Multisite Fe3+ Luminescent Centers in the LiGaO2:Fe Nanocrystalline Phosphor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
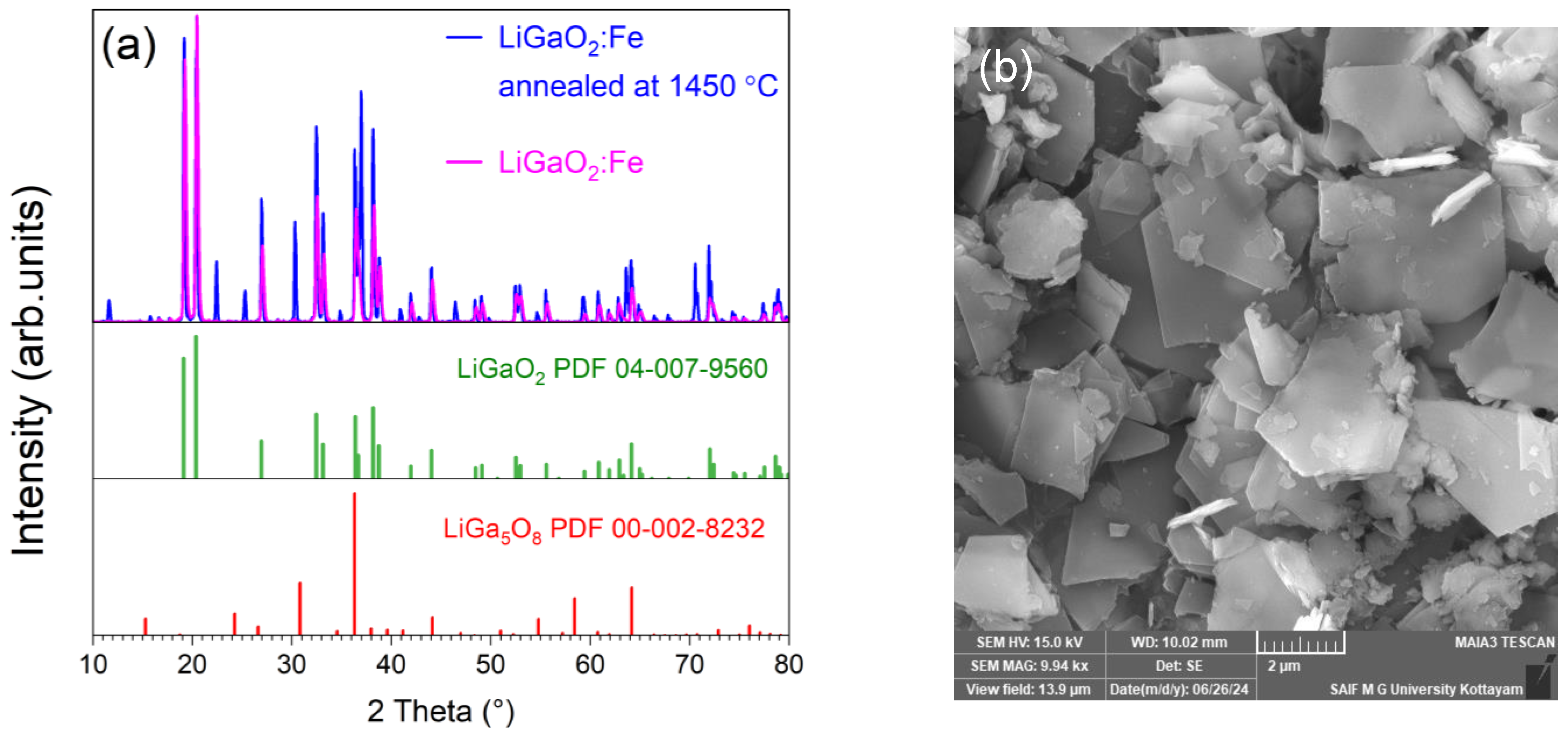
2.1. Structural and Raman Studies
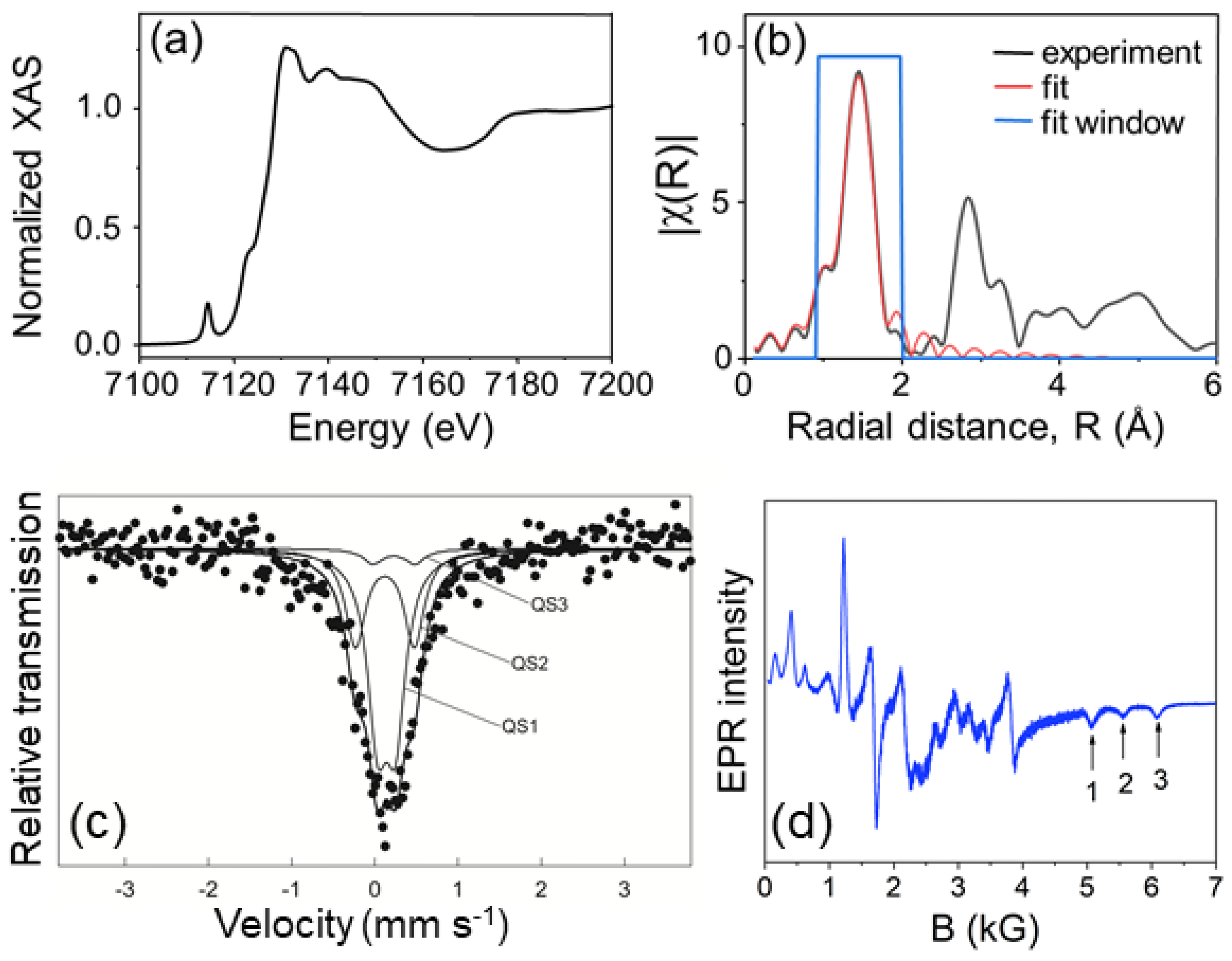
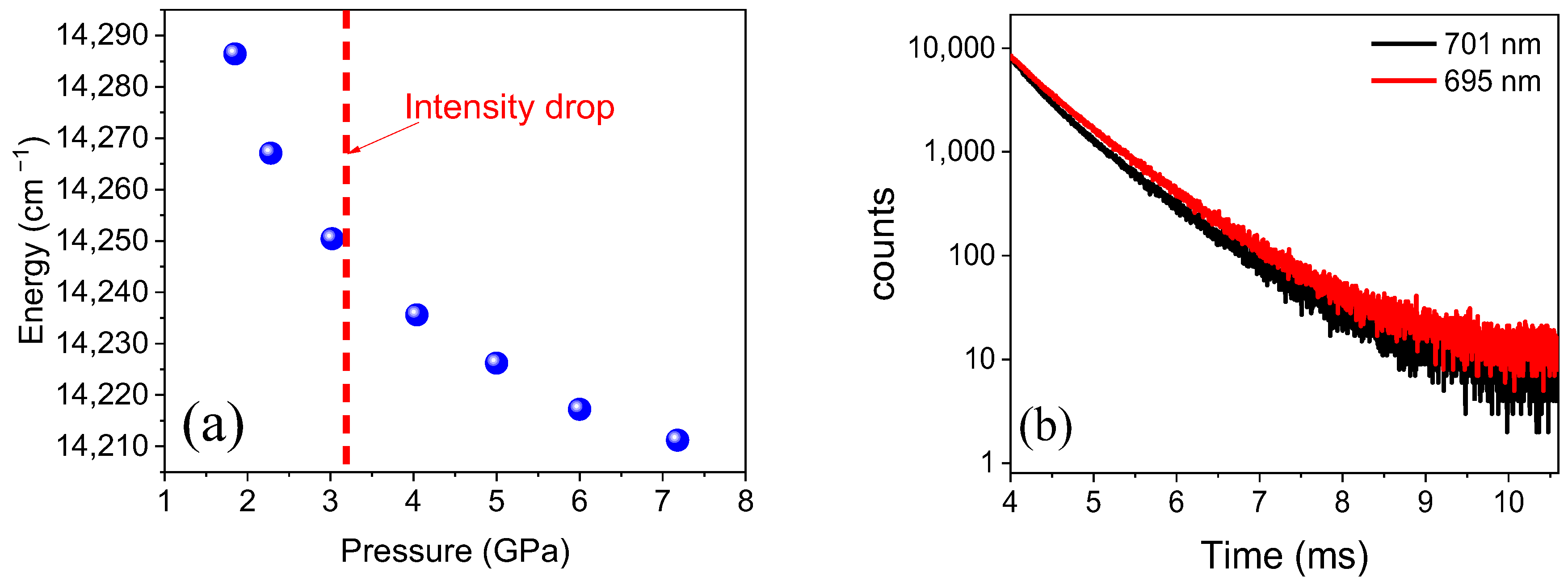
2.2. XAS, EXAFS, Mössbauer & EPR Measurements
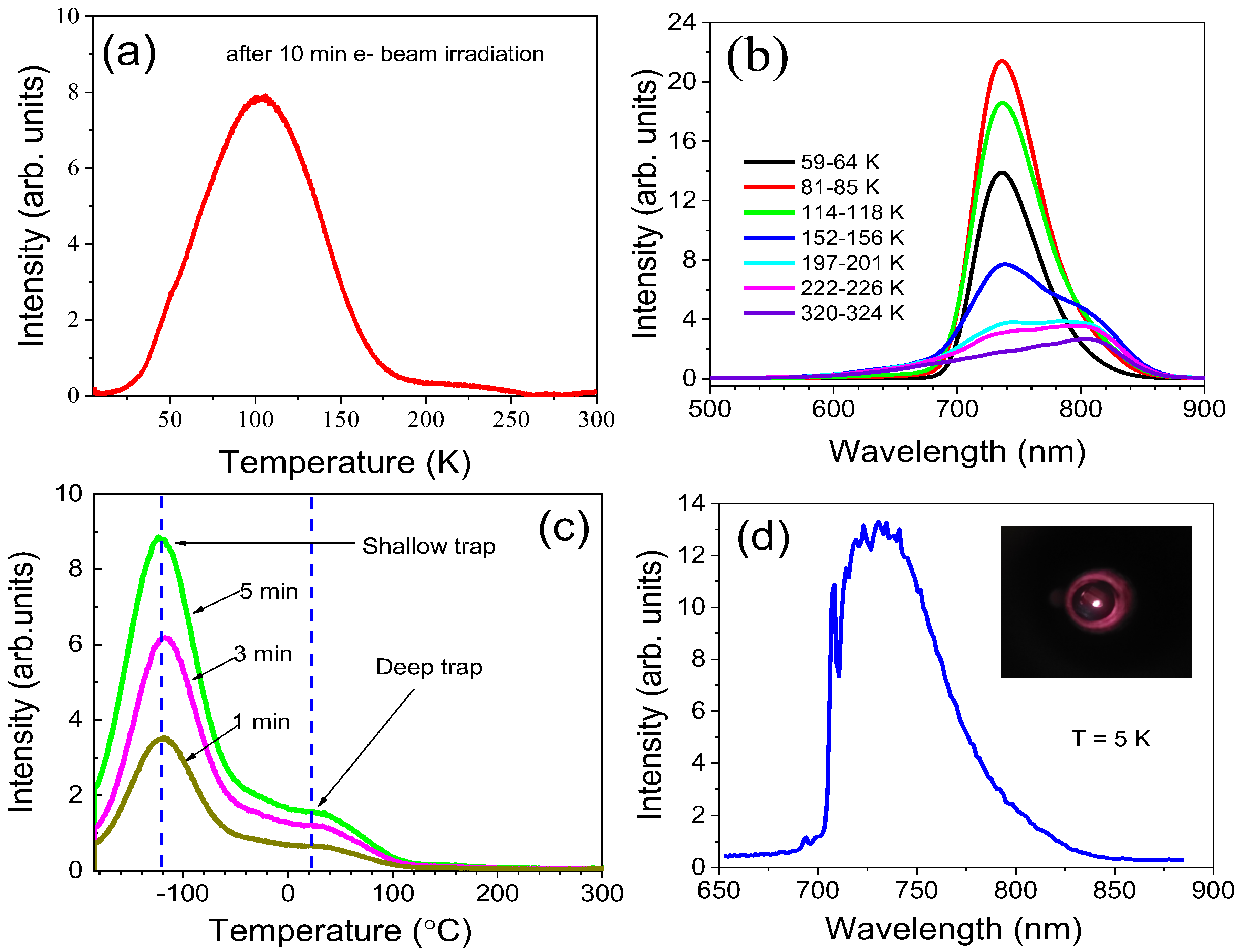
2.3. Low-Temperature Photoluminescence
2.4. Thermo-Stimulated Luminescence & Cathodoluminescence
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Experimental Methods
4. Summary and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CTB | Charge transfer band |
| CL | Cathodoluminescence |
| EPR | Electron paramagnetic resonance |
| EXAFS | Extended X-ray absorption fine structure |
| EDS | Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy |
| FE-SEM | Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| NIR | Near-infrared |
| PL | Photoluminescence |
| VUV | Vacuum UV |
| XAS | X-ray absorption spectroscopy |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| ZPL | Zero phonon line |
References
