Diffusion of Sodium Hyaluronate in Artificial Saliva to Optimize Its Topical Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Diffusion Measurements
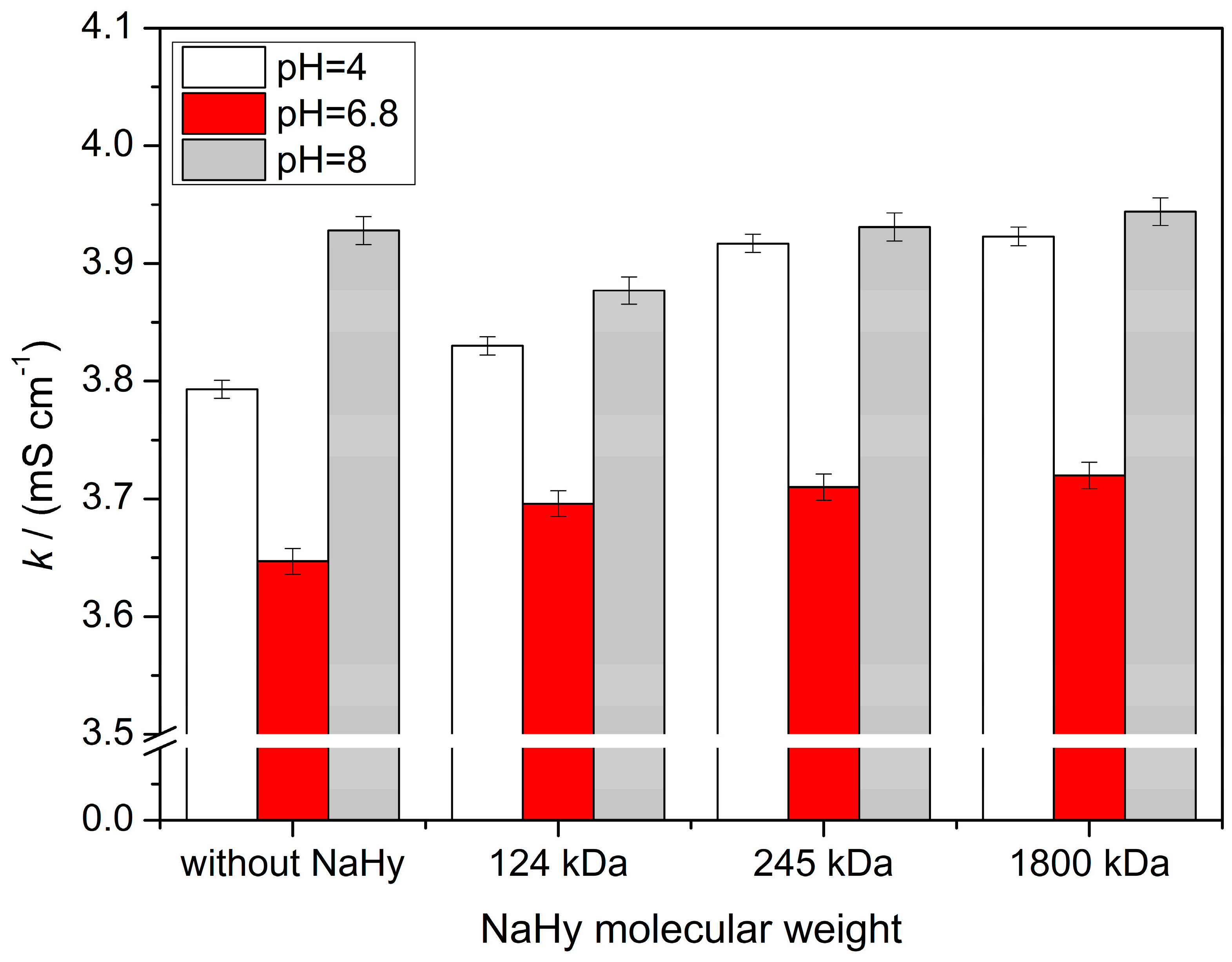
2.2. Conductivity Measurements
2.3. Density and Viscosity Measurements
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Experimental Techniques
4.2.1. pH Measurements
4.2.2. Taylor Dispersion Technique
4.2.3. Conductivity
4.2.4. Density
4.2.5. Viscosity
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Makdisi, J.; Akbari, S.; Zayeri, F.; AslRoosta, H.; Yaghobee, S. Application of Hyaluronic Acid for Treatment of Interdental Papillary Deficiency: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Dent. 2023, 20, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucchi, D. Hyaluronic Acid and Its Use in Dentistry. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2021, 35, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casale, M.; Moffa, A.; Vella, P.; Sabatino, L.; Capuano, F.; Salvinelli, B.; Lopez, M.A.; Carinci, F.; Salvinelli, F. Hyaluronic Acid: Perspectives in Dentistry. A Systematic Review. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2016, 29, 572–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.Y.J.; Abatangelo, G. Functions of Hyaluronan in Wound Repair. Wound Repair Regen. 1999, 7, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boccalari, E.; Tadakamadla, S.K.; Occhipinti, C.; Lanteri, V.; Maspero, C. Evaluation of the Effectiveness of a Novel Mouth Rinse Containing Hyaluronic Acid and Hydrogen Peroxide on Gingivitis: A Randomized Pilot Controlled Trial. Clin. Exp. Dent. Res. 2022, 8, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodero, A.; Williams, R.; Gagliardi, S.; Vicini, S.; Alloisio, M.; Castellano, M. A Micro-Rheological and Rheological Study of Biopolymers Solutions: Hyaluronic Acid. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 203, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccone, V.; Zazzetta, M.; Morbidelli, L. Comparison of the Effect of Two Hyaluronic Acid Preparations on Fibroblast and Endothelial Cell Functions Related to Angiogenesis. Cells 2019, 8, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Tian, X.; Liu, L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, B.; Dong, J. Clinical Therapy of Shujin Huoxue Tablet Combined with Sodium Hyaluronate on Inflammatory Factors of Synovial Fluid (IL-6, TNF-α) in the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis: Clinical Trial Study. Pak. J. Zool 2021, 53, 