Enhanced Molecularly Imprinted Fluorescent Test Strip for Rapid and Visual Detection of Norfloxacin via a Smartphone
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
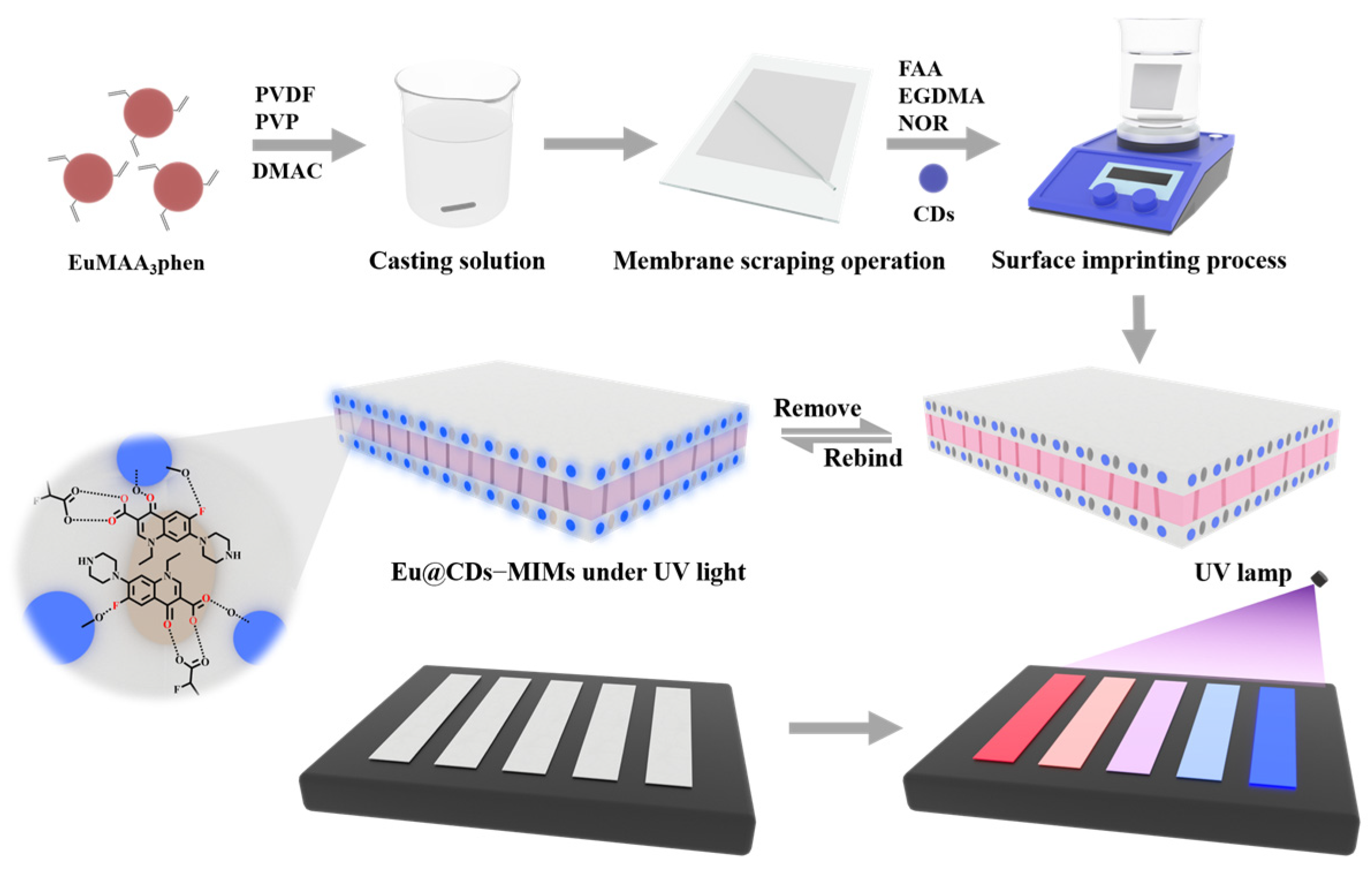
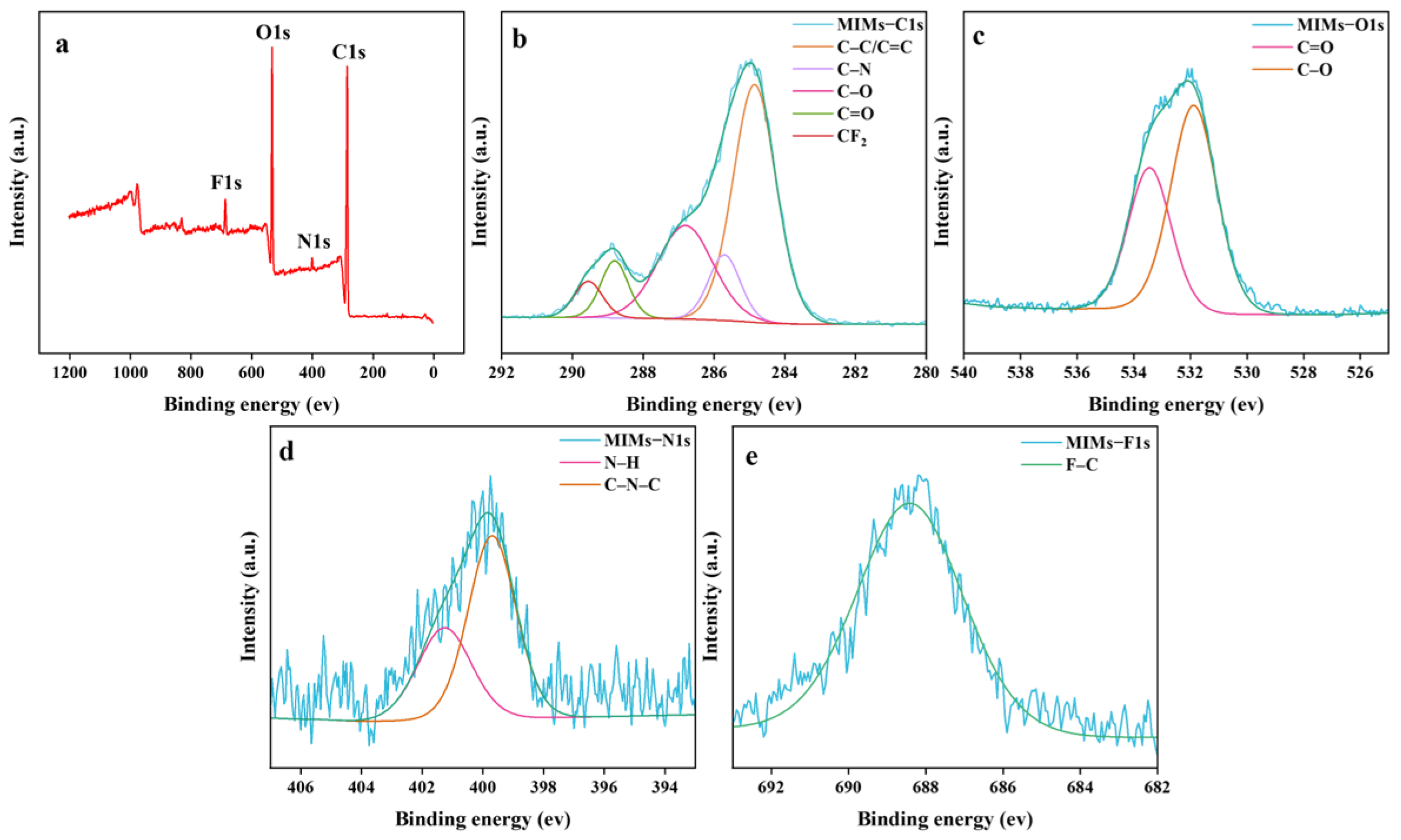
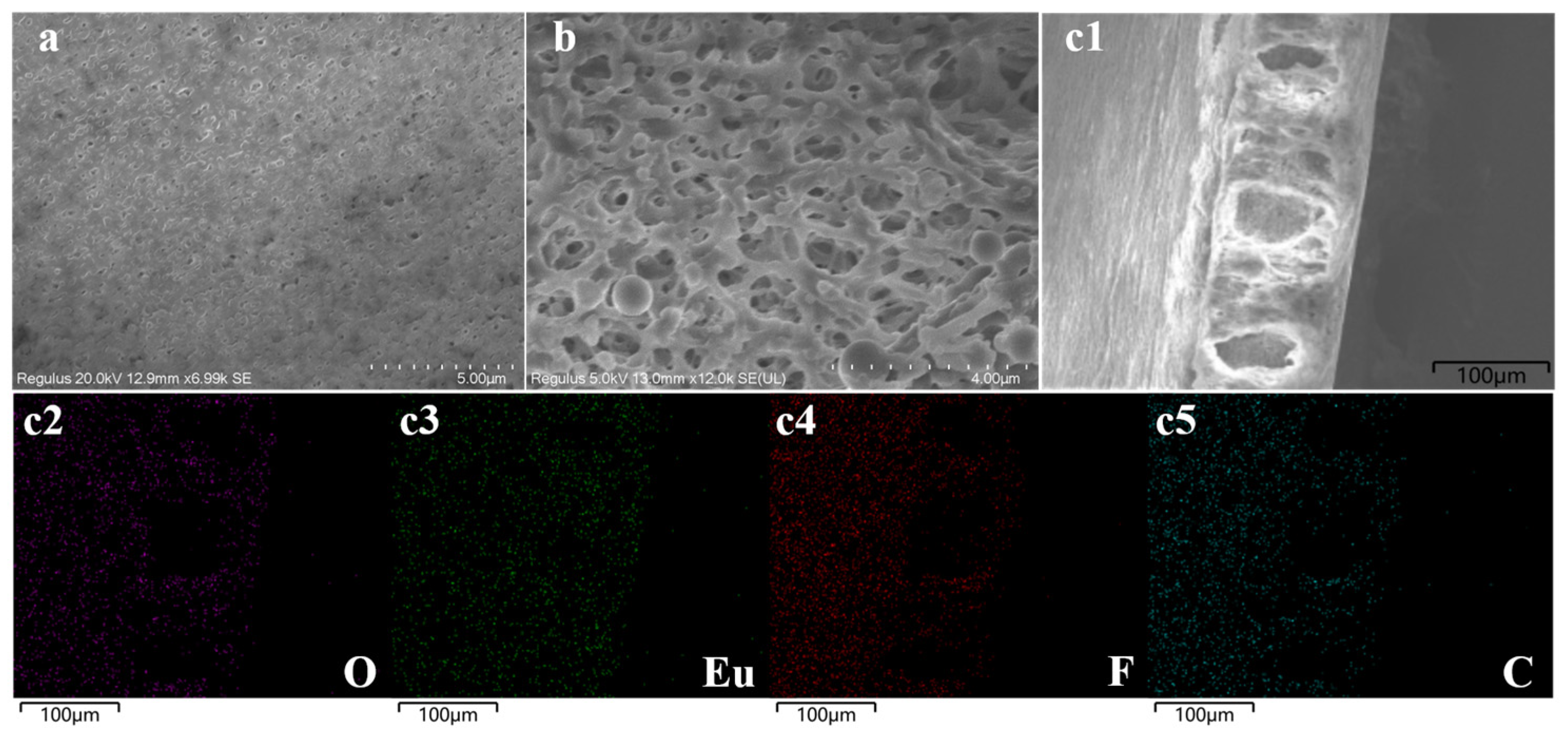
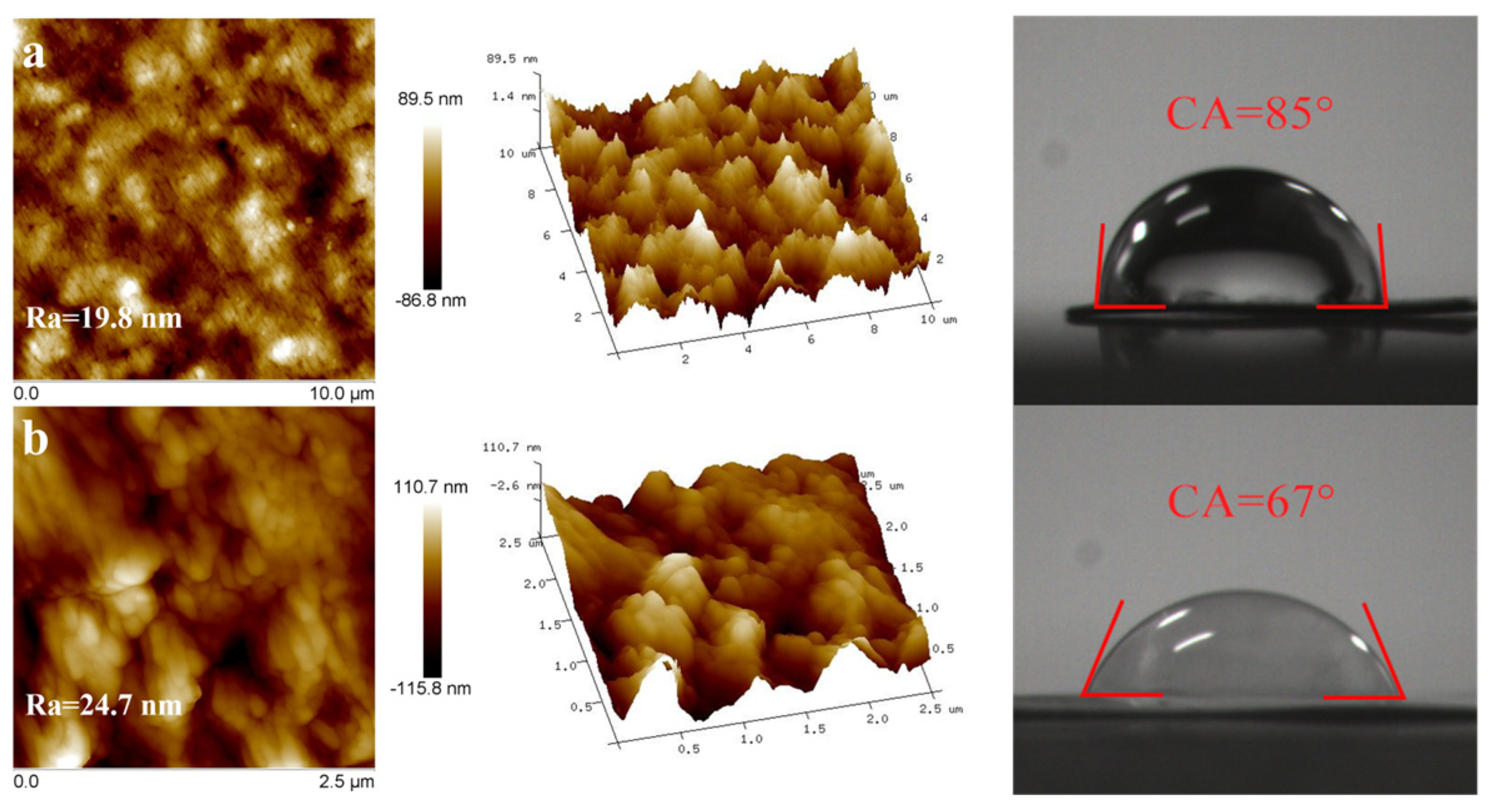
2.1. Characterization of Eu@CDs-MIMs
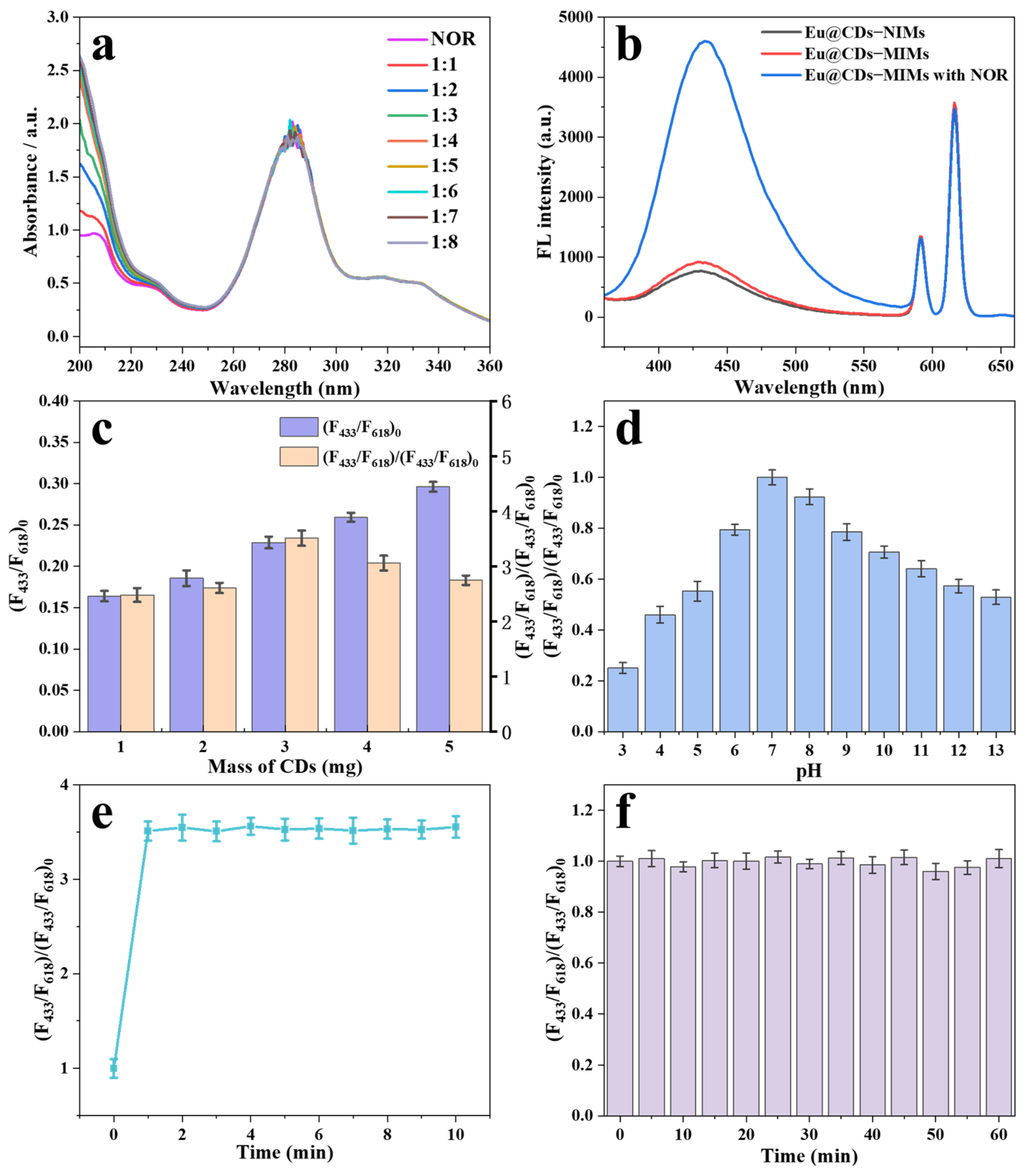
2.2. Optimization of the Molar Ratio of NOR to FAA
2.3. Optimization of the Excitation Wavelength
2.4. Optimize Doping Amount of CDs
2.5. Optimization of the Detection Conditions
2.6. Fluorescence Detection of Eu@CDs-MIMs and Eu@CDs-NIMs
2.7. Selectivity Determination of Eu@CDs-MIMs and Eu@CDs-NIMs
2.8. Interference of Ions on Eu@CDs-MIMs and Eu@CDs-NIMs
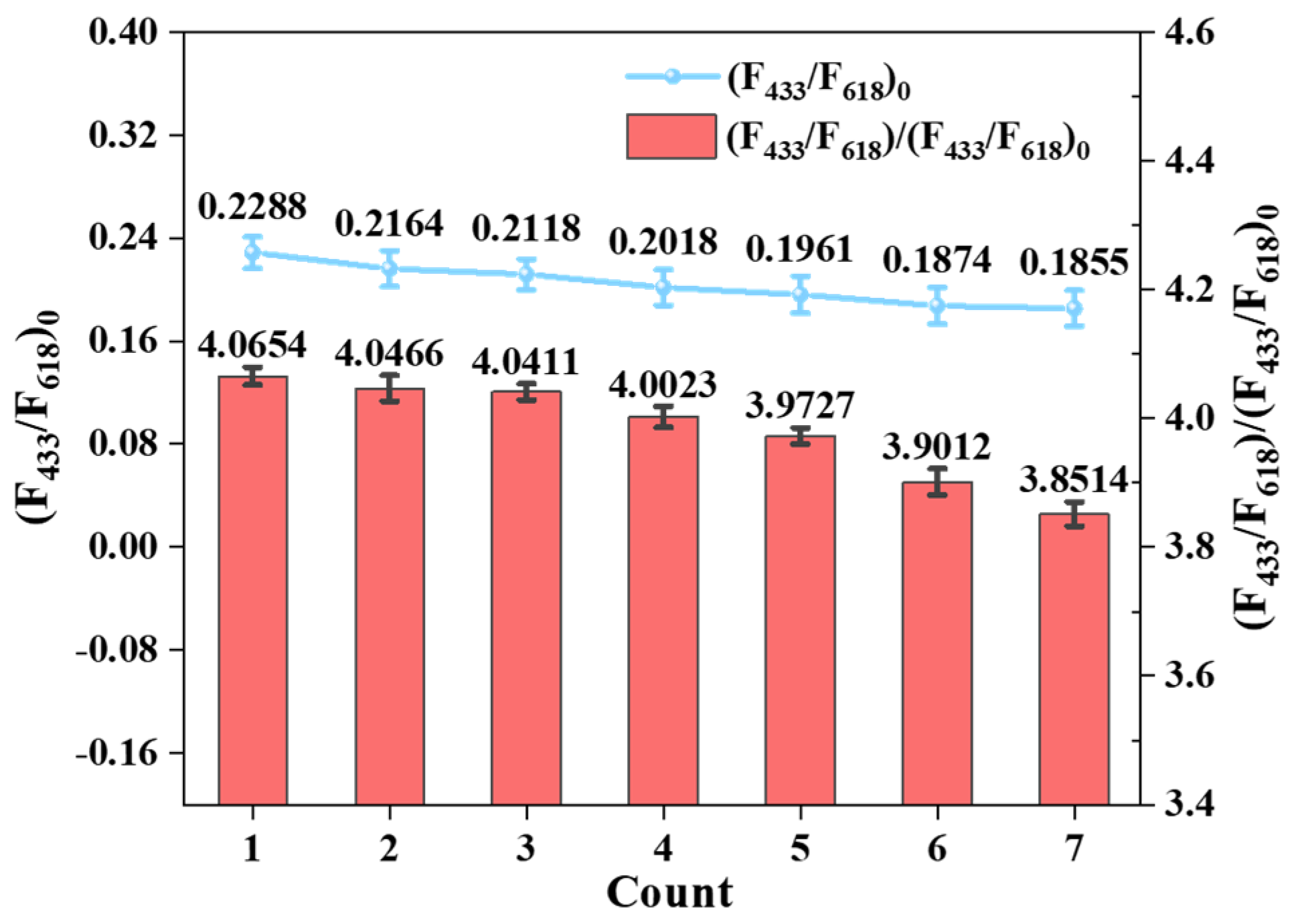
2.9. Reusability Research on Eu@CDs-MIMs
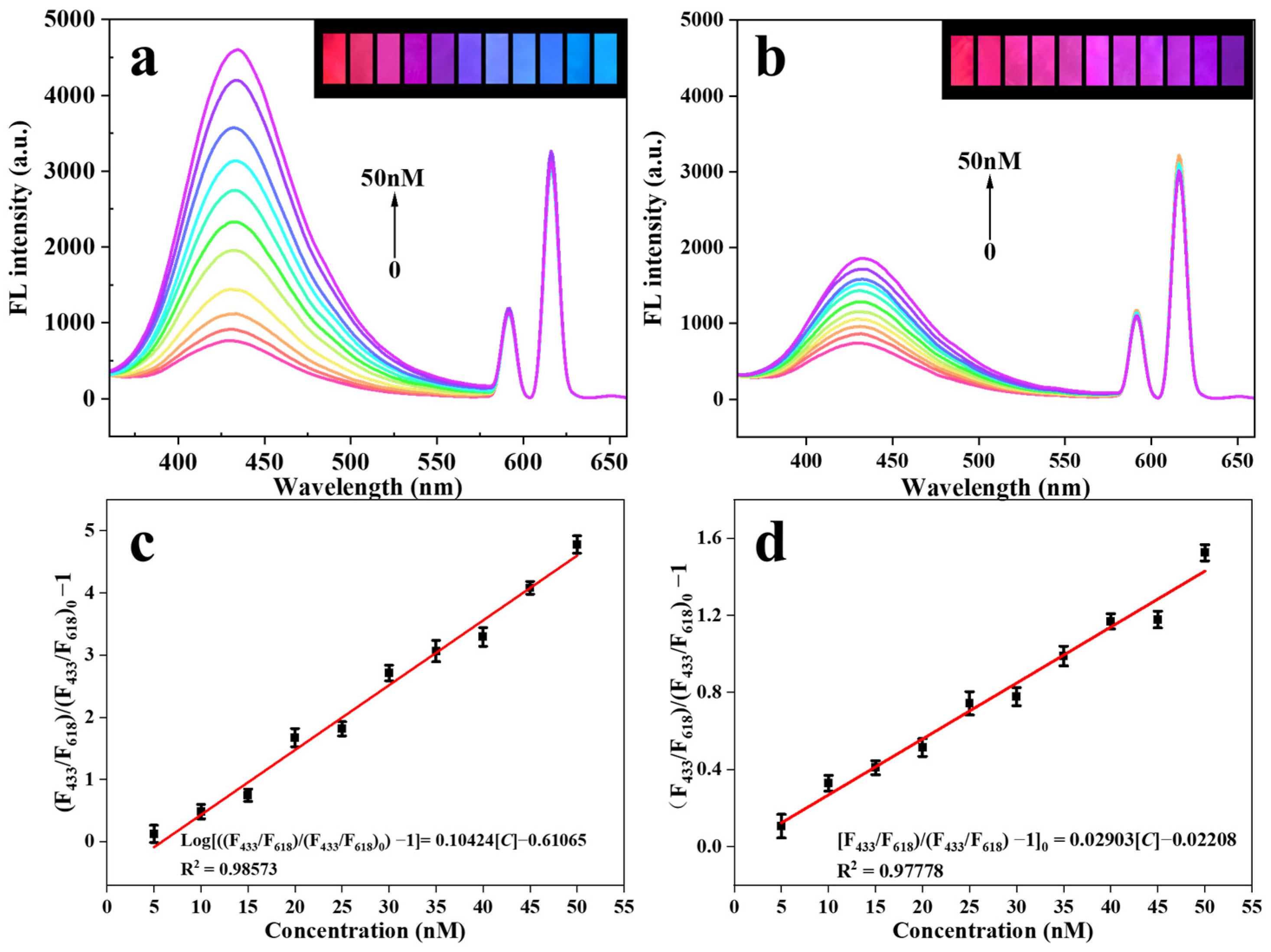
2.10. Fluorescent Test Strip Detection of NOR
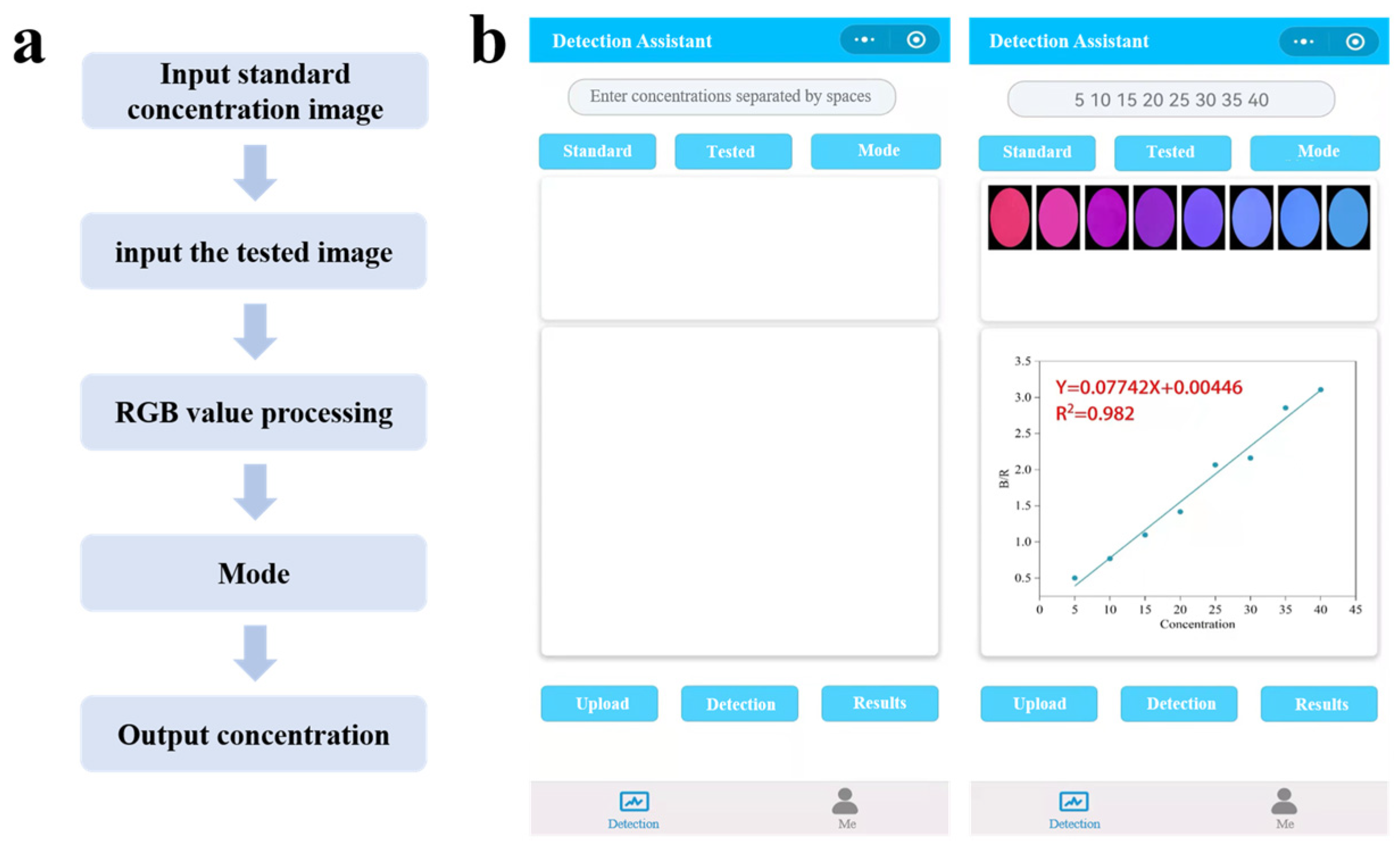
2.11. Smartphone-Assisted Visual Sensing Detection
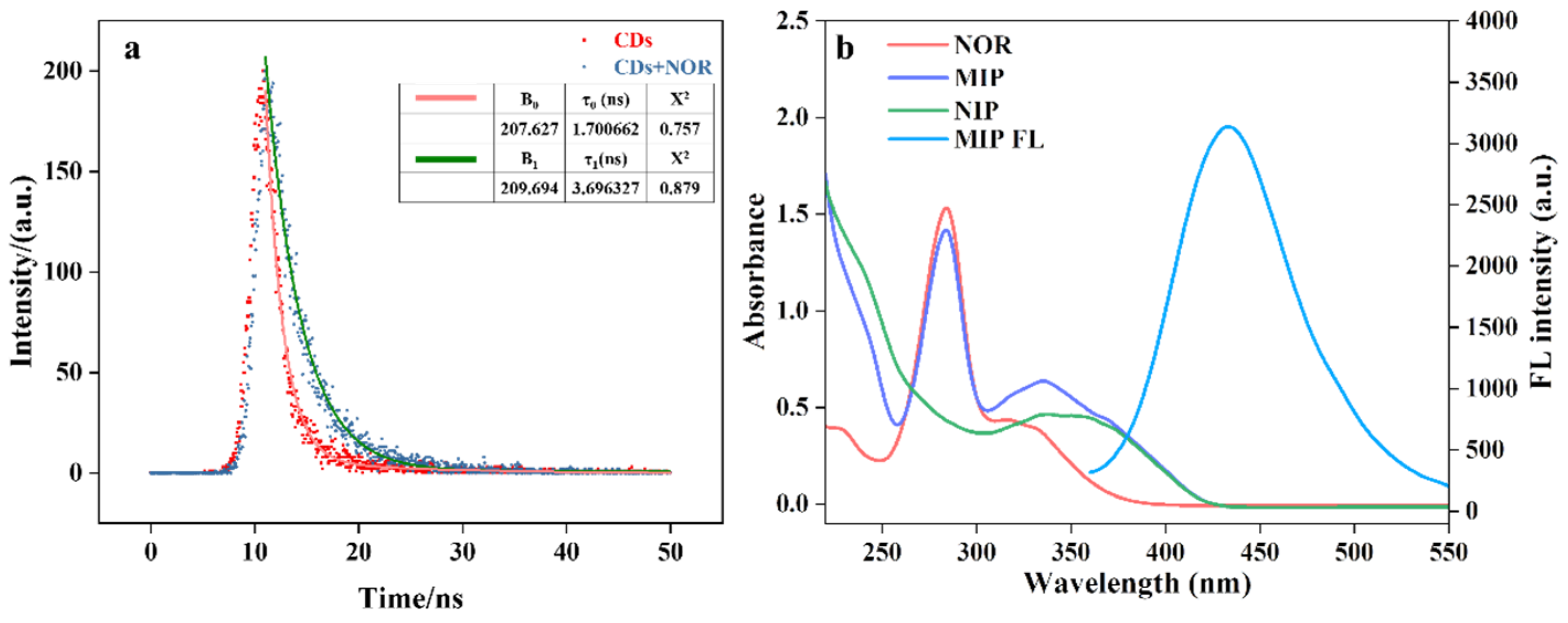
2.12. Study on the Mechanism of Fluorescence Enhancement
2.13. Real Water Sample Analysis
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Apparatus
3.3. Synthesis of CDs
3.4. Preparation of Eu(MAA)3phen
3.5. Preparation of Eu/CDs-MIPs
3.6. Preparation of Eu@PVDF
3.7. Preparation of Eu@CDs-MIMs
3.8. Fluorescence Measurements
3.9. HPLC Analysis of Actual Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andriole, V.T. The quinolones: Past, present, and future. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 41, S113–S119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldred, K.J.; Kerns, R.J.; Osheroff, N. Mechanism of quinolone action and resistance. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 1565–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolle, L.E.; Madsen, K.S.; Debeeck, G.O.; Blochlinger, E.; Borrild, N.; Bru, J.P.; McKinnnon, C.; O’Doherty, B.; Spiegel, W.; Van Balen, F.A.M.; et al. Three days of pivmecillinam or norfloxacin for treatment of acute uncomplicated urinary infection in women. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 34, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beberok, A.; Wrzesniok, D.; Otreba, M.; Milinski, M.; Rok, J.; Buszman, E. Effect of norfloxacin and moxifloxacin on melanin synthesis and antioxidant enzymes activity in normal human melanocytes. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2015, 401, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, C.; Meirelles, G.C.; Barp, C.G.; Assreuy, J.; Silva, M.A.S.; Ponchel, G. Cyclodextrin based nanosponge of norfloxacin: Intestinal permeation enhancement and improved antibacterial activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 195, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janecko, N.; Pokludova, L.; Blahova, J.; Svobodova, Z.; Literak, I. Implications of fluoroquinolone contamination for the aquatic environment—A review. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 2647–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; Zhang, J.; Hu, J.; Li, X.; Li, B. Fluoroquinolone Residues in the Environment Rapidly Induce Heritable Fluoroquinolone Resistance in Escherichia coli. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 4784–4795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Liu, Q.; Pan, Y.; Xu, S.; Li, H.; Tang, J. The Research Status, Potential Hazards and Toxicological Mechanisms of Fluoroquinolone Antibiotics in the Environment. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Lin, C.; Lian, M.; Wang, A.; He, M.; Liu, X.; Ouyang, W. Riverine antibiotic occurrence and potential ecological risks in a low-urbanized and rural basin of the middle Yangtze River: Socioeconomic, land use, and seasonal effects. Environ. Res. 2023, 228, 115827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Sun, S.; Geng, J.; Ma, L.; Jiang, J.; Li, B.; Yabo, S.D.; Lu, L.; Fu, D.; Shen, J.; et al. Occurrence, distribution, and risk assessment of quinolone antibiotics in municipal sewage sludges throughout China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 453, 131322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Shi, H.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, H.; Feng, S. Molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor based on metal-covalent organic framework for specifically recognizing norfloxacin from unpretreated milk. Food Chem. 2023, 429, 136921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Lang, Y.; Guo, B.; Cao, Z.; Cheng, J.; Cai, D.; Shentu, X.; Yu, X. Indirect