Green Synthesis of Antimicrobial Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs) from the Mucus of the Garden Snail Cornu aspersum
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from the Mucus Extract of C. aspersa (AgNPs-Muc)
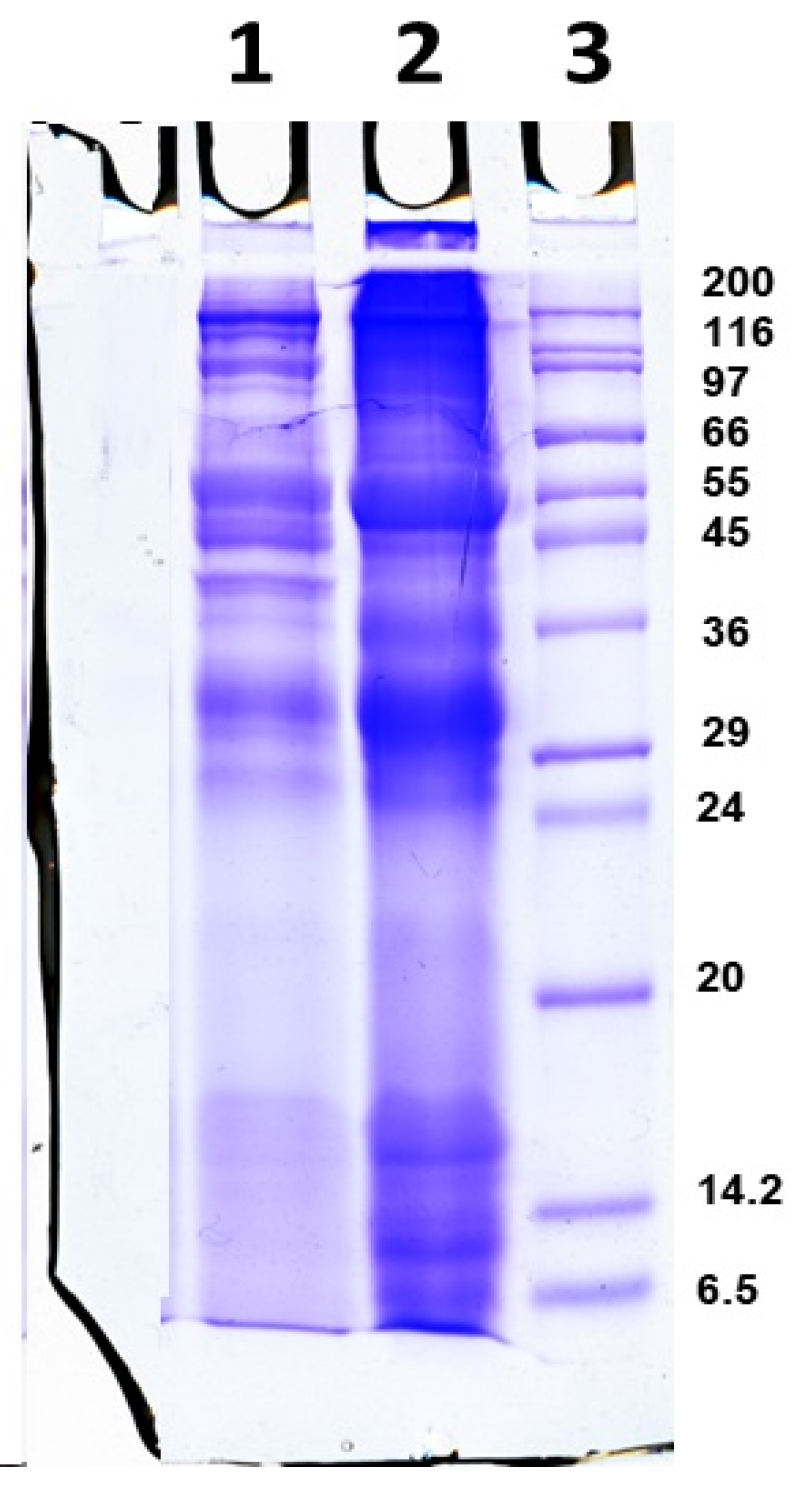
2.1.1. Isolation and Characterization of the Mucus Extract
2.1.2. Green Synthesis of AgNPs in the Mucus Matrix with MW > 20 kDa
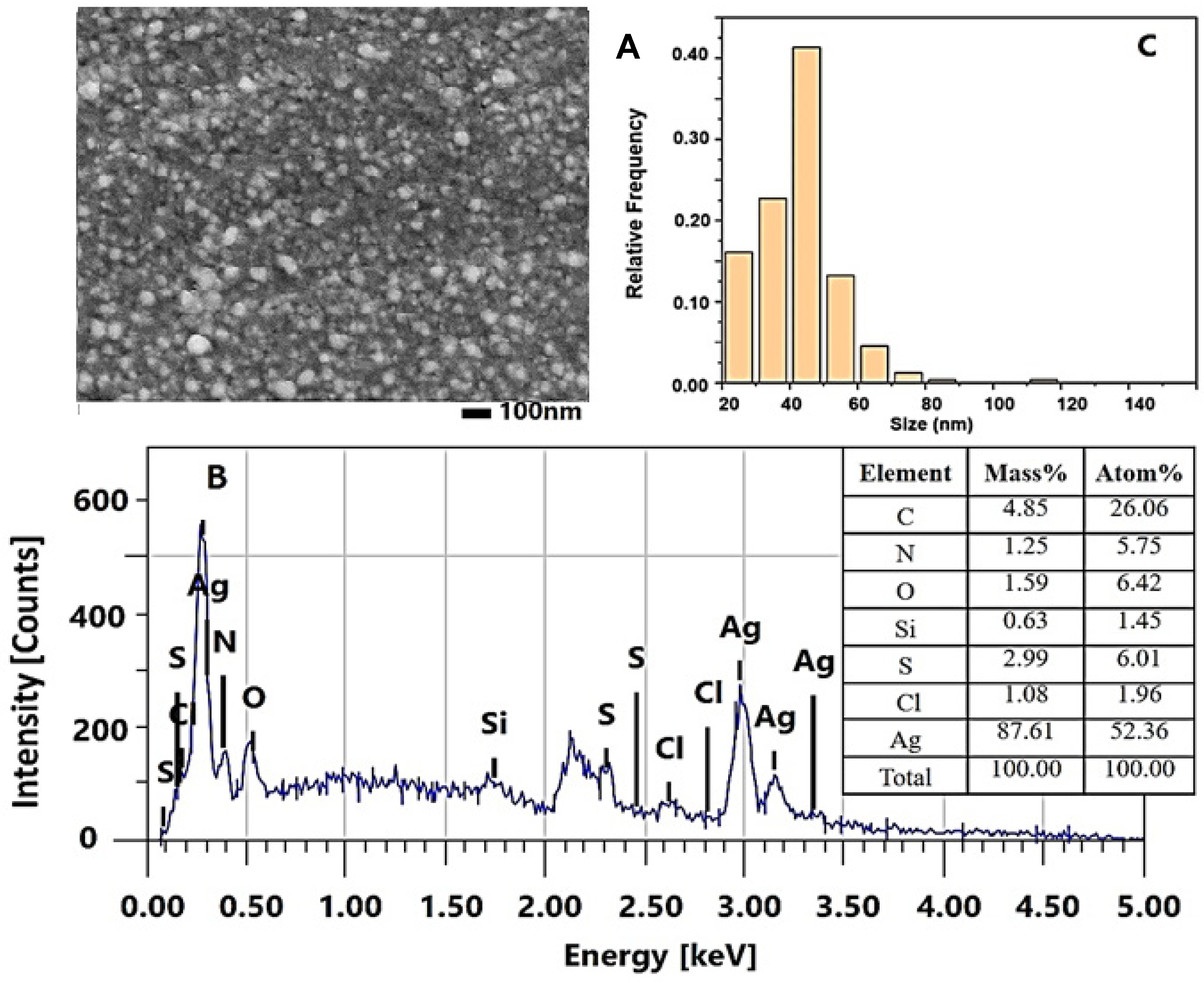
