In Vitro and Ex Vivo Antifungal Activities of Metconazole against the Rice Blast Fungus Pyricularia oryzae
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
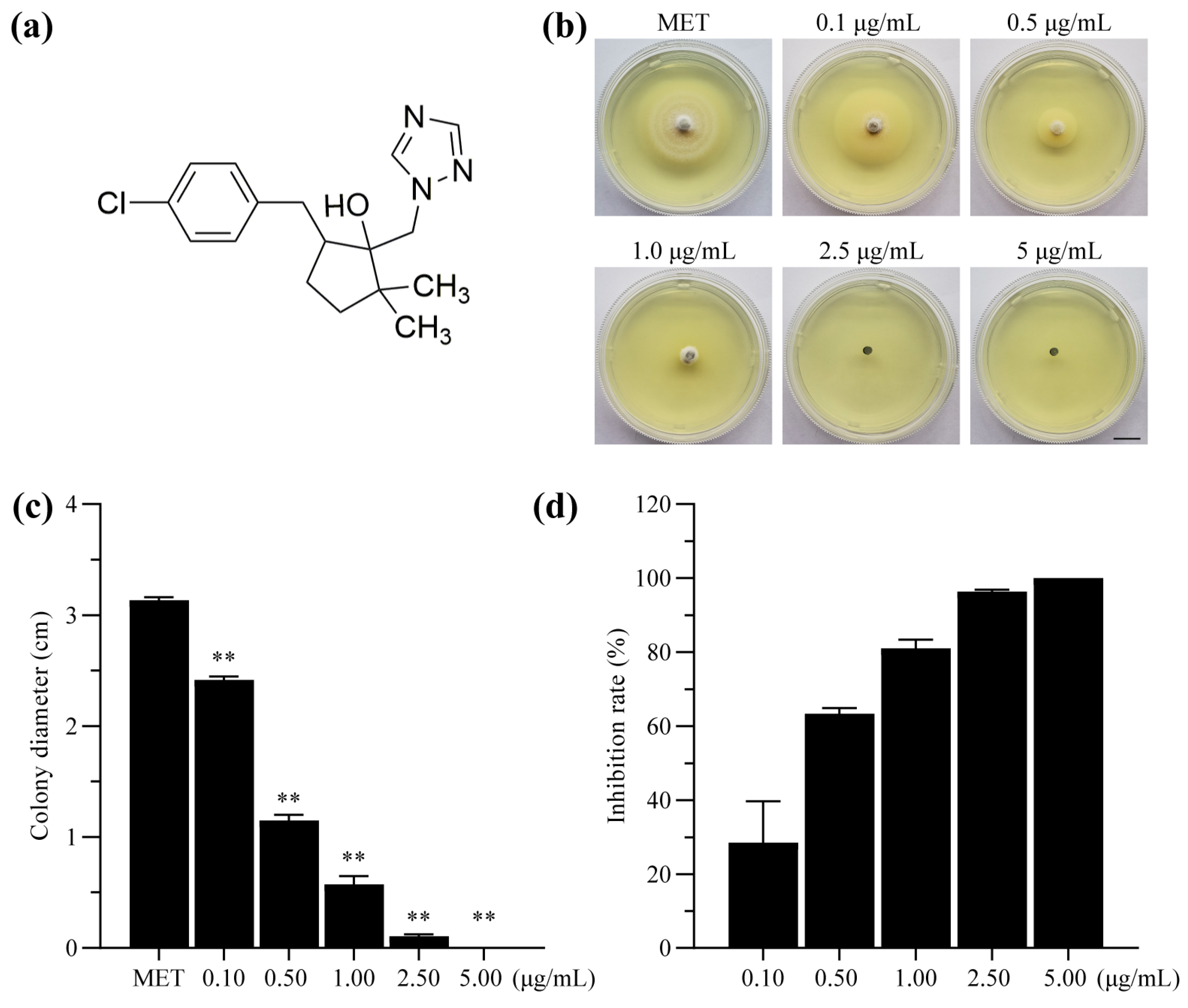
2.1. Sensitivity of P. oryzae to Metconazole
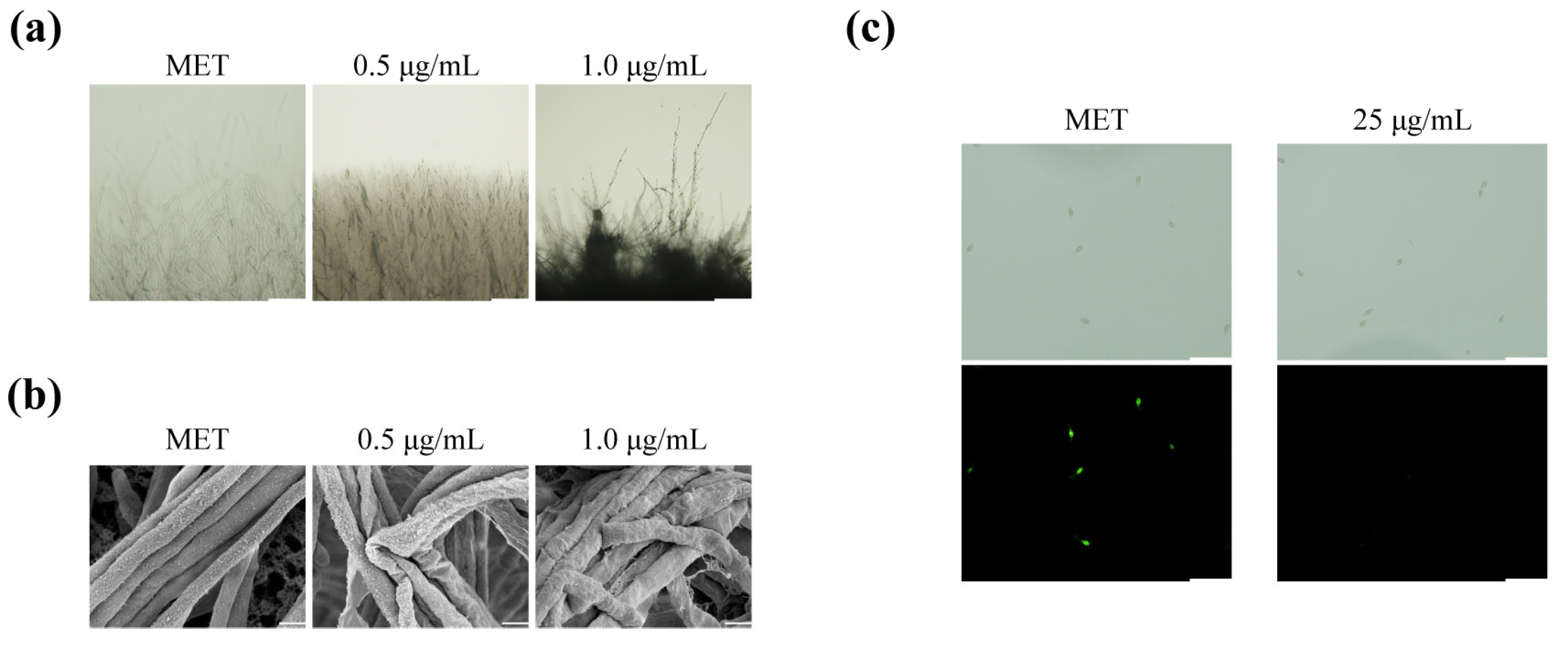
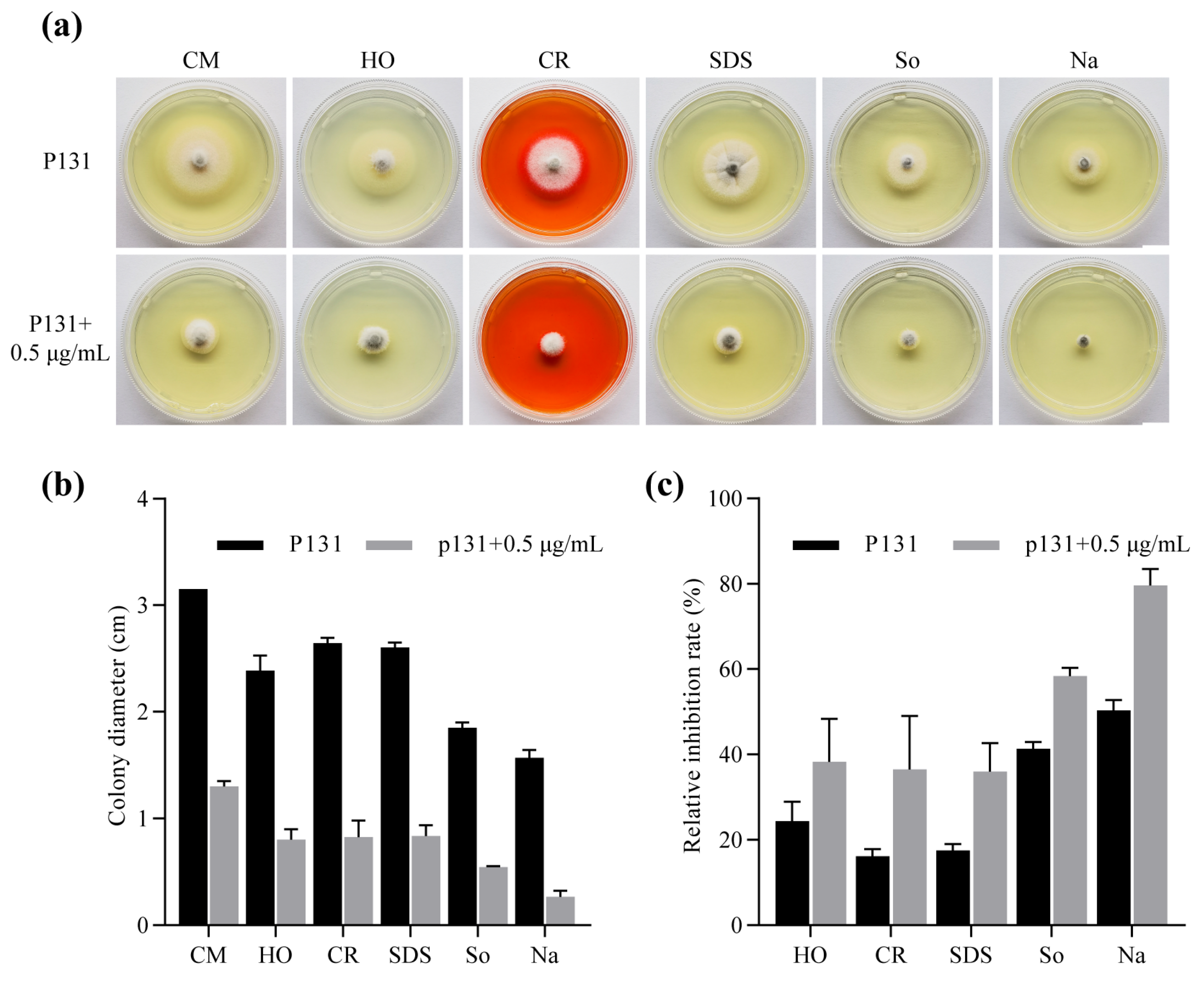
2.2. Metconazole Treatment Damaged the Cell Wall Integrity and Cell Membrane Permeability of P. oryzae
2.3. The Effects of Metconazole on P131 Conidial Germination and Germ Tube Elongation
2.4. Metconazole Treatment Hindered Appressorium Formation, Penetration and Invasive Hyphal Development of P131
2.5. Metconazole Treatment Destroyed Full Virulence of P. oryzae
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Fungicide and Pyricularia oryzae Isolates
4.2. Sensitivity of P. oryzae Isolates to Metconazole
4.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Fluorescein Diacetate (FDA) Staining
4.4. Evaluation of Metconazole Activity against Conidial Germination and Germ Tube Elongation
4.5. Evaluation of Metconazole Activity against Appressorium Morphogenesis and Infection Hypae Development in Host Tissues
4.6. Control Efficacy of Metaconazole to the Virulence of P. oryzae in Barley and Rice
4.7. Statistics Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilson, R.A.; Talbot, N.J. Under pressure: Investigating the biology of plant infection by Magnaporthe oryzae. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, R.; Van Kan, J.A.; Pretorius, Z.A.; Hammond-Kosack, K.E.; Di Pietro, A.; Spanu, P.D.; Rudd, J.J.; Dickman, M.; Kahmann, R.; Ellis, J.; et al. The Top 10 fungal pathogens in molecular plant pathology. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 13, 414–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, M.C.; Henk, D.A.; Briggs, C.J.; Brownstein, J.S.; Madoff, L.C.; McCraw, S.L.; Gurr, S.J. Emerging fungal threats to animal, plant and ecosystem health. Nature 2012, 484, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, J.; Orth, K. Rise of a cereal killer: The biology of Magnaporthe oryzae biotrophic growth. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 582–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wu, C.; Jiang, G.; Wang, L.; He, Y. Dynamic analyses of rice blast resistance for the assessment of genetic and environmental effects. Plant Breed. 