Abstract
Chemical investigation of Penicillium sp. GDGJ-N37, a Sophora tonkinensis-associated fungus, yielded two new azaphilone derivatives, N-isoamylsclerotiorinamine (1) and 7-methoxyl-N-isoamylsclerotiorinamine (2), and four known azaphilones (3–6), together with two new chromone derivatives, penithochromones X and Y (7 and 8). Their structures were elucidated based on spectroscopic data, CD spectrum, and semi-synthesis. Sclerotioramine (3) showed significant antibacterial activities against B. subtilis and S. dysentery, and it also showed most potent anti-plant pathogenic fungi activities against P. theae, C. miyabeanus, and E. turcicum.
1. Introduction
Azaphilones, known as fungal pigments, are a family of fungal polyketide metabolites with a highly oxygenated pyranoquinone bicyclic core [1,2,3]. They are mainly obtained from fungal genera including Aspergillus sp., Talaromyces sp., and Penicillium sp. [4,5,6]. These compounds have been proven with a variety of biological activities, such as antiviral activity, cytotoxicity, anti-inflammatory activity, as well as antimicrobial activity [7,8,9,10,11]. For example, chaephilone C and chaetoviridides A–C, which were isolated from a marine-derived fungus Chaetomium sp. NA-S01-R1, exhibited notable antibacterial activities against Vibrio rotiferianus and V. vulnificus, and anti-methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (anti-MRSA) activities [12]. Due to their structural diversity and promising bioactivity, azaphilones have received increased attention, and more than 600 naturally-derived azaphilones have been reported [13].
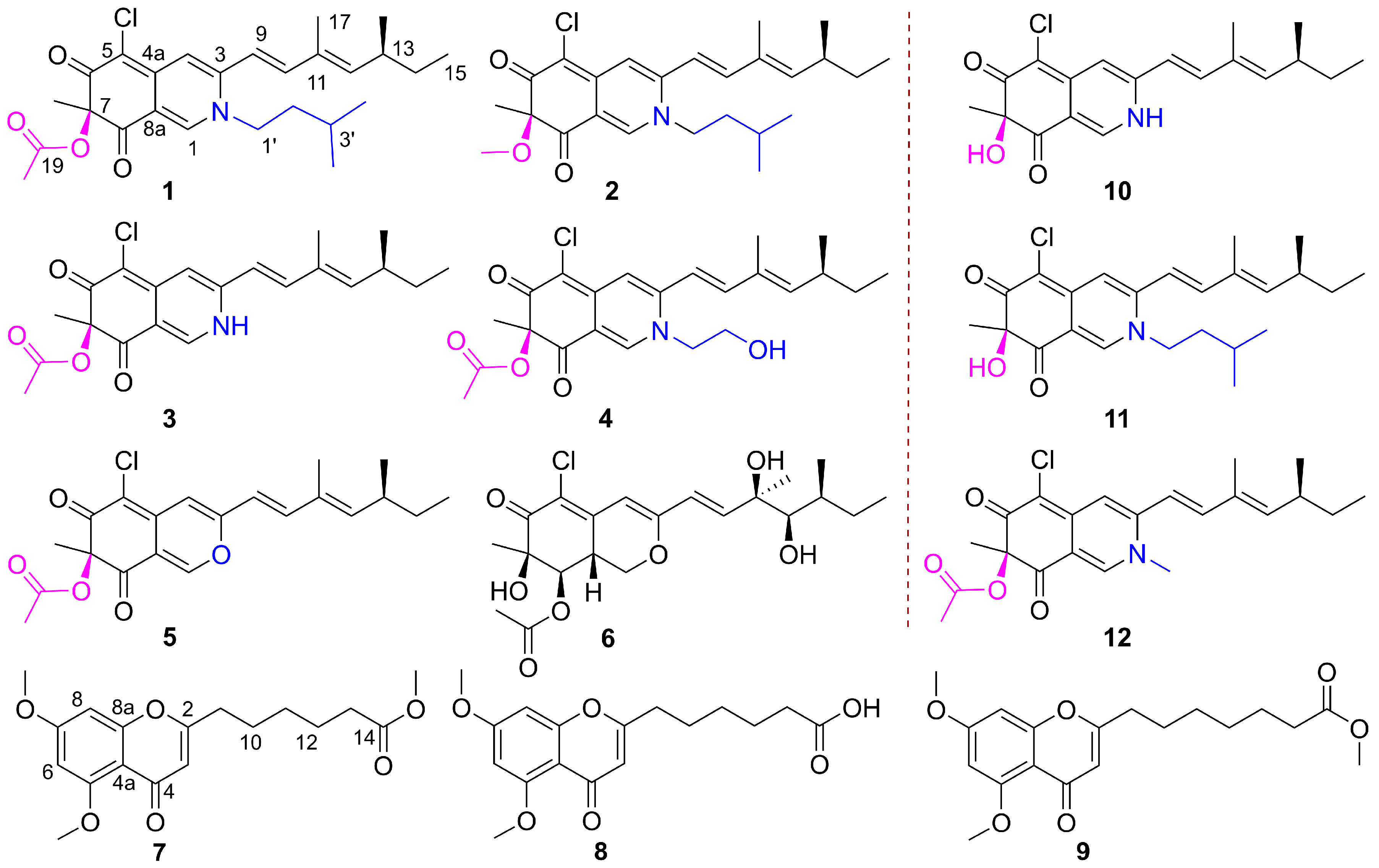
Fungi are a promising source of novel and biologically active natural products for drug discovery [14]. Penicillium fungi, recognized for their ability to generate structurally novel and bioactive compounds [15,16], are an important source of antimicrobial agents. In our ongoing search for bioactive metabolites from endophytic fungi [17,18,19], a Sophora tonkinensis-associated fungus, Penicillium sp. GDGJ-N37, was investigated. The EtOAc extract of this fungus showed antibacterial activity to Bacillus subtilis and antifungal activity to Setosphaeria turcica. A follow-up chemical investigation of the extract led to the isolation of two new