Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Molecules Involved in Its Imunopathogenesis, Clinical Features, and Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Most Systemic Lesions Are Due to Loss of Tolerance to Self-Antigens
3. SLE Immunopathogenesis
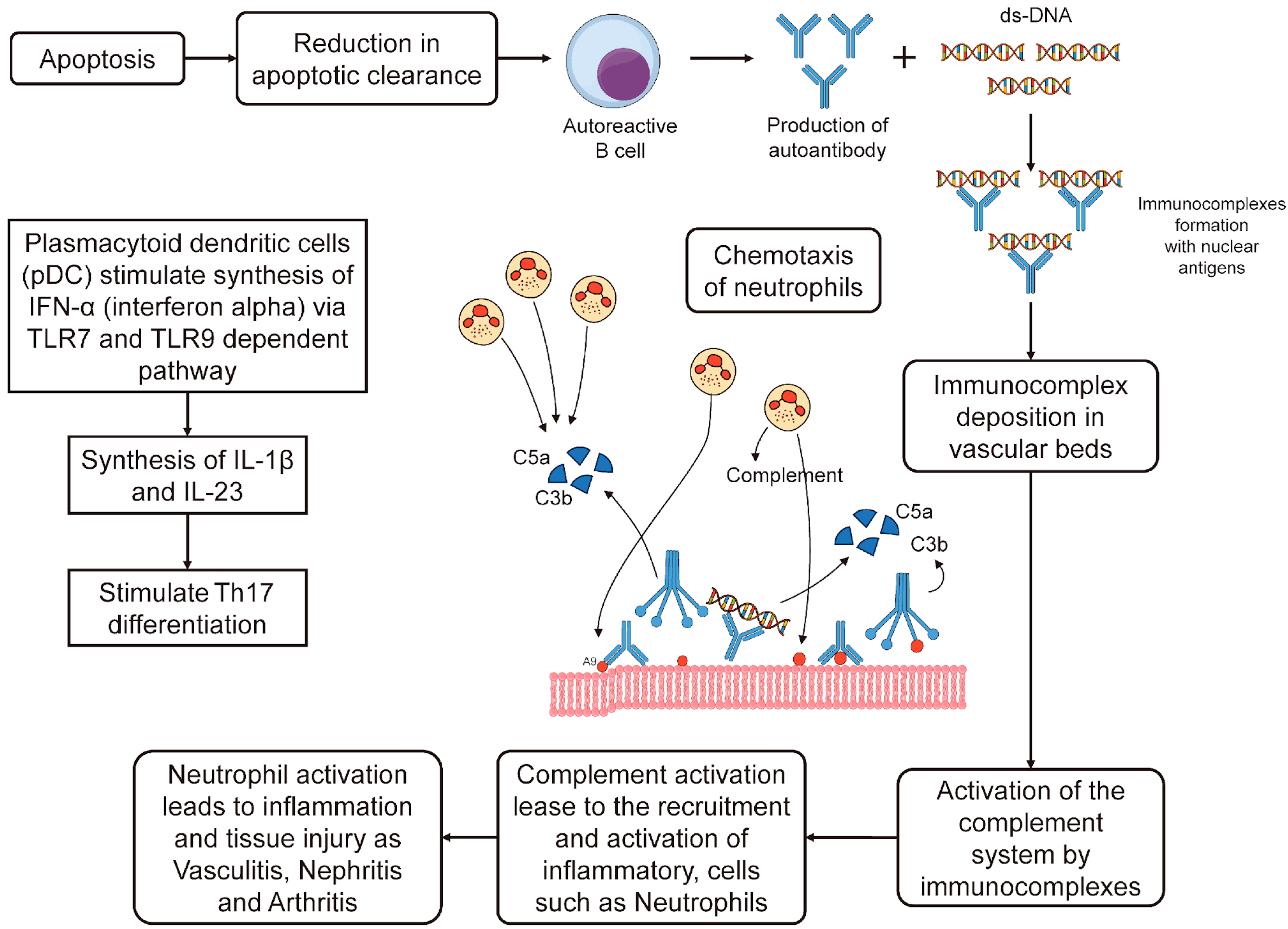
3.1. Apoptosis Cascade and Role of IFN-α in SLE
3.2. Increased Association of HLA System and SLE in a Population
3.3. Immunopathogenesis of NPSLE
3.3.1. Genetic Factors
- Transcriptomic data analysis has revealed several pathways and immune responses that are associated with SLE, such as interferons, T cell differentiation, complement pathways, and coagulation;
- Eight genes (SOCE, CXCL8, MMP9, IL1B, JUN, TNF, NFKBIA, and FOS) are up-regulated in SLE and have interactions with different pathways. These genes are also linked to SNPs that are identified by GWAS;
- Several other genes with known SLE-related variations are detected by integrating GWAS and pathway analysis, such as TYK2, SH2B, C5, IL2RA, IRF5, FCGR2A, TNFAIP3, STAT4, LYN, IL7R, and HLA-DRB;
- One of the relevant pathways that is identified by pathway-based analysis is the TSLP signaling pathway, which is connected to rs7574865, LYN, STAT4, and IL7R;
3.3.2. Comorbidities
3.3.3. Summary of NPSLE Immunopathogenesis
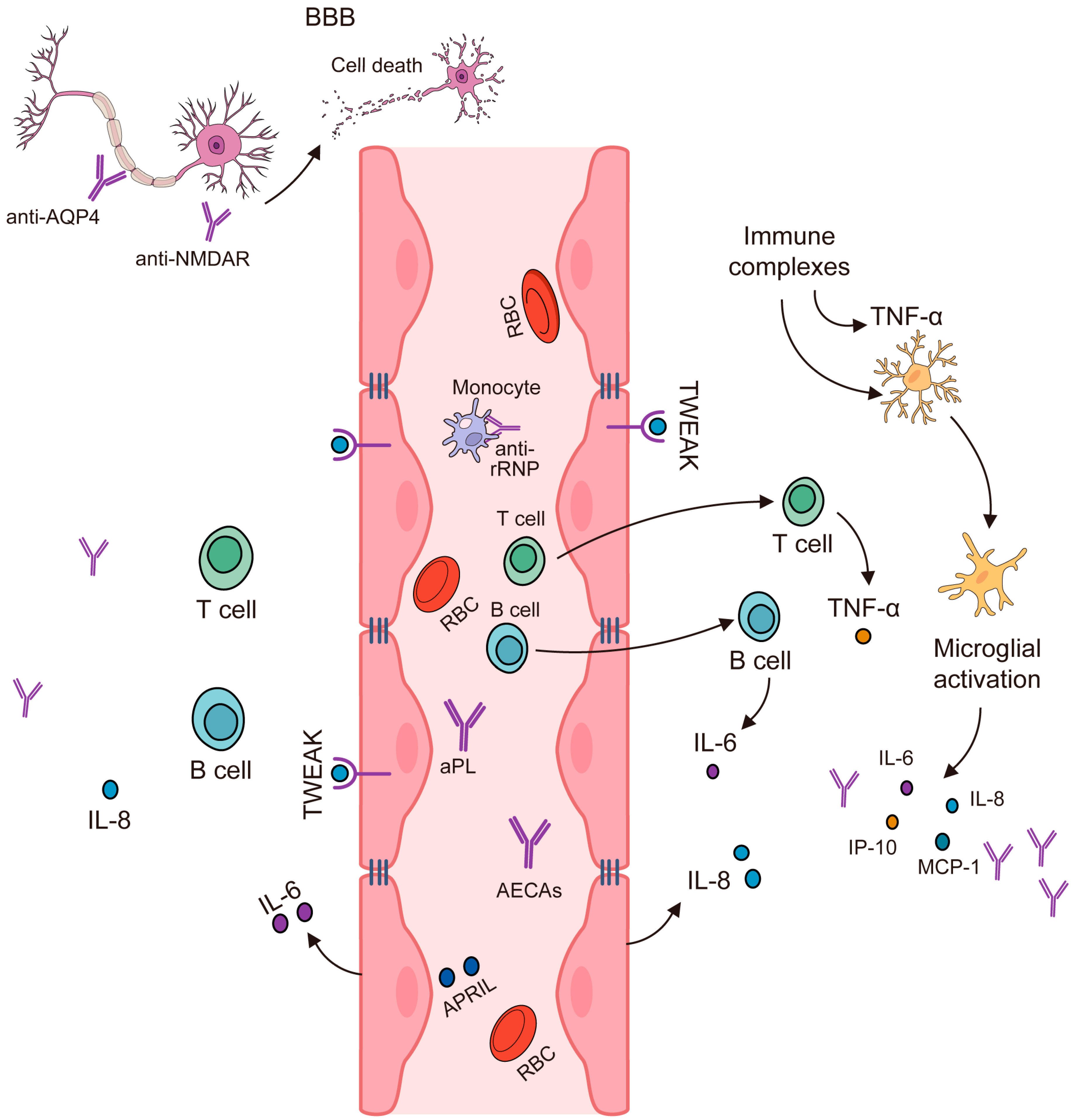
3.4. IL-2, IL-10, and IFN-γ Produced by T-Helper Cells Are Elevated in NPSLE
3.5. Noninflammatory or Thrombotic/Ischemic Vascular Injury
4. Autoantibodies Can Lead to Neuronal Damage in NPSLE
4.1. Antiphospholipid Antibodies (β2-Glycoprotein 1, Cardiolipin Anticardiolipin (Anti-CL) and Lupus Anticoagulant (LA)
4.2. Ribosomal P Protein (Anti-Ribosmal P Ab)
4.3. Anti-Human N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor Abs (Anti-NMDA)
4.4. Microtubule-Associated Protein (Anti-MAP-2 Ab)
4.5. U1 Ribonucleoprotein (Anti-U1RNP Ab)
4.6. Structural Endothelial Proteins (AECA)
4.7. Triosephophate Isomerase (Anti-TPI Ab)
4.8. Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Antibodies (Anti-GAPDH)
4.9. Anti-Aquaporin Four Antibodies (NMO-IgG/AQP4-Ab)
4.10. Anti-Endothelial Cell Antibodies (AECAb)
4.11. Anti-Ubiquitin Carboxyl Hydrolase L 1 Antibodies (Anti-UCH-L1 Ab)
5. Investigations
5.1. Biomarkers
5.2. Serum and CSF Analyses
5.3. Biomarkers in NPSLE
6. NPSLE Complications Caused Directly by NPSLE or the Treatment
6.1. Steroid Induced Psychosis
6.2. Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML)
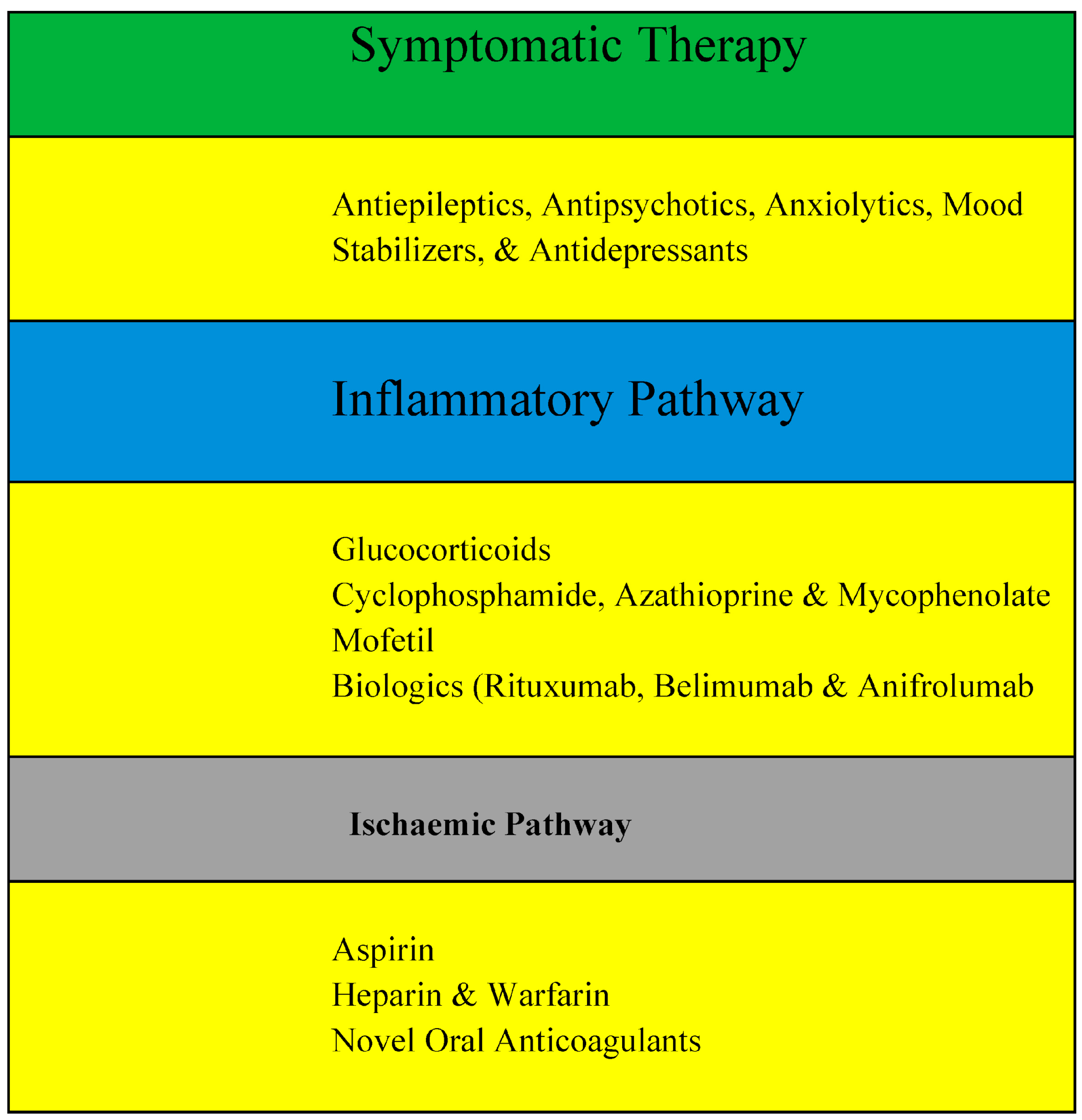
7. Management of NPSLE
7.1. Symptomatic Therapy
7.1.1. Antiepileptics
7.1.2. Antipsychotics in NPSLE
7.1.3. Anxiolytics in NPSLE
7.1.4. Mood Stabilizers in NPSLE
7.2. Inflammatory Pathway
7.2.1. Glucocorticoids
