A Novel Method for Rapid Screening of Salmonidae Ingredients and Accurate Detection of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) Simultaneously Using Duplex Real-Time PCR Coupled with Melting Curve Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
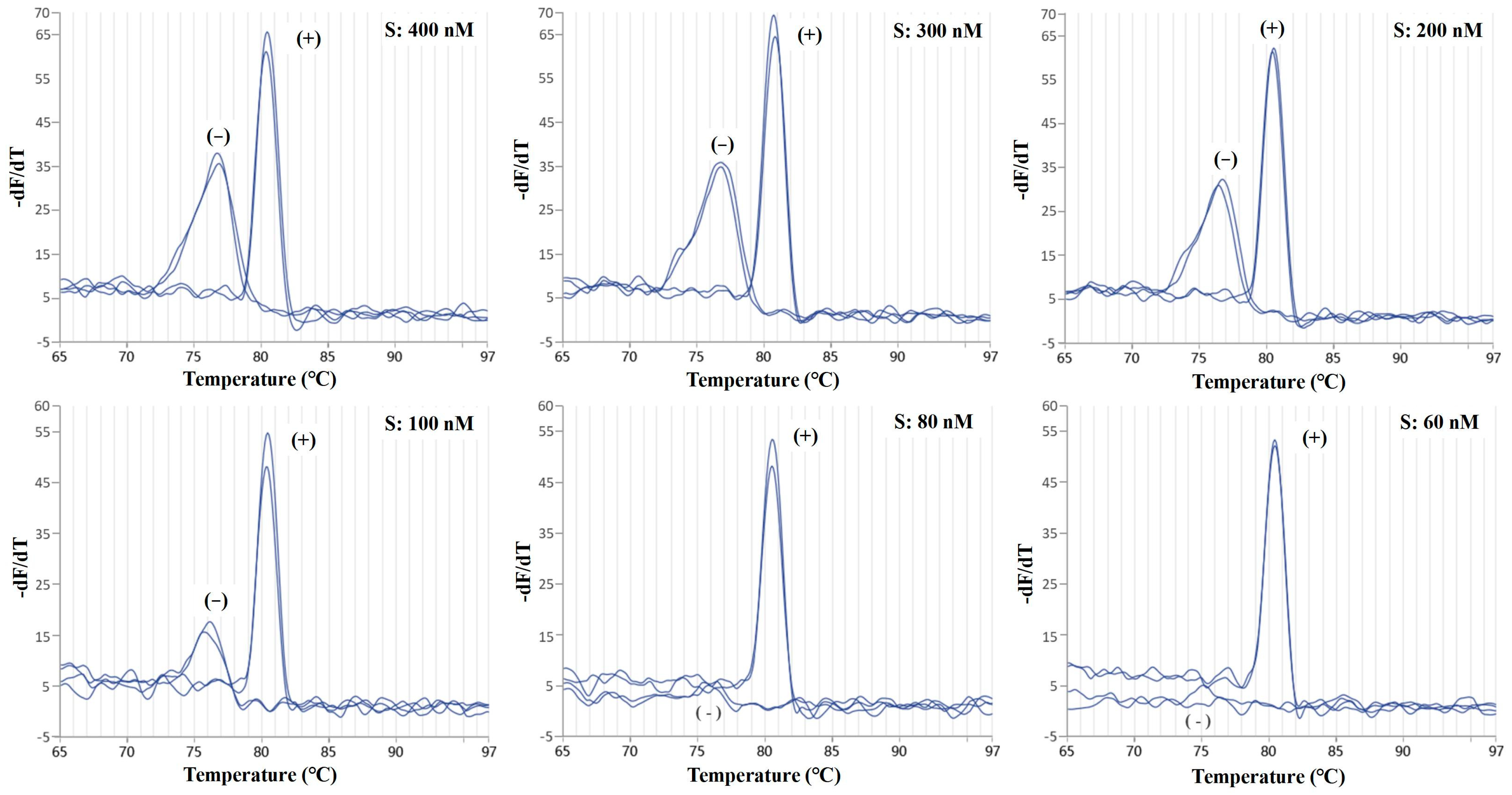
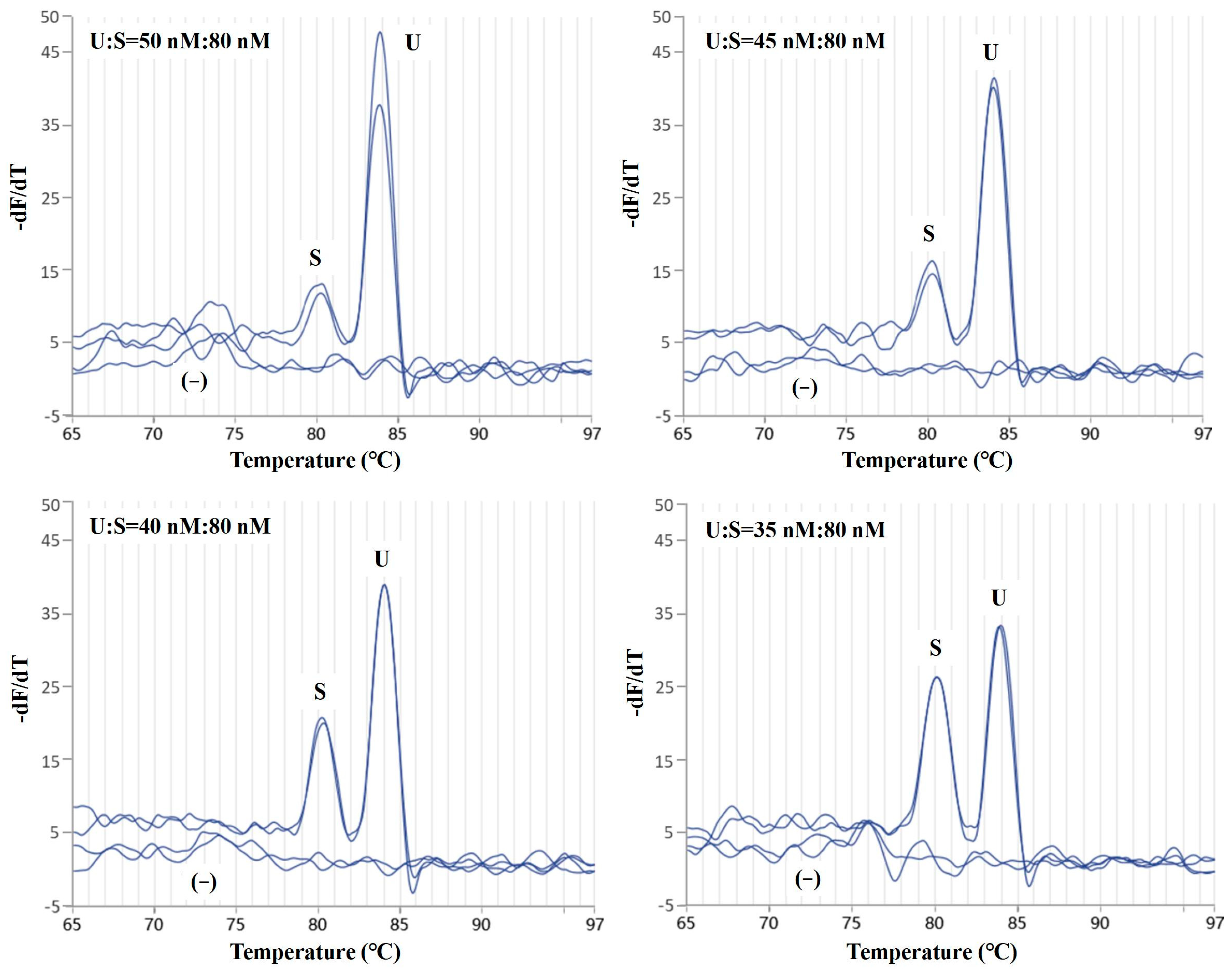
2.1. Optimization of the Duplex Real-Time PCR Assay
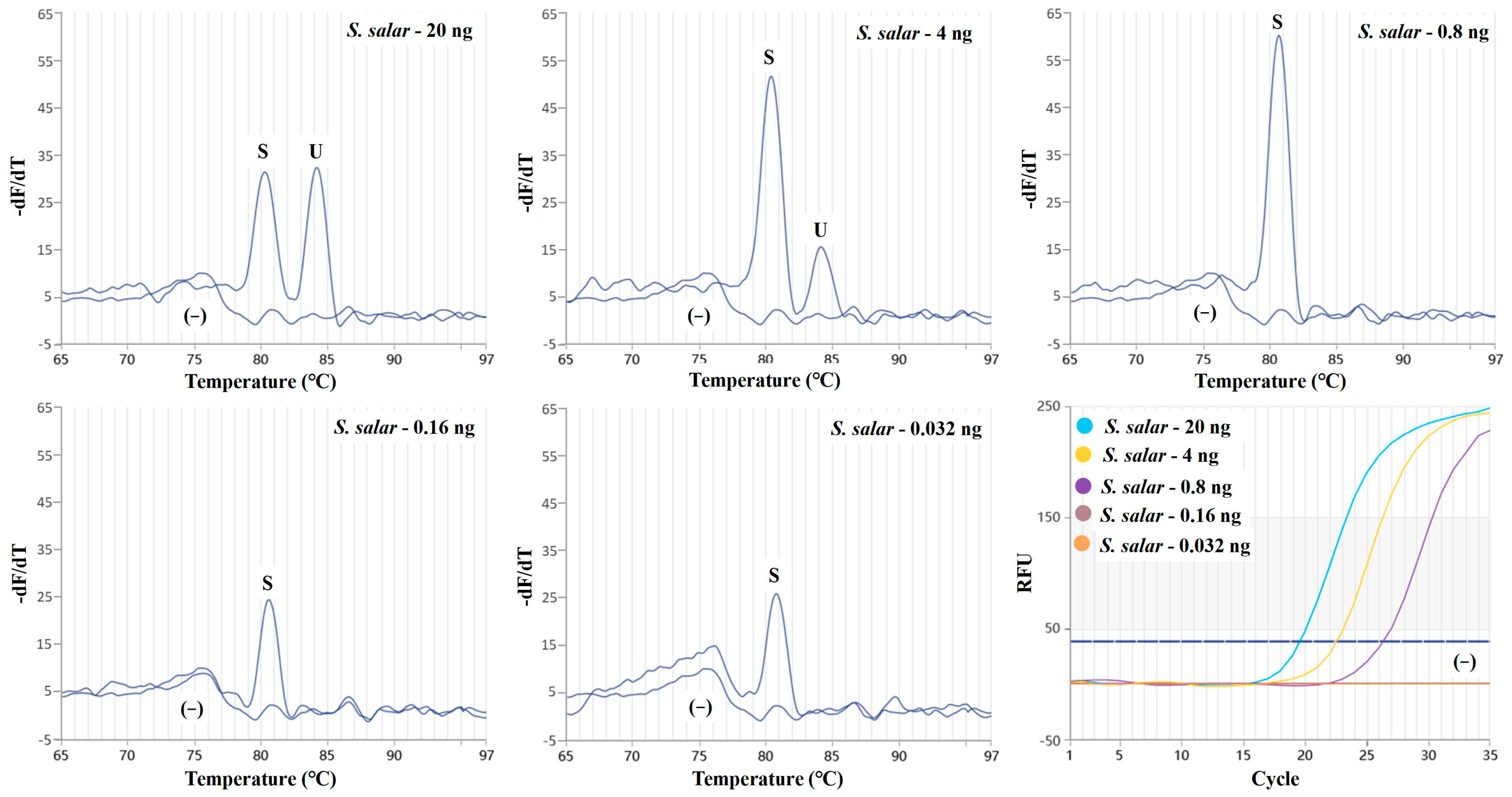
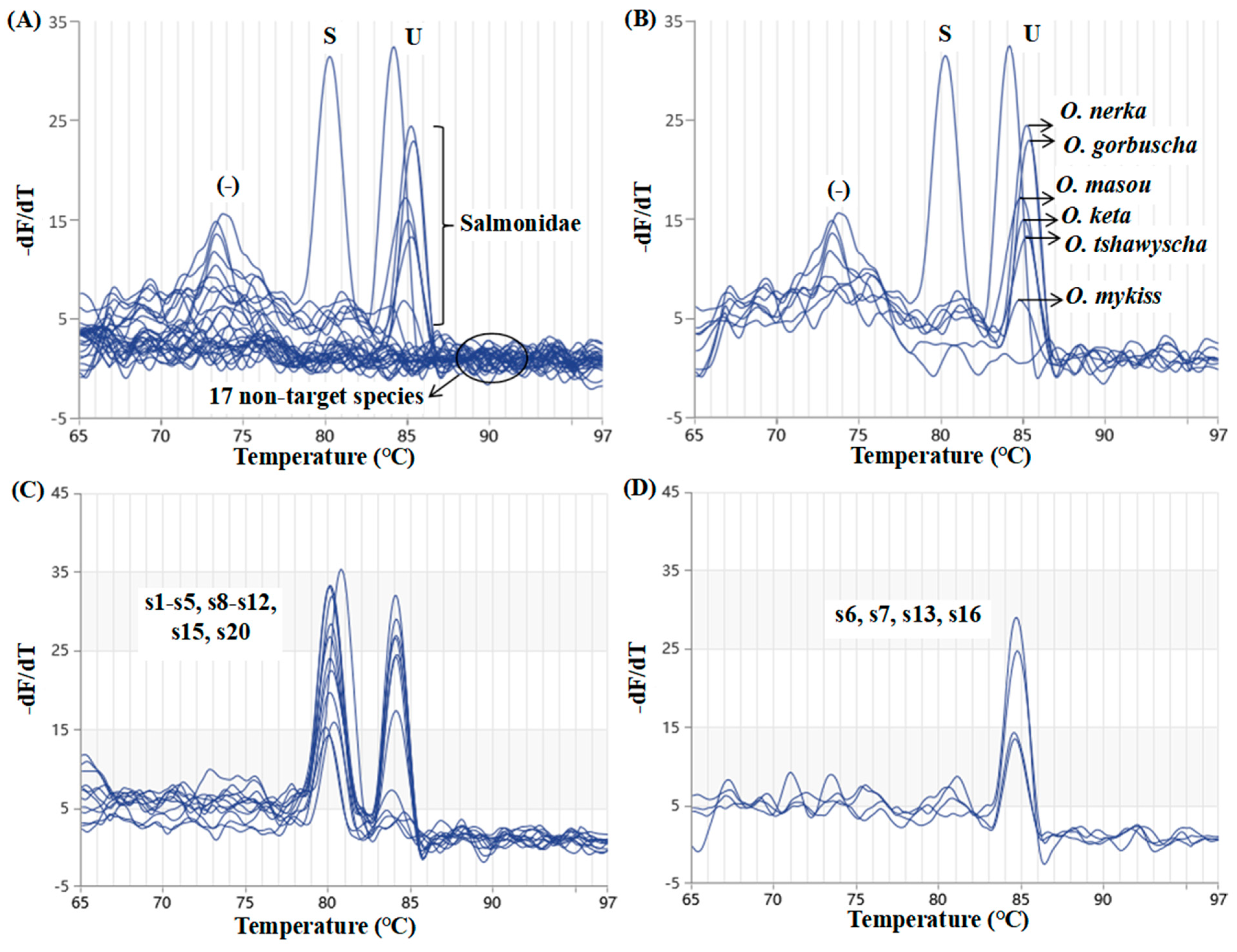
2.2. Evaluation of Sensitivity and Specificity
2.3. Method Validation Using Commercial Products
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sample Collection
3.2. DNA Extraction
3.3. PCR Amplification and Sequencing
3.4. Duplex Real-Time PCR Coupled with Melting Curve Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pandey, R.; Asche, F.; Misund, B.; Nygaard, R.; Adewumi, O.M.; Straume, H.M.; Zhang, D. Production growth, company size, and concentration: The case of salmon. Aquaculture 2023, 577, 739972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, S.M.; Mazal, X. Investigation of the nutritional composition of different types of salmon available to Canadian consumers. J. Agric. Food Res. 2020, 2, 100056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straume, H.M.; Asche, F.; Landazuri-Tveteraas, U.; Misund, B.; Pettersen, I.K.; Zhang, D. Product forms and price transmission in major European salmon markets. Aquaculture 2024, 582, 740508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, T.T.H.; Choi, J.; Park, D.; Park, S.; Kim, H. Evaluation of the nutritional potential of farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) tissues based on the contents of essential fatty acids. Aquac. Rep. 2024, 36, 102119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Val, O.T.; Jakobsen, A.N.; Lerfall, J.O.R. The use of atomized purified condensed smoke (PCS) in cold-smoke processing of Atlantic salmon-Effects