Anti-Aging in Caenorhabditis elegans of Polysaccharides from Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
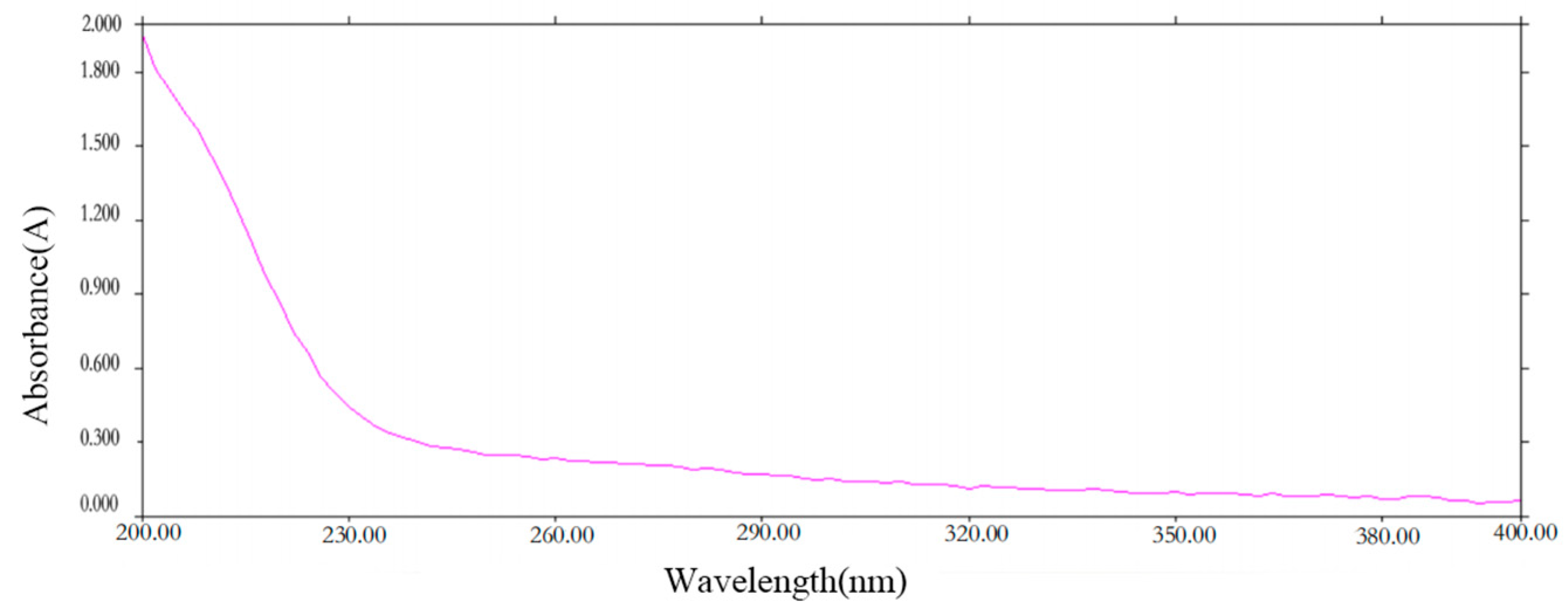
2.1. UV Spectroscopy of PCP-1
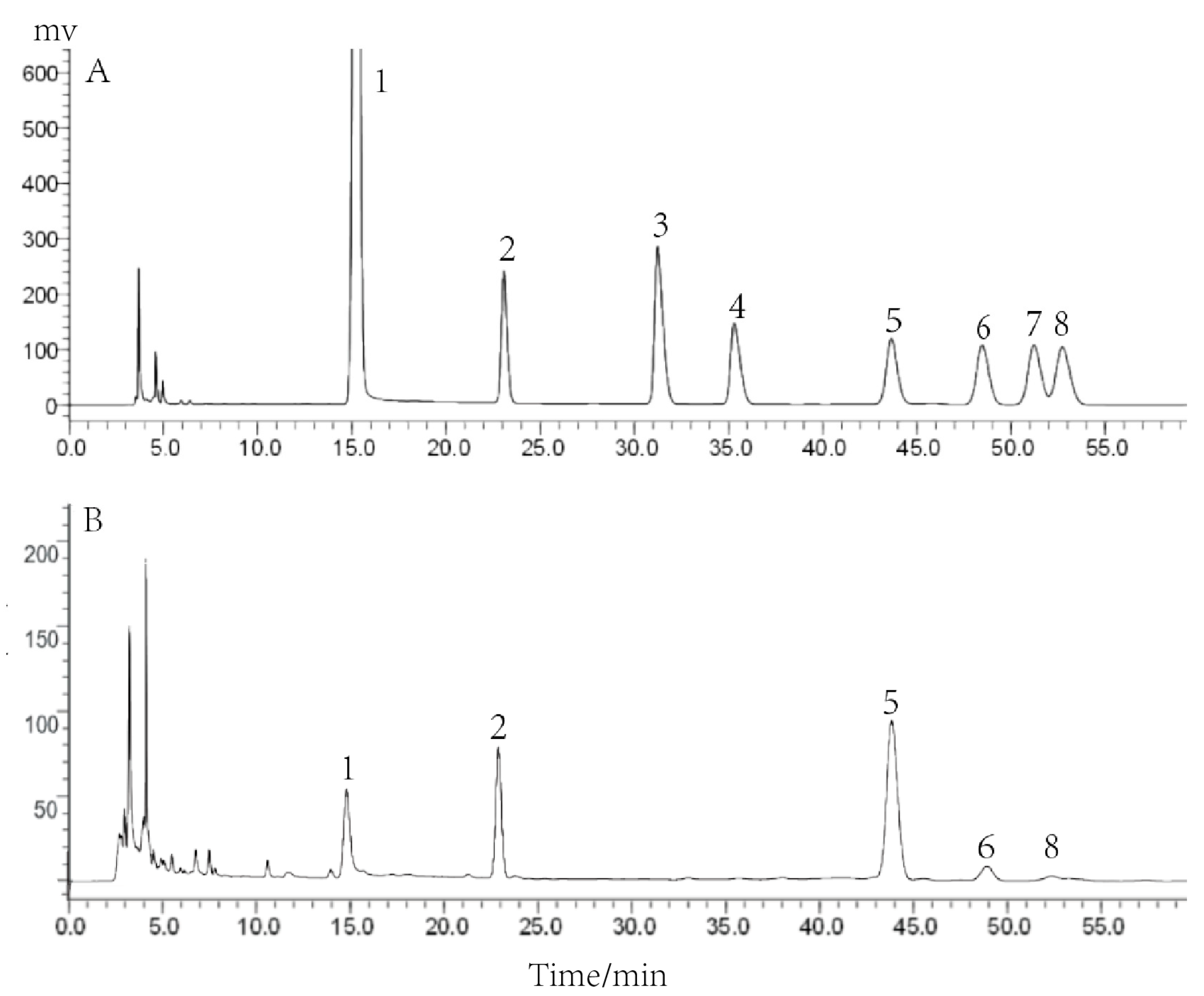
2.2. Monosaccharide Composition of PCP-1
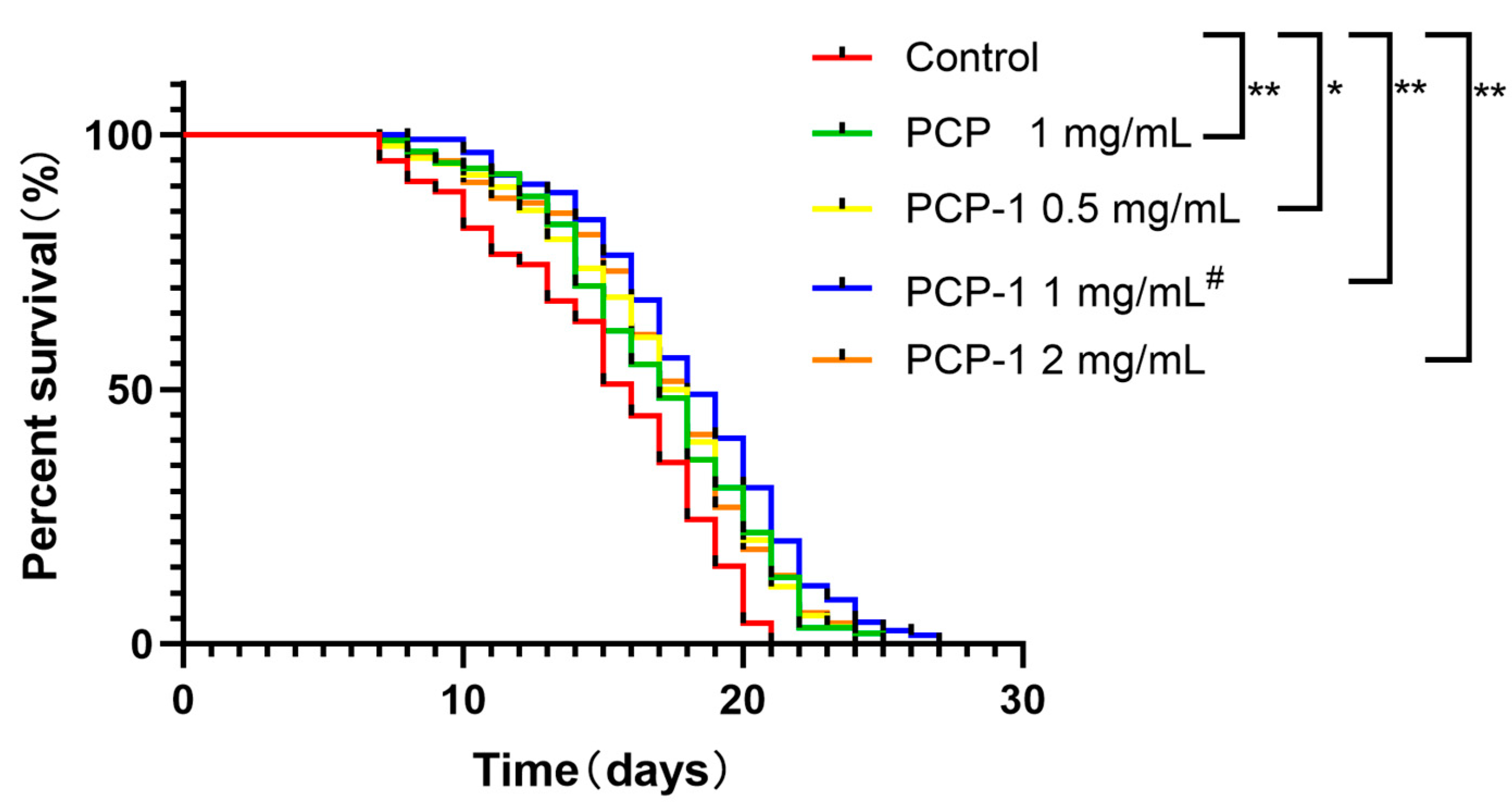
2.3. Lifespan Analysis
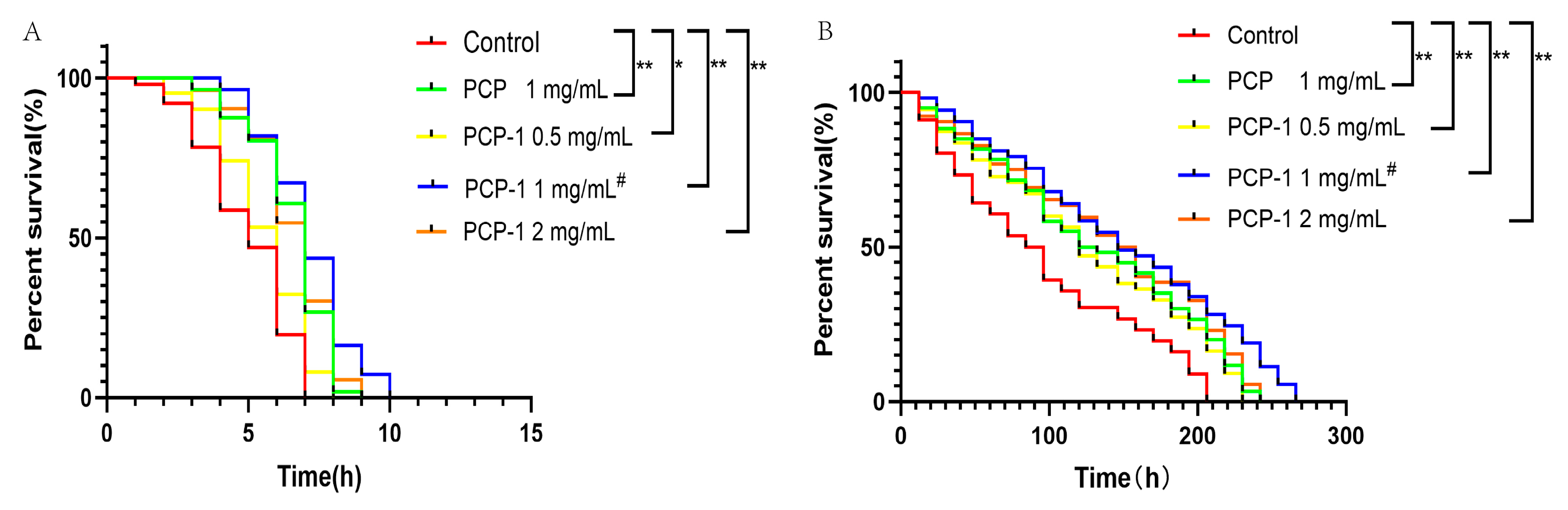
2.4. Effect of Polysaccharides on Stress Resistance in Nematodes
2.5. Effect of Polysaccharides on the Reproductive Capacity of Nematodes
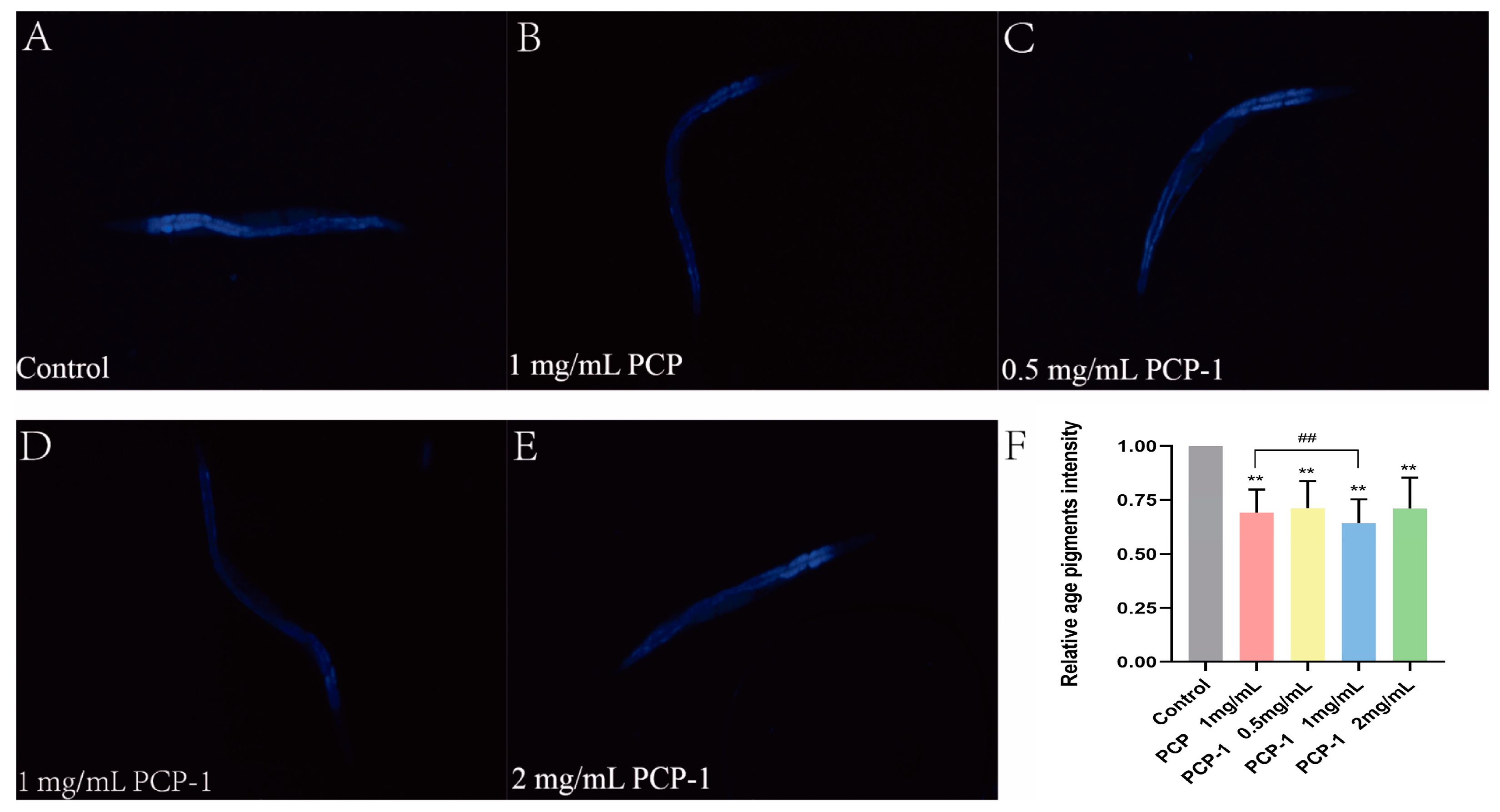
2.6. Reduction of Lipofuscin Accumulation by Polysaccharides in C. elegans
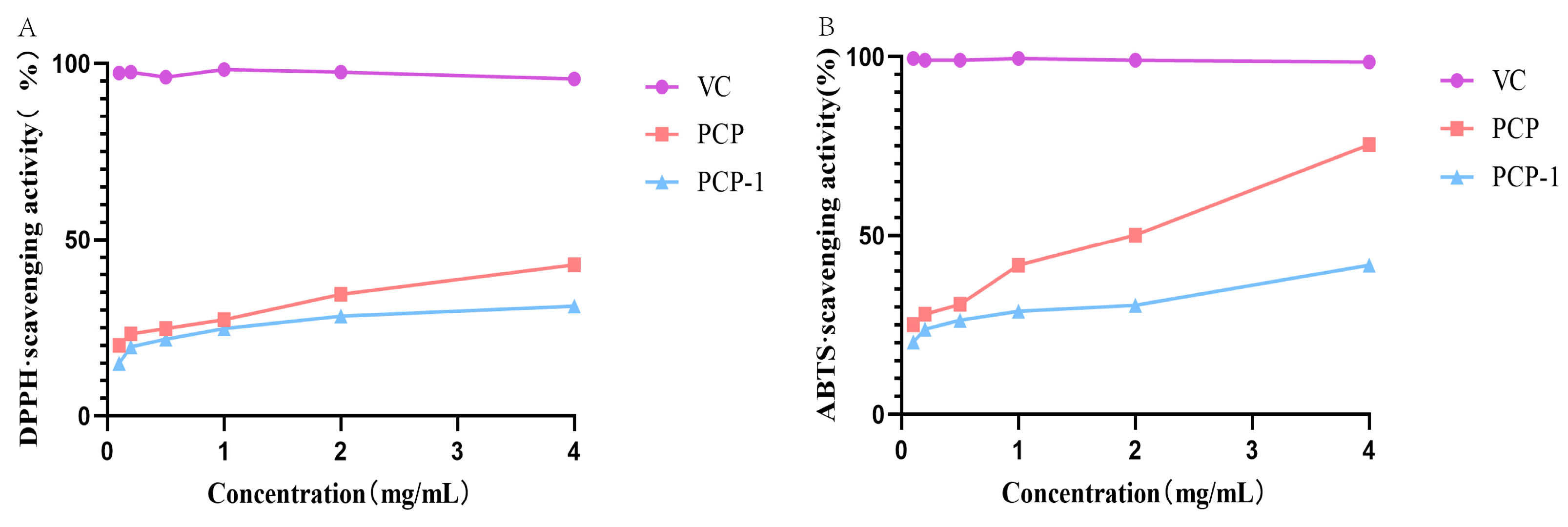
2.7. ABTS and DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity of PCP and PCP-1
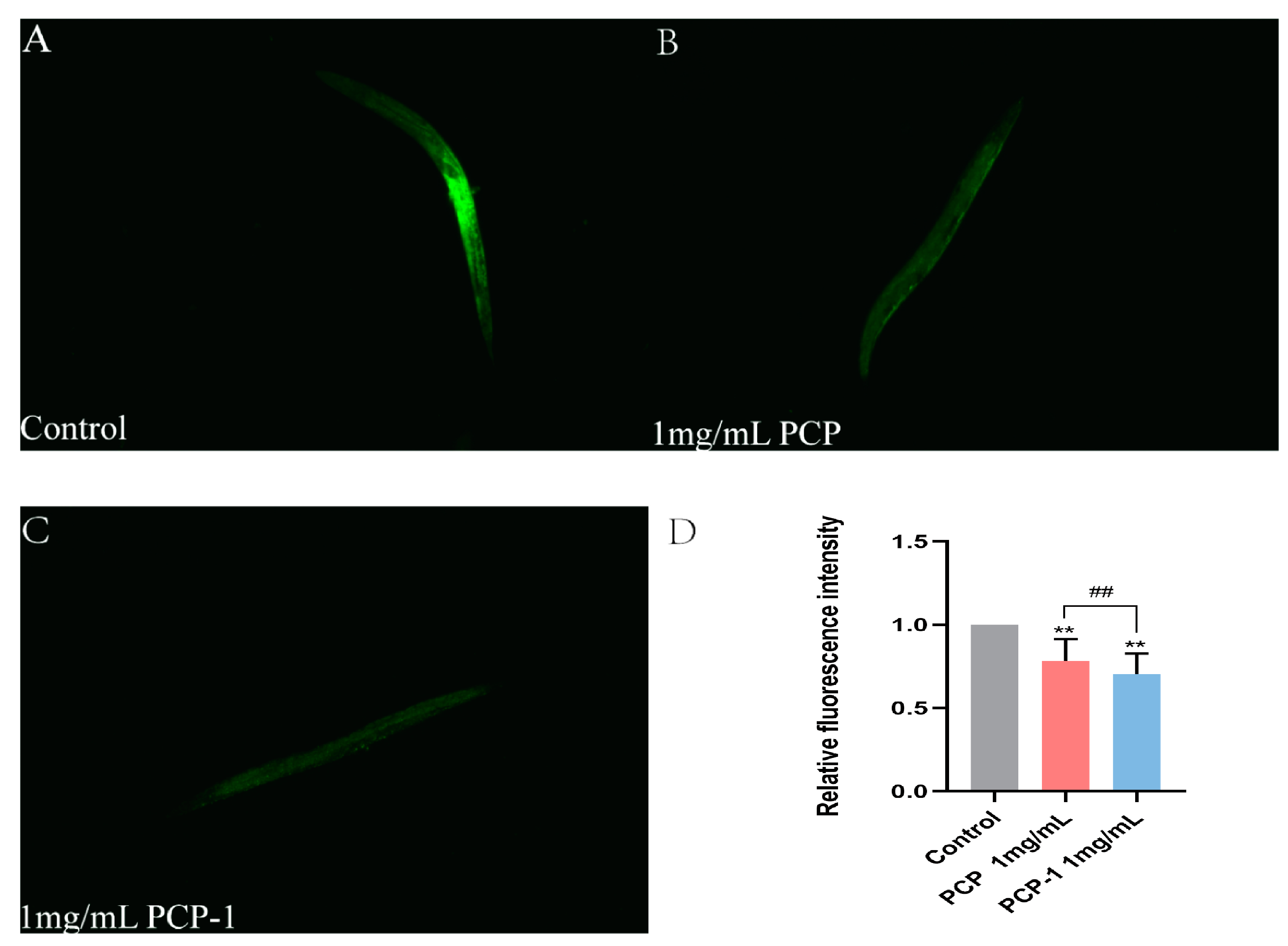
2.8. PCP and PCP-1 Reduce ROS Accumulation in C. elegans
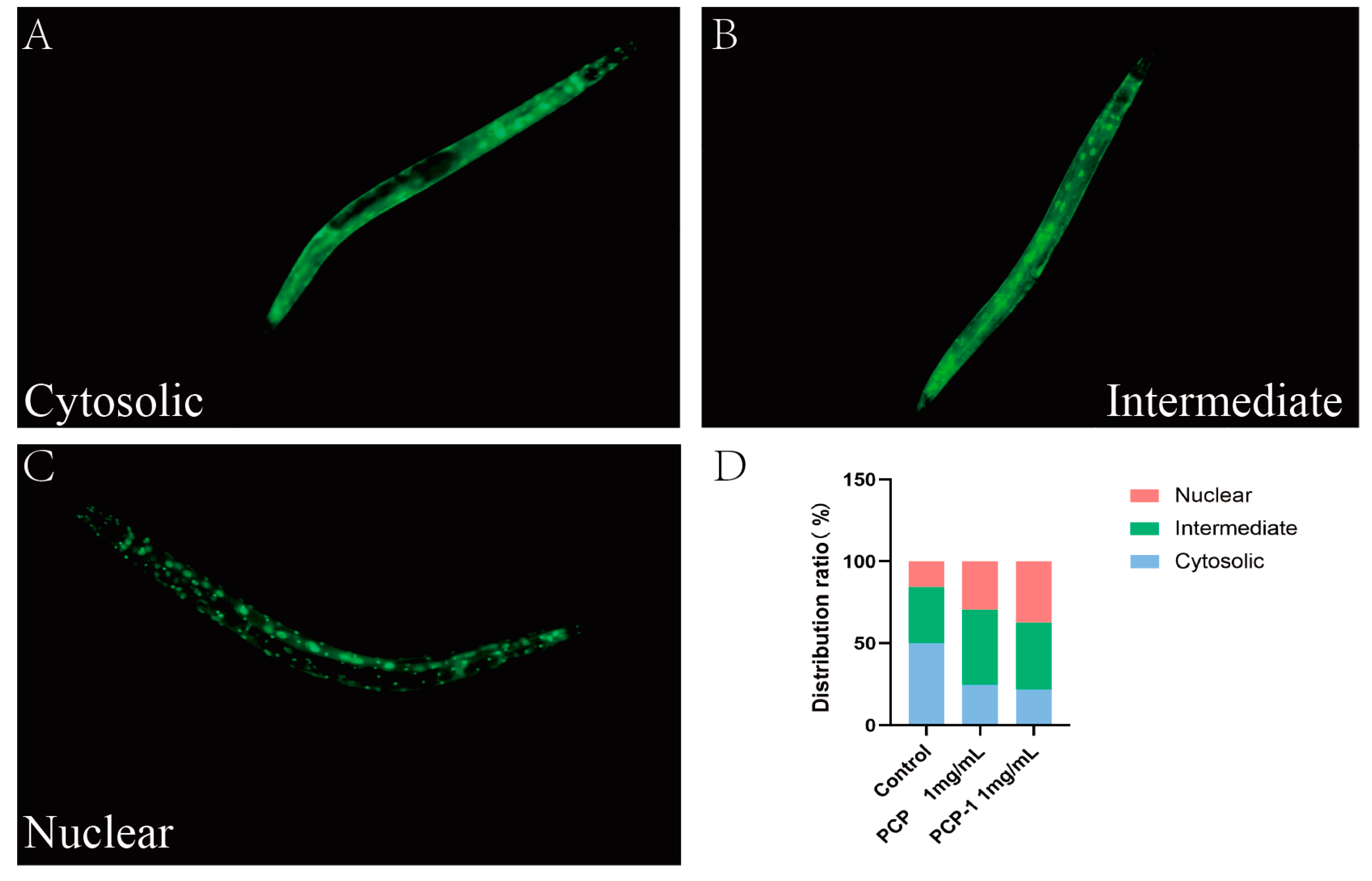
2.9. PCP and PCP-1 Can Induce the Nuclear Localization of DAF-16::GFP
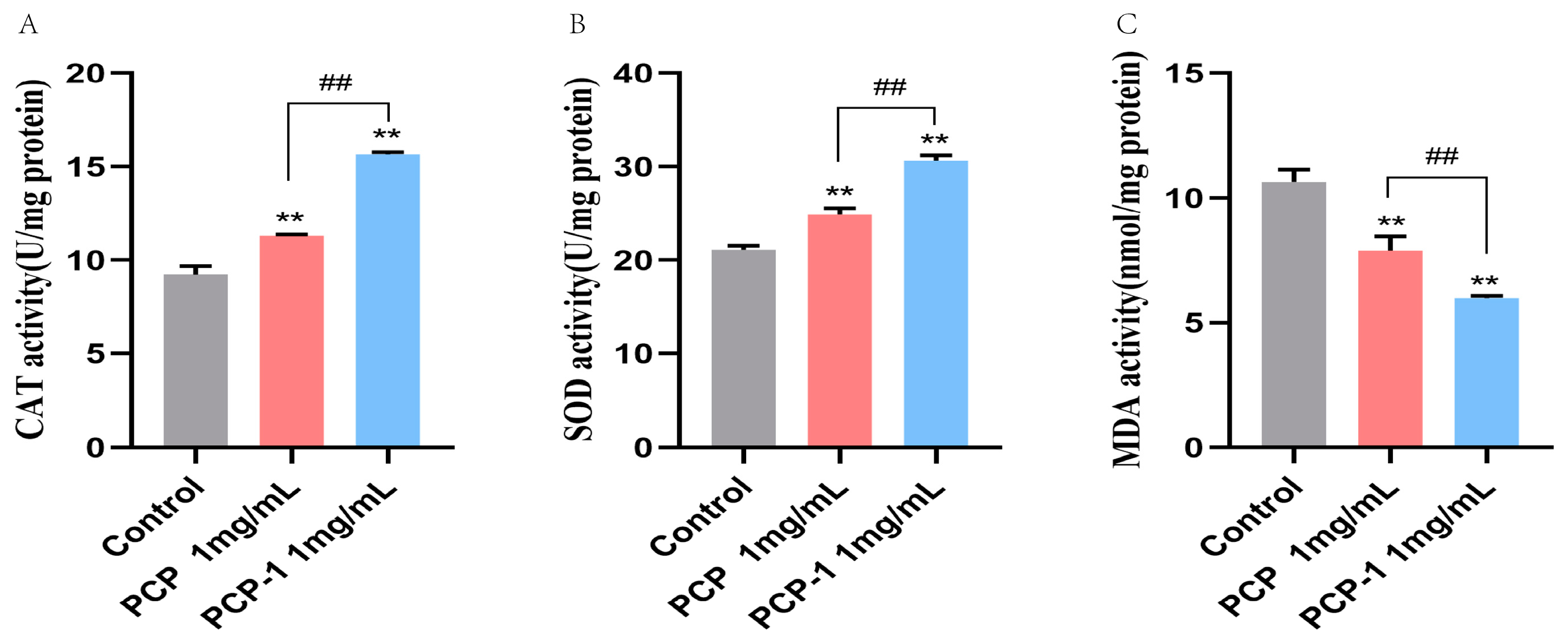
2.10. Effect of PCP and PCP-1 on Antioxidant Enzyme Activities and MDA Levels in C. elegans
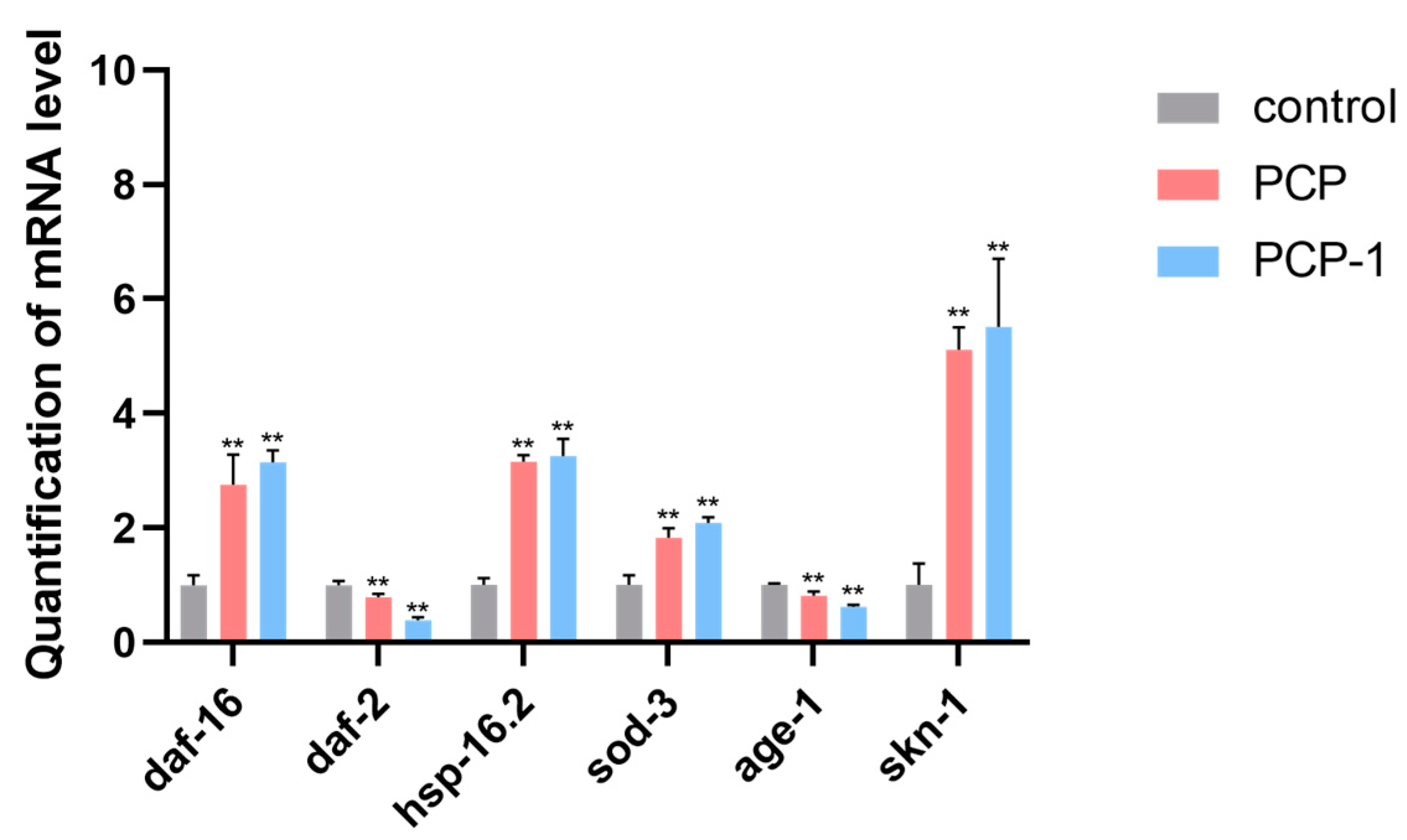
2.11. Effect of PCP and PCP-1 on the Expression Levels of Genes Related to the IIS Pathway in C. elegans
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Extraction and Purification of PCP and PCP-1
4.3. UV Spectroscopy
4.4. Analysis of Monosaccharide Compositions
4.5. Anti-Aging Activities
4.5.1. Exposure Experiments