- Rashkeev, S.N.; Limpijumnong, S.; Lambrecht, W.R.L. Theoretical evaluation of LiGaO2 for frequency upconversion to ultraviolet. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 1999, 16, 2217–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Guan, S.; Wang, Y.J.; Liu, Z.; Li, W. Lithium gallium oxide (LiGaO2): High-performance anode material for lithium-ion batteries. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 976, 173197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Vangipuram, V.G.T.; Huang, H.L.; Hwang, J.; Zhao, H. Discovery of a Robust p-Type Ultrawide Bandgap Oxide Semiconductor: LiGa5O8. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2023, 11, 2300550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.T.; Leśniewski, T.; Majewska, N.; Kamiński, M.; Barzowska, J.; Liu, E.P.; Chen, W.T.; Mahlik, S.; Fang, M.H. Pressure/temperature-assisted crystallographic engineering–A strategy for developing the infrared phosphors. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 490, 151596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Townsend, P.D.; Hreniak, D. LiGa5O8: Fe3+: A novel and super long near-infrared persistent material. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 35359–35367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riesen, H. On the 6A1 ←4T1 luminescence of Fe3+ in disordered nanocrystalline LiGa5O8 prepared by a combustion reaction. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2008, 461, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Yi, X.; Xiong, P.; Xu, X.; Ma, Z.; Peng, M. Cr3+-Free near-infrared persistent luminescence material LiGaO2:Fe3+: Optical properties, afterglow mechanism and potential bioimaging. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 14100–14108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, V.C.; Manali, I.F.; Gallo, T.M.; Galante, D.; Barbosa, D.A.B.; Paschoal, C.W.A.; Silva, R.S.; Rezende, M.V.D.S. Luminescent properties of Li(Ga1-xCrx)5O8 (LGCO) phosphors. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 15779–15785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kniec, K.; Tikhomirov, M.; Pozniak, B.; Ledwa, K.; Marciniak, L. LiAl5O8:Fe3+ and LiAl5O8:Fe3+, Nd3+ as a new luminescent nanothermometer operating in 1st biological optical window. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somakumar, A.K.; Bulyk, L.I.; Tsiumra, V.; Barzowska, J.; Xiong, P.; Lysak, A.; Zhydachevskyy, Y.; Suchocki, A. High-Pressure Near-Infrared Luminescence Studies of Fe3+-Activated LiGaO2. Inorg. Chem. 2023, 62, 12434–12444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marezio, M. The crystal structure of LiGaO2. Acta Crystallogr. 1965, 18, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawn, C.J.; Chaudhuri, J. High temperature X-ray diffraction study of LiGaO2. J. Cryst. Growth 2001, 225, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Ohfuji, H.; Qin, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, F.; Irifune, T. High-pressure Raman spectroscopy study of LiGaO2. Solid State Commun. 2013, 164, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Song, Z.; Zhang, J. Structural characterization &, optical and electrical properties of LiGaO2 & LiGa5O8 micro-nanoparticles-based photodetectors. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 887, 161438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waychunas, G.A.; Rossman, G.R. Spectroscopic standard for tetrahedrally coordinated ferric iron: γ LiAlO2:Fe3+. Phys. Chem. Miner. 1983, 9, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravel, B.; Newville, M. ATHENA and ARTEMIS: Interactive graphical data analysis using IFEFFIT. Phys. Scr. 2005, 2005, 1007–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosowska, J.; Kaszewski, J.; Witkowski, B.S.; Wachnicki, Ł.; Wolska, A.; Klepka, M.T.; Grabias, A.; Kuryliszyn-Kudelska, I.; Godlewski, M. ZnO:Fe nanoparticles with Fe fraction up to 10%mol—Growth and characterization. J. Lumin. 2023, 263, 119944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, B.; Stewart, G.A.; Riesen, H. Structural and Optical Properties of Nanocrystalline LiGa5O8:Fe3+. In Proceedings of the 36th Annual Condensed Matter and Materials Meeting, Wagga Wagga, Australia, 31 January–3 February 2012; pp. 72–75. Available online: https://inis.iaea.org/search/search.aspx?orig_q=RN:49070025 (accessed on 19 March 2025).