on quality and microbiological stability of a lightly salted product. Food Control 2020, 112, 107155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astruc, T.; Vénien, A.; Clerjon, S.; Favier, R.; Loison, O.; Mirade, P.S.; Portanguen, S.; Rouel, J.; Lethiec, M.; Germond, A. Effect of dry salt versus brine injection plus dry salt on the physicochemical characteristics of smoked salmon after filleting. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamoorthi, L.; Lee, Y.; Brewer, S. Effect of food matrix and heat treatment on the rheological properties of salmon-based baby food. J. Food Eng. 2009, 95, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, S.; Elliott, C.; Huisman, W.; Dean, M.; van Ruth, S. Food fraud threats in UK post-harvest seafood supply chains; an assessment of current vulnerabilities. Npj Sci. Food 2024, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusti, A.; Malloggi, C.; Tinacci, L.; Nucera, D.; Armani, A. Mislabeling in seafood products sold on the Italian market: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Food Control 2023, 145, 109395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Xing, R.R.; Zhou, M.Y.; Sun, R.X.; Han, J.X.; Zhang, J.K.; Zheng, W.J.; Chen, Y. Application of DNA barcoding and metabarcoding for species identification in salmon products. Food Addit.Contam. Part A 2021, 38, 754–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panprommin, D.; Manosri, R. DNA barcoding as an approach for species traceability and labeling accuracy of fish fillet products in Thailand. Food Control 2022, 136, 108895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitch, C.J.; Tabb, A.M.; Marquis, G.E.; Hellberg, R.S. Species substitution and mislabeling of ceviche, poke, and sushi dishes sold in Orange County, California. Food Control 2023, 146, 109525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; D’Amico, P.; Guardone, L.; Castigliego, L.; Guidi, A.; Gianfaldoni, D.; Armani, A. The