Piceatannol Alleviates Deoxynivalenol-Induced Damage in Intestinal Epithelial Cells via Inhibition of the NF-κB Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
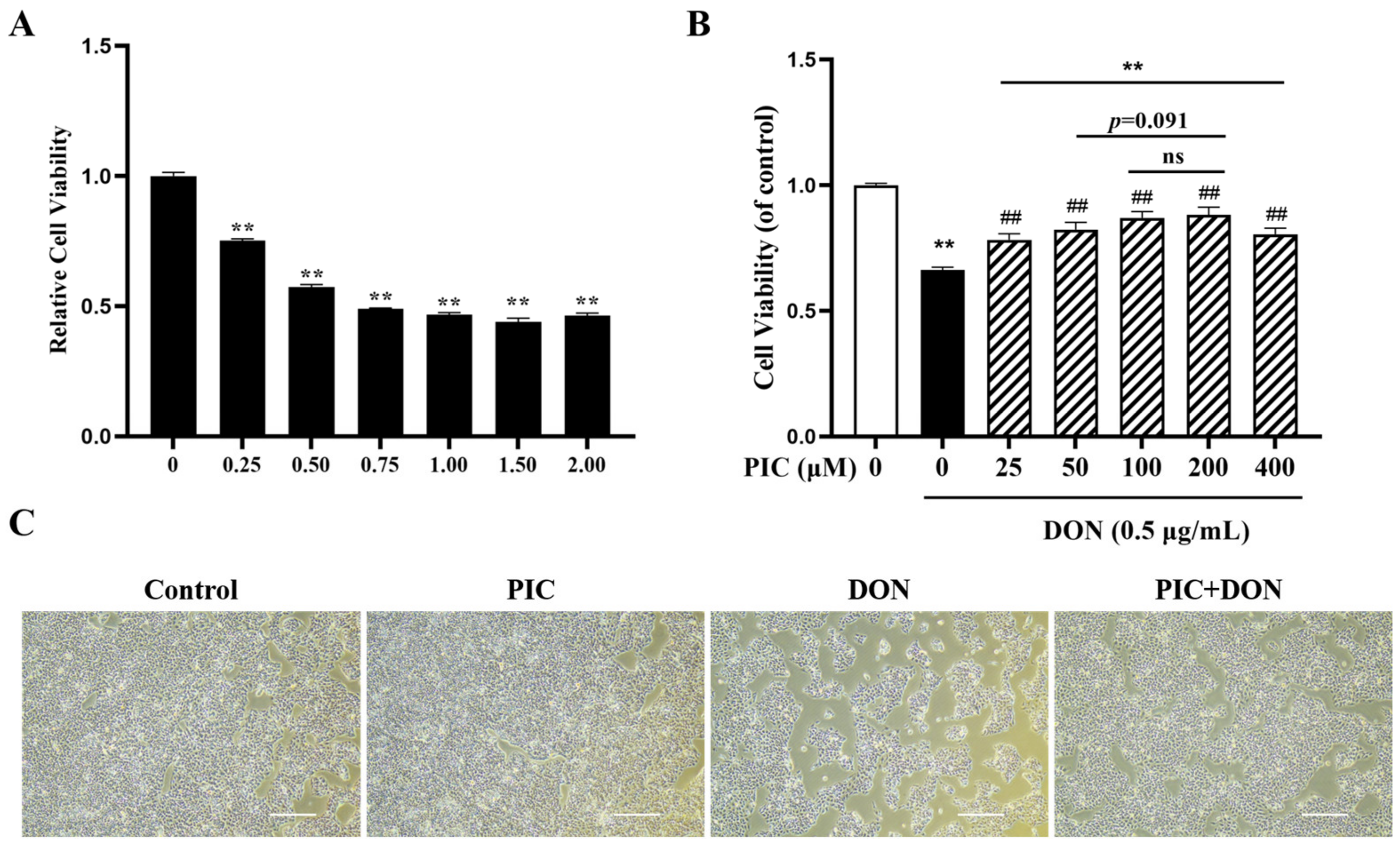
2.1. Effects of PIC on the Viability of IPEC-J2 Cells
2.2. PIC Alleviates the Cytotoxicity of IPEC-J2 Cells Induced by DON
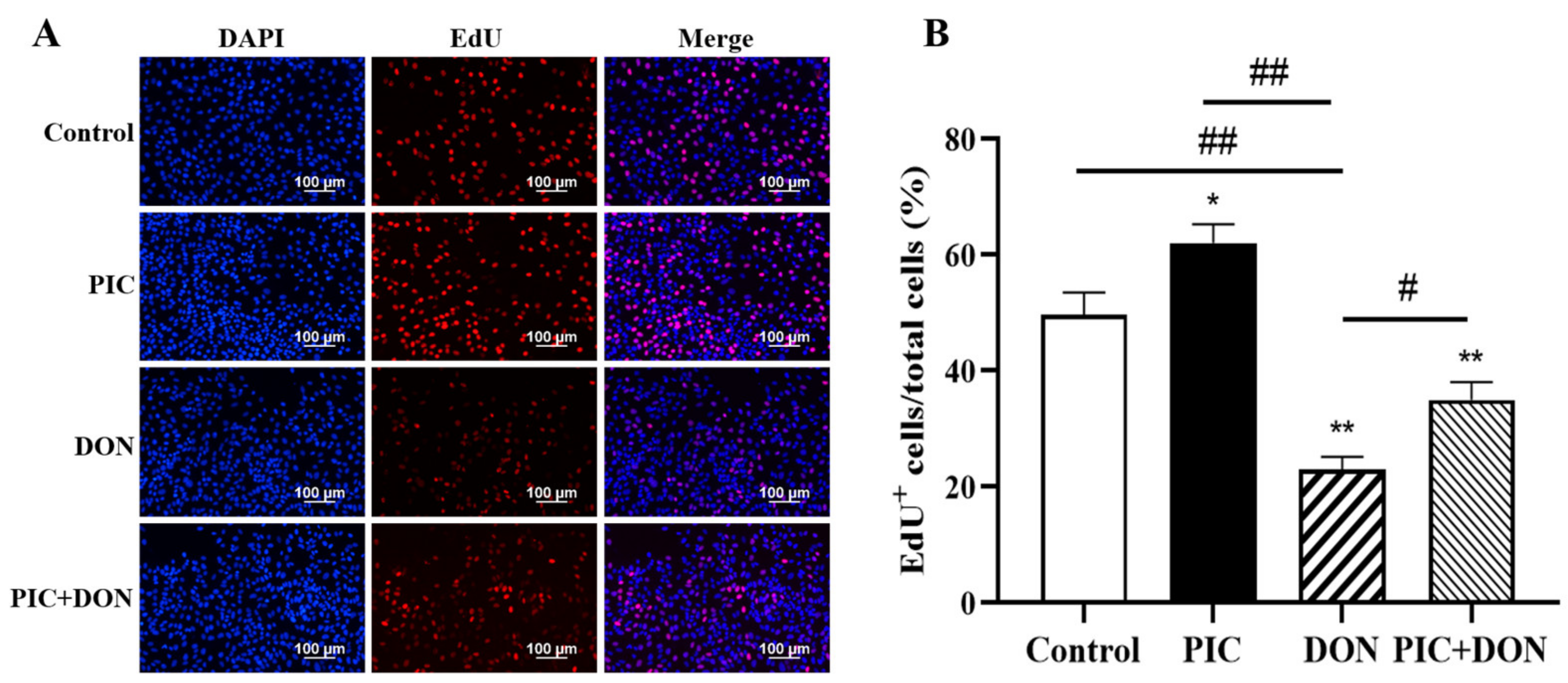
2.3. Effects of DON and PIC on IPEC-J2 Cell Growth
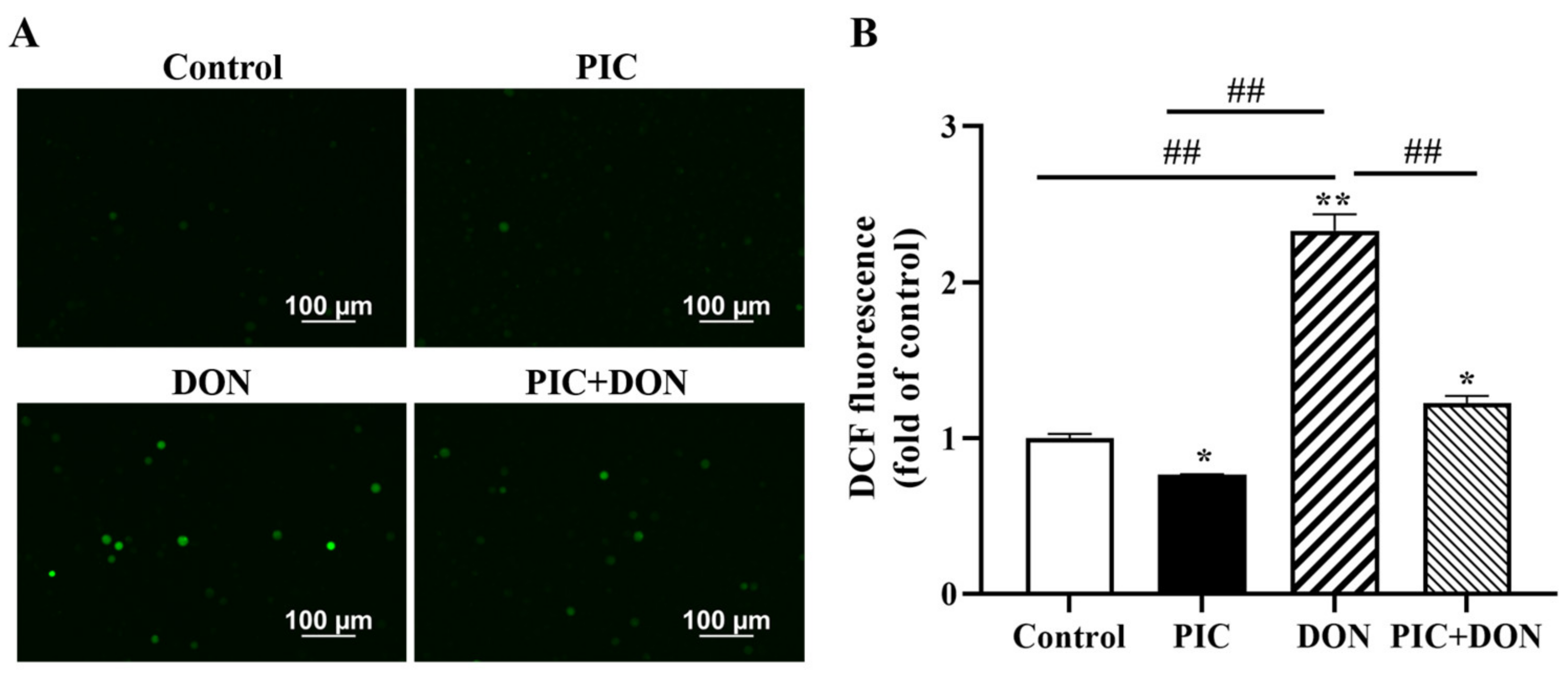
2.4. PIC Eliminates DON-Induced Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Production
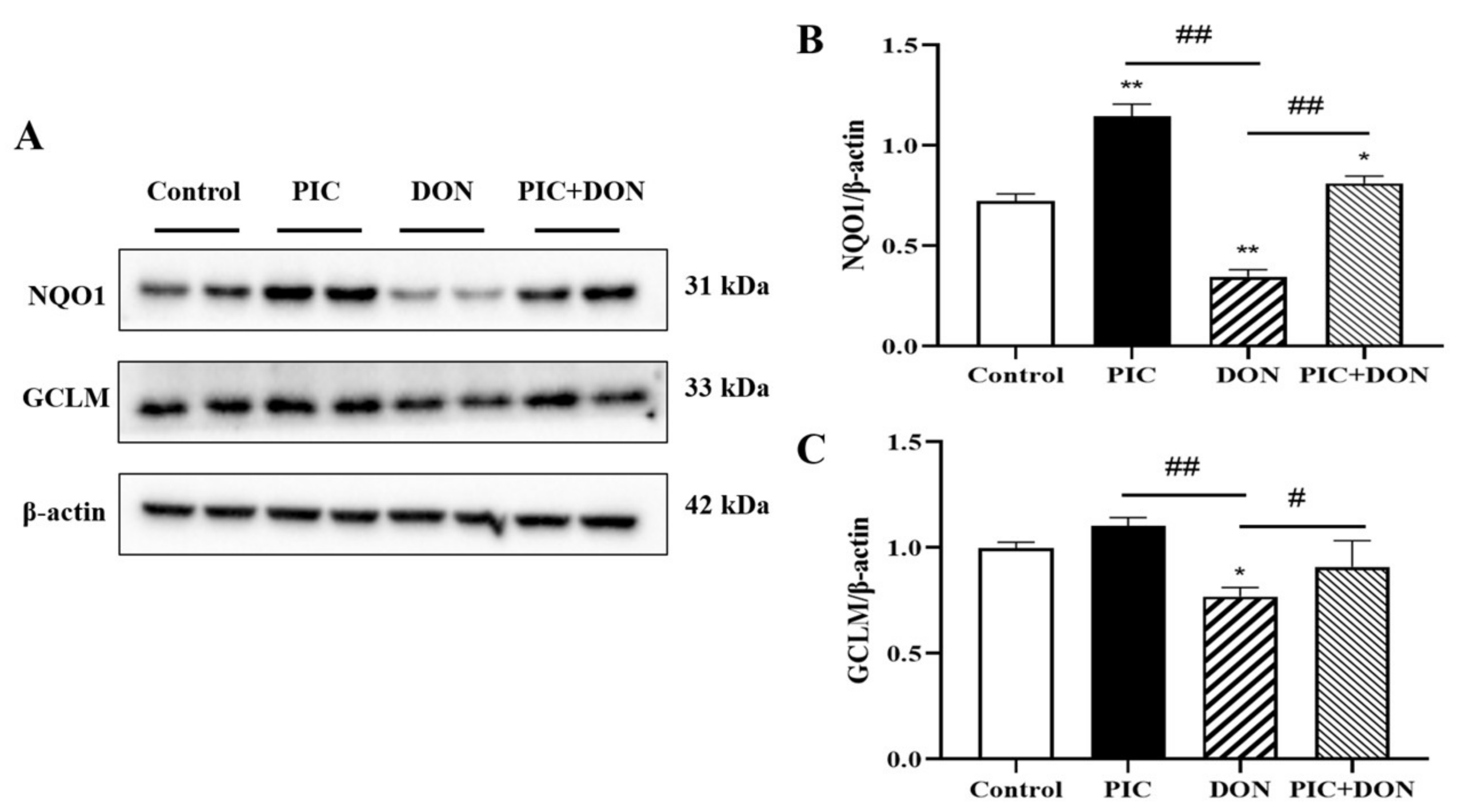
2.5. PIC Protected IPEC-J2 Cells from DON-Induced Oxidative Damage
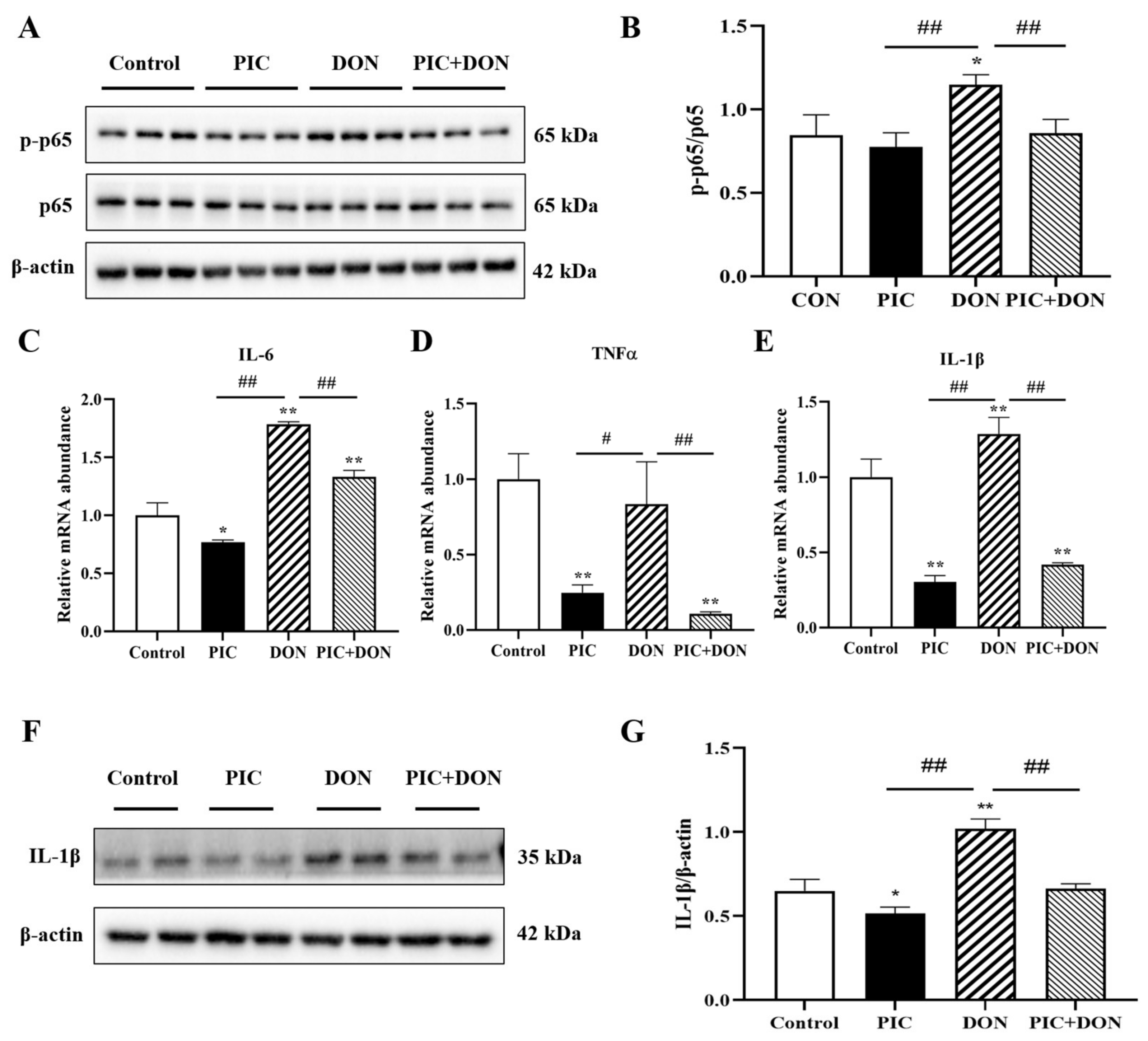
2.6. PIC Reduced DON-Induced Inflammation in IPEC-J2 Cells
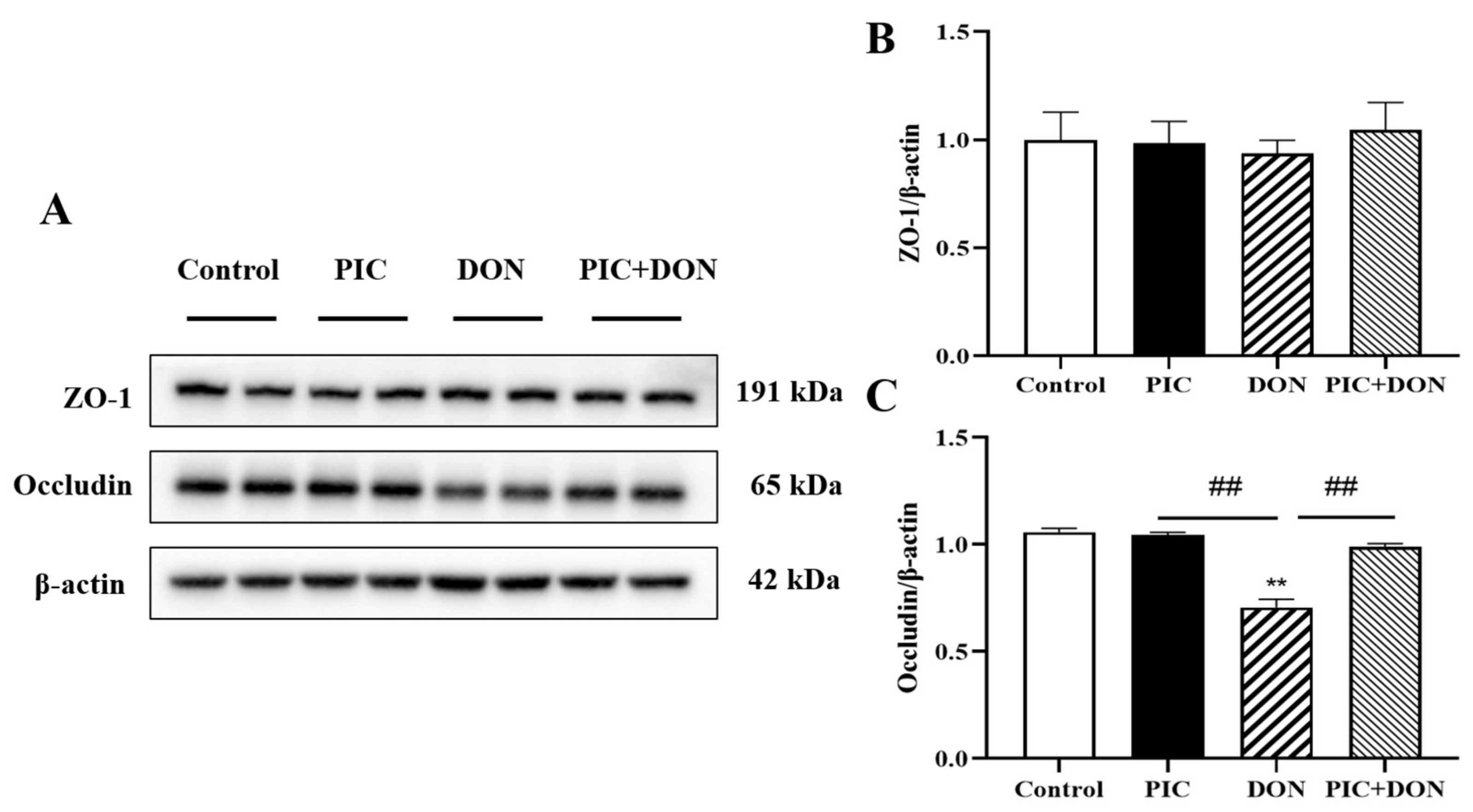
2.7. PIC Regulated the Expression of DON-Induced Tight Junction Proteins in IPEC-J2 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Cell Treatment
4.4. Cell Viability and Cell Morphology
4.5. Cell Proliferation Assay
4.6. Intracellular ROS Assay
4.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.8. Western Blotting
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liao, Y.; Peng, Z.; Chen, L.; Nussler, A.K.; Liu, L.; Yang, W. Deoxynivalenol, gut microbiota and immunotoxicity: A potential approach? Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 112, 342–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestka, J.J. Deoxynivalenol: Mechanisms of action, human exposure, and toxicological relevance. Arch. Toxicol. 2010, 84, 663–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dll, S.; Dnicke, S.; Valenta, H. Residues of deoxynivalenol (don) in pig tissue after feeding mash or pellet diets containing low concentrations. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 52, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostry, V.; Malir, F.; Toman, J.; Grosse, Y. Mycotoxins as human carcinogens—The IARC monographs classification. Mycotoxin Res. 2017, 33, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooft, J.M.; Bureau, D.P. Deoxynivalenol: Mechanisms of action and its effects on various terrestrial and aquatic species. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 157, 112616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Deng, H.; Deng, Y.; Liang, Z.; Deng, J.; Zuo, Z.; Hu, Y.; Shen, L.; Yu, S.; Cao, S. Combined effects of deoxynivalenol and zearalenone on oxidative injury and apoptosis in porcine splenic lymphocytes in vitro. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2017, 69, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, R.; Li, R.; Dai, P.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, C. Deoxynivalenol induced apoptosis and inflammation of IPEC-J2 cells by promoting ROS production. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 251, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Long, M. The biological detoxification of deoxynivalenol: A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 145, 111649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savard, C.; Pinilla, V.; Provost, C.; Segura, M.; Gagnon, C.A.; Chorfi, Y. In vitro effect of deoxynivalenol (DON) mycotoxin on porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus replication. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 65, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groschwitz, K.R.; Hogan, S.P. Intestinal barrier function: Molecular regulation and disease pathogenesis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 124, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinton, P.; Tsybulskyy, D.; Lucioli, J.; Laffitte, J.; Callu, P.; Lyazhri, F.; Grosjean, F.; Bracarense, A.P.; Kolf-Clauw, M.; Oswald, I.P. Toxicity of deoxynivalenol and its acetylated derivatives on the intestine: Differential effects on morphology, barrier function, tight junction proteins, and mitogen-activated protein kinases. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 130, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosnahan, A.J.; Brown, D.R. Porcine IPEC-J2 intestinal epithelial cells in microbiological investigations. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 156, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Ye, L.; Hou, Q.; Yu, Q. Effects of arginine on intestinal epithelial cell integrity and nutrient uptake. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 14, 1675–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.W.; Tian, G.; Chen, D.W.; Yao, Y.; He, J.; Zheng, P.; Mao, X.B.; Yu, J.; Huang, Z.Q.; Yu, B. Involvement of PKA signalling in anti-inflammatory effects of chitosan oligosaccharides in IPEC-J2 porcine epithelial cells. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 102, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yang, J.; Zhang, B.; Wu, K.; Yang, A.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Rajput, S.; Zhang, N.; et al. Deoxynivalenol Impairs Porcine Intestinal Host Defense Peptide Expression in Weaned Piglets and IPEC-J2 Cells. Toxins 2018, 10, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, P.; Liao, M.; Li, L.; Tan, B.; Yin, Y. Effect of deoxynivalenol on apoptosis, barrier function, and expression levels of genes involved in nutrient transport, mitochondrial biogenesis and function in IPEC-J2 cells. Toxicol. Res. 2017, 6, 866–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, Y.; Sugiyama, K.; Kamei, M.; Takahashi, T.; Suzuki, T.; Katagata, Y.; Ito, T. Extract of passion fruit (Passiflora edulis) seed containing high amounts of piceatannol inhibits melanogenesis and promotes collagen synthesis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 11112–11118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piotrowska, H.; Kucinska, M.; Murias, M. Biological activity of piceatannol: Leaving the shadow of resveratrol. Mutat. Res. 2012, 750, 60–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Yang, R.; Yao, H.; Wu, Y.; Pan, W.; Jia, A.Q. Inhibiting the formation of advanced glycation end-products by three stilbenes and the identification of their adducts. Food Chem. 2019, 295, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, I.; Damodar, K.; Kim, J.; Ryoo, S.; Jun, J. Synthesis, Anti-inflammatory, and Arginase Inhibitory Activity of Piceatannol and Its Analogs. Bull. Kor. Chem. Soc. 2017, 38, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Yang, J.; Wei, Y.; Li, J. Effects of piceatannol and pterostilbene against beta-amyloid-induced apoptosis on the PI3K/Akt/Bad signaling pathway in PC12 cells. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 1014–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yang, P.; Chang, Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Lv, Y.; Wang, T.; Gao, B.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, L.L. Inhibitory Effect of Piceatannol on TNF-alpha-Mediated Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 4634–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djoko, B.; Chiou, R.Y.; Shee, J.J.; Liu, Y.W. Characterization of immunological activities of peanut stilbenoids, arachidin-1, piceatannol, and resveratrol on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation of RAW 264.7 macrophages. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 2376–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, B.; Sun, T.; Li, W.; Sun, X.; Yao, X.; Sun, X. Piceatannol protects ARPE-19 cells against vitamin A dimer-mediated photo-oxidative damage through activation of Nrf2/NQO1 signalling. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 26, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, N.; Li, G. Piceatannol attenuates behavioral disorder and neurological deficits in aging mice via activating the Nrf2 pathway. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghareeb, K.; Awad, W.A.; Bohm, J.; Zebeli, Q. Impacts of the feed contaminant deoxynivalenol on the intestine of monogastric animals: Poultry and swine. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2015, 35, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danicke, S.; Valenta, H.; Doll, S. On the toxicokinetics and the metabolism of deoxynivalenol (DON) in the pig. Arch. Anim. Nutr. 2004, 58, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracarense, A.P.; Lucioli, J.; Grenier, B.; Drociunas, P.G.; Moll, W.D.; Schatzmayr, G.; Oswald, I.P. Chronic ingestion of deoxynivalenol and fumonisin, alone or in interaction, induces morphological and immunological changes in the intestine of piglets. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 107, 1776–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, Y.; Su, Y.; Shen, D.; Dai, P.; Li, C. Short-term ingestion of deoxynivalenol in naturally contaminated feed alters piglet performance and gut hormone secretion. Anim. Sci. J. 2018, 89, 1134–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chang, J.; Wang, P.; Yin, Q.; Liu, C.; Li, M.; Song, A.; Zhu, Q.; Lu, F. Effect of chlorogenic acid on alleviating inflammation and apoptosis of IPEC-J2 cells induced by deoxyniyalenol. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 205, 111376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.; Yu, R.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, P.; Liu, Z.; Bian, Y. Naringenin prevents TNF-alpha-induced gut-vascular barrier disruption associated with inhibiting the NF-kappaB-mediated MLCK/p-MLC and NLRP3 pathways. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 2715–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Li, B.R.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, X.H.; Wang, L. Pretreatment of IEC-6 cells with quercetin and myricetin resists the indomethacin-induced barrier dysfunction via attenuating the calcium-mediated JNK/Src activation. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 147, 111896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Che, H.; Yang, J.; Jin, Y.; Yu, H.; Wang, C.; Fu, Y.; Li, N.; Zhang, J. Astaxanthin Alleviates Aflatoxin B1-Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in IPEC-J2 Cells via the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Toxins 2023, 15, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhu, C.; Ye, J.; Lv, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, Z. Protection of Porcine Intestinal-Epithelial Cells from Deoxynivalenol-Induced Damage by Resveratrol via the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 1726–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Shi, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, P.; Zhang, S.; Wu, T.; Yan, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Ren, Y.; Rong, X.; et