- Kakazey, M.; Vlasova, M.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, G.; Salazar-Hernández, B. Fine structure of EPR spectra of Fe3+ in α-Al2O3 crystal, powders, and textured ceramics. Mat. Sci. Eng. B 2002, 90, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopmans, H.J.A.; Perik, M.M.A.; Nieuwennuijse, B.; Gellings, P.J. The Simulation and Interpretation of the EPR Powder Spectra of Gd3+-Doped LaAlO3. Phys. Status Solidi B 1984, 122, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldú, J.L.; Muñoz P, E.; Chen, Y.; Abraham, M.M. EPR power pattern analysis for cubic sites of Fe3+ in MgO. J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 80, 574–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McShera, C.; Colleran, P.J.; Glynn, T.J.; Imbusch, G.F.; Remeika, J.P. Luminescence study of LiGa5−xFexO8. J. Lumin. 1983, 28, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marezio, M.; Remeika, J.P. High pressure phase of LiGaO2. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1965, 26, 1277–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weise, S.; Neumann, H. Thermal Analysis of LiGaO2 and NaGaO2. Cryst. Res. Technol. 1996, 1, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, P.; Yan, Y.; Song, Y.; Yakovlev, A.N.; Hu, T.; Cherkasova, T.G.; Xu, X.; Guo, H.; et al. Employing defect luminescence of LiGaO2 to realize dynamic readout and multiplexing of optical information. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 40112–40119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayama, S.; Duller, G.; Sutter, J.P.; Amboage, M.; Boada, R.; Freeman, A.; Keenan, L.; Nutter, B.; Cahill, L.; Leicester, P.; et al. The scanning four-bounce monochromator for beamline I20 at the Diamond Light Source. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2018, 25, 1556–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somakumar, A.K.; Zhydachevskyy, Y.; Wlodarczyk, D.; Haider, S.S.; Barzowska, J.; Bindu, K.R.; Edathumkandy, Y.K.; Zayarniuk, T.; Szewczyk, A.; Narayanan, S.; et al. Temperature and pressure dependent luminescence mechanism of a zinc blende structured ZnS:Mn nanophosphor under UV excitation. J. Mater. Chem. C 2024, 12, 7041–7052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| LiGaO2:Fe3+ (cm−1) | LiGa5O8:Fe3+ (cm−1) | LiGaO2 [13] | LiGaO2 [14] | LiGa5O8 [14] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 129 | 128.4 | 128.7 | ||
| 139.2 | 135.1 | |||
| 202 | 204.2 | |||
| 219 | ||||
| 249.5 | 252.1 | 252 | ||
| 271.3 | 270 | |||
| 287.2 | 289.0 | 289 | ||
| 318.6 | 344 | 344 | ||
| 397 | 371 | 372 | ||
| 425 | 424 | |||
| 435 | 444.3 | 443 | ||
| 495.3 | 502.8 | 502.1 | 501 | 512 |
| 556 | 578 | 579 | ||
| 605.4 | 605 | |||
| 640 | 643.9 | 643 | ||
| 649 | 654 | 653.8 | 655 | 655 |
| 714 | ||||
| 760 | 760 | 763 | 763 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Somakumar, A.K.; Romet, I.; Grabias, A.; Kruk, M.; Hayama, S.; Wlodarczyk, D.; Barzowska, J.; Edathumkandy, Y.K.; Feldbach, E.; Xiong, P.; et al. Multisite Fe3+ Luminescent Centers in the LiGaO2:Fe Nanocrystalline Phosphor. Molecules 2025, 30, 2331. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112331
Somakumar AK, Romet I, Grabias A, Kruk M, Hayama S, Wlodarczyk D, Barzowska J, Edathumkandy YK, Feldbach E, Xiong P, et al. Multisite Fe3+ Luminescent Centers in the LiGaO2:Fe Nanocrystalline Phosphor. Molecules. 2025; 30(11):2331. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112331
Chicago/Turabian StyleSomakumar, Ajeesh Kumar, Ivo Romet, Agnieszka Grabias, Marcin Kruk, Shusaku Hayama, Damian Wlodarczyk, Justyna Barzowska, Yadhu Krishnan Edathumkandy, Eduard Feldbach, Puxian Xiong, and et al. 2025. "Multisite Fe3+ Luminescent Centers in the LiGaO2:Fe Nanocrystalline Phosphor" Molecules 30, no. 11: 2331. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112331
APA StyleSomakumar, A. K., Romet, I., Grabias, A., Kruk, M., Hayama, S., Wlodarczyk, D., Barzowska, J., Edathumkandy, Y. K., Feldbach, E., Xiong, P., Zhydachevskyy, Y., Trzaskowska, M., Przybylinska, H., & Suchocki, A. (2025). Multisite Fe3+ Luminescent Centers in the LiGaO2:Fe Nanocrystalline Phosphor. Molecules, 30(11), 2331. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112331









