Comparison of ZrO2 Particles and Polyaniline as Additives in Polystyrene-Based Sorbents for the Micro-Solid Phase Extraction of Psychoactive Drugs from Biofluids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of ZrO2 Particles
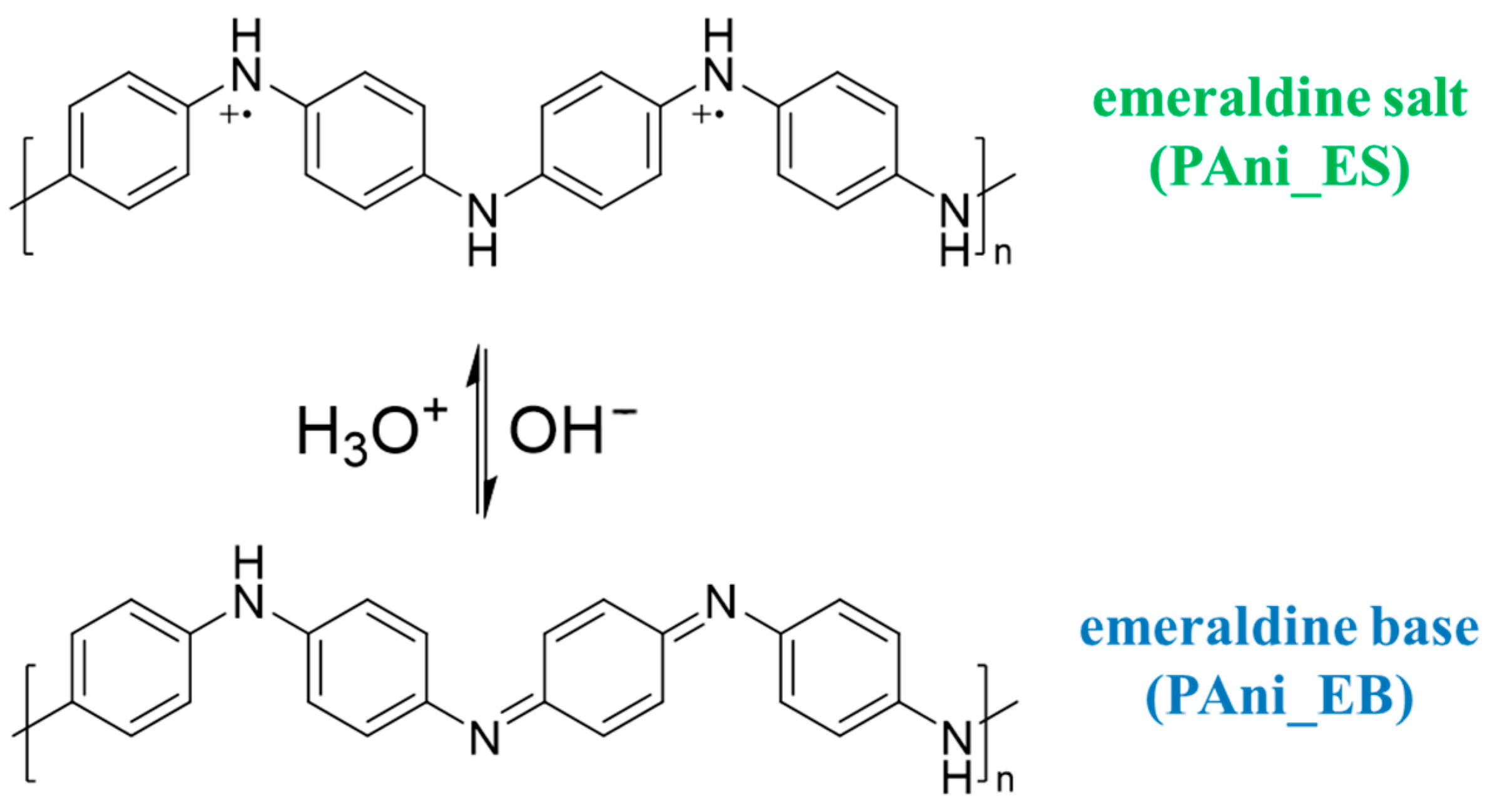
2.2. Characterization of PAni
2.3. Characterization of PS-Based Fibers
2.4. Biological Samples Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.2. Synthesis of ZrO2 Particles
3.3. Synthesis of PAni
3.4. Characterization of Synthesis Products
3.5. Preparation of Solutions for Electrospinning
3.6. Electrospinning Process
3.7. Characterization of Fibers
3.8. Preparation of Spiked Biological Samples
3.9. Preparation of μ-SPE Needles
3.10. μ-SPE Extraction
3.11. LC-MS Conditions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mehdinia, A.; Aziz-Zanjani, M.O. Recent advances in nanomaterials utilized in fiber coatings for solid-phase microextraction. Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 42, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Teng, Y. Application trends of nanofibers in analytical chemistry. Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 131, 115992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, D.; Singh, D.; Sharma, R.; Verma, N.; Bhari, R.; Asadnia, M. Applications of Nanomaterials for Greener Food Analysis. In Green Chemical Analysis and Sample Preparations; El-Maghrabey, M.H., Sivasankar, V., El-Shanhey, R.N., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 471–511. ISBN 978-3-030-96533-4. [Google Scholar]