2007, 126, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couch, B.C.; Kohn, L.M. A multilocus gene geneology concordant with host preference indicates segregation of a new species, Magnaporthe oryzae, from Magnaporthe grisea. Mycologia 2002, 94, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbot, N.J. On the trail of a cereal killer: Exploring the biology of Magnaporthe grisea. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2003, 57, 177–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.T.; Croll, D.; Gladieux, P.; Soanes, D.M.; Persoons, A.; Bhattacharjee, P.; Hossain, M.S.; Gupta, D.R.; Rahman, M.; Mahboob, M.G.; et al. Emergence of wheat blast in Bangladesh was caused by a South American lineage of Magnaporthe oryzae. BMC Biol. 2016, 14, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pordel, A.; Ravel, S.; Charriat, F.; Gladieux, P.; Cros-Arteil, S.; Milazzo, J.; Adreit, H.; Javan-Nikkhah, M.; Mirzadi-Gohari, A.; Moumeni, A.; et al. Tracing the origin and evolutionary history of Pyricularia oryzae infecting maize and barnyard grass. Phytopathology 2021, 111, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonman, J.M.; Khush, G.S.; Nelson, R.J. Breeding rice for resistance to pests. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1992, 30, 507–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Valent, B. Durable resistance to rice blast. Science 2017, 355, 906–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawa, A.S.; Anilakumar, K.R. Genetically modified foods: Safety, risks and public concerns—A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 50, 1035–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woloshuk, C.P.; Wolkow, P.M.; Sisler, H.D. The effect of three fungicides, specific for the control of rice blast disease, on the growth and melanin biosynthesis by Pyricularia oryzae cav. Pest Manag. Sci. 1981, 12, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, C.A.; Webster, R.K. Occurrence, distribution, epidemiology, cultivar reaction, and management of rice blast disease in California. Plant Dis. 2001, 85, 1096–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, M.; Fukada, M. Effect of a rice blast controlling agent, isoprothiolane, on Nilaparvata Lugens stal with different levels of susceptibility to diazinon. In Pest Resistance to Pesticides; Georghiou, G.P., Saito, T., Eds.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1983; pp. 421–428. [Google Scholar]
