Identification of the Hypoglycemic Active Components of Lonicera japonica Thunb. and Lonicera hypoglauca Miq. by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
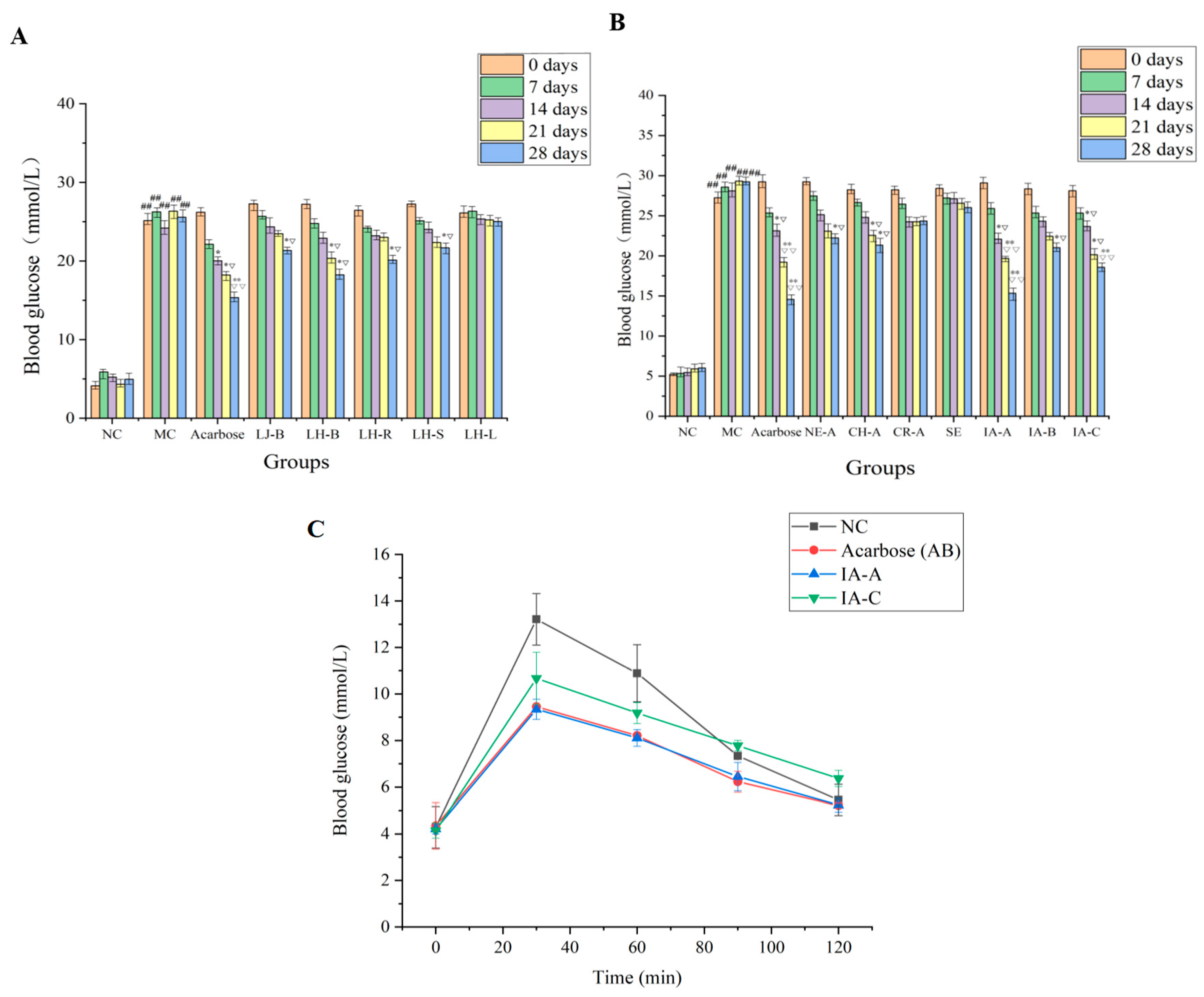
2.1. Evaluation of the Hypoglycemic Activity of L. japonica and Different Parts of L. hypoglauca Extract
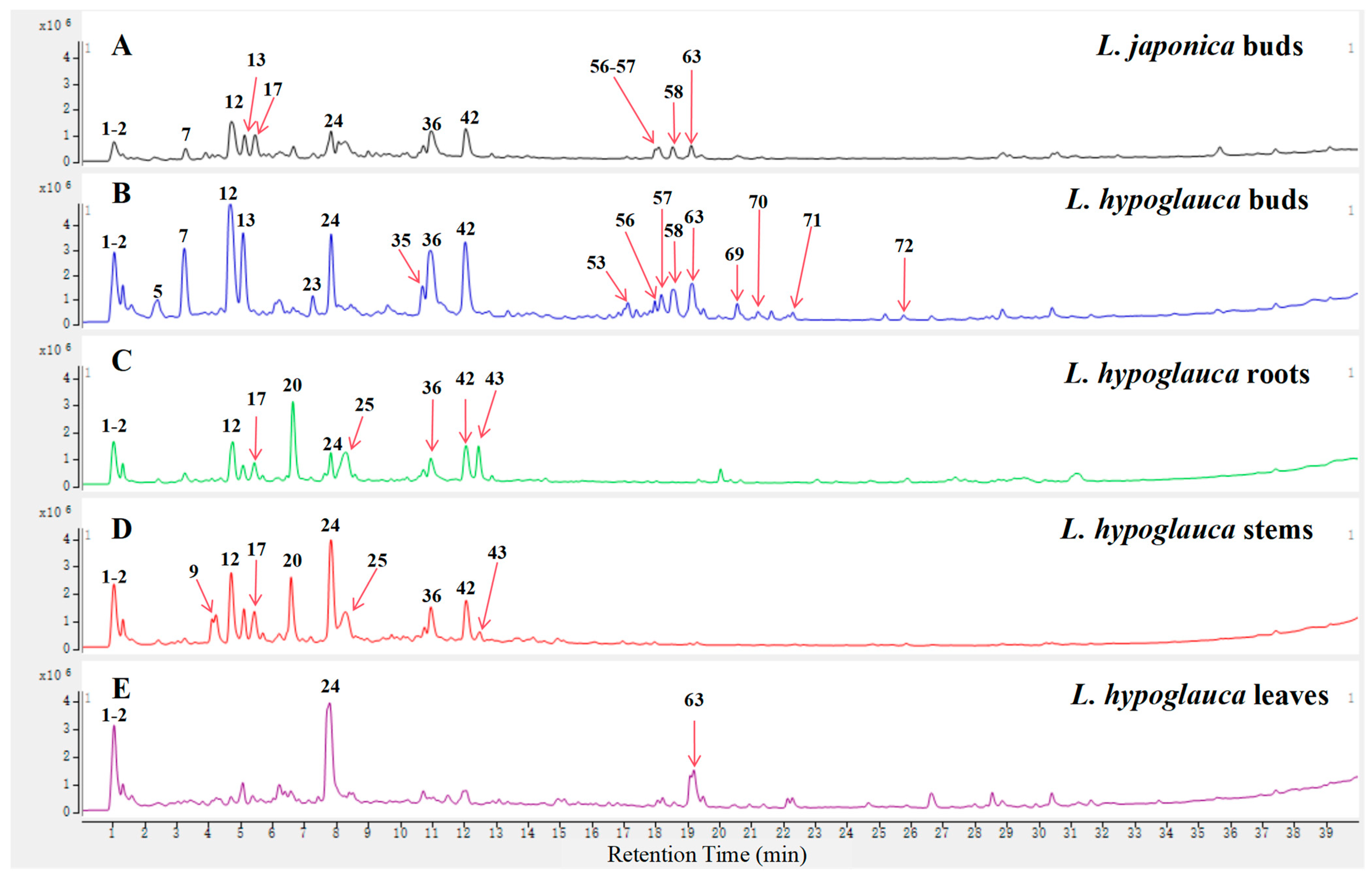
2.2. Identification of the Main Components of L. japonica and Different Parts of L. hypoglauca Extracts
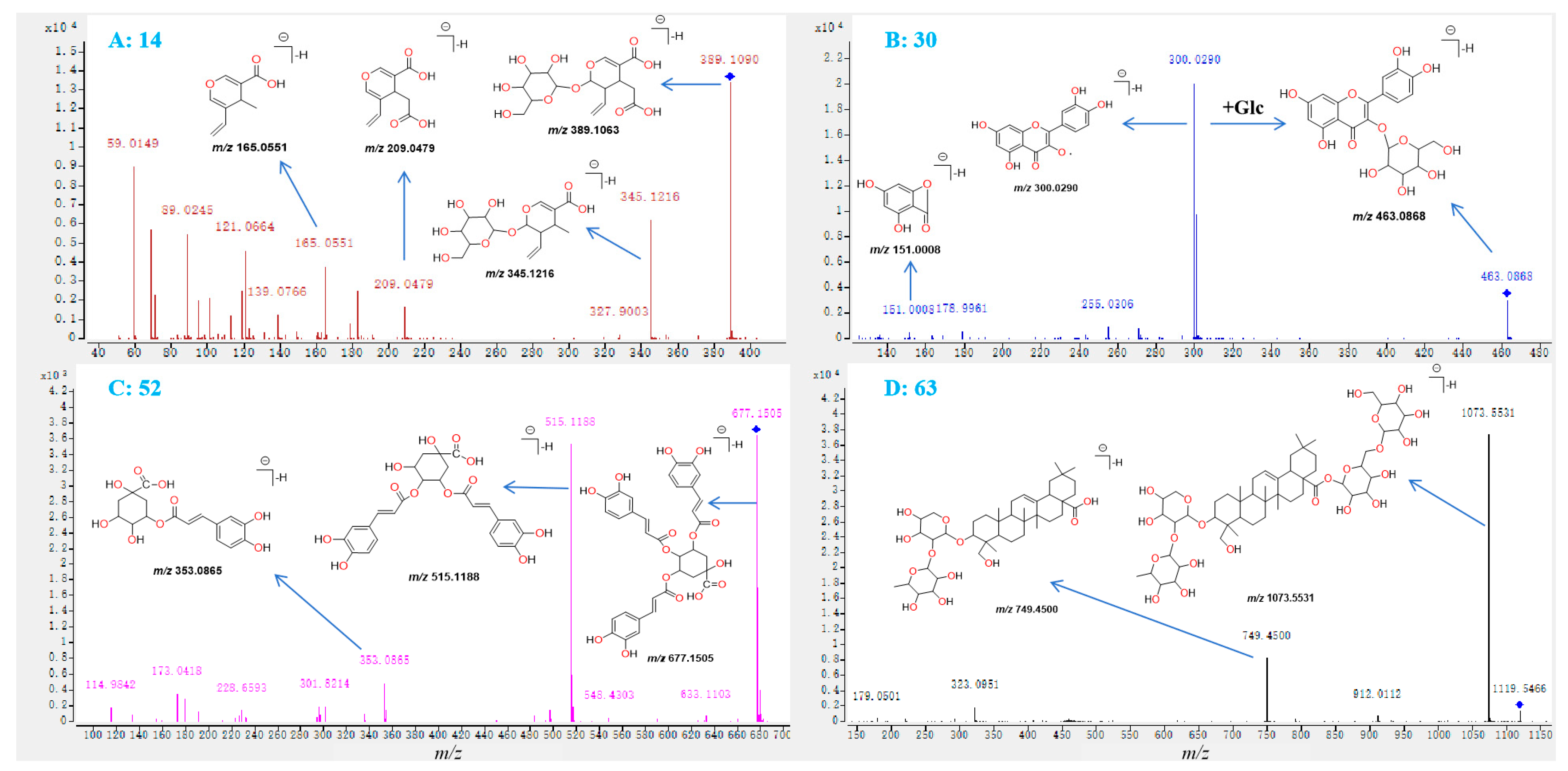
2.2.1. Investigation of the Fragmentation Behaviors of Standards
2.2.2. Identification of the Iridoid Glycosides, Flavonoids, Organic Acid, and Saponins
2.3. Evaluation of the Hypoglycemic Activity of Seven High-Content Compounds in L. japonica and L. hypoglauca Extracts
2.4. The Effect of Isochlorogenic Acid A (36) and Isochlorogenic Acid C (42) on the Postprandial Glycemia
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Chemicals
3.2. Extracts Experiment
3.3. UPLC-Q-TOF-MS Conditions
3.4. Experimental Animal
3.5. Establishment of High-Glucose Mouse Model (T2D) and the Drug Administration
3.6. The Experiment on Postprandial Glycemia of the Normal Mice
3.7. Statistical Method
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Z.H.; Zou, Q.F.; Jiang, L.J.; Liu, C.J.; Li, J.J.; Shi, W.; Chen, Z.F.; Zhang, F.X. The comparative analysis of Lonicerae japonicae flos and Lonicerae flos: A systematical review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 323, 117697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Cai, W.; Weng, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, X.; et al. Lonicerae Japonicae Flos and Lonicerae Flos: A systematic pharmacology review. Evid.-Based Compl. Alt. 2015, 1, 905063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Quan, Q.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, Y.; Lan, Y.; Li, S.; Yu, Y.; Cheng, Z. A comparative study of Lonicera japonica with related species: Morphological characteristics, ITS sequences and active compounds. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2014, 54, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhang, L.; He, P.; Li, H.; Pan, X.; Zhang, W.; Xiao, M.; He, F. Traditional uses, botany, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of Lonicerae japonicae flos and Lonicerae flos: A systematic comparative review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 322, 117278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.H.; Zhang, G.D.; Zhu, P.C.; Zhu, W.H.; Li, Y.Z.; Fan, X.W. Metabolite profiles and antibacterial and antioxidant activities of leaf extracts of five Lonicera species: A comparative study. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2023, 10, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Pan, H.; Li, M.; Miao, X.; Ding, H. Lonicera japonica Thunb.: Ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacology of an important traditional Chinese medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 138, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, C.; Wang, X.; Huang, L. Exploiting genes and functional diversity of chlorogenic acid and luteolin biosyntheses in Lonicera japonica and their substitutes. Gene 2014, 534, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, H.; Bai, X.; Liu, P.; Yang, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhou, L.; Min, X. Fractionation and antioxidant activities of the water-soluble polysaccharides from Lonicera japonica Thunb. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 151, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, W.; Fu, C.; Song, Y.; Fu, Q. Lonicerae japonicae flos and Lonicerae flos: A systematic review of ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacology. Phytochem. Rev. 2020, 19, 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, S.K.; Wu, X.X.; Jiang, Z.; Tong, C.W.S.; Chow, W.Y.L.; Au, D.C.T. Pharmacological Activities of Lonicerae japonicae flos and Its Derivative—“Chrysoeriol” in Skin Diseases. Molecules 2024, 29, 1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhong, X.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, L.; Huang, X.; Dong, Z.; Yang, S.; He, W.; Zeng, J.; Qing, Z. Systematic identification metabolites of Hemerocallis citrina Borani by high-performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry combined with a screening method. J. Phar. Biomed Anal. 2020, 186, 113314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qing, Z.X.; Zhao, H.; Tang, Q.; Mo, C.M.; Huang, P.; Cheng, P.; Yang, P.; Yang, X.Y.; Liu, X.B.; Zheng, Y.J.; et al. Systematic identification of flavonols, flavonol glycosides, triterpene and siraitic acid glycosides from Siraitia grosvenorii using high-performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry combined with a screening strategy. J. Phar. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 138, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pferschy-Wenzig, E.M.; Ortmann, S.; Atanasov, A.G.; Hellauer, K.; Hartler, J.; Kunert, O.; Gold-Binder, M.; Ladurner, A.; Heiß, E.H.; Latkolik, S.; et al. Characterization of constituents with potential anti-inflammatory activity in Chinese Lonicera species by UHPLC-HRMS based metabolite profiling. Metabolites 2022, 12, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Yang, H.; Qi, L.W.; Liu, E.H.; Ren, M.T.; Yan, Y.T.; Chen, J.; Li, P. Unbiased metabolite profiling by liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry and multivariate data analysis for herbal authentication: Classification of seven Lonicera species flower buds. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1245, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Liu, K.; Wang, R.; Liu, X.G.; Li, X.S.; Li, P.; Yang, H. Integration of targeted metabolite profiling and sequential optimization method for discovery of chemical marker combination to identify the closely-related plant species. Phytomedicine 2019, 61, 152829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurukar, M.S.A.; Chilkunda, N.D. Morus alba leaf bioactives modulate peroxisome proliferator activated receptor γ in the kidney of diabetic rat and impart beneficial effect. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 7923–7934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, R.H.; Thaku, N.; Timalsina, B.; Park, S.E.; Choi, J.S.; Jung, H.A. Inhibition mechanism of components isolated from Morus alba branches on diabetes and diabetic complications via experimental and molecular docking analyses. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Li, D.X.; Lu, D.Y.; Zhang, R.; Zheng, X.X.; Xu, B.J.; Zhao, Y.L.; Ji, S.; Guo, M.Z.; Wang, L.; et al. Morus alba L. water extract changes gut microbiota and fecal metabolome in mice induced by high-fat and high-sucrose diet plus low-dose streptozotocin. Phytother Res. 2022, 36, 1241–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Kongstad, K.T.; Jäger, A.K.; Nielsen, J.; Staerk, D. Quadruple