- Prednisone is a synthetic glucocorticoid that is converted to its active form prednisolone in the liver. It has a moderate potency and a short half-life of about 3–4 h. Prednisone is usually given orally in doses ranging from 0.5 to 1 mg/kg/day for NPSLE [160];
- Methylprednisolone is a synthetic glucocorticoid that has a higher potency and a longer half-life than prednisone of about 18–36 h. It can be given orally or intravenously in doses from 0.5 to 1 g/day for severe NPSLE [160];
- Dexamethasone is a synthetic glucocorticoid that has a very high potency and a long half-life of about 36–54 h. It can be given orally or intravenously in doses from 10 to 100 mg/day for refractory NPSLE [160].
7.2.2. Cyclophosphamide
7.2.3. Azathioprine
7.2.4. Mycophenolate Mofetil
7.2.5. Biologics
7.3. Ischaemic Pathway
7.3.1. Use of Aspirin in NPSLE
- Prevention of thrombotic events: Aspirin inhibits the enzyme cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1), which reduces the production of thromboxane A2, a prothrombotic mediator. This prevents platelet aggregation and reduces the risk of arterial and venous thrombosis, which can cause stroke, transient ischemic attack, or other neurological complications in NPSLE patients [174,175];
- Treatment of headache: Aspirin has analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties that can relieve headaches, one of the most common symptoms of NPSLE [176];
- Modulation of type I interferon response: Aspirin may have immunomodulatory effects on the type I interferon pathway, which is implicated in the pathogenesis of SLE and NPSLE. Aspirin may reduce the expression of interferon-stimulated genes and the levels of interferon-alpha, a cytokine that promotes inflammation and autoimmunity in NPSLE patients [177,178].
7.3.2. Use of Heparin and Warfarin in NPSLE
7.3.3. Novel Oral Anticoagulants (NOACs)
- Dabigatran etexilate: a direct thrombin inhibitor that is approved for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation, the prevention and treatment of venous thromboembolism, and the prevention of thromboembolism after hip or knee replacement surgery [183];
- Rivaroxaban: a direct factor Xa inhibitor that is approved for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation, the prevention and treatment of venous thromboembolism, the prevention of thromboembolism after hip or knee replacement surgery, and the secondary prevention of acute coronary syndrome [182];
- Apixaban: a direct factor Xa inhibitor that is approved for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation, the prevention and treatment of venous thromboembolism, and the prevention of thromboembolism after hip or knee replacement surgery [184];
- Edoxaban: a direct factor Xa inhibitor that is approved for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation and the treatment of venous thromboembolism [185].