- Pramesh, D.; Nataraj, K.; Guruprasad, G.S.; Mahantashivayogayya, K.; Reddy, B.G.M. Evaluation of a new strobilurin group of fungicide for the management of blast disease of paddy. Am. J. Exp. Agric. 2016, 13, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, A.; Miki, N.; Yukioka, H.; Tamura, H.; Masuko, M. A possible mechanism of control of rice blast disease by a novel alkoxyiminoacetamide fungicide, SSF126. Phytopathology 1996, 86, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoghavarsha, C.; Pramesh, D.; Chidanandappa, E.; Sharanabasav, H.; Raghunandana, A.; Prasanna Kumar, M.K.; Hosahatti, R.; Saddamhusen, A. Chemicals for the management of paddy blast disease. In Blast Disease of Cereal Crops; Nayaka, S.C., Hosahatti, R., Prakash, G., Satyavathi, C.T., Sharma, R., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 59–81. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Che, Z.; Chen, G. Multiple-fungicide resistance to carbendazim, diethofencarb, procymidone, and pyrimethanil in field isolates of Botrytis cinerea from tomato in Henan Province, China. Crop Prot. 2016, 84, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.C.; He, L.; Zhou, M. Development and application of loop-mediated isothermal amplification for detecting the highly benzimidazole-resistant isolates in Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ge, C.; Wang, Y.; Cao, J.; Jia, X.; Wang, J.; Zhou, M. Development and application of loop-mediated isothermal amplification for detection of the F167Y mutation of carbendazim-resistant isolates in Fusarium graminearum. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, H.; Sugihara, M.; Takagaki, M.; Nagayama, K. Monitoring and characterization of Magnaporthe grisea isolates with decreased sensitivity to scytalone dehydratase inhibitors. Pest Manag. Sci. 2004, 60, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, M.; Shao, Z.; Liang, G. Detection of sensitivity and resistance variation of Magnaporthe grisea to kitazin P, carbendazim and tricyclazole. Rice Sci. 2004, 18, 317–323. [Google Scholar]