high-resolution α-glucosidase/α-amylase/PTP1B/radical scavenging profiling combined with high-performance liquid chromatography-high-resolution mass spectrometry-solid-phase extraction-nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy for identification of antidiabetic constituents in crude root bark of Morus alba L. J Chromatogr A. 2018, 1556, 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Jha, S.; Gupta, S.K.; Bhattacharyya, P.; Ghosh, A.; Mandal, P. In vitro antioxidant and antidiabetic activity of oligopeptides derived from different mulberry (Morus alba L.) cultivars. Pharmacogn Res. 2018, 10, 361–367. [Google Scholar]
- Taghizadeh, M.; Zadeh, A.M.; Asemi, Z.; Farrokhnezhad, A.H.; Memarzadeh, M.R.; Banikazemi, Z.; Shariat, M.; Shafabakhsh, R. Morus Alba leaf extract affects metabolic profiles, biomarkers inflammation and oxidative stress in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A double-blind clinical trial. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2022, 49, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, D.; Qin, L.; Yang, X.; Gao, C. Comparative investigation for hypoglycemic effects of polysaccharides from four substitutes of Lonicera japonica in Chinese medicine. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Xie, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xia, B.; Li, Y.; Lin, Y.; Li, M.; Wu, P.; Lin, L. Recent advances in medicinal and edible homologous plant polysaccharides: Preparation, structure and prevention and treatment of diabetes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 258, 128873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y. Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effects of a polysaccharide from flower buds of Lonicera japonica in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 102, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimamura, Y.; Shibata, M.; Sato, M.; Nagai, R.; Yang, P.; Shiokawa, K.I.; Kikuchi, H.; Masuda, S. Anti-hyperglycemic activity and inhibition of advanced glycation end products by lonicera japonica thunb. in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2020, 26, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, X.; Sun, X.; Meng, X.; Fan, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y. Comparative