Human Tyrosinase Displayed on the Surface of Chinese Hamster Ovary Cells for Ligand Fishing of Tyrosinase Inhibitors from Medicinal Plants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
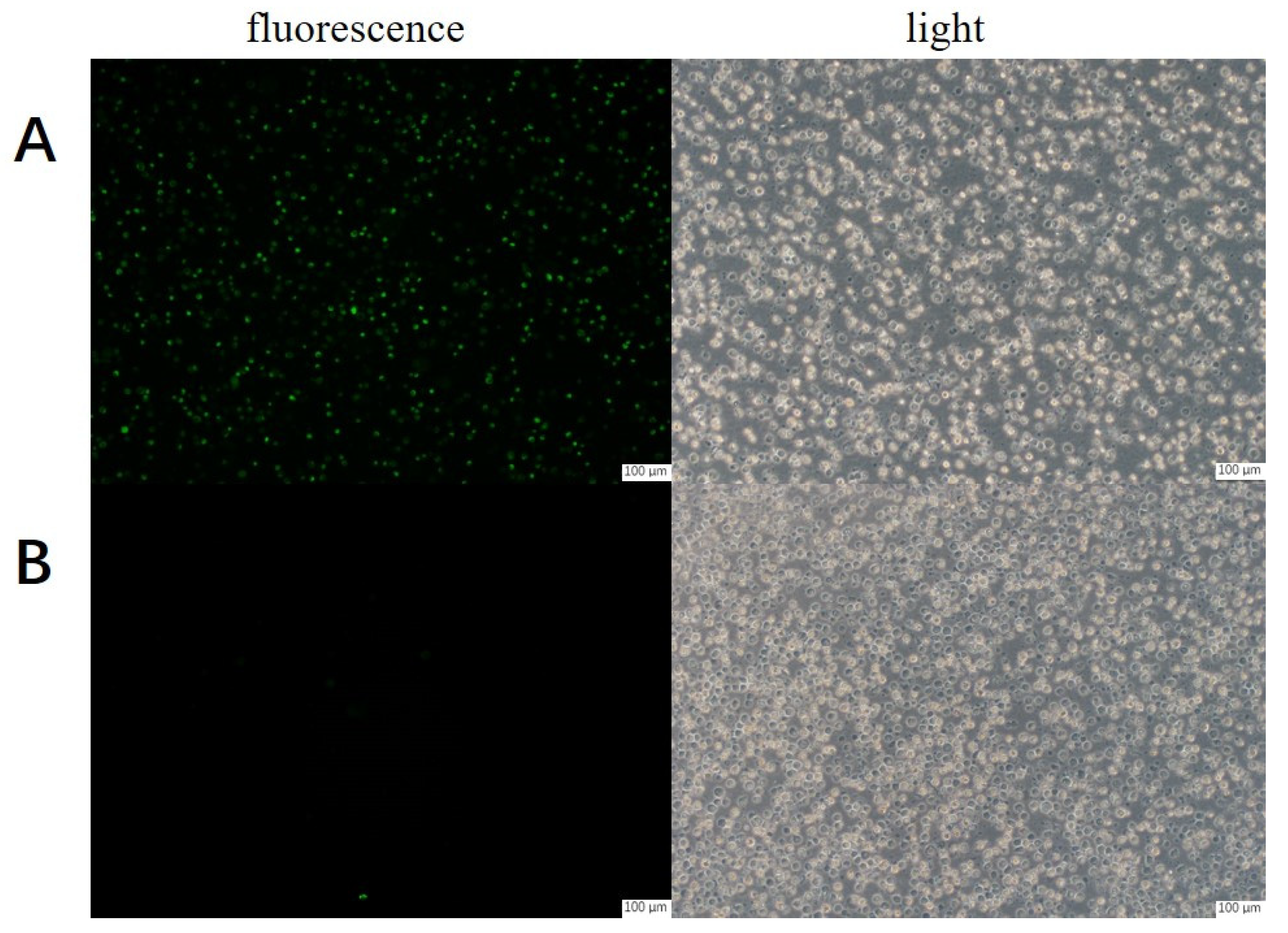
2.1. Localization of Human Tyrosinase on CHO Cells
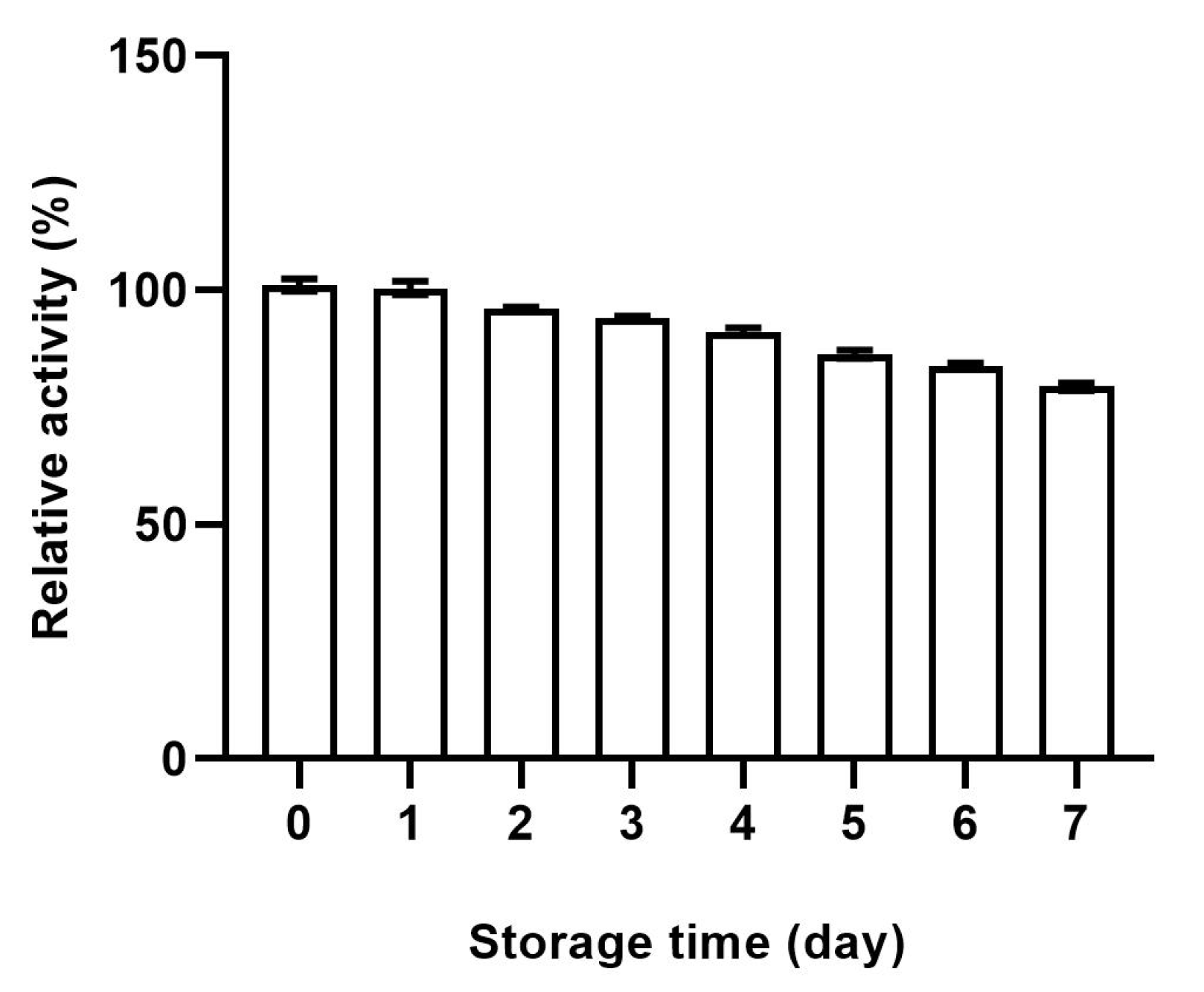
2.2. Enzymatic Activity and Stability of CHO@hTYR
2.3. Optimization of the Conditions for Ligand Fishing
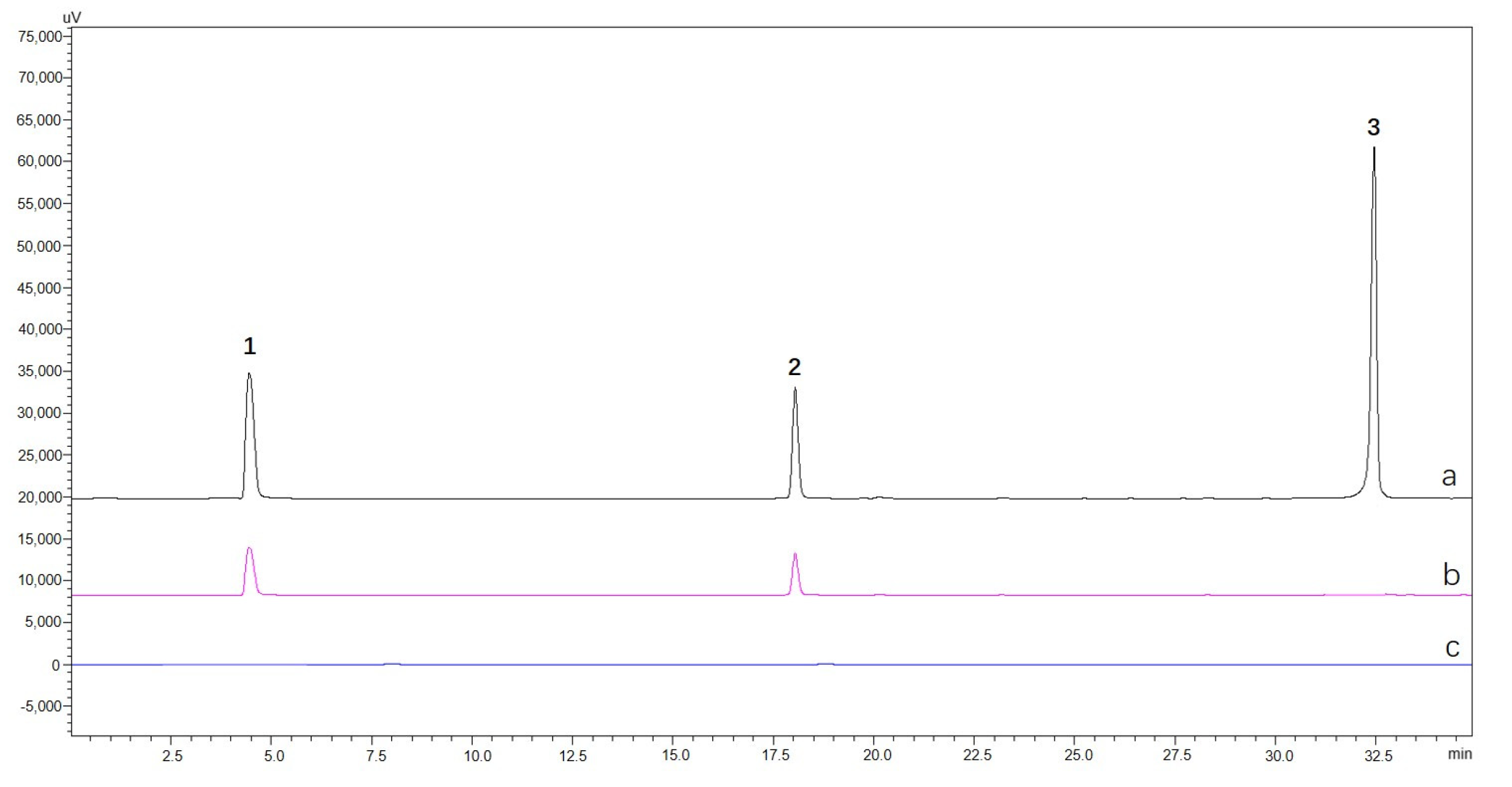
2.4. Selectivity of CHO@hTYR in Ligand Fishing
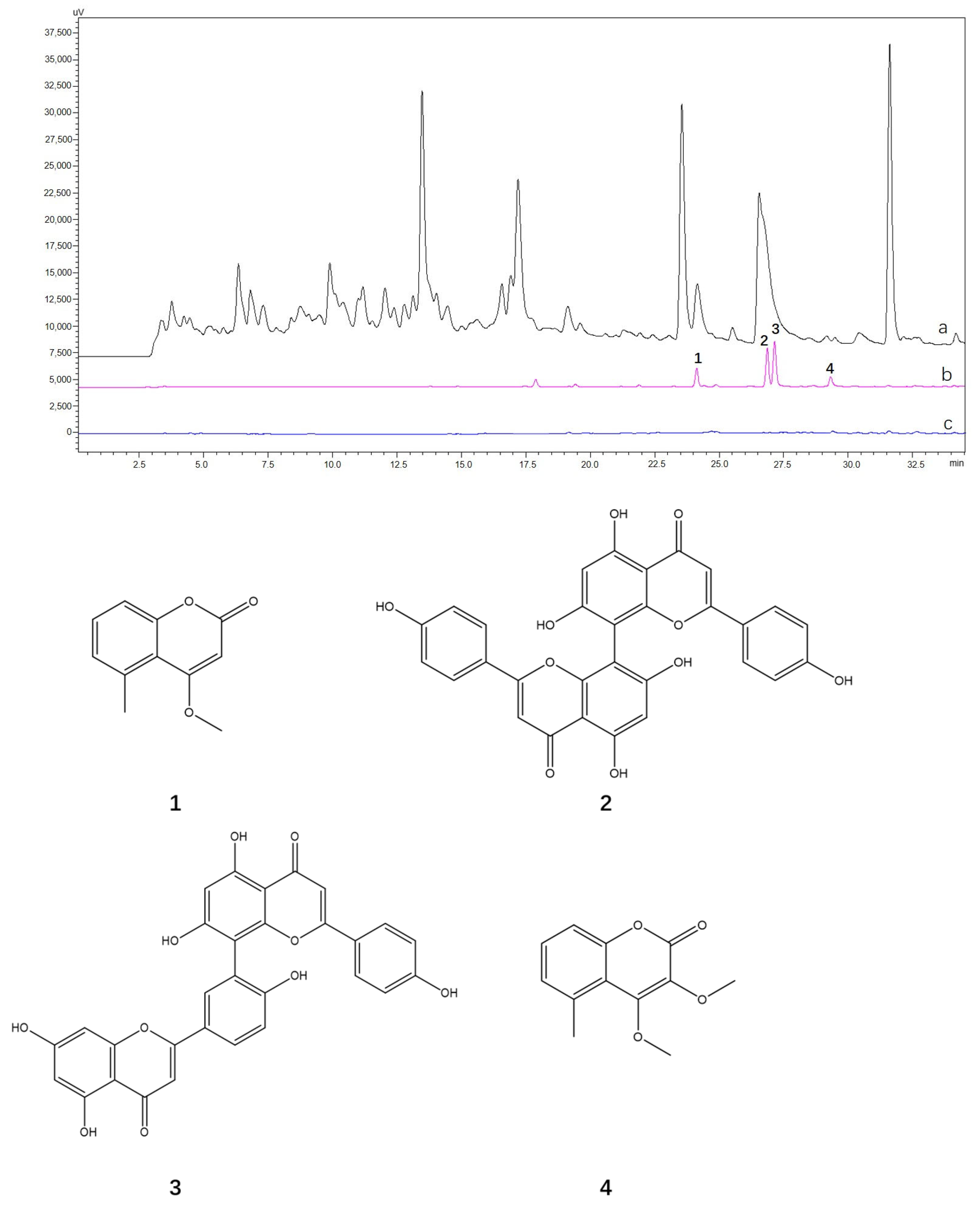
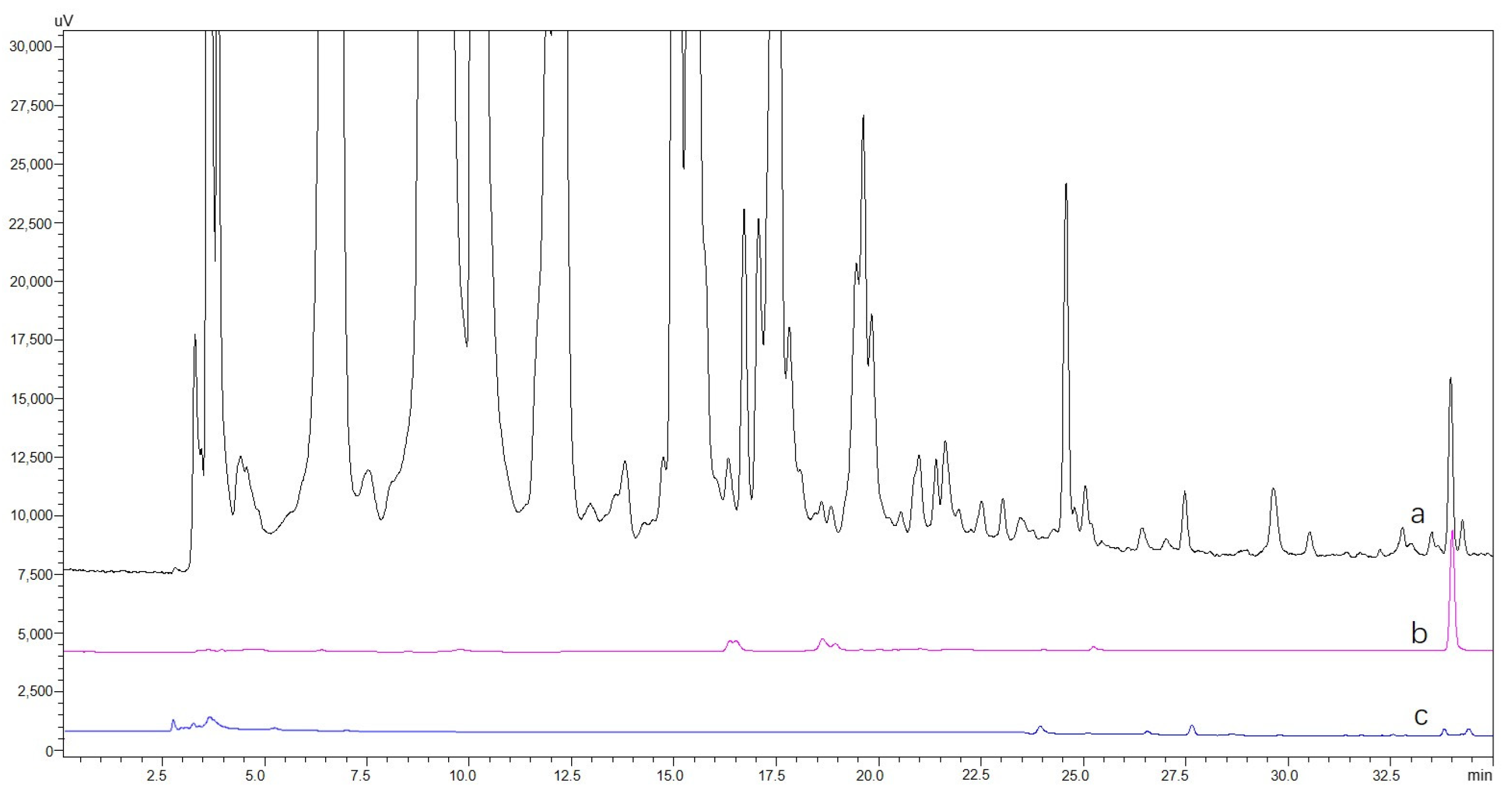
2.5. Screening and Identification of the hTYR Ligands from Extract of A. sparsifolia and C. arabica
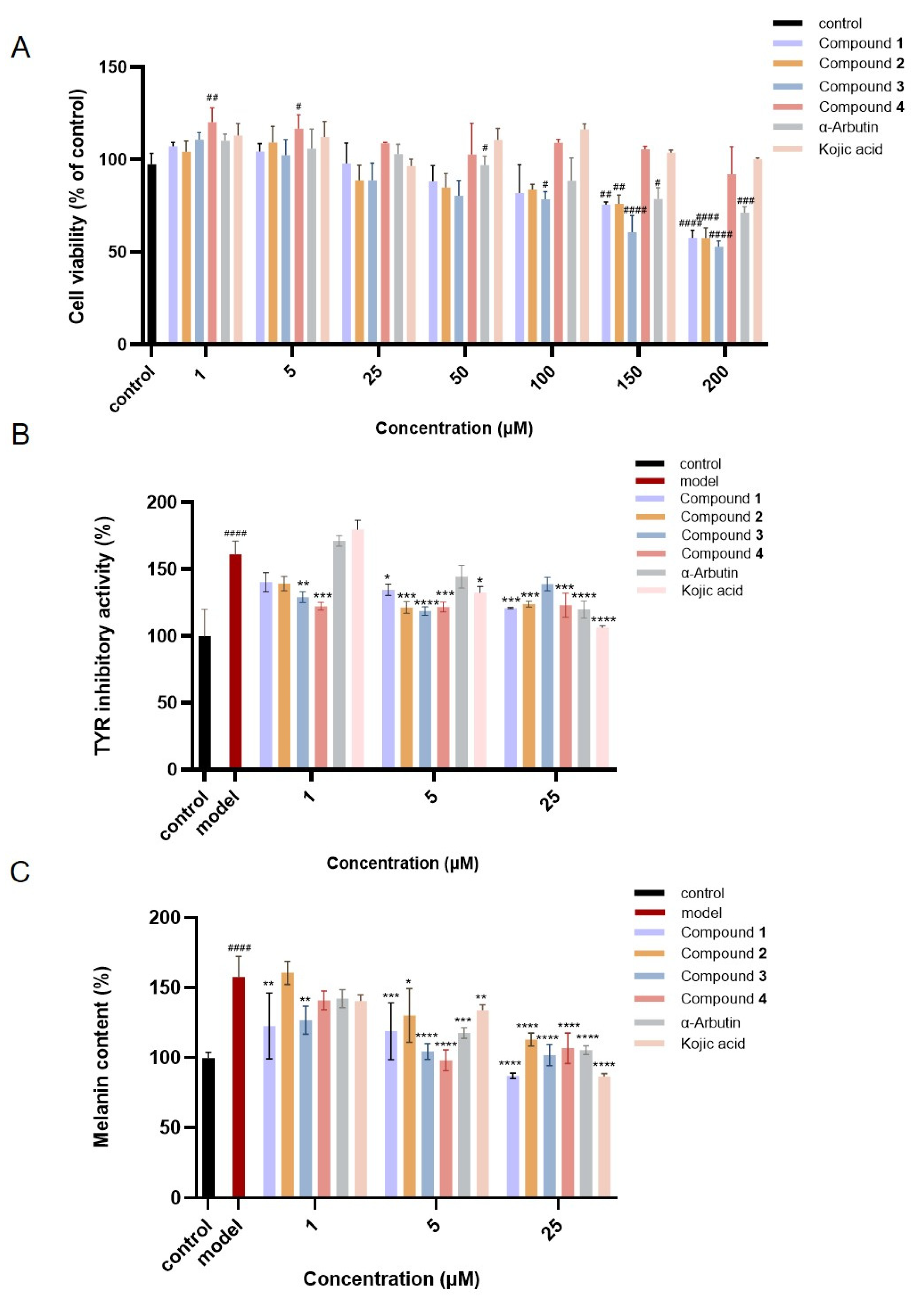
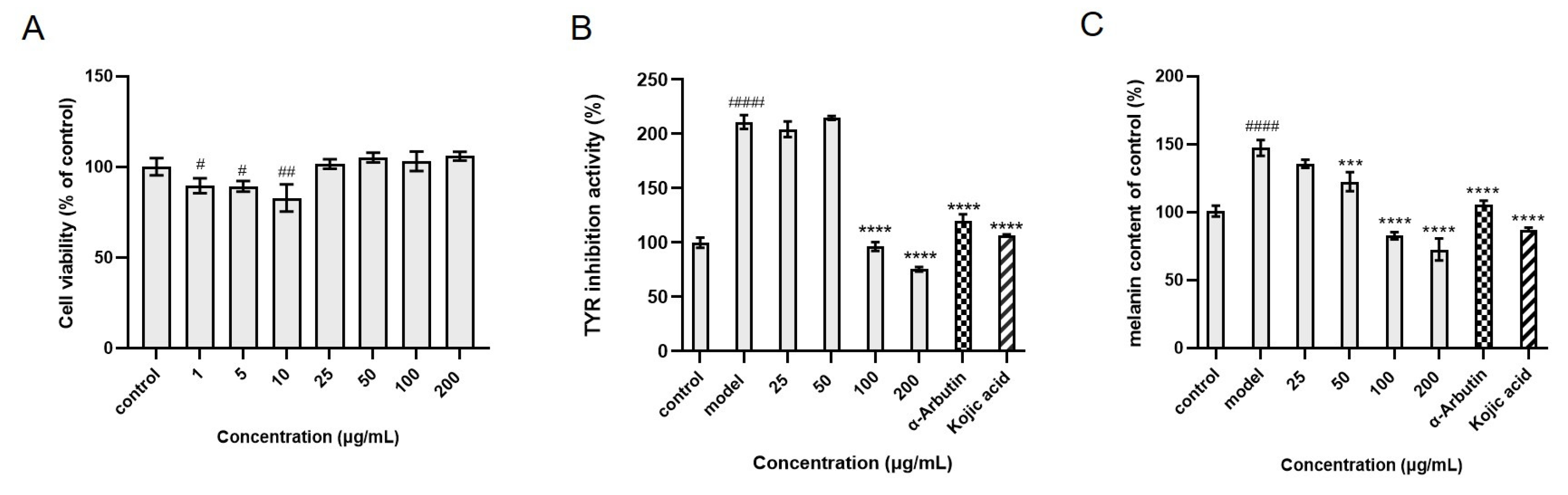
2.6. Inhibitory Effects on Tyrosinase Activity and Melanin Content in α-MSH-Induced B16 Melanoma Cells
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Chemicals
3.2. Cell Culture and CHO@hTYR Construction
3.3. Fluorescence Assay of CHO@hTYR
3.4. Enzymatic Activity and Stability of CHO@hTYR
3.5. Optimization of Ligand Fishing Procedure
3.6. Selectivity Validation of Ligand Fishing with CHO@hTYR
3.7. Ligand Fishing from A. sparsifolia and C. arabica
3.8. Isolation and Identification of Tyrosinase Ligands
3.9. Tyrosinase Inhibitory Activity in B16 Melanoma Cells
3.9.1. Cell Culture and Cytotoxicity Test
3.9.2. Tyrosinase Activity Assay
3.9.3. Melanin Content Assay