azaphilones, N-isoamylsclerotiorinamine (1) and 7-methoxyl-N-isoamylsclerotiorinamine (2), together with four known azaphilone derivatives, sclerotioramine (3) [20], isochromophilone VI (4) [21], sclerotiorin (5) [21], and hypocrellone A (6) [22]. Two new chromone derivatives, penithochromones X and Y (7 and 8), together with a known one, penithochromone F (9) (Figure 1) [23], were also obtained from the fungus. Among these azaphilones, 3 could be obtained by semi-synthesis from 5 in a yield over 30% by a one-step process. Additionally, azaphilone derivatives 10–12 were semi-synthesized for structure elucidation and structure–activity relationship (SAR) studies. Herein, we described the isolation, structure elucidation, and antimicrobial activity of these compounds. Preliminary SAR of the azaphilone derivatives were also discussed.
Figure 1.
Structures of natural compounds 1–9, and semi-synthetic compounds 10–12.
2. Results and Discussion
N-Isoamylsclerotiorinamine (1) was obtained as a red amorphous powder. Its molecular formula was assigned as C26H34ClNO4 with 10 degrees of unsaturation based on the HRESIMS at m/z 460.2275 [M + H]+ (calcd. for C26H35ClNO4+, 460.2255). The intensity of an isotope peak at m/z 462.2255 (calcd. for C26H3537ClNO4+, 460.2220) is about 30%, indicating the presence of a chlorine atom in 1. The 1H NMR spectrum of 1 (Table 1) presented seven methyls at δH 2.12 (3H, s), 1.92 (3H, d, J = 1.2 Hz), 1.50 (3H, s), 1.04 (3H, d, J = 6.4 Hz), 0.99 (6H, d, J = 6.0 Hz), and 0.90 (3H, t, J = 7.6 Hz), five olefinic protons at δH 8.18 (1H, s), 7.16 (1H, s), 7.12 (1H, d, J = 15.6 Hz), 6.46 (1H, d, J = 15.6 Hz), and 5.80 (1H, d, J = 9.6 Hz). The 13C NMR spectrum (Table 1) revealed the presence of 20 carbons, including two ketones (δC 194.9 and 185.4) and one ester carbonyl group (δC 171.6), ten olefinic carbons (δC 151.2, 149.0, 148.2, 146.5, 143.7, 133.7, 116.8, 116.7, 112.6, and 101.1), one oxygenated quaternary carbon (δC 86.2), two methine carbons (δC 36.2 and 27.3), three methylene carbons (δC 54.3, 40.0, and 31.2), and seven methyl carbons (δC 23.8, 22.7 × 2, 20.6, 20.2, 12.8, and 12.4). The combination of δH 0.99 (6H, d, J = 6.0 Hz) and δC 22.7 × 2 indicated the presence of an isopropyl group in the structure.

Table 1.
1H and 13C NMR assignments for compounds 1 and 2 (CD3OD).