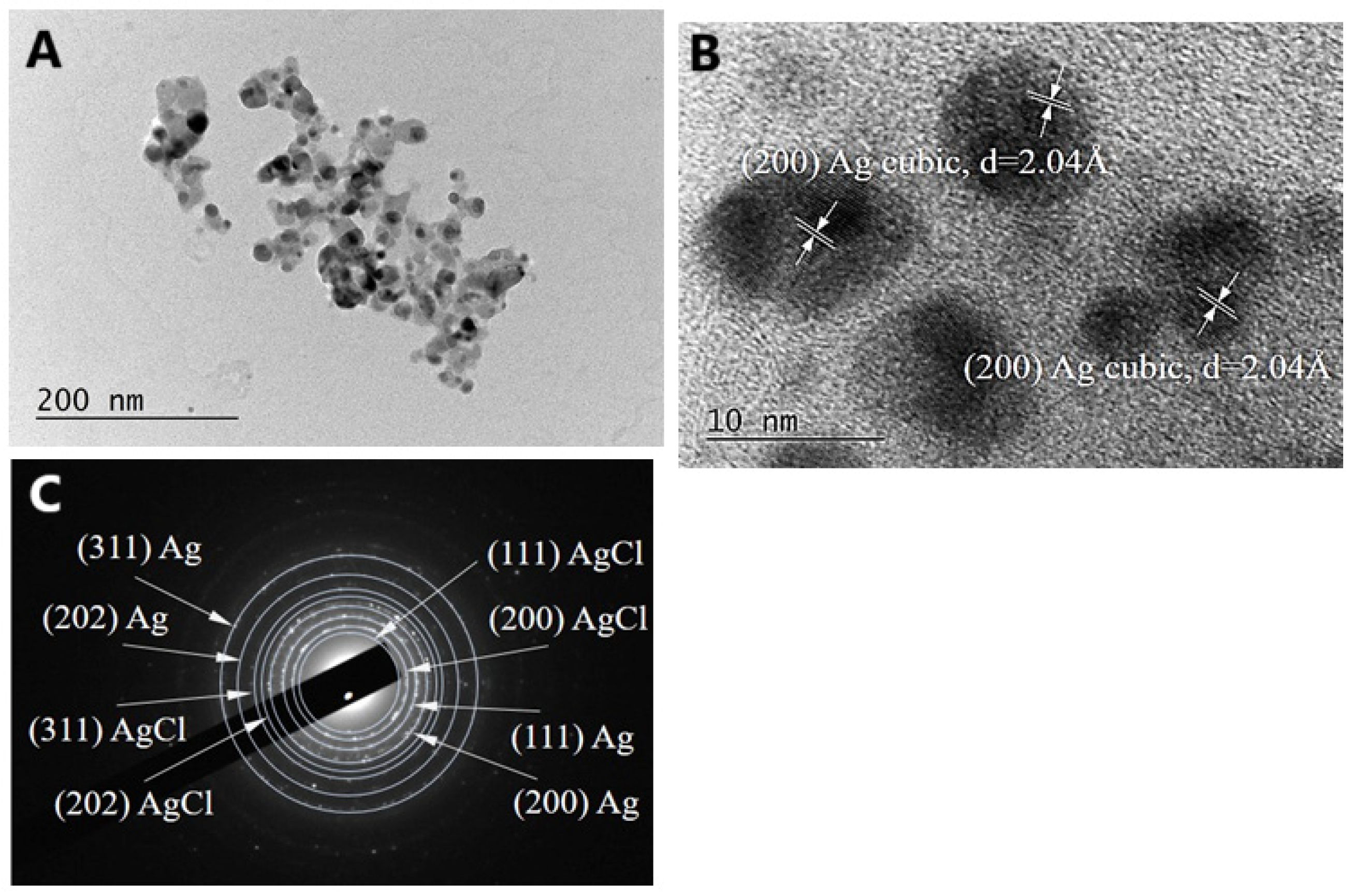
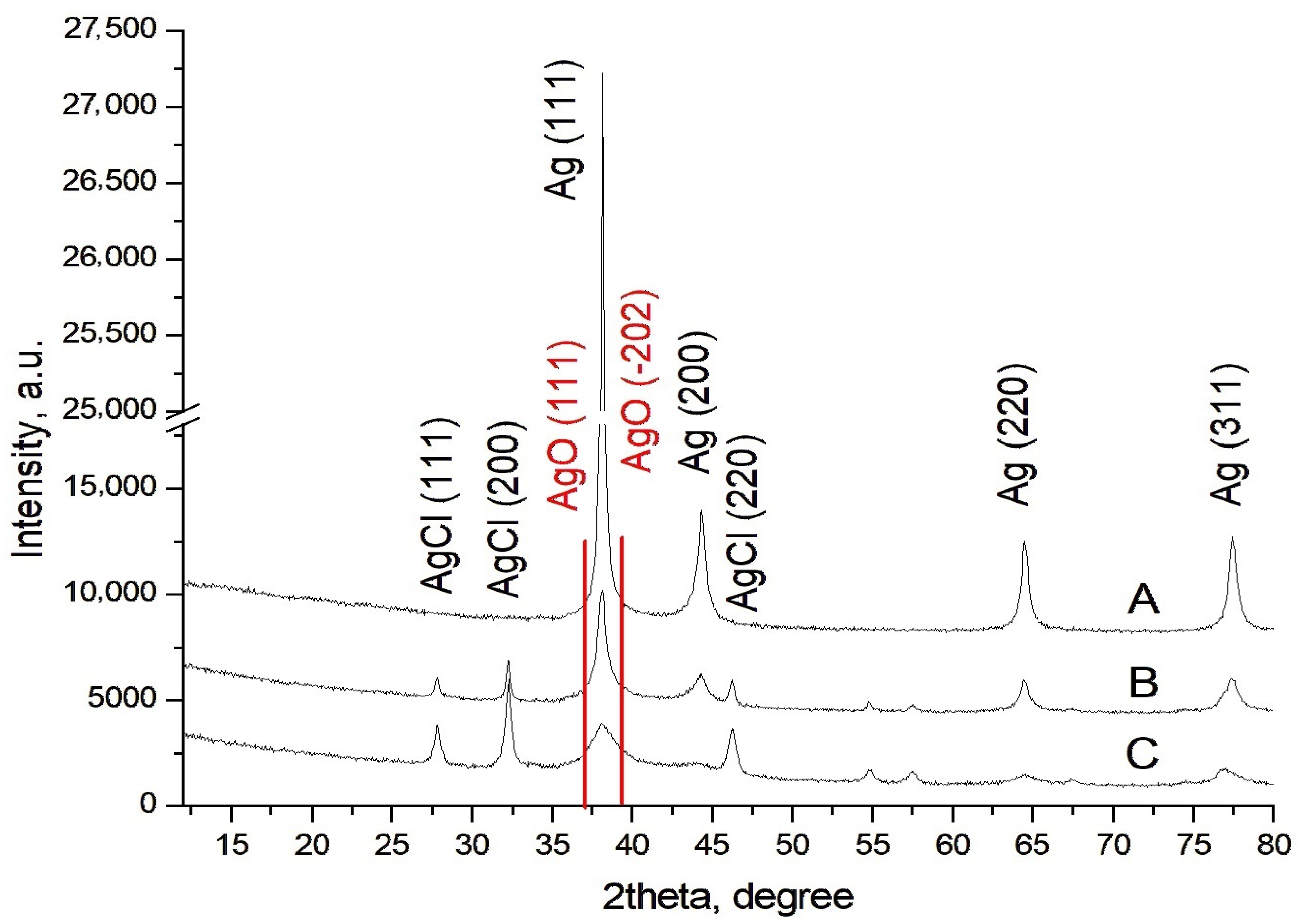
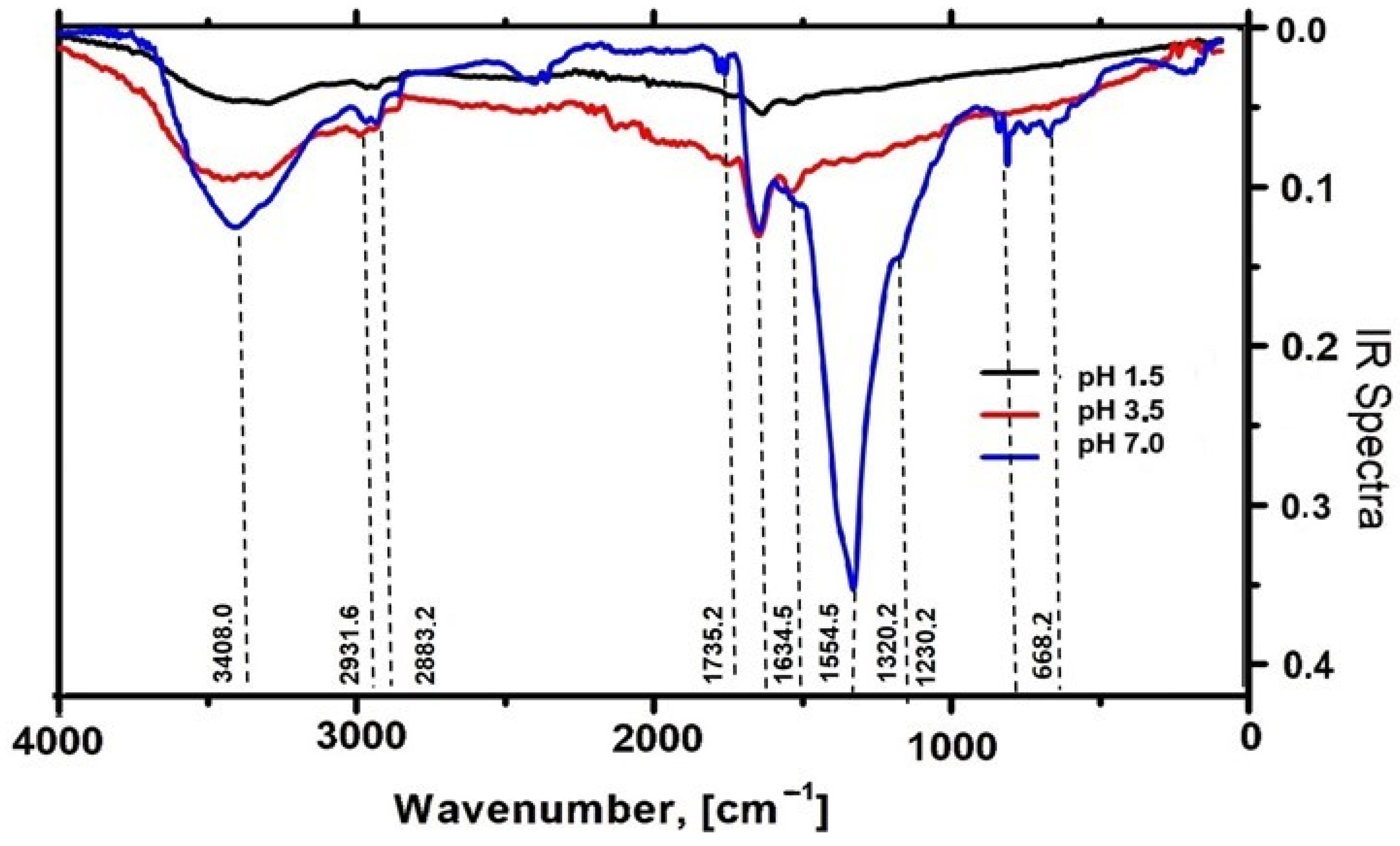
2.2. Characterization of the Obtained AgNPs-Muc
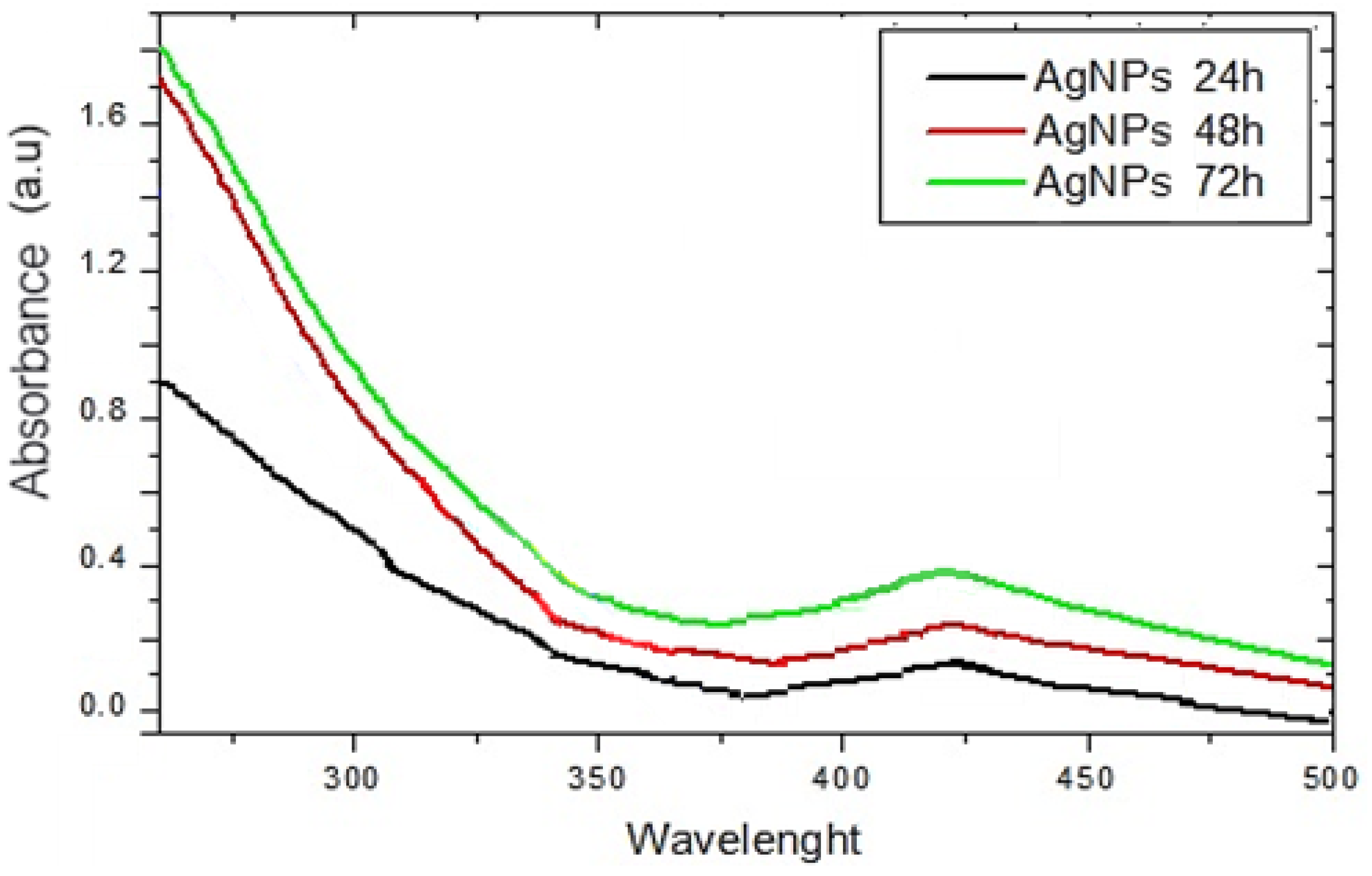
2.2.1. UV–Vis Analyses of AgNPs-Muc
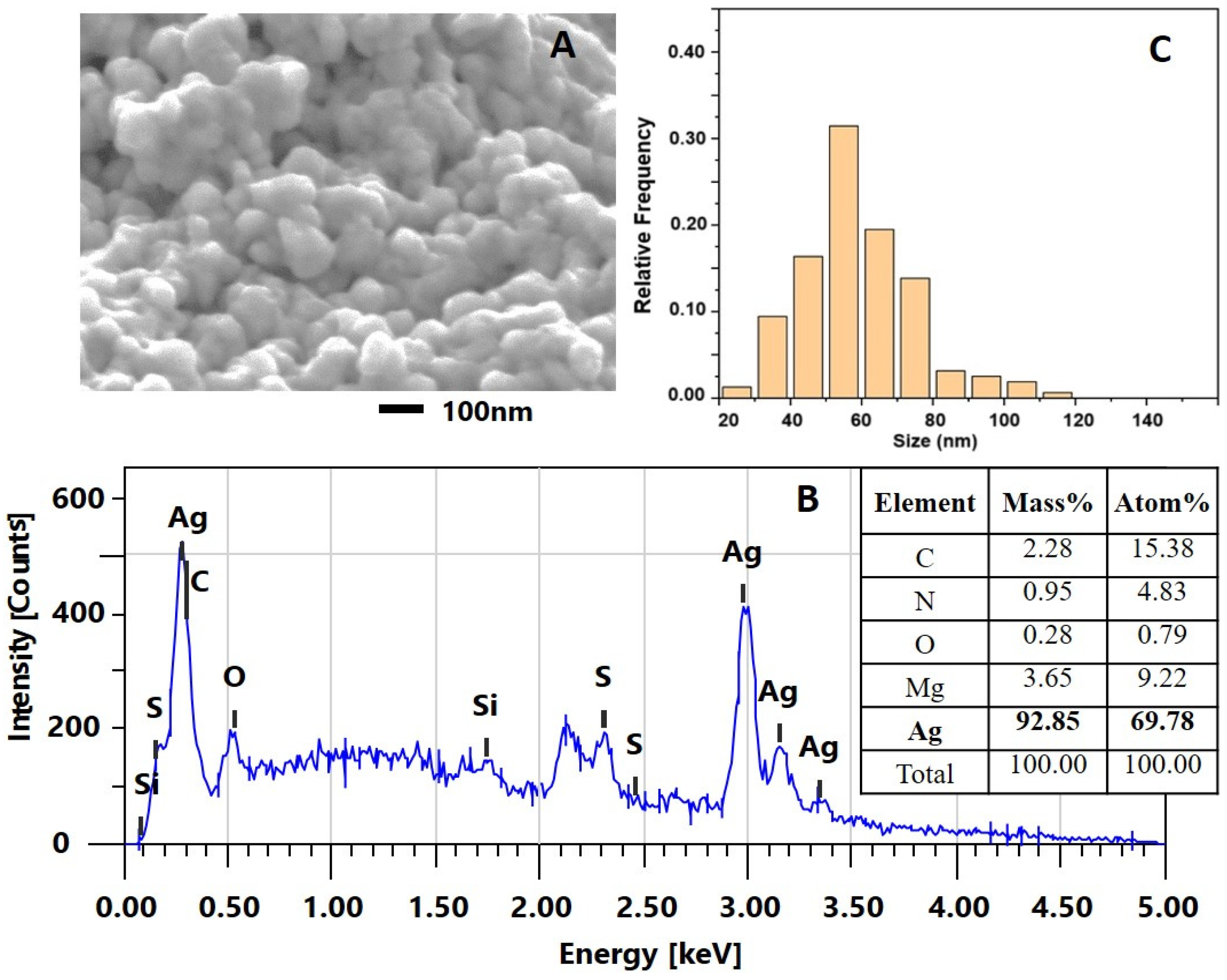
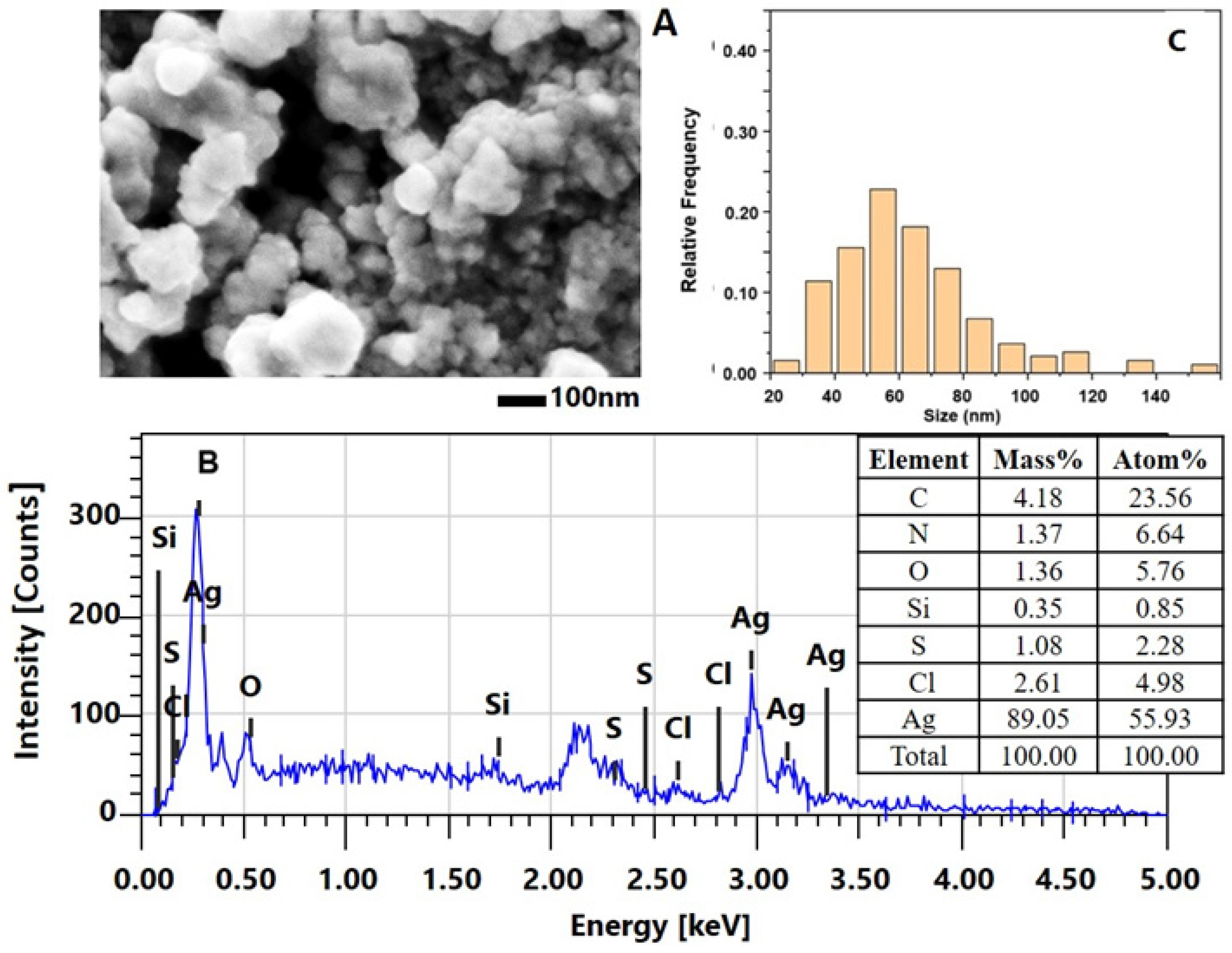
2.2.2. Characterization of the AgNPs-Muc Using Scanning Electron Microscopy Combined with Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (SEM/EDS)
