Research and Performance Evaluation of Environmentally Friendly Shale Inhibitor TIL-NH2 for Shale Gas Horizontal Wells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
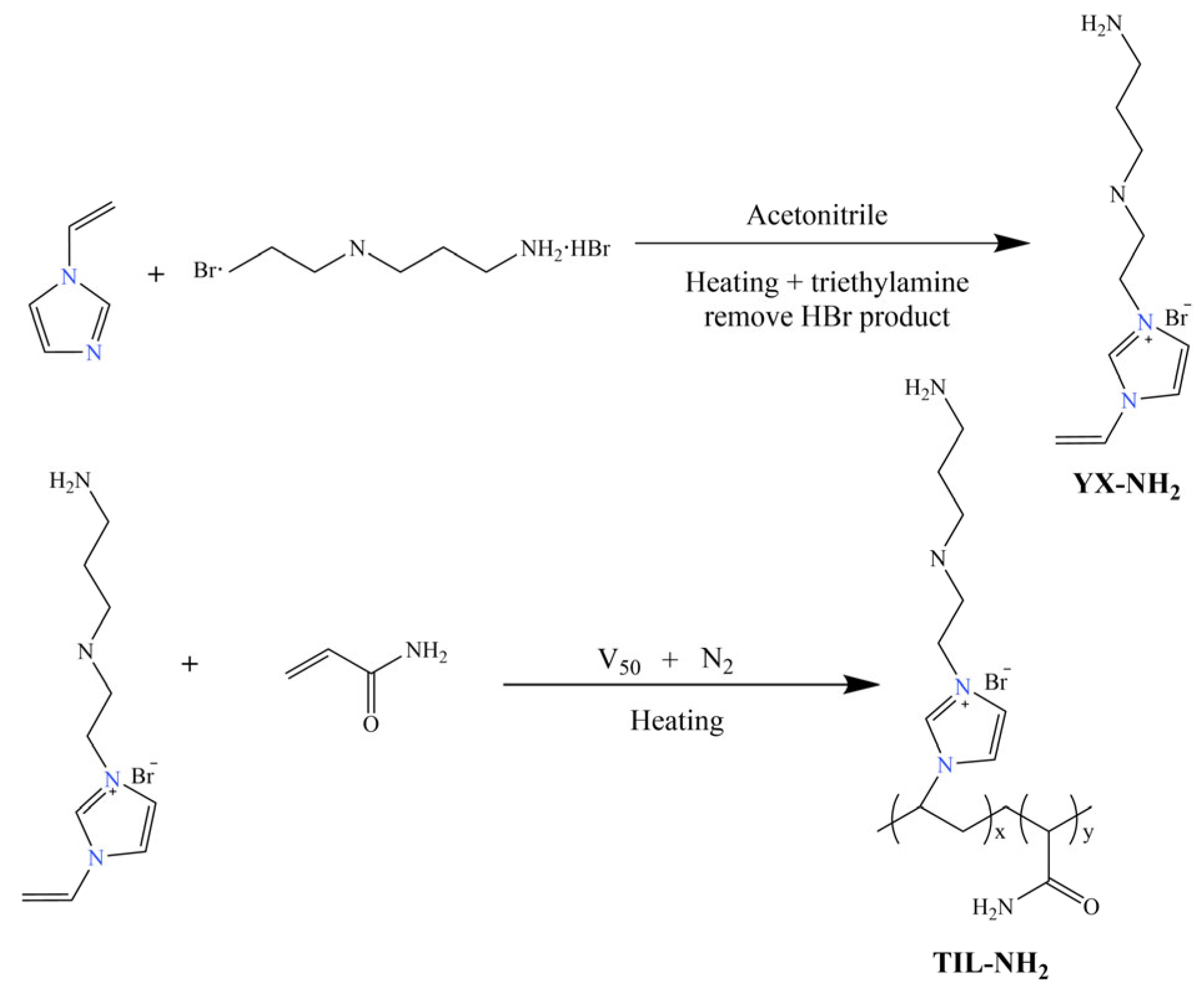
2.1. Preparation of the Inhibitor TIL-NH2
2.2. Physicochemical Characterization of TIL-NH2
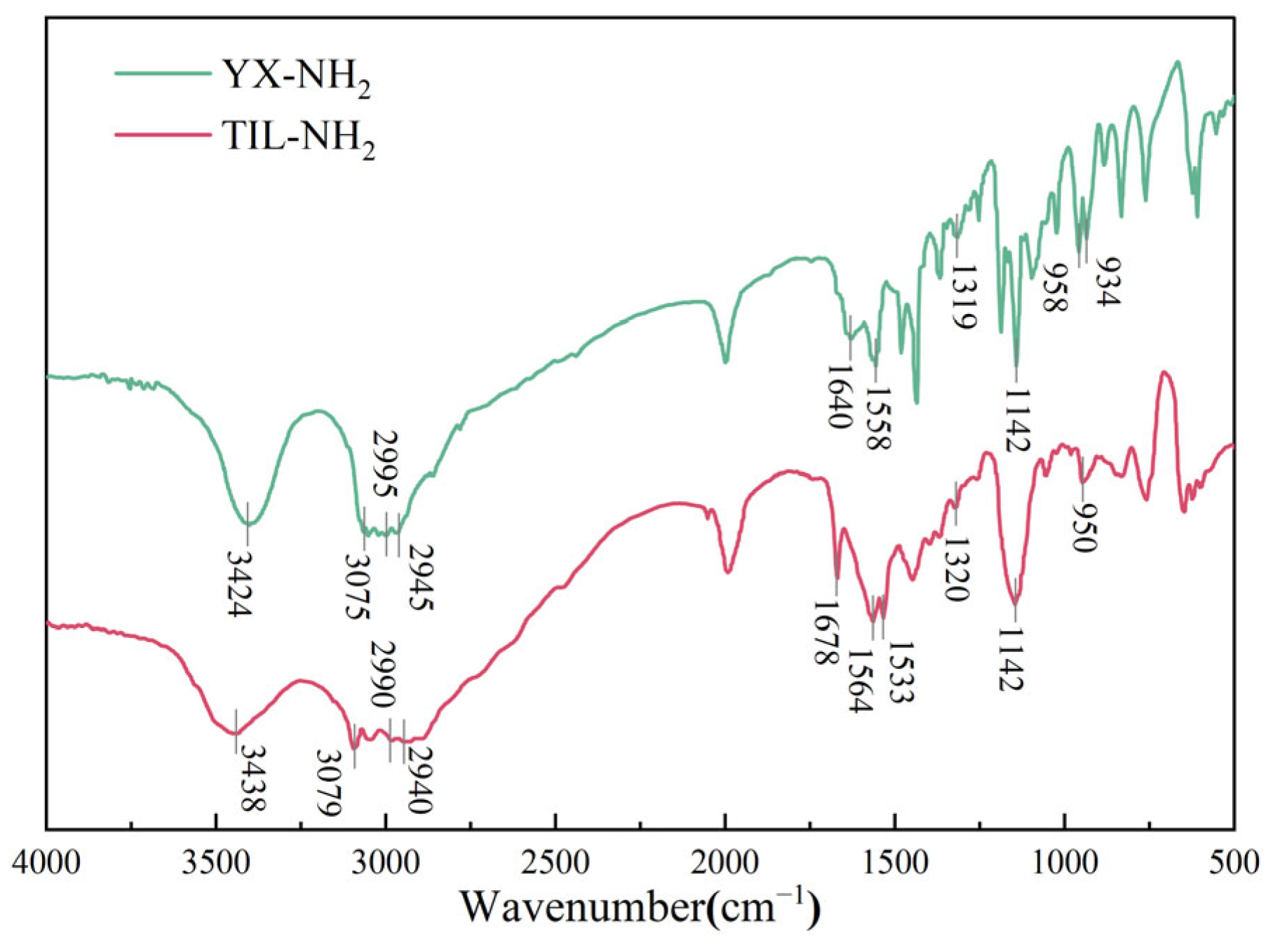
2.2.1. Infrared Spectroscopy
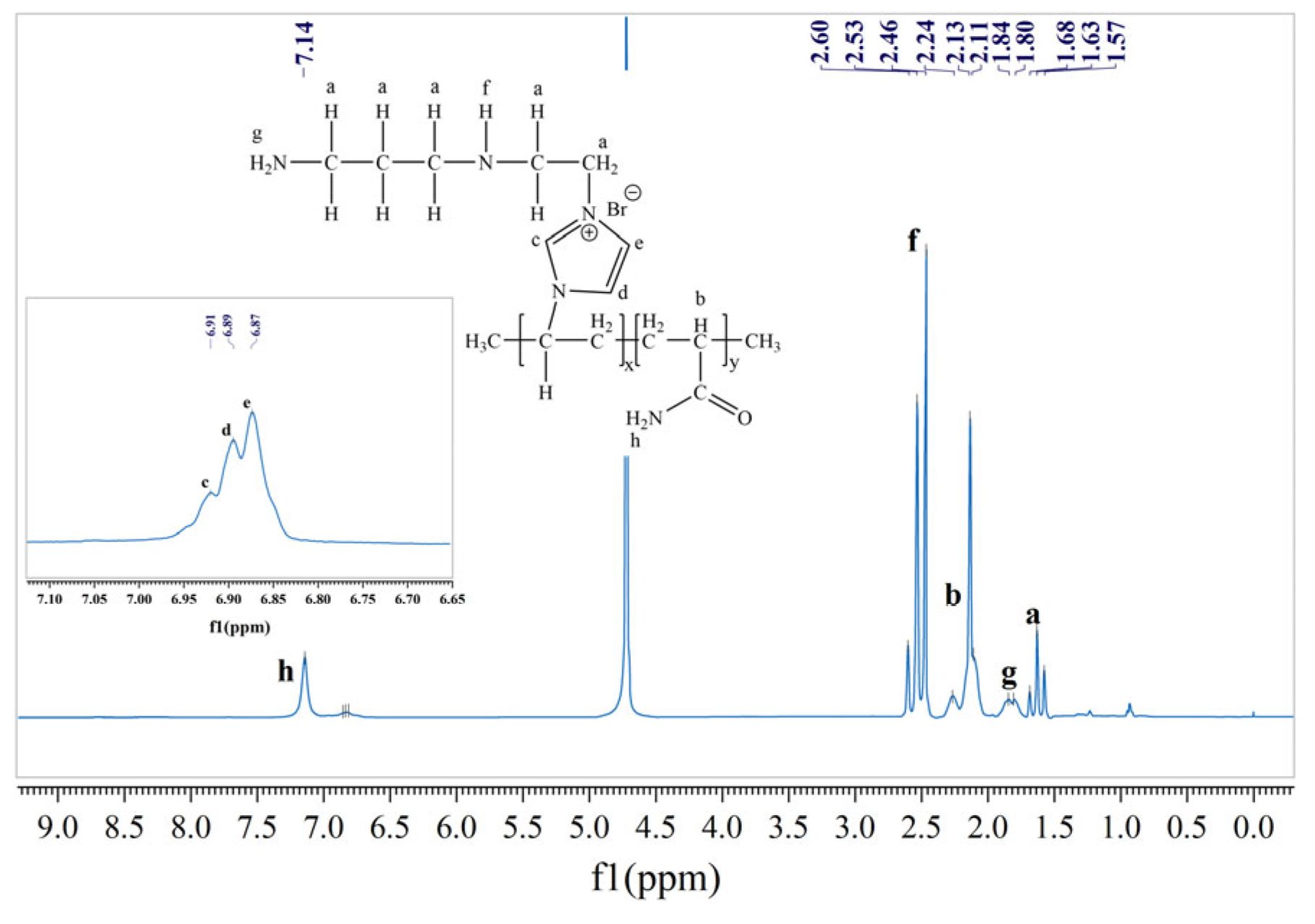
2.2.2. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectral Analysis
2.3. Performance Evaluation of TIL-NH2
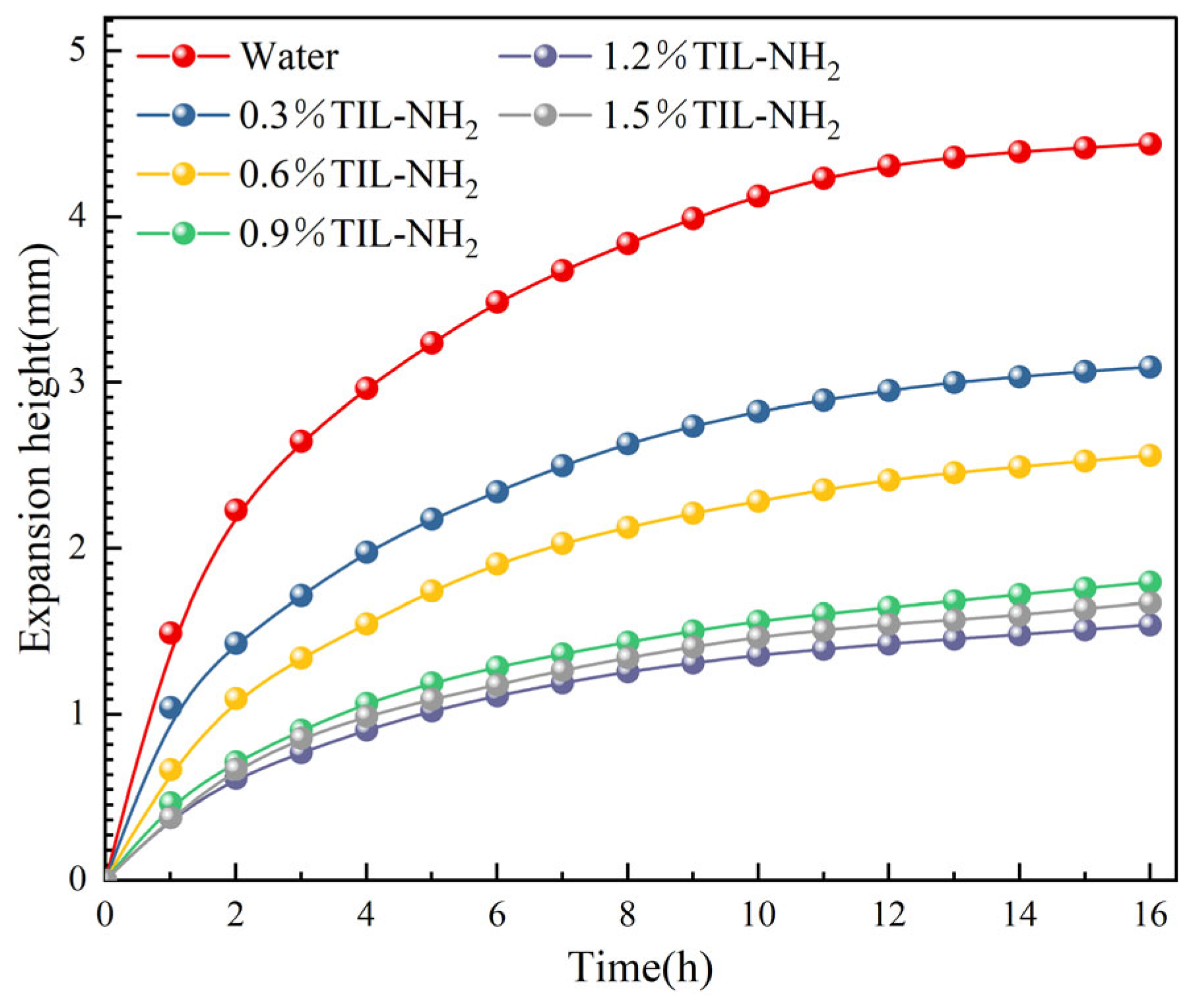
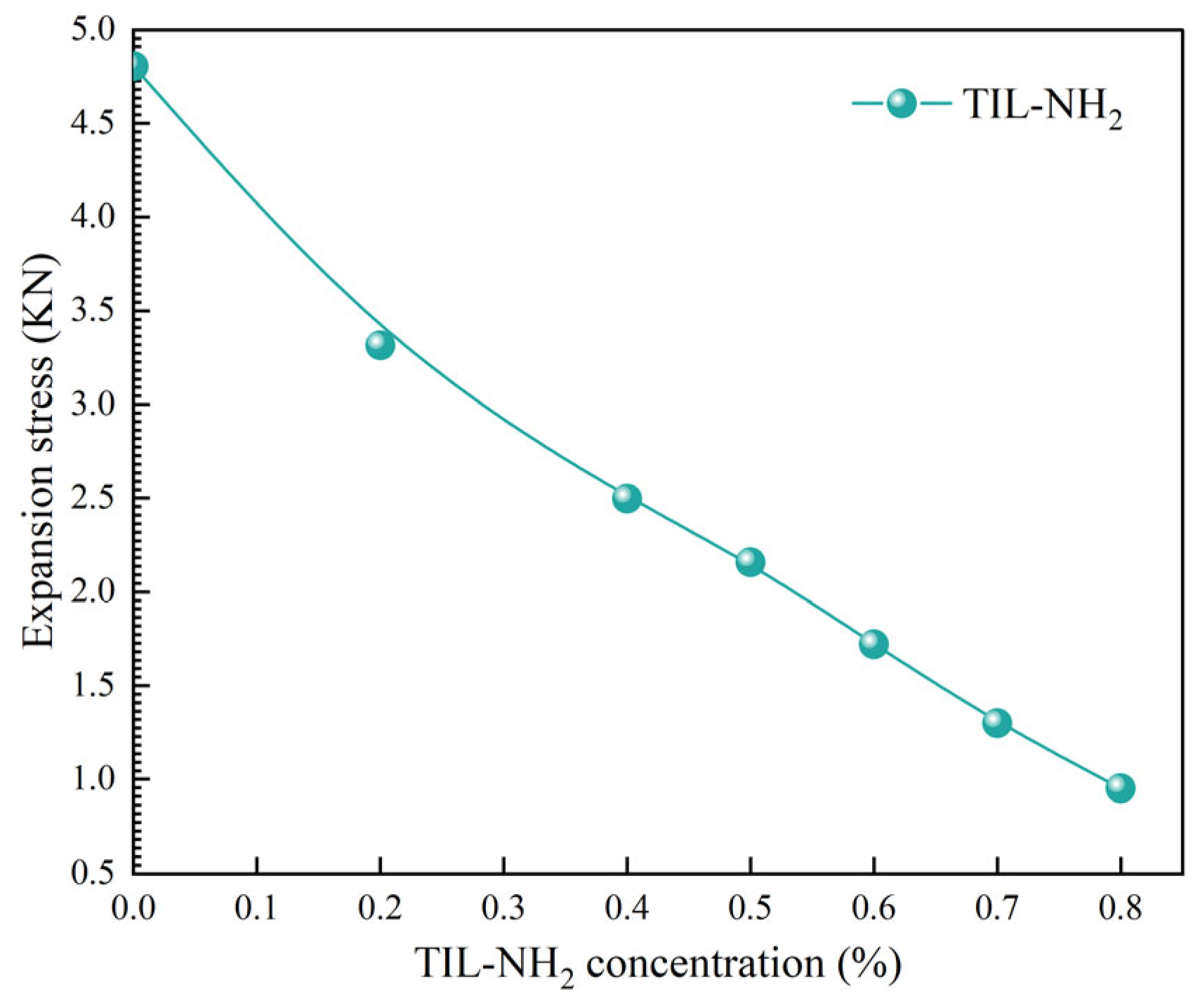
2.3.1. Linear Expansion Experiments
2.3.2. Rock Chip Rolling Recovery Experiment
2.3.3. Inhibitory Properties of Inhibitors on Ilmenite Hydration
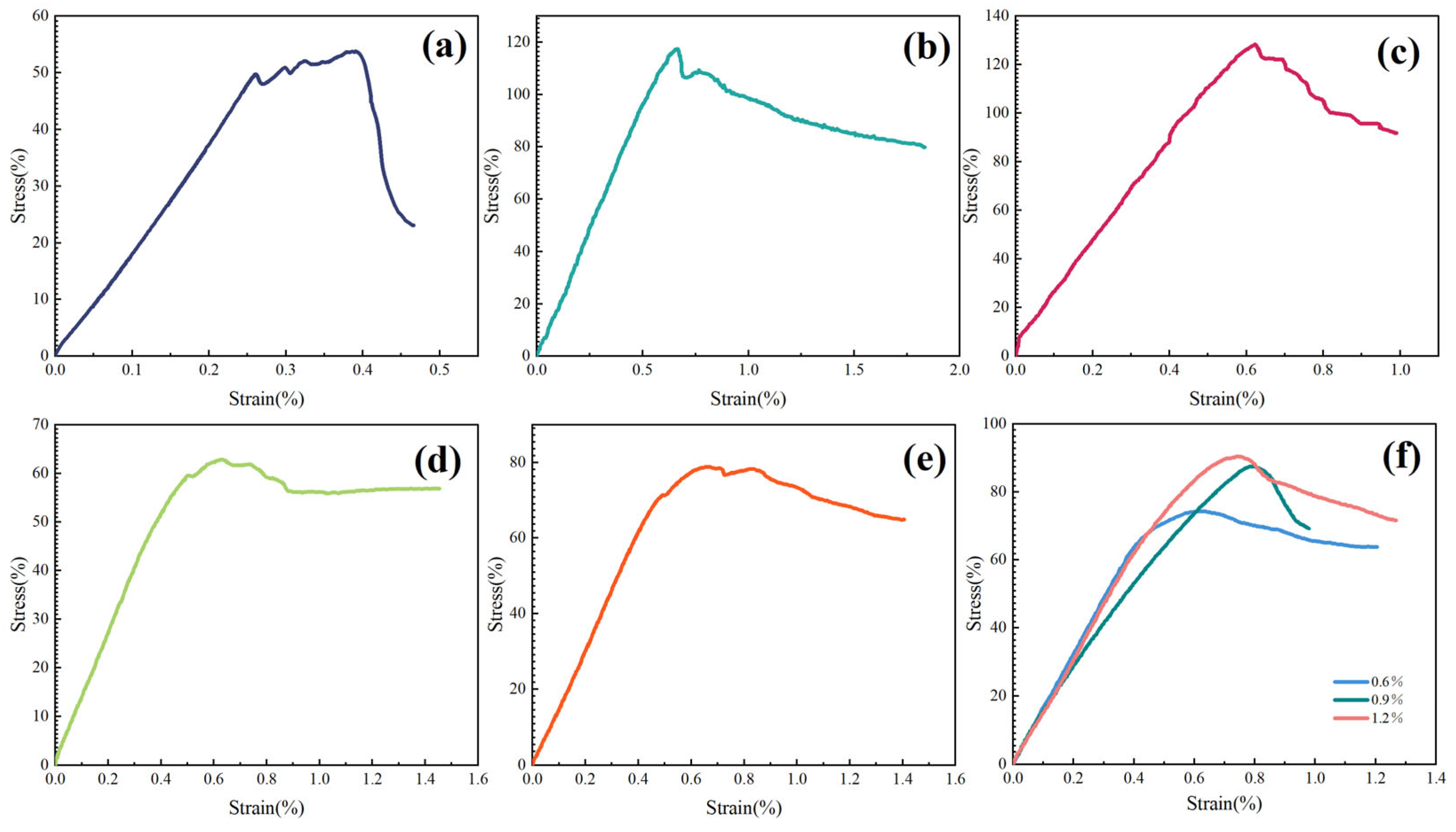
2.3.4. Effect of Inhibitors on Shale Compressive Strength
2.3.5. Effect of Inhibitors on Acoustic Time Differences in Shale Cores
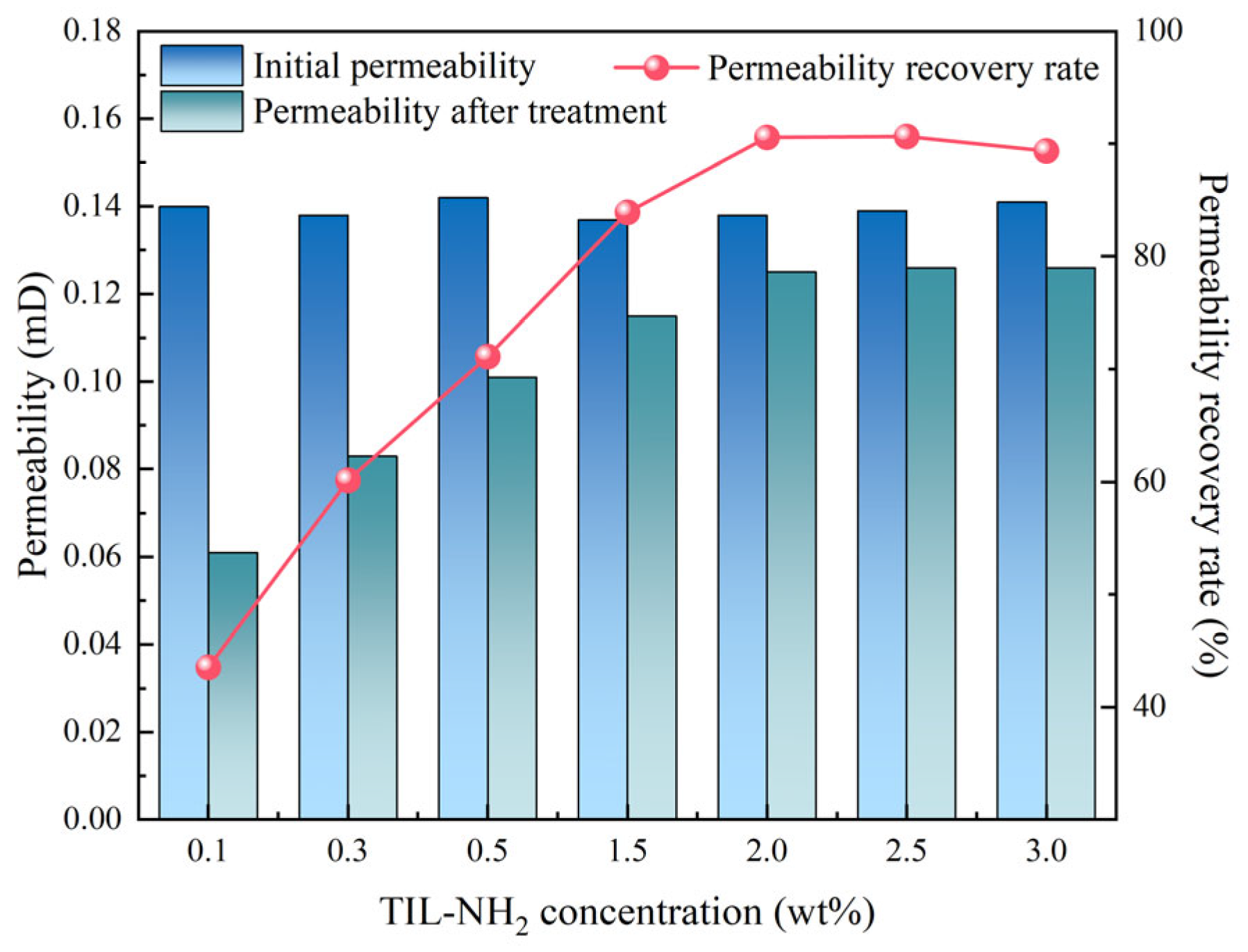
2.3.6. Effect of Inhibitors on Shale Permeability Recoverability
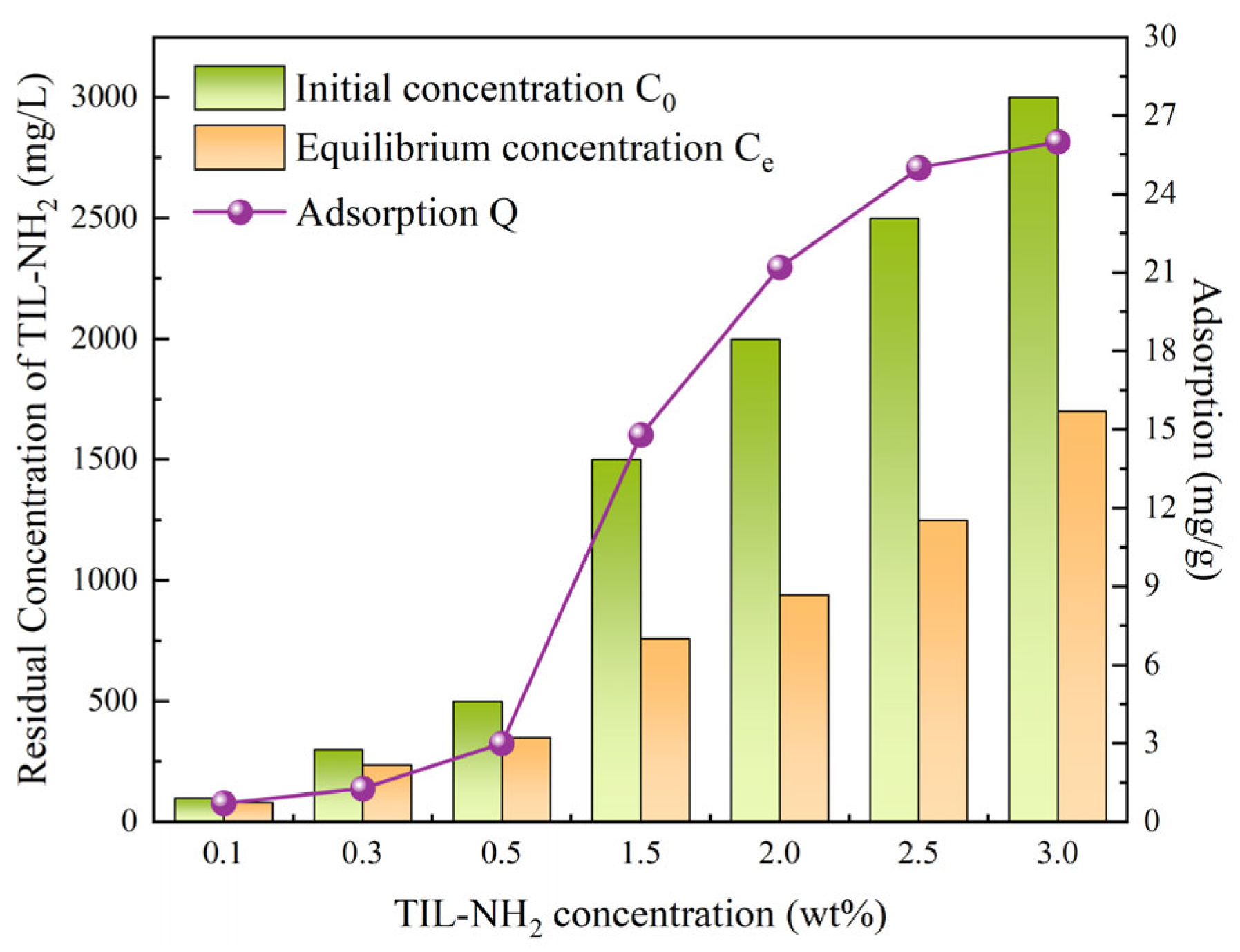
2.3.7. Analysis of the Dynamic Adsorption Behavior of Inhibitors
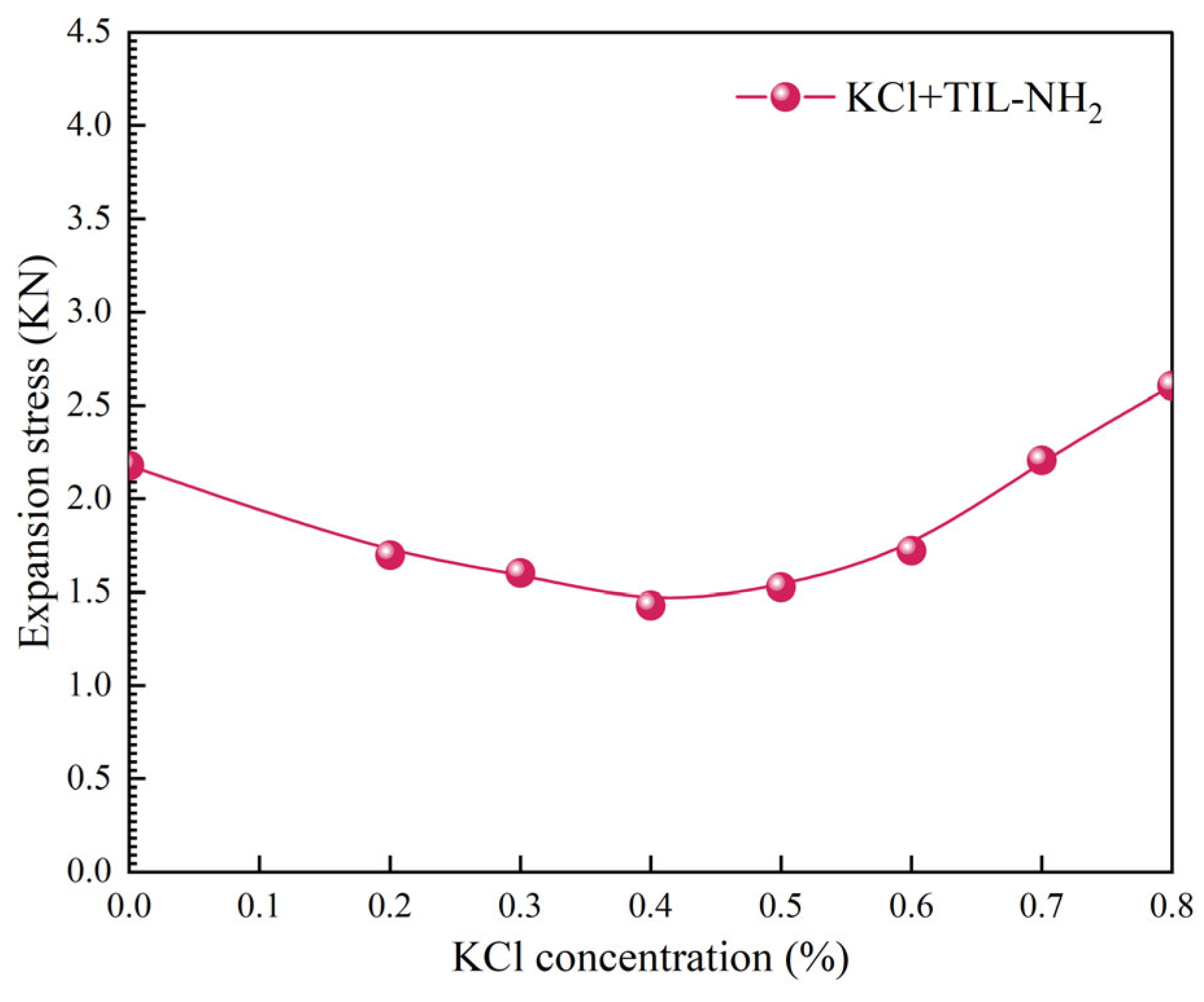
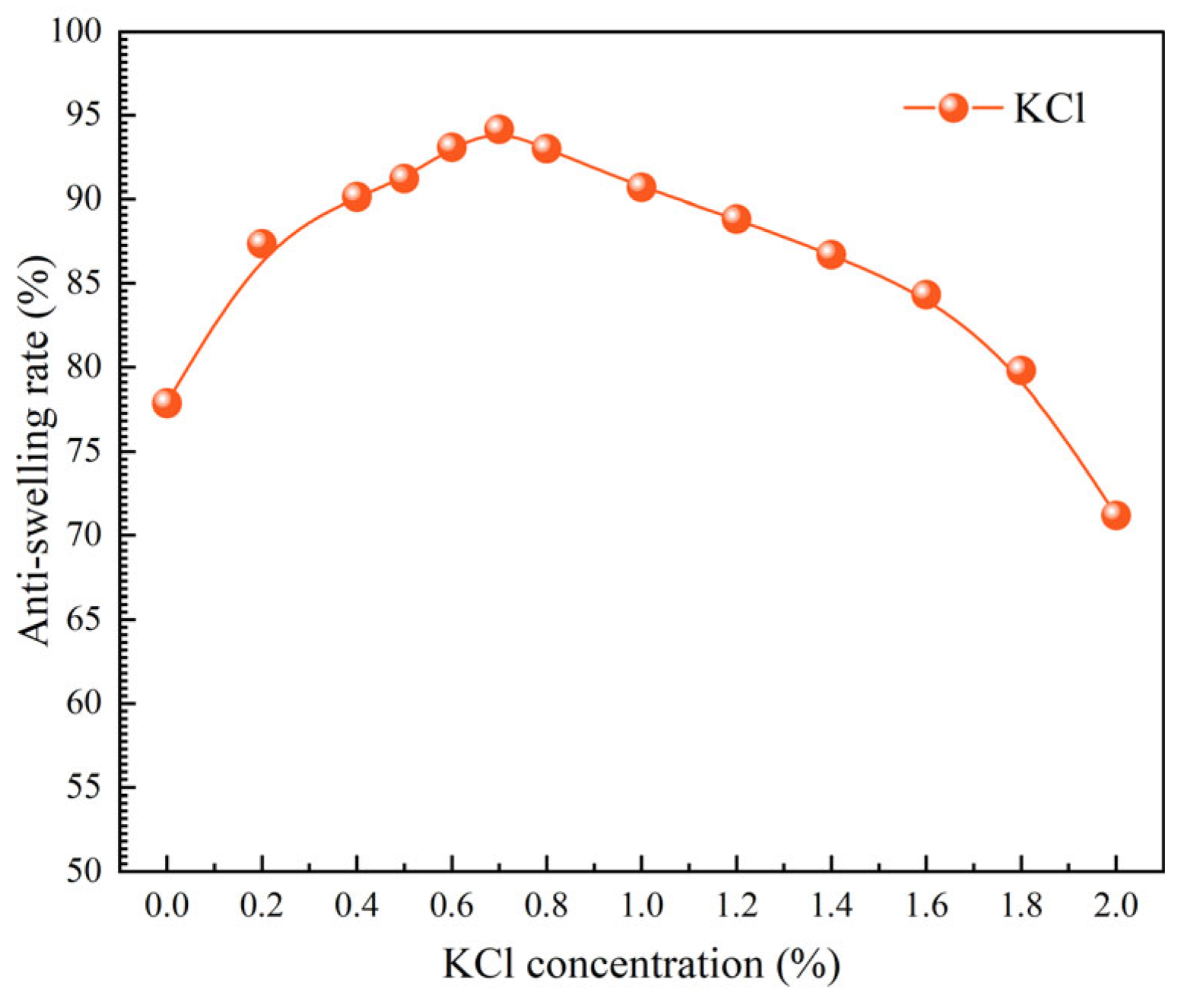
2.3.8. Evaluation of Salt Resistance
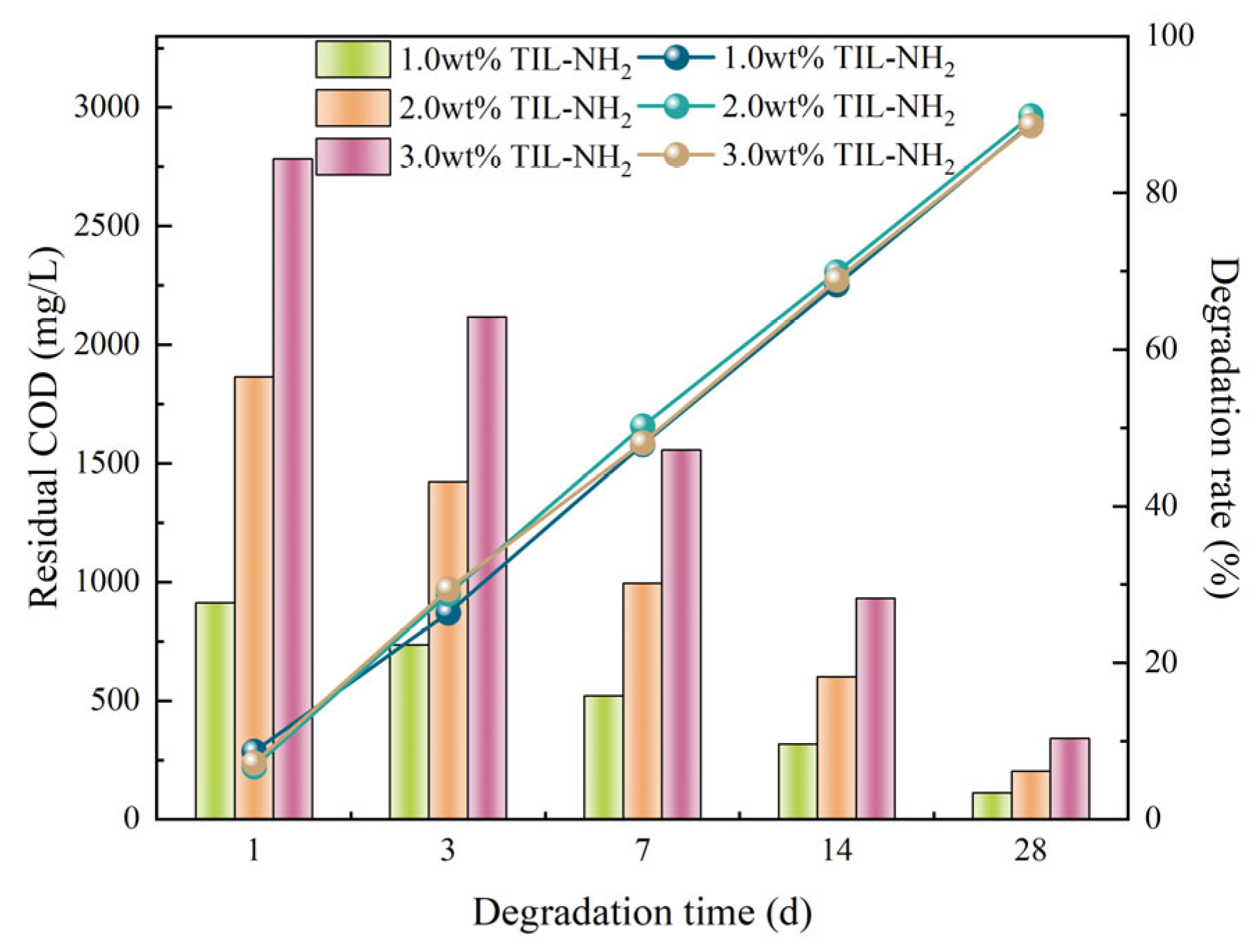
2.3.9. Environmental Friendliness Analysis
Biodegradability Performance
Toxicity Testing
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Materials and Instruments
4.1.1. Experimental Materials
4.1.2. Experimental Apparatus
4.2. Experimental Methods
4.2.1. Infrared Spectral Analysis
4.2.2. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectral Test
4.2.3. Rock Chip Rolling Recovery Experiments
4.2.4. Analysis of Anti-Expansion Properties
4.2.5. Core Acoustic Time Difference Analysis
4.2.6. Penetration Rate Resilience Analysis
4.2.7. Adsorption Behavior Analysis
4.2.8. Environmental Friendliness Test
Biodegradability Test
Acute Toxicity Test
Microbial Activity Inhibition Test