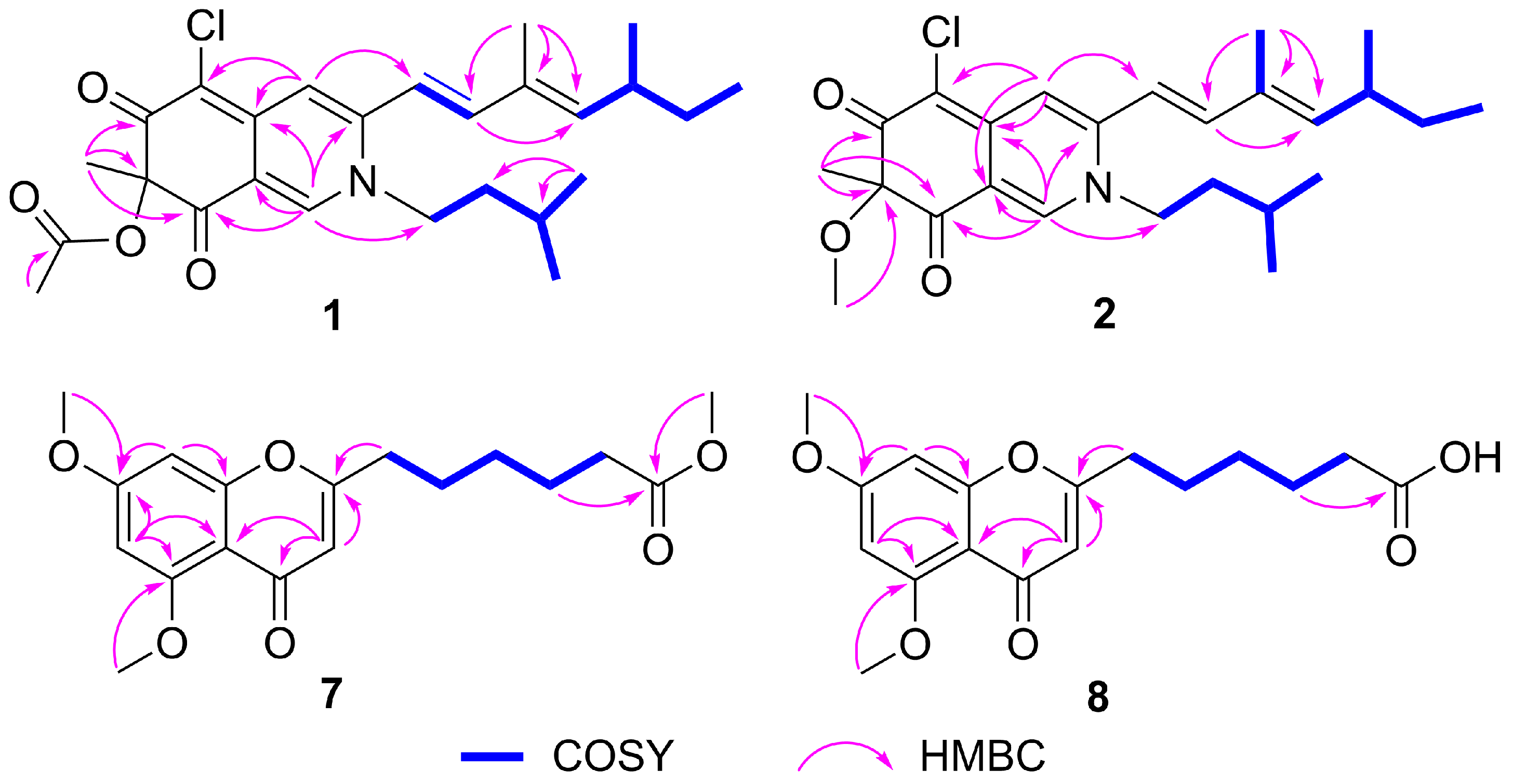
The HMBC correlations (Figure 2) from H-1 to C-3, C-4a, C-8, and C-8a, from H-4 to C-4a and C-5, and from H-18 to C-6, C-7, and C-8, indicated the existence of an isoquinoline-6,8(2H,7H)-dione moiety, a typical structural core in azaphilone skeleton. The HMBC correlations (Figure 2) from H-10 to C-12, from H-17 to C-10, C-11, and C-12, combined with the 1H-1H COSY correlations between H-9/H-10, H-12/H-13/H-14/H-15, and H-13/H-16 indicated the presence of a 3,5-dimethyl-1,3-heptadiene group. This side chain moiety linked to C-3 was proved by the HMBC correlations from H-9 to C-3 and H-4 to C-9. Comparing the NMR data of 1 and sclerotioramine (3) [20] indicated that 1 was a sclerotioramine derivative. The major difference was that 1 had an isoamyl fragment located at N-2, which was confirmed by the HMBC correlations from H-1 to C-1’, from H-4’ /H-5’ to C-2’ and C-3’, and by the 1H-1H COSY correlations between H-1’/H-2’/H-3’/H-4’ and H-5’. Thus, the planar structure of 1 was established (Figure 1).
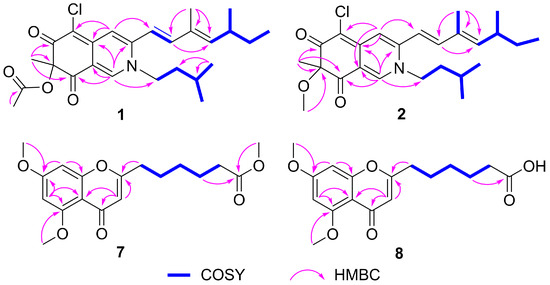
Figure 2.
Key HMBC and COSY correlations of compounds 1, 2, 7, and 8.