1723–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallacara, A.; Baldini, E.; Manfredini, S.; Vertuani, S. Hyaluronic Acid in the Third Millennium. Polymers 2018, 10, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, P.; Yu, H.; Jiang, T.; Ma, J.; Du, J.; Fang, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, R.; Yang, Q.; Cheng, Y.; et al. Development of a Sodium Hyaluronate-Enriched Therapeutic Formulation with Stevia Glycoside and Mogroside V for the Comprehensive Management of Diabetes and Its Complications. Int. J. Biol Macromol. 2025, 293, 139487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Su, Y.; Song, N.; Li, C.; Shi, Z.; Li, L. Clinical Outcome of Sodium Hyaluronate Injection into the Superior and Inferior Joint Space for Osteoarthritis of the Temporomandibular Joint Evaluated by Cone-Beam Computed Tomography: A Retrospective Study of 51 Patients and 56 Joints. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 5793–5801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, S.; Ohi, H.; Taya, M. Gelatin/Hyaluronic Acid Content in Hydrogels Obtained through Blue Light-Induced Gelation Affects Hydrogel Properties and Adipose Stem Cell Behaviors. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, S.K.; Ohri, R.; Giachelli, C.M. Anti-Calcification of Bovine Pericardium for Bioprosthetic Heart Valves after Surface Modification with Hyaluronic Acid Derivatives. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2005, 10, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khafaji, M.Q.M.; Althobaiti, N.S.A.; Alhassani, N.F.M.; Alnahwi, Z.A.H.; Aldawsari, W.A.; Alquraini, S.K.; Abdrabalameer, A.H.; Alharamlah, F.S.S.; Almalki, A.S.; Alotaibi, N.A.; et al. The Application and Efficacy of Hyaluronic Acid Fillers for Chin Enhancement and Retrusion Correction: A Systematic Review of Patient-Reported Outcomes. Cureus 2023, 15, e48807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Żurek, J.; Niemczyk, W.; Dominiak, M.; Niemczyk, S.; Wiench, R.; Skaba, D. Gingival Augmentation Using Injectable Platelet-Rich Fibrin (i-PRF)—A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moseley, R.; Waddington, R.J.; Embery, G. Hyaluronan and Its Potential Role in Periodontal Healing. Dent Update 2002, 29, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Jiang, D.; Noble, P.W. Hyaluronan as a Therapeutic Target in Human Diseases. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 97, 186–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynnekleiv, L.; Magno, M.; Moschowits, E.; Tønseth, K.A.; Vehof, J.; Utheim, T.P. A Comparison between Hyaluronic Acid and Other Single Ingredient Eye Drops for Dry Eye, a Review. Acta Ophthalmol. 