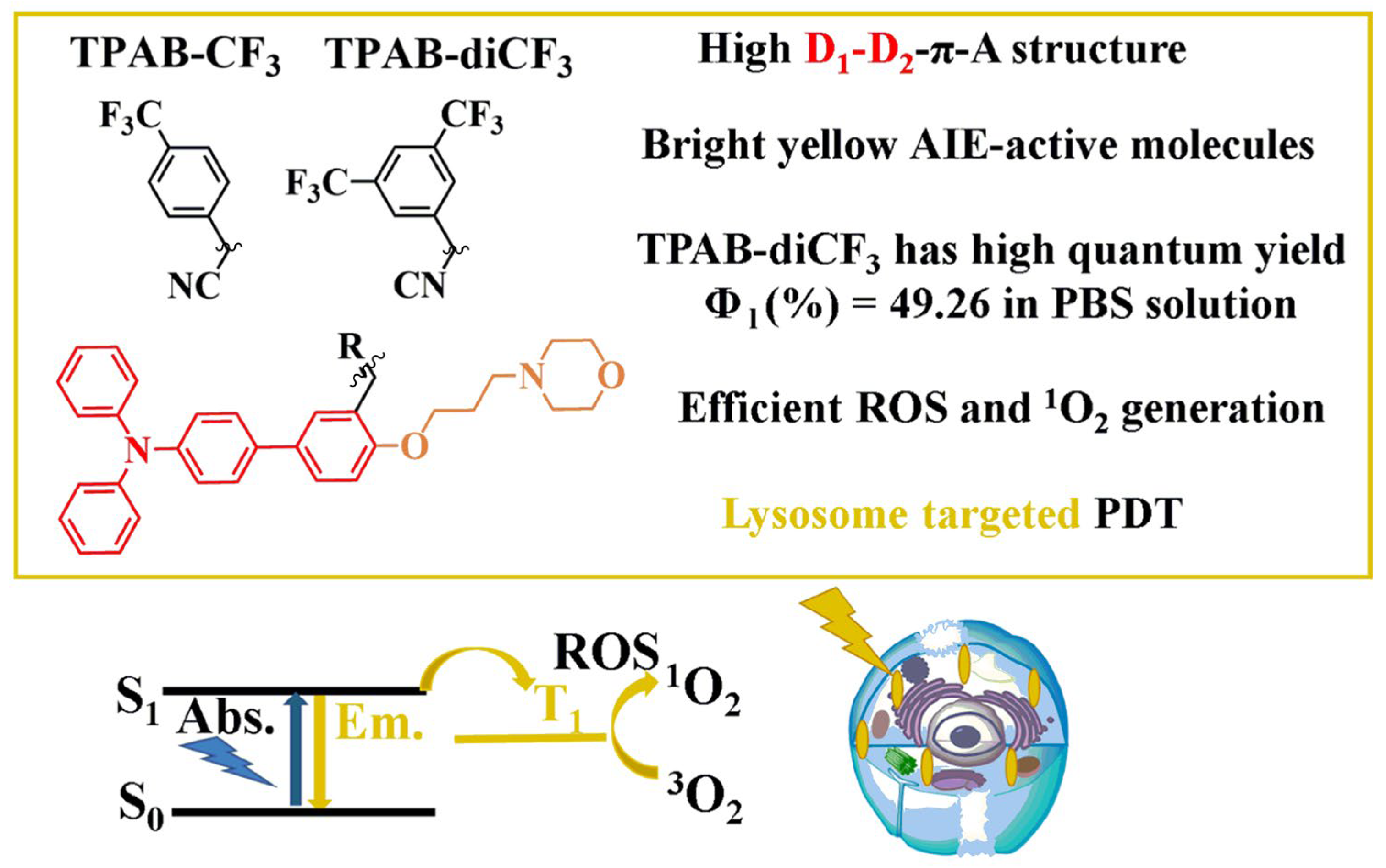
Construction of Triphenylamine-Based Aggregation-Induced Emission Luminogens for Lysosomes Imaging and Its Application in the Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis and Structural Analysis of Compounds TPAB-CF3 and TPAB-diCF3
2.2. Spectral Properties of Compounds TPAB-CF3 and TPAB-diCF3
2.3. DFT Analysis of Compounds TPAB-CF3 and TPAB-diCF3
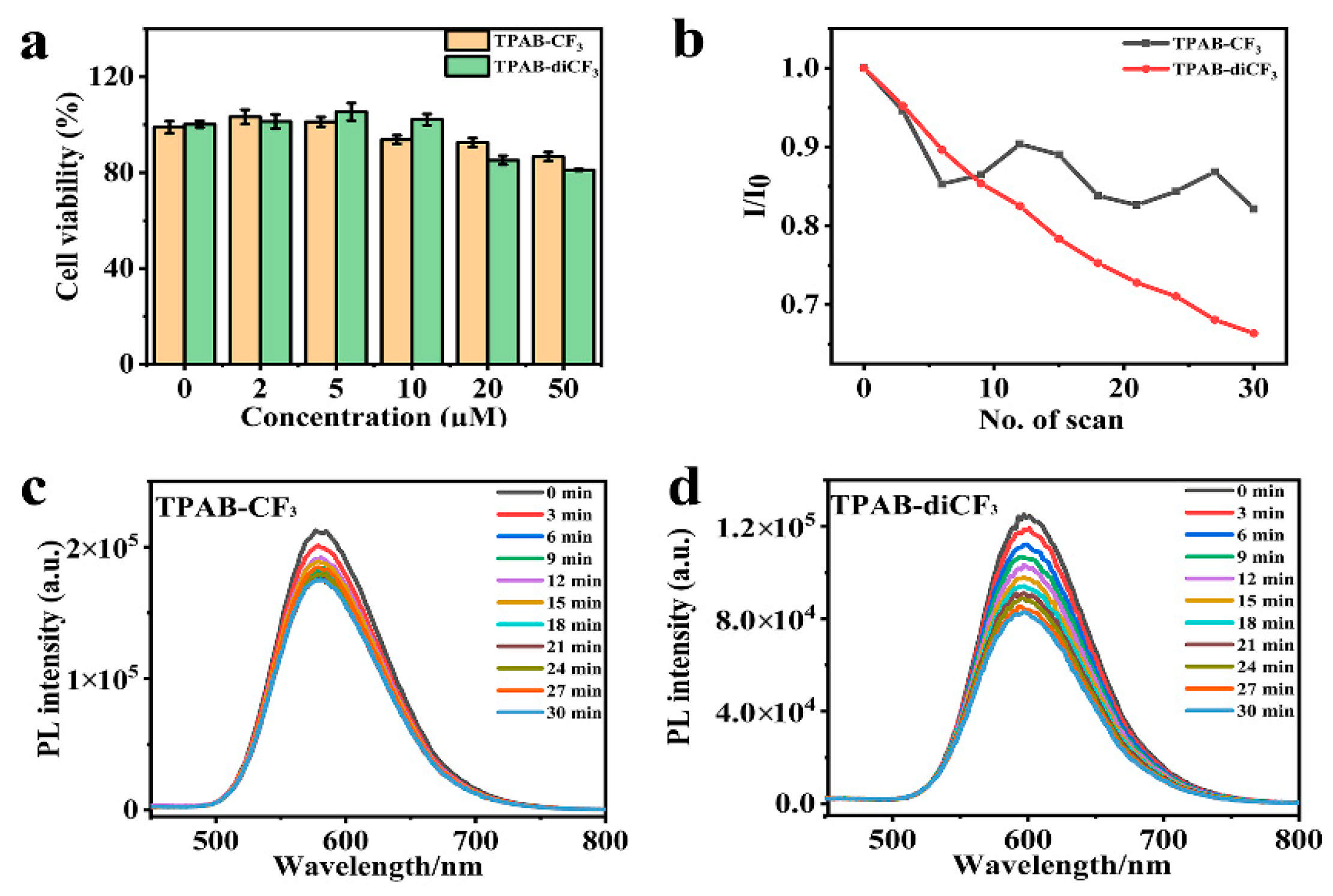
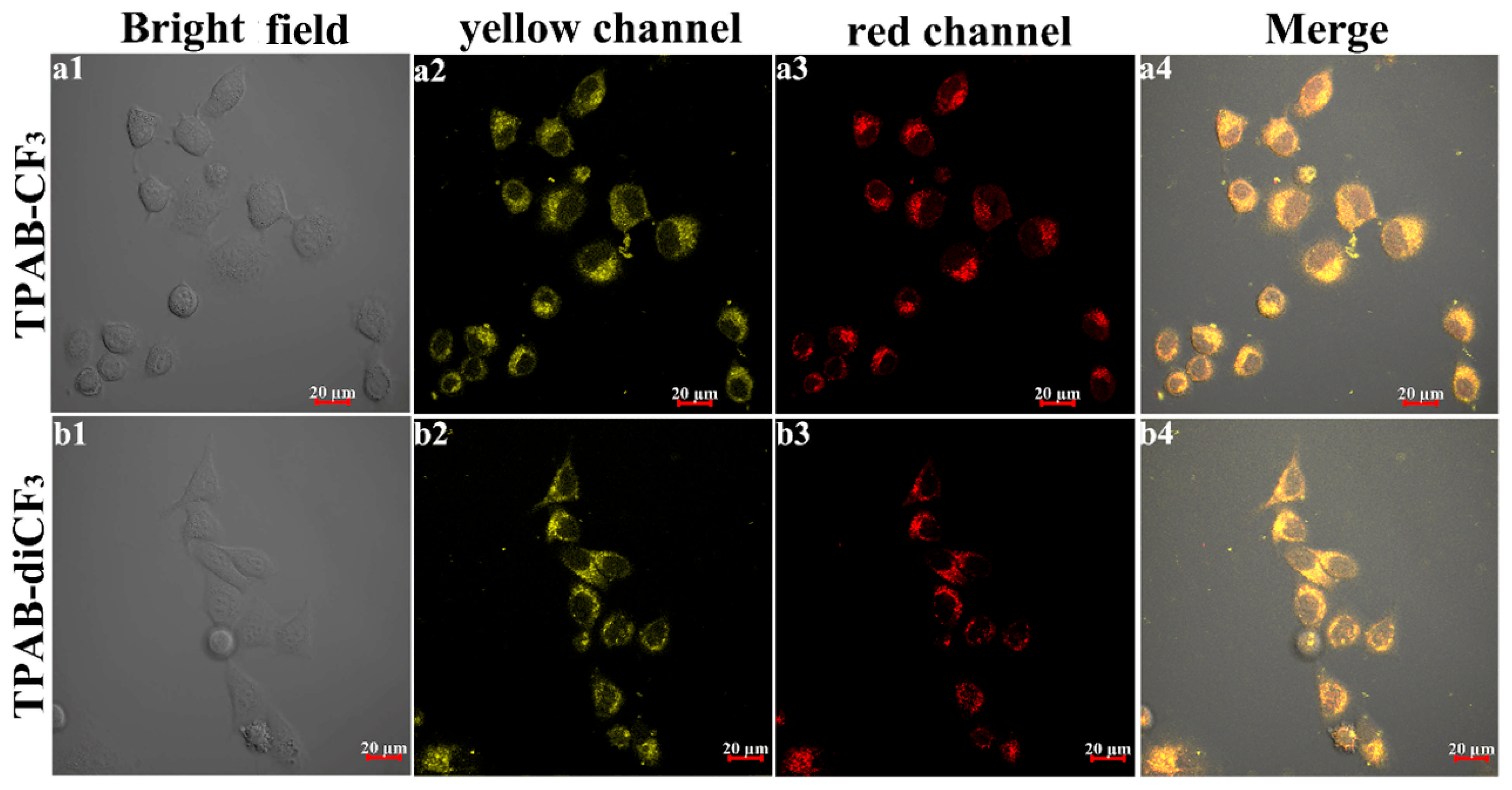
2.4. Lysosome Imaging on HeLa Cells
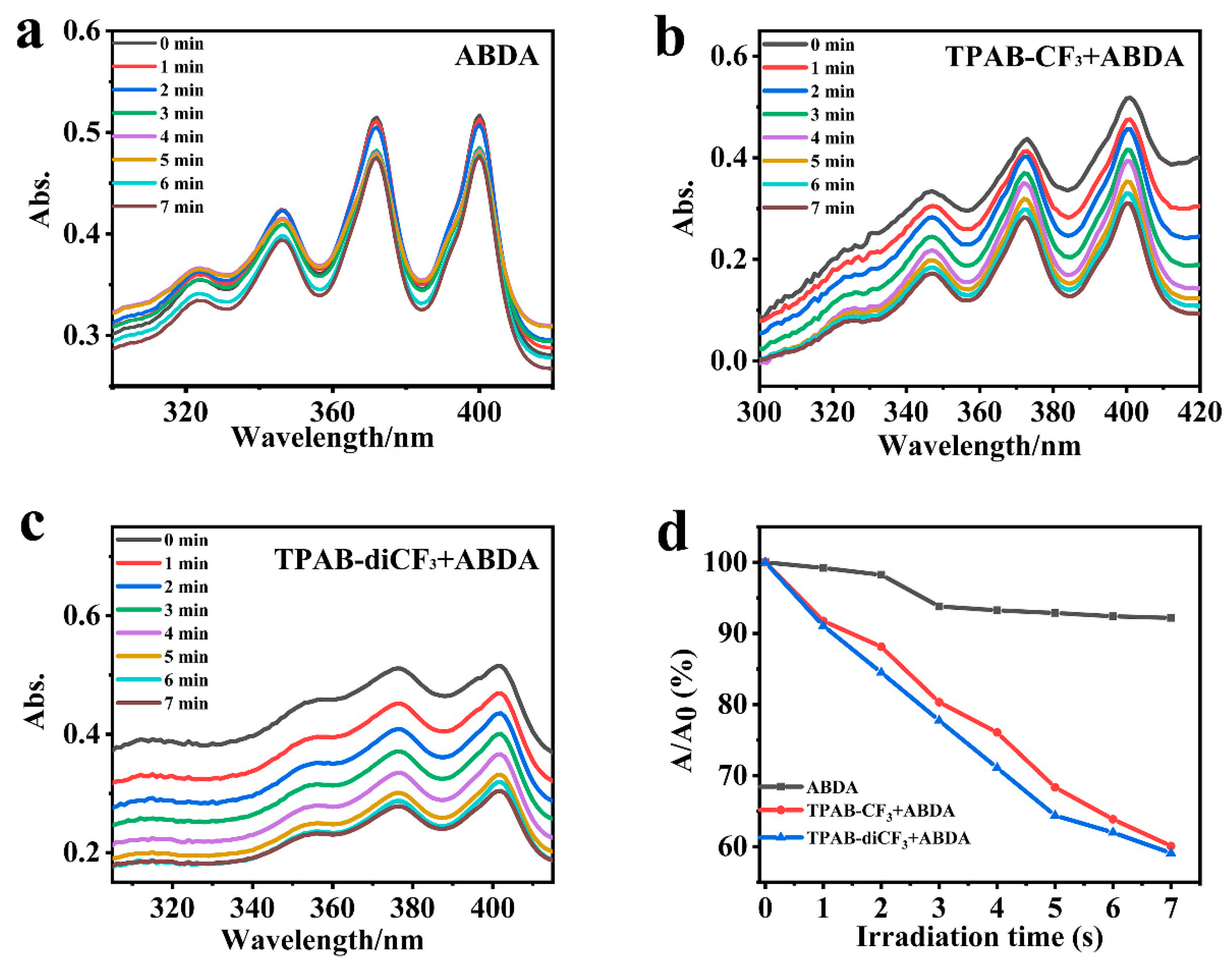
2.5. Photodynamic Therapy
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of the Probe TPAB-CF3 and TPAB-diCF3
3.2.1. Synthesis of Precursor 1 and Precursor 2
3.2.2. Synthesis of TPAB-CF3
3.2.3. Synthesis of TPAB-diCF3
3.3. Spectral Measurement
3.4. DFT Calculations
3.5. Cytotoxicity and Cellular Imaging
3.6. ROS and 1O2 Production and Phototoxicity of AIEgens on Hela Cells Under Irradiation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luzio, J.P.; Pryor, P.R.; Bright, N.A. Lysosomes: Fusion and function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebecca, V.W.; Nicastri, M.C.; McLaughlin, N.; Fennelly, C.; McAfee, Q.; Ronghe, A.; Nofal, M.; Lim, C.-Y.; Witze, E.; Chude, C.I.; et al. A unified approach to targeting the lysosome’s degradative and growth signaling roles. Cancer Discov. 2017, 11, 1266–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesen, M.H.; Pegan, K.; Spes, A.; Turk, B. Lysosomal pathways to cell death and their therapeutic applications. Exp. Cell Res. 2012, 318, 1245–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, R.E.; Zoncu, R. The lysosome as a cellular centre for signalling, metabolism and quality control. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Li, W.M.; Liao, G.J.; Xie, J.P. Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific phagosome proteome and underlying signaling pathways. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 2635–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyarzun, J.E.; Lagos, J.; Vazquez, M.C.; Valls, C.; De la Fuente, C.; Yuseff, M.I.; Alvarez, A.R.; Zanlungo, S. Lysosome motility and distribution: Relevance in health and disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2019, 1865, 1076–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devany, J.; Chakraborty, K.; Krishnan, Y. Subcellular nanorheology reveals lysosomal viscosity as a reporter for Lysosomal storage diseases. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 1351–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, R.E.; Lee, G.; Rybczynski, P.; Benjamin, E.R.; Khanna, R.; Wustman, B.A.; Valenzano, K.J. Pharmacological chaperones as therapeutics for lysosomal storage diseases. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 2705–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelqvist, H.; Wäster, P.; Kågedal, K.; Öllinger, K. The lysosome: From waste bag to potential therapeutic target. J Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 5, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallunki, T.; Olsen, O.D.; Jäättelä, M. Cancer-associated lysosomal changes: Friends or foes? Oncogene 2013, 32, 1995–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyparaki, M.T.; Papavassiliou, A.G. Lysosome: The cell’s ‘suicidal bag’ as a promising cancer target. Trends Mol. Med. 2014, 20, 239–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsubone, T.M.; Martins, W.K.; Pavani, C.; Junqueira, H.C.; Itri, R.; Baptista, M.S. Enhanced efficiency of cell death by lysosome-specific photodamage. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Yu, Y.; Xu, L.T.; Wang, S.Y.; Li, Z.J.; Liu, Y.; Kwok, R.T.K.; Sun, J.; Lam, J.W.Y.; He, G.; et al. Aggregation-induced emission luminogen based wearable visible-light penetrator for deep photodynamic therapy. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 29930–29941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.H.; Pu, K.Y. Activatable Phototheranostic materials for imaging-guided cancer therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 5286–5299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.F.; Shen, H.C.; Sun, F.Y.; Li, P.; Sun, J.W.; Kwok, R.T.K.