7-Methoxyl-N-isoamylsclerotiorinamine (2) was isolated as a red powder. The molecular formula was determined as C25H34ClNO3 with 9 degrees of unsaturation by the HRESIMS at m/z 432.2322 [M + H]+ (calcd. for C25H35ClNO3+, 432.2305). An isotope peak at m/z 434.2298 (calcd. for C25H3537ClNO3+, 434.2271) indicated the presence of a chlorine atom in 2. The 1H NMR and 13C NMR data of 2 (Table 1) were similar to those of 1, except that the acetyl group (δC 171.6, 20.2; δH 2.12) in 1 was replaced by a methoxy group (δC 54.9, δH 3.15) in 2. This observation was further confirmed by the HMBC correlation (Figure 2) from H-19 (δH 3.15) to C-7 (δC 90.4). On the basis of the spectroscopic data, the planar structure of 2 was assigned as shown in Figure 1.
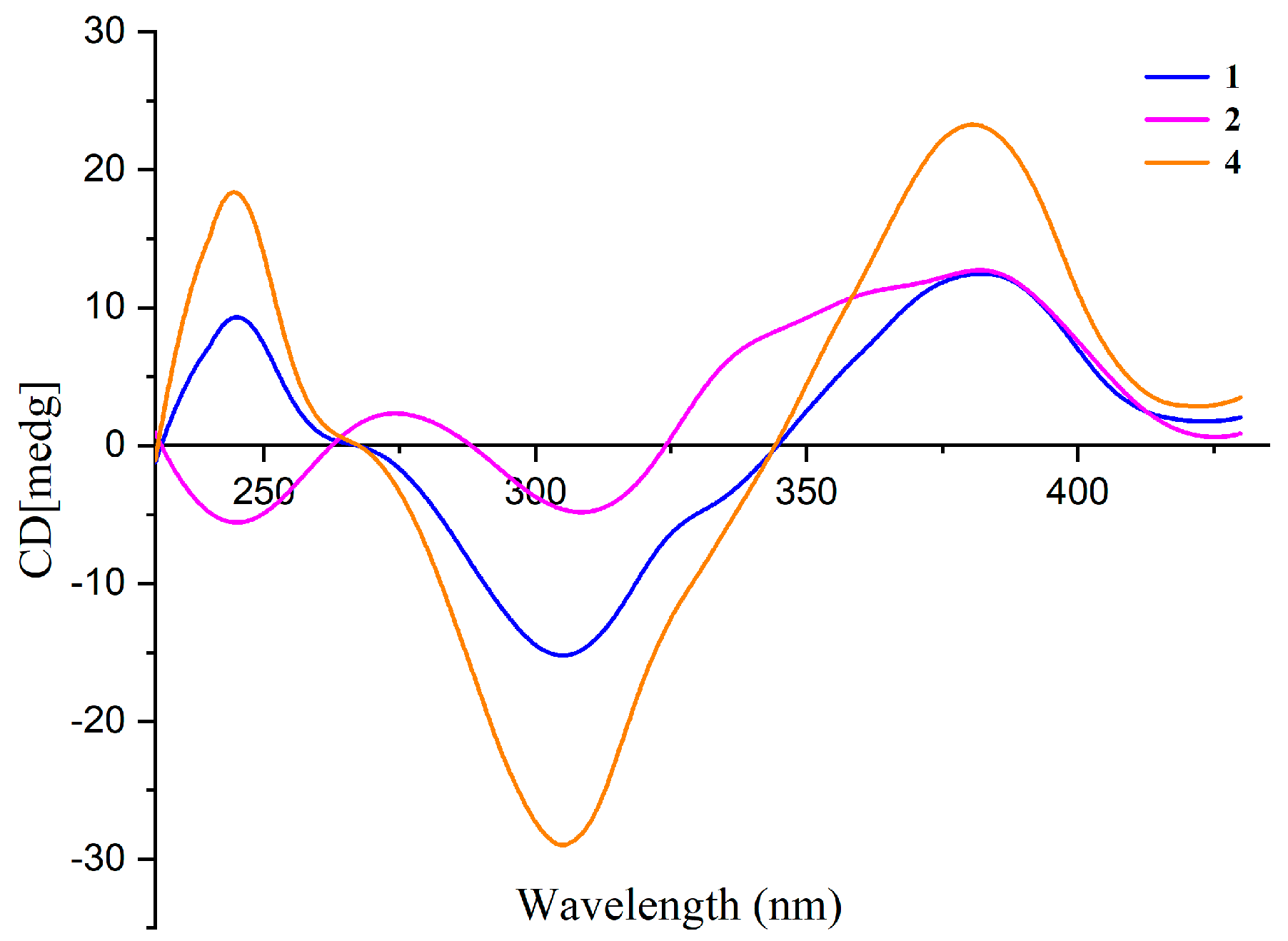
The absolute configuration at C-7 of 1 and 2 was elucidated by comparing their CD spectra with that of isochromophilone VI (4) (Figure 3). Compounds 1, 2, and 4 had similar CD spectra, which showed a positive Cotton effect at 380 nm and a negative Cotton effect at 300 nm. It revealed that the absolute configuration of C-7 was R in 1 and 2 [24,25]. The absolute configuration of the C-13 stereocenter in 1 and 2 was determined by semi-synthesis. Isoamylamine was employed to provide 1 and the deacetylate analogue 11 from the known sclerotiorin (5). Compound 11 was further methylated with CH3I to give 2. The 1H NMR spectra of the semisynthetic products 1 and 2 were identical to those of the natural products 1 and 2, respectively. On the other hand, compounds 1 and 2 are most likely derived from the same biogenetic pathway as 3 and 4. It meant that the absolute configuration of C-13 in 1 and 2 was an S-configuration, just the same as the absolute configuration of C-13 in 3 and 4. Thus, the absolute configurations of 1 and 2 were 7R, 13S.