- Kumazawa, S.; Ito, A.; Saishoji, T.; Chuman, H. Development of new fungicides, ipconazole and metconazole. J. Pestic. Sci. 2000, 25, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardis, J.; Walsh, E.J. Studies of the effectiveness of metconazole in controlling Fusarium Head Blight caused by Fusarium culmorum in spring wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Cereal Res. Commun. 2000, 28, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateishi, H.; Miyake, T.; Mori, M.; Kimura, R.; Sakuma, Y.; Saishoji, T. Sensitivity of Japanese Fusarium graminearum species complex isolates to metconazole. J. Pestic. Sci. 2010, 35, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Li, M.; Zhao, H.; Lu, F.; Wang, J.; Zhou, M. Molecular and biological characteristics of laboratory metconazole-resistant mutants in Fusarium graminearum. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2018, 152, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, T.; Ma, D.; Gao, Y.; Mu, W.; Liu, F. Baseline sensitivity of Corynespora cassiicola to metconazole and efficacy of this fungicide. Crop Prot. 2020, 130, 105056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Fan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Luo, J.; Liu, C. Toxicity, bioactivity of triazole fungicide metconazole and its effect on mycotoxin production by Fusarium verticillioides: New perspective from an enantiomeric level. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 828, 154432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Fan, Z.; Wu, J.; Wang, L.; He, D.; Mohamed, S.R.; Dawood, D.H.; Shi, J.; Gao, T.; et al. Antifungal activities of metconazole against the emerging wheat pathogen Fusarium pseudograminearum. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2023, 190, 105298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skamnioti, P.; Gurr, S.J. Against the grain: Safeguarding rice from rice blast disease. Trends Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woloshuk, C.P.; Sisler, H.D.; Vigil, E.L. Action of the antipenetrant, tricyclazole, on appressoria of Pyricularia oryzae. Physiol. Plant Pathol. 1983, 22, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurahashi, Y. Melanin biosynthesis inhibitors (MBIs) for control of rice blast. Inst. Phys. Chem. Res. 2001, 12, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Moya, F.; Martin-Urdiroz, M.; Oses-Ruiz, M.; Were, V.M.; Fricker, M.D.; Littlejohn, G.; Lopez-Llorca, L.V.; Talbot, N.J. Chitosan inhibits septin-mediated plant infection by the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae in a protein kinase C and Nox1 NADPH oxidase-dependent manner. New Phytol. 