7.4. Other Treatments
7.4.1. Intravenous Immunoglobulins (IVIGs)
7.4.2. Non-Pharmacological Intervention in NPSLE
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schwartz, N.; Stock, A.D.; Putterman, C. Neuropsychiatric Lupus: New Mechanistic Insights and Future Treatment Directions. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2019, 15, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stock, A.D.; Wen, J.; Putterman, C. Neuropsychiatric Lupus, the Blood Brain Barrier, and the TWEAK/Fn14 Pathway. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.I.; Lee, K.H.; Park, S.; Yang, J.W.; Kim, H.J.; Song, K.; Lee, S.; Na, H.; Jang, Y.J.; Nam, J.Y.; et al. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Lung Involvement: A Comprehensive Review. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2022, 11, 6714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanouriakis, A.; Tziolos, N.; Bertsias, G.; Boumpas, D.T. Update οn the Diagnosis and Management of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasparotto, M.; Gatto, M.; Binda, V.; Doria, A.; Moroni, G. Lupus Nephritis: Clinical Presentations and Outcomes in the 21st Century. Rheumatology 2020, 59, v39–v51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durcan, L.; O’Dwyer, T.; Petri, M. Management Strategies and Future Directions for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Adults. Lancet 2019, 393, 2332–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.A.; Khandker, S.S.; Kotyla, P.J.; Hassan, R. Immunomodulatory Effects of Diet and Nutrients in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE): A Systematic Review. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santacruz, J.C.; Mantilla, M.J.; Rueda, I.; Pulido, S.; Rodriguez-Salas, G.; Londono, J. A Practical Perspective of the Hematologic Manifestations of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Cureus 2022, 14, e22938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, J.T.; Hughes, P.; Lin, A.; Siebenlist, U.; Jain, R.; Yaprianto, K.; Gray, D.H.D.; Gerondakis, S.; Strasser, A.; O’Reilly, L.A. Impact of Loss of NF-κB1, NF-κB2 or c-REL on SLE-like Autoimmune Disease and Lymphadenopathy in Fas(lpr/lpr) Mutant Mice. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2016, 94, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, D.; Young, L. Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia as a Manifestation of SLE and Secondary Sjogren’s Syndrome. BMJ Case Rep. 2013, 2013, bcr2013009598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariri, L.P.; Unizony, S.; Stone, J.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Sharma, A.; Matsubara, O.; Mark, E.J. Acute Fibrinous and Organizing Pneumonia in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Pathol. Int. 2010, 60, 755–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudsi, M.; Nahas, L.D.; Alsawah, R.; Hamsho, A.; Omar, A. The Prevalence of Oral Mucosal Lesions and Related Factors in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2021, 23, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brewer, B.N.; Kamen, D.L. Gastrointestinal and Hepatic Disease in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 44, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kivity, S.; Agmon-Levin, N.; Zandman-Goddard, G.; Chapman, J.; Shoenfeld, Y. Neuropsychiatric Lupus: A Mosaic of Clinical Presentations. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uramoto, K.M.; Michet, C.J., Jr.; Thumboo, J.; Sunku, J.; O’Fallon, W.M.; Gabriel, S.E. Trends in the Incidence and Mortality of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, 1950–1992. Arthritis Rheum. 1999, 42, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, M.H.; Corzillius, M.; Bae, S.C.; Lew, R.A.; Fortin, P.R.; Gordon, C.; Isenberg, D.; Alarcón, G.S.; Straaton, K.V.; Denburg, J.; et al. The American College of Rheumatology Nomenclature and Case Definitions for Neuropsychiatric Lupus Syndromes. Arthritis Rheum. 1999, 42, 599–608. [Google Scholar]
- Nived, O.; Sturfelt, G.; Liang, M.H.; De Pablo, P. The ACR Nomenclature for CNS Lupus Revisited. Lupus 2003, 12, 872–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, S.; Mohamed, A.S.; Rogers, S.; Sarmast, S.T.; Kataria, S.; Mohamed, K.H.; Khalid, M.Z.; Saeeduddin, M.O.; Shiza, S.T.; Ahmad, S.; et al. Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A 2021 Update on Diagnosis, Management, and Current Challenges. Cureus 2021, 13, e17969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.A.; Taylor, K.E.; Graham, R.R.; Nititham, J.; Lee, A.T.; Ortmann, W.A.; Jacob, C.O.; Alarcón-Riquelme, M.E.; Tsao, B.P.; Harley, J.B.; et al. Differential Genetic Associations for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Based on Anti-dsDNA Autoantibody Production. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1001323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisetsky, D.S. Pathogenesis of Autoimmune Disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2023, 19, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagopoulos, D.; Themistocleous, M. Central Nervous System Manifestation of Lupus Erythematosus Resembling Brain Abscess. Int. J. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2019, 6, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govoni, M.; Hanly, J.G. The Management of Neuropsychiatric Lupus in the 21st Century: Still so Many Unmet Needs? Rheumatology 2020, 59, v52–v62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, D.; Rijnink, E.C.; Nabuurs, R.J.A.; Steup-Beekman, G.M.; Versluis, M.J.; Emmer, B.J.; Zandbergen, M.; van Buchem, M.A.; Allaart, C.F.; Wolterbeek, R.; et al. Brain Histopathology in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Identification of Lesions Associated with Clinical Neuropsychiatric Lupus Syndromes and the Role of Complement. Rheumatology 2017, 56, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutanto, H.; Yuliasih, Y. Disentangling the Pathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Close Ties between Immunological, Genetic and Environmental Factors. Medicina 2023, 59, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Motwee, S.; Jawdat, D.; Jehani, G.S.; Anazi, H.; Shubaili, A.; Sutton, P.; Uyar, A.F.; Hajeer, A.H. Association of HLA-DRB1*15 and HLADQB1*06 with SLE in Saudis. Ann. Saudi Med. 2013, 33, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini, S.A.; Labilloy, A. Genetics, TREX1 Mutations. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lehtinen, D.A.; Harvey, S.; Mulcahy, M.J.; Hollis, T.; Perrino, F.W. The TREX1 Double-Stranded DNA Degradation Activity Is Defective in Dominant Mutations Associated with Autoimmune Disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 31649–31656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.L.; Harvey, S.; Perrino, F.W.; Hollis, T. Defects in DNA Degradation Revealed in Crystal Structures of TREX1 Exonuclease Mutations Linked to Autoimmune Disease. DNA Repair 2012, 11, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraja, M.; Chin, V.K.; Abdullah, M.; Arip, M.; Amin-Nordin, S. HLA-DRB1*04 as a Risk Allele to Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Lupus Nephritis in the Malay Population of Malaysia. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 598665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorji, A.E.; Roudbari, Z.; Alizadeh, A.; Sadeghi, B. Investigation of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) with Integrating Transcriptomics and Genome Wide Association Information. Gene 2019, 706, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Sandling, J.K.; Hagberg, N.; Berggren, O.; Sigurdsson, S.; Karlberg, O.; Rönnblom, L.; Eloranta, M.-L.; Syvänen, A.-C. Genome-Wide Profiling of Target Genes for the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus-Associated Transcription Factors IRF5 and STAT4. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Kumar, S.; Pratap, A.; Singh, R.; Kumari, R.; Kumar, S.; Aggarwal, A.; Misra, R. Association of ITGAM, TNFSF4, TNFAIP3 and STAT4 Gene Polymorphisms with Risk of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in a North Indian Population. Lupus 2018, 27, 1973–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheikh, M.M.; Bahakim, A.K.; Aljabri, M.K.; Alharthi, S.M.; Alharthi, S.M.; Alsaeedi, A.K.; Alqahtani, S.F. Neuropsychiatric Lupus and Lupus Nephritis Successfully Treated with Combined IVIG and Rituximab: An Alternative to Standard of Care. Case Rep. Rheumatol. 2022, 2022, 5899188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UpToDate. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/neurologic-and-neuropsychiatric-manifestations-of-systemic-lupus-erythematosus (accessed on 15 December 2023).