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zou, C.; Zhao, Q.; Dong, D.; Yang, Z.; Qiu, Z.; Liang, F.; Wang, N.; Huang, Y.; Duan, A.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Geological characteristics, main challenges and future prospect of shale gas. J. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2017, 2, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Nie, H.; Dang, W.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, G.; Li, W.; Lu, Z. Shale gas exploration and development in China: Current status, geological challenges, and future directions. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 6359–6379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. Shale gas exploitation: Status, problems and prospect. Natural Gas Ind. B 2018, 5, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zeng, W.; Liang, L.; Lei, M. Wellbore stability analysis for horizontal wells in shale formations. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 31, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A. A review of mathematical modelling approaches to tackling wellbore instability in shale formations. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2021, 89, 103870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokhani, V.; Yu, M.; Bloys, B. A wellbore stability model for shale formations: Accounting for strength anisotropy and fluid induced instability. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 32, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Liu, X.; Liang, L.; Xiong, J. Analysis of influencing factors of wellbore stability in shale formations. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Chang, Y.; Peng, K.; Bai, Y.; Luo, K.; Wu, T.; Ma, T. Research Progress on the Mechanisms and Control Methods of Rockbursts under Water-Rock Interactions. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Tang, W.; Chen, S.; Wang, E.; Wang, C.; Li, T.; Zhang, G. Damage Effect and Deterioration Mechanism of Mechanical Properties of Fractured Coal-Rock Combined Body Under Water-Rock Interaction. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2024, in press. [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Zhu, P.; Chen, Z. Impact of water-rock interactions on indicators of hydraulic fracturing flowback fluids produced from the Jurassic shale of Qaidam Basin, NW China. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, F. Theoretical insights, core technologies and practices concerning “volume development” of shale gas in China. Nat. Gas Ind. B 2019, 6, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Zou, C.; Dai, J.; Huang, S.; Zheng, J.; Gong, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Guan, Q.; Zhang, C.; et al. Suggestions on the development strategy of shale gas in China. J. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2016, 1, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Bian, X.; Wang, H.; Li, S.; Jia, C.; Liu, H.; Sun, H. Volume fracturing of deep shale gas horizontal wells. Nat. Gas Ind. B 2017, 4, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Sun, J.; Xie, S.; Huang, X.; Wang, R.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q. Novel use of a superhydrophobic nanosilica performing wettability alteration and plugging in water-based drilling fluids for wellbore strengthening. Energy Fuels 2022, 36, 6144–6158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Cui, Y.; Meng, Q.; He, M.; Yan, X. The effect of inorganic salt on the mechanical properties of montmorillonite and its mechanism: A molecular dynamics study. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2021, 781, 138982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Li, X.; Zhu, H.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, T.; Wu, X. Improved shale hydration inhibition with combination of gelatin and KCl or EPTAC, an environmentally friendly inhibitor for water-based drilling fluids. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Wang, X.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J.; Slaný, M. Synthesis, property and mechanism analysis of a novel polyhydroxy organic amine shale hydration inhibitor. Minerals 2020, 10, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Huang, P.; Wang, Q.; Han, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, F.; Pan, W.; Lv, K. Investigation of inhibition mechanism of three deep eutectic solvents as potential shale inhibitors in water-based drilling fluids. Fuel 2019, 244, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Dai, Z.; Li, C.; Lv, K.; Huang, X.; Sun, J.; Wei, B. Inhibition of the hydration expansion of sichuan gas shale by adsorption of compounded surfactants. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 6020–6026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtaza, M.; Kamal, M.S.; Hussain, S.S.; Mahmoud, M.; Syed, N.A. Quaternary ammonium gemini surfactants having different spacer length as clay swelling inhibitors: Mechanism and performance evaluation. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 308, 113054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.A.; Saleh, T.A. Synthesis of efficient stable dendrimer-modified carbon for cleaner drilling shale inhibition. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 9, 104792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, K.; Huang, X.; Li, H.; Sun, J.; Du, W.; Li, M. Modified biosurfactant cationic alkyl polyglycoside as an effective additive for inhibition of highly reactive shale. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 1680–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, A.; Saleh, T.A. An investigation of polymer-modified activated carbon as a potential shale inhibitor for water-based drilling muds. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 216, 110763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.A.; Zamir, A.; Elraies, K.A.; Mahmood, S.M.; Rasool, M.H. A critical parametric review of polymers as shale inhibitors in water-based drilling fluids. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 204, 108745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, G.; Yang, L.; Wang, K.; Shi, H.; Li, G.; Wu, X. Application of gelatin quaternary ammonium salt as an environmentally friendly shale inhibitor for water-based drilling fluids. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 9342–9350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Jiang, G.; Li, X.; He, Y.; Yang, L.; Cui, K.; Li, W. Application of carboxylated cellulose nanocrystals as eco-friendly shale inhibitors in water-based drilling fluids. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 627, 127182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed Khan, R.; Murtaza, M.; Abdulraheem, A.; Kamal, M.S.; Mahmoud, M. Imidazolium-based ionic liquids as clay swelling inhibitors: Mechanism, performance evaluation, and effect of different anions. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 26682–26696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, B.; Qasim, A.; Mohammad Shariff, A.; Lal, B.; Qasim, A.; Mohammad Shariff, A. Ionic Liquids Usage in Oil and Gas Industry. In Ionic Liquids in Flow Assurance; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, J.; Forcada, J.; Hidalgo-Alvarez, R. Cationic polymer nanoparticles and nanogels: From synthesis to biotechnological applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 367–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Pu, X. Structure and inhibition properties of a new amine-terminated hyperbranched oligomer shale inhibitor. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh Kumar, S.; Shaiju, P.; O’Connor, K.E. Bio-based and biodegradable polymers-State-of-the-art, challenges and emerging trends. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2020, 21, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrison, T.F.; Murawski, A.; Quirino, R.L. Bio-based polymers with potential for biodegradability. Polymers 2016, 8, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, T.; Chen, G. The study on the relationship between the molecular structures of chitosan derivatives and their hydrate inhibition performance. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 364, 120007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, C.; Quraishi, M.A. Chelation capability of chitosan and chitosan derivatives: Recent developments in sustainable corrosion inhibition and metal decontamination applications. Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 4, 100184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Alexandridis, P. Ionic liquid and nanoparticle hybrid systems: Emerging applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 244, 54–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghavikish, M.; Subianto, S.; Choudhury, N.R.; Dutta, N.K. Effect of polymerized ionic liquid based gel inhibitor on electrochemical performance of self-assembled nanophase coating. Prog. Org. Coat. 2018, 120, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, D.M.; Fernandes, L.C.; Martins, P.M.; García-Astrain, C.; Costa, C.M.; Reguera, J.