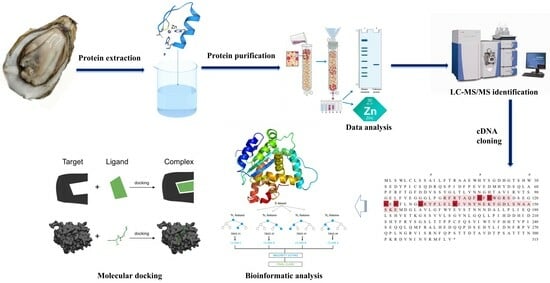
Purification, Characterization, cDNA Cloning, and Bioinformatic Analysis of Zinc-Binding Protein from Magallana hongkongensis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
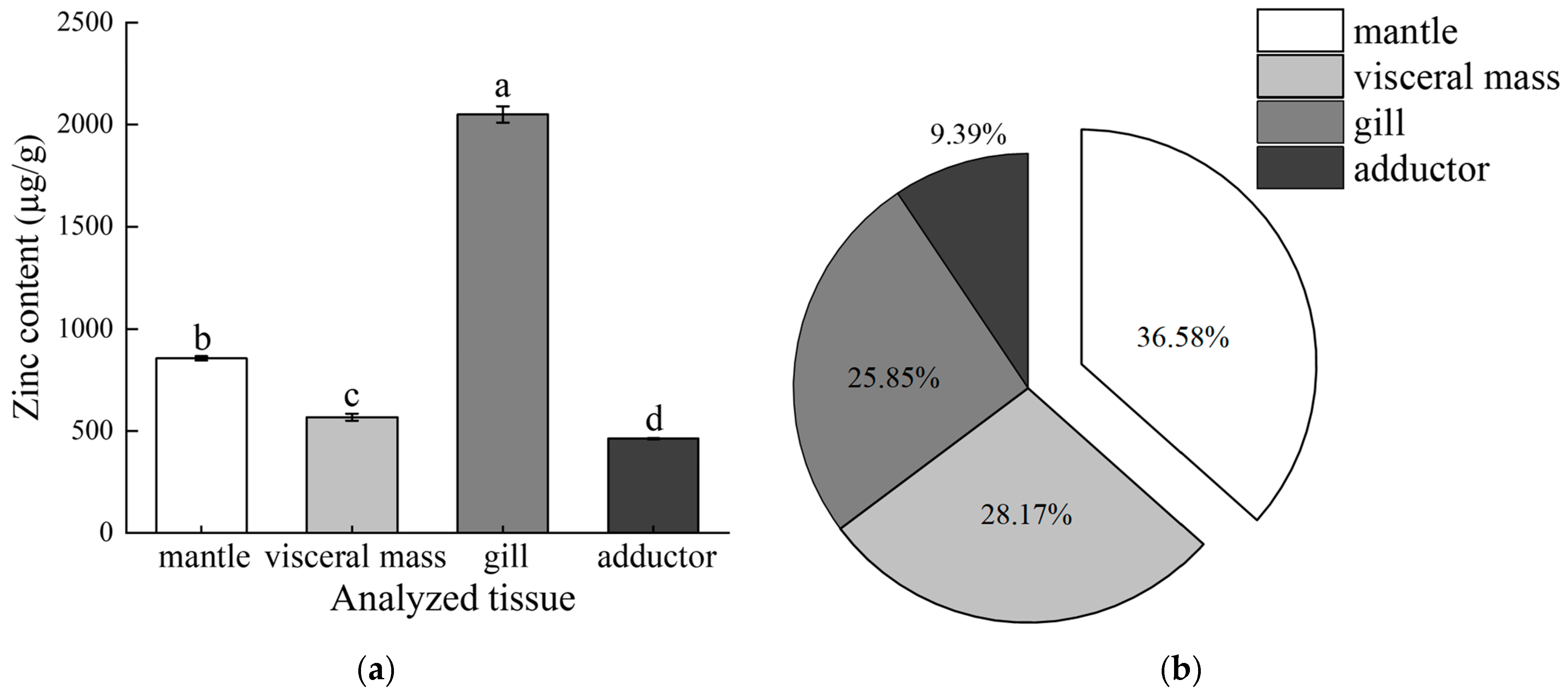
2.1. The Distribution of Zinc Content in Tissues
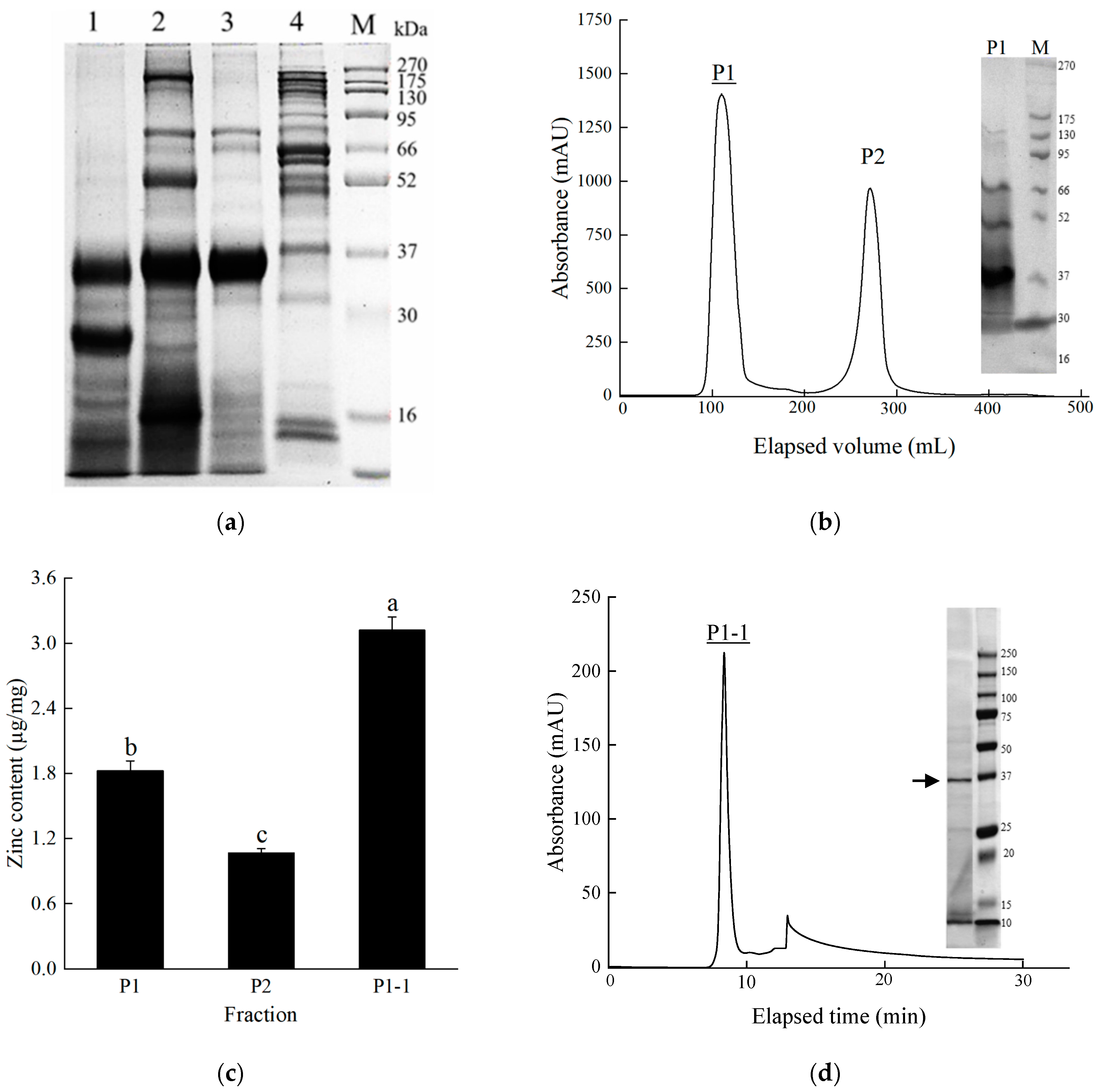
2.2. Isolation and Purification of Zinc-Binding Protein
2.3. Identification of Zinc-Binding Protein
| Observed Peptide (m/z) | Calculated Peptide Mass | Sequence | Corresponding Position of MhCA 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 513.2501 | 1024.4825 | KYGDLSNAASKE | 143–154 |
| 643.8151 | 1285.6105 | RTAQFHFHWGRS | 106–117 |
| 795.4011 | 1588.78 | RFRTAQFHFHWGRS | 104–117 |
| 816.4278 | 1630.8355 | RYPLELHIVNYNEKY | 130–144 |

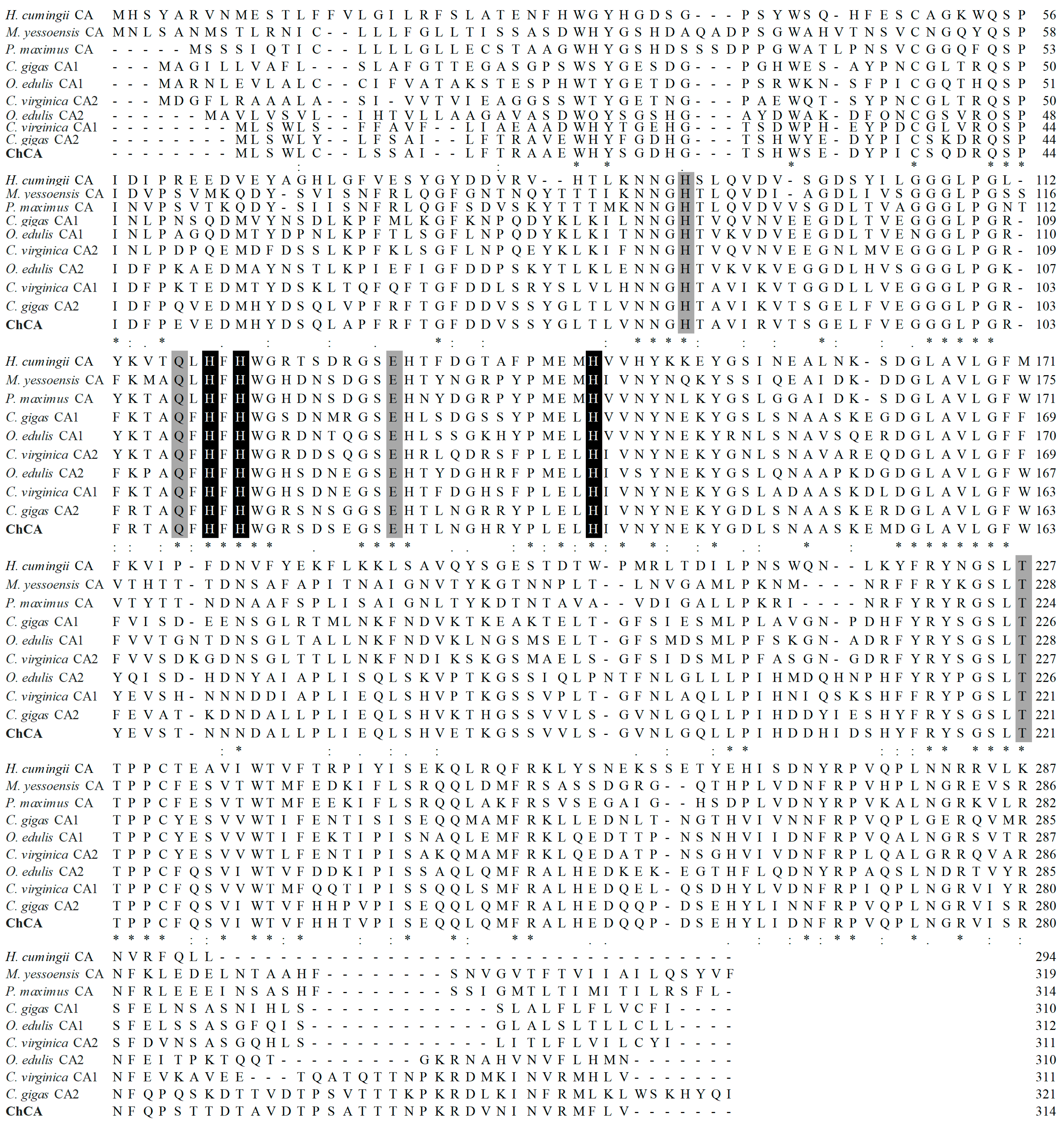
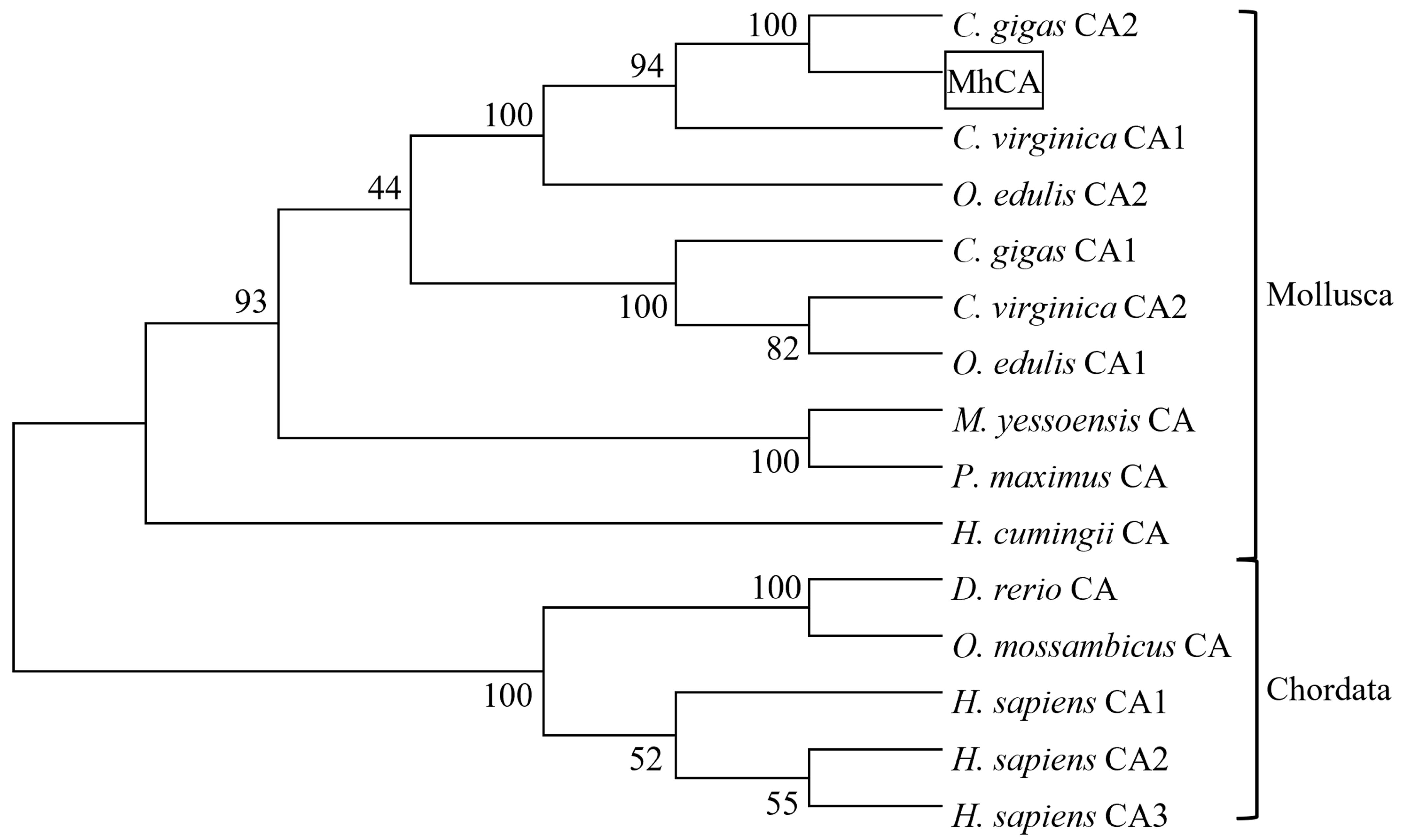
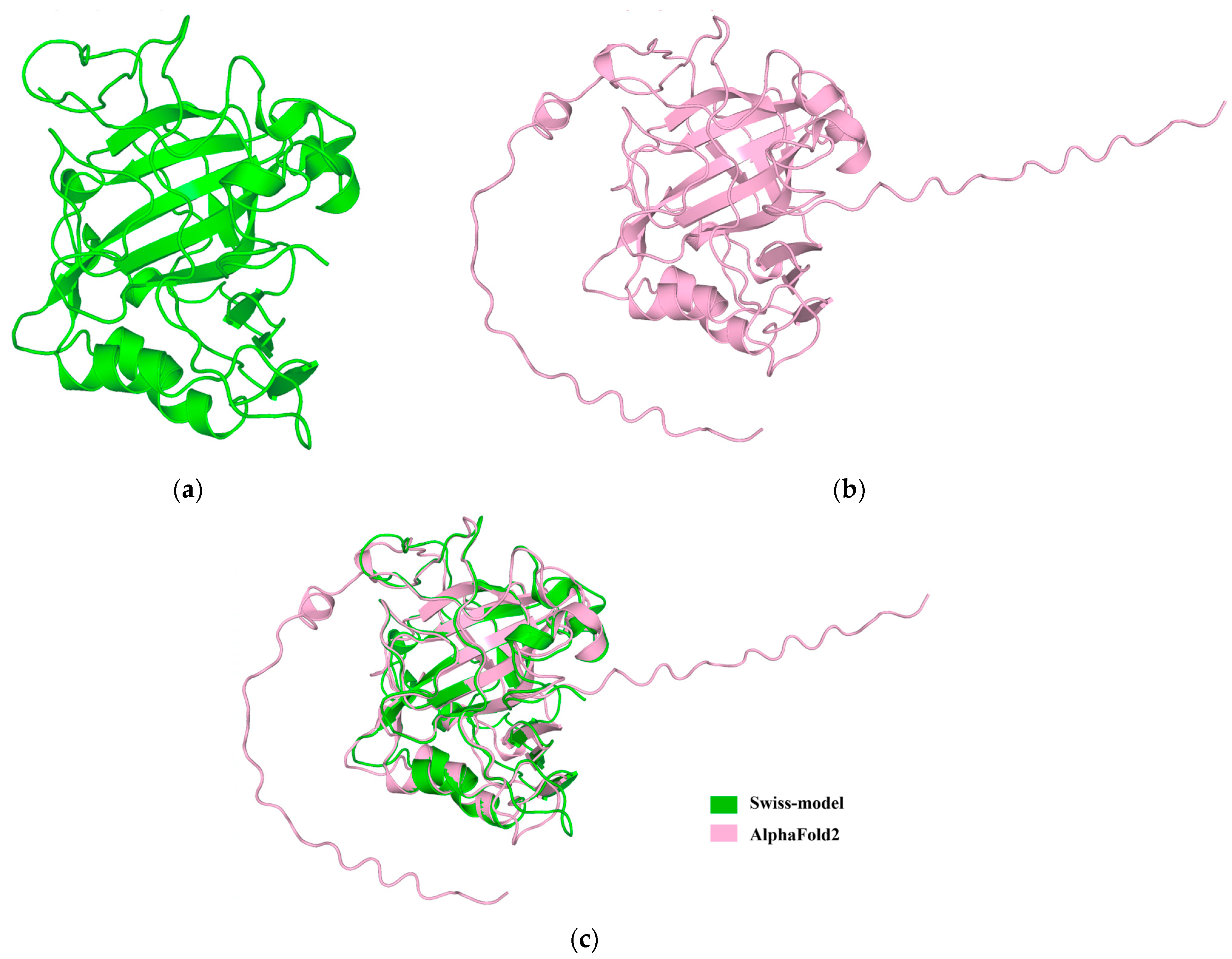
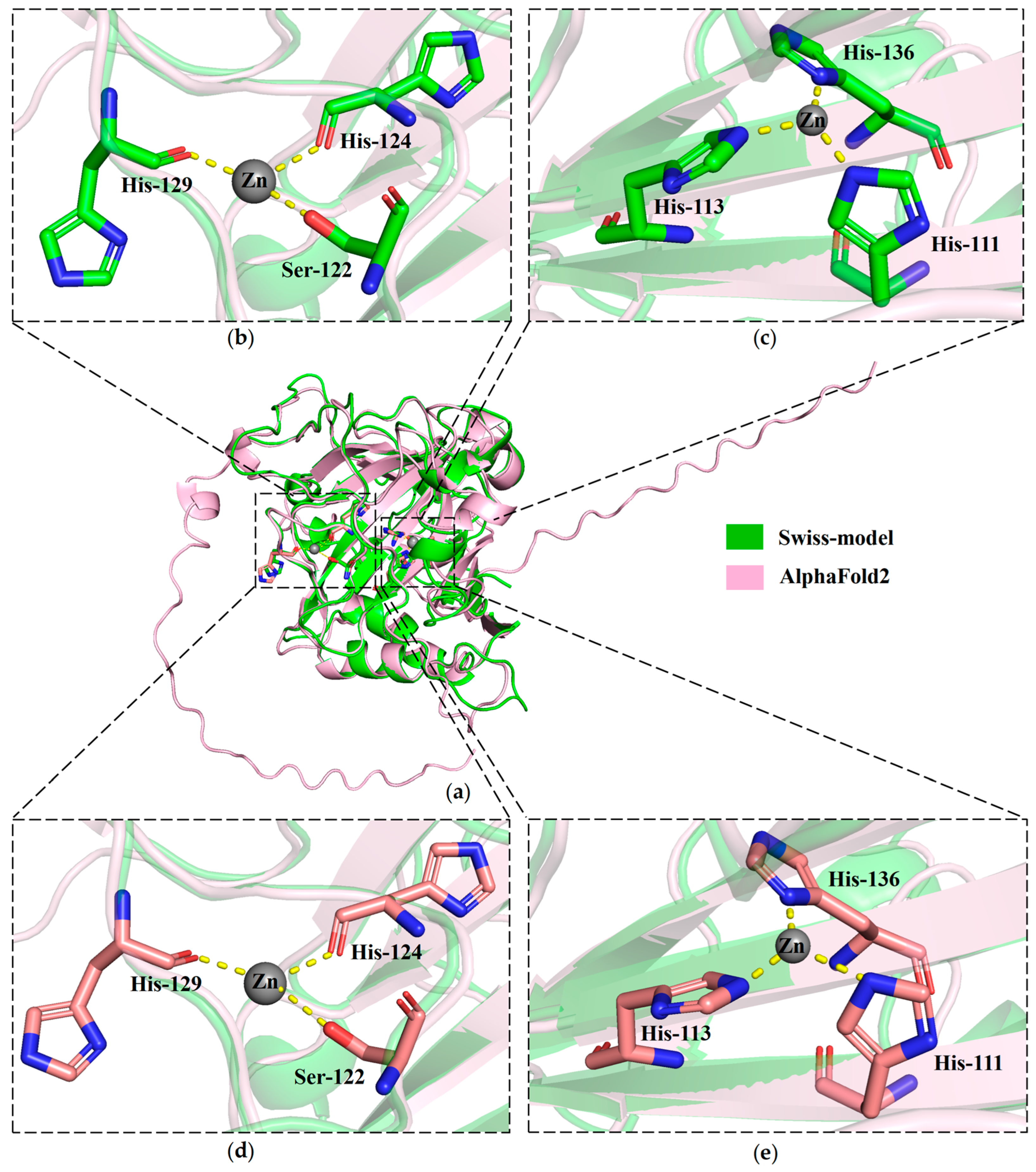
2.4. cDNA Cloning and Sequence Characterization of MhCA
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Oyster and Tissue Sampling
4.2. Determination of Zinc Content from Different Tissues
4.3. Protein Extraction and Purification
4.3.1. Extraction of Water-Soluble Proteins
4.3.2. Purification of Zinc-Binding Protein
4.4. Peptides Identification of Zinc-Binding Protein
4.5. cDNA Cloning
4.5.1. RNA Isolation and cDNA Synthesis
4.5.2. Full-Length cDNA Amplification and Cloning
4.6. Sequence Analysis
4.7. Molecular Docking
4.8. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SDS-PAGE | sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| MhCA | carbonic anhydrase from Magallana hongkongensis |
| MT | metallothionein |
| WSP | water-soluble protein |
| MW | molecular weight |
