Amorphous Fe-Doped Manganese Carbonate for Efficient Activation of Peroxymonosulfate: Mechanism and Performance Toward Orange II Degradation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
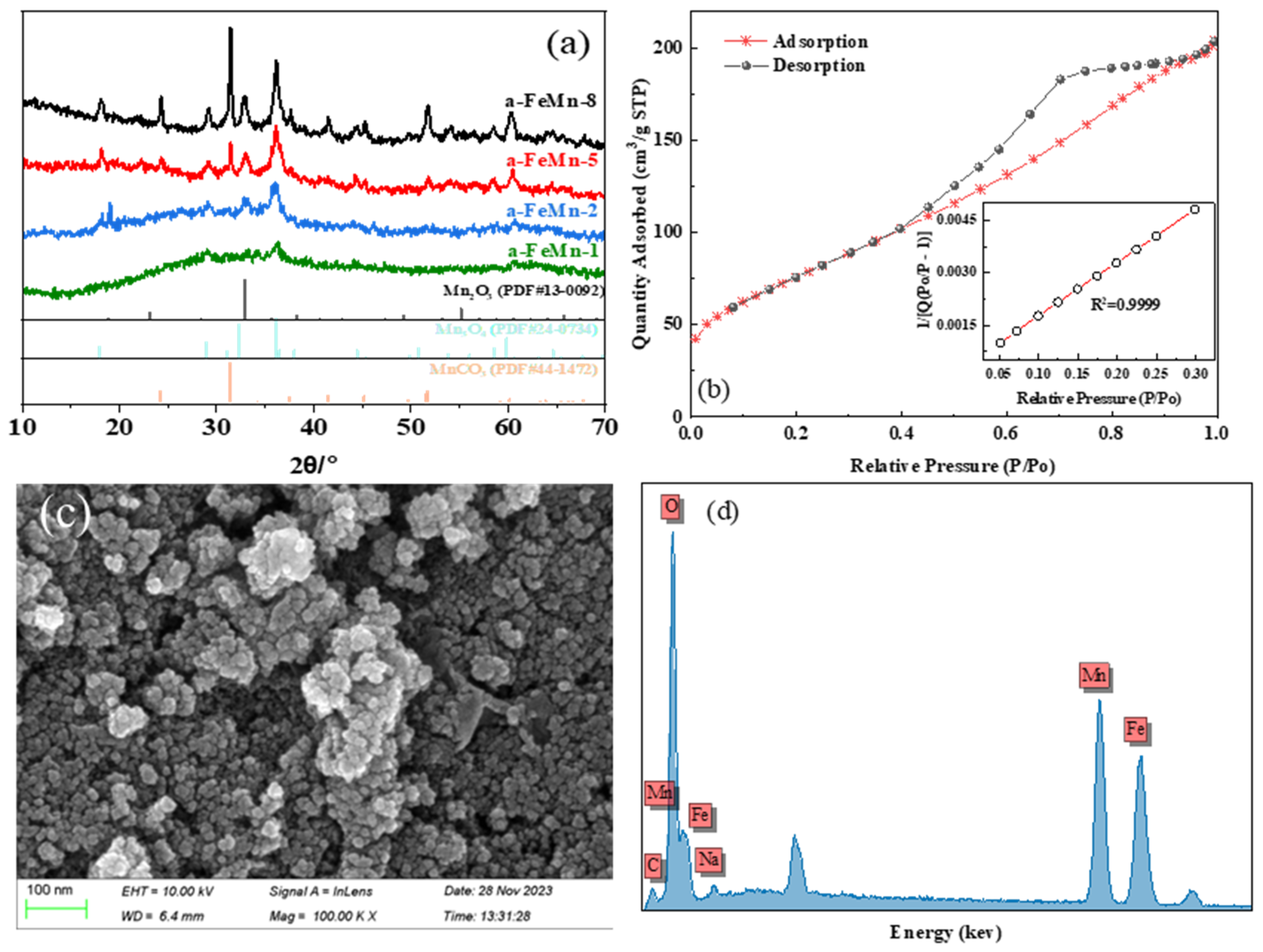
2.1. Characterizations
2.2. Catalytic Activity of Fe-Doped Manganese Carbonate with Different Fe/Mn Ratios
2.3. The Investigation of Orange II Degradation via a-FeMn-1/PMS System
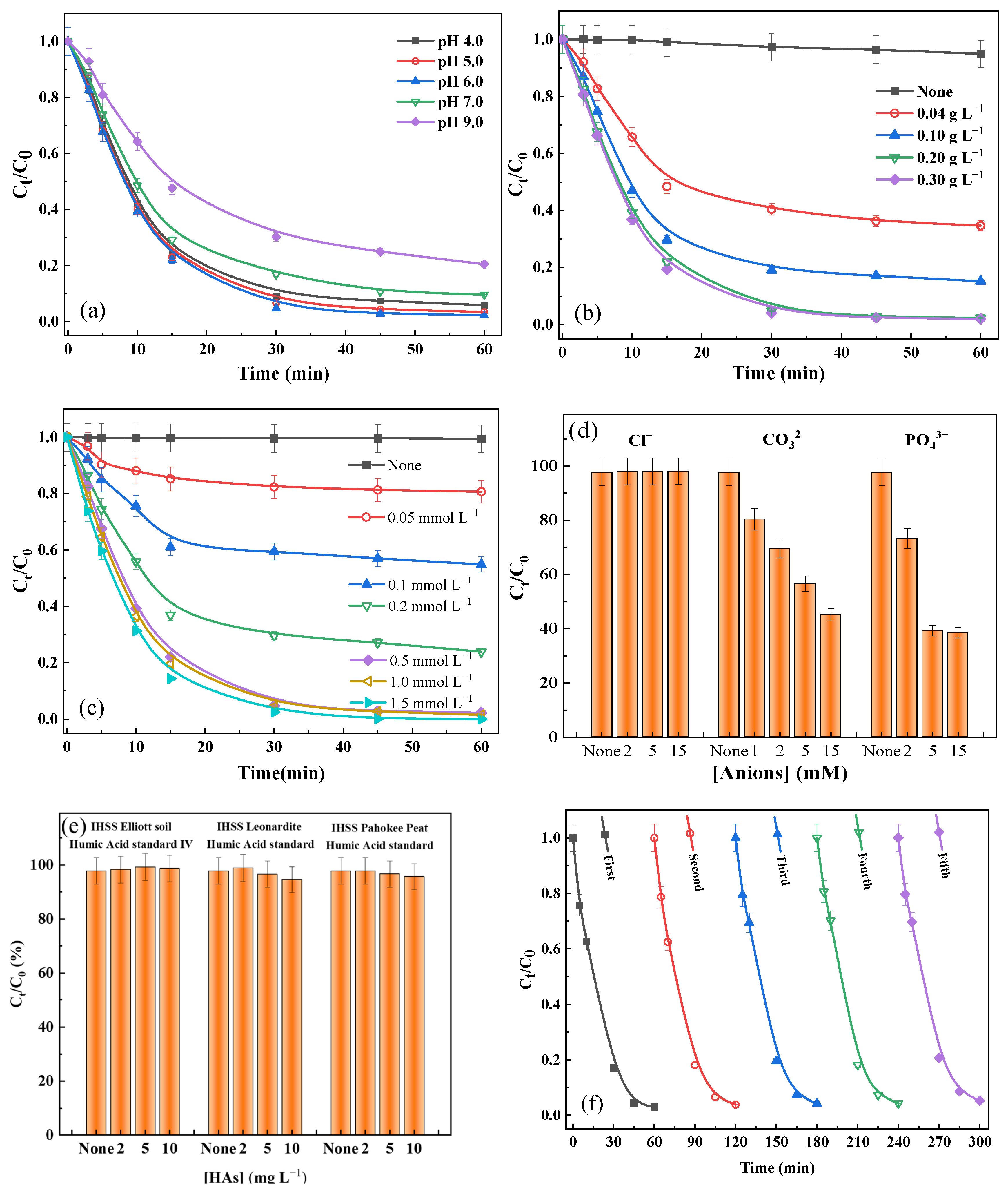
2.3.1. Effect of Different Parameters
2.3.2. Effect of Co-Existing Anions and Natural Organic Matter (NOM)
2.3.3. Reusability of a-FeMn-1
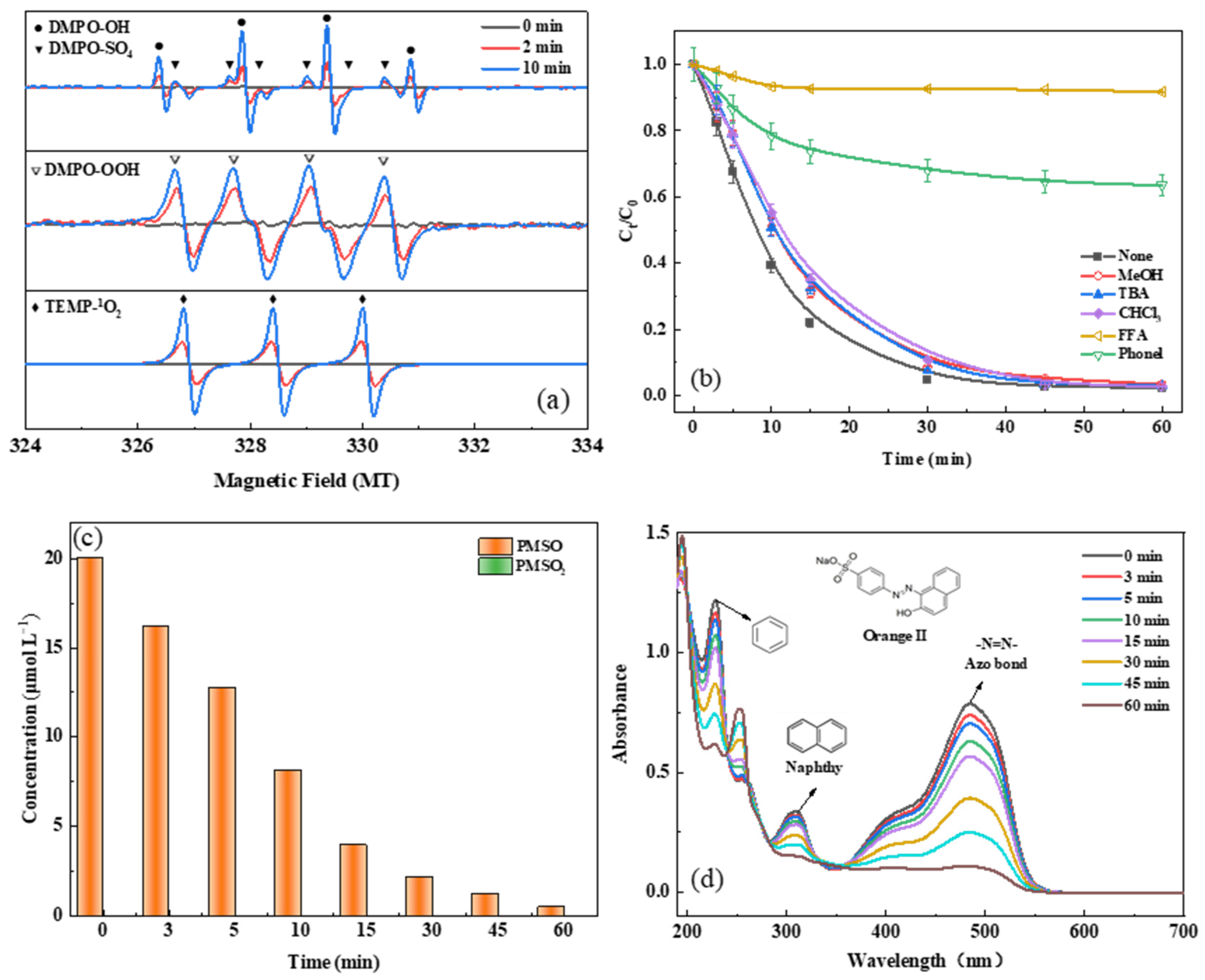
2.4. Identification of the Main Oxidant
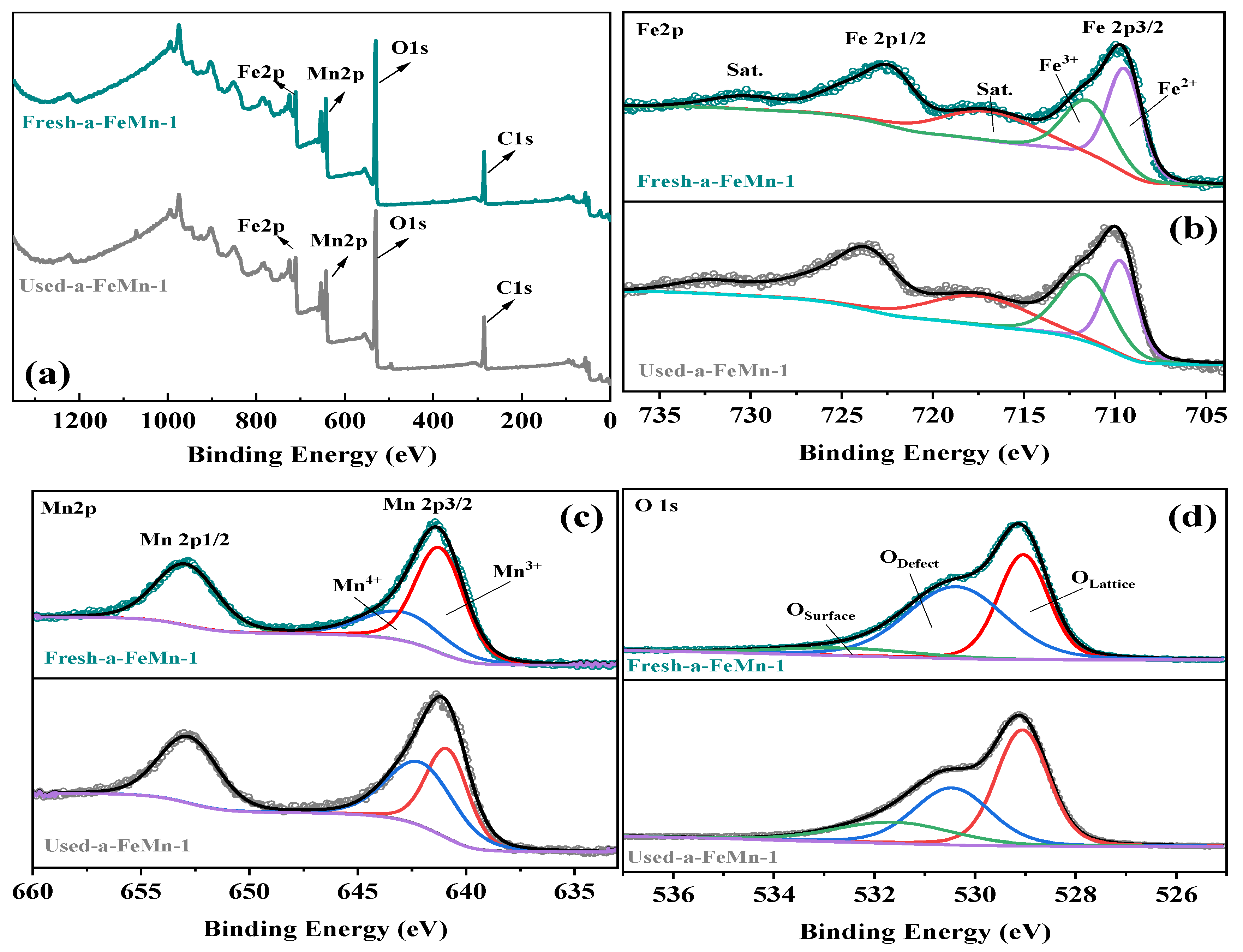
2.5. XPS Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Synthesis of Fe-Doped Amorphous Manganese Carbonate
3.3. Catalyst Characterization
3.4. Experiment Procedure
3.5. Analysis Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.; Wang, S. Activation of Persulfate (PS) and Peroxymonosulfate (PMS) and Application for the Degradation of Emerging Contaminants. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 1502–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zou, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; Deng, C.; Yu, Z.; Monfort, O.; Cheng, P. Z-Scheme g-C3N4/α-FOD Heterojunction-Assisted Persulfate Activation for Degradation of Tetracycline Hydrochloride under Visible Light: Insights into Mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 479, 147224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zeng, G.; Deng, Y.; Dong, H.; Feng, H.; Wang, J.; Peng, B. Enhanced Activation Process of Persulfate by Mesoporous Carbon for Degradation of Aqueous Organic Pollutants: Electron Transfer Mechanism. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 231, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qiu, C.; Cheng, P.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; Tao, X.; Weng, B.; Mailhot, G. Enhanced Orange II Removal Using Fe/Mn/Mg2-LDH Activated Peroxymonosulfate: Synergistic Radical Oxidation and Adsorption. Catalysts 2024, 14, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Niu, X.; Gao, J.; Wacławek, S.; Tang, L.; Dionysiou, D.D. Comparison of Sulfate Radical with Other Reactive Species. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2022, 38, 100867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cope, J.D.; Bates, K.H.; Tran, L.N.; Abellar, K.A.; Nguyen, T.B. Sulfur Radical Formation from the Tropospheric Irradiation of Aqueous Sulfate Aerosols. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2202857119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Zou, J.; Lin, J.; Li, Q.; Li, J.; Huang, Y.; Yang, H.; Yuan, B.; Ma, J. Elimination of Acetaminophen in Sodium Carbonate-Enhanced Thermal/Peroxymonosulfate Process: Performances, Influencing Factors and Mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 449, 137765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Ruan, Y.; Feng, Y.; Diao, Z.; Shih, K.; Hou, L.; Chen, D.; Kong, L. Ultrasound Assisted Zero Valent Iron Corrosion for Peroxymonosulfate Activation for Rhodamine-B Degradation. Chemosphere 2019, 228, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Liu, X.; Ma, J.; Lin, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, H. Activation of Peroxymonosulfate by Base: Implications for the Degradation of Organic Pollutants. Chemosphere 2016, 151, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, X.; Liu, C.; Cheng, P.; Mailhot, G. Efficient Decolorization of Azo Dye Orange II in a UV-Fe3+-PMS-Oxalate System. Processes 2023, 11, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Huang, X.; Qiu, R. Gallic Acid Accelerated BDE47 Degradation in PMS/Fe(III) System: Oxidation Intermediates Autocatalyzed Redox Cycling of Iron. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 384, 123248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Sun, Y.; Dong, Y.; Hou, H.; Kai, M.-F.; Lan, J. Efficient Carbamazepine Degradation by Modified Copper Tailings and PMS System: Performance Evaluation and Mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Y.; Guan, X.; Xu, J.; Feng, Y.; Mao, Y.; Xu, L.; Chu, H.; Wu, D. Unraveling the Overlooked Involvement of High-Valent Cobalt-Oxo Species Generated from the Cobalt(II)-Activated Peroxymonosulfate Process. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 16231–16239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.; Zhang, D.; Fan, C.; Shang, C. A Fe(II)/Citrate/UV/PMS Process for Carbamazepine Degradation at a Very Low Fe(II)/PMS Ratio and Neutral pH: The Mechanisms. Water Res. 2017, 124, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.-E.; Kim, C.; Hwang, I. Continuous Fe(II)-Dosing Scheme for Persulfate Activation: Performance Enhancement Mechanisms in a Slurry Phase Reactor. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Niu, X.; Zhang, D.; Lv, M.; Ye, X.; Ma, J.; Lin, Z.; Fu, M. Metal-Based Catalysts for Persulfate and Peroxymonosulfate Activation in Heterogeneous Ways: A Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Du, P.; Zhou, B.; Meng, F.; Wei, C.; Zhou, L.; Wen, G.; Wang, Y. Manganese Oxide Catalytic Materials for Degradation of Organic Pollutants in Advanced Oxidation Processes: A Review. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 66, 106048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Luo, M.; Wang, J.; Li, M.; He, Z.; Zhong, H.; Sun, W.; Ye, M.; Tang, Y. Self-Formed MnCO3/FeS2@SiO2 in Modified Electrolytic Manganese Residues as an Enhanced Peroxymonosulfate Activator for Ammonium Dibutyl Dithiophosphate Removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 472, 144915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, J.; Sun, W.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, K. Challenges and Perspectives for Doping Strategy for Manganese-Based Zinc-Ion Battery Cathode. Energies 2022, 15, 4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wan, Y.; Zhu, C.; Chen, G.; Li, X. FeNi Bimetallic Modified Pg-C3N4-x and Its Photoelectrocatalytic Hydrogen Production Coupling Anodic Oxidation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 357, 130142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, X. Robust Photoelectrocatalytic Degradation of Antibiotics by Organic-Inorganic PDISA/Bi2WO6 S-Scheme Heterojunction Membrane. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Cao, Y.; Lu, Z.; Ding, P.; Wang, Z.; Ma, F.; Wang, Z.; Pei, R. A Hypoxia-Irrelevant Fe-Doped Multivalent Manganese Oxide Sonosensitizer via a Vacancy Engineering Strategy for Enhanced Sonodynamic Therapy. Nano Today 2022, 43, 101434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.-D.; Shi, Y.; He, Y.-L.; Yang, S.-R.; Yu, S.-Y.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, H.; Yao, G.; He, C.-S.; Lai, B. Synthesis of Fe–Mn-Based Materials and Their Applications in Advanced Oxidation Processes for Wastewater Decontamination: A Review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 10828–10848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Shen, Q.; Nan, T.; Zhou, M.; Xia, Y.; Hu, G.; Zheng, Q.; Wu, Y.; Bian, T.; Wei, T.; et al. Cobalt-Based Catalysts for Heterogeneous Peroxymonosulfate (PMS) Activation in Degradation of Organic Contaminants: Recent Advances and Perspectives. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 958, 170370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Yang, X.; Hu, Q.; Cai, Z.; Liu, L.-M.; Guo, L. Recent Progress of Amorphous Nanomaterials. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 8859–8941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Li, L.; Wang, Z. Recent Development and Future Perspectives of Amorphous Transition Metal-Based Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Evolution Reaction. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2200827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Liu, G.; Zhang, B.; Zheng, J.; Yin, K.; Lin, J.; Han, C.; Fan, X.; Xu, M.; Ye, L. General Modification Strategy on Amorphous Materials to Boost Catalytic Performance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2405867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Shen, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhang, H.; Xu, B.; Song, Y.; Liang, J.; Guo, J. Recent Advances of Amorphous-Phase-Engineered Metal-Based Catalysts for Boosted Electrocatalysis. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 127, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshvar, N.; Ashassi-Sorkhabi, H.; Tizpar, A. Decolorization of Orange II by Electrocoagulation Method. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2003, 31, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpov, M.; Seiwert, B.; Mordehay, V.; Reemtsma, T.; Polubesova, T.; Chefetz, B. Transformation of oxytetracycline by redox-active Fe(III)- and Mn(IV)-containing minerals: Processes and mechanisms. Water Res. 2018, 145, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xie, F. Highly Efficient Removal of As(III) by Fe-Mn-Ca Composites with the Synergistic Effect of Oxidation and Adsorption. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 145289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Li, X.; Yang, Q.; Chen, F.; Wang, S.; Ma, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Huang, X.; Wang, D. Heterogeneous Activation of Peroxymonosulfate Using Mn-Fe Layered Double Hydroxide: Performance and Mechanism for Organic Pollutant Degradation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 663, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, C.; Zhou, D.; Chen, X.; Zhang, M.; Lin, K. Degradation of Bisphenol a Using Peroxymonosulfate Activated by Single-Atomic Cobalt Catalysts: Different Reactive Species at Acidic and Alkaline pH. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 439, 135002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Ferronato, C.; Salvador, A.; Yang, X.; Chovelon, J.-M. Degradation of Ciprofloxacin and Sulfamethoxazole by Ferrous-Activated Persulfate: Implications for Remediation of Groundwater Contaminated by Antibiotics. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 800–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liangdy, A.; Lee, W.J.; Tonanon, P.; Webster, R.D.; Snyder, S.A.; Lim, T. Unravelling the synergism of catalytic oxidation and filtration in Co-Mn-oxide impregnated ceramic membrane for intensified degradation of recalcitrant micropollutant with peroxymonosulfate. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.-Y.; Choi, J.; Kim, M.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, D.; Bang, W.H.; Yun, E.-T.; Lee, H.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, C.; et al. Chloride-Mediated Enhancement in Heat-Induced Activation of Peroxymonosulfate: New Reaction Pathways for Oxidizing Radical Production. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 5382–5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Ma, J.; Miao, C.; Song, Y.; Lian, L.; Yan, S.; Song, W. Carbonate Radical Oxidation of Cylindrospermopsin (Cyanotoxin): Kinetic Studies and Mechanistic Consideration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 10118–10127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, P.; Liu, X.; Liu, B.; Akram, M.; Li, Y.; Pan, J.; Yue, Q.; Gao, B.; Xu, X. Effect of Phosphate on Peroxymonosulfate Activation: Accelerating Generation of Sulfate Radical and Underlying Mechanism. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 298, 120532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, X. Constant Oxidation of Atrazine in Fe(III)/PDS System by Enhancing Fe(III)/Fe(II) Cycle with Quinones: Reaction Mechanism, Degradation Pathway and DFT Calculation. Chemosphere 2023, 317, 137883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Ma, W.; Song, W.; Chen, C.; Tang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Huang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zang, L. Fenton Degradation of Organic Pollutants in the Presence of Low-Molecular-Weight Organic Acids: Cooperative Effect of Quinone and Visible Light. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milh, H.; Cabooter, D.; Dewil, R. Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole by Ferrous Iron Activated Peroxymonosulfate: Elucidation of the Degradation Mechanism and Influence of Process Parameters. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Wu, F. Natural Montmorillonite Induced Photooxidation of As(III) in Aqueous Suspensions: Roles and Sources of Hydroxyl and Hydroperoxyl/Superoxide Radicals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 260, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelfatah-Aldayyat, E.; González-Rojo, S.; Gómez, X. Reviewing Digestate Thermal Valorization: Focusing on the Energy Demand and the Treatment of Process Water. Environments 2024, 11, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Guo, J.; Zhou, G.; Wan, X.; Shi, H. Photodegradation of Orange II Using Waste Paper Sludge-Derived Heterogeneous Catalyst in the Presence of Oxalate under Ultraviolet Light Emitting Diode Irradiation. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 47, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xiong, Z.; Li, L.; Burt, R.; Zhao, X.S. Uptake and Degradation of Orange II by Zinc Aluminum Layered Double Oxides. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 469, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Feng, S.; Ma, X.; Tan, C.; Wang, H.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, T.; Li, J. Heterogeneous Degradation of Orange II with Peroxymonosulfate Activated by Ordered Mesoporous MnFe2O4. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 167, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Lin, T.; Chen, W.; Xu, H.; Tao, H. Significant Role of High-Valent Iron-Oxo Species in the Degradation and Detoxification of Indomethacine. Chemosphere 2020, 251, 126451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, P.; Fu, Q.; Li, R.; He, C.; Yao, W.; Wang, L.; Xie, S.; Xie, Z.; Ma, J. Strong Degradation of Orange II by Activation of Peroxymonosulfate Using Combination of Ferrous Ion and Zero-Valent Copper. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 278, 119509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Sarakha, M.; Mousty, C.; Bonnet, P.; Mailhot, G. Oxidation Mechanism from an Innovative Ternary Catalytic Process Based on Intrasystem Interaction: Decatungstate/Fe3O4/H2O2. Catal. Today 2023, 413–415, 114004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Sarakha, M.; Mousty, C.; Bonnet, P.; Mailhot, G. Tetra-n-Butylammonium Decatungstate Supported on Fe3O4 Nanoparticles: A Novel Nanocatalyst for Green Synthesis of Nitroso Compounds. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2023, 13, 1000–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, K.; Liu, J.; He, Q.; Li, G.; Li, F. Efficiently Enhancing Electrocatalytic Activity of α-MnO2 Nanorods/N-Doped Ketjenblack Carbon for Oxygen Reduction Reaction and Oxygen Evolution Reaction Using Facile Regulated Hydrothermal Treatment. Catalysts 2018, 8, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashkovtsev, M.A.; Kosykh, A.S.; Ishchenko, A.V.; Chukin, A.V.; Kukharenko, A.I.; Troshin, P.A.; Zhidkov, I.S. Unraveling Oxygen Vacancies Effect on Chemical Composition, Electronic Structure and Optical Properties of Eu Doped SnO2. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, G.; Xu, T.; Faheem, M.; Xi, Y.; Zhou, T.; Moryani, H.T.; Bao, J.; Du, J. Evolution of Singlet Oxygen by Activating Peroxydisulfate and Peroxymonosulfate: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.; Tian, X.; Nie, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Y. Promoted Peroxymonosulfate Activation into Singlet Oxygen over Perovskite for Ofloxacin Degradation by Controlling the Oxygen Defect Concentration. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 828–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, X. PMS Activation by Natural Pyrite for APAP Degradation: Underlying Mechanism and Long-Term Removal of APAP. Catal. Commun. 2023, 177, 106661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viollier, E.; Inglett, P.W.; Hunter, K.; Roychoudhury, A.N.; Van Cappellen, P. The Ferrozine Method Revisited: Fe(II)/Fe(III) Determination in Natural Waters. Appl. Geochem. 2000, 15, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Cheng, P.; Li, J.; Wu, F.; Sarakha, M.; Mailhot, G.; Brigante, M. Toward a Better Understanding of Peroxymonosulfate and Peroxydisulfate Activation Using a Nano Zero-Valent Iron Catalyst Supported on Graphitized Carbon: Mechanisms and Application to the Degradation of Estrogenic Compounds in Different Water Matrix. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 414, 137702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Materials | pH | [PMS] (mM) | [Catalyst] (g L−1) | [Orange II] (μM) | Removal Rate | kobs (min−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a-FeMn-1 | 6.0 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 50 | 97.7% | 0.378 ± 0.001 |