2024, 102, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.Y.; Jing, S.L.; Sun, Y.; Gong, Z.C.; Guo, Z.C. A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial of Concentrated Growth Factor Combined with Sodium Hyaluronate in the Treatment of Temporomandibular Joint Osteoarthritis. BMC Oral Health 2024, 24, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurkar, H.; Venkatesh, O.Y.; Somashekar, J.M.; Gowda, M.H.L.; Dwivedi, M.; Ningthoujam, I. Prosthodontic Management of Xerostomic Patient: A Technical Modification. Case Rep. Dent. 2016, 8905891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anil, S.; Vellappally, S.; Hashem, M.; Preethanath, R.S.; Patil, S.; Samaranayake, L.P. Xerostomia in Geriatric Patients: A Burgeoning Global Concern. J. Investig. Clin. Dent. 2016, 7, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.D.; Ship, J.A. Dry Mouth and Its Effects on the Oral Health of Elderly People. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2007, 138, S15–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremolati, M.; Farronato, M.; Ferrantino, L.; Rusconi, F.; Lodi, G.; Maspero, C. Clinical Performance Evaluation of a Hyaluronic Acid Dental Gel for the Treatment of Traumatic Ulcers in Patients with Fixed Orthodontic Appliances: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemura, A.; Hashimoto, K.; Ho, A.; Bessinger, M.; Law, S.; Schifferle, R.E.; Ciancio, S.G. Efficacy of New Oral Rinse Containing Sodium Hyaluronate in Xerostomia: A Randomized Crossover Study. Oral Dis. 2023, 29, 2747–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zero, D.T. Dentifrices, Mouthwashes, and Remineralization/Caries Arrestment Strategies. BMC Oral Health 2006, 6, S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boccalari, E.; Khijmatgar, S.; Occhipinti, C.; Del Fabbro, M.; Inchingolo, F.; Tartaglia, G.M. Effect of Hydrogen Peroxide and Hyaluronic Acid in Mouth Rinse after Third Molar Extraction: A Triple-Blind Parallel Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2024, 28, 3946–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Wang, X.; Feng, Q.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J. Thickening, Lubricating and Wetting Capabilities of Sodium Hyaluronate in Comparison with Commercial Polysaccharides for Applications in Artificial Saliva. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 153, 109996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musilová, L.; Mráček, A.; Azevedo, E.F.G.; Valente, A.J.M.; Cabral, A.M.T.D.P.V.; Ribeiro, A.C.F.; Esteso, M.A. Interactions between Sodium Hyaluronate and β-Cyclodextrin as Seen by Transport Properties. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veríssimo, L.M.P.; Valada, T.I.C.; Sobral, A.J.F.N.; Azevedo, E.E.F.G.; Azevedo, M.L.G.; Ribeiro, A.C.F. Mutual Diffusion of Sodium Hyaluranate in Aqueous Solutions. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2014, 71, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horasawa, N.; Takahashi, S.; Marek, M. Galvanic Interaction between Titanium and Gallium Alloy or Dental Amalgam. Dent. Mater. 1999, 15, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovesi, A.; Barone, A.; Toti, P.; Covani, U. The Efficacy of 0.12% Chlorhexidine versus 0.12% Chlorhexidine plus Hyaluronic Acid Mouthwash on Healing of Submerged Single Implant Insertion Areas: A Short-term Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Int. J. Dent. Hyg. 2017, 15, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fangaia, S.I.G.; Nicolau, P.M.G.; Guerra, F.A.D.R.A.; Rodrigo, M.M.; Utzeri, G.; Cabral, A.M.T.D.P.V.; Valente, A.J.M.; Esteso, M.A.; Ribeiro, A.C.F. Effect of Cobalt and Chromium Ions on the Chlorhexidine Digluconate as Seen by Intermolecular Diffusion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrrell, H.J.V.; Harris, K.R. Diffusion in Liquids: A Theoretical and Experimental Study; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1984; ISBN 9780408175913. [Google Scholar]
- Maleki, A.; Kjøniksen, A.; Nyström, B. Effect of PH on the Behavior of Hyaluronic Acid in Dilute and Semidilute Aqueous Solutions. Macromol. Symp. 2008, 274, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snetkov, P.; Zakharova, K.; Morozkina, S.; Olekhnovich, R.; Uspenskaya, M. Hyaluronic Acid: The Influence of Molecular Weight on Structural, Physical, Physico-Chemical, and Degradable Properties of Biopolymer. Polymers 2020, 12, 1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatej, I.; Popa, M.; Rinaudo, M. Role of the PH on Hyaluronan Behavior in Aqueous Solution. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faro, M.P.R.T.; Barros, M.C.F.; Santos, C.I.A.V.; Ribeiro, A.C.F. Coupled Mutual Diffusion in Aqueous Calcium Sulphate + Sulphuric Acid Solutions. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2022, 165, 106659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.C.F.; Ortona, O.; Simões, S.M.N.; Santos, C.I.A.V.; Prazeres, P.M.R.A.; Valente, A.J.M.; Lobo, V.M.M.; Burrows, H.D. Binary Mutual Diffusion Coefficients of Aqueous Solutions of Sucrose, Lactose, Glucose, and Fructose in the Temperature Range from (298.15 to 328.15) K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2006, 51, 1836–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.C.F.; Santos, C.I.A.V.; Lobo, V.M.M.; Cabral, A.M.T.D.P.V.; Veiga, F.J.B.; Esteso, M.A. Diffusion Coefficients of the Ternary System (2-Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin+caffeine+water) at T=298.15K. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2009, 41, 1324–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.C.F.; Barros, M.C.F.; Verissimo, L.M.P.; Esteso, M.A.; Leaist, D.G. Coupled Mutual Diffusion in Aqueous Sodium (Salicylate + sodium Chloride) Solutions at 25 °C. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2019, 138, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, C.M.C.; Verissimo, L.M.P.; Valente, A.J.M.; Ribeiro, A.C.F. Limiting Diffusion Coefficients of Sodium Octanoate, and Octanoic Acid in Aqueous Solutions without and with α-Cyclodextrin. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2016, 94, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, C.M.; Trujillo, G.P.; Verissimo, L.M.P.; Esteso, M.A.; Ramos, M.L.; Ribeiro, A.C.F. Limiting Diffusion Coefficients of α,ω-Amino Acids in Water and in Sodium Chloride Aqueous Solutions at 298.15 K. Eur. Phys. J. E 2019, 42, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barthel, J.; Feuerlein, F.; Neueder, R.; Wachter, R. Calibration of Conductance Cells at Various Temperatures. J. Solut. Chem. 1980, 9, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
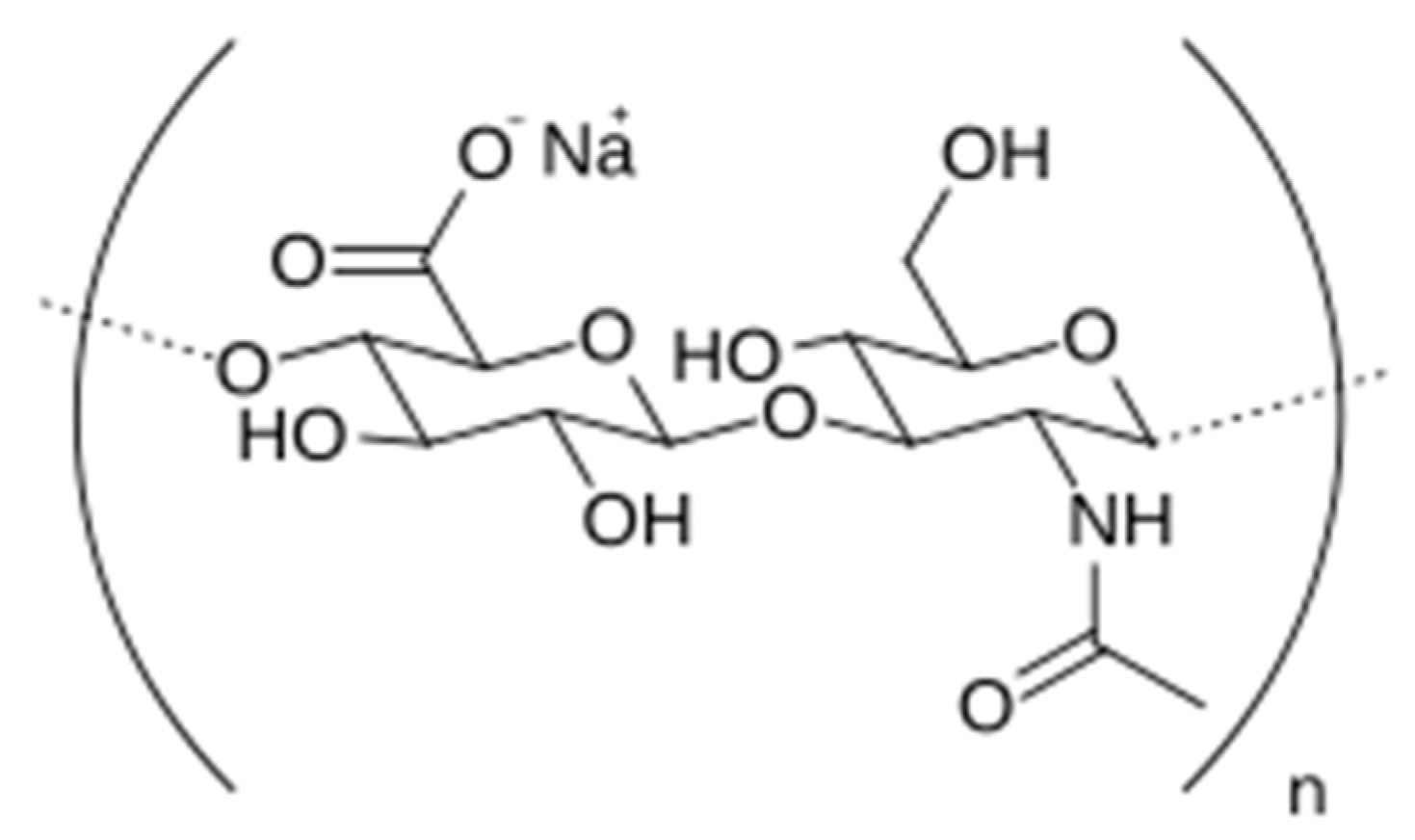
| Solutions | Solutions at Different pHs | D ± SD a) /(10−9m2 s−1) |
|---|---|---|
| Sodium hyaluronate (Mw = 124 kDa) 0.01 g in 10 mL (0.1%) + Water | 4.0 6.8 8.0 | 0.815 ± 0.010 0.698 ± 0.007 0.560 ± 0.003 |
| Sodium hyaluronate (Mw = 245 kDa) 0.01 g in 10 mL (0.1%) + Water | 4.0 6.8 8.0 | 0.880 ± 0.010 0.708 ± 0.007 0.580 ± 0.003 |
| Sodium hyaluronate (Mw = 1.8 MDa) 0.01 g in 10 mL (0.1%) + Water | 4.0 6.8 8.0 | 0.970 ± 0.010 0.880 ± 0.014 0.770 ± 0.021 |
| Sodium hyaluronate (Mw = 124 kDa) 0.01 g in 10 mL (0.1%) + Artificial Saliva | 2.3 4.0 5.0 6.8 8.0 | 0.960 ± 0.021 0.862 ± 0.018 0.810 ± 0.014 0.696 ±0.012 0.562 ± 0.013 |
| Sodium hyaluronate (Mw = 245 kDa) 0.01 g in 10 mL (0.1%) + Artificial Saliva | 2.3 4.0 5.0 6.8 8.0 | 0.964 ± 0.016 0.880 ± 0.028 0.850 ± 0.024 0.710 ± 0.021 0.611 ± 0.025 |
| Sodium hyaluronate (Mw = 1800 kDa) 0.01 g in 10 mL (0.1%) + Artificial Saliva | 2.3 4.0 5.0 6.8 8.0 | 0.997 ± 0.029 0.990 ± 0.030 0.870 ± 0.025 0.811 ± 0.027 0.780 ± 0.020 |