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-induced emission luminogens for cell death research. ACS Bio Med. Chem. Au 2022, 2, 236–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, G.; Kwon, B.; Kang, H.; Modigunta, J.K.R.; Park, S.; Lee, S.; Lee, H.; Park, Y.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, S.Y.; et al. Hematoporphyrin photosensitizer-linked carbon quantum dots for photodynamic therapy of cancer cells. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 4376–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usama, S.M.; Thavornpradit, S.; Burgess, K. Optimized heptamethine cyanines for photodynamic therapy. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2018, 1, 1195–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, C.J.; Qian, Y. Novel indole-BODIPY photosensitizers based on iodine promoted intersystem crossing enhancement for lysosome-targeted imaging and photodynamic therapy. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 18082–18089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Song, S.; Ren, J.; Liu, C.; Li, Z.H.; Qi, H.; Yu, C. Controlled aggregation of a perylene-derived probe for near Infrared fluorescence imaging and phototherapy. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 5008–5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, S.; Forzano, J.A.; Dirak, M.; Chan, J. Activatable porphyrin-based sensors, photosensitizers and combination therapeutics. JACS Au 2025, 5, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.F.; Sun, R.; Cheng, J.H.; Liu, J.Y.; Gou, F.; Xiang, H.F.; Zhou, X.G. Fluorescence aggregation-caused quenching versus aggregation induced emission: A visual teaching technology for undergraduate chemistry students. J. Chem. Educ. 2016, 93, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.B.; Shi, L.L.; Duan, Y.K.; Xu, S.D.; Gao, X.H.; Zhu, X.Y.; Liu, B. Metabolizable photosensitizer with aggregation-induced emission for photodynamic therapy. Chem. Mater. 