| CA | carbonic anhydrase |
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| ORF | open reading frame |
| RMSD | root mean square deviation |
References
- Wang, Z.; Cheng, S.; Wu, D.; Xu, Z.; Xu, S.; Chen, H.; Du, M. Hydrophobic peptides from oyster protein hydrolysates show better zinc-chelating ability. Food Biosci. 2021, 41, 100985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambe, T.; Tsuji, T.; Hashimoto, A.; Itsumura, N. The physiological, biochemical, and molecular roles of zinc transporters in zinc homeostasis and metabolism. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 749–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.T.; Malik, A.; Alwarthan, A.; Shaik, M.R. The enormity of the zinc deficiency problem and available solutions; an overview. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 103668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambe, T.; Hashimoto, A.; Fujimoto, S. Current understanding of ZIP and ZnT zinc transporters in human health and diseases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 3281–3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, W.H.; Lin, Y.C.; Chen, B.R.; Wu, S.C.; Lee, B.H. The neuronal protection of a zinc-binding protein isolated from oyster. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 114, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nistor, N.; Ciontu, L.; Frasinariu, O.E.; Lupu, V.V.; Ignat, A.; Streanga, V. Acrodermatitis enteropathica: A case report. Medicine 2016, 95, e3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Brazier, A.K.M.; Lowe, N.M. Zinc deficiency in low-and middle-income countries: Prevalence and approaches for mitigation. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2020, 33, 624–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alemán, A.; Gómez-Guillén, M.C.; Montero, P. Identification of ace-inhibitory peptides from squid skin collagen after in vitro gastrointestinal digestion. Food Res. Int. 2013, 54, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udechukwu, M.C.; Collins, S.A.; Udenigwe, C.C. Prospects of enhancing dietary zinc bioavailability with food-derived zinc-chelating peptides. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 4137–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zhou, Z.; Yao, X.; Fu, Y. Mineral-chelating peptides derived from fish collagen: Preparation, bioactivity and bioavailability. LWT 2020, 134, 110209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilandžić, N.; Sedak, M.; Đokić, M.; Varenina, I.; Kolanović, B.S.; Božić, Đ.; Brstilo, M.; Šimić, B. Determination of zinc concentrations in foods of animal origin, fish and shellfish from Croatia and assessment of their contribution to dietary intake. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2014, 35, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, W.; Caihuan, K.; Weidong, L.; Weiwei, Y. Studies of morphological parameters and nutritional compositions for yellow shell color variant of Haliotis diversicolor. J. Xiamen Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2015, 54, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, N.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, C.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Gao, L.; Wang, L.; Song, L. The involvement of zinc transporters in the zinc accumulation in the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. Gene 2020, 750, 144759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Kambe, T. The functions of metallothionein