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Ionic liquid–polymer composites: A new platform for multifunctional applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1909736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtaza, M.; Gbadamosi, A.; Hussain, S.M.S.; Alarifi, S.A.; Mahmoud, M.; Patil, S.; Kamal, M.S. Experimental investigation of pyrrolidinium-based ionic liquid as shale swelling inhibitor for water-based drilling fluids. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 231, 212374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Dong, H.; Zhang, G.; Su, B.; Huang, J. Preparation and Mechanism of Shale Inhibitor TIL-NH2 for Shale Gas Horizontal Wells. Molecules 2024, 29, 3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.; Liu, Y.; Li, P.; Guo, Y.; Yu, W.; Li, B. Reservoir Sensitivity Analysis of Tight Sandstone and Its Controlling Factors: A Case Study from Chang 4+ 5 to Chang 6 Reservoirs in N 212 Well Block of Nanniwan Oilfield, Ordos Basin. Geofluids 2023, 2023, 8878837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhou, L.; Yang, C.; Xia, H.; He, Y.; Feng, M. A complex based on imidazole ionic liquid and copolymer of acrylamide and phenoxyacetamide modification for clay stabilizer. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 41536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
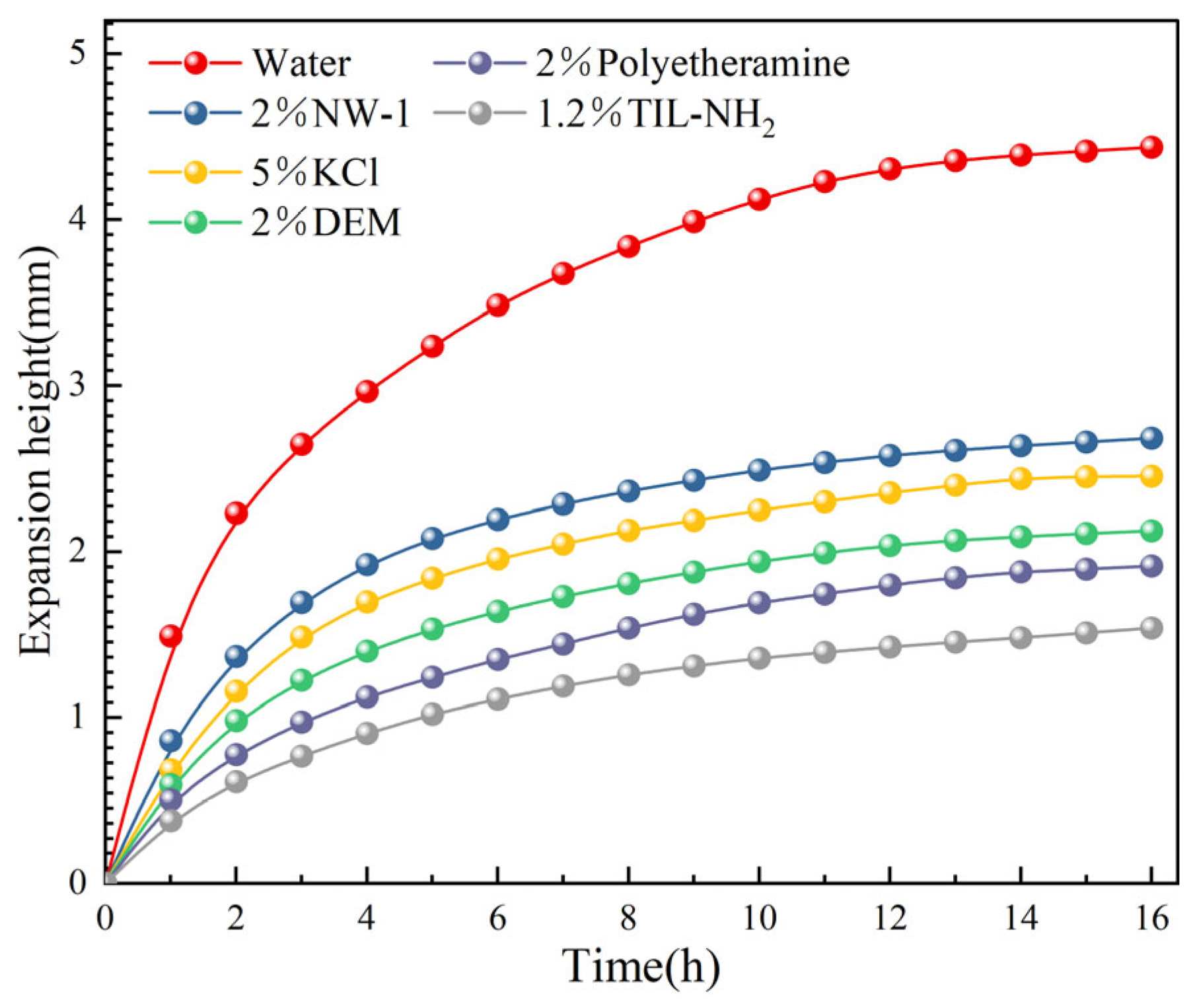
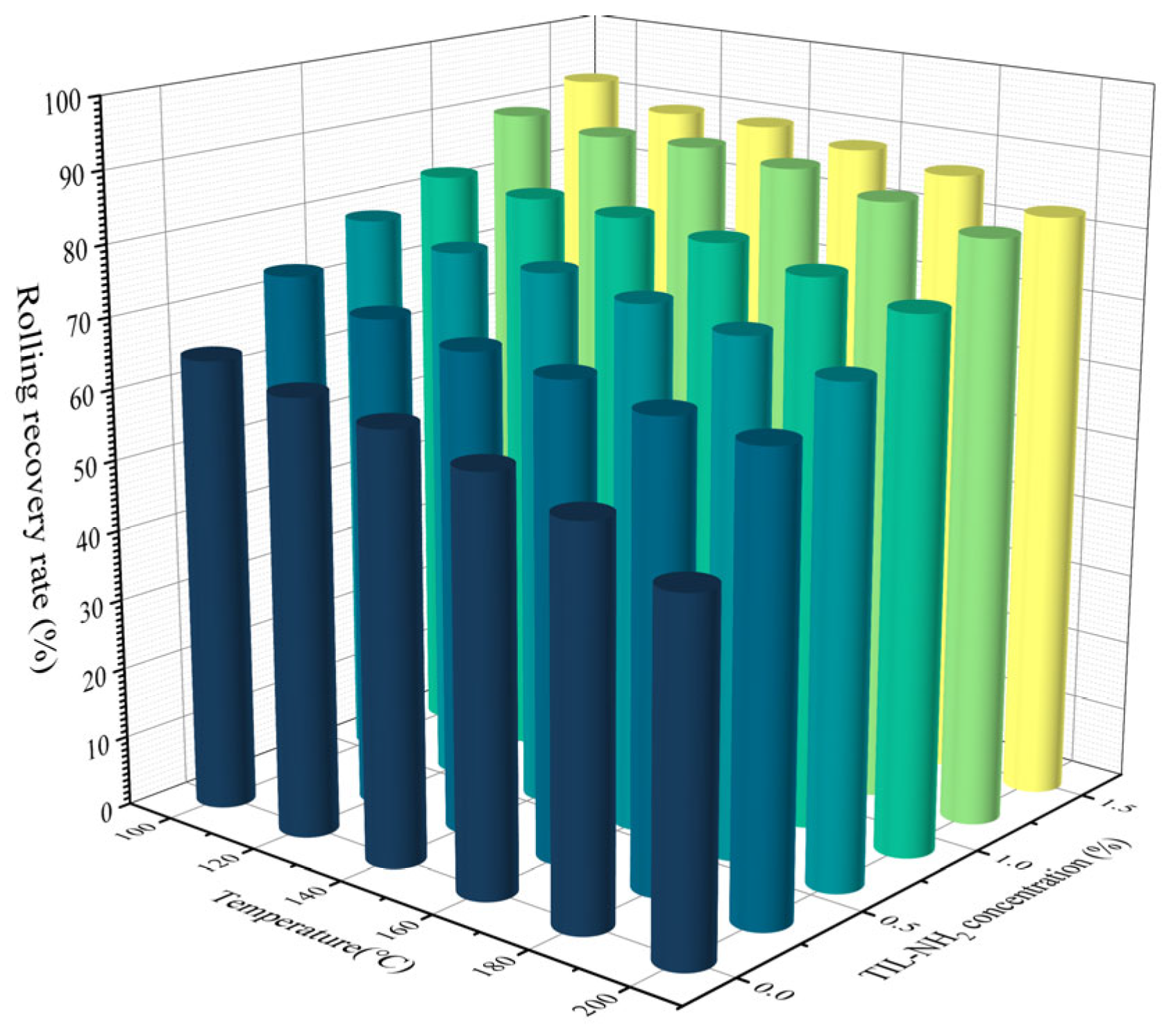
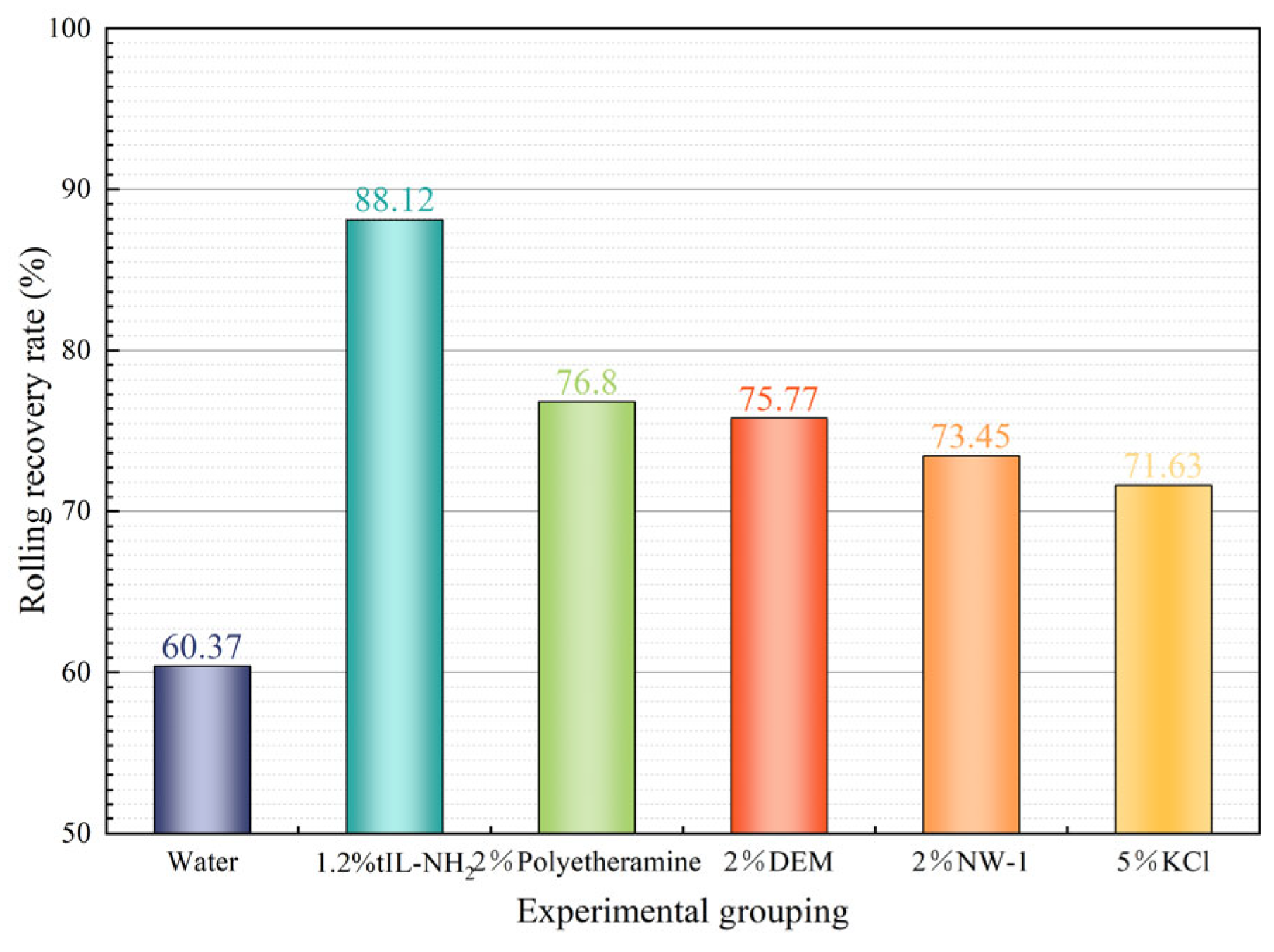
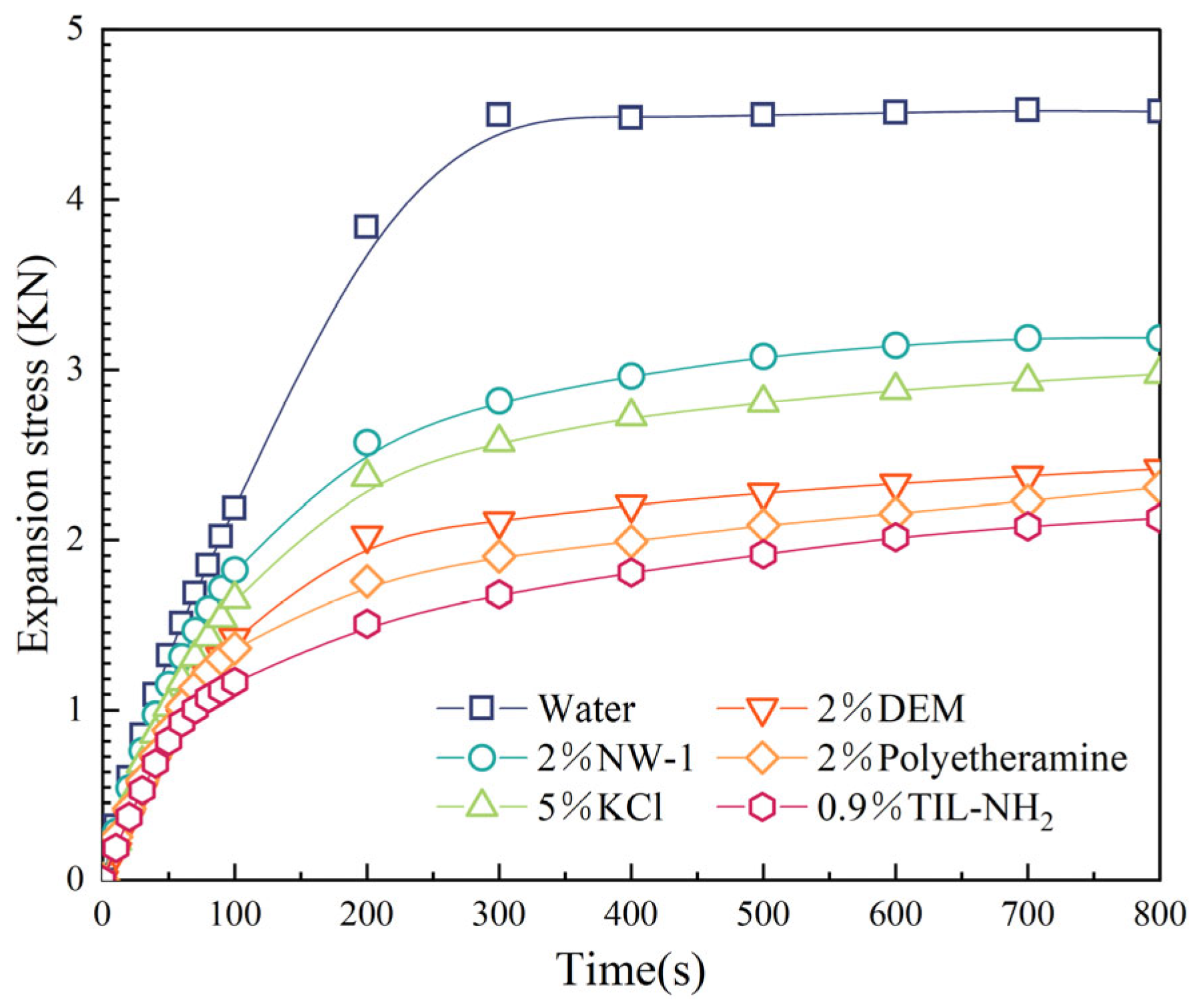

| Experimental Group | Immersion Solution | Protolith | After Immersion | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drying | Undried | After Drying | ||||||
| Lengths | Calibre | Mass (In Physics) | Lengths | Calibre | Mass (In Physics) | Mass (In Physics) | ||
| (mm) | (mm) | (g) | (mm) | (mm) | (g) | (g) | ||
| distilled water | 50.22 | 25.20 | 61.17 | 50.23 | 25.20 | 62.58 | 60.84 | |
| NaCl | 0.3 mol/L | 50.13 | 25.22 | 62.97 | 50.28 | 25.15 | 63.90 | 62.59 |
| 0.6 mol/L | 50.24 | 25.21 | 63.22 | 50.21 | 25.25 | 64.18 | 62.87 | |