2021, 33, 5974–5980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, J.; Xie, Z.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Cheng, L.; Chen, H.; Qiu, C.; Kwok, H.S.; Zhan, X.W.; Liu, Y.Q.; Zhu, D.B.; et al. Aggregation-induced emission of 1-methyl-1,2,3,4,5-pentaphenylsilole. Chem. Commun. 2001, 18, 1740–1741. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.J.; Xin, Z.Y.; Su, X.X.; Hao, L.; Qiu, Z.J.; Li, K.; Luo, Y.M.; Cai, X.-M.; Zhang, J.Q.; Alam, P.; et al. Aggregation-induced emission luminogens realizing high-contrast bioimaging. ACS Nano 2025, 19, 281–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.X.; Cao, Y.; Shi, W.J.; Li, J.C.; Lu, W.L.; Fan, T.; Zheng, L.; Yan, J.-W.; Han, D.; Niu, L. Construction of cationic meso-thiazolium BODIPY AIE fluorescent probes for viscosity imaging in dual organelles. Chem. Commun. 2024, 60, 8864–8867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingle, J.; Basu, S. Mitochondria targeted AIE probes for cancer phototherapy. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 8925–8935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.G.; Shi, S.M.; Guan, P.L.; Liu, B. Construction of heteroaryl-bridged NIR AIEgens for specific imaging of lipid droplets and its application in photodynamic therapy. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 272, 120946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.X.; Wu, X.X.; Wang, D.; He, Y.L.; Cheng, H.; Fan, B.L.; Zhu, D.; Li, M.; et al. Engineered strategies for lipid droplets-targeted AIEgens. Molecules 2024, 29, 5904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Mo, R.F.; Yang, M.W.; Xie, H.L.; Ma, F.L.; Ding, Z.Y.; Wu, S.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Du, J.; Zhang, J.Q.; et al. Mitochondria-targeting AIEgens as pyroptosis inducers for boosting Type-I photodynamic therapy of tongue squamous cell carcinoma. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 26140–26152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.P.; He, F.R.; Ji, H.F.; Zhao, X.X.; Misal, S.; Qi, Z.J. Dual-functional NIR AIEgens for high-fidelity imaging of lysosomes in cells and photodynamic therapy. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.D.; Zhang, Y.J.; Tan, X.Y.; Wang, N.; Wang, J.H.; He, M.L.; Peng, J.; Hu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, S. An AIEgen-based photosensitizer for lysosome imaging and photodynamic therapy in tumor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 335, 129698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncali, J. Synthetic principles for bandgap control in linear π-conjugated systems. Chem. Rev. 1997, 97, 173–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, J.; Fan, J.; Chao, H.; Peng, X. Recent progress in photosensitizers for overcoming the challenges of photodynamic therapy: From molecular design to application. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 4185–4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, P.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wan, J.; Yin, X.Y.; Liu, T.; Yin, J.Y.; et al. NIR light triggered dual-cascade targeting core-shell nanoparticles enhanced photodynamic therapy and immunotherapy. Nano Today 2021, 41, 101288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Li, X.S.; Yoon, J.Y. Organelle-targeted photosensitizers for precision photodynamic therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 19543–19571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.G.; Zheng, Y.D.; Zhao, X.W.; Wang, L.J.; Ma, S.Q.; Han, X.Q.; Xu, B.; Tian, W.J.; Gao, H. Highly efficient far red/near-infrared solid fluorophores: Aggregation-induced emission, intramolecular charge transfer, twisted molecular conformation, and bioimaging applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.G.; Zhao, E.G.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Peng, Q.; Xie, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.L.; Wong, K.S.; Sung, H.H.; Williams, I.D.; Tang, B.Z. Mitochondrion-specific live-cell bioprobe operated in a fluorescence turn-on manner and a well-designed photoactivatable mechanism. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 7093–7100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhuang, Z.Y.; Zhao, Z.J.; Tang, B.Z. Type I AIE photosensitizers: Mechanism and application. View 2021, 3, 20200121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.Q.; Ou, H.; Liu, Q.; Ding, D. Gathering brings strength: How organic aggregates boost disease phototheranostics. Aggregate 2021, 2, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeRose, M.C.; Crutchley, R.J. Photosensitized singlet oxygen and its applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2002, 233, 351–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Ren, T.H.; Dong, W.J. Tuning photophysical properties of triphenylamine and aromatic cyano conjugate-based wavelength-shifting compounds by manipulating intramolecular charge transfer strength. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2013, 251, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.B.; Yang, H.X.; Li, Y.; Wang, B.; Li, N.; Zhao, N. Efficient photosensitizers with aggregation-induced emission characteristics for lysosome- and Gram-positive bacteria-targeted photodynamic therapy. Chem. Commun. 2020, 17, 2630–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.R.; Yang, M.Q.; Li, C.; Liu, G.Y.; Sun, Q.; Luo, X.G.; Wu, F.S. Single molecular-based nanoparticles with aggregation-induced emission characteristics for fluorescence imaging and efficient cancer phototherapy. Dyes Pigments 2021, 187, 109130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.P.; Zhang, D.; He, G.H.; Liu, C.; Tu, Y.N.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.B.; Wu, X.; Liu, R.Y. A lysosomal targeted NIR photosensitizer for photodynamic therapy and two-photon fluorescence imaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.H.; Wang, R.L.; Wang, S.Z.; Xie, Y.F.; Chen, H.H.; Huang, R.J.; Shao, L.Q.; Zhu, Q.H.; Liu, Y.S. Highly efficient multifunctional organic photosensitizer