997 | 64.63 |
| C6H11O7Na | 0.019 | 35.24 | 0.909 | 0.00324 | 54.02 | 0.999 | 51.77 |
| Detergent | T (°C) | pH | (g·L−1) | γ (L0.5·g−0.5) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C6H11O7Na | 25.0 | 4.83 | 86.80 | 0.015 | 0.982 |
| 25.0 | 6.80 | 16.34 | 0.184 | 0.995 | |
| 25.0 | 11.58 | 13.30 | 0.193 | 0.997 | |
| 40.0 | 6.80 | 17.10 | 0.198 | 0.997 | |
| 55.0 | 6.80 | 18.38 | 0.216 | 0.998 | |
| 75.0 | 6.80 | 20.62 | 0.231 | 0.999 | |
| C6H5O7Na3 | 25.0 | 8.50 | 7.48 | 0.188 | 0.995 |
| C6H14N4O2 | 25.0 | 11.38 | 6.28 | 0.186 | 0.994 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, S.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Liang, J.; Lu, G.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L. Kinetics and Solid Effect Investigations During Oil Droplet Desorption from Oil-Contaminated Soil Using the Chemical Cleaning Method. Molecules 2025, 30, 2502. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122502
Jiang S, Wang L, Wang S, Liang J, Lu G, Li L, Zhang Y, Wang Q, Zhang L. Kinetics and Solid Effect Investigations During Oil Droplet Desorption from Oil-Contaminated Soil Using the Chemical Cleaning Method. Molecules. 2025; 30(12):2502. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122502
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Song, Lu Wang, Shuo Wang, Jiling Liang, Guang Lu, Lin Li, Yan Zhang, Qinghua Wang, and Lunqiu Zhang. 2025. "Kinetics and Solid Effect Investigations During Oil Droplet Desorption from Oil-Contaminated Soil Using the Chemical Cleaning Method" Molecules 30, no. 12: 2502. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122502
APA StyleJiang, S., Wang, L., Wang, S., Liang, J., Lu, G., Li, L., Zhang, Y., Wang, Q., & Zhang, L. (2025). Kinetics and Solid Effect Investigations During Oil Droplet Desorption from Oil-Contaminated Soil Using the Chemical Cleaning Method. Molecules, 30(12), 2502. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122502