Competitive Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay Based on Broad-Spectrum Antibody for Simultaneous Determination of Thirteen Fluoroquinolone Antibiotics in Rana catesbeianus. Foods 2023, 12, 2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Fan, X.; Ding, Y.; Yi, L.; Ge, K.; Gu, Y. Design and fabrication of Zn@ZnO@Ag chip for Raman scattering analysis of norfloxacin in liquid milk, fish and animal feeds. Food Chem. 2023, 429, 136928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.; Zhao, M.; Wang, J.; Lian, Z. Selective extraction and detection of norfloxacin from marine sediment and seawater samples using molecularly imprinted silica sorbents coupled with HPLC. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 150, 110677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narenderan, S.T.; Meyyanathan, S.N.; Babu, B. Review of pesticide residue analysis in fruits and vegetables. Pre-treatment, extraction and detection techniques. Food Res. Int. 2020, 133, 109141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Yao, J.C.; Quan, Y.N.; Hu, M.Y.; Su, R.; Gao, M.; Han, D.L.; Yang, J.H. Monitoring the charge-transfer process in a Nd-doped semiconductor based on photoluminescence and SERS technology. Light-Sci. Appl. 2020, 9, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.L.; You, E.M.; Panneerselvam, R.; Ding, S.Y.; Tian, Z.Q. Advances of surface-enhanced Raman and IR spectroscopies: From nano/microstructures to macro-optical design. Light-Sci. Appl. 2021, 10, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Shi, G. Rational design of MoS2 QDs and Eu3+ as a ratiometric fluorescent probe for point-of-care visual quantitative detection of tetracycline via smartphone-based portable platform. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1198, 339572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Li, J.H.; Wang, X.Y.; Peng, H.L.; Xiong, H.; Chen, L.X. Strategies of molecular imprinting-based fluorescence sensors for chemical and biological analysis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 112, 54–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Wang, P.; Zheng, R.; Zhao, Z.; An, J.; Hao, C.; Kang, M. Preparation of molecularly imprinted ratiometric fluorescence