Characterization of the Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Soluble Dietary Fiber from Peanut Shells Prepared by Pulsed Electric Fields with Three-Phase Partitioning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Proximate Composition Analysis
2.2. Physicochemical Properties
2.2.1. WHC, SC, and OHC
2.2.2. EA, ES, and LGC
2.3. Functional Properties
2.3.1. Glucose Absorption Capacity (GAC)
2.3.2. Nitrite Ion Adsorption Capacity (NIAC)
2.3.3. Cholesterol Adsorption Capacity (CAC)
2.3.4. Pancreatic Lipase Inhibition Capacity (PLIC)
2.3.5. Antioxidant Capacities Analysis
2.4. Structural Analysis
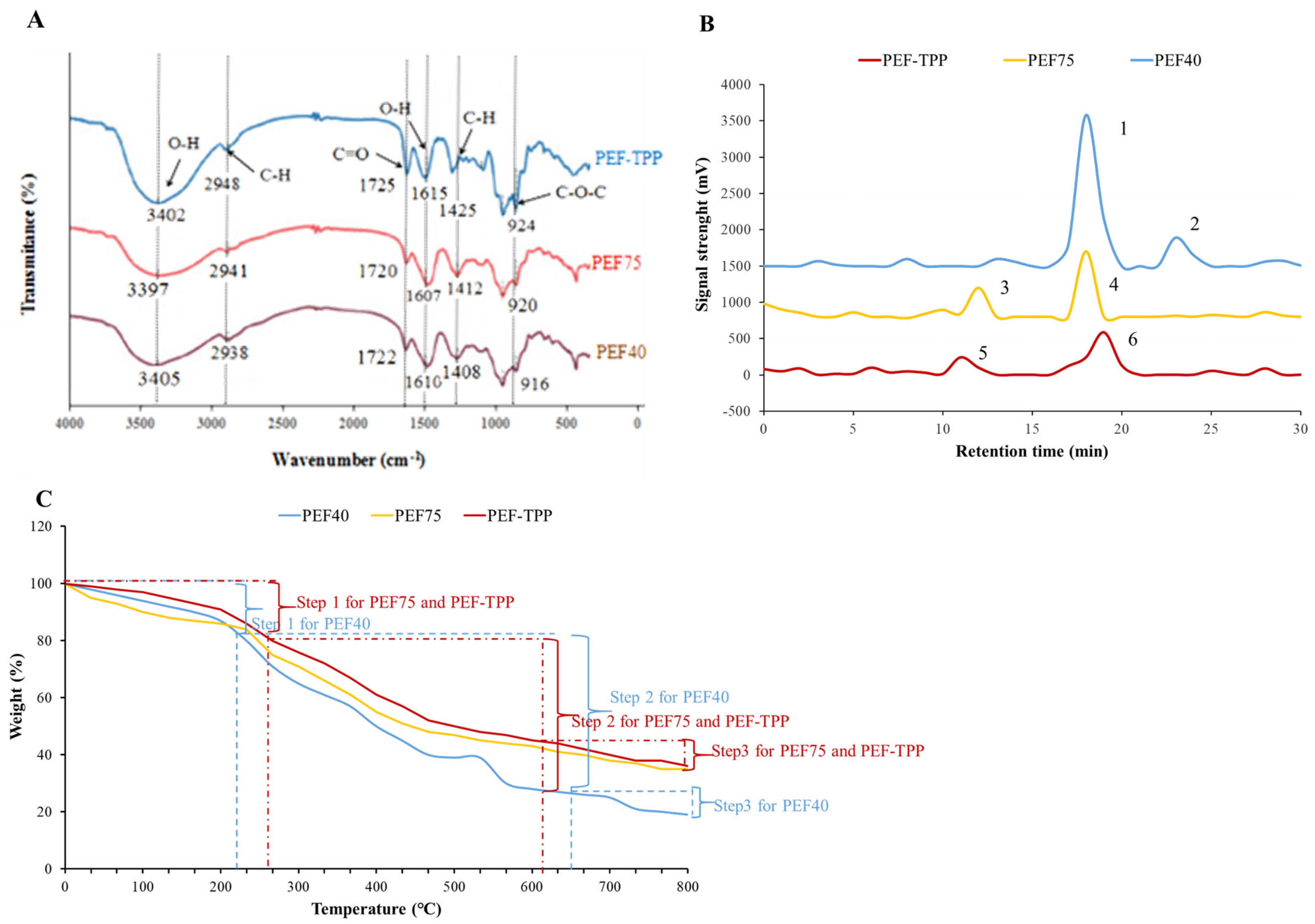
2.4.1. FT-IR Analysis
2.4.2. Mw Distribution Analysis
2.4.3. Monosaccharide Composition Analysis
2.4.4. TG Analysis
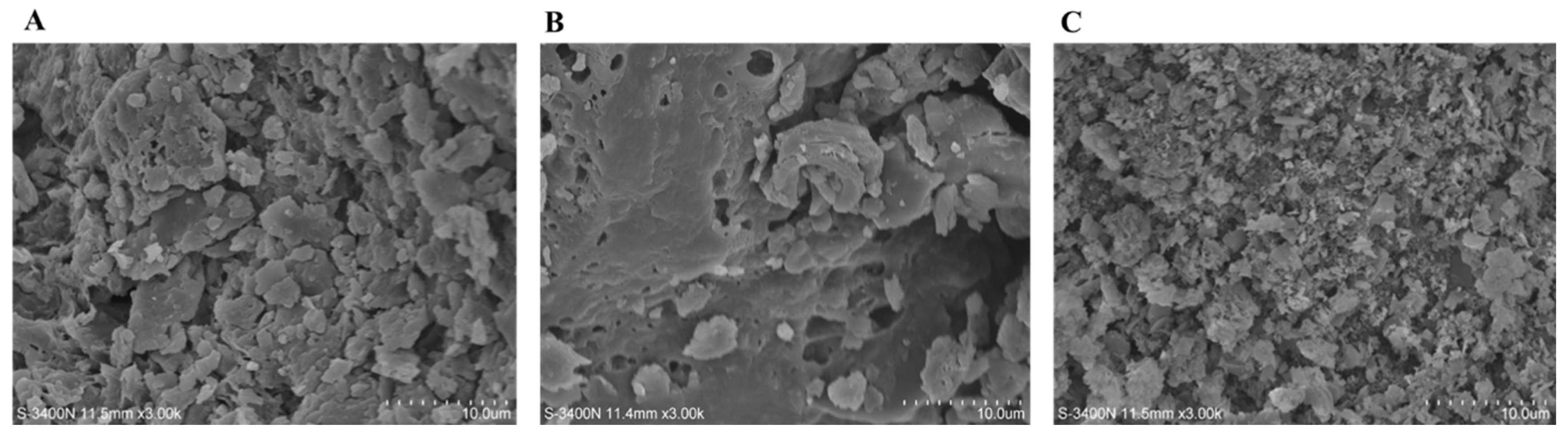
2.4.5. SEM Analysis
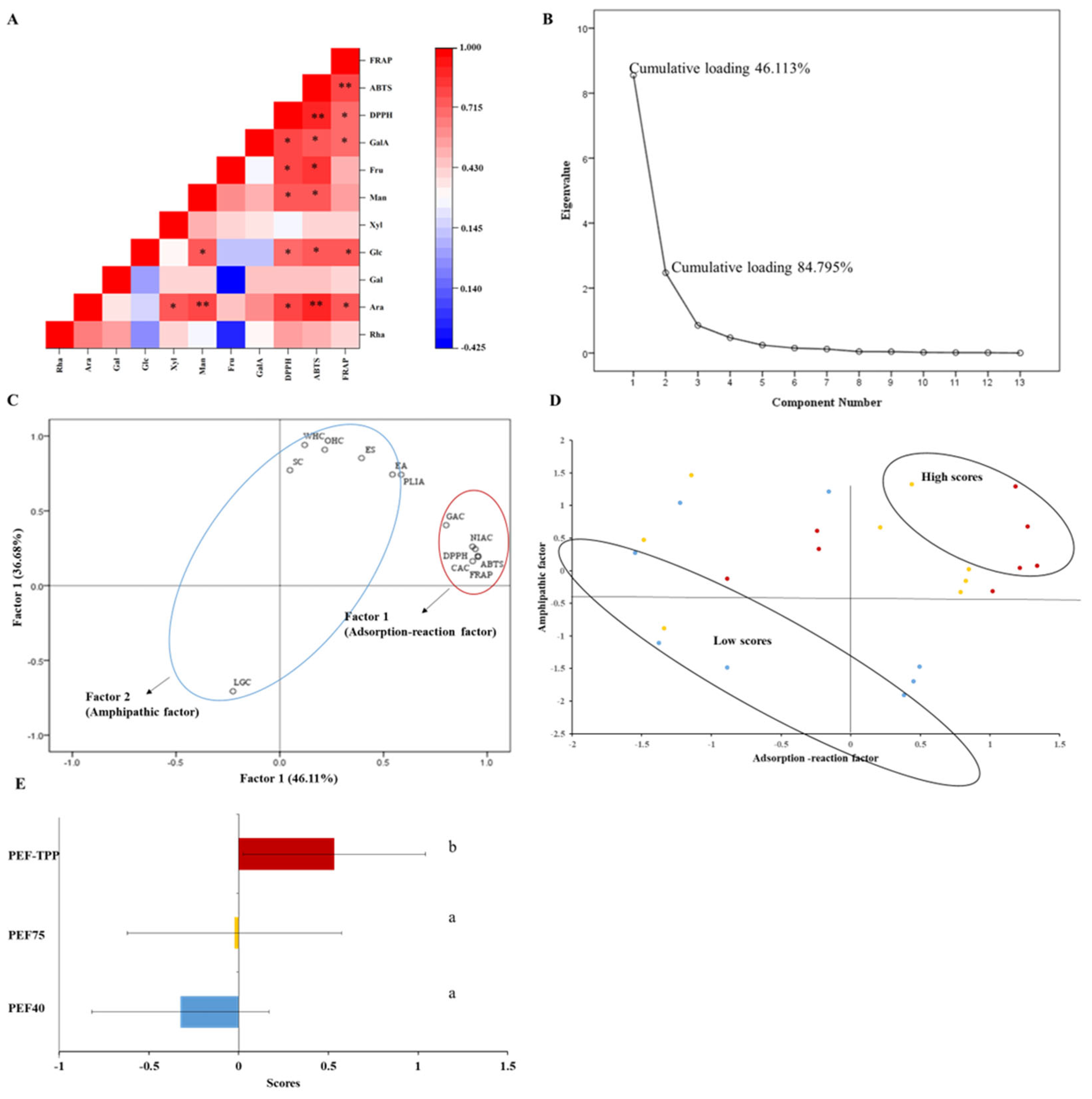
2.4.6. Correlation between Antioxidant Capacities and Structures of the SDFs
2.5. Principal Component Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Preparation of SDF
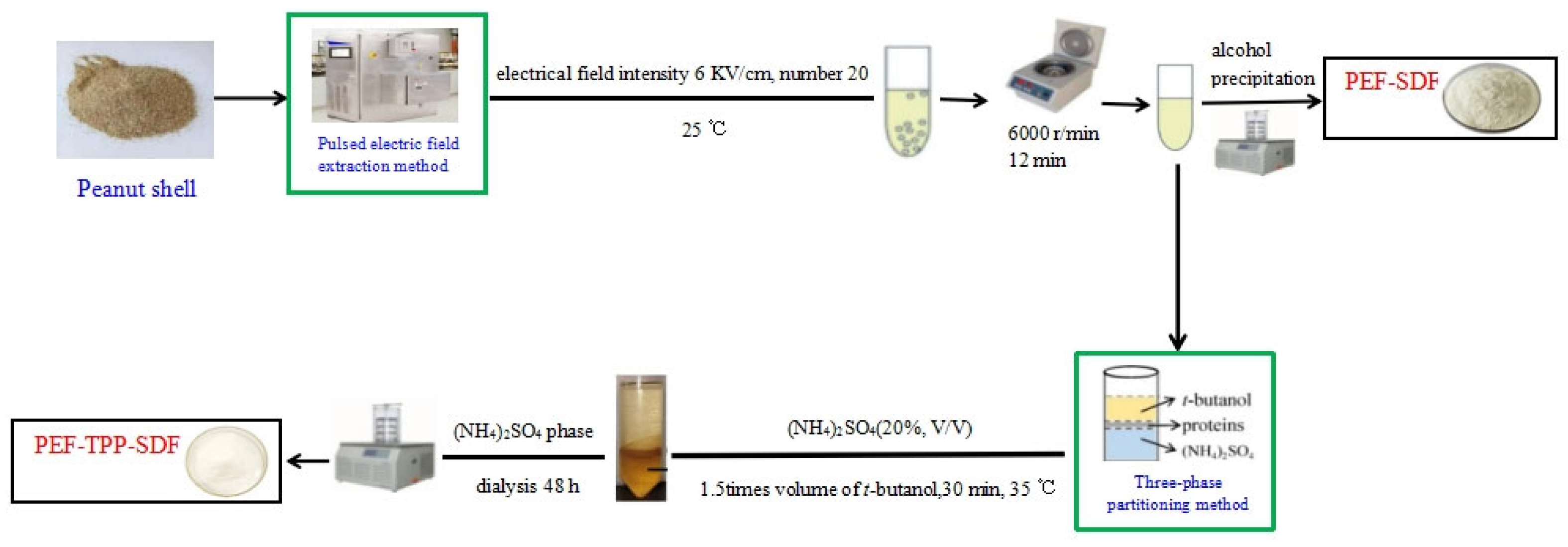
3.2.1. Extraction of SDF
3.2.2. Separation of SDF
Ethanol Precipitation
Three-Phase Partitioning
3.3. Chemical Composition Analysis
3.4. Physicochemical Properties
3.4.1. Water-Holding Capacity (WHC), Oil-Holding Capacity (OHC), and Swelling Capacity (SC)
3.4.2. Emulsifying Activity, Emulsion Stability, and Least Gelation Concentration
3.5. Functional Properties
3.5.1. Glucose Adsorption Capacity (GAC)
3.5.2. Pancreatic Lipase Inhibition Capacity (PLIC)
3.5.3. Cholesterol Adsorption Capacity (CAC)
3.5.4. Nitrite Ion Adsorption Capacity (NIAC)
3.5.5. Antioxidant Capacity
3.6. Structural Analysis
3.6.1. Fourier-Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectra Analysis
3.6.2. Molecular Weight (Mw) Distribution
3.6.3. Monosaccharide Composition
3.6.4. Thermogravimetric (TG) Analysis
3.6.5. Surface Morphological Analysis
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oulidi, O.; Nakkabi, A.; Boukhlifi, F.; Fahim, M.; Lgaz, H.; Alrashdi, A.A.; Elmoualij, N. Peanut shell from agricultural wastes as a sustainable filler for polyamide biocomposites fabrication. J. King Saud. Univ.-Sci. 2022, 4, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Wei, H.; You, Z.; Wu, H.; Xu, X.; Xie, H. Energetic and exergetic performances during drying of freshly harvested peanut with industrial mixed-flow dryer. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 7457–7467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Li, Z.; Yang, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, D. Effect of Drying Methods on Peanut Quality during Storage. J. Oleo Sci. 2021, 71, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wang, J.; Yu, J.-X.; Wang, Y.; Chi, R.-A. Effects of surface modification on heavy metal adsorption performance and stability of peanut shell and its extracts of cellulose, lignin, and hemicellulose. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 26502–26510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binici, H.; Aksogan, O. Insulation material production from onion skin and peanut shell fibres, fly ash, pumice, perlite, barite, cement and gypsum. Mater. Today Commun. 2017, 10, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.T.; Lin, L.Y. Novel design of TiO2 goober structure/microcone array photoanode for fiber-type dye-sensitized solar cell: Effect of peanut growth duration and TiO2 precursor concentration. J. Power Sources 2021, 482, 228954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Jing, Z.; Qiu, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Qiu, F.; Pan, J.; Zhang, T.; Li, C. Multifunctional biomass carbon fiber aerogel based on resource utilization of agricultural waste-peanut shells for fast and efficient oil-water/emulsion separation. Mater. Sci. Eng. B-Adv. Funct. Solid-State Mater. 2022, 283, 115819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Bansal, S.; Mangal, M.; Dixit, A.K.; Gupta, R.K.; Mangal, A. Utilization of Food Processing By-products as Dietary, Functional, and Novel Fiber: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 1647–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Alam, M.J.; Marques, F.Z.; Mackay, C.R. A major mechanism for immunomodulation: Dietary fibres and acid metabolites. Semin. Immunol. 2023, 66, 1044–5323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; He, Y.; Zou, Y.; Liu, Z. Modification of insoluble dietary fibres in soya bean okara and their physicochemical properties. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 2606–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimanian, Y.; Sanou, I.; Turgeon, S.L.; Canizares, D.; Khalloufi, S. Natural plant fibers obtained from agricultural residue used as an ingredient in food matrixes or packaging materials: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 371–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.; Niu, M.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, S.; Xiong, S. Structural characteristics and functional properties of rice bran dietary fiber modified by enzymatic and enzyme micronization treatments. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, D.; Ren, E.-F.; Li, J.; Zeng, X.-A.; Li, S.-L. Effects of pulsed electric field-assisted treatment on the extraction, antioxidant activity and structure of naringin. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 265, 118480–118485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, J.M.; Delso, C.; Angulo, J.; Álvarez, I.; Raso, J. Pulsed electric field-assisted extraction of carotenoids from fresh biomass of Rhodotorula glutinis. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2018, 47, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Fan, R.; Yan, Y.; Yang, S.; Wang, X.; Zheng, B. Characterization of the structural, physicochemical, and functional properties of soluble dietary fibers obtained from the peanut shell using different extraction methods. Front. Nutr. 2023, 9, 1103673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Gong, Q.; Yang, Q.; Sun, J.; Bi, J.; Zhang, C. Technology Optimization for Microwave-assisted Extraction of Water Soluble Dietary Fiber from Peanut Hull and Its Antioxidant Activity. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2011, 17, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.-K.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Qiu, W.-Y.; Ma, H.; Wang, Z.-B.; Wu, J.-Y. Three-phase partitioning as an elegant and versatile platform applied to nonchromatographic bioseparation processes. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2018, 58, 2416–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Li, T.; Liu, C.; Zheng, L. Effects of high hydrostatic pressure and superfine grinding treatment on physicochemical/functional properties of pear pomace and chemical composition of its soluble dietary fibre. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 107, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adapa, S.; Dingeldein, H.; Schmidt, K.; Herald, T. Rheological properties of ice cream mixes and frozen ice creams containing fat and fat replacers. J. Dairy Sci. 2000, 83, 2224–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, S.; Li, J.; Jin, W.; Yan, S.; Wang, Q. Effect of micronisation on dietary fibre content and hydration properties of lotus node powder fractions. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 590–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Yang, Z.; Wu, W.; Gao, H.; Zhou, C.; Sun, P.; Wu, C.; Xia, Q.; Chen, J. Physicochemical properties improvement and structural changes of bamboo shoots (phyllostachys praecox f. Prevernalis) dietary fiber modified by subcritical water and high pressure homogenization: A comparative study. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 3659–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, M.; Lin, Y.; Dong, L.; Jia, X.; Shen, Y.; Liu, L.; Chi, J.; Huang, F.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, R. Physicochemical and functional properties of dietary fiber from pummelo (Citrus grandis L. Osbeck) and grapefruit (Citrus paradisi Mcfad) cultivars. Food Biosci. 2021, 40, 100890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, Y.; Nozaki, S.; Makita, M.; Yokozuka, S.; Fukudome, S.-I.; Yanagisawa, T.; Aoe, S. Effects of whole grain wheat bread on visceral fat obesity in Japanese subjects: A randomized double-blind study. Plant Food Hum. Nutr. 2018, 73, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.M.; Mu, T.H. Effects of extraction methods and particle size distribution on the structural, physicochemical, and functional properties of dietary fiber from deoiled cumin. Food Chem. 2016, 94, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Yuan, M.; Liu, Y.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Shao, Y.; Wang, T.; Jiang, L. Effects of steam explosion on yield and properties of soluble dietary fiber from wheat bran. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2021, 27, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zeng, G.; Pan, Y.; Chen, W.; Huang, W.; Chen, H.; Li, Y. Properties of soluble dietary fiber polysaccharide from papaya peel obtained through alkaline or ultrasound assisted alkaline extraction. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 172, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tejada-Ortigoza, V.; Eduardo, G.; Amezquita, S.S. High hydrostatic pressure and mild heat treatments for the modification of orange peel dietary fiber: Effects on hygroscopic properties and functionality. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2018, 11, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yi, C.; Quan, K.; Lin, B. Chemical composition, structure, physicochemical and functional properties of rice bran dietary fiber modified by cellulase treatment. Food Chem. 2021, 42, 128352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.G.; Ye, R.; Chen, Y. Blasting extrusion processing: The increase of soluble dietary fiber content and extraction of soluble-fiber polysaccharides from wheat bran. Food Chem. 2015, 180, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namir, M.; Siliha, H.; Amadan, M.F. Fiber pectin from tomato pomace: Characteristics, functional properties and application in low-fat beef burger. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2015, 9, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, J.d.S.O.d.; Dias, C.O.; Arriola, N.D.; de Freitas, B.S.; de Francisco, A.; Petkowicz, C.L.; Araujo, L.; Guerra, M.P.; Nodari, R.O.; Amboni, R.D. Feijoa (Acca sellowiana) peel flours: A source of dietary fibers and bioactive compounds. Food Biosci. 2020, 38, 00789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahloko, L.M.; Silungwe, H.; Mashau, M.E.; Kgatla, T.E. Bioactive compounds, antioxidant activity and physical characteristics of wheat-prickly pear and banana biscuits. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngouémazong, E.D.; Christiaens, S.; Shpigelman, A.; Van Loey, A.; Hendrickx, M. The Emulsifying and Emulsion-Stabilizing Properties of Pectin: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2015, 14, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shi, Z.; Shangguan, W.; Fang, Y.; Nishinari, K.; Phillips, G.O.; Jiang, F. Emulsification properties of sugar beet pectin after modification with horseradish peroxidase. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Wang, L.; Fan, J.; Sun, W.; Dong, H. The pulsed electric field assisted extraction enhanced the yield and the physicochemical properties of soluble dietary fiber from orange peel. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 925642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xu, H.; Yuan, F.; Pan, Q.; Fan, R.; Gao, Y. Physicochemical characterization of five types of citrus dietary fibers. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2015, 4, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Wu, L.; Cao, C.; Wang, S.; Zhang, D. Improved function of bamboo shoot fiber by high-speed shear dispersing combined with enzyme treatment. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 844–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Wang, W.H.; Cao, L. Soluble dietary fibers from black soybean hulls: Physical and enzymatic modification, structure, physical properties, and cholesterol binding capacity. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 1668–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vangoori, Y.; Dakshinamoorthi, A.; Kavimani, S. Prominent pancreatic lipase inhibition and free radical scavenging activity of a myristica fragrans ethanolic extract in vitro. Maedica 2019, 14, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Dou, W.; Alaxi, S.; Niu, Y.; Yu, L. Modified soluble dietary fiber from black bean coats with its rheological and bile acid binding properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 62, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-H.; Wang, L.-H.; Zeng, X.-A.; Han, Z.; Wang, M.-S. Effect of pulsed electric fields (PEFs) on the pigments extracted from spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.). Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 43, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pataro, G.; Bobinaitė, R.; Bobinas, Č.; Satkauskas, S.; Raudonis, R.; Visockis, M.; Ferrari, G.; Viskelis, P. Improving the extraction of juice and anthocyanins from blueberry fruits and their by-products by application of pulsed electric fields. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2017, 10, 1595–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, D.; Zhang, D.; Huang, B.; Yi, P.; Yan, C. Structural characterization and DPPH radical scavenging activity of a polysaccharide from Guara fruits. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 103, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Y.; Fang, H.; Huo, T.; Sun, X.; Gong, Q.; Yu, L. A novel fat replacer composed by gelatin and soluble dietary fibers from black bean coats with its application in meatballs. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 22, 109000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, J.; Zhu, Z.; Cheng, S.; He, J.; Lamikanra, O. Soluble dietary fiber and polyphenol complex in lotus root: Preparation, interaction and identification. Food Chem. 2020, 314, 126219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Fang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, B.; Piao, J.; Zhu, L.; Yao, L.; Liu, K.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Q.; et al. The effects of different extraction methods on physicochemical, functional and physiological properties of soluble and insoluble dietary fiber from Rubus chingii Hu. Fruits. J. Funct. Food. 2022, 93, 105081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-B.; Pei, J.-J.; Ma, H.-L.; Cai, P.-F.; Yan, J.-K. Effect of extraction media on preliminary characterizations and antioxidant activities of Phellinus linteus polysaccharides. Carbohyd. Polym. 