- Obermeier, B.; Daneman, R.; Ransohoff, R.M. Development, Maintenance and Disruption of the Blood-Brain Barrier. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1584–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Tu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Du, K.; Xie, Z.; Lin, Z. Pathogenesis and Treatment of Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Review. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 998328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeltsch-David, H.; Muller, S. Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Pathogenesis and Biomarkers. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2014, 10, 579–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, E.; Huang, M.W.; Putterman, C. Advances in the Diagnosis, Pathogenesis and Treatment of Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2020, 32, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Q.; Tian, X.; Li, M.; Zeng, X. Progress in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2022, 11, 4955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gono, T.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Yamanaka, H. Discoveries in the Pathophysiology of Neuropsychiatric Lupus Erythematosus: Consequences for Therapy. BMC Med. 2013, 11, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Study Discovers Antibodies Leading to Development of Neuropsychiatric Lupus. Available online: https://www.lupus.org/news/study-discovers-antibodies-leading-to-development-of-neuropsychiatric-lupus (accessed on 15 December 2023).
- Sato, S.; Temmoku, J.; Fujita, Y.; Yashiro-Furuya, M.; Matsuoka, N.; Asano, T.; Kobayashi, H.; Watanabe, H.; Migita, K. Autoantibodies Associated with Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: The Quest for Symptom-Specific Biomarkers. Fukushima J. Med. Sci. 2020, 66, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshio, T.; Okamoto, H. Pathogenesis of Neuropsychiatric Syndromes of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Open J. Rheumatol. Autoimmune Dis. 2015, 5, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Okamoto, H.; Kobayashi, A.; Yamanaka, H. Cytokines and Chemokines in Neuropsychiatric Syndromes of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 2010, 268436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, E.; Jorgensen, T.N. Neuropsychiatric SLE: From Immune Mechanisms to Clinical Management. In Lupus—New Advances and Challenges; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020; ISBN 9781838801694. [Google Scholar]
- Barile-Fabris, L.; Hernández-Cabrera, M.F.; Barragan-Garfias, J.A. Vasculitis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2014, 16, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wildner, P.; Stasiołek, M.; Matysiak, M. Differential Diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis and Other Inflammatory CNS Diseases. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2020, 37, 101452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciascia, S.; Bertolaccini, M.L.; Roccatello, D.; Khamashta, M.A.; Sanna, G. Autoantibodies Involved in Neuropsychiatric Manifestations Associated with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Systematic Review. J. Neurol. 2014, 261, 1706–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleki, K.; Shirzad, M.; Banazadeh, M.; Hosein Mohamadi, M.; Alijanizadeh, P.; Javanmehr, N.; Pourahmad, R.; Shakeri, M.; Nikkhoo Amiri, R.; Payandeh, P.; et al. Lupus and the Nervous System: A Neuroimmunoloigcal Update on Pathogenesis and Management of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus with Focus on Neuropsychiatric SLE. In Systemic Lupus Erythematosus—Pathogenesis and Management; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zandman-Goddard, G.; Chapman, J.; Shoenfeld, Y. Autoantibodies Involved in Neuropsychiatric SLE and Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 36, 297–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmon, J.E.; de Groot, P.G. Pathogenic Role of Antiphospholipid Antibodies. Lupus 2008, 17, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackworth-Young, C.G. Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Multiple Mechanisms. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2004, 136, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, B.E.; Wills, R.; Pierangeli, S.S. Pathophysiological Mechanisms in Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Int. J. Clin. Rheumtol. 2011, 6, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzav, A.; Ben-Ziv, T.; Blank, M.; Pick, C.G.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Chapman, J. Antibody-Specific Behavioral Effects: Intracerebroventricular Injection of Antiphospholipid Antibodies Induces Hyperactive Behavior While Anti-Ribosomal-P Antibodies Induces Depression and Smell Deficits in Mice. J. Neuroimmunol. 2014, 272, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho, J.F.; Pasoto, S.G.; Appenzeller, S. Seizures in Primary Antiphospholipid Syndrome: The Relevance of Smoking to Stroke. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012, 981519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, Y. Antiphospholipid syndrome and stroke. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 2005, 45, 852–855. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Harris, E.N.; Pierangeli, S. Antiphospholipid Antibodies and Cerebral Lupus. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1997, 823, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peluso, S.; Antenora, A.; De Rosa, A.; Roca, A.; Maddaluno, G.; Brescia Morra, V.; De Michele, G. Antiphospholipid-Related Chorea. Front. Neurol. 2012, 3, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerjefors, L.; Andretta, S.; Bonato, G.; Mainardi, M.; Carecchio, M.; Antonini, A. Antiphospholipid-Related Chorea: Two Case Reports and Role of Metabolic Imaging. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2022, 9, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanna, G.; Bertolaccini, M.L.; Cuadrado, M.J.; Laing, H.; Khamashta, M.A.; Mathieu, A.; Hughes, G.R.V. Neuropsychiatric Manifestations in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Prevalence and Association with Antiphospholipid Antibodies. J. Rheumatol. 2003, 30, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.-R.; Han, Y.-F.; Yin, J.; Zhang, Y.-P.; Jiang, Z.-X.; Zheng, L.; Tan, G.-Z.; Wang, L. The Diagnostic Benefit of Antibodies against Ribosomal Proteins in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Adv. Rheumatol. 2020, 60, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caponi, L.; Bombardieri, S.; Migliorini, P. Anti-Ribosomal Antibodies Bind the Sm Proteins D and B/B’. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1998, 112, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mader, S.; Brimberg, L.; Diamond, B. The Role of Brain-Reactive Autoantibodies in Brain Pathology and Cognitive Impairment. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brimberg, L.; Mader, S.; Fujieda, Y.; Arinuma, Y.; Kowal, C.; Volpe, B.T.; Diamond, B. Antibodies as Mediators of Brain Pathology. Trends Immunol. 2015, 36, 709–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alajangi, H.K.; Kaur, M.; Sharma, A.; Rana, S.; Thakur, S.; Chatterjee, M.; Singla, N.; Jaiswal, P.K.; Singh, G.; Barnwal, R.P. Blood-Brain Barrier: Emerging Trends on Transport Models and New-Age Strategies for Therapeutics Intervention against Neurological Disorders. Mol. Brain 2022, 15, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Nasser, A.M.; Ghaleb, R.M.; Mahmoud, J.A.; Khairy, W.; Mahmoud, R.M. Association of Anti-Ribosomal P Protein Antibodies with Neuropsychiatric and Other Manifestations of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Clin. Rheumatol. 2008, 27, 1377–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirohata, S.; Arinuma, Y.; Takayama, M.; Yoshio, T. Association of Cerebrospinal Fluid Anti-Ribosomal P Protein Antibodies with Diffuse Psychiatric/neuropsychological Syndromes in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2007, 9, R44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, Q.; Su, J.; Wang, X.; Zhuang, B.; Liu, L.; Deng, X.; Li, Y. Anti-Ribosomal P Protein Antibodies and Insomnia Correlate with Depression and Anxiety in Patients Suffering from Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Li, M.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Q.; You, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Zeng, X. Clinical Features and Outcomes of Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in China. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 1349042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanly, J.G.; Urowitz, M.B.; Siannis, F.; Farewell, V.; Gordon, C.; Bae, S.C.; Isenberg, D.; Dooley, M.A.; Clarke, A.; Bernatsky, S.; et al. Autoantibodies and Neuropsychiatric Events at the Time of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Diagnosis: Results from an International Inception Cohort Study. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshio, T.; Hirata, D.; Onda, K.; Nara, H.; Minota, S. Antiribosomal P Protein Antibodies in Cerebrospinal Fluid Are Associated with Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 2005, 32, 34–39. [Google Scholar]