- Hakova, M.; Chocholousova Havlikowa, L.; Solich, P.; Svec, F.; Satinsky, D. Electrospun nanofiber polymers as extraction phases in analytical chemistry—The advances of the last decade. Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 110, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, A.; Haider, S.; Kang, I. REVIEW A comprehensive review summarizing the effect of electrospinning parameters and potential applications of nanofibers in biomedical and biotechnology. Arab. J. Chem. 2018, 11, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majd, M.; Nojavan, S.; Maghsoudi, M. Preparation of electrospun polyacrylonitrile/γ-cyclodextrin metal—Organic framework nanofibers for extraction of multi-classes herbicides from cereal samples before HPLC-UV analysis. Food Chem. 2022, 393, 133350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahi, S.S.; Yamini, Y.; Mani-varnosfaderani, A. A green approach for in-tube solid phase microextraction of acidic red dyes from juice samples using chitosan / poly vinyl alcohol electrospun nanofibers. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 106, 104339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yu, Z.; Liu, S.; Chen, Y.; Lv, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lin, C.; Ye, X.; Shi, Y.; Liu, M.; et al. Efficient extraction of trace organochlorine pesticides from environmental samples by a polyacrylonitrile electrospun nanofiber membrane modified with covalent organic framework. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollahosseini, A.; Rastegari, M.; Panahi-Dehghan, M. Electrospun Polyacrylonitrile/Clinoptilolite Coating for SPME of PAHs from Water Samples. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2022, 60, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoseinpour Kouhestany, R.; Tamaddon, A.; Ahmad Panahi, H.; Afshar Ebrahimi, A.; Amiri, R. Electrophoretic deposition of polyaniline nanofibers on a stainless steel wire as an adsorbent for determination of tamoxifen by SPME/GC—FID in urine samples. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2022, 36, e5284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Pan, C.; Xu, Q.; Yao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qi, D.; Gu, Z. The investigation of electrospun polymer nanofibers as a solid-phase extraction sorbent for the determination of trazodone in human plasma. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 587, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, S.; Ebrahimzdeh, H.; Seidi, S.; Jalilian, N. Preparation of electrospun polyacrylonitrile/Ni-MOF-74 nanofibers for extraction of atenolol and captopril prior to HPLC-DAD. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, J.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yan, Y.; Kang, W.; Lian, K. Development of a simple nanofiber-based solid phase extraction procedure coupled with high performance liquid chromatography analysis for the quantification of eight sedative-hypnotic drugs in human urine samples. Microchem. J. 2021, 168, 106475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandeh, S.H.; Amini, S.; Ebrahimzadeh, H. Simultaneous trace-level monitoring of seven opioid analgesic drugs in biological samples by pipette-tip micro solid phase extraction based on PVA-PAA/CNT-CNC composite nanofibers followed by HPLC-UV analysis. Microchim. Acta 2021, 188, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, H.; Khanipour, P.; Roostaie, A. A flow injection μ-solid phase extraction system based on electrospun polyaniline nanocomposite. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1433, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, N.G.; Liang, S.H.; Cao, J.K.; Di, Q.N.; Kang, K.; Xu, Q. A nanofiber mat prepared from sulfonated polyaniline for solid-phase extraction of fluoroquinolones from water and biological fluids prior to their quantitation by UPLC-MS/MS. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, L.; Du, T.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, D.; Sun, J.; Yue, T.; Wang, Y.C.; et al. Conductive polyaniline-graphene oxide sorbent for electrochemically assisted solid-phase extraction of lead ions in aqueous food samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1100, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, H.; Khan, R.A.; Alsalme, A. Covalently linked mercaptoacetic acid on ZrO2 coupled cellulose nanofibers for solid phase extraction of Hg(ii): Experimental and DFT studies. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 35712–35721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, N.; Zhao, M.; Liang, S.; Cao, J.; Wang, C.; Xu, Q.; Li, J. High-Throughput and High-Efficient Micro-solid Phase Extraction Based on Sulfonated-Polyaniline/Polyacrylonitrile Nanofiber Mats for Determination of Fluoroquinolones in Animal-Origin Foods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 6892–6901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, N.; Qian, L.; Wang, C.; Li, R.; Xu, Q.; Li, J. Novel nanofibers mat as an efficient, fast and reusable adsorbent for solid phase extraction of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in environmental water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 363, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behbahani, M.; Bide, Y.; Salarian, M.; Niknezhad, M.; Bagheri, S.; Bagheri, A.; Nabid, M.R. The use of tetragonal star-like polyaniline nanostructures