study on chemical constituents of different medicinal parts of Lonicera japonica Thunb. Based on LC-MS combined with multivariate statistical Analysis. Heliyon 2024, 10, e31722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| No. | tR (min.) | (m/z) | Error (ppm) | Molecular Formula | Belongs | MS/MS Fragment Ions (m/z) | Identification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.96 | 191.0544 | −3.1 | C7H12O6 | All | 173.0421, 127.0396, 109.0302 | Citric acid |
| 2 | 1.04 | 191.0553 | −3.6 | C7H12O6 | All | 173.0452, 127.0388 | Quinic acid |
| 3 | 1.31 | 387.1305 | −4.9 | C17H24O10 | All | 341.1096, 179.0579, 119.0388 | Secologanin |
| 4 | 1.61 | 161.0448 | −1.2 | C6H10O5 | All | 101.0170, 57.0362 | Meglutol |
| 5 | 2.46 | 329.0874 | 2.1 | C14H18O9 | All | 167.0344, 152.0089, 108.0231 | Phaseoloidin |
| 6 | 2.54 | 218.1029 | 3.2 | C9H17NO5 | All | 146.0801, 125.0219, 116.0684 | Pantothenic acid |
| 7 c | 3.25 | 353.0882 | 2.5 | C16H18O9 | All | 191.0565, 179.0352, 135.0456 | Neochlorogenic acid |
| 8 | 4.09 | 299.0770 | 1.0 | C13H16O8 | All | 137.0244, 101.0247 | Protamin sulfate- 4-glucoside |
| 9 | 4.11 | 375.1304 | 4.8 | C16H24O10 | All | 213.0779, 179.0509, 169.0840 | Loganic acid |
| 10 | 4.41 | 175.0598 | −1.1 | C7H12O5 | All | 157.0569, 115.0420, 113.0620 | Isopropylmalic acid |
| 11 | 4.61 | 329.0860 | −2.1 | C14H18O9 | All | 167.0356 | Isophaseoloidin |
| 12 c | 4.70 | 353.0872 | −0.2 | C16H18O9 | All | 191.0560, 179.0351, 135.0454 | Chlorogenic acid |
| 13 c | 5.08 | 353.0878 | 1.4 | C16H18O9 | All | 191.0560, 179.0351, 135.0454 | Cryptochlorogenic acid |
| 14 | 5.10 | 389.1090 | 3.0 | C16H22O11 | All | 345.1191, 209.0425, 165.0551 | Secologanoside- 7-methyl ester |
| 15 | 5.15 | 389.1063 | 3.8 | C16H22O11 | All | 345.1205, 209.0440, 183.0642, 165.0545 | Secologanoside |
| 16 | 5.31 | 179.0332 | −3.9 | C9H8O4 | All | 135.0453, 107.0505 | Caffeic acid |
| 17 | 5.34 | 373.1098 | −8.3 | C16H22O10 | All | 193.0492, 179.0563, 149.0586 | Swertiamarine |
| 18 | 6.24 | 187.0976 | 2.6 | C9H16O4 | All | 125.0900, 97.0657 | Azelaic Acid |
| 19 | 6.28 | 337.0922 | −0.2 | C16H18O9 | All | 191.0554, 173.0436, 163.0397 | 5-O-p-coumaroylquinic acid |
| 20 a | 6.51 | 435.1545 | 9.6 | C17H26O10 | All | 227.0935, 165.0539, 101.0252 | Dihydrogen-vogeloside |