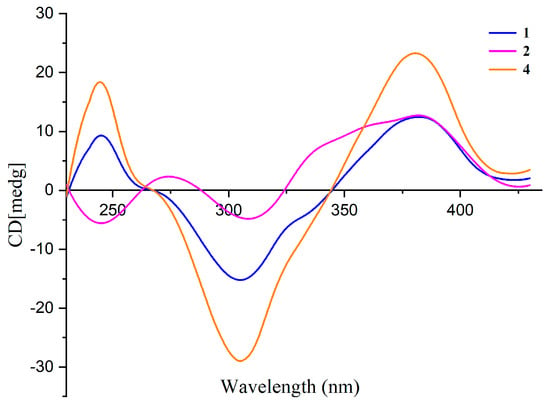
Figure 3.
CD spectra of compounds 1, 2, and 4 in MeOH.
Penithochromone X (7) was isolated as a light-yellow oil. Its molecular formula was established as C18H22O6 by HRESIMS at m/z 335.1490 [M + H]+ (calcd. for C18H23O6+, 335.1489), indicating 8 degrees of unsaturation. The 1H NMR spectrum of 10 (Table 2) revealed one pair of meta coupled protons [δH 6.40 (1H, d, J = 2.3 Hz) and 6.32 (1H, d, J = 2.3 Hz)], one olefinic proton [δH 5.98 (1H, s)], three methoxy groups [δH 3.91 (3H, s), 3.86 (3H, s), and 3.65 (3H, s)], and five methylenes [δH 2.50 (2H, t, J = 7.4 Hz), 2.31 (2H, t, J = 7.4 Hz), 1.72 (2H, m), 1.68 (2H, m), and 1.40 (2H, m)]. The 13C NMR spectrum (Table 2) displayed 18 carbon signals, including two carbonyl carbons (δC 177.7 and 174.1), eight olefinic carbons (δC 166.2, 163.9, 161.0, 160.3, 111.3, 109.1, 96.0, and 92.8), three methoxy carbons (δC 56.5, 55.8, and 51.6), and five methylene carbons (δC 33.9, 33.4, 28.5, 26.3, and 24.6). The HMBC correlations from H-3 to C-2, C-4, and C-4a, from H-6 to C-4a, C-5, and C-7, from H-8 to C-7 and C-8a, from 5-OCH3 to C-5, and 7-OCH3 to C-7, together with the remaining 7 degrees of unsaturation supported the existence of the 5,7-dioxygenated chromone moiety. The 1H-1H COSY correlations (Figure 2) of H-9/H-10/H-11/H-12/H-13, and the HMBC correlations (Figure 2) from H-12 to C-14, and from 14-OCH3 to C-14 defined the side chain. The HMBC correlation from H-9 to C-2 confirmed that the chain was located at C-2. The NMR data of 7 were similar to that of penithochromone F (9) [23], except for the disappearance of a CH2 unit in the side chain in 7. Hence, the structure of 7 was assigned as shown in Figure 1.

Table 2.
1H and 13C NMR assignments for compounds 7 (CDCl3) and 8 (DMSO-d6).
Penithochromone Y (8) was isolated as a light-yellow oil. Its molecular formula was determined as C17H20O6 on the basis of HRESIMS analysis. Its NMR data resembled those of 7 (Table 2). The only distinction was the absence of 14-OCH3 in 8. It was confirmed by the HMBC correlation from H-12 (δH 1.53) to C-14 (δC 174.7) (Figure 2). The structure of 8 is shown in Figure 1.
Semi-synthesis plays a pivotal role in providing enough material for further biological studies, determination of the absolute configurations, as well as investigation of the structure–activity relationship. During the study, the structure–activity relationship of these azaphilone derivatives was investigated. The semisynthetic transformation of 5 into 3 was achieved by one step using NH3·H2O [26], and deacelysclerotioramine (10) was also obtained as a byproduct. N-methylsclerotiorinamine (12) was semi-synthesized from 3 by methylating with CH3I [27].
The antibacterial activities of the natural products 1–9 and the semi-synthetic analogs 10–12 against Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis, Escherichia coli, Bacillus megaterium, and Shigella dysentery were evaluated. As shown in Table S1, 3 showed antibacterial activities against S. aureus, B. subtilis, B. megaterium, and S. dysentery with MIC values of 12.5, 3.125, 3.125, and 6.25 μg/mL, respectively, while 5 was inactive to these five strains except for B. subtilis (MIC value 100 μg/mL). In light of the structures and antibacterial activity results, we could see that when the O-atom at the 2-position was replaced by a N-atom, just like compounds 5 and 3, the bacterial activities would increase. It suggested that a N-atom at the 2-position in 3 was essential for its antibacterial activity. In addition, a comparison of the activities of 3 with 1, 4 and 12 revealed that an alkyl group substitution of 2-NH might lose or decrease their antibacterial activities. It should be mentioned that all the tested compounds showed no inhibitory effect on E. coli.