2.2.3. Characterization of AgNPs-Muc Using Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.2.4. Characterization of AgNPs-Muc Using X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.2.5. Characterization of AgNPs-Muc by Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
2.3. Antibacterial Effect of AgNPs-Muc
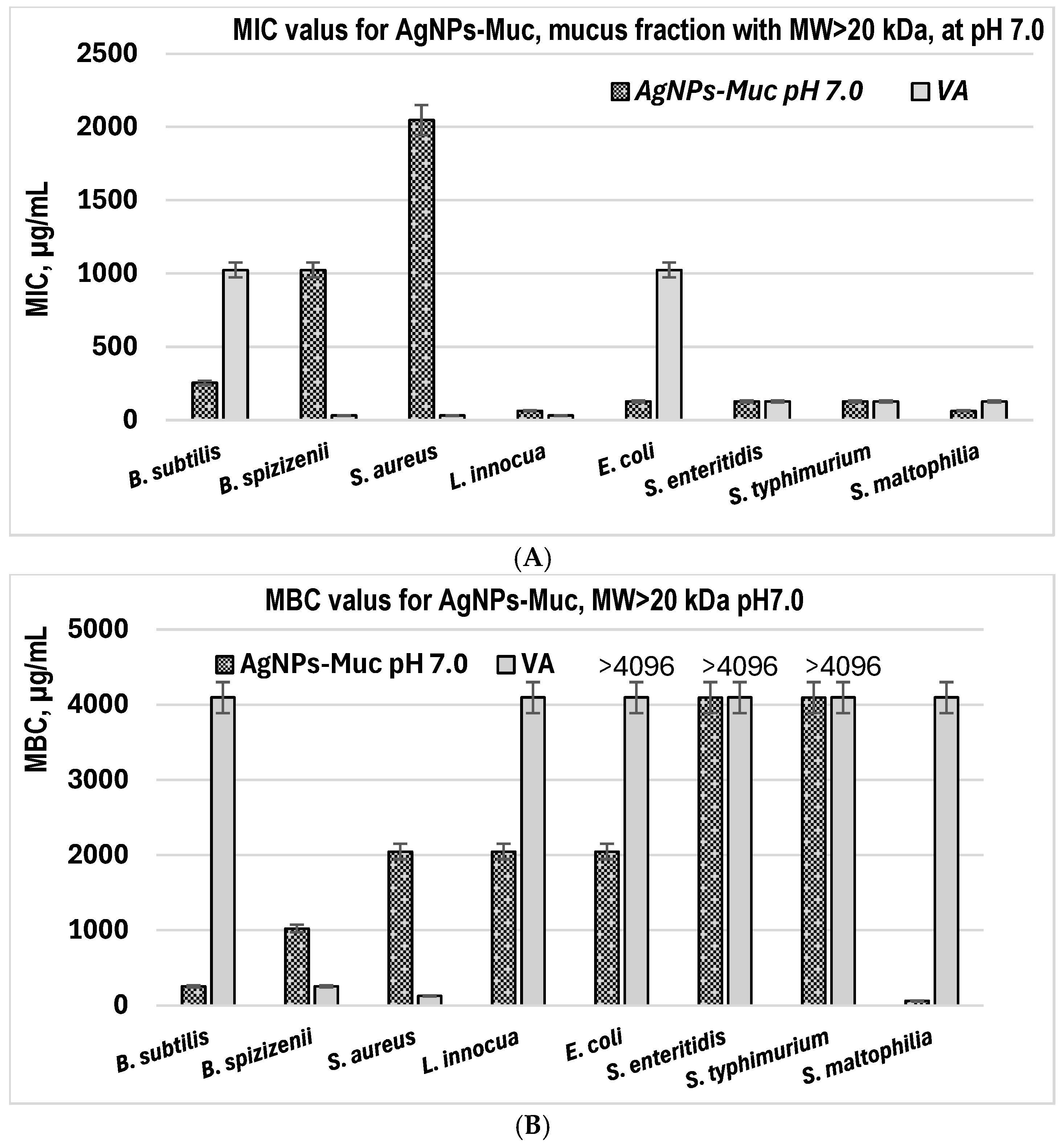
2.4. Evaluation of the MIC and MBC of AgNPs-Muc
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Mucus Samples
4.2. 1D-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (1D-PAGE)
4.3. Synthesis of AgNPs-Muc
- (1)
- To the obtained solution of 0.5 g of lyophilized mucus fraction with MW > 20 kDa in 100 mL of distilled H2O, 50 mL of a solution of 50 mM AgNO3 was added and homogenized for about 40 min on a magnetic stirrer. The obtained solution was titrated to pH 1.5 with a solution of 250 mM ascorbic acid (AsA).
- (2)
- The obtained solution of mucus fraction with MW > 20 kD and 50 mL of a solution of 50 mM AgNO3 was titrated to pH 3.5 with a solution of 250 mM AsA.
- (3)
- The green synthesis of AgNPs-Muc was performed at pH 7.0 (without titration by AsA) under the same conditions mentioned above in a solution of 0.5 g of lyophilized mucus fraction with MW > 20 kDa, 100 mL of distilled H2O, and 50 mL of 50 mM AgNO3 with moderate homogenization on a magnetic stirrer.