| 21 | 6.61 | 153.0176 | −3.9 | C7H6O4 | All | 135.0092, 109.0281 | Protocatechuic acid |
| 22 | 6.85 | 153.0186 | 2.6 | C7H6O4 | All | 135.0028, 109.0261 | Hypogallic acid |
| 23 | 7.24 | 367.1020 | 2.4 | C17H20O9 | All | 193.0503, 191.0550, 173.0439 | Methyl-chlorogenic acid |
| 24 c | 7.81 | 403.1239 | −0.2 | C17H24O11 | All | 371.0983, 223.0636, 179.0606, 165.0566, 121.0303 | Secoxyloganin |
| 25 | 8.29 | 609.1471 | 2.2 | C27H30O16 | All | 301.0343, 300.0247 | Lutin |
| 26 | 8.38 | 595.1269 | −5.0 | C26H28O16 | All | 301.0330, 300.0243 | Quercetin-7-glucoside- rhamnose |
| 27 | 8.43 | 367.1025 | 0.2 | C17H20O9 | All | 191.0562, 173.0446, 1111.0441 | Methyl- cryptochlorogenic acid |
| 28 a | 8.69 | 417.1412 | 3.5 | C18H26O11 | All | 237.0762, 191.0606 | Methyl-secoxyloganin |
| 29 | 9.43 | 463.0872 | −2.1 | C21H20O12 | All | 301.0365, 300.0290, 151.0034 | Quercetin-7-glucoside |
| 30 | 9.68 | 463.0868 | −3.2 | C21H20O12 | All | 301.0365, 300.0290 | Hyperoside |
| 31 | 9.69 | 593.1509 | −0.1 | C27H30O14 | All | 430.0789, 285.0349, 284.0281 | Luteolin-7-glucoside-4′- rhamnose |
| 32 | 9.92 | 447.0961 | 7.3 | C21H20O11 | All | 285.0388 | Luteolin-7-glucoside |
| 33 | 10.10 | 609.1467 | 1.6 | C27H30O16 | All | 315.0522, 314.0450 | Isorhamnetin- 3-rutinoside |
| 34 | 10.11 | 593.1505 | −0.8 | C27H30O14 | All | 285.0401, 284.0312 | Luteolin-7-rutinoside |
| 35 c | 10.61 | 515.1187 | −0.5 | C25H24O12 | All | 353.0885, 335.0793, 191.0561, 179.0356, 173.0458, 135.0457 | Isochlorogenic acid B |
| 36 c | 10.98 | 515.1192 | 0.3 | C25H24O12 | All | 353.0870, 335.0770, 191.0547, 179.0329, 173.0436, 135.0428 | Isochlorogenic acid A |
| 37 | 11.02 | 447.0967 | 8.2 | C21H20O11 | All | 285.0418, 284.0349 | Kaempferol-3-glucoside |
| 38 | 11.42 | 477.1078 | 9.3 | C22H22O12 | All | 314.0441, 271.0264 | Isorhamnetin-7-glucoside |
| 39 | 11.60 | 431.1021 | 9.5 | C25H24O12 | All | 269.0430, 268.0359 | Apigenin-7-glucoside |
| 40 | 11.63 | 193.0518 | 8.8 | C10H10O4 | All | 161.0258, 134.0357, 133.0287 | Isoferulic acid |
| 41 | 11.73 | 193.0493 | −4.1 | C10H10O4 | All | 161.0243, 134.0384 | Ferulic acid |
| 42 c | 12.05 | 515.1188 | −0.3 | C25H24O12 | All | 353.0886, 335.0749, 191.0554, 179.0353, 173.0460, 135.0462 | Isochlorogenic acid C |
| 43 | 12.42 | 537.1596 | −1.1 | C25H30O13 | All | 375.1291, 179.0343, 161.0254 | Grandiforoside |