The antifungal activities of all compounds except 9 against the five plant pathogenic fungi, Alternaria citri, A. oleracea, Pestalotiopsis theae, Cochliobolus miyabeanus, and Exserohilum turcicum, were tested. As shown in Table S2, 3 was found to exhibit significant antifungal activity against these fungi with MIC values ranging from 3.125 to 25 μg/mL surpassing the efficacy of the positive control carbendazim. Notably, 3 showed the most potent activity against P. theae, C. miyabeanus, and E. turcicum. Compound 5 exhibited a potent effect on C. miyabeanus and E. turcicum with MIC values of 6.25 and 12.5 μg/mL but showed inhibitory to A. citri, A. oleracea, and P. theae with MICs ranging from 50 to 100 μg/mL. These results indicated that a N-atom at the 2-position in 3 played a positive role in their antifungal activity. On the other hand, 3 displayed better activity than 1, 4 and 12, suggesting that the presence of 2-NH might increase its antifungal activity.
In the antimicrobial screening, sclerotioramine (3) exhibited significant antifungal efficacy, which is better than carbendazim. Compound 3 is a N-containing azaphilone, which was mainly obtained from Penicillium sp. and Chaetomium sp. [13]. It has demonstrated diverse biological activities, including anti-inflammatory [24], cytotoxic [28], and antibacterial activities [29]. However, few studies on the antifungal activity of 3 against plant pathogens have been reported. The present results contribute valuable insights into the potential applications of compound 3 as an effective antifungal agent.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
The NMR spectral data were measured on Bruker AV 400 or 600 spectrometers (400 MHz for 1H NMR and 100 MHz for 13C NMR; 600 MHz for 1H NMR and 150 MHz for 13C NMR). Circular dichroism (CD) spectra were recorded on a JASCO J-1500 CD spectrometer (JASCO, Tokyo, Japan). Optical rotations were measured on a Bellingham-Stanley ADP 440+ polarimeter at 20 °C. The HRESI-MS data were measured on a Micro Mass Q-TOF spectrometer (Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA). Column chromatography was performed using silica gel (100–200 mesh, Qingdao Haiyang Chemical Co. Ltd., Qingdao, China), ODS (50 μm, YMC, Kyoto, Japan) and Sephadex LH-20 (GE) were used for column chromatography. Semi-preparative High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) was performed on a Shimadzu LC-20A system (Shimadzu Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) using an ODS column (250 × 10 mm, 5 μm, 2.0 mL/min, YMC).
3.2. Fungal Material
The fungus Penicillium sp. GDGJ-N37 was a Sophora tonkinensis-associated fungus obtained from Baise, Guangxi Province, China in 2017. The genomic DNA extraction was carried out using the Fungal DNA kits (E.Z.N.A., Omega, Norcross, GA, USA) in accordance with the manufacturer’s guidelines. The internal transcribed spacer (ITS1-5.8S-ITS2) regions of the fungi were amplified utilizing the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) with universal ITS primers, ITS1F (5′-CTTGGTCATTTAGAGGAAGTAA-3′) and ITS4 (5′-TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC-3′) [30]. The PCR involved an initial denaturation at 94 °C for 5 min, followed by 30 cycles of 94 °C denaturation for 40 s, 52 °C annealing for 40 s, and a 72 °C extension for 1 min, concluding with a final extension at 72 °C for 10 min. Subsequently, the amplified products underwent sequencing (Invitrogen, Shanghai, China), and a BLASTN search was employed to identify sequences with the closest match in the GenBank using the Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (NCBI). The sequence of its rDNA ITS region had been submitted to GenBank (the GenBank accession number OP622861). The strain was preserved at the State Key Laboratory for Chemistry and Molecular Engineering of Medicinal Resources, Guangxi Normal University.
3.3. Fermentation, Extraction and Isolation
The fungal strain was cultivated on rice solid medium in 270 Erlenmeyer flasks at room temperature for 30 days, each containing 80 g of rice and 100 mL of water. The fermented material was extracted with EtOAc (3 × 10 L) to afford the crude extract (90.0 g).