| Solution | (b) | 106 σ (c) | η/(mPa s) (d) | 103 σ (e) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saliva (pH 8) | 1.007105 | 1.6 | 0.9101 | 0.9 |
| Saliva + NaHy (124 kDa) pH 8 | 1.002205 | 2.2 | 4.1101 | 0.9 |
| Saliva + NaHy (1800 kDa) pH 8 | 1.016001 | 1.8 | 1.0800 | 0.8 |
| Saliva (pH 6.8) | 1.006911 | 2.8 | 0.9102 | 1.2 |
| Saliva + NaHy (1800 kDa) pH 6.8 | 0.978590 | 2.9 | 1.2510 | 0.9 |
| Saliva + NaHy (124 kDa) pH 6.8 | 0.979500 | 2.5 | 1.2090 | 1.1 |
| Saliva (pH 4) | 0.984423 | 2.7 | 0.9100 | 1.0 |
| Saliva + NaHy (124 kDa) pH 4 | 0.983599 | 3.0 | 3.2010 | 0.7 |
| Saliva + NaHy (1800 kDa) pH 4 | 0.985598 | 2.8 | 1.1701 | 0.8 |
| Chemical Name | Source | CAS Number | Mass Fraction Purity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium hyaluronate (a) (Mw = 124 kDa) Sodium hyaluronate (a) ((Mw = 245 kDa) Sodium hyaluronate (a) ((Mw = 1800 kDa) | Contipro Ltd. (Dolní Dobrouč, Czech Republic) Contipro Ltd. (Dolní Dobrouč, Czech Republic) Contipro Ltd. (Dolní Dobrouč, Czech Republic) | 9067-32-7 9067-32-7 9067-32-7 | >0.99 >0.99 >0.99 |
| Artificial Saliva (b) | Dentistry area at the University of Coimbra of the Faculty of Medicine | - | - |
| Millipore-Q water = 0.99710 g cm−3 at 298.15 K) | - | 7732-18-5 | >0.97 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carmo, F.J.R.; Salote, E.P.Z.; Valente, A.J.M.; Ribeiro, A.C.F.; Nicolau, P.M.G.; Fangaia, S.I.G. Diffusion of Sodium Hyaluronate in Artificial Saliva to Optimize Its Topical Application. Molecules 2025, 30, 2140. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30102140
Carmo FJR, Salote EPZ, Valente AJM, Ribeiro ACF, Nicolau PMG, Fangaia SIG. Diffusion of Sodium Hyaluronate in Artificial Saliva to Optimize Its Topical Application. Molecules. 2025; 30(10):2140. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30102140
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarmo, Francisco J. R., Esmeraldo P. Z. Salote, Artur J. M. Valente, Ana C. F. Ribeiro, Pedro M. G. Nicolau, and Sónia I. G. Fangaia. 2025. "Diffusion of Sodium Hyaluronate in Artificial Saliva to Optimize Its Topical Application" Molecules 30, no. 10: 2140. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30102140
APA StyleCarmo, F. J. R., Salote, E. P. Z., Valente, A. J. M., Ribeiro, A. C. F., Nicolau, P. M. G., & Fangaia, S. I. G. (2025). Diffusion of Sodium Hyaluronate in Artificial Saliva to Optimize Its Topical Application. Molecules, 30(10), 2140. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30102140