| 1.2 mol/L | 50.28 | 25.24 | 65.15 | 50.32 | 25.24 | 66.04 | 64.69 | |
| KCl | 0.3 mol/L | 50.30 | 25.13 | 64.96 | 50.21 | 25.08 | 65.56 | 64.50 |
| 0.6 mol/L | 50.24 | 25.21 | 62.98 | 50.20 | 25.25 | 64.01 | 62.60 | |
| 1.2 mol/L | 50.20 | 25.22 | 63.07 | 50.14 | 25.28 | 64.17 | 62.76 | |
| CaCl2 | 0.3 mol/L | 50.28 | 25.22 | 61.20 | 50.34 | 25.27 | 62.07 | 60.88 |
| 0.6 mol/L | 50.16 | 25.21 | 63.45 | 50.20 | 25.23 | 64.13 | 63.15 | |
| 1.2 mol/L | 50.45 | 25.11 | 61.44 | 50.19 | 25.18 | 61.02 | 60.30 | |
| DEM | 0.3 mol/L | 50.08 | 25.21 | 62.21 | 50.26 | 25.20 | 62.58 | 61.34 |
| 0.6 mol/L | 50.17 | 25.18 | 62.87 | 50.05 | 25.25 | 63.95 | 62.59 | |
| 1.2 mol/L | 50.33 | 25.23 | 63.32 | 50.12 | 25.23 | 64.33 | 62.87 | |
| polyetheramine | 0.3 mol/L | 50.02 | 25.21 | 65.25 | 50.12 | 25.56 | 66.27 | 64.70 |
| 0.6 mol/L | 50.32 | 25.27 | 64.17 | 50.20 | 25.45 | 65.61 | 64.51 | |
| 1.2 mol/L | 50.35 | 25.28 | 62.26 | 50.14 | 25.39 | 64.21 | 62.55 | |
| TIL-NH2 | 0.3 mol/L | 50.17 | 25.36 | 63.30 | 50.15 | 25.47 | 64.89 | 62.46 |
| 0.6 mol/L | 50.20 | 25.24 | 61.22 | 50.14 | 25.31 | 62.37 | 60.91 | |
| 1.2 mol/L | 50.23 | 25.14 | 63.51 | 50.12 | 25.25 | 64.38 | 63.20 | |
| Experimental Group | Solution Concentration | △tc-100 khz Pre-Soaking | △tc-100 khz After Immersion | △tc-100 khz Difference (The Result of Subtraction) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| distilled water | 237.33 | 255.79 | 18.46 | |
| NaCl | 0.3 mol/L | 281.83 | 300.82 | 18.99 |
| 0.6 mol/L | 277.52 | 294.90 | 17.38 | |
| 1.2 mol/L | 279.13 | 287.15 | 8.02 | |
| KCl | 0.3 mol/L | 253.44 | 273.88 | 20.44 |
| 0.6 mol/L | 248.97 | 261.83 | 12.86 | |
| 1.2 mol/L | 256.21 | 262.42 | 6.21 | |
| CaCl2 | 0.3 mol/L | 288.31 | 303.98 | 15.67 |
| 0.6 mol/L | 272.28 | 282.67 | 10.39 | |
| 1.2 mol/L | 278.33 | 284.51 | 6.18 | |
| DEM | 0.3 mol/L | 276.27 | 291.51 | 15.24 |
| 0.6 mol/L | 254.48 | 265.35 | 10.87 | |
| 1.2 mol/L | 268.03 | 273.45 | 5.42 | |
| polyetheramine | 0.3 mol/L | 290.31 | 304.65 | 14.34 |
| 0.6 mol/L | 310.25 | 320.18 | 9.93 | |
| 1.2 mol/L | 324.57 | 329.84 | 5.27 | |
| TIL-NH2 | 0.3 mol/L | 287.38 | 299.93 | 12.55 |
| 0.6 mol/L | 281.27 | 289.32 | 8.05 | |
| 1.2 mol/L | 300.16 | 304.42 | 4.26 |