and ZIP and ZnT transporters: An overview and perspective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, T.; Takeda, T.A.; Takagishi, T.; Fukue, K.; Kambe, T.; Fukada, T. Physiological roles of zinc transporters: Molecular and genetic importance in zinc homeostasis. J. Physiol. Sci. 2017, 67, 283–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Liu, Z.; Huang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, S.; Zeng, M. Purification and characterisation of a zinc-binding peptide from oyster protein hydrolysate. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanidou, M.; Maravelias, C.; Dona, A.; Spiliopoulou, C. Zinc: A multipurpose trace element. Arch. Toxicol. 2006, 80, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christianson, D.W.; Fierke, C.A. Carbonic anhydrase: Evolution of the zinc binding site by nature and by design. Acc. Chem. Res. 1996, 29, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maret, W.; Li, Y. Coordination dynamics of zinc in proteins. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 4682–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, M.; Jia, Z.; Qiu, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, A.; Song, L. A carbonic anhydrase serves as an important acid-base regulator in pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas exposed to elevated CO2: Implication for physiological responses of mollusk to ocean acidification. Mar. Biotechnol. 2017, 19, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boone, C.D.; Tu, C.; McKenna, R. Structural elucidation of the hormonal inhibition mechanism of the bile acid cholate on human carbonic anhydrase II. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2014, 70, 1758–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J. Analysis and evaluation of mineral contents in different tissues of Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas) with five shell colors. J. Fish. China 2018, 42, 1358–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blindauer, C.A.; Sadler, P.J. How to hide zinc in a small protein. Acc. Chem. Res. 2005, 38, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyle, P.; Philcox, J.C.; Carey, L.C.; Rofe, A.M. Metallothionein: The multipurpose protein. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2002, 59, 627–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Lv, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, G.; Ma, C. Zn2+ rather than Ca2+ or Mg2+ used as a cofactor in non-muscular actin from the oyster to control protein polymerization. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 2013, 1830, 4179–4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozensoy Guler, O.; Capasso, C.; Supuran, C.T. A magnificent enzyme superfamily: Carbonic anhydrases, their purification and characterization. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurst, T.K.; Wang, D.; Thompson, R.B.; Fierke, C.A. Carbonic anhydrase II-based metal ion sensing: Advances and new perspectives. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Proteins Proteom. 2010, 1804, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, L.; Halanych, K.M.; Henry, R.P. Salinity-stimulated changes in expression and activity of two carbonic anhydrase isoforms in the blue crab Callinectes sapidus. J. Exp. Biol. 2007, 210, 2320–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christianson, D.W.; Alexander, R.S. Carboxylate-histidine-zinc interactions in protein structure and function. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 6412–6419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongsomboon, S.; Udomlertpreecha, S.; Amparyup, P.; Wuthisuthimethavee, S.; Tassanakajon, A. Gene expression and activity of carbonic anhydrase in salinity stressed Penaeus monodon. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2009, 152, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Liu, S.; Hu, Y.; Pan, L. Cloning and expression analysis of two carbonic anhydrase genes in white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei, induced by pH and salinity stresses. Aquaculture 2015, 448, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.L.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Z.C.; Wang, Y.Y.; Li, J.L. Identification, structural characterization and expression analysis of a novel carbonic anhydrase from freshwater mussel Hyriopsis cumingii. Gene 2017, 636, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, H. Sequence of the pearl oyster carbonic anhydrase-related protein and its evolutionary implications. Biochem. Genet. 2012, 50, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ireland, S.M.; Martin, A.C. ZincBind—The database of zinc binding sites. Database 2019, 2019, baz006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, N.; Zhou, T.; Hovmöller, S. Prediction of zinc-binding sites in proteins from sequence. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Cui, P.; Li, D.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, S.; Lin, S. Formation of crystalline nanoparticles by iron binding to pentapeptide (Asp-His-Thr-Lys-Glu) from egg white hydrolysates. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 3297–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Rocca, R.; Tsvetkov, P.O.; Golovin, A.V.; Allegro, D.; Barbier, P.; Malesinski, S.; Guerlesquin, F.; Devred, F. Identification of the three zinc-binding sites on tau protein. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 209, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Jiang, S.; Feng, X.; Wang, R.; Zeng, M.; Zhao, Y. Physicochemical state and in vitro digestibility of heat treated wa-ter-soluble protein from Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas). Food Biosci. 2020, 34, 100528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Han, J.; Zhang, J.; Hu, J.; Fu, Y.; Qi, H.; Sun, Y.; Yu, C. Omics-prediction of bioactive peptides from the edible cyanobacterium Arthrospira platensis proteome. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 98, 984–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.L.; Zhang, W.B.; Mai, K.S.; Liang, X.F.; Xu, W.; Wang, J.; Ma, H.M. Molecular cloning, characterization and mRNA expression of selenium-binding protein in abalone (Haliotis discus hannai Ino): Response to dietary selenium, iron and zinc. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 29, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos-Martins, D.; Forli, S.; Ramos, M.J.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4Zn: An improved AutoDock force field for small-molecule docking to zinc metalloproteins. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 2371–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primer | Sequence (5′–3′) | Application |
|---|---|---|
| CA-F1 (forward) | GCYCAGTTMCACTTCCACTGG | Partial sequence |
| CA-R1 (reverse) | CAWGGSGGVGTGGTSARACT | |
| CA-R2 (reverse) | GCTCCAGTGGATATCGGT | 5′ terminal sequence |
| CA-R3 (reverse) | GAGCCCTCGCTGTCACTG | |
| 5-F-1 (forward) | GGCCACGCGTCGACTAGTACGGGIIGGGIIGGGIIG | |