sensor for visual detection of tetrabromobisphenol A in water samples. Mikrochim. Acta 2023, 190, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Xu, W.; Hong, J.Q.; Zheng, Y.N.; Fan, H.Z.; Zhang, J.; Fei, J.W.; Zhu, W.Y.; Hong, J.L. A molecularly imprinted ratiometric fluorescence sensor based on blue/red carbon quantum dots for the visual determination of thiamethoxam. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 238, 115559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Chen, H. Ratiometric fluorescence molecularly imprinted sensor based on dual-emission quantum dots hybrid for determination of tetracycline. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 5809–5816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Dai, J.; Xu, Y.; Dai, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, W.; Sellergren, B.; Pan, G. Molecularly Imprinted Fluorescent Test Strip for Direct, Rapid, and Visual Dopamine Detection in Tiny Amount of Biofluid. Small 2019, 15, e1803913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Zheng, B.; Wei, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Kou, L.; Shang, N. Portable smartphone-assisted ratiometric fluorescent test paper based on one-pot synthesized dual emissive carbon dots for visualization and quantification of mercury ions. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2023, 415, 5769–5779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Huo, X.; Lu, H.; Feng, S.; Wang, D.; Liu, H. Recyclable fluorescent paper sensor for visual detection of nitroaromatic explosives. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 265, 476–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ning, D.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, T.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Z. Dual-Colored Carbon Dot Ratiometric Fluorescent Test Paper Based on a Specific Spectral Energy Transfer for Semiquantitative Assay of Copper Ions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 18897–18903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Nian, Q.; Dai, H.; Wan, X.; Xu, Q. A nanofiber-mat-based solid-phase sensor for sensitive ratiometric fluorescent sensing and fine visual colorimetric detection of tetracycline. Food Chem. 2022, 395, 133597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, X.; Tian, Y.; Duan, Y. Electrospun nanofiber-based indicatorpaper sensing platform for fluorescence and visualization detection of norfloxacin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 238, 115562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.C.