4.4. Characterization of Biogenic AgNPs-Muc
4.4.1. Characterization of AgNPs-Muc Using UV–Vis Spectroscopy
4.4.2. Characterization of AgNPs-Muc Using SEMT
4.4.3. Characterization of AgNPs-Muc Using X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
4.4.4. Analysis of AgNPs-Muc Using Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
4.4.5. Characterization of AgNPs-Muc Using FT-IR
4.5. Antibacterial Activity Assessment
4.5.1. Strains and Growth Conditions
4.5.2. Agar Well Diffusion Assay
4.5.3. Evaluation of MIC and MBC
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rane, A.V.; Kanny, K.; Abitha, V.K.; Thomas, S. Methods for Synthesis of Nanoparticles and Fabrication of Nanocomposites. In Synthesis of Inorganic Nanomaterials; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2018; pp. 121–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailova, E.O. Green Silver Nanoparticles: An Antibacterial Mechanism. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iravani, S.; Korbekandi, H.; Mirmohammadi, S.V.; Zolfaghari, B. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles: Chemical, Physical and Biological Methods. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 9, 385–406. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, H.; Wang, D.; Li, Y. Green Chemistry for Nanoparticle Synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 5778–5792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinoi, P.; Chen, Y.T.; Vittur, V.; Marquez, M.D.; Lee, T.R. Bimetallic nanoparticles: Enhanced magnetic and optical properties for merging biological applications. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubitosa, J.; Rizzi, V.; Fini, P.; Laurenzana, A.; Fibbi, G.; Veiga-Villauriz, C.; Fanelli, F.; Fracassi, F.; Onzo, A.; Bianco, G.; et al. Biomolecules from Snail Mucus (Helix aspersa) Conjugated Gold Nanoparticles, Exhibiting Potential Wound Healing and Anti-Inflammatory Activity. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 10876–10888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikh, W.A.; Chakraborty, S.; Owens, G.; Islam, R.U. A Review of the Phytochemical Mediated Synthesis of AgNP (Silver Nanoparticle): The Wonder Particle of the Past Decade. Appl. Nanosci. 2021, 11, 2625–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajan, R.; Huo, P.; Chandran, K.; Dakshinamoorthi, B.M.; Yun, S.I.; Liu, B. A review on the toxicity of silver nanoparticles against different biosystems. Chemosphere 2022, 292, 133397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, A.; Singh, S.; Ravichandiran, V. Toxicity, preparation methods and applications of silver nanoparticles: An update. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2022, 32, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, S.S.; Yi, D.K. Recent Advances in Synergistic Effect of Nanoparticles and Its Biomedical Application. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, N.; Iqbal, D.; Al Othaim, A.; Kamal, M.; Albadrani, H.M.; Algehainy, N.A.; Alyenbaawi, H.; Alghofaili, F.; Amir, M.; Roohi. Antibacterial efficacy of synthesized silver nanoparticles of Microbacterium proteolyticum LA2(R) and Streptomyces rochei LA2(O) against biofilm forming meningitis causing microbes. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadhasivam, S.; Shanmugam, P.; Yun, K. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles by Streptomyces hygroscopicus and antimicrobial activity against medically important pathogenic microorganisms. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 81, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Sagar, A.; Rana, J.; Rani, R. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its antibacterial activity using fungus Talaromyces purpureogenus isolated from Taxus baccata Linn. Micro Nano Syst. Lett. 2022, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.S.; Yousef, N.M.; Nafady, N.A. Application of Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles for the Control of Land Snail Eobania vermiculata and Some Plant Pathogenic Fungi. J. Nanomater. 2015, 1, 218904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Dash, S.K.; Mandal, D.; Ghosh, T.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Tripathy, S.; Das, S.; Dey, S.K.; Das, D.; Roy, S. Green synthesized silver nanoparticles destroy multidrug resistant bacteria via reactive oxygen species mediated membrane damage. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, 862–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyeyemi, O.; Babalola, B.; Akinmulero, T.; Adesida, P.; Oyeyemi, I. Molluscicidal activities of green-synthesized Alstonia congensis silver nanoparticles. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2023, 13, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussin, J.; Robles-Botero, V.; Casañas-Pimentel, R.; Rojas, F.; Angiolella, L.; San Martín-Martínez, E.; Giusiano, G. Antimicrobial and cytotoxic activity of green synthesis silver nanoparticles targeting skin and soft tissue infectious agents. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, V.; Sagadevan, S.; Muthukrishnan, L.; Johan, M.R.; Podder, J. Eco-friendly approach in synthesis of silver nanoparticles and evaluation of optical, surface morphological and antimicrobial properties. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2019, 9, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatimah, I.; Hidayat, H.; Purwiandono, G.; Khoirunisa, K.; Zahra, H.A.; Audita, R.; Sagadevan, S. Green Synthesis of Antibacterial Nanocomposite of Silver Nanoparticle-Doped Hydroxyapatite Utilizing Curcuma longa Leaf Extract and Land Snail (Achatina fulica) Shell Waste. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, S.; Kalishwaralal, K.; Vaidyanathan, R.; Venkataraman, D.; Pandian, S.R.; Muniyandi, J.; Hariharan, N.; Eom, S.H. Biosynthesis, purification and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Escherichia coli. Colloids Surf. B Biointer. 2009, 74, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, S.; Han, J.W.; Kim, E.S.; Park, J.H.; Kim, J.H. Reduction of graphene oxide by resveratrol: A novel and simple biological method for the synthesis of an effective anticancer nanotherapeutic molecule. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 2951–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mane, P.; Sayyed, S.; Kadam, D.; Shinde, M.; Fatehmulla, A.; Aldhafiri, A.; Alghamdi, E.; Amalnerkar, D.; Chaudhari, R. Terrestrial snail-mucus mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and in vitro investigations on their antimicrobial and anticancer activities. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surowka, K.; Ligaszewski, M.; Szymczyk, B.; Anthony, B. Amino acid profile and nutritional quality parameters of small brown snail (Cornu aspersum aspersum) edible parts protein from commercial production in field pens. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 140, 107221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Filippo, M.F.; Di Matteo, V.; Dolci, L.S.; Albertini, B.; Ballarin, B.; Cassani, M.C.; Passerini, N.; Gentilomi, G.A.; Bonvicini, F.; Panzavolta, S. Effectiveness of Snail Mucus in the Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topalova, Y.; Belouhova, M.; Velkova, L.; Dolashki, A.; Zheleva, N.; Daskalova, E.; Kaynarov, D.; Voelter, W.; Dolashka, P. Effect and mechanisms of antibacterial peptide fraction from mucus of Cornu aspersum against Escherichia coli NBIMCC 8785. Biomedicine 2022, 10, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velkova, L.; Dolashki, A.; Petrova, V.; Pisareva, E.; Kaynarov, D.; Kermedchiev, M.; Todorova, M.; Dolashka, P. Antibacterial Properties of Peptide and Protein Fractions from Cornu aspersum Mucus. Molecules 2024, 29, 2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daskalova, E.; Belouhova, M.; Zheleva, N.; Topalova, Y.; Velkova, L.; Dolashki, A.; Dolashka, P. Antibacterial activity of combined nanodiamonds and snail fractions with biocompounds with MW below 10 kDa and above 30 kDa. C. R. Acad. Bulg. Sci. 2023, 76, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilev, N.; Simova, S.; Dangalov, M.; Velkova, L.; Atanasov, V.; Dolashki, A.; Dolashka, P. An 1H NMR and MS based study of metabolomics profiling of garden snail Helix aspersa mucus. Metabolites 2020, 10, 360–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolashka, P.; Marinova, K.; Petrov, P.; Petrova, V.; Ranguelov, B.; Atanasova-Vladimirova, S.; Kaynarov, D.; Stoycheva, I.; Pisareva, E.; Tomova, A.; et al. Development of CuO Nanoparticles from the Mucus of Garden Snail Cornu aspersum as New Antimicrobial Agents. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorova, M.; Kosateva, A.; Petrova, V.; Ranguelov, B.; Atanasova-Vladimirova, S.; Avdeev, G.; Stoycheva, I.; Pisareva, E.; Tomova, A.; Velkova, L.; et al. Green Synthesis of Antibacterial CuO Nanoparticles Based on the Synergy Between Cornu aspersum Snail Mucus and Ascorbic Acid. Molecules 2025, 30, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolashka, P.; Atanasov, D. Device for Collecting Extracts from Garden Snail. BG Utility Model Application Number 2656, 08.11.2013. Patent Number 2097, 31 August 2015. Available online: https://portal.bpo.bg/bpo_online/-/bpo/utility-model-detail (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Dolashki, A.; Velkova, L.; Daskalova, E.; Zheleva, N.; Topalova, Y.; Atanasov, V.; Voelter, W.; Dolashka, P. Antimicrobial activities of different fractions from mucus of the garden snail Cornu aspersum. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govarthanan, M.; Selvankuma, T.; Manoharan, K.; Rathika, P.; Shanthi, K.; Lee, K.; Cho, M.; Kamala-Kannan, S.; Oh, B. Biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using panchakavya, an Indian traditional farming formulating agent. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 4, 1593–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habubi, N.F.; Abd, A.N.; Dawood, M.O.; Reshak, A.H. Fabrication and characterization of a p-AgO/PSi/n-Si heterojunction for solar cell applications. Silicon 2018, 10, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardar, R.; Funston, A.M.; Mulvaney, P.; Murray, R.W. Gold nanoparticles: Past, present, and future. Langmuir 2009, 25, 13840–13851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Liu, Z.G.; Shen, W.; Gurunathan, S. Silver Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, Properties, Applications, and Therapeutic Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugliandolo, E.; Cordaro, M.; Fusco, R.; Peritore, A.F.; Siracusa, R.; Genovese, T.; D’Amico, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Di Paola, R.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Protective Effect of Snail Secretion Filtrate against Ethanol-Induced Gastric Ulcer in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noothuan, N.; Apitanyasai, K.; Panha, S.; Tassanakajon, A. Snail Mucus from the Mantle and Foot of Two Land Snails, Lissachatina fulica and Hemiplecta distincta, Exhibits Different Protein Profile and Biological Activity. BMC Res. Notes 2021, 14, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onzo, A.; Pascale, R.; Acquavia, M.A.; Cosma, P.; Gubitosa, J.; Gaeta, C.; Iannece, P.; Tsybin, Y.; Rizzi, V.; Guerrieri, A.; et al. Untargeted Analysis of Pure Snail Mucus and Snail Mucus-Induced Au Nanoparticles Metabolome with MALDI FT-ICR MS. J. Mass Spectrom. 2021, 56, 4722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uthayakumar, V.; Ramasubramanian, V.; Senthilkumar, D.; Priyadarisini, V.B.; Harikrishanan, R. Biochemical characterization, antimicrobial and hemolytic studies on skin mucus of freshwater spiny eel Mastacembelus armatus. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2012, 2, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, U.I.; Mirela, S.; Ionel, J. Quantification of mucoproteins (glycoproteins) from snails mucus, Helix aspersa and Helix pomatia. J. Agroaliment. Process. Technol. 2011, 17, 410–413. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Wang, D.I.C.; Ting, Y.P. Silver Nanoplates: From Biological to Biomimetic Synthesis. ACS Nano 2007, 1, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, B.; Tang, R.C. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles with Antibacterial Activities Using Aqueous Eriobotrya Japonica Leaf Extract. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 015014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darroudi, M.; Bin Ahmad, M.; Abdullah, A.H.; Ibrahim, N.A. Green Synthesis and Characterization of Gelatin-Based and Sugar-Reduced Silver Nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algotiml, R.; Gab-Alla, A.; Seoudi, R.; Abulreesh, H.H.; El-Readi, M.Z.; Elbanna, K. Anticancer and Antimicrobial Activity of Biosynthesized Red Sea Marine Algal Silver Nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, P.; Luo, Q.X.; Naz, A.; Khan, I.A.; Liu, X.; Yu, C.; Wei, J. Silver Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Structure, Properties and Applications. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurunathan, S.; Han, J.W.; Kwon, D.N.; Kim, J.H. Enhanced antibacterial and anti-biofilm activities of silver nanoparticles against Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahverdi, A.R.; Fakhimi, A.; Shahverdi, H.R.; Minaian, S. Synthesis and Effect of Silver Nanoparticles on the Antibacterial Activity of Different Antibiotics against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Nanomedicine 2007, 3, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stengel, D.; Jörgensen, A.M.; Polidori, I.; Kapitza, P.; Ricci, F.