uncertainty of seafood labeling in China: A case study on Cod, Salmon and Tuna. Mar. Policy 2016, 68, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shan, R.; Muhammad, W.T.; Zhang, H. Recent advances in recognition molecule-based detection methods for prevention and monitoring of estrogen disruptors related food fraud. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 146, 104395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinothkanna, A.; Dar, O.I.; Liu, Z.; Jia, A.Q. Advanced detection tools in food fraud: A systematic review for holistic and rational detection method based on research and patents. Food Chem. 2024, 446, 138893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Song, H.W.; Wang, T.L.; Xue, H.Y.; Fei, Y.J.; Xiong, X. Recent advancements with loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) in assessment of the species authenticity with meat and seafood products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrias, S.; Ibáñez, J.; Fernandes, J.R.; Martins-Lopes, P. The role of DNA-based biosensors in species identification for food authenticity assessment. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 145, 104350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Kong, J.Q.; Xie, R.B.; Yu, W.J.; Chen, A.L. Comparative rapid identification of Salmo salar, Oncorhynchus mykiss, and Oncorhynchus keta components based on loop-mediated isothermal amplification and quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Aquaculture 2022, 550, 737835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Y.J.; Xue, H.Y.; Xiong, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, L.B.; Xiong, X.H. Detection of Salmonidae ingredient using mini-DNA barcoding in conjunction with a rapid visual inspection method. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 118, 105198. [Google Scholar]