with Aggregation-Induced Emission for In vivo bioimaging and photodynamic therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 54783–54793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Qing, D.Y.; Zhao, S.J.; Wu, X.L.; Yang, K.; Ren, X.J.; Zheng, X.L.; Lan, M.H.; Ye, J.; Zeng, L.T.; et al. Acceptor-donor-acceptor structured deep-red AIE photosensitizer: Lysosome-specific targeting, in vivo long-term imaging, and effective photodynamic therapy. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Mao, D.; Xu, S.; Ji, S.; Hu, F.; Ding, D.; Kong, D.; Liu, B. High performance photosensitizers with aggregation-induced emission for image-guided photodynamic anticancer therapy. Mater. Horiz. 2017, 4, 1110–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Z.; Liu, B.; Liu, H. Construction of Triphenylamine-Based Aggregation-Induced Emission Luminogens for Lysosomes Imaging and Its Application in the Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer Cells. Molecules 2025, 30, 2272. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112272
Sun Z, Liu B, Liu H. Construction of Triphenylamine-Based Aggregation-Induced Emission Luminogens for Lysosomes Imaging and Its Application in the Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer Cells. Molecules. 2025; 30(11):2272. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112272
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Zhanguo, Bin Liu, and Huijun Liu. 2025. "Construction of Triphenylamine-Based Aggregation-Induced Emission Luminogens for Lysosomes Imaging and Its Application in the Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer Cells" Molecules 30, no. 11: 2272. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112272
APA StyleSun, Z., Liu, B., & Liu, H. (2025). Construction of Triphenylamine-Based Aggregation-Induced Emission Luminogens for Lysosomes Imaging and Its Application in the Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer Cells. Molecules, 30(11), 2272. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112272