3.10. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramsden, C.A.; Riley, P.A. Tyrosinase: The four oxidation states of the active site and their relevance to enzymatic activation, oxidation and inactivation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 2388–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae-Harboe, Y.S.; Park, H.Y. Tyrosinase: A central regulatory protein for cutaneous pigmentation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 2678–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tedasen, A.; Chiabchalard, A.; Tencomnao, T.; Yamasaki, K.; Majima, H.J.; Phongphithakchai, A.; Chatatikun, M. Anti-melanogenic activity of ethanolic extract from Garcinia atroviridis fruits using in vitro experiments, network pharmacology, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics simulation. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, S.; Guo, L.; Liang, J.; Wang, K.; Liao, Q.; He, S.; Lyu, W.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, J.; Luo, X.; et al. A new strategy for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease: Discovery and bio-evaluation of the first central-targeting tyrosinase inhibitor. Bioorg. Chem. 2024, 150, 107612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Shi, S.; Chen, X.; Peng, M. Analysis of tyrosinase binders from Glycyrrhiza uralensis root: Evaluation and comparison of tyrosinase immobilized magnetic fishing-HPLC and reverse ultrafiltration-HPLC. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2013, 932, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.M.; Chen, J.; Shi, Y.P. Tyrosinase immobilization on aminated magnetic nanoparticles by physical adsorption combined with covalent crosslinking with improved catalytic activity, reusability and storage stability. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1006, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, L.; Wang, Y.; Gao, X.; Cheng, Y. An ultrafiltration high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with diode array detector and mass spectrometry approach for screening and characterising tyrosinase inhibitors from mulberry leaves. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 719, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Zhang, H.; Niu, L.; Wang, X. Efficient screening of a novel antimicrobial peptide from Jatropha curcas by cell membrane affinity chromatography. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 1145–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.C.; Bai, X.L.; Liu, Y.M.; Tang, X.Y.; Yuan, H.; Liao, X. Ligand fishing based on cell surface display of enzymes for inhibitor screening. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1156, 338359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ablat, A.; Li, M.J.; Zhai, X.R.; Wang, Y.; Bai, X.L.; Shu, P.; Liao, X. Fast screening of tyrosinase inhibitors in Coreopsis tinctoria Nutt. by ligand fishing based on paper-immobilized tyrosinase. Molecules 2024, 29, 4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Hu, J.J.; Bai, X.L.; Liu, H.P.; Qi, X.W.; Liao, X. Fast screening of tyrosinase inhibitors from traditional Chinese medicinal plants by ligand fishing in combination with in situ fluorescent assay. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 2265–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzemińska, A.; Kwiatos, N.; Arenhart Soares, F.; Steinbüchel, A. Theoretical studies of cyanophycin dipeptides as inhibitors of tyrosinases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, T.; Gerwat, W.; Batzer, J.; Eggers, K.; Scherner, C.; Wenck, H.; Stäb, F.; Hearing, V.J.; Röhm, K.H.; Kolbe, L. Inhibition of human tyrosinase requires molecular motifs distinctively different from mushroom tyrosinase. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 1601–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khvatkov, P.; Firsov, A.; Shvedova, A.; Shaloiko, L.; Kozlov, O.; Chernobrovkina, M.; Pushin, A.; Tarasenko, I.; Chaban, I.; Dolgov, S. Development of Wolffia arrhiza as a producer for recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalim, M.; Ali, H.; Rehman, A.U.; Lu, Y.; Zhan, J. Bioengineering and computational analysis of programmed cell death ligand-1 monoclonal antibody. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1012499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Jin, M.; Huang, W.; Liu, W.; Xian, M. Whole-cell catalysis by surface display of fluorinase on Escherichia coli using N-terminal domain of ice nucleation protein. Microb. Cell Fact. 2021, 20, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Tariq, A.; Zeng, F.; Graciano, C.; Zhang, B. Nitrogen application mitigates drought-induced metabolic changes in Alhagi sparsifolia seedlings by regulating nutrient and biomass allocation patterns. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 155, 828–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Yang, X.; Pang, K.; Tang, H. Traditional uses, chemistry, pharmacology, toxicology and quality control of Alhagi sparsifolia Shap.: A Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 761811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheweita, S.A.; Mashaly, S.; Newairy, A.A.; Abdou, H.M.; Eweda, S.M. Changes in oxidative stress and antioxidant enzyme activities in streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus in rats: Role of Alhagi maurorum extracts. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2016, 2016, 5264064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, H.A.; Shalaby, S.I.; Abdelaziz, A.S. Alhagi maurorum aqueous extract protects against norfloxacin-induced hepa-to-nephrotoxicity in rats. Chin. Herb. Med. 2019, 12, 156–162. [Google Scholar]
- Saber, T.M.; Abo-Elmaaty, A.M.A.; Said, E.N.; Beheiry, R.R.; Moselhy, A.A.A.; Abdelgawad, F.E.; Arisha, M.H.; Saber, T.; Arisha, A.H.; Fahmy, E.M. Alhagi maurorum ethanolic extract rescues hepatoneurotoxicity and neurobehavioral alterations induced by lead in rats via abrogating oxidative stress and the caspase-3-dependent apoptotic pathway. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Xiang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Chang, J. Saccharum Alhagi polysaccharide-1 and -2 promote the immunocompetence of RAW264.7 macrophages in vitro. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 3556–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Wei, H.; Jiang, Z.; Li, X.; Jiao, K.; Jia, X.; Hou, Y.; Li, N. Natural potential neuroinflammatory inhibitors from Alhagi sparsifolia Shap. Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholamhoseinian, A.; Razmi, Z. Screening the methanolic extracts of some plants for tyrosinase inhibitory activity. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2024, 94, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, C.C.; Jin, A.; Yuan, J.M.; Koh, W.P. Coffee, tea, caffeine, and risk of nonmelanoma skin cancer in a Chinese population: The Singapore Chinese Health Study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 81, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwabara, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Yasuoka, S.; Fukui, K.; Takata, J.; Karube, Y.; Okamoto, Y.; Asano, S.; Katoh, E.; Tsuzuki, T.; et al. Topical application of gamma-tocopherol derivative prevents UV-induced skin pigmentation. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 29, 1175–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, B.; Carmo, H.; Garrido, J.; Sousa Lobo, J.M.; Almeida, I.F. In vitro evaluation of the photoreactivity and phototoxicity of natural polyphenol antioxidants. Molecules 2021, 27, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluemsamran, T.; Onkoksoong, T.; Panich, U. Caffeic acid and ferulic acid inhibit UVA-induced matrix metalloproteinase-1 through regulation of antioxidant defense system in keratinocyte HaCaT cells. Photochem. Photobiol. 2012, 88, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.G.; Thappa, R.K.; Dhar, K.L. Chemical constituents of Juniperus semiglobosa. Fitoterapia 1996, 67, 178–179. [Google Scholar]