- Cermakova, E.; Lencova, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Horka, P.; Vobruba, S.; Demnerova, K.; Zdenkova, K. Identification of fish species and targeted genetic modifications based on DNA analysis: State of the art. Foods 2023, 12, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.J.; Fu, M.Y.; Huang, M.H.; Cui, X.W.; Li, Y.; Cao, M.; Wang, L.B.; Xiong, X.H.; Xiong, X. Duplex real-time PCR combined with melting curve analysis for rapid detection of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) and rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 97, 103765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibowo, T.; Cahyadi, M.; Pramono, A.; Volkandari, S.D. Evaluation of commercial meat product food label conformity using multiplex PCR assay. Food Control 2023, 149, 109712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.J.; Liu, J.J.; Zhang, Q.D.; Zhou, X.; Liu, B. Multiplex PCR assay for identification and quantification of bovine and equine in minced meats using novel specific nuclear DNA sequences. Food Control 2019, 105, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.Y.; Suh, S.M.; Lee, Y.M.; Kim, H.Y. Multiplex PCR assay for simultaneous identification of five types of tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis, Thunnus alalonga, T. albacares, T. obesus and T. thynnus). Foods 2022, 11, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, C.S.; Deconinck, D.; Eljasik, P.; Sobczak, M.; Derycke, S.; Panicz, R.; Kane, N.; Mazloomrezaei, M.; Devlin, R.; Faria, M.A. A fast HRMA tool to authenticate eight salmonid species in commercial food products. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 156, 112440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, S.; Motalib Hossain, M.A.; Azlan, A.; Johan, M.R.; Chowdhury, Z.Z.; Eaqub Ali, M. TaqMan probe based multiplex quantitative PCR assay for determination of bovine, porcine and fish DNA in gelatin admixture, food products