4.5.2. Lifespan Assay
4.5.3. Stress Assay
Thermal Stress
Oxidative Stress
4.5.4. Progeny and Length Assay
4.5.5. Measurement of Lipofuscin Accumulation
4.5.6. In Vitro Antioxidant Assay
4.6. Anti-Aging Mechanisms
4.6.1. Exposure Experiments
4.6.2. In Situ Measurement of Intracellular ROS Generation
4.6.3. Nuclear Localization of DAF-16
4.6.4. Kit Assay
4.6.5. RT-PCR Assay
4.7. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fang, J.; Yue, H.; Ma, S.; Guan, F. Aging and age-related diseases: From mechanisms to therapeutic strategies. Biogerontology 2021, 22, 165–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinzina, E.D.; Podolskiy, D.I.; Dmitriev, S.E.; Gladyshev, V.N. Patterns of Aging Biomarkers, Mortality, and Damaging Mutations Illuminate the Beginning of Aging and Causes of Early-Life Mortality. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 4276–4284.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tissenbaum, H.A. Using C. elegans for aging research. Invertebr. Reprod. Dev. 2015, 59 (Suppl. S1), 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Li, F.; Zhou, T.; Wang, G.; Li, Z. Caenorhabditis elegans as a Useful Model for Studying Aging Mutations. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 554994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigon, V.M.; Félix, M.-A. History of research on C. elegans and other free-living nematodes as model organisms. WormBook 2017, 2017, 1–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.