| Suppressant | KCl | 132 | Bop-3 | TIL-NH2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inflatability (%) | 94.95 | 82.90 | 80.00 | 80.35 |
| Type of Inhibitor | Concentration (wt%) | Zebrafish Mortality (%) | LC50 (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TIL-NH2 | 0.1 | 0.0 | - |
| 0.3 | 5.8 | - | |
| 0.5 | 18.6 | - | |
| 1.0 | 44.7 | 1080.3 | |
| 2.0 | 65.4 | - | |
| KCl solution | 0.1 | 5.0 | - |
| 0.3 | 20.3 | - | |
| 0.5 | 45.0 | - | |
| 1.0 | 70.2 | 385.4 | |
| 2.0 | 89.7 | - |
| Type of Inhibitor | Concentration (wt%) | Initial BOD5 (mg/L) | BOD After Treatment5 (mg/L) | Inhibition Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TIL-NH2 | 0.1 | 202.4 | 201.8 | 0.30 |
| 1.0 | 201.7 | 183.5 | 9.03 | |
| 2.0 | 200.9 | 160.7 | 20.01 | |
| KCl solution | 0.1 | 200.8 | 192.5 | 4.14 |
| 1.0 | 198.3 | 142.8 | 28.00 | |
| 2.0 | 199.2 | 100.6 | 49.46 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Dong, H.; Zhang, G.; Su, B.; Liu, X.; Hu, Y.; Huang, J.; Lu, Z. Research and Performance Evaluation of Environmentally Friendly Shale Inhibitor TIL-NH2 for Shale Gas Horizontal Wells. Molecules 2024, 29, 5950. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29245950
Tian Y, Liu X, Liu Y, Dong H, Zhang G, Su B, Liu X, Hu Y, Huang J, Lu Z. Research and Performance Evaluation of Environmentally Friendly Shale Inhibitor TIL-NH2 for Shale Gas Horizontal Wells. Molecules. 2024; 29(24):5950. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29245950
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Yuexin, Xiangjun Liu, Yintao Liu, Haifeng Dong, Guodong Zhang, Biao Su, Xiaofeng Liu, Yifan Hu, Jinjun Huang, and Zeze Lu. 2024. "Research and Performance Evaluation of Environmentally Friendly Shale Inhibitor TIL-NH2 for Shale Gas Horizontal Wells" Molecules 29, no. 24: 5950. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29245950
APA StyleTian, Y., Liu, X., Liu, Y., Dong, H., Zhang, G., Su, B., Liu, X., Hu, Y., Huang, J., & Lu, Z. (2024). Research and Performance Evaluation of Environmentally Friendly Shale Inhibitor TIL-NH2 for Shale Gas Horizontal Wells. Molecules, 29(24), 5950. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29245950