2021, 230, 1578–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Su, J.; Xu, Y.; Chen, J.; Chern, M.; Lei, M.; Qi, T.; Wang, Z.; Ryder, L.S.; Tang, B.; et al. Discovery of broad-spectrum fungicides that block septin-dependent infection processes of pathogenic fungi. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 1565–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yao, J.; Wang, W.; Gao, T.; Yang, X.; Zhang, A. Effect of epoxiconazole on rice blast and rice grain yield in China. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2013, 135, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Miao, J.; Chen, F.; Li, B.; Liu, X. Survival cost and diverse molecular mechanisms of Magnaporthe oryzae isolate resistance to epoxiconazole. Plant Dis. 2021, 105, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, M.; Yan, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Ma, Z. Sensitivity of Magnaporthe grisea to the sterol demethylation inhibitor fungicide propiconazole. J. Phytopathol. 2009, 157, 568–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spolti, P.; de Jorge, B.C.; Del Ponte, E.M. Sensitivity of Fusarium graminearum causing head blight of wheat in Brazil to tebuconazole and metconazole fungicides. Trop. Plant Pathol. 2012, 37, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateishi, H.; Miyake, T.; Mori, M.; Sakuma, Y.; Saishoji, T. Effect of application timing of metconazole on Fusarium head blight development and mycotoxin contamination in wheat and barley. J. Pestic. Sci. 2014, 39, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Zhai, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Sang, H.; Han, G.; Keller, N.P.; Lu, L. The Aspergillus fumigatus damage resistance protein family coordinately regulates ergosterol biosynthesis and azole susceptibility. mBio 2016, 7, e01919-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Zhou, M.; Wang, W.; Sun, X.; Yarden, O.; Li, S. Abnormal ergosterol biosynthesis activates transcriptional responses to antifungal azoles. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, N.; Mo, P.; Shen, J.; Liu, M.; Zhang, H.