and dietary supplements. Food Chem. 2020, 325, 126756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Rio-Lavin, A.; Jimenez, E.; Pardo, M.A. SYBR-Green real-time PCR assay with melting curve analysis for the rapid identification of Mytilus species in food samples. Food Control 2021, 130, 108257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.C.; Li, J.P.; Liu, R.X.; Wei, Y.X.; Wang, S.W. Identification of eleven meat species in foodstuff by a hexaplex real-time PCR with melting curve analysis. Food Control 2021, 121, 107599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castigliego, L.; Armani, A.; Tinacci, L.; Gianfaldoni, D.; Guidi, A. Two alternative multiplex PCRs for the identification of the seven species of anglerfish (Lophius spp.) using an end-point or a melting curve analysis real-time protocol. Food Chem. 2015, 166, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, A.; Ghosh, S.K. Rapid seafood fraud detection powered by multiple technologies: Food authenticity using DNA-QR codes. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 131, 106204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Yuan, F.Y.; Huang, M.H.; Xiong, X.H. Exploring the possible reasons for fish fraud in China based on results from monitoring sardine products sold on Chinese markets using DNA barcoding and real time PCR. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2020, 37, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Yao, L.L.; Ying, X.G.; Lu, L.X.; Guardone, L.; Armani, A.; Guidi, A.; Xiong, X.H. Multiple fish species identified from China’s roasted Xue Yu fillet products using DNA and mini-DNA barcoding: Implications on human health and marine sustainability. Food Control 2018, 88, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.J.; Du, B.Y.; Ma, Q.H.; Ma, Y.H.; Yu, W.Y.; Li, T.