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Shan, C.X.; Feng, Z.Q.; Li, J.S.; Song, C.L.; Bao, Y.N.; Qi, X.H.; Dong, B. A flexible and superhydrophobic upconversion-luminescence membrane as an ultrasensitive fluorescence sensor for single droplet detection. Light-Sci. Appl. 2016, 5, e16136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Xu, Y.Q.; Meng, M.J.; Li, C.X. PVDF-based molecularly imprinted ratiometric fluorescent test paper with improved visualization effect for catechol monitoring. Microchem. J. 2022, 178, 107369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, H.; Ma, A.; Wang, J.; Sun, B. Sensitive detection of Pyrraline using a ZnCdSe/ZnS quantum dot molecularly imprinted polyethersulfone fluorescent membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 685, 121948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Shao, H.; Xiao, M.; Sun, J.; Jin, M.; Jin, F.; Wang, J.; Abd El-Aty, A.M.; She, Y. Development of a time-resolved fluorescence microsphere Eu lateral flow test strip based on a molecularly imprinted electrospun nanofiber membrane for determination of fenvalerate in vegetables. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 957745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.; Shi, H.; Han, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, R.; Men, J. Molecularly imprinted polymers by the surface imprinting technique. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 145, 110231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, D. Molecularly Imprinted Ratiometric Fluorescence Nanosensors. Langmuir 2022, 38, 13305–13312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Li, H.; Liu, J.; Kong, W.; Zhao, S.; Li, C.; Huang, H.; Liu, Y.; Kang, Z. Convenient and sensitive detection of norfloxacin with fluorescent carbon dots. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 7964–7970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Yan, Y.; Chen, J.; Dai, J.; Dai, X. Separation of adjacent heavy rare earth Lutetium (III) and Ytterbium (III) by task-specific ionic liquid Cyphos IL 104 embedded polymer inclusion membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 610, 118263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BelBruno, J.J. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 94–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polishchuk, A.V.; Karaseva, É.T.; Emelina, T.B.; Nikolenko, Y.M.; Karasev, V.E. Electronic structure and specroscopic properties of norfloxacin, enoxacin, and nalidixic acid. J. Struct. Chem. 2009, 50, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Yi, C.; Sun, J.; Zang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, M.; Xu, J. Self-quenching-resistant solid-state carbon dots for mechanism and applications. Mikrochim. Acta 2021, 188, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Chen, L. Preparation of molecularly imprinted polymer coated quantum dots to detect nicosulfuron in water samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 8087–8095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroughirad, S.; Haddadi-Asl, V.; Khosravi, A.; Salami-Kalajahi, M. Magnetic halloysite-based molecularly imprinted polymer for specific recognition of sunset yellow in dyes mixture. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2020, 32, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Gong, Z.; Yang, S.; Xiong, T.; Wang, D.; Fan, M. Fluorescent and visual detection of norfloxacin in aqueous solutions with a molecularly imprinted polymer coated paper sensor. Talanta 2020, 208, 120435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jiang, Y.H.; Liu, Y.; Yao, C. Y3+@CdTe quantum dot nanoprobe as a fluorescence signal enhancement sensing platform for the visualization of norfloxacin. Analyst 2023, 148, 3776–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Ouyang, F.; Zheng, Z.; Huang, X.; Zhang, H.; He, D.; He, S.; Wei, H.; Yu, C.Y. A smartphone-integrated portable platform based on polychromatic ratiometric fluorescent paper sensors for visual quantitative determination of norfloxacin. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1279, 341837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Hu, B.; Lv, J.; Li, Y.; Shao, J.; Ma, Y.; Cui, Y. Enhanced ratiometric fluorescence molecularly imprinted nanosensor based on CDs for selective and visual detection of NOR in water samples. Opt. Mater. 