for efficient solid phase extraction and trace detection of Pb(II) and Cu(II) in agricultural products, sea foods, and water samples. Food Chem. 2014, 158, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirani, M.; Aslani, A.; Ansari, F.; Parandi, E.; Nodeh, H.R.; Jahanmard, E. Zirconium oxide/titanium oxide nanorod decorated nickel foam as an efficient sorbent in syringe filter based solid-phase extraction of pesticides in some vegetables. Microchem. J. 2023, 189, 108507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadi, A.; Xie, M.; Li, J.; Shon, H.; Zheng, C.; Zhao, S. Polyaniline-based adsorbents for aqueous pollutants removal: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 418, 129425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangla, O.; Roy, S. Monoclinic Zirconium Oxide Nanostructures Having Tunable Band Gap Synthesized under Extremely Non-Equilibrium Plasma Conditions. Proceedings 2019, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauta, P.R.; Manivasakan, P.; Rajendran, V.; Sahu, B.B.; Panda, B.K.; Mohapatra, P. Phase transformation of ZrO2 nanoparticles produced from zircon. Phase Transit. 2012, 85, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, D.H.; Koopal, L.K. Manual of symbols and terminology for physicochemical quantities and units Appendix ii De nitions, Terminology and Symbols in Colloid and Surface Chemistry. Pure Appl. Chem. 1972, 31, 577–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhawan, S.K.; Singh, N.; Rodrigues, D. Electromagnetic shielding behaviour of conducting polyaniline composites. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2003, 4, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoli, A.; Steffens, C.; Paschoalin, R.T.; Correa, A.A.; Alves, W.F.; Leite, F.L.; Herrmann, P.S.P. Low-cost gas sensors produced by the graphite line-patterning technique applied to monitoring banana ripeness. Sensors 2011, 11, 6425–6434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maddah, B.; Javadi, S.S.; Mirzaei, A.; Rahimi-Nasrabadi, M. Application of electrospun polystyrene nanofibers as solid phase extraction sorbent for the preconcentration of diazinon and fenitrothion in environmental waters. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2015, 38, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wietecha-Posłuszny, R.; Lendor, S.; Garnysz, M.; Zawadzki, M.; Kościelniak, P. Human bone marrow as a tissue in post-mortem identification and determination of psychoactive Substances—Screening methodology. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2017, 1061–1062, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
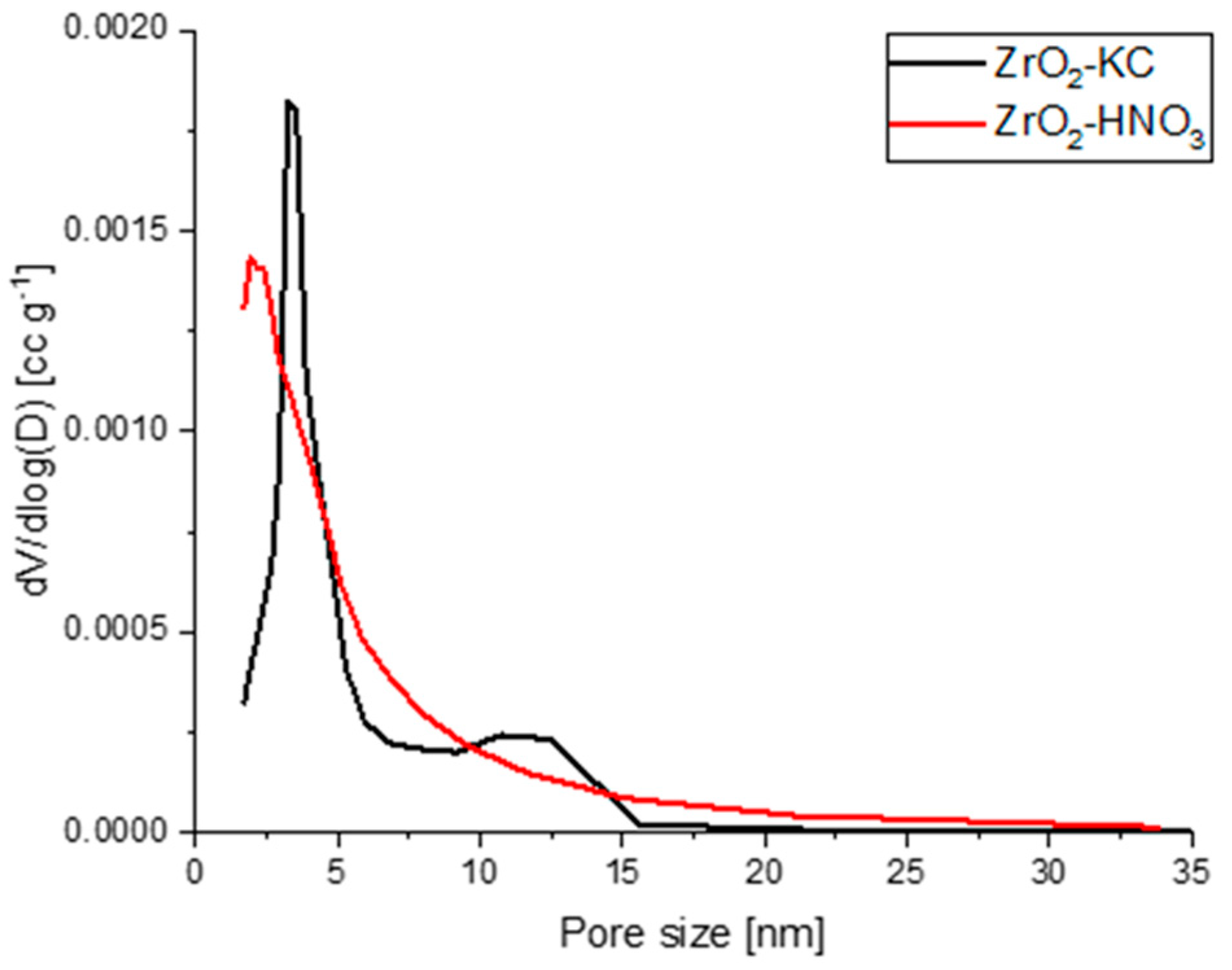
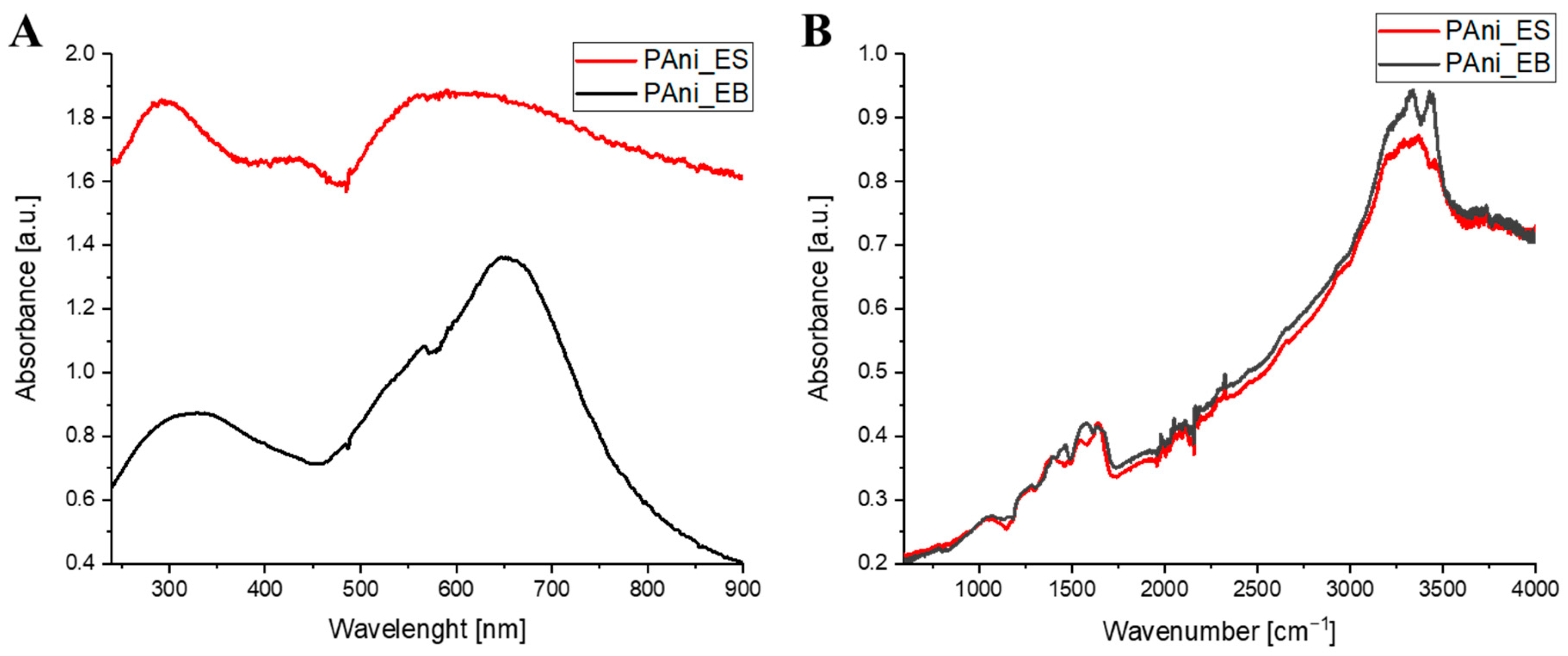
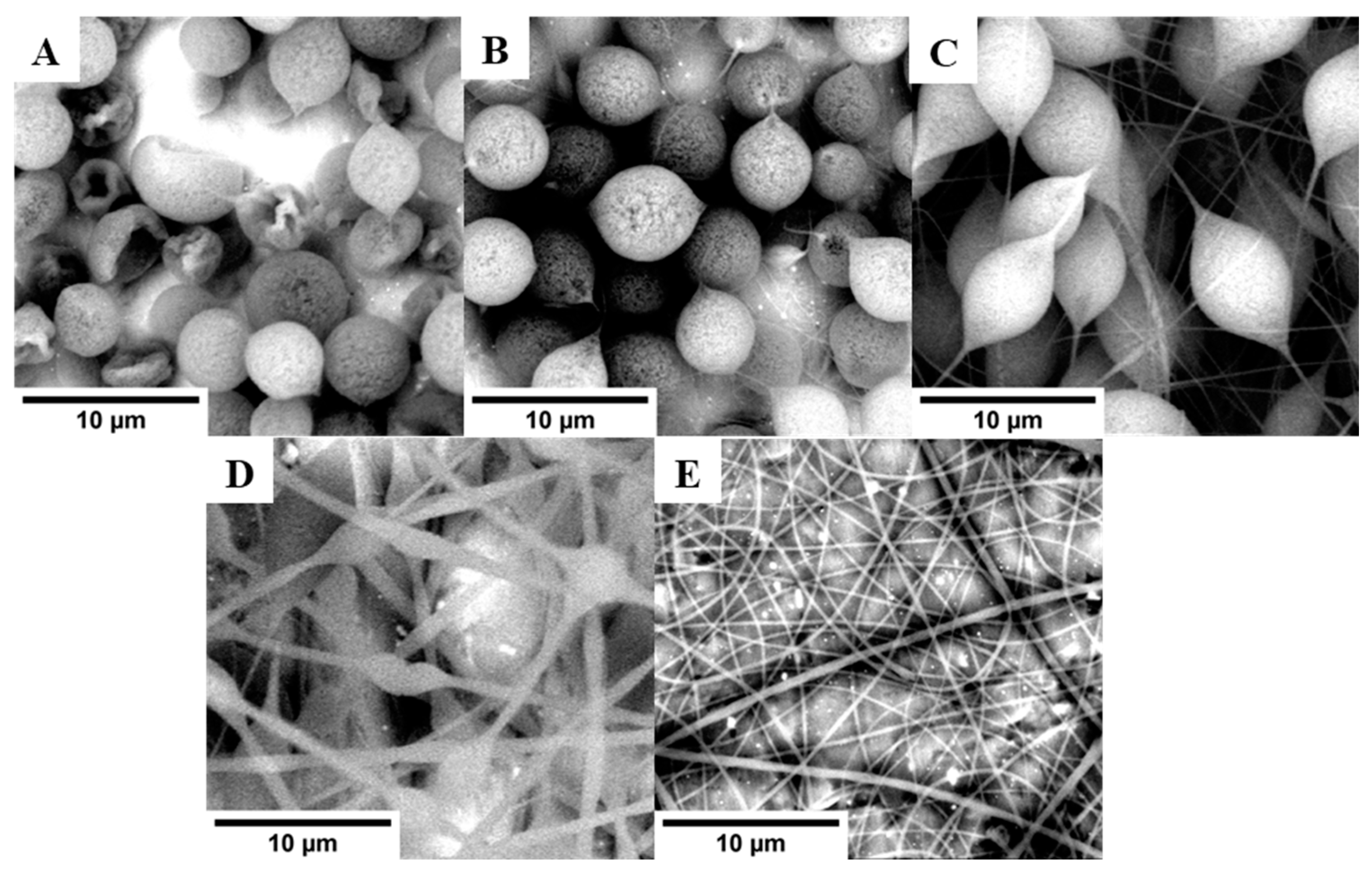
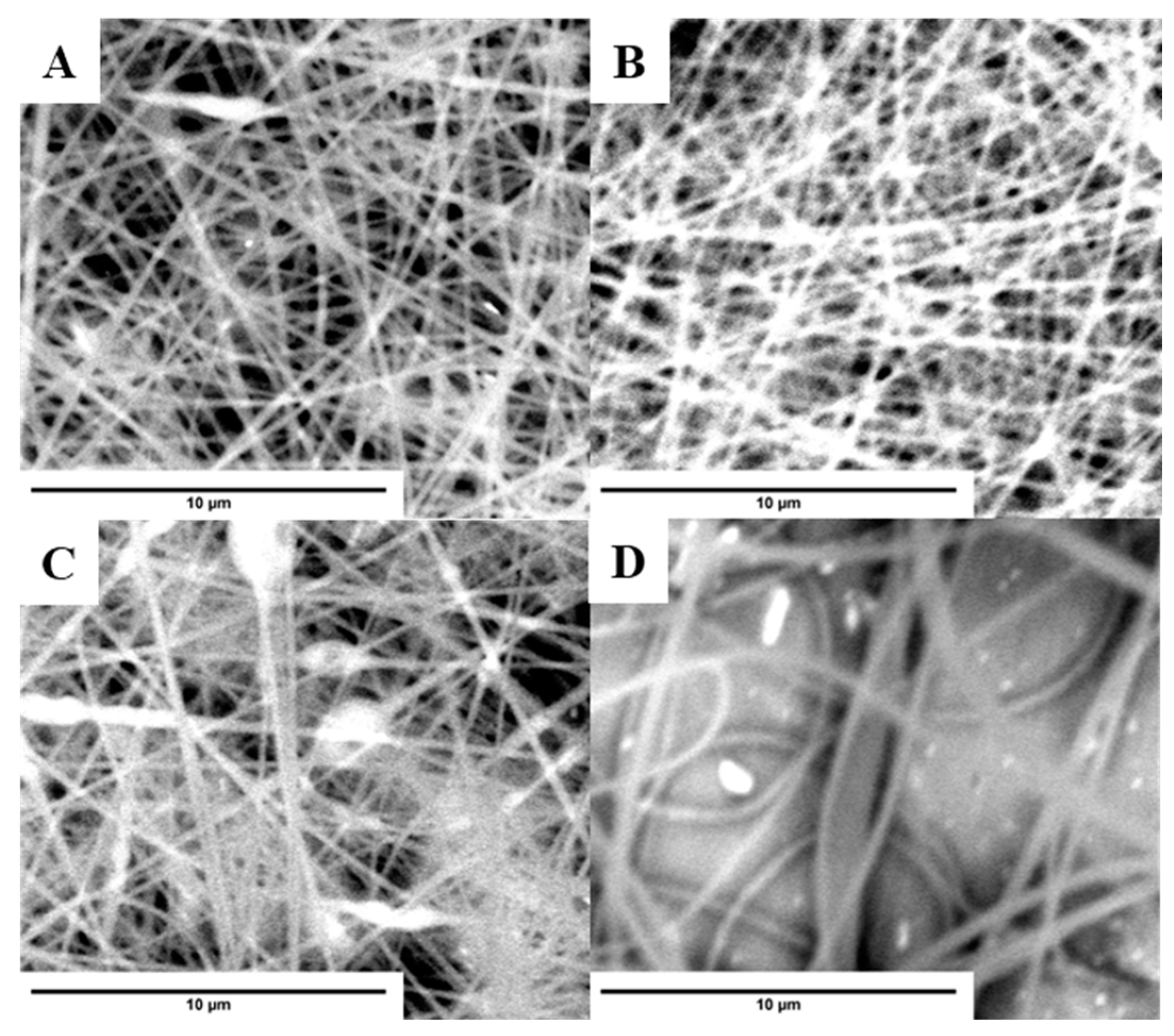
| Sample | SSA (m2/g) | Average Pore Size (nm) | Average Pore Volume (cm3/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZrO2-KC | 39.85 | 5.018 | 0.0547 |
| ZrO2-HNO3 | 76.30 | 4.013 | 0.0765 |
| Electrospinning Solution Composition | Average Fiber Diameter (µm) | F Value |
|---|---|---|
| PS 10.0% | 4.38 | 12.6 |
| PS 12.5% | 3.86 | 14.9 |
| PS 15.0% | 2.39 | 30.6 |
| PS 17.5% | 1.01 | 40.3 |
| PS 20.0% | 0.26 | 34.4 |
| PS 17.5% + PAni_ES | 0.20 | 49.6 |
| PS 17.5% + PAni_EB | 0.25 | 25.4 |
| PS 17.5% + ZrO2-KC | 0.23 | 21.4 |
| PS 17.5% + ZrO2-HNO3 | 0.44 | 48.4 |
| Analyte | Precision—CV (%) (n = 3) | |
|---|---|---|
| Urine | Plasma | |
| Ketamine | 3.7 | 26.0 |