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Z. Membrane component ergosterol builds a platform for promoting effector secretion and virulence in Magnaporthe oryzae. New Phytol. 2022, 237, 930–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Ma, W.B.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Que, Y.W.; Ma, Z.H.; Talbot, N.J.; Wang, Z.Y. A sterol 14α-demethylase is required for conidiation, virulence and for mediating sensitivity to sterol demethylation inhibitors by the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2011, 48, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, L.; Lu, W.; Xu, X.; Yan, F.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Bai, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhao, W.; Yang, J.; et al. A rapid approach for isolating a single fungal spore from rice blast diseased leaves. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 1415–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Shishiyama, J. Temporal sequence of cytological events in rice leaves infected with Pyricularia oryzae. Can. J. Bot. 1988, 66, 730–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.L.; Shi, T.; Yang, J.; Shi, W.; Gao, X.; Chen, D.; Xu, X.; Xu, J.R.; Talbot, N.J.; Peng, Y.L. N-glycosylation of effector proteins by an α-1, 3-mannosyltransferase is required for the rice blast fungus to evade host innate immunity. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 1360–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fei, L.; Hao, L. In Vitro and Ex Vivo Antifungal Activities of Metconazole against the Rice Blast Fungus Pyricularia oryzae. Molecules 2024, 29, 1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29061353
Fei L, Hao L. In Vitro and Ex Vivo Antifungal Activities of Metconazole against the Rice Blast Fungus Pyricularia oryzae. Molecules. 2024; 29(6):1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29061353
Chicago/Turabian StyleFei, Liwang, and Lingyun Hao. 2024. "In Vitro and Ex Vivo Antifungal Activities of Metconazole against the Rice Blast Fungus Pyricularia oryzae" Molecules 29, no. 6: 1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29061353
APA StyleFei, L., & Hao, L. (2024). In Vitro and Ex Vivo Antifungal Activities of Metconazole against the Rice Blast Fungus Pyricularia oryzae. Molecules, 29(6), 1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29061353