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, G.X. Multiplex-PCR method application to identify duck blood and its adulterated varieties. Food Chem. 2024, 444, 138673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Huang, M.H.; Xu, W.J.; Li, Y.; Cao, M.; Xiong, X.H. Using real time fluorescence loop-mediated isothermal amplification for rapid species authentication of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 95, 103659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunther, B.; Raupach, M.J.; Knebelsberger, T. Full-length and mini-length DNA barcoding for the identification of seafood commercially traded in Germany. Food Control 2017, 73, 922–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Barbuto, M.; Galimberti, A.; Ferri, E.; Labra, M.; Malandra, R.; Galli, P.; Casiraghi, M. DNA barcoding reveals fraudulent substitutions in shark seafood products: The Italian case of “palombo” (Mustelus spp.). Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Target Species | Target Gene | Primer | Sequence (5′→3′) | Amplicon (bp) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit I (COI) | mlCOIintF (F) | GGWACWGGWTGAACWGTWTAYCCY CC | 313 | [31] |
| jgHCO2198 (R) | TAIACYTCIGGRTGICCRAARAAYCA | ||||
| Salmonidae | Cytochrome b (Cyt b) | FCYTB346 | CGGAGTTGTACTTCTACTTCTCAC | 159 | [19] |
| RCYTB530 | AAGTGGAAGGCGAAAAATCGT | ||||
| Atlantic salmon (S. salar) | COI | SalmonF-1 | CCTCCATTTGGCTGGTATTTCT | 220 | [32] |
| SalmonR-1 | GAGGGAGAGTAACAAAAGGACG |
| Sample Code | Processed Method | Duplex Real-Time PCR | DNA Barcoding (Similarity ≥ 98%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cq | S. salar | Salmonidae | |||
| s1 | Frozen products | 17.6 | + | + | S. salar |
| s2 | 15.2 | + | + | S. salar | |
| s3 | 15.8 | + | + | S. salar | |
| s4 | 18.8 | + | + | S. salar | |
| s5 | 15.5 | + | + | S. salar | |
| s6 | 17.6 | − | + | O. mykiss | |
| s7 | 15.2 | − | + | O. mykiss | |
| s8 | 15.5 | + | + | S. salar | |
| s9 | 15.0 | + | + | S. salar | |
| s10 | 17.4 | + | + | S. salar | |