- Venditti, A.; Maggi, F.; Quassinti, L.; Bramucci, M.; Lupidi, G.; Ornano, L.; Ballero, M.; Sanna, C.; Bruno, M.; Rosselli, S.; et al. Bioactive constituents of Juniperus turbinata Guss. from La Maddalena archipelago. Chem. Biodivers. 2018, 15, e1800148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Benavides, J.C.; Atiencie-Valarezo, N.C.; Duarte-Casar, R. Flavonoid composition and antioxidant activity of Tragia volubilis L. methanolic extract. Plants 2023, 12, 3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahluwalia, V.K.; Chandra, P.; Singh, R.P. Synthesis of some novel 3, 4-dimethoxycoumarins: 3-methoxypereflorin and 3, 7-dimethoxypereflorin. Chem. Ind. 1980, 11, 464–465. [Google Scholar]
- GB 5009.168-2016; National Food Safety Standard Determination of Fatty Acids in Foods. National Health and Family Planning Commission of People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016; Volume 24, pp. 1–6.
- Long, Y.; Wang, W.P.; Yuan, H.; Ma, S.P.; Feng, N.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.L. Functional comparison of the reverse mode of Na+/Ca2+ exchangers NCX1.1 and NCX1.5 expressed in CHO cells. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2013, 34, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Srinivasan, S.; Zhu, C.; McShan, A.C. Structure, function, and immunomodulation of the CD8 co-receptor. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1412513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Ku, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Park, J.W. IDH2 deficiency accelerates skin pigmentation in mice via enhancing melanogenesis. Redox Biol. 2018, 17, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Yang, Y.; Jia, B.