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. The power of sulfhydryl groups: Thiolated lipid-based nanoparticles enhance cellular uptake of nucleic acids. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 654, 1136–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, K.N.; Mhatre, S.S.; Parikh, R.Y. Biological synthesis of metallic nanoparticles. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2010, 6, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Chiang, Y.W.; Santos, R.M. X-ray Diffraction Techniques for Mineral Characterization: A Review for Engineers of the Fundamentals, Applications, and Research Directions. Minerals 2022, 12, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryshchepa, O.; Pomastowski, P.; Buszewski, B. Silver Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Investigation Techniques, and Properties. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 284, 102246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skingsley, D.R.; White, A.J.; Weston, A. Analysis of Pulmonate mucus by infrared spectroscopy. J. Moll. Stud. 2000, 66, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, D.M.; Man, Y.B.C.; Norakasha, R.; Shuhaimi, M.; Salmah, Y.; Syahariza, Z.A. Potential Use of Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy for Differentiation of Bovine and Porcine Gelatins. Food Chem. 2010, 118, 856–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S. Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 2638–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, C.; Khoshnamvand, M.; Liu, P.; Yuan, C.-G.; Cao, W. Eco-friendly approach for biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Citrus maxima peel extract and their characterization, catalytic, antioxidant and antimicrobial characteristics. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 015010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailov, O.V.; Mikhailova, E.O. Elemental silver nanoparticles. Biosynthesis and bio application. Materials 2019, 12, 3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailova, E.O. Silver Nanoparticles: Mechanism of Action and Probable Bio-Application. J. Funct. Biomater. 2020, 11, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morones, J.R.; Elechiguerra, J.L.; Camacho, A.; Holt, K.; Kouri, J.B.; Ramírez, J.T.; Yacaman, M.J. The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 2346–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Tak, Y.K.; Song, J.M. Does the antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles depend on the shape of the nanoparticle? A study of the Gram-negative bacterium. Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1712–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvekar, P.; Palaskar, J.; Metgud, S.; Maria, R.; Dutta, S. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) of silver nanoparticles against Staphylococcus aureus. Biomater. Investig. Dent. 2020, 7, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dalen, R.; Peschel, A.; van Sorge, N.M. Wall Teichoic Acid in Staphylococcus aureus Host Interaction. Trends Microbiol. 2020, 28, 985–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balouiri, M.; Sadiki, M.; Ibnsouda, S.K. Methods for in vitro evaluating antimicrobial activity: A review. J. Pharm. Anal. 2016, 6, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sriram, M.I.; Kalishwaralal, K.; Barathmanikanth, S.; Gurunathani, S. Size-based cytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in bovine retinal endothelial cells. Nanosci. Methods 2012, 1, 56–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoehr, L.C.; Gonzalez, E.; Stampfl, A.; Casals, E.; Duschl, A.; Puntes, V.; Oostingh, G.J. Shape matters: Effects of silver nanospheres and wires on human alveolar epithelial cells. Part. Fiber Toxicol. 2011, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, A.K.; Pelletier, D.A.; Wang, W.; Morrell-Falvey, J.L.; Gu, B.H.; Doktycz, M.J. Cytotoxicity induced by engineered silver nanocrystallites is dependent on surface coatings and cell Types. Langmuir 2012, 28, 2727–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

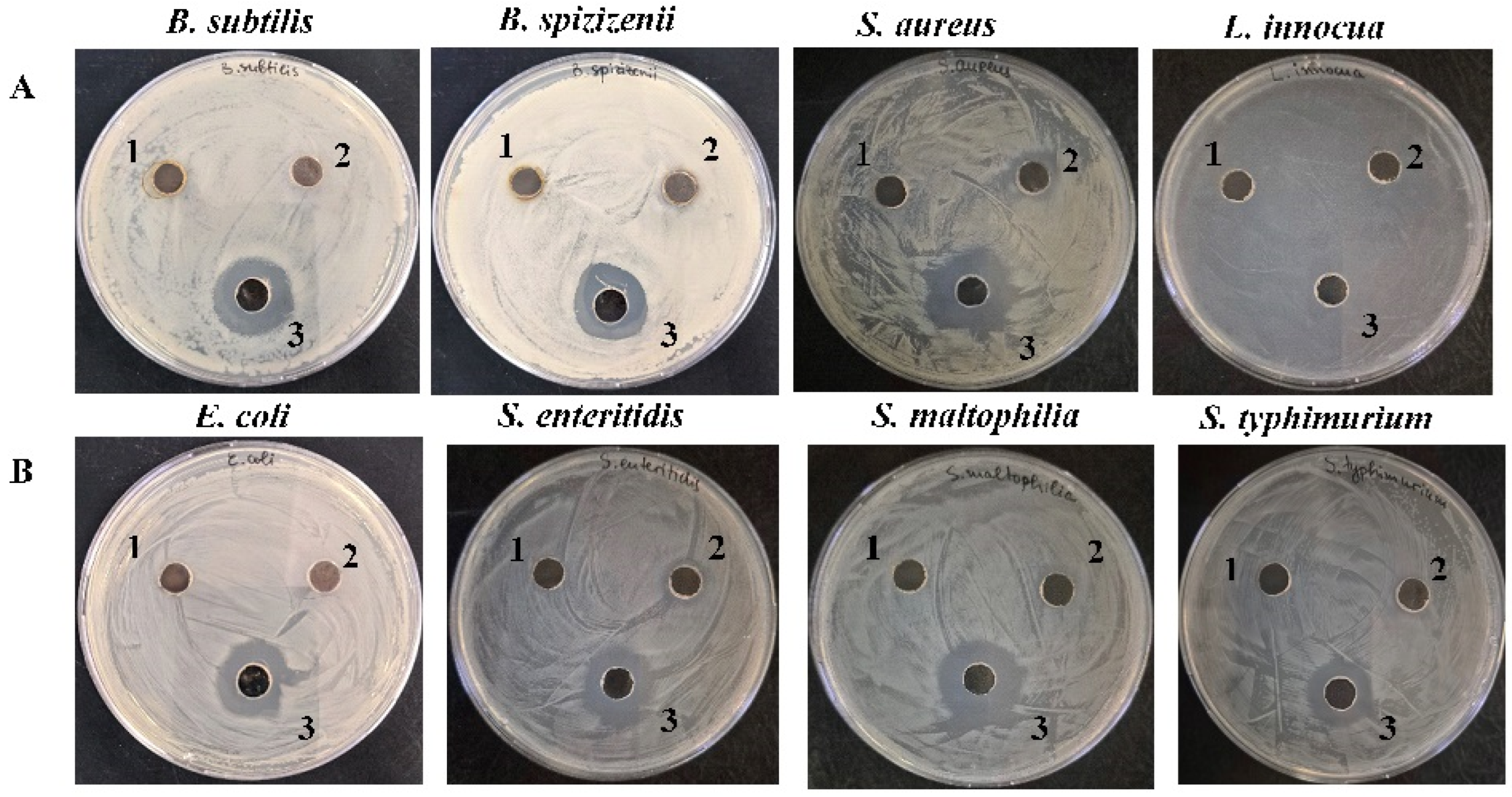
| Growth Inhibition Zone (D, mm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nanoparticle type | ||||
| AgNPs-Muc pH 7.0 | AgNPs-Muc pH 3.0 | AgNPs-Muc pH 1.5 | ||
| Gram+ strains | B. subtilis | 20 ± 0.5 | 0 | 0 |
| B. spizizenii | 18 ± 1.0 | 0 | 0 | |
| S. aureus | 21 ± 1.0 | 13 ± 0.50 | 0 | |
| L. innocua | 19 ± 1.0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Gram− strains | E. coli | 19 ± 0.5 | 0 | 0 |
| S. typhimurium | 17 ± 0.5 | 0 | 0 | |
| S. enteritidis | 19 ± 1.0 | 0 | 0 | |
| S. maltophilia | 23 ± 1.0 | 0 | 0 | |
| MIC (μg/mL) | MBC (μg/mL) | |
|---|---|---|
| AgNPs-Muc | 4096 | 4096 |
| VA | 32 | 128 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Todorova, M.; Petrova, V.; Ranguelov, B.; Avdeev, G.; Velkova, L.; Atanasova-Vladimirova, S.; Pisareva, E.; Tankov, C.; Tomova, A.; Dolashki, A.; et al. Green Synthesis of Antimicrobial Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs) from the Mucus of the Garden Snail Cornu aspersum. Molecules 2025, 30, 2150. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30102150
Todorova M, Petrova V, Ranguelov B, Avdeev G, Velkova L, Atanasova-Vladimirova S, Pisareva E, Tankov C, Tomova A, Dolashki A, et al. Green Synthesis of Antimicrobial Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs) from the Mucus of the Garden Snail Cornu aspersum. Molecules. 2025; 30(10):2150. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30102150
Chicago/Turabian StyleTodorova, Maria, Ventsislava Petrova, Bogdan Ranguelov, Georgy Avdeev, Lyudmila Velkova, Stela Atanasova-Vladimirova, Emiliya Pisareva, Chavdar Tankov, Anna Tomova, Aleksandar Dolashki, and et al. 2025. "Green Synthesis of Antimicrobial Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs) from the Mucus of the Garden Snail Cornu aspersum" Molecules 30, no. 10: 2150. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30102150
APA StyleTodorova, M., Petrova, V., Ranguelov, B., Avdeev, G., Velkova, L., Atanasova-Vladimirova, S., Pisareva, E., Tankov, C., Tomova, A., Dolashki, A., & Dolashka, P. (2025). Green Synthesis of Antimicrobial Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs) from the Mucus of the Garden Snail Cornu aspersum. Molecules, 30(10), 2150. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30102150