- Katzav, A.; Solodeev, I.; Brodsky, O.; Chapman, J.; Pick, C.G.; Blank, M.; Zhang, W.; Reichlin, M.; Shoenfeld, Y. Induction of Autoimmune Depression in Mice by Anti-Ribosomal P Antibodies via the Limbic System. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 938–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matus, S.; Burgos, P.V.; Bravo-Zehnder, M.; Kraft, R.; Porras, O.H.; Farías, P.; Barros, L.F.; Torrealba, F.; Massardo, L.; Jacobelli, S.; et al. Antiribosomal-P Autoantibodies from Psychiatric Lupus Target a Novel Neuronal Surface Protein Causing Calcium Influx and Apoptosis. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 3221–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo-Zehnder, M.; Toledo, E.M.; Segovia-Miranda, F.; Serrano, F.G.; Benito, M.J.; Metz, C.; Retamal, C.; Álvarez, A.; Massardo, L.; Inestrosa, N.C.; et al. Anti-Ribosomal P Protein Autoantibodies from Patients with Neuropsychiatric Lupus Impair Memory in Mice. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, A.; Massardo, L. Antibodies and the Brain: Antiribosomal P Protein Antibody and the Clinical Effects in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2018, 31, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín, J.-D.; Vargas, S.; Ruiz-Ordoñez, I.; Posso-Osorio, I.; Nieto-Aristizábal, I.; Barrera, M.C.; Ríos-Serna, L.J.; Tobón, G.J. Association of Antiribosomal P Antibody with Neurological and Systemic Manifestations in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Southwestern Colombia. J. Appl. Lab. Med. 2022, 7, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Tsien, J.Z. Memory and the NMDA Receptors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 302–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levite, M. Glutamate Receptor Antibodies in Neurological Diseases: Anti-AMPA-GluR3 Antibodies, Anti-NMDA-NR1 Antibodies, Anti-NMDA-NR2A/B Antibodies, Anti-mGluR1 Antibodies or Anti-mGluR5 Antibodies Are Present in Subpopulations of Patients with Either: Epilepsy, Encephalitis, Cerebellar Ataxia, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) and Neuropsychiatric SLE, Sjogren’s Syndrome, Schizophrenia, Mania or Stroke. These Autoimmune Anti-Glutamate Receptor Antibodies Can Bind Neurons in Few Brain Regions, Activate Glutamate Receptors, Decrease Glutamate Receptor’s Expression, Impair Glutamate-Induced Signaling and Function, Activate Blood Brain Barrier Endothelial Cells, Kill Neurons, Damage the Brain, Induce Behavioral/psychiatric/cognitive Abnormalities and Ataxia in Animal Models, and Can Be Removed or Silenced in Some Patients by Immunotherapy. J. Neural Transm. 2014, 121, 1029–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schüler, T.; Mesic, I.; Madry, C.; Bartholomäus, I.; Laube, B. Formation of NR1/NR2 and NR1/NR3 Heterodimers Constitutes the Initial Step in N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor Assembly. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, Y.; Long, T.; Li, Z. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Associated with Recurrent Anti-NMDA Receptor Encephalitis during Pregnancy. Arch. Women’s Ment. Health 2021, 24, 525–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samanta, D.; Lui, F. Anti-NMDA Receptor Encephalitis; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lauvsnes, M.B.; Omdal, R. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, the Brain, and Anti-NR2 Antibodies. J. Neurol. 2012, 259, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanly, J.G.; Legge, A.; Kamintsky, L.; Friedman, A.; Hashmi, J.A.; Beyea, S.D.; Fisk, J.; Omisade, A.; Calkin, C.; Bardouille, T.; et al. Role of Autoantibodies and Blood-Brain Barrier Leakage in Cognitive Impairment in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Lupus Sci. Med. 2022, 9, e000668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirohata, S.; Arinuma, Y.; Yanagida, T.; Yoshio, T. Blood-Brain Barrier Damages and Intrathecal Synthesis of Anti-N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor NR2 Antibodies in Diffuse Psychiatric/neuropsychological Syndromes in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, R77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomalla, V.; Schmeisser, M.J.; Weinmann-Menke, J. Mouse Models, Antibodies, and Neuroimaging: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives in Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (NPSLE). Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1078607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeGiorgio, L.A.; Konstantinov, K.N.; Lee, S.C.; Hardin, J.A.; Volpe, B.T.; Diamond, B. A Subset of Lupus Anti-DNA Antibodies Cross-Reacts with the NR2 Glutamate Receptor in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 1189–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, C.; Díaz-Nido, J.; Avila, J. Phosphorylation of Microtubule-Associated Protein 2 (MAP2) and Its Relevance for the Regulation of the Neuronal Cytoskeleton Function. Prog. Neurobiol. 2000, 61, 133–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izant, J.G.; McIntosh, J.R. Microtubule-Associated Proteins: A Monoclonal Antibody to MAP2 Binds to Differentiated Neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 4741–4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, R.C., Jr.; Sugiura, K.; Tan, E.M. Antibodies to Microtubule-Associated Protein 2 in Patients with Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, L.B.; Johnson, N.; Byne, W. Alterations in MAP2 Immunocytochemistry in Areas 9 and 32 of Schizophrenic Prefrontal Cortex. Psychiatry Res. 2002, 114, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosoklija, G.; Keilp, J.G.; Toomayan, G.; Mancevski, B.; Haroutunian, V.; Liu, D.; Malespina, D.; Hays, A.P.; Sadiq, S.; Latov, N.; et al. Altered Subicular MAP2 Immunoreactivity in Schizophrenia. Prilozi 2005, 26, 13–34. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, H.J.; Voleti, B.; Hajszan, T.; Rajkowska, G.; Stockmeier, C.A.; Licznerski, P.; Lepack, A.; Majik, M.S.; Jeong, L.S.; Banasr, M.; et al. Decreased Expression of Synapse-Related Genes and Loss of Synapses in Major Depressive Disorder. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1413–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachoyiannopoulos, P.G.; Guialis, A.; Tzioufas, G.; Moutsopoulos, H.M. Predominance of IgM Anti-U1RNP Antibodies in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1996, 35, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dema, B.; Charles, N. Autoantibodies in SLE: Specificities, Isotypes and Receptors. Antibodies 2016, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Venrooij, W.J.; Hoet, R.; Castrop, J.; Hageman, B.; Mattaj, I.W.; van de Putte, L.B. Anti-(U1) Small Nuclear RNA Antibodies in Anti-Small Nuclear Ribonucleoprotein Sera from Patients with Connective Tissue Diseases. J. Clin. Investig. 1990, 86, 2154–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattah, N.H.; Kattah, M.G.; Utz, P.J. The U1-snRNP Complex: Structural Properties Relating to Autoimmune Pathogenesis in Rheumatic Diseases. Immunol. Rev. 2010, 233, 126–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito-Garcia, E.; Schur, P.H.; Lahita, R.; American College of Rheumatology Ad Hoc Committee on Immunologic Testing Guidelines. Guidelines for Immunologic Laboratory Testing in the Rheumatic Diseases: Anti-Sm and Anti-RNP Antibody Tests. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 51, 1030–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; Fujii, T.; Yokoyama, T.; Fujita, Y.; Imura, Y.; Yukawa, N.; Kawabata, D.; Nojima, T.; Ohmura, K.; Usui, T.; et al. Anti-U1 RNP Antibodies in Cerebrospinal Fluid Are Associated with Central Neuropsychiatric Manifestations in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Mixed Connective Tissue Disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 3730–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risau, W.; Flamme, I. Vasculogenesis. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1995, 11, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergkamp, S.C.; Wahadat, M.J.; Salah, A.; Kuijpers, T.W.; Smith, V.; Tas, S.W.; van den Berg, J.M.; Kamphuis, S.; Schonenberg-Meinema, D. Dysregulated Endothelial Cell Markers in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Inflamm. 2023, 20, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alessandri, C.; Bombardieri, M.; Valesini, G. Pathogenic Mechanisms of Anti-Endothelial Cell Antibodies (AECA): Their Prevalence and Clinical Relevance. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2006, 42, 297–326. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Del Papa, N.; Raschi, E.; Moroni, G.; Panzeri, P.; Borghi, M.O.; Ponticelli, C.; Tincani, A.; Balestrieri, G.; Meroni, P.L. Anti-Endothelial Cell IgG Fractions from Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients Bind to Human Endothelial Cells and Induce a pro-Adhesive and a pro-Inflammatory Phenotype in Vitro. Lupus 1999, 8, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atehortúa, L.; Rojas, M.; Vásquez, G.M.; Castaño, D. Endothelial Alterations in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Rheumatoid Arthritis: Potential Effect of Monocyte Interaction. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 9680729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, T.D.; Palladino, M.J. Newly Discovered Roles of Triosephosphate Isomerase Including Functions within the Nucleus. Mol. Med. 2023, 29, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Yashiro, M.; Asano, T.; Kobayashi, H.; Watanabe, H.; Migita, K. Association of Anti-Triosephosphate Isomerase Antibodies with Aseptic Meningitis in Patients with Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 36, 1655–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasajima, T.; Watanabe, H.; Sato, S.; Sato, Y.; Ohira, H. Anti-Triosephosphate Isomerase Antibodies in Cerebrospinal Fluid Are Associated with Neuropsychiatric Lupus. J. Neuroimmunol. 