2014, 10, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Mayanga, P.; Azambuja, S.; Tyufekchiev, M.; Tompsett, G.; Timko, M.; Goldbeck, R.; Rostagno, M.; Forster-Carneiro, T. Subcritical water hydrolysis of brewer’s spent grains: Selective production of hemicellulosic sugars (c-5 sugars). J. Supercrit. Fluids 2019, 145, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, I.M.V.; Machado, F.; Moreno, M.J.; Nunes, C.; Coimbra, M.A.; Coreta-Gomes, F. Polysaccharide Structures and Their Hypocholesterolemic Potential. Molecules 2021, 26, 4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Feng, Z.; Aila, R.; Hou, Y.; Carne, A.; Bekhit, A.E.-D.A. Effect of pulsed electric fields (PEF) on physico-chemical properties, β-carotene and antioxidant activity of air-dried apricots. Food Chem. 2019, 291, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amoudi, R.H.; Taylan, O.; Kutlu, G. Characterization of chemical, molecular, thermal and rheological properties of medlar pectin extracted at optimum conditions as determined by Box-Behnken and ANFIS models. Food Chem. 2019, 271, 650–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, X.; Xu, S.; Wang, M. Effects of high-speed homogenization and high-pressure homogenization on structure of tomato residue fibers. Food Chem. 2017, 232, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ognyanov, M.; Remoroza, C.; Schols, H.A. Structural, rheological and functional properties of galactose-rich pectic polysaccharide fraction from leek. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 229, 115549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, L.; Wu, T.; Liu, R.; Li, K.; Zhang, M. Structural variation and microrheological properties of a homogeneous polysaccharide from wheat germ. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 2977–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Ma, X.; Jiang, P.; Hu, L.; Zhi, Z.; Chen, J.; Ding, T.; Ye, X.; Liu, D. Characterization of pectin from grapefruit peel: A comparison of ultrasound-assisted and conventional heating extractions. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 61, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Jing, H.; Ye, X.; Gao, W.; Bai, X.; Wang, H. Effects of different extraction methods on structure and properties of soluble dietary fiber from defatted coconut flour. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 143, 11031–111035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Jiang, B.; Luo, Y.; Fu, X.; Kong, H.; Shan, Y.; Ding, S. Effects of ultrasonic and ozone pretreatment on the structural and functional properties of soluble dietary fiber from lemon peel. J. Food Process Eng. 2021, 45, e13916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Q.; Chen, G.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Kan, J. Effects of different thermal processing methods on bioactive components, phenoliccompounds, and antioxidant activities of Qingke (highland hull-less barley). Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2023, 12, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. AOAC official method 968.28. In Total Sugars in Molasses as Invert Sugar; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. AOAC official method 991.43. In Total, Soluble, and Insoluble Dietary Fiber in Foods; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Huang, C.; Ou, S. In Vitro binding capacities of three dietary fibers and their mixture for four toxic elements, cholesterol, and bile acid. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, C.; Cheung, K.; Wong, Y. Functional properties of protein concentrate from three Chinese indigenous legume seeds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 2500–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffman, A.W.; Garcia, V.V. Functional properties and amino acid contents of protein isolate from mung bean flour. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 1977, 12, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, Q.; Huang, J.; Fang, D.; Zhuang, W.; Luo, X.; Zou, X.; Zheng, B.; Cao, H. Hypoglycemic effect of dietary fibers from bamboo shoot shell: An in vitro and in vivo study. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 127, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chau, C.F.; Wang, Y.T.; Wen, Y.L. Different micronization methods significantly improve the functionality of carrot insoluble fibre. Food Chem. 2007, 100, 1402–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Xie, M.; Nie, S.; Chen, Y.; Xie, J.; Yu, Q. Structural characteristics and functional properties of soluble dietary fiber from defatted rice bran obtained through Trichoderma viride fermentation. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 4, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Chu, J.; Lu, Z.; Lv, F.; Bie, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, H. Physicochemical and functional properties of dietary fiber from foxtail millet (Setaria italic) bran. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 79, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Lin, S.; Fu, Y.; Nie, X.-R.; Liu, W.; Su, Y.; Han, Q.-H.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, D.-R.; et al. Effects of extraction methods on the physicochemical characteristics and biological activities of polysaccharides from okra (Abelmoschus esculentus). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 127, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Proximate Composition (g/100 g) | PS | Obtained SDFs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEF40 | PEF75 | PEF-TPP | ||
| Dietary fiber | 83.91 ± 0.75 a | 86.04 ± 0.53 b | 90.04 ± 0.43 c | 96.02 ± 0.58 d |
| Protein | 5.89 ± 0.47 a | 4.48 ± 0.22 b | 3.33 ± 0.28 c | 0.87 ± 0.14 d |
| Fat | 4.45 ± 0.32 a | 2.08 ± 0.21 a | 1.68 ± 0.11 b | 1.33 ± 0.07 c |
| Moisture | 2.84 ± 0.11 a | 1.93 ± 0.12 b | 1.71 ± 0.08 c | 1.01 ± 0.05 d |
| Ash | 1.78 ± 0.04 a | 1.51 ± 0.11 b | 1.21 ± 0.04 c | 0.95 ± 0.12 d |
| Total sugar | 11.25 ± 0.25 a | 22.47 ± 0.62 b | 31.47 ± 1.47 c | 33.18 ± 1.27 c |
| Yield (%) | - | 27.31 ± 1.42 a | 22.31 ± 2.12 b | 21.43 ± 2.45 b |