| 5-F-2 (forward) | GGCCACGCGTCGACTAGTAC | |
| CA-F2 (forward) | GAGGGCTCGGAACACACCTTGAATG | 3′ terminal sequence |
| CA-F3 (forward) | GTATGGTGACCTCTCCAATGCGGC | |
| 3-R-1 (reverse) | GCTGTCAACGATACGCTACGTAAC | |
| 3-R-2 (reverse) | GCTACGTAACGGCATGACAGTG | |
| CA-F4 (forward) | CGGATTTTGTAGATCGGAGG | Complete sequence |
| CA-R4 (reverse) | GCATTTTATTGCTGTGATTT | |
| SP6 (forward) | ATTTAGGTGACACTATAG | Subclonal sequence |
| T7 (reverse) | GCTAGTTATTGCTCAGCGG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, C.; Li, W.; Gao, J.; Cao, W.; Qin, X.; Zheng, H.; Lin, H.; Chen, Z. Purification, Characterization, cDNA Cloning, and Bioinformatic Analysis of Zinc-Binding Protein from Magallana hongkongensis. Molecules 2024, 29, 900. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040900
Chen C, Li W, Gao J, Cao W, Qin X, Zheng H, Lin H, Chen Z. Purification, Characterization, cDNA Cloning, and Bioinformatic Analysis of Zinc-Binding Protein from Magallana hongkongensis. Molecules. 2024; 29(4):900. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040900
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Citing, Wan Li, Jialong Gao, Wenhong Cao, Xiaoming Qin, Huina Zheng, Haisheng Lin, and Zhongqin Chen. 2024. "Purification, Characterization, cDNA Cloning, and Bioinformatic Analysis of Zinc-Binding Protein from Magallana hongkongensis" Molecules 29, no. 4: 900. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040900
APA StyleChen, C., Li, W., Gao, J., Cao, W., Qin, X., Zheng, H., Lin, H., & Chen, Z. (2024). Purification, Characterization, cDNA Cloning, and Bioinformatic Analysis of Zinc-Binding Protein from Magallana hongkongensis. Molecules, 29(4), 900. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040900