2006, 181, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirover, M.A. Role of the Glycolytic Protein, Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase, in Normal Cell Function and in Cell Pathology. J. Cell. Biochem. 1997, 66, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Li, X.; Zhou, H.; Liu, X.; Jia, J.; Xie, Q.; Peng, S.; Sun, X.; Wang, Q.; Yi, L. Anti-GAPDH Autoantibody Is Associated with Increased Disease Activity and Intracranial Pressure in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 7430780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delunardo, F.; Soldati, D.; Bellisario, V.; Berry, A.; Camerini, S.; Crescenzi, M.; Alessandri, C.; Conti, F.; Ceccarelli, F.; Francia, A.; et al. Anti-GAPDH Autoantibodies as a Pathogenic Determinant and Potential Biomarker of Neuropsychiatric Diseases. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 2708–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, H.; Miyanaga, K.; Yamamoto, N. Immunomodulatory Effects of Extracellular Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase of Exopolysaccharide-Producing Lactiplantibacillus Plantarum JCM 1149. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, M.L.; Dagan, S.; Eren, R.; Gozalbo, D. Evaluation of the Usefulness of Anti-Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Antibodies as a Treatment for Invasive Candidiasis in a Murine Model. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2006, 89, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Závada, J.; Nytrová, P.; Wandinger, K.P.; Jarius, S.; Svobodová, R.; Probst, C.; Peterová, V.; Tegzová, D.; Pavelka, K.; Vencovský, J. Seroprevalence and Specificity of NMO-IgG (anti-Aquaporin 4 Antibodies) in Patients with Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Rheumatol. Int. 2013, 33, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, A.; Ford, I.; Morrison, R.; Barker, R.N.; Greaves, M.; Erwig, L.-P. Anti-Endothelial Antibodies Interfere in Apoptotic Cell Clearance and Promote Thrombosis in Patients with Antiphospholipid Syndrome. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 1756–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, X.; Li, R.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H.; Cao, S.; Li, R.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q.; et al. Utility of Autoantibody against an UCH-L1 Epitope as a Serum Diagnostic Marker for Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2022, 40, 2078–2087. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Sun, J.; Mu, R.; Gan, Y.; Wang, G.; He, J.; Yi, L.; Wang, Q.; Sun, X.; Li, Z. The Clinical Significance of Ubiquitin Carboxyl Hydrolase L1 and Its Autoantibody in Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2019, 37, 474–480. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; Huang, W.; Chen, H.; Song, G.; Li, P.; Shan, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, H.; Wu, L.; et al. Autoantibody Profiling on Human Proteome Microarray for Biomarker Discovery in Cerebrospinal Fluid and Sera of Neuropsychiatric Lupus. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sissons, B. Neuropsychiatric Lupus: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and More. Available online: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/neuropsychiatric-lupus (accessed on 23 June 2023).
- Monov, S.; Monova, D. Classification Criteria for Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Do They Need a Discussion? Hippokratia 2008, 12, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Conti, F.; Ceccarelli, F.; Perricone, C.; Massaro, L.; Marocchi, E.; Miranda, F.; Spinelli, F.R.; Truglia, S.; Alessandri, C.; Valesini, G. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus with and without Anti-dsDNA Antibodies: Analysis from a Large Monocentric Cohort. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 328078. [Google Scholar]
- Sandhu, G.; Bansal, A.; Ranade, A.; Aggarwal, R.; Narayanswami, G.; Jones, J.; Smith, S.D. Negative Double Stranded DNA and Anti-Smith Antibodies in Lupus Nephritis. Nephrol. Res. Rev. 2012, 4, 55–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.M.; Dai, C.; Zhao, Z.; Gaskin, F. Anti-dsDNA Antibodies Are One of the Many Autoantibodies in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. F1000Research 2015, 4, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, G.V.; Marques, M.; Balbi, V.; Gormezano, N.W.S.; Kozu, K.; Sakamoto, A.P.; Pereira, R.M.R.; Terreri, M.T.; Magalhães, C.S.; Guariento, A.; et al. Anti-RO/SSA and Anti-La/SSB Antibodies: Association with Mild Lupus Manifestations in 645 Childhood-Onset Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimi, R.; Ueda, A.; Ozato, K.; Ishigatsubo, Y. Clinical and Pathological Roles of Ro/SSA Autoantibody System. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012, 606195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chedid, A.; Rossi, G.M.; Peyronel, F.; Menez, S.; Atta, M.G.; Bagnasco, S.M.; Arend, L.J.; Rosenberg, A.Z.; Fine, D.M. Low-Level Proteinuria in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Kidney Int. Rep. 2020, 5, 2333–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, P.; Guo, T.; Zou, L.; Shi, J.; Chen, P. Study on the Correlation between Anti-Ribosomal P Protein Antibody and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Medicine 2020, 99, e20192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Shen, Y.; He, J.; Jia, R.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, D.; Han, L.; Zhu, L.; Chi, X.; et al. Significance of Antibodies against the Native Ribosomal P Protein Complex and Recombinant P0, P1, and P2 Proteins in the Diagnosis of Chinese Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2013, 27, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.K.; Ho, L.Y.; Lee, C.; To, C.H.; Mok, C.C. Validation of the 2019 EULAR/ACR Classification Criteria for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in ANA-Positive Chinese Patients. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2022, 14, 1759720X221100300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magallares, B.; Lobo-Prat, D.; Castellví, I.; Moya, P.; Gich, I.; Martinez-Martinez, L.; Park, H.; Millán, A.M.; Laiz, A.; Díaz-Torné, C.; et al. Assessment of EULAR/ACR-2019, SLICC-2012 and ACR-1997 Classification Criteria in SLE with Longstanding Disease. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2021, 10, 2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimojima, Y.; Matsuda, M.; Gono, T.; Ishii, W.; Ikeda, S.-I. Relationship between Clinical Factors and Neuropsychiatric Manifestations in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Clin. Rheumatol. 2005, 24, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abialmouna, J.; Shoemaker, D.W.; Pullicino, P.M.; Baer, A.N. Marked Cerebrospinal Fluid Pleocytosis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Related Cerebral Ischemia. J. Rheumatol. 1992, 19, 626–629. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Joseph, F.G.; Lammie, G.A.; Scolding, N.J. CNS Lupus: A Study of 41 Patients. Neurology 2007, 69, 644–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinitz, E.; Hubbard, D.; Grayzel, A.I. Central Nervous System Systemic Lupus Erythematosus versus Central Nervous System Infection: Low Cerebral Spinal Fluid Glucose and Pleocytosis in a Patient with a Prolonged Course. Arthritis Rheum. 1982, 25, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, T.; Myers, A.R. Nervous System Involvement in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1975, 35, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinglass, E.J.; Arnett, F.C.; Dorsch, C.A.; Zizic, T.M.; Stevens, M.B. Neuropsychiatric Manifestations of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Diagnosis, Clinical Spectrum, and Relationship to Other Features of the Disease. Medicine 1976, 55, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerson, J.S.; Gruenewald, S.M.; Gomes, L.; Lin, M.-W.; Swaminathan, S. The Conundrum of Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Current and Novel Approaches to Diagnosis. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1111769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Chen, C.; Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Tan, L.; Lu, L.; Fan, Y.; Hou, Y.; Dou, H.; Liang, J. Novel CSF Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Integrated Analysis of Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Based on Antibody Profiling. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2023, 25, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachu, A.K.; Davis, V.; Abdulrahim, M.; Harbaugh, L.; Prasad, S.; Kotapati, V.P.; Srinivas, S. Corticosteroid-Induced Psychosis: A Report of Three Cases. Cureus 2023, 15, e39221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, A.; Kao, A.H. Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2011, 9, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Han, H.; Chu, L. Neuropsychiatric Lupus Erythematosus: Future Directions and Challenges: A Systematic Review and Survey. Clinics 2020, 75, e1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janes, M.; Kuster, S.; Goldson, T.M.; Forjuoh, S.N. Steroid-Induced Psychosis. In Baylor University Medical Center Proceedings; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2019; Volume 32, pp. 614–615. [Google Scholar]