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Gao, R. The inhibitory effect of curcumin derivative J147 on melanogenesis and melanosome transport by facilitating ERK-mediated MITF degradation. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 783730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhai, X.-R.; Li, M.-J.; Yin, X.; Ablat, A.; Wang, Y.; Shu, P.; Liao, X. Human Tyrosinase Displayed on the Surface of Chinese Hamster Ovary Cells for Ligand Fishing of Tyrosinase Inhibitors from Medicinal Plants. Molecules 2025, 30, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30010030
Zhai X-R, Li M-J, Yin X, Ablat A, Wang Y, Shu P, Liao X. Human Tyrosinase Displayed on the Surface of Chinese Hamster Ovary Cells for Ligand Fishing of Tyrosinase Inhibitors from Medicinal Plants. Molecules. 2025; 30(1):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30010030
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhai, Xiao-Rui, Ming-Jie Li, Xiang Yin, Ayzohra Ablat, Yuan Wang, Peng Shu, and Xun Liao. 2025. "Human Tyrosinase Displayed on the Surface of Chinese Hamster Ovary Cells for Ligand Fishing of Tyrosinase Inhibitors from Medicinal Plants" Molecules 30, no. 1: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30010030
APA StyleZhai, X.-R., Li, M.-J., Yin, X., Ablat, A., Wang, Y., Shu, P., & Liao, X. (2025). Human Tyrosinase Displayed on the Surface of Chinese Hamster Ovary Cells for Ligand Fishing of Tyrosinase Inhibitors from Medicinal Plants. Molecules, 30(1), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30010030






