Selective PPARδ Agonist GW501516 Protects Against LPS-Induced Macrophage Inflammation and Acute Liver Failure in Mice via Suppressing Inflammatory Mediators
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
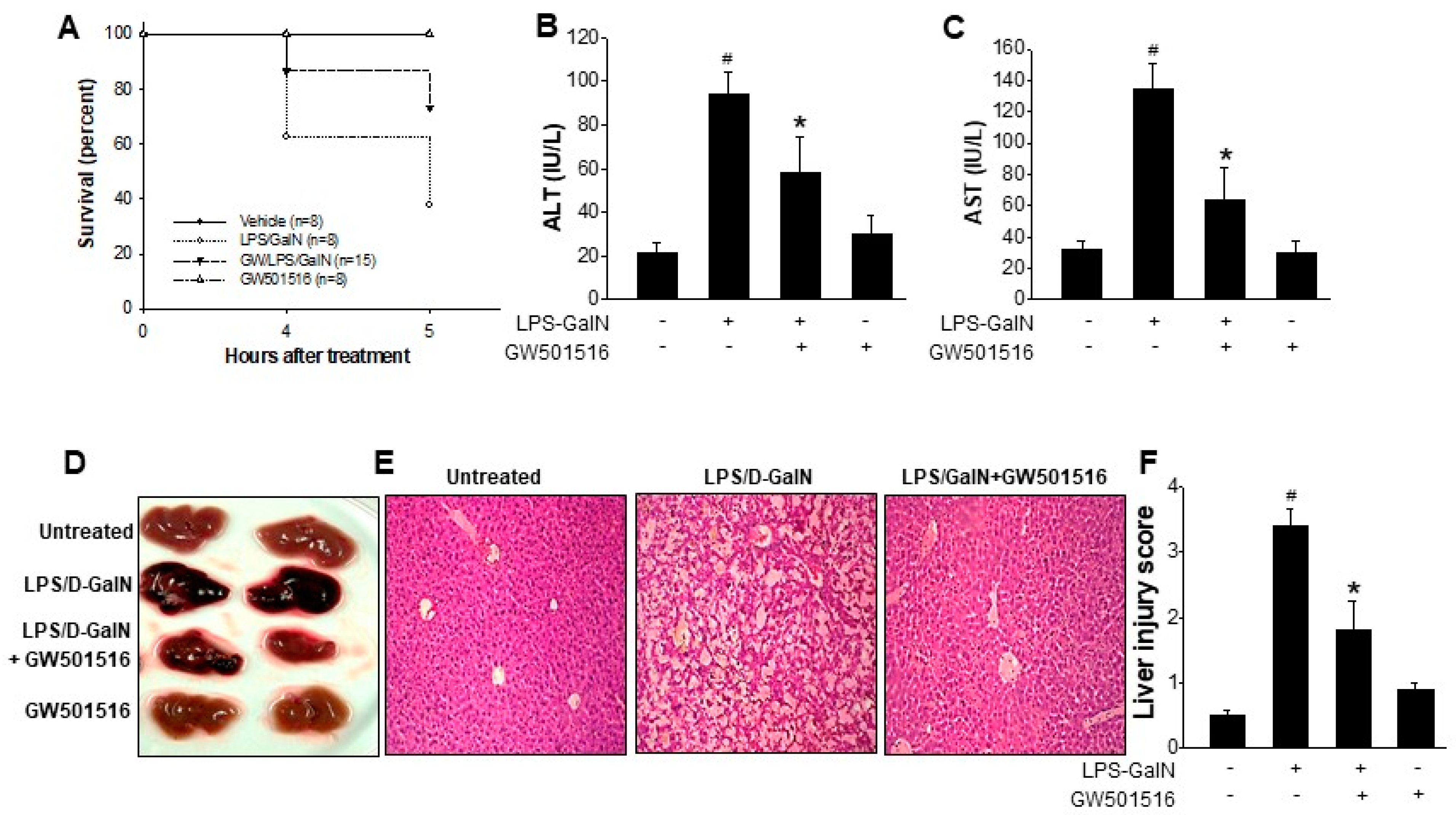
2.1. GW501516 Reduced the Mortality and Liver Damage on LPS/D-GalN-Induced ALF in Mice
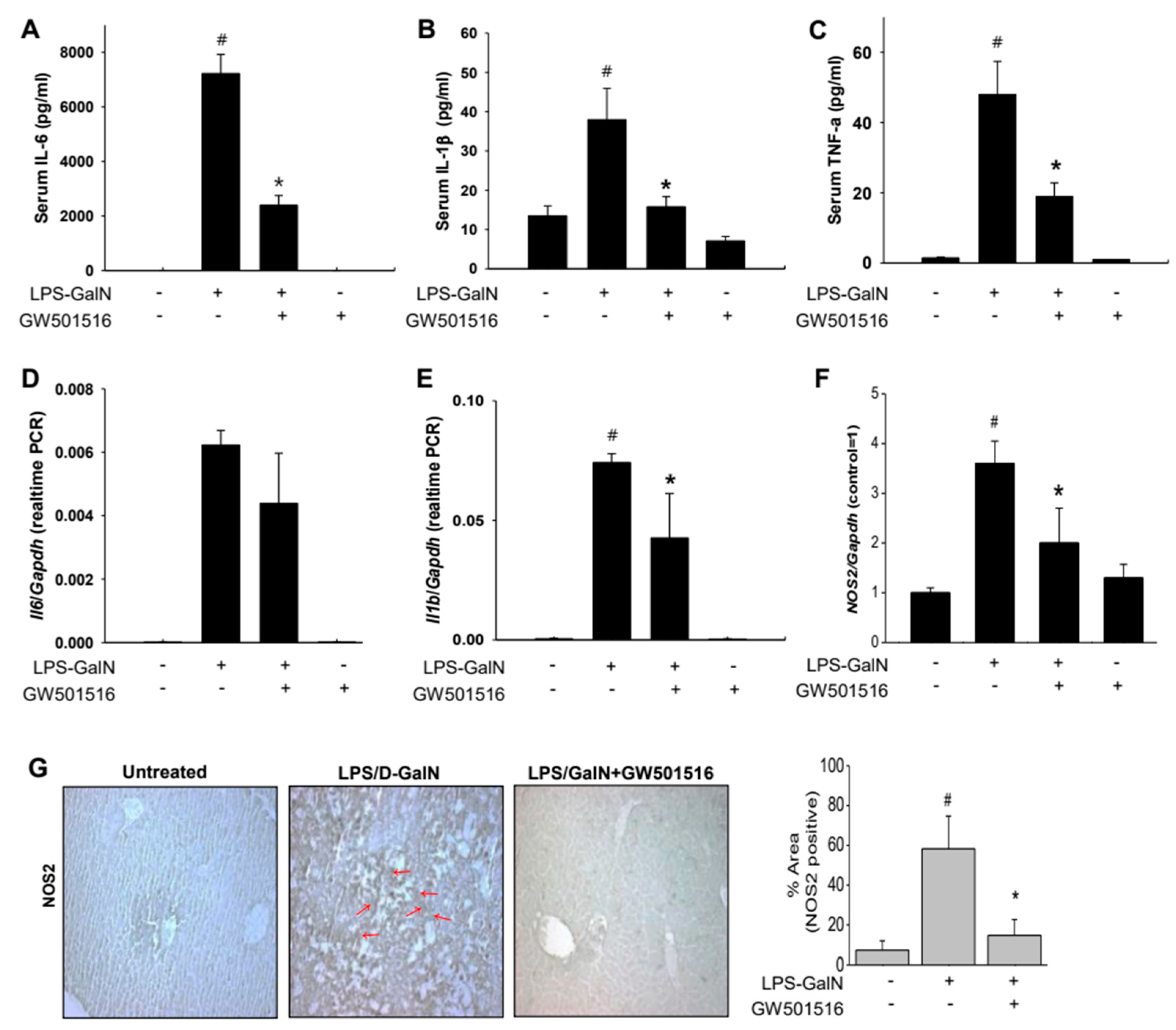
2.2. GW501516 Decreased Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines and NOS2 in LPS/D-GalN-Induced ALF in Mice
2.3. GW501516 Suppresses NOS2 Expression in LPS-Activated RAW264.7 Cells
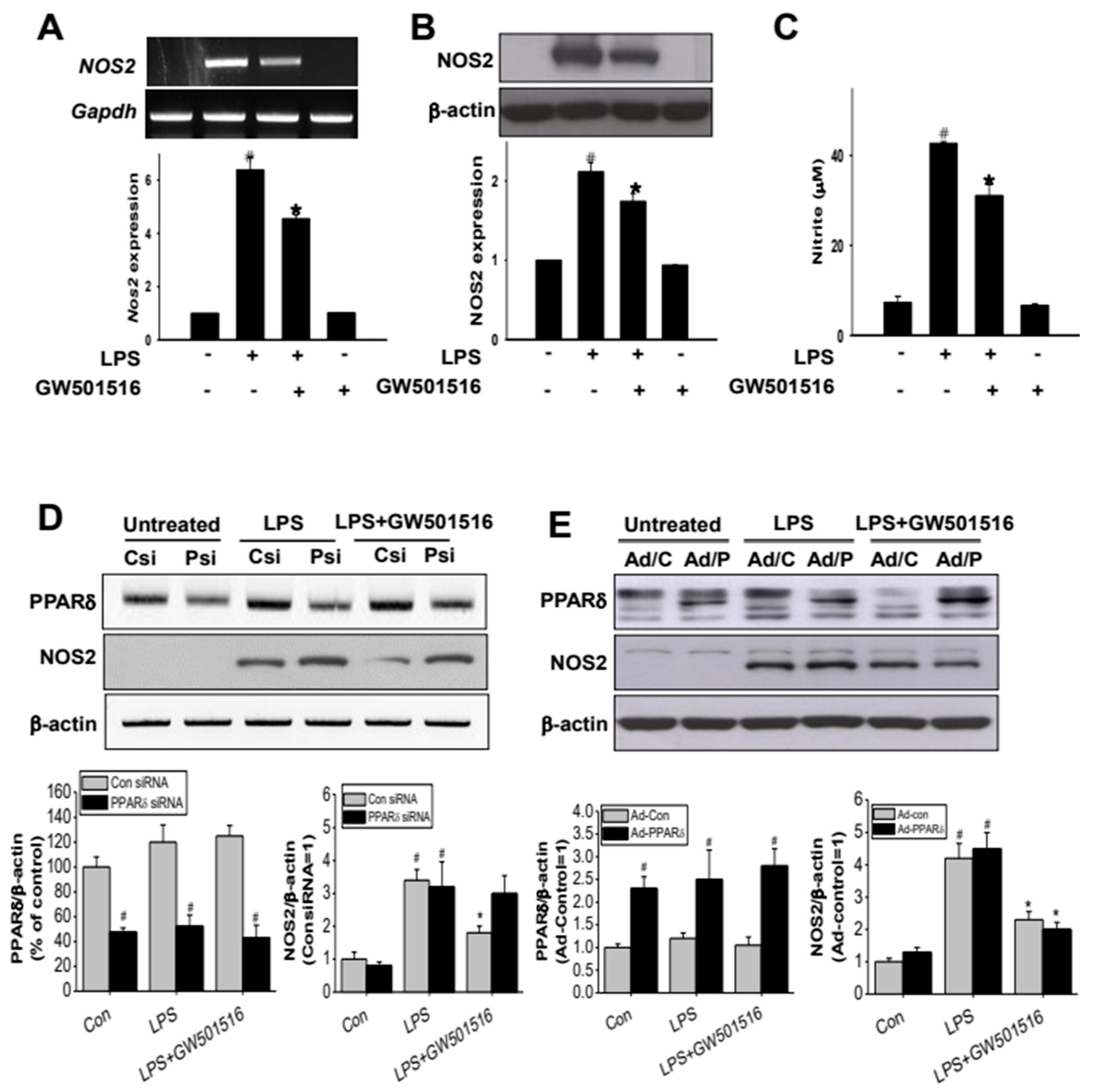
2.4. The Effect of GW501516 on NOS2 Regulation Is Dependent on Activating of PPARδ
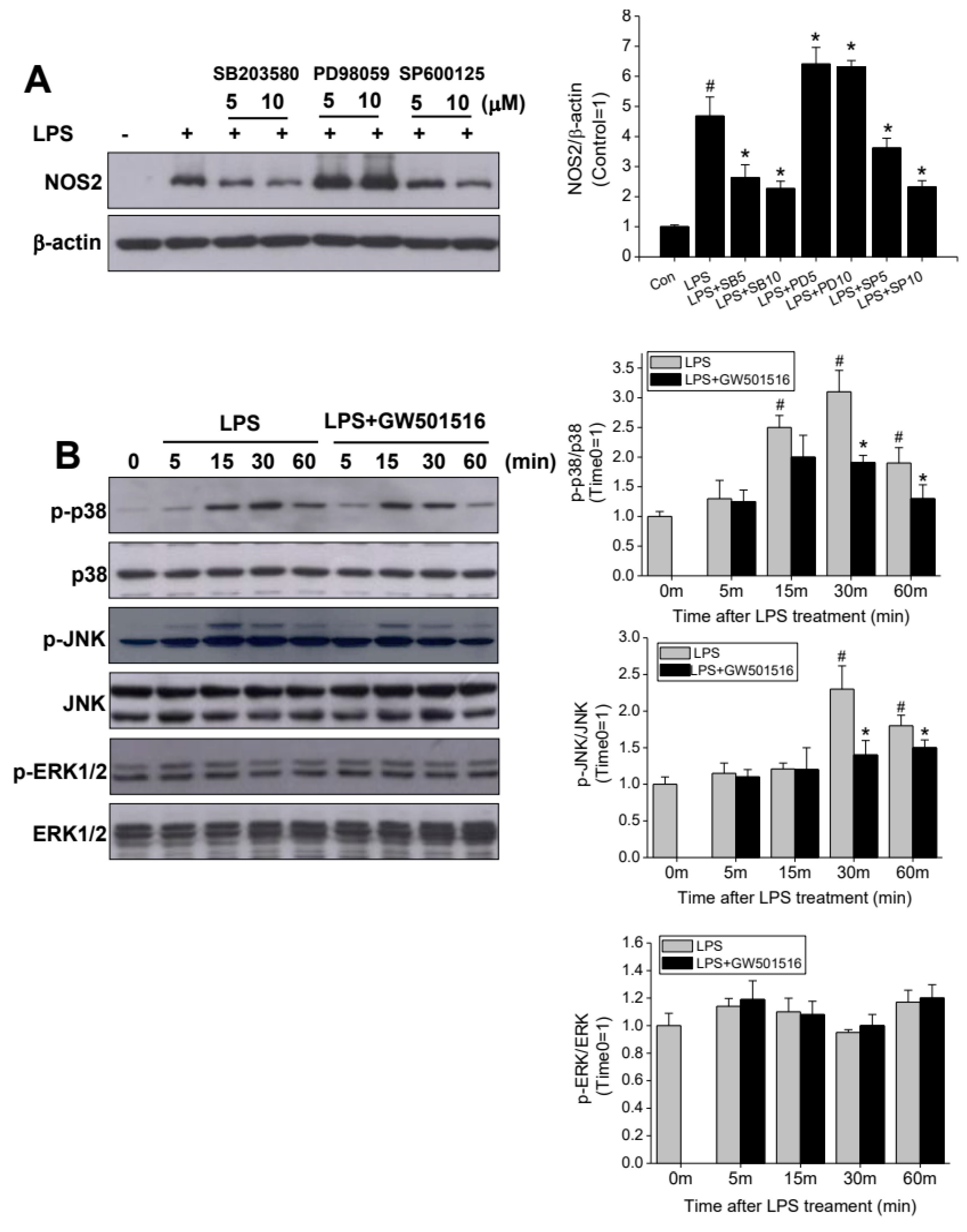
2.5. GW501516 Attenuates NOS2 Induction Through p38- and JNK-Dependent Mechanism
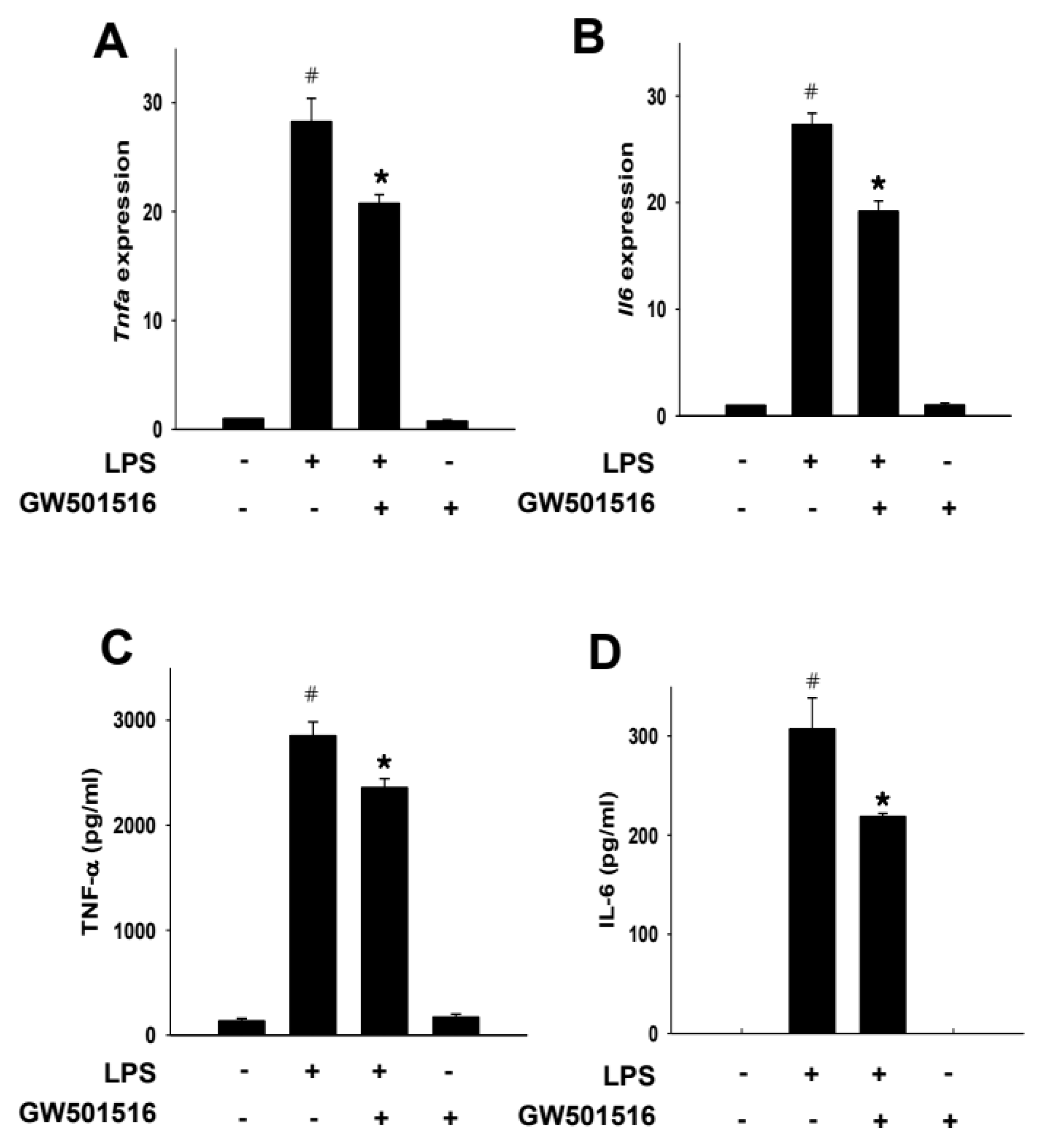
2.6. GW501516 Decreases TNF-α and IL-6 Production in LPS-Activated RAW264.7 Cells
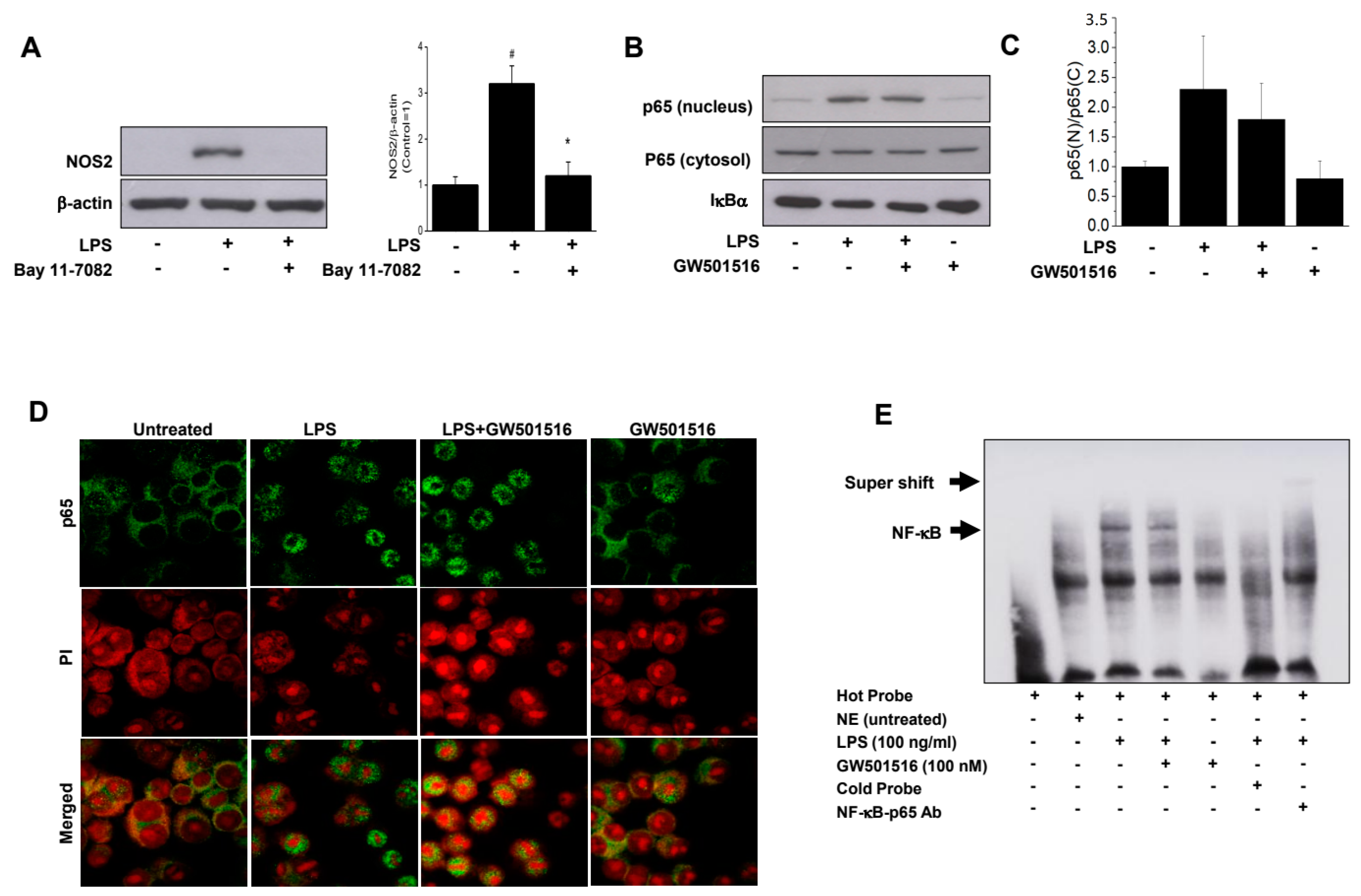
2.7. GW501516 Exerts Its Anti-Inflammatory Effect by Inhibition of NF-κB Binding to DNA, Not the Nuclear Translocation of p65 Subunit
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Reagents
4.2. Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction Analysis
4.3. Western Blot Analysis
4.4. Measurement of Nitrite
4.5. ELISA for IL-6 and TNF-α
4.6. Anlysis of ALT and AST
4.7. Gene Silencing with siRNA Transfection
4.8. Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA)
4.9. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.10. Immunocytochemistry
4.11. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining and Histological Assessment
4.12. In Vivo ALF Model
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kersten, S.; Desvergne, B.; Wahli, W. Roles of PPARs in health and disease. Nature 2000, 405, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kliewer, S.A.; Xu, H.E.; Lambert, M.H.; Willson, T.M. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: From genes to physiology. Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 2001, 56, 239–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpe, F.; Ehrenborg, E.E. PPAR delta in humans: Genetic and pharmacological evidence for a significant metabolic function. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2009, 20, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barak, Y.; Liao, D.; He, W.M.; Ong, E.S.; Nelson, M.C.; Olefsky, J.M.; Boland, R.; Evans, R.M. Effects of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta on placentation, adiposity, and colorectal cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, N.S.; Michalik, L.; Di-Poi, N.; Desvergne, B.; Wahli, W. Critical roles of the nuclear receptor PPAR beta (peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptor beta) in skin wound healing. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2004, 32, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Calvo, R.; Serrano, L.; Coll, T.; Moullan, N.; Sanchez, R.M.; Merlos, M.; Palomer, X.; Laguna, J.C.; Michalik, L.; Wahli, W.; et al. Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor beta/delta inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced cytokine production in adipocytes by lowering nuclear factor-kappa B activity via extracellular signal-related kinase 1/2. Diabetes 2008, 57, 2149–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamaya, R.; Ogawa, M.; Suzuki, J.; Kobayashi, N.; Hirata, Y.; Nagai, R.; Komuro, I.; Isobe, M. A selective peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-beta/delta agonist attenuates neointimal hyperplasia after wire-mediated arterial injury. Expert Opin. Inv. Drug 2013, 22, 1095–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.B.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Z.H.; Zhang, H.; Qin, X.M.; Zhu, Y.; Guan, Y.F.; Wang, X.; Staels, B.; Chien, S.; et al. Suppression of pro-inflammatory adhesion molecules by PPAR-delta in human vascular endothelial cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rival, Y.; Beneteau, N.; Taillandier, T.; Pezet, M.; Dupont-Passelaigue, E.; Patoiseau, J.F.; Junquero, D.; Colpaert, F.C.; Delhon, A. PPARalpha and PPARdelta activators inhibit cytokine-induced nuclear translocation of NF-kappaB and expression of VCAM-1 in EAhy926 endothelial cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 435, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, G.L.; Cheng, L.H.; Qin, Q.H.; Frontin, S.; Yang, Q.L. PPAR delta modulates lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF alpha inflammation signaling in cultured cardiomyocytes. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2006, 40, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Chawla, A.; Urbiztondo, N.; Liao, D.; Boisvert, W.A.; Evans, R.M. Transcriptional repression of atherogenic inflammation: Modulation by PPAR delta. Science 2003, 302, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moraes, L.A.; Piqueras, L.; Bishop-Bailey, D. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and inflammation. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 110, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, K.; Reilly, S.M.; Karabacak, V.; Gangl, M.R.; Fitzgerald, K.; Hatano, B.; Lee, C.H. Adipocyte-derived Th2 cytokines and myeloid PPAR delta regulate macrophage polarization and insulin sensitivity. Cell Metab. 2008, 7, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konttinen, H.; Gureviciene, I.; Oksanen, M.; Grubman, A.; Loppi, S.; Huuskonen, M.T.; Korhonen, P.; Lampinen, R.; Keuters, M.; Belaya, I.; et al. PPARbeta/delta-agonist GW0742 ameliorates dysfunction in fatty acid oxidation in PSEN1DeltaE9 astrocytes. Glia 2019, 67, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahli, W.; Julve, J.; Vazquez-Carrera, M.; Jauhiainen, M.; Blanco-Vaca, F.; Escola-Gil, J.C. PPAR-beta/delta activation promotes phospholipid transfer protein expression. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 94, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, H.S.; Ku, P.M.; Niu, C.S.; Cheng, J.T.; Lee, K.S. Development of PPAR-agonist GW0742 as antidiabetic drug: Study in animals. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2015, 9, 5625–5632. [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs, C.D.; Radun, R.; Dixon, E.D.; Mlitz, V.; Timelthaler, G.; Halilbasic, E.; Herac, M.; Jonker, J.W.; Ronda, O.; Tardelli, M.; et al. Hepatocyte-specific deletion of adipose triglyceride lipase (adipose triglyceride lipase/patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 2) ameliorates dietary induced steatohepatitis in mice. Hepatology 2022, 75, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhe, R.; Guo, X.; Chen, Y.; Zou, Y.