| 44 a | 12.80 | 499.1287 | 10.0 | C25H24O11 | All | 353.0931, 337.0893, 191.0558 179.0405 | Dehydrogen- isochlorogenic acid A |
| 45 | 12.89 | 491.1249 | 9.6 | C23H24O12 | All | 329.0670 | Tricin-7-glucoside |
| 46 | 13.30 | 529.1350 | −1.7 | C25H24O11 | All | 367.1037, 353.0879, 191.0555, 179.0363, 161.0221 | Methyl- isochlorogenic acid B |
| 47 | 13.81 | 337.0930 | 2.0 | C16H18O9 | All | 191.0560, 173.0453, 163.0400 | 3-O-p-coumaroylquinic acid |
| 48 a | 13.90 | 499.1202 | −7.0 | C25H24O11 | All | 353.0844, 191.0575, 179.0396 | Dehydrogen- isochlorogenic acid B |
| 49 a | 14.24 | 529.1352 | −1.3 | C25H24O11 | All | 367.1027, 353.0862, 191.0549, 179.0337, 173.0435 | Methyl- isochlorogenic acid A |
| 50 | 14.60 | 367.1030 | 1.6 | C17H20O9 | All | 193.0499, 129.0555, 101.0612 | Methyl 4-caffeoylquinate |
| 51 | 15.22 | 529.1329 | −5.6 | C25H24O11 | All | 367.1043, 179.0348, 161.0235 | Methyl- isochlorogenic acid C |
| 52 | 15.98 | 677.1505 | −0.59 | C34H30O15 | All | 515.1188, 353.0865, 173.0418 | 3,4,5-tricaffeoylquinic acid |
| 53 a | 17.15 | 1397.6613 | 1.7 | C65H106O32 | All | 1073.5528, 643.1071 | Dipsacoside B- diglucoside |
| 54 a | 17.77 | 1559.7124 | 0.4 | C71H116O37 | All | 1235.6122, 1073.5249, 652.6374 | Dipsacoside B- triglucoside |
| 55 a | 17.82 | 1543.7128 | −2.5 | C71H116O36 | All | 1381.6549, 1219.6052 | Dipsacoside B-rutinoside-glucoside |
| 56 a,b | 18.01 | 1135.5944 | 4.7 | C53H86O23 | All | 1089.5447, 765.4313, 323.0779 | Hydroxyl-dipsacoside B |
| 57 | 18.25 | 1397.6597 | 0.4 | C65H106O32 | All | 1073.5499 | Isodipsacoside B- diglucoside |
| 58 a | 18.54 | 1235.6060 | 4.7 | C59H96O27 | All | 1073.5509, 911.4954, 527.3396 | Dipsacoside B-glucoside |
| 59 | 18.70 | 1235.6084 | 5.8 | C59H96O27 | All | 911.5006, 749.4477 | Isodipsacoside-B- glucoside |
| 60 a | 18.98 | 327.2184 | 3.6 | C18H32O5 | All | 229.1477, 221.1116, 211.1333 | Dehydroxypinellic acid |
| 61 a,b | 19.00 | 1105.5577 | 2.1 | C52H84O22 | All | 1059.5310, 889.1119, 735.4228, 469.7788, 323.0942 | Demethyl-dipsacoside B |
| 62 | 19.03 | 329.0658 | 0.6 | C17H14O7 | All | 167.0344, 152.0089 | Tricin |
| 63 b | 19.16 | 1119.5466 | 0.3 | C53H86O22 | All | 1073.5531, 749.4500, 323.0951 | Dipsacoside B |
| 64 b | 19.25 | 1119.5545 | 8.7 | C53H86O22 | All | 1073.5517, 911.5158, 749.4457, 323.0971 | Macranthoside B |
