Rapid Enantiomeric Ratio Determination of Multiple Amino Acids Using Ion Mobility-Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
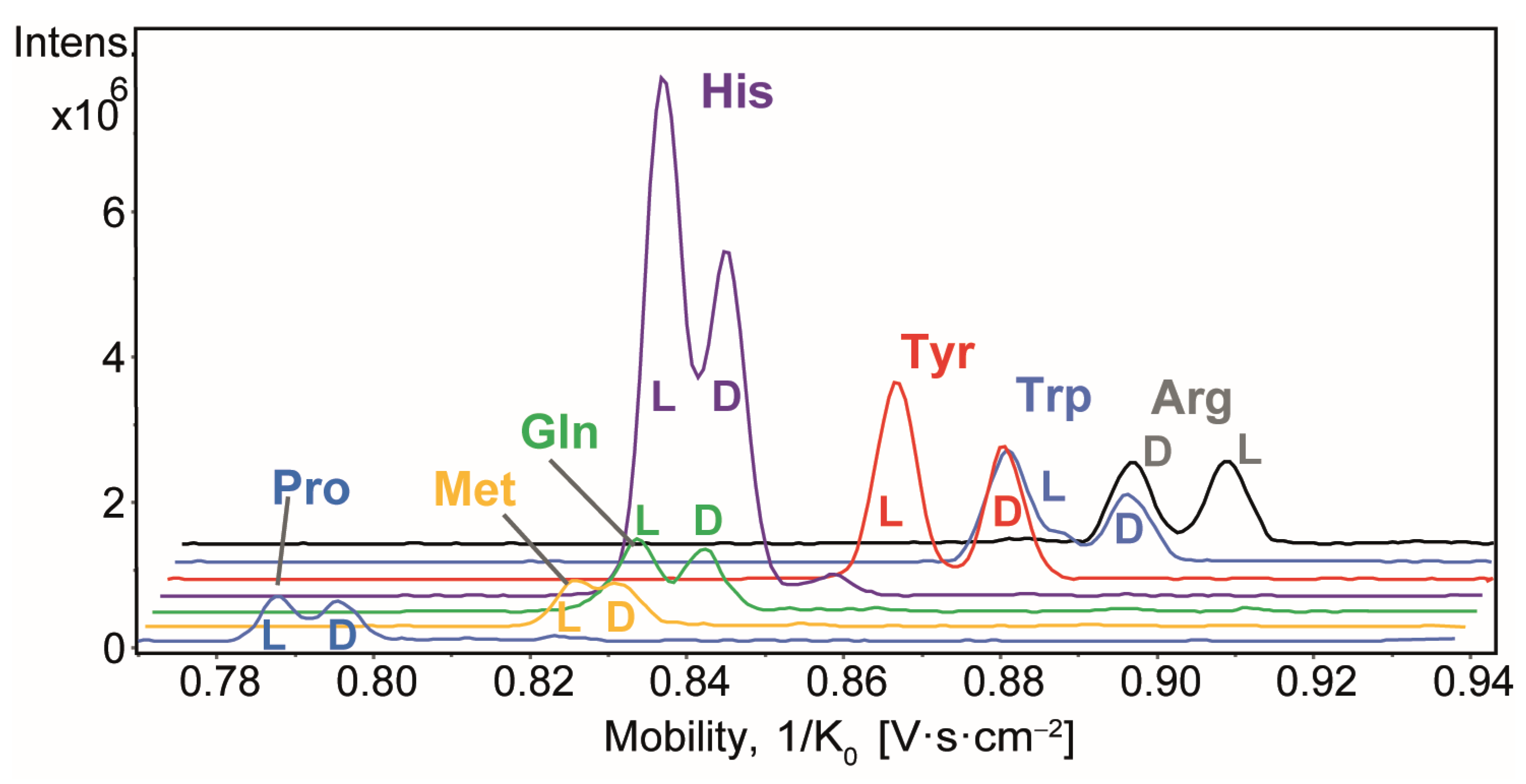
2. Results
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Ion Mobility-Mass Spectrometry
3.3. Procedure for Enantiomeric Ratio Determination
3.3.1. Preparation of Standard Solutions and Data Collection
3.3.2. Regression Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Friedman, M. Chemistry, Nutrition, and Microbiology of d -Amino Acids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 3457–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grishin, D.V.; Zhdanov, D.D.; Pokrovskaya, M.V.; Sokolov, N.N. D-Amino Acids in Nature, Agriculture and Biomedicine. All Life 2020, 13, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulbagi, M.; Wang, L.; Siddig, O.; Di, B.; Li, B. D-Amino Acids and D-Amino Acid-Containing Peptides: Potential Disease Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets? Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiritan, M.E.; Fernandes, C.; Maia, A.S.; Pinto, M.; Cass, Q.B. Enantiomeric Ratios: Why so Many Notations? J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1569, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, H.-L.; Xu, S.-T.; Yan, X.-P. Recent Advances in Separation and Analysis of Chiral Compounds. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 304–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gübitz, G.; Schmid, M.G. Chiral Separation Principles: An Introduction. In Chiral Separations; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2003; Volume 243, pp. 001–028. ISBN 978-1-59259-648-5. [Google Scholar]
- Bogos, L.-G.; Pralea, I.-E.; Moldovan, R.-C.; Iuga, C.-A. Indirect Enantioseparations: Recent Advances in Chiral Metabolomics for Biomedical Research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Yao, Z.-P. Chiral Recognition and Determination of Enantiomeric Excess by Mass Spectrometry: A Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 968, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.-Q.; Yao, Z.-P. Chiral Mass Spectrometry: An Overview. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 123, 115763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, B.L.; Wu, L.; Cooks, R.G. Mass Spectral Methods of Chiral Analysis. In Chiral Analysis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 595–659. ISBN 978-0-444-51669-5. [Google Scholar]
- Afonso, C.; Lesage, D.; Fournier, F.; Mancel, V.; Tabet, J.-C. Origin of Enantioselective Reduction of Quaternary Copper d,l Amino Acid Complexes under Vibrational Activation Conditions. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 312, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.-P.; Wan, T.S.M.; Kwong, K.-P.; Che, C.-T. Chiral Analysis by Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry/Mass Spectrometry. 2. Determination of Enantiomeric Excess of Amino Acids. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 5394–5401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, J.N.; May, J.C.; McLean, J.A. Investigation of the Complete Suite of the Leucine and Isoleucine Isomers: Toward Prediction of Ion Mobility Separation Capabilities. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 952–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper-Shepherd, D.A.; Olivos, H.J.; Wu, Z.; Palmer, M.E. Exploiting Self-Association to Evaluate Enantiomeric Composition by Cyclic Ion Mobility–Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 8441–8448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, B.; Wang, K.; Zhang, J.; Sun, W.; Zhang, L.; Guo, Y. Powerful Steroid-Based Chiral Selector for High-Throughput Enantiomeric Separation of α-Amino Acids Utilizing Ion Mobility–Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 13589–13596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Sun, W.; Tseng, K.