| s11 | 15.6 | + | + | S. salar | |
| s12 | 15.0 | + | + | S. salar | |
| s13 | 20.6 | − | + | O. keta | |
| s14 | Dried products | - | − | − | − |
| s15 | 21.3 | + | + | S. salar | |
| s16 | 20.4 | − | + | O. gorbuscha | |
| s17 | - | − | − | − | |
| s18 | - | − | − | − | |
| s19 | - | − | − | − | |
| s20 | 22.5 | + | + | S. salar | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Xiong, X.; Song, H.; Wang, T.; Li, Y.; Wang, L. A Novel Method for Rapid Screening of Salmonidae Ingredients and Accurate Detection of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) Simultaneously Using Duplex Real-Time PCR Coupled with Melting Curve Analysis. Molecules 2024, 29, 4904. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29204904
Wang S, Xiong X, Song H, Wang T, Li Y, Wang L. A Novel Method for Rapid Screening of Salmonidae Ingredients and Accurate Detection of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) Simultaneously Using Duplex Real-Time PCR Coupled with Melting Curve Analysis. Molecules. 2024; 29(20):4904. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29204904
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shihui, Xiong Xiong, Hongwei Song, Tianlong Wang, Yi Li, and Libin Wang. 2024. "A Novel Method for Rapid Screening of Salmonidae Ingredients and Accurate Detection of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) Simultaneously Using Duplex Real-Time PCR Coupled with Melting Curve Analysis" Molecules 29, no. 20: 4904. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29204904
APA StyleWang, S., Xiong, X., Song, H., Wang, T., Li, Y., & Wang, L. (2024). A Novel Method for Rapid Screening of Salmonidae Ingredients and Accurate Detection of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) Simultaneously Using Duplex Real-Time PCR Coupled with Melting Curve Analysis. Molecules, 29(20), 4904. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29204904