The extract was subjected to silica gel chromatography using a petroleum ether-ethyl acetate (100:0, 90:10, 70:30, 50:50, 30:70, 0:100) gradient system to give six fractions (Fr.1–Fr.6). Fr.1 (65.2 g) was isolated by silica gel chromatography using a petroleum ether-ethyl acetate (95:5, 90:10, 85:15, 80:20, 75:35, 70:30) gradient system to afford six subfractions (Fr.1.1–Fr.1.6). Fr.1.3 was purified by ODS eluting with MeOH-H2O (50:50–100:0) to yield 5 (12.0 g). Fr. 1.4 was chromatographed by ODS and semi-preparative HPLC (MeOH-H2O, 57:43) to afford 6 (40.6 mg). Fr.3 (12.5 g) was isolated by RP C18 with MeOH-H2O (40:60–100:0) gradient system to give four subfractions (Fr.3.1–Fr.3.4). Fr.3.3 (200.3 mg) was chromatographed on Sephadex LH-20 (MeOH) and semi-preparative HPLC (MeOH-H2O, 80:20) to afford 1 (8.2 mg) and 2 (4.1 mg). Fr.5 (9.3 g) was chromatographed by ODS and semi-preparative HPLC (MeOH-H2O, 76:24) to give 4 (10.2 mg). Fr.5 (500.6 mg) was isolated by ODS using a MeOH-H2O (45:55–100:0) to yield six fractions (Fr.5. 1–Fr.5. 6). Fr.5.6.4 (400.6 mg) was further purified by Sephadex LH-20 (CH2Cl2-CH3OH, 2:3) and semi-preparative HPLC (MeOH-H2O, 80:20) to afford 3 (100.0 mg). Fr.6 (3.3 g) was further purified by ODS using a MeOH-H2O (40:50–100:0) and to give five subfractions (Fr.6.1–Fr.6.5). Subfraction Fr.6.3 was further purified by Sephadex LH-20 (CH2Cl2-MeOH, 2:8) to afford subfractions Fr.6.3.1–Fr.6.3.4. Compound 9 (8.6 mg) was obtained from Fr.6.3.1 by semi-preparative HPLC (MeOH-H2O, 68:32). Fr.6.3.2 was purified by semi-preparative HPLC (MeOH-H2O, 58:42) to yield 8 (9.4 mg). Fr.6.3.4 was purified by semi-preparative HPLC (MeOH-H2O, 62:38) to give 7 (9.3 mg).
- N-Isopenthysclerotiorinamine (1): red amorphous powder; +196.6 (c 0.1, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 230 (2.40), 362 (2.52); CD (0.4 mM, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 246 (+3.7), 307 (−5.98), and 382 (+4.6) nm; 1H and 13C NMR data (Table 1); HRESIMS m/z 460.2256 [M + H]+ (calcd. for C26H35ClNO4+, 460.2255); 462.2249 (calcd. for C26H3537ClNO4+, 460.2220).
- 7-Methoxyl -N-isopenthysclerotiorinamine (2): red amorphous powder; +188.4 (c 0.1, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 230 (2.40), 362 (2.52); CD (0.4 mM, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 247 (−3.5), 311 (−3.3), and 382 (+4.5) nm; 1H and 13C NMR data (Table 1); HRESIMS m/z 432.2314 [M + H]+ (calcd. for C25H35ClNO3+, 432.2305); 434.2294 (calcd. for C25H3537ClNO3+, 434.2271).
- Penithochromone X (7): light yellow oil; UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 246 (4.09), 292 (3.75) nm; 1H and 13C NMR data (Table 2); HRESIMS m/z 335.1514 [M + H]+ (calcd. for C18H23O6+, 335.1489); 373.1014 [M + K]+ (calcd. for C18H22O6K+, 373.1048).
- Penithochromone Y (8): light yellow oil; UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 250 (4.14), 290 (3.86) nm; 1H and 13C NMR data (Table 2); HRESIMS m/z 321.1341 [M + H]+ (calcd. for C17H21O6+, 321.1333); 343.1148 [M + Na]+ (calcd. for C17H20O6Na+, 343.1152).
3.4. General Procedure for the Semi-Synthesis of 1–3, and 10–12
- Experimental details for 1 and 11
A mixture of compound 5 (500.0 mg, 1.38 mmol, 1 equiv.) and excess isoamylamine (1.28 mL, 11.02 mmol, 8 equiv.) in reaction vials was stirred at 42 °C. The progress of the reaction was monitored by TLC. Upon completion, the reaction mixture was purified by silica gel column chromatography (EtOAc-petroleum, 25:75) and reverse-phase semi-preparative HPLC (MeOH-H2O, 20:80) to give 1 and its deacetylate analog 11.
Compound 11: amorphous powder; HRESIMS m/z 440.1982 [M + Na]+ (calcd. for C24H32ClNO3Na+, 440.1963); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δH: 7.76 (1H, s, H-1), 7.02 (1H, d, J = 15.6 Hz, H-10), 7.01 (1H, s, H-4), 6.14 (1H, d, J = 15.6 Hz, H-9), 5.73 (1H, d, J = 9.6 Hz, H-12), 4.14 (1H, br s, 7-OH), 3.87 (2H, m, H-1’), 2.49 (1H, m, H-13), 1.85 (3H, d, J = 1.2 Hz, H-17), 1.69 (2H, m, H-2’), 1.66 (1H, m, H-3’), 1.55 (3H, s, H-18), 1.46 (1H, m, H-14α), 1.34 (1H, m, H-14β), 1.02 (3H, d, J = 6.6 Hz, H-16), 1.01 (3H, d, J = 5.6 Hz, H-4’), 0.99 (3H, d, J = 5.6 Hz, H-5’), 0.88 (3H, t, J = 7.4 Hz, H-15).