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Y. Efficient Determination of Enantiomeric Ratios of α-Hydroxy/Amino Acids from Fermented Milks via Ion Mobility−mass Spectrometry. Food Chem. 2023, 400, 134092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Will, J.M.; Behrens, A.; Macke, M.; Quarles, C.D.; Karst, U. Automated Chiral Analysis of Amino Acids Based on Chiral Derivatization and Trapped Ion Mobility–Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 878–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, F.; Wang, J.; Pu, L.; Ding, C.-F. Simultaneous Chirality Separation of Amino Acids and Their Derivative by Natamycin Based on Mobility Measurements. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1227, 340298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Gu, L.; Wu, F.; Dai, X.; Xu, F.; Li, Q.; Fang, X.; Yu, S.; Ding, C.-F. The Chirality Determination of Amino Acids by Forming Complexes with Cyclodextrins and Metal Ions Using Ion Mobility Spectrometry, and a DFT Calculation. Talanta 2022, 243, 123363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Wu, X.; Xu, F.; Han, J.; Tian, H.; Ding, C.-F. Recognition of Cis–Trans and Chiral Proline and Its Derivatives by Ion Mobility Measurement of Their Complexes with Natamycin and Metal Ion. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 3553–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlibut, E.; May, J.C.; McLean, J.A. Enantiomer Differentiation of Amino Acid Stereoisomers by Structural Mass Spectrometry Using Noncovalent Trinuclear Copper Complexes. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2022, 33, 996–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Yao, Z.-P. Chiral Differentiation of Amino Acids through Binuclear Copper Bound Tetramers by Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 981, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.D.; Kabir, K.M.M.; Donald, W.A. Metal-Ion Free Chiral Analysis of Amino Acids as Small as Proline Using High-Definition Differential Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1036, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mie, A.; Jörntén-Karlsson, M.; Axelsson, B.-O.; Ray, A.; Reimann, C.T. Enantiomer Separation of Amino Acids by Complexation with Chiral Reference Compounds and High-Field Asymmetric Waveform Ion Mobility Spectrometry: Preliminary Results and Possible Limitations. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 2850–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mie, A.; Ray, A.; Axelsson, B.-O.; Jörntén-Karlsson, M.; Reimann, C.T. Terbutaline Enantiomer Separation and Quantification by Complexation and Field Asymmetric Ion Mobility Spectrometry−Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 4133–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czekner, J.; Schneider, E.K.; Weis, P.; Kappes, M.M. Quantitation of Enantiomeric Excess in an Achiral Environment Using Trapped Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2022, 33, 1692–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalet, C.; Rathahao-Paris, E.; Alves, S. Single Ion Mobility Monitoring (SIM2) Stitching Method for High-Throughput and High Ion Mobility Resolution Chiral Analysis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2024, 416, 4581–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Lima, F.A.; Kaplan, D.A.; Park, M.A. Note: Integration of Trapped Ion Mobility Spectrometry with Mass Spectrometry. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2011, 82, 126106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridgeway, M.E.; Lubeck, M.; Jordens, J.; Mann, M.; Park, M.A. Trapped Ion Mobility Spectrometry: A Short Review. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2018, 425, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathahao-Paris, E.; Delvaux, A.; Li, M.; Guillon, B.; Venot, E.; Fenaille, F.; Adel-Patient, K.; Alves, S. Rapid Structural Characterization of Human Milk Oligosaccharides and Distinction of Their Isomers Using Trapped Ion Mobility Spectrometry Time-of-flight Mass Spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 2022, 57, e4885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathahao-Paris, E.; Abdoun, S.; Paris, A.; Guillon, B.; Venot, E.; Fenaille, F.; Adel-Patient, K.; Alves, S. Innovative Direct Introduction-ion Mobility–Mass Spectrometry (DI-IM-MS) Approach for Fast and Robust Isomer-specific Quantification in a Complex Matrix: Application to 2′-fucosyllactose (2’-FL) in Breast Milk. J. Mass Spectrom. 2024, 59, e5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Chiral | Calibration Curves (a) | Mean Calculated er and Standard Deviations (b) | |||||
| AA | Equation (c) | R2 | %RSD | Theoretical er of 0.95 | Theoretical er of 0.99 | ||
| Arg | Y = 0.0037 + 0.9821 X | 0.9988 | 2.3 | 0.95 | ± 0.01 | 0.99 | ± 0.01 |
| Y = 0.0111 + 0.9283 X + 0.0538 X2 | 0.9991 | 2.0 | 0.95 | ± 0.01 | 0.98 | ± 0.01 | |
| Gln | Y = −0.023 + 0.9566X | 0.9949 | 5.1 | 0.95 | ± 0.02 | 1.01 | ± 0.02 |
| Y = −0.0015 + 0.8003 X + 0.1563 X2 | 0.9971 | 3.8 | 0.94 | ± 0.02 | 0.98 | ± 0.01 | |
| His | Y = 0.0244 + 0.8744 X | 0.9445 | 15.1 | 0.98 | ± 0.02 | 1.06 | ± 0.01 |
| Y = 0.1164 + 0.2239 X + 0.6525 X2 | 0.9914 | 6.0 | 0.93 | ± 0.01 | 0.97 | ± 0.01 | |
| Met | Y = 0.0221 + 0.9777 X | 0.9853 | 7.6 | 0.95 | ± 0.01 | 0.99 | ± 0.01 |
| Y = 0.0328 + 0.8978 X + 0.0802 X2 | 0.9859 | 7.5 | 0.95 | ± 0.01 | 0.98 | ± 0.01 | |
| Pro | Y = 0.0031 + 0.9788 X | 0.9952 | 4.7 | 0.95 | ± 0.01 | 1.00 | ± 0.01 |
| Y = 0.0187 + 0.8656 X + 0.1132 X2 | 0.9963 | 4.1 | 0.94 | ± 0.01 | 0.99 | ± 0.01 | |
| Trp | Y = −0.0557 + 0.9696 X | 0.9738 | 12.6 | 1.01 | ± 0.01 | 1.06 | ± 0.01 |
| Y = 0.0161 + 0.4467 X + 0.5229 X2 | 0.9978 | 3.7 | 0.96 | ± 0.01 | 0.99 | ± 0.003 | |
| Tyr | Y = −0.0497 + 0.9635 X | 0.9760 | 11.9 | 1.00 | ± 0.01 | 1.06 | ± 0.002 |
| Y = 0.0199 + 0.456 X + 0.5075 X2 | 0.9989 | 2.6 | 0.95 | ± 0.01 | 0.99 | ± 0.001 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, W.; Rathahao-Paris, E.; Alves, S. Rapid Enantiomeric Ratio Determination of Multiple Amino Acids Using Ion Mobility-Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2025, 30, 2497. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122497
Xu W, Rathahao-Paris E, Alves S. Rapid Enantiomeric Ratio Determination of Multiple Amino Acids Using Ion Mobility-Mass Spectrometry. Molecules. 2025; 30(12):2497. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122497
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Wenqing, Estelle Rathahao-Paris, and Sandra Alves. 2025. "Rapid Enantiomeric Ratio Determination of Multiple Amino Acids Using Ion Mobility-Mass Spectrometry" Molecules 30, no. 12: 2497. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122497
APA StyleXu, W., Rathahao-Paris, E., & Alves, S. (2025). Rapid Enantiomeric Ratio Determination of Multiple Amino Acids Using Ion Mobility-Mass Spectrometry. Molecules, 30(12), 2497. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122497