| Flunitrazepam | 4.9 | 9.4 |
| Diazepam | 2.7 | 1.8 |
| Temazepam | 3.9 | 5.0 |
| Nitrazepam | 3.2 | 14.5 |
| Lorazepam | 2.6 | 11.6 |
| Amitriptyline | 6.5 | not found 1 |
| Imipramine | 12.6 | 6.9 |
| Desipramine | 9.6 | 15.1 |
| Paroxetine | 9.3 | not found 1 |
| Citalopram | 5.3 | not found 1 |
| Cocaine | 2.7 | 6.0 |
| Norcocaine | 6.1 | 13.7 |
| Cocaethylene | 5.4 | 12.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stelmaszczyk, P.; Iwan, M.; Pawcenis, D.; Wietecha-Posłuszny, R. Comparison of ZrO2 Particles and Polyaniline as Additives in Polystyrene-Based Sorbents for the Micro-Solid Phase Extraction of Psychoactive Drugs from Biofluids. Molecules 2024, 29, 761. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040761
Stelmaszczyk P, Iwan M, Pawcenis D, Wietecha-Posłuszny R. Comparison of ZrO2 Particles and Polyaniline as Additives in Polystyrene-Based Sorbents for the Micro-Solid Phase Extraction of Psychoactive Drugs from Biofluids. Molecules. 2024; 29(4):761. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040761
Chicago/Turabian StyleStelmaszczyk, Paweł, Mateusz Iwan, Dominika Pawcenis, and Renata Wietecha-Posłuszny. 2024. "Comparison of ZrO2 Particles and Polyaniline as Additives in Polystyrene-Based Sorbents for the Micro-Solid Phase Extraction of Psychoactive Drugs from Biofluids" Molecules 29, no. 4: 761. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040761
APA StyleStelmaszczyk, P., Iwan, M., Pawcenis, D., & Wietecha-Posłuszny, R. (2024). Comparison of ZrO2 Particles and Polyaniline as Additives in Polystyrene-Based Sorbents for the Micro-Solid Phase Extraction of Psychoactive Drugs from Biofluids. Molecules, 29(4), 761. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040761