al. Piceatannol alleviates inflammation and oxidative stress via modulation of the Nrf2/HO-1 and NF-kappaB pathways in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2019, 310, 108754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Yu, L.L.; Wang, J. Piceatannol Protects Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells against Hydrogen Peroxide Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis through Modulating PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herring, T.A.; Cuppett, S.L.; Zempleni, J. Genomic implications of H2O2 for cell proliferation and growth of Caco-2 cells. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2007, 52, 3005–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Vergauwen, H.; Tambuyzer, B.; Jennes, K.; Degroote, J.; Wang, W.; De Smet, S.; Michiels, J.; Van Ginneken, C. Trolox and Ascorbic Acid Reduce Direct and Indirect Oxidative Stress in the IPEC-J2 Cells, an In Vitro Model for the Porcine Gastrointestinal Tract. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, C.; Cunningham-Bussel, A. Beyond oxidative stress: An immunologist’s guide to reactive oxygen species. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, F.; Hu, C.A.; Liao, P.; Tan, K.; Tan, B.; Xiong, X.; Liu, G.; Li, T.; et al. Autophagy protects intestinal epithelial cells against deoxynivalenol toxicity by alleviating oxidative stress via IKK signaling pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 89, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyrkkänen, H.K.; Kansanen, E.; Inkala, M.; Kivelä, A.M.; Hurttila, H.; Heinonen, S.E.; Goldsteins, G.; Jauhiainen, S.; Tiaiene, S.; Makkonen, H.; et al. Nrf2 regulates antioxidant gene expression evoked by oxidized phospholipids in endothelial cells and murine arteries in vivo. Circ. Res. 2008, 103, e1–e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouam, A.F.; Yuan, F.; Njayou, F.N.; He, H.T.; Tsayem, R.F.; Oladejo, B.O.; Song, F.H.; Moundipa, P.F.; Gao, G.F. Induction of