- Sirois, F. Steroid Psychosis: A Review. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2003, 25, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissert, R. Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy. J. Neuroimmunol. 2011, 231, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortese, I.; Reich, D.S.; Nath, A. Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy and the Spectrum of JC Virus-Related Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 17, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-C.; Ahearn, J.M. The Search for Lupus Biomarkers. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2009, 23, 507–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Magro-Checa, C.; Zirkzee, E.J.; Huizinga, T.W.; Steup-Beekman, G.M. Management of Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Current Approaches and Future Perspectives. Drugs 2016, 76, 459–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertsias, G.K.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Aringer, M.; Bollen, E.; Bombardieri, S.; Bruce, I.N.; Cervera, R.; Dalakas, M.; Doria, A.; Hanly, J.G.; et al. EULAR Recommendations for the Management of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus with Neuropsychiatric Manifestations: Report of a Task Force of the EULAR Standing Committee for Clinical Affairs. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 2074–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modica, R.F.; Thatayatikom, A.; Bell-Brunson, D.H.; Elder, M.E. Bortezomib Is Efficacious in the Treatment of Severe Childhood-Onset Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus with Psychosis: A Case Series and Mini-Review of B-Cell Immunomodulation in Antibody-Mediated Diseases. Clin. Rheumatol. 2023, 42, 1965–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, A.; Ho, R.C.M.; Lau, C.S. Clinical Implications of Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Adv. Psychiatr. Treat. 2009, 15, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamfil, C.; Fanouriakis, A.; Damian, L.; Rinzis, M.; Sidiropoulos, P.; Tsivgoulis, G.; Rednic, S.; Bertsias, G.; Boumpas, D.T. EULAR Recommendations for Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus vs. Usual Care: Results from Two European Centres. Rheumatology 2015, 54, 1270–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, W. Review of Lithium Effects on Brain and Blood. Cell Transplant. 2009, 18, 951–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Khalil, B.W. Update on Antiepileptic Drugs 2019. Continuum 2019, 25, 508–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaar, S.J.; Natesan, S.; McCutcheon, R.; Howes, O.D. Antipsychotics: Mechanisms Underlying Clinical Response and Side-Effects and Novel Treatment Approaches Based on Pathophysiology. Neuropharmacology 2020, 172, 107704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monahan, R.C.; Beaart-van de Voorde, L.J.J.; Fronczek, R.; de Bresser, J.; Eikenboom, J.; Kloppenburg, M.; Middelkoop, H.A.M.; Terwindt, G.M.; van der Wee, N.J.A.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; et al. Clinical Outcome in Patients with Suspected Inflammatory Neuropsychiatric Lupus Treated with Immunosuppression: An Observational Cohort Study. Lupus Sci. Med. 2023, 10, e000850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, D.W.; Cidlowski, J.A. Immune Regulation by Glucocorticoids. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahluwalia, A. Topical Glucocorticoids and the Skin-Mechanisms of Action: An Update. Mediat. Inflamm. 1998, 7, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichlin, S. Neuroendocrine-Immune Interactions. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 1246–1253. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz-Topete, D.; Cidlowski, J.A. Glucocorticoids: Molecular Mechanisms of Action. In Immunopharmacology and Inflammation; Riccardi, C., Levi-Schaffer, F., Tiligada, E., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 249–266. ISBN 9783319776583. [Google Scholar]
- Vandewalle, J.; Luypaert, A.; De Bosscher, K.; Libert, C. Therapeutic Mechanisms of Glucocorticoids. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 29, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munck, A.; Guyre, P.M.; Holbrook, N.J. Physiological Functions of Glucocorticoids in Stress and Their Relation to Pharmacological Actions. Endocr. Rev. 1984, 5, 25–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapolsky, R.M.; Romero, L.M.; Munck, A.U. How Do Glucocorticoids Influence Stress Responses? Integrating Permissive, Suppressive, Stimulatory, and Preparative Actions. Endocr. Rev. 2000, 21, 55–89. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J.; Jiang, W. Cyclophosphamide-Induced Seizures in a Patient with Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (NPSLE): A Case Report. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1122629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, A.; Cui, H.; Deng, R.; Wei, X. Cyclophosphamide in the Treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus-Related Guillain-Barré Syndrome: A Systematic Review of Case Reports. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2023, 18, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanouriakis, A.; Pamfil, C.; Sidiropoulos, P.; Damian, L.; Flestea, A.; Gusetu, G.; Rednic, S.; Bertsias, G.; Boumpas, D.T. Cyclophosphamide in Combination with Glucocorticoids for Severe Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Retrospective, Observational Two-Centre Study. Lupus 2016, 25, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivity, S.; Baker, B.; Arango, M.-T.; Chapman, J.; Shoenfeld, Y. Pharmacologic Management of Neuropsychiatric Lupus. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 9, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanna, G.; Bertolaccini, M.L.; Khamashta, M.A. Neuropsychiatric Involvement in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Current Therapeutic Approach. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 1261–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirunsatitpron, P.; Hanprasertpong, N.; Noppakun, K.; Pruksakorn, D.; Teekachunhatean, S.; Koonrungsesomboon, N. Mycophenolic Acid and Cancer Risk in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 88, 476–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamanamool, N.; McEvoy, M.; Attia, J.; Ingsathit, A.; Ngamjanyaporn, P.; Thakkinstian, A. Efficacy and Adverse Events of Mycophenolate Mofetil versus Cyclophosphamide for Induction Therapy of Lupus Nephritis: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2010, 89, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.B.; Hiemstra, T.F.; Ballarin, J.; Blockmans, D.E.; Brogan, P.; Bruchfeld, A.; Cid, M.C.; Dahlsveen, K.; de Zoysa, J.; Espigol-Frigolé, G.; et al. Mycophenolate Mofetil versus Cyclophosphamide for Remission Induction in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: A Randomised, Non-Inferiority Trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anolik, J.H.; Barnard, J.; Cappione, A.; Pugh-Bernard, A.E.; Felgar, R.E.; Looney, R.J.; Sanz, I. Rituximab Improves Peripheral B Cell Abnormalities in Human Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 3580–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barra, M.E.; Soni, D.; Vo, K.H.; Chitnis, T.; Stankiewicz, J.M. Experience with Long-Term Rituximab Use in a Multiple Sclerosis Clinic. Mult. Scler. J. Exp. Transl. Clin. 2016, 2, 2055217316672100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parodis, I.; Gomez, A.; Frodlund, M.; Jönsen, A.; Zickert, A.; Sjöwall, C.; Bengtsson, A.A.; Gunnarsson, I. Smoking Reduces the Efficacy of Belimumab in Mucocutaneous Lupus. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2018, 18, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Higgs, B.W.; Bay-Jensen, A.C.; Karsdal, M.A.; Yao, Y.; Roskos, L.K.; White, W.I. Suppression of T Cell Activation and Collagen Accumulation by an Anti-IFNAR1 mAb, Anifrolumab, in Adult Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 2402–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tektonidou, M.G.; Andreoli, L.; Limper, M.; Amoura, Z.; Cervera, R.; Costedoat-Chalumeau, N.; Cuadrado, M.J.; Dörner, T.; Ferrer-Oliveras, R.; Hambly, K.; et al. EULAR Recommendations for the Management of Antiphospholipid Syndrome in Adults. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 1296–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaud, L.; Mathian, A.; Ruffatti, A.; Erkan, D.; Tektonidou, M.; Cervera, R.; Forastiero, R.; Pengo, V.; Lambert, M.; Martinez-Zamora, M.A.; et al. Efficacy of Aspirin for the Primary Prevention of Thrombosis in Patients with Antiphospholipid Antibodies: An International and Collaborative Meta-Analysis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2014, 13, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaud, L.; Mathian, A.; Devilliers, H.; Ruffatti, A.; Tektonidou, M.; Forastiero, R.; Pengo, V.; Lambert, M.; Lefevre, G.; Martinez-Zamora, M.A.; et al. Patient-Level Analysis of Five International Cohorts Further Confirms the Efficacy of Aspirin for the Primary Prevention of Thrombosis in Patients with Antiphospholipid Antibodies. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auriel, E.; Regev, K.; Korczyn, A.D. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Exposure and the Central Nervous System. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2014, 119, 577–584. [Google Scholar]