- Experimental details for 2
Compound 11 (50.0 mg, 119.6 µmol, 1 equiv.) and NaH (14.35 mg, 358.9 µmol, 3 equiv.) were dissolved in dry DMF (2 mL), CH3I (22.15 µL, 358.9 µmol, 3 equiv.) was then added, then the solution was stirred at 40 ℃ for 2 h. The reaction mixture was washed with an aqueous saturated NaHCO3 solution, and then the organic layer was evaporated to dryness to leave the crude product. The product was purified by silica gel column chromatography (EtOAc-petroleum, 25:75) and reverse-phase semi-preparative HPLC (MeOH-H2O, 20:80) to give 2.
- Experimental details for 3 and 10
A mixture of compound 5 (500.0 mg, 1.28 mmol, 1 equiv.) and K2CO3 (571.3 mg, 4.13 mmol, 3 equiv.) in excess NH3·H2O (1.5 mL) was stirred at 50 ℃. The progress of the reaction was monitored by TLC. Upon completion, the reaction mixture was purified by silica gel column chromatography (EtOAc-petroleum, 75:25) and reverse-phase semi-preparative HPLC (MeOH-H2O, 80:20) to give 3 (129.3 mg) and its deacetylate analogue 10.
Compound 10: amorphous powder; HRESIMS m/z 348.1390 [M + H]+ (calcd. for C19H23ClNO3+, 348.1361); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δH: 8.30 (1H, s, H-1), 7.27 (1H, d, J = 15.8 Hz, H-10), 6.98 (1H, s, H-4), 6.40 (1H, d, J = 15.8 Hz, H-9), 5.74 (1H, s, H-12), 2.47 (1H, br s, H-13), 1.87 (3H, s, H-17), 1.58 (3H, s, H-18), 1.41 (1H, s, H-14α), 1.30 (1H, m, H-14β), 0.99 (3H, d, J = 6.6 Hz, H-16), 0.86 (3H, t, J = 7.4, H-15).
- Experimental details for 12
Compound 12 was semi-synthesized from 3 by using a similar procedure as the conversion of compound 11 to 2.
Compound 12: amorphous powder; HRESIMS m/z 426.1462 [M + Na]+ (calcd. for C22H26ClNO4Na+, 426.1443); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CD3OD) δH: 8.19 (1H, s, H-1), 7.22 (1H, s, H-4), 7.14 (1H, d, J = 15.5 Hz, H-10), 6.48 (1H, d, J = 15.5 Hz, H-9), 5.81 (1H, d, J = 9.8 Hz, H-12), 3.80 (3H, s, H-21), 2.55 (1H, m, H-13), 2.12 (3H, s, H-20), 1.94 (3H, s, H-17), 1.50 (3H, s, H-18), 1.46 (1H, m, H-14α), 1.36 (1H, m, H-14β), 1.04 (3H, d, J = 6.9 Hz, H-16), 0.90 (3H, t, J = 7.5 Hz, H-15). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CD3OD) δC: 195.0 (C-8), 185.2 (C-6), 171.5 (C-19), 152.1 (C-12), 149.2 (C-5), 148.5 (C-10), 146.5 (C-3), 144.6 (C-1), 133.9 (C-11), 116.8 (C-8a), 116.4 (C-9), 112.0 (C-4), 100.9 (C-4a), 86.2 (C-7), 42.9 (C-1’), 36.3 (C-13), 31.2 (C-14), 23.8 (C-18), 20.6 (C-20), 20.2 (C-16), 12.7 (C-17), 12.4 (C-15).
3.5. Antimicrobial Assay
Antimicrobial evaluation against bacteria Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis, Escherichia coli, Bacillus megaterium, and Shigella dysentery was carried out by the serial-dilution method following reports found in the literature [18,31,32]. Anti-phytopathogenic activities against Alternaria citri, A. oleracea, Pestalotiopsis theae, Cochliobolus miyabeanus, and Exserohilum turcicum were assessed using a modified version of the two-fold serial dilutions method as the literature described [33,34]. The test compounds were dissolved in DMSO to prepare a stock solution. Ciprofloxacin and carbendazim were used as the positive controls with respect to bacteria and plant pathogenic fungi.
4. Conclusions
In summary, we described a chemical investigation of the fungus Penicillium sp. GDGJ-N37. Two new nitrogenated azaphilones, N-isoamylsclerotiorinamine (1) and 7-methoxyl-N-isoamylsclerotiorinamine (2), together with four known azaphilones (3–6), and two new chromone derivatives, penithochromones X and Y (7 and 8), were obtained from the fermentation culture of the fungus. Remarkably, compound 3 exhibited significant anti-plant pathogenic fungi activities. The present research not only