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Z. The Role of PPARdelta Agosnist GW501516 in Rats with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2020, 13, 2307–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobita, Y.; Arima, T.; Nakano, Y.; Uchiyama, M.; Shimizu, A.; Takahashi, H. Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Beta/Delta Agonist Suppresses Inflammation and Promotes Neovascularization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvado, L.; Barroso, E.; Gomez-Foix, A.M.; Palomer, X.; Michalik, L.; Wahli, W.; Vazquez-Carrera, M. PPARbeta/delta prevents endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated inflammation and insulin resistance in skeletal muscle cells through an AMPK-dependent mechanism. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 2126–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belghiti, J.; Sommacale, D.; Dondero, F.; Zinzindohoue, F.; Sauvanet, A.; Durand, F. Auxiliary liver transplantation for acute liver failure. HPB Off. J. Int. Hepato Pancreato Biliary Assoc. 2004, 6, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoniades, C.G.; Berry, P.A.; Wendon, J.A.; Vergani, D. The importance of immune dysfunction in determining outcome in acute liver failure. J. Hepatol. 2008, 49, 845–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Possamai, L.A.; Antoniades, C.G.; Anstee, Q.M.; Quaglia, A.; Vergani, D.; Thursz, M.; Wendon, J. Role of monocytes and macrophages in experimental and human acute liver failure. World J. Gastroentero 2010, 16, 1811–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zingarelli, B.; Piraino, G.; Hake, P.W.; O’Connor, M.; Denenberg, A.; Fan, H.K.; Cook, J.A. Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor delta Regulates Inflammation via NF-kappa B Signaling in Polymicrobial Sepsis. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 1834–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trewby, P.N.; Williams, R. Pathophysiology of hypotension in patients with fulminant hepatic failure. Gut 1977, 18, 1021–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsikas, D. Methods of quantitative analysis of the nitric oxide metabolites nitrite and nitrate in human biological fluids. Free Radic. Res. 2005, 39, 797–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, J.S.; Ricote, M.; Akiyama, T.E.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Glass, C.K. PPARgamma and PPARdelta negatively regulate specific subsets of lipopolysaccharide and IFN-gamma target genes in macrophages. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 6712–6717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, R.; Lahti, A.; Kankaanranta, H.; Moilanen, E. Nitric oxide production and signaling in inflammation. Curr. Drug Targets. Inflamm. Allergy 2005, 4, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNaughton, L.; Puttagunta, L.; Martinez-Cuesta, M.A.; Kneteman, N.; Mayers, I.; Moqbel, R.; Hamid, Q.; Radomski, M.W. Distribution of nitric oxide synthase in normal and cirrhotic human liver. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 17161–17166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leifeld, L.; Fielenbach, M.; Dumoulin, F.L.; Speidel, N.; Sauerbruch, T.; Spengler, U. Inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) expression in fulminant hepatic failure. J. Hepatol. 2002, 37, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tak, P.P.; Firestein, G.S. NF-kappaB: A key role in inflammatory diseases. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galuppo, M.; Di Paola, R.; Mazzon, E.; Genovese, T.; Crisafulli, C.; Paterniti, I.; Cuzzocrea, E.; Bramanti, P.; Kapoor, A.; Thiemermann, C.; et al. Role of PPAR-delta in the development of zymosan-induced multiple organ failure: An experiment mice study. J. Inflamm. 2010, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delerive, P.; De Bosscher, K.; Besnard, S.; Vanden Berghe, W.; Peters, J.M.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Fruchart, J.C.; Tedgui, A.; Haegeman, G.; Staels, B. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha negatively regulates the vascular inflammatory gene response by negative cross-talk with transcription factors NF-kappaB and AP-1. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 32048–32054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planavila, A.; Rodriguez-Calvo, R.; Jove, M.; Michalik, L.; Wahli, W.; Laguna, J.C.; Vazquez-Carrera, M. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor beta/delta activation inhibits hypertrophy in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. Cardiovasc. Res. 2005, 65, 832–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, G.; Fong, A.L.; Ogawa, S.; Gamliel, A.; Li, A.C.; Perissi, V.; Rose, D.W.; Willson, T.M.; Rosenfeld, M.G.; Glass, C.K. A SUMOylation-dependent pathway mediates transrepression of inflammatory response genes by PPAR-gamma. Nature 2005, 437, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straus, D.S.; Glass, C.K. Anti-inflammatory actions of PPAR ligands: New insights on cellular and molecular mechanisms. Trends Immunol. 2007, 28, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y. The regulatory role of nitric oxide in proinflammatory cytokine expression during the induction and resolution of inflammation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2010, 88, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.J.; Park, J.H.; Lee, S.; Choi, H.E.; Lee, K.S.; Park, H.Y. PPAR delta ligand L-165041 ameliorates Western diet-induced hepatic lipid accumulation and inflammation in LDLR-/- mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 622, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nagasawa, T.; Inada, Y.; Nakano, S.; Tamura, T.; Takahashi, T.; Maruyama, K.; Yamazaki, Y.; Kuroda, J.; Shibata, N. Effects of bezafibrate, PPAR pan-agonist, and GW501516, PPAR delta agonist, on development of steatohepatitis in mice fed a methionine- and choline-deficient diet. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 536, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Siles, A.A.; Ishimura, N.; Rumi, M.A.; Tamagawa, Y.; Ito, S.; Ishihara, S.; Nabika, T.; Kinoshita, Y. Administration of PPARbeta/delta agonist reduces copper-induced liver damage in mice: Possible implications in clinical practice. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2011, 49, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunon, M.J.; Alvarez, M.; Culebras, J.M.; Gonzalez-Gallego, J. An overview of animal models for investigating the pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies in acute hepatic failure. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2009, 15, 3086–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, T.M.; Hodgson, H.J. Animal models of acute hepatic failure. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2000, 81, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, W.; Nicol, C.J.; Ito, S.; Bility, M.T.; Kennett, M.J.; Ward, J.M.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Peters, J.M. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-beta/delta protects against chemically induced liver toxicity in mice. Hepatology 2008, 47, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galanos, C.; Freudenberg, M.A.; Reutter, W. Galactosamine-induced sensitization to the lethal effects of endotoxin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 5939–5943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignon, A.; Rouquet, N.; Fabre, M.; Martin, S.; Pages, J.C.; Dhainaut, J.F.; Kahn, A.; Briand, P.; Joulin, V. LPS challenge in D-galactosamine-sensitized mice accounts for caspase-dependent fulminant hepatitis, not for septic shock. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 159 Pt 1, 1308–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Y.; Ren, F.; Zhang, H.Y.; Wen, T.; Piao, Z.F.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, S.J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Han, Y.P.; et al. Inhibition of Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3 beta Ameliorates D-GalN/LPS-Induced Liver Injury by Reducing Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Triggered Apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45202. [Google Scholar]
- Eipel, C.; Kidess, E.; Abshagen, K.; LeMinh, K.; Menger, M.D.; Burkhardt, H.; Vollmar, B. Antileukoproteinase protects against hepatic inflammation, but not apoptosis in the response of D-galactosamine-sensitized mice to lipopolysaccharide. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 151, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhla, A.; Eipel, C.; Siebert, N.; Abshagen, K.; Menger, M.; Vollmar, B. Hepatocellular apoptosis is mediated by TNF alpha-dependent Fas/FasLigand cytotoxicity in a murine model of acute liver failure. Apoptosis 2008, 13, 1427–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakama, T.; Hirono, S.; Moriuchi, A.; Hasuike, S.; Nagata, K.; Hori, T.; Ido, A.; Hayashi, K.; Tsubouchi, K. Etoposide prevents apoptosis in mouse liver with D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide-induced fulminant hepatic failure resulting in reduction of lethality. Hepatology 2001, 33, 1441–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirono, S.; Nakama, T.; Tsubouchi, H. Molecular mechanisms of D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide-induced fulminant hepatic failure in mice and the effects of therapeutic agents. In Trends in Gastroenterology and Hepatology; Asakura, H., Aoyagi, Y., Nakazawa, S., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2001; pp. 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Kostadinova, R.; Montagner, A.; Gouranton, E.; Fleury, S.; Guillou, H.; Dombrowicz, D.; Desreumaux, P.; Wahli, W. GW501516-activated PPAR beta/delta promotes liver fibrosis via p38-JNK MAPK-induced hepatic stellate cell proliferation. Cell Biosci. 2012, 2, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lim, H.-J.; Kwak, H.J. Selective PPARδ Agonist GW501516 Protects Against LPS-Induced Macrophage Inflammation and Acute Liver Failure in Mice via Suppressing Inflammatory Mediators. Molecules 2024, 29, 5189. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29215189
Lim H-J, Kwak HJ. Selective PPARδ Agonist GW501516 Protects Against LPS-Induced Macrophage Inflammation and Acute Liver Failure in Mice via Suppressing Inflammatory Mediators. Molecules. 2024; 29(21):5189. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29215189
Chicago/Turabian StyleLim, Hyun-Joung, and Hyun Jeong Kwak. 2024. "Selective PPARδ Agonist GW501516 Protects Against LPS-Induced Macrophage Inflammation and Acute Liver Failure in Mice via Suppressing Inflammatory Mediators" Molecules 29, no. 21: 5189. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29215189
APA StyleLim, H.-J., & Kwak, H. J. (2024). Selective PPARδ Agonist GW501516 Protects Against LPS-Induced Macrophage Inflammation and Acute Liver Failure in Mice via Suppressing Inflammatory Mediators. Molecules, 29(21), 5189. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29215189