| a-FeMn-2 | 6.0 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 50 | 87.5% | 0.079 ± 0.002 |
| a-FeMn-5 | 6.0 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 50 | 80.0 | 0.054 ± 0.003 |
| a-FeMn-8 | 6.0 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 50 | 14.0 | 0.009 ± 0.001 |
| Material | pH | Time min | [Catalyst] g/L | [PMS] mM | [Orange II] μM | Removal Rate | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a-FeMn-1 | 6.0 | 30 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 50.0 | 95.0% | This study |
| WPS-Fe-350 ☉ | 3.0 | 80 | 1.0 | - | 85.7 | 83.0% | [41] |
| Zn-Al-LDO ☉ | - | 100 | 0.1 | - | 210.0 | 74.3% | [42] |
| Fe/Mn/Mg2-LDH | 7.0 | 30 | 1.6 | 1.0 | 50.0 | 98.0% | [4] |
| om-MnFe2O4 | - | 30 | 0.2 | 2.0 | 143 | 97.3 | [43] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, P.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; Qiu, C.; Fu, T.; Wang, Y.; Wu, F. Amorphous Fe-Doped Manganese Carbonate for Efficient Activation of Peroxymonosulfate: Mechanism and Performance Toward Orange II Degradation. Molecules 2025, 30, 2325. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112325
Cheng P, Li Y, Ma Y, Qiu C, Fu T, Wang Y, Wu F. Amorphous Fe-Doped Manganese Carbonate for Efficient Activation of Peroxymonosulfate: Mechanism and Performance Toward Orange II Degradation. Molecules. 2025; 30(11):2325. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112325
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Peng, Yuqing Li, Yunlong Ma, Cui Qiu, Tengfei Fu, Yajie Wang, and Feng Wu. 2025. "Amorphous Fe-Doped Manganese Carbonate for Efficient Activation of Peroxymonosulfate: Mechanism and Performance Toward Orange II Degradation" Molecules 30, no. 11: 2325. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112325
APA StyleCheng, P., Li, Y., Ma, Y., Qiu, C., Fu, T., Wang, Y., & Wu, F. (2025). Amorphous Fe-Doped Manganese Carbonate for Efficient Activation of Peroxymonosulfate: Mechanism and Performance Toward Orange II Degradation. Molecules, 30(11), 2325. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112325