| 65 a | 19.30 | 1395.6466 | 2.3 | C65H104O32 | All | 1071.5376 | Dehydrogen- dipsacoside B-maltose |
| 66 | 19.38 | 1119.5559 | 9.3 | C53H86O22 | All | 1073.5501, 911.5094, 749.4431, 323.1027 | Isodipsacoside B |
| 67 a | 20.55 | 1247.7241 | 5.6 | C65H106O32 | All | 1381.6554, 1238.1004, 1057.5537 | Dipsacoside B-rutinoside |
| 68 a | 20.73 | 329.2340 | 3.6 | C18H34O5 | All | 229.1538, 171.1070 | Pinellic acid |
| 69 a | 20.82 | 1381.6681 | 2.9 | C65H106O32 | All | 1057.5602 | Dipsacoside B- glucoside-rhamnose |
| 70 a | 21.23 | 1219.6150 | 3.1 | C59H96O26 | All | 895.5042, 733.4157, 517.0624 | Dipsacoside B-rhamnose |
| 71 a | 22.13 | 1103.5547 | −3.4 | C52H82O22 | All | 1057.5556, 733.4597, 323.0945 | Demethyl-dehydrogen- dipsacoside B |
| 72 a | 25.73 | 911.4995 | −1.0 | C47H76O17 | All | 749.4421, 603.3780 | Deglucoside- dipsacoside B |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Q.; Zhao, D.; Leng, Y.; Chen, C.; Xiao, K.; Wu, Z.; Chen, F. Identification of the Hypoglycemic Active Components of Lonicera japonica Thunb. and Lonicera hypoglauca Miq. by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS. Molecules 2024, 29, 4848. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29204848
Wu Q, Zhao D, Leng Y, Chen C, Xiao K, Wu Z, Chen F. Identification of the Hypoglycemic Active Components of Lonicera japonica Thunb. and Lonicera hypoglauca Miq. by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS. Molecules. 2024; 29(20):4848. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29204848
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Qinxuan, Di Zhao, Ying Leng, Canhui Chen, Kunyu Xiao, Zhaoquan Wu, and Fengming Chen. 2024. "Identification of the Hypoglycemic Active Components of Lonicera japonica Thunb. and Lonicera hypoglauca Miq. by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS" Molecules 29, no. 20: 4848. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29204848
APA StyleWu, Q., Zhao, D., Leng, Y., Chen, C., Xiao, K., Wu, Z., & Chen, F. (2024). Identification of the Hypoglycemic Active Components of Lonicera japonica Thunb. and Lonicera hypoglauca Miq. by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS. Molecules, 29(20), 4848. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29204848