- Miyachi, K.; Iwamoto, T.; Kojima, S.; Ida, T.; Suzuki, J.; Yamamoto, T.; Mimura, N.; Sugiyama, T.; Tanaka, S.; Furuta, S.; et al. Relationship of Systemic Type I Interferon Activity with Clinical Phenotypes, Disease Activity, and Damage Accrual in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Treatment-Naive Patients: A Retrospective Longitudinal Analysis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2023, 25, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruera, S.; Chavula, T.; Madan, R.; Agarwal, S.K. Targeting Type I Interferons in Systemic Lupus Erythematous. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1046687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Guan, F. Thrombosis and Anticoagulation Therapy in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Autoimmune Dis. 2022, 2022, 3208037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petri, M. Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Transl. Res. 2020, 225, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, G.W. Testing for Lupus Anticoagulants. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2022, 48, 643–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, H.; Chen, Y.-M.; Dai, Y.-L.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, Y.-F.; Zhou, Y.-F. Safety and Efficacy of Vitamin K Antagonists vs. Novel Oral Anticoagulants in Patients with Left Ventricular Thrombus: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 636491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khouja, C.; Brunton, G.; Richardson, M.; Stokes, G.; Blanchard, L.; Burchett, H.; Khatwa, M.; Walker, R.; Wright, K.; Sowden, A.; et al. Oral Anticoagulants: A Systematic Overview of Reviews on Efficacy and Safety, Genotyping, Self-Monitoring, and Stakeholder Experiences. Syst. Rev. 2022, 11, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potpara, T.S.; Polovina, M.M.; Licina, M.M.; Stojanovic, R.M.; Prostran, M.S.; Lip, G.Y.H. Novel Oral Anticoagulants for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation: Focus on Apixaban. Adv. Ther. 2012, 29, 491–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milling, T.J., Jr.; Ziebell, C.M. A Review of Oral Anticoagulants, Old and New, in Major Bleeding and the Need for Urgent Surgery. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 30, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandman-Goddard, G.; Levy, Y.; Shoenfeld, Y. Intravenous Immunoglobulin Therapy and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2005, 29, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakthiswary, R.; D’Cruz, D. Intravenous Immunoglobulin in the Therapeutic Armamentarium of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2014, 93, e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulhearn, B.; Bruce, I.N. Indications for IVIG in Rheumatic Diseases. Rheumatology 2015, 54, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zervides, K.A.; Jern, A.; Nystedt, J.; Gullstrand, B.; Nilsson, P.C.; Sundgren, P.C.; Bengtsson, A.A.; Jönsen, A. Serum S100A8/A9 Concentrations Are Associated with Neuropsychiatric Involvement in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Cross-Sectional Study. BMC Rheumatol. 2022, 6, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, S.; Li, G.; Xiao, J. Exercise Regulates the Immune System. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1228, 395–408. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, R.J.; Kunz, H.; Agha, N.; Graff, R. Exercise and the Regulation of Immune Functions. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2015, 135, 355–380. [Google Scholar]
- Wessels, I.; Fischer, H.J.; Rink, L. Dietary and Physiological Effects of Zinc on the Immune System. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2021, 41, 133–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyh, C.; Krüger, K.; Peeling, P.; Castell, L. The Role of Minerals in the Optimal Functioning of the Immune System. Nutrients 2022, 14, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohari, A.; Baumann, B.; Jen, R.; Ayas, N. Sleep Deficiency: Epidemiology and Effects. Clin. Chest Med. 2022, 43, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousfi, N.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Briki, W.; Zmijewski, P.; Chamari, K. The COVID-19 Pandemic: How to Maintain a Healthy Immune System during the Lockdown—A Multidisciplinary Approach with Special Focus on Athletes. Biol. Sport 2020, 37, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oster, M.; Scheel, M.; Muráni, E.; Ponsuksili, S.; Zebunke, M.; Puppe, B.; Wimmers, K. The Fight-or-Flight Response Is Associated with PBMC Expression Profiles Related to Immune Defence and Recovery in Swine. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parodis, I.; Gomez, A.; Tsoi, A.; Chow, J.W.; Pezzella, D.; Girard, C.; Stamm, T.A.; Boström, C. Systematic literature review informing the EULAR recommendations for the non-pharmacological management of systemic lupus erythematosus and systemic sclerosis. RMD Open 2023, 9, e003297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrada, A.A.; Escobedo, N.; Iruretagoyena, M.; Valenzuela, R.A.; Burgos, P.I.; Cuitino, L.; Llanos, C. Innate Immune Cells’ Contribution to Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amitani, M.; Amitani, H.; Sloan, R.A.; Suzuki, H.; Sameshima, N.; Asakawa, A.; Nerome, Y.; Owaki, T.; Inui, A.; Hoshino, E. The translational aspect of complementary and alternative medicine for cancer with particular emphasis on Kampo. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condor, D.; Culcițchi, C.; Blum, R.; Baru, O.; Buduru, S.; Kui, A.; Țig, I. A Review of CO2 Laser-Mediated Therapy for Oral Mucosal Lesions. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. The Potential of Collagen Treatment for Comorbid Diseases. Polymers 2023, 15, 3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredi, C.; Spirito, L.; Calace, F.P.; Balsamo, R.; Terribile, M.; Stizzo, M.; Romano, L.; Napolitano, L.; Califano, G.; Cirillo, L.; et al. Oral Preparation of Hyaluronic Acid, Chondroitin Sulfate, Curcumin, and Quercetin (Ialuril® Soft Gels) for the Prevention of LUTS after Intravesical Chemotherapy. Pathophysiology 2022, 29, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantin, M.M.; Nita, I.E.; Olteanu, R.; Constantin, T.; Bucur, S.; Matei, C.; Raducan, A. Significance and impact of dietary factors on systemic lupus erythematosus pathogenesis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 17, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Central Nervous System | Neurological syndromes (focal): Seizure disorder Aseptic meningitis Cerebrovascular disease Demyelinating syndromes Headache Myelopathy Movement disorders Neuropsychiatric syndrome (diffuse): Anxiety disorders Psychosis Mood disorders Acute confusional state Cognitive dysfunction |
| Peripheral Central Nervous System | Neurological syndromes (focal): Autonomic disorders Myasthenia gravis Polyneuropathy Guillian Barre Syndrome Plexopathy Mononeuropathy |
| Autoantibody | Location Isolated | Associated NPSLE Symptoms | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phospholipid: β2-glycoprotein 1 and cardiolipin (aCL-Ab) | Serum, CSF | CVD, seizures, chorea cognitive dysfunction, psychosis, depression, headache | [54,55,56,57,58] |
| Ribosomal P protein (anti-ribosmal P Ab) | Serum, CSF | psychosis, depression, cognitive impairment | [66,67,68] |
| NMDA receptor (anti-NMDA) | Serum, CSF | depression cognitive dysfunction | [84] |
| MAP-2 (anti-MAP-2 Ab) | Serum, CSF | seizures, chorea, sensory neuropathy, psychosis, headache) | [90,91,92] |
| U1 ribonucleoprotein (Anti-U1RNP Ab) | Serum, CSF | Diffuse NPSLE symptoms | [98] |
| Structural endothelial proteins (AECA) | Serum | Psychosis, depression | [102,103] |
| Triosephosphate isomerase(anti-TPI Ab) | Serum, CSF | aseptic meningitis | [105] |
| GAPDH (anti-GAPDH Ab) | Serum | Involved in various in neurodegenerative disorders, increased intracranial pressure, cognitive dysfunction | [108,110,111] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Justiz-Vaillant, A.A.; Gopaul, D.; Soodeen, S.; Arozarena-Fundora, R.; Barbosa, O.A.; Unakal, C.; Thompson, R.; Pandit, B.; Umakanthan, S.; Akpaka, P.E. Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Molecules Involved in Its Imunopathogenesis, Clinical Features, and Treatment. Molecules 2024, 29, 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040747
Justiz-Vaillant AA, Gopaul D, Soodeen S, Arozarena-Fundora R, Barbosa OA, Unakal C, Thompson R, Pandit B, Umakanthan S, Akpaka PE. Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Molecules Involved in Its Imunopathogenesis, Clinical Features, and Treatment. Molecules. 2024; 29(4):747. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040747
Chicago/Turabian StyleJustiz-Vaillant, Angel A., Darren Gopaul, Sachin Soodeen, Rodolfo Arozarena-Fundora, Odette Arozarena Barbosa, Chandrashehkar Unakal, Reinand Thompson, Bijay Pandit, Srikanth Umakanthan, and Patrick E. Akpaka. 2024. "Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Molecules Involved in Its Imunopathogenesis, Clinical Features, and Treatment" Molecules 29, no. 4: 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040747
APA StyleJustiz-Vaillant, A. A., Gopaul, D., Soodeen, S., Arozarena-Fundora, R., Barbosa, O. A., Unakal, C., Thompson, R., Pandit, B., Umakanthan, S., & Akpaka, P. E. (2024). Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Molecules Involved in Its Imunopathogenesis, Clinical Features, and Treatment. Molecules, 29(4), 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040747