2022, 132, 112784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Gao, S.; Han, X.; Yang, L. Comparison of Immunochromatographic Strips Using Colloidal Gold, Quantum Dots, and Upconversion Nanoparticles for Visual Detection of Norfloxacin in Milk Samples. Food Anal. Methods 2020, 13, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.F.; Li, M.Y.; Wang, L.; Song, Y.H. Linker engineering to regulate the fluorescence of hydrazone-linked covalent organic frameworks for the real-time visual detection of norfloxacin and multiple information encryption. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 23829–23836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Q.H.; Xia, Y.; Kang, Y.K.; Jiang, Y.M.; Hu, J.H.; Ma, P.H.; Tao, Z.; Xiao, X. A new supramolecular fluorescent probe based on cucurbit[8]uril for visual determination of norfloxacin: Multi-color, quantitative detection, and practical applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 477, 146922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.X.; Wen, X.H.; Shi, C.T.; Wu, L.; Long, Z.; He, J.; Hou, X.D. Multi-color fluorescence sensing platform for visual determination of norfloxacin based on a terbium (III) functionalized covalent organic framework. Food Chem. 2023, 417, 135883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serna-Galvis, E.A.; Jojoa-Sierra, S.D.; Berrio-Perlaza, K.E.; Ferraro, F.; Torres-Palma, R.A. Structure-reactivity relationship in the degradation of three representative fluoroquinolone antibiotics in water by electrogenerated active chlorine. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 315, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Chen, L.; Yu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Dai, J.; Yan, Y.; Ma, Z. Hollow molecularly imprinted fluorescent sensor using europium complex as functional monomer for the detection of trace 2,4,6-trichlorophenol in real water samples. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 246, 119051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Visual Sensor Name | Target | LOD | Response Time (min) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eu@CDs-MIMs | NOR | 1.35 nM | 1 | This work |