| Samples | WHC (g/g) | OHC (g/g) | SC (mL/g) | EA (mL/100 mL) | ES (mL/100 mL) | LGC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEF40 | 3.98 ± 0.29 a | 2.88 ± 0.20 a | 4.57 ± 0.36 a | 66.37 ± 1.83 a | 55.11 ± 1.13 a | 11.26 ± 0.71 a |
| PEF75 | 4.96 ± 0.17 b | 3.74 ± 0.14 b | 5.49 ± 0.27 b | 73.69 ± 1.01 b | 63.54 ± 1.24 b | 10.02 ± 0.31 b |
| PEF-TPP | 5.67 ± 0.67 c | 3.89 ± 0.41 b | 6.96 ± 0.88 c | 79.69 ± 2.36 c | 70.36 ± 2.13 c | 8.18 ± 0.28 c |
| Sample | Peak Number | RT (min) | Mw (kDa) | Mn (kDa) | Pd (Mw/Mn) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEF40 | 1 | 18.25 | 324 | 104 | 3.12 |
| 2 | 23.48 | 142 | 78 | 1.82 | |
| PEF75 | 3 | 12.31 | 268 | 81 | 3.31 |
| 4 | 18.01 | 115 | 52 | 2.21 | |
| PEF-TPP | 5 | 11.29 | 245 | 95 | 2.58 |
| 6 | 18.95 | 110 | 47 | 2.34 |
| Monosaccharide (mg/g db) | PEF40 | PEF75 | PEF-TPP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rhamnose (Rha) | 11.68 ± 1.14 | 12.05 ± 0.95 | 12.47 ± 1.24 |
| Arabinose (Ara) | 68.54 ± 3.58 | 72.61 ± 2.58 | 78.32 ± 5.21 |
| Galactose (Gal) | 18.98 ± 2.01 | 19.05 ± 1.35 | 20.13 ± 1.34 |
| Glucose (Glc) | 15.12 ± 1.45 | 15.21 ± 1.05 | 21.17 ± 0.64 |
| Xylose (Xyl) | 15.60 ± 1.51 | 16.98 ± 1.75 | 16.48 ± 1.56 |
| Mannose (Man) | 10.57 ± 1.37 | 13.25 ± 1.21 | 15.52 ± 0.54 |
| Fructose (Fru) | 6.02 ± 1.06 | 7.48 ± 1.35 | 7.32 ± 0.54 |
| Galacturonic acid (GalA) | 33.25 ± 3.44 | 36.98 ± 2.18 | 35.48 ± 2.54 |
| HG = GalA − Rha | 21.59 ± 1.86 | 24.93 ± 2.14 | 21.86 ± 3.04 |
| RG-I = 2 Rha + Ara + Gal | 110.88 ± 2.15 | 115.84 ± 1.95 | 123.39 ± 13.10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, R.; Wang, L.; Cao, H.; Du, R.; Yang, S.; Yan, Y.; Zheng, B. Characterization of the Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Soluble Dietary Fiber from Peanut Shells Prepared by Pulsed Electric Fields with Three-Phase Partitioning. Molecules 2024, 29, 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071603
Fan R, Wang L, Cao H, Du R, Yang S, Yan Y, Zheng B. Characterization of the Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Soluble Dietary Fiber from Peanut Shells Prepared by Pulsed Electric Fields with Three-Phase Partitioning. Molecules. 2024; 29(7):1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071603
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Rui, Lei Wang, Huihui Cao, Ruihuan Du, Shuo Yang, Yanhua Yan, and Baiqin Zheng. 2024. "Characterization of the Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Soluble Dietary Fiber from Peanut Shells Prepared by Pulsed Electric Fields with Three-Phase Partitioning" Molecules 29, no. 7: 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071603
APA StyleFan, R., Wang, L., Cao, H., Du, R., Yang, S., Yan, Y., & Zheng, B. (2024). Characterization of the Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Soluble Dietary Fiber from Peanut Shells Prepared by Pulsed Electric Fields with Three-Phase Partitioning. Molecules, 29(7), 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071603