mkp-1 and nuclear translocation of nrf2 by limonoids from khaya grandifoliola c.dc protect l-02 hepatocytes against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanschmann, E.M.; Godoy, J.R.; Berndt, C.; Hudemann, C.; Lillig, C.H. Thioredoxins, glutaredoxins, and peroxiredoxins—Molecular mechanisms and health significance: From cofactors to antioxidants to redox signaling. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 1539–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C. Therapeutic modulation of virus-induced oxidative stress via the nrf2-dependent antioxidative pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 6208067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, R.; Yin, Z.; Sun, J.; Wang, B.; Zhao, D.; Zeng, X.A.; Li, H.; Huang, M.; Sun, B. Optimization of Jiuzao protein hydrolysis conditions and antioxidant activity in vivo of Jiuzao tetrapeptide Asp-Arg-Glu-Leu by elevating the Nrf2/Keap1-p38/PI3K-MafK signaling pathway. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 4808–4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.; Yang, M.; Liang, Z.; Yang, C.; Kong, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, S.; Fan, H.; Ning, C.; Xiao, W.; et al. PI3K/AKT/mTOR, NF-κB and ERS pathway participated in the attenuation of H2O2-induced IPEC-J2 cell injury by koumine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 304, 116028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Yu, W.; Duan, N.; Wang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Wu, S. Protective Effects of Ferulic Acid on Deoxynivalenol-Induced Toxicity in IPEC-J2 Cells. Toxins 2022, 14, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashida, H.; Ogawa, M.; Kim, M.; Mimuro, H.; Sasakawa, C. Bacteria and host interactions in the gut epithelial barrier. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2012, 8, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenier, B.; Applegate, T.J. Modulation of intestinal functions following mycotoxin ingestion: Meta-analysis of published experiments in animals. Toxins 2013, 5, 396–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.H.; Xiao, K.; Luan, Z.S.; Song, J. Early weaning increases intestinal permeability, alters expression of cytokine and tight junction proteins, and activates mitogen-activated protein kinases in pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 91, 1094–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Genes | Forward Primer (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer (5′-3′) | Product Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| IL-6 | AGCAAGGAGGTACTGGCAGA | GTGGTGGCTTTGTCTGGATT | 257 |
| TNFα | ATGAGCACTGAGAGCATGATC | CGATAACCTCGAAGTGCAGT | 169 |
| IL-1β | GTTCTCTGAGAAATGGGAGC | CTGGTCATCATCACAGAAGG | 143 |
| β-Actin | TGCGGGACATCAAGGAGAAG | AGTTGAAGGTAGTTTCGTGG | 216 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, M.; Lu, E.-Q.; Fang, Y.-X.; Liu, G.-W.; Cheng, Y.-J.; Huang, K.; Xu, E.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Wang, X.-J. Piceatannol Alleviates Deoxynivalenol-Induced Damage in Intestinal Epithelial Cells via Inhibition of the NF-κB Pathway. Molecules 2024, 29, 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040855
Zhu M, Lu E-Q, Fang Y-X, Liu G-W, Cheng Y-J, Huang K, Xu E, Zhang Y-Y, Wang X-J. Piceatannol Alleviates Deoxynivalenol-Induced Damage in Intestinal Epithelial Cells via Inhibition of the NF-κB Pathway. Molecules. 2024; 29(4):855. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040855
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Min, En-Qing Lu, Yong-Xia Fang, Guo-Wei Liu, Yu-Jie Cheng, Ke Huang, E Xu, Yi-Yu Zhang, and Xiao-Jing Wang. 2024. "Piceatannol Alleviates Deoxynivalenol-Induced Damage in Intestinal Epithelial Cells via Inhibition of the NF-κB Pathway" Molecules 29, no. 4: 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040855
APA StyleZhu, M., Lu, E.-Q., Fang, Y.-X., Liu, G.-W., Cheng, Y.-J., Huang, K., Xu, E., Zhang, Y.-Y., & Wang, X.-J. (2024). Piceatannol Alleviates Deoxynivalenol-Induced Damage in Intestinal Epithelial Cells via Inhibition of the NF-κB Pathway. Molecules, 29(4), 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040855