-L.; Jin, S.; Liu, Y.-J. Research Progress in Pharmacological Efficacy of Plant Polysaccharides. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2020, 41, 335–341. [Google Scholar]
- Gems, D.; Partridge, L. Insulin/IGF signalling and ageing: Seeing the bigger picture. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2001, 11, 287–292. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Kang, N.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tan, P. Study of the Effect of Neutral Polysaccharides from Rehmannia glutinosa on Lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans. Molecules 2019, 24, 4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuo, W.; Wang, S.; Shi, Y.; Cao, W.; Liu, Y.; Su, Y.; Xiu, M.; He, J. Angelica sinensis polysaccharide extends lifespan and ameliorates aging-related diseases via insulin and TOR signaling pathways, and antioxidant ability in Drosophila. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 241, 124639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; He, Y.; Zhong, S.; Li, Y.; Di, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ren, D.; Liu, S.; Li, D.; Cao, F. Antioxidant and Anti-Aging Properties of Polyphenol–Polysaccharide Complex Extract from Hizikia fusiforme. Foods 2023, 12, 3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loboda, A.; Damulewicz, M.; Pyza, E.; Jozkowicz, A.; Dulak, J. Role of Nrf2/HO-1 system in development, oxidative stress response and diseas-es: An evolutionarily conserved mechanism. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 3221–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.-T.; Tao, M.-F.; Li, R.; Wu, T. Study on alleviating thermal stress of Caenorhabditis elegans by ginger extract. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 2022, 41, 223–231. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Hu, Y. Regulation Mechanisms of Redox Homeostasis and Cancer Therapy. Chin. J. Cell Biol. 2022, 44, 583–593. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.-L.; Wu, L.; Tu, J.-X.; Deng, L.-F.; Huang, H.-L. Research progress of free radical induced aging. Chin. J. Dis. Control Prev. 2022, 26, 589–594. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.-J.; Wang, Z.-Z.; Li, J.-J.; Fan, H.-A.; Sha, R.-Y.; Mao, J.-W. Antioxidant Activity in Vitro and Promoting Resistance to Oxidative Stress in Caeno-rhabditis elegans of Blueberry Jiaosu. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2021, 42, 343–350. [Google Scholar]
- An, M.-Q.; Xu, Y.-N.; Zhuo, Q.-T.; Xie, S.-W.; Chen, H.-Z.; Du, B.; Li, P. Study on the Anti-aging Effect of Guilu Erxian Jiao on Caenorhabditis Elegans in Vivo. J. Guangzhou Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2022, 39, 1863–1870. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, H.; Xin, A.; Cui, H.; Jin, H.; Yang, X.; Liu, H.; Qin, B. Anti-aging effects on Caenorhabditis elegans of a polysaccharide, O-acetyl glucomannan, from roots of Lilium davidii var. unicolor Cotton. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 846–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamawaki, T.M.; Arantes-Oliveira, N.; Berman, J.R.; Zhang, P.; Kenyon, C. Distinct Activities of the Germline and Somatic Reproductive Tissues in the Regulation of Caenorhabditis elegans’ Longevity. Genetics 2008, 178, 513–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsin, H.; Kenyon, C. Signals from the reproductive system regulate the lifespan of C. elegans. Nature 1999, 399, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddle, D.L. Ageing. A message from the gonads. Nature 1999, 399, 308–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terman, A.; Brunk, U.T. Lipofuscin: Mechanisms of formation and increase with age. APMIS 1998, 106, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, K.; Ga, L.; Ma, Y.-H.; Yang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, H. Research progress of reactive oxygen species (ROS)-dependent anticancer drugs. J. Guangdong Pharm. Univ. 2022, 38, 130–136. [Google Scholar]
- Terman, A.; Brunk, U.T. Lipofuscin. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 36, 1400–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.-T.; Qian, T.-T.; Yang, L. Detection of Reactive Species Using H2DCFDA Probe in Plant. Chin. Bull. Bot. 2022, 57, 320–326. [Google Scholar]
- Tabibzadeh, S. Signaling pathways and effectors of aging. Front. Biosci. 2021, 26, 50–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L. Study on the Effect of Pyrroloquinoline Quinone on the Aging of Caenorhabditis Elegans and Its Mechanisms. Ph.D. Thesis, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.-W.; Cao, J.-R.; He, L.-J. Research Progress in Antioxidation Mechanism on Cellular Level. Med. Recapitul. 2016, 22, 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Tsikas, D.; Tsikas, S.A.; Mikuteit, M.; Ückert, S. Circulating and Urinary Concentrations of Malondialdehyde in Aging Humans in Health and Disease: Review and Discussion. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, G.L.; Spagnuolo, C.; Russo, M.; Tedesco, I.; Moccia, S.; Cervellera, C. Mechanisms of aging and potential role of selected polyphenols in extending healthspan. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 173, 113719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.-C.; Bao, X.-W.; Wang, J.; He, M.-M.; Zeng, L.-J.; Zhang, Y.-T. Isolation, Purification and Antioxidant Activity of Polysaccharides from the Fruit of Hippophae rhamnoides. Food Sci. 2021, 42, 227–232. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.; Xu, J.-W. Isolation, Purification and Antioxidant Activity of Polysaccharides from Zizyphus jujube cv. Dongzao. Food Sci. 2016, 37, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Lapierre, L.R.; Hansen, M. Lessons from C. elegans: Signaling pathways for longevity. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 23, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartwig, K.; Heidler, T.; Moch, J.; Daniel, H.; Wenzel, U. Feeding a ROS-generator to Caenorhabditis elegans leads to increased expression of small heat shock protein HSP-16.2 and hormesis. Genes Nutr. 2009, 4, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motta, H.S.; Roos, D.; Tabarelli, G.; Rodrigues, O.E.; Ávila, D.; Quines, C.B. Activation of SOD-3 is involved in the antioxidant effect of a new class of β-aryl-chalcogenium azide compounds in Caenorhabditis elegans. An. Acad. Bras. Ciências 2020, 92, e20181147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.-L.; Chen, L.-Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhao, C.-J.; Liu, Y.-G.; Ma, Z.-Q. Immune Function Regulation of Polygonatum cytonema Hua Polysaccharides Based on Zebrafish Model. World Chin. Med. 2023, 18, 761–772. [Google Scholar]

| Sample | Average Lifespan/d | Life Extension Rate/% |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 15.13 ± 4.06 | - |
| PCP (1 mg/mL) | 16.92 ± 3.98 | 11.83 |
| PCP-1 (0.5 mg/mL) | 16.98 ± 4.07 | 12.23 |
| PCP-1 (1 mg/mL) | 18.18 ± 3.97 | 20.16 |
| PCP-1 (2 mg/mL) | 17.18 ± 3.99 | 13.55 |
| Gene | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| daf-16-F | GGAGCCAAGAAGAGGATAAAGG |
| daf-16-R | GGAGAAACACGAGACGACGAT |
| daf-2-F | CGACTGAAGTGAATGGTGGA |
| daf-2-R | CGCCGTTACTGAGACAAAATA |
| age-1-F | CGCTGGCATCAAAATCTACA |
| age-1-R | ATTGGCAGTCGGTTCAGGAG |
| hsp-16.2-F | CGCTATCAATCCAAGGAGAAC |
| hsp-16.2-R | GAAGCAACTGCACCAACATC |
| sod-3-F | AGCATCATGCCACCTACGTGA |
| sod-3-R | CACCACCATTGAATTTCAGCG |
| skn-1-F | TAGCCGACGACGAAGAAGAG |
| skn-1-R | AGGTGTTGGACGATGGTGAA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Chen, Q.; Chen, L.; Chen, X.; Ma, Z. Anti-Aging in Caenorhabditis elegans of Polysaccharides from Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua. Molecules 2024, 29, 1276. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29061276
Zhang X, Chen Q, Chen L, Chen X, Ma Z. Anti-Aging in Caenorhabditis elegans of Polysaccharides from Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua. Molecules. 2024; 29(6):1276. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29061276
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xue, Qi Chen, Linzhen Chen, Xiaolu Chen, and Zhiqiang Ma. 2024. "Anti-Aging in Caenorhabditis elegans of Polysaccharides from Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua" Molecules 29, no. 6: 1276. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29061276
APA StyleZhang, X., Chen, Q., Chen, L., Chen, X., & Ma, Z. (2024). Anti-Aging in Caenorhabditis elegans of Polysaccharides from Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua. Molecules, 29(6), 1276. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29061276