| MIP-CP | NOR | 81 nM | 30 | [42] |
| Y3+@CdTe QDs | NOR | 31.8 nM | 5 | [43] |
| B/RCDs@Fe3+ | NOR | 6.84 nM | 3 | [44] |
| PAN/ATP/Tb | NOR | 16 nM | 3 | [28] |
| CdTe@SiO2@FMIPs | NOR | 3.28 nM | 1 | [45] |
| UCNPs-FICS | NOR | 6.04 nM | 10 | [46] |
| COFBMTH-HB | NOR | 0.159 μM | 1 | [47] |
| DBXPY@Q [8] | NOR | 0.72 μM | 1 | [48] |
| Tb@COF-Ru | NOR | 0.33 nM | 1 | [49] |
| Samples | Eu@CDs-MIMs | HPLC Method | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Added (nM) | Found (nM) | Recover (%) | RSD (%, n = 3) | Found (nM) | Recover (%) | |
| Tap water | 10 | 9.3 | 93 | 3.2 | 9.8 | 98 |
| 20 | 21.2 | 106 | 2.9 | 20.2 | 101 | |
| 30 | 30.6 | 102 | 2.7 | 29.7 | 99 | |
| 40 | 41.5 | 103.8 | 3.6 | 39.8 | 99.5 | |
| 50 | 50.7 | 101.4 | 2.0 | 50.3 | 100.6 | |
| River water | 10 | 10.4 | 104 | 3.3 | 10.2 | 102 |
| 20 | 19.6 | 98 | 2.9 | 19.7 | 98.5 | |
| 30 | 31.5 | 105 | 2.6 | 30.3 | 101 | |
| 40 | 42.7 | 106.8 | 3.1 | 40.1 | 100.2 | |
| 50 | 49.3 | 98.6 | 2.4 | 49.8 | 99.6 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, B.; Zhao, W.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Z.; Yan, Y.; Meng, M. Enhanced Molecularly Imprinted Fluorescent Test Strip for Rapid and Visual Detection of Norfloxacin via a Smartphone. Molecules 2024, 29, 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29030661
Hu B, Zhao W, Chen L, Liu Y, Ma Z, Yan Y, Meng M. Enhanced Molecularly Imprinted Fluorescent Test Strip for Rapid and Visual Detection of Norfloxacin via a Smartphone. Molecules. 2024; 29(3):661. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29030661
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Bo, Wenshi Zhao, Li Chen, Yang Liu, Zhongfei Ma, Yongsheng Yan, and Minjia Meng. 2024. "Enhanced Molecularly Imprinted Fluorescent Test Strip for Rapid and Visual Detection of Norfloxacin via a Smartphone" Molecules 29, no. 3: 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29030661
APA StyleHu, B., Zhao, W., Chen, L., Liu, Y., Ma, Z., Yan, Y., & Meng, M. (2024). Enhanced Molecularly Imprinted Fluorescent Test Strip for Rapid and Visual Detection of Norfloxacin via a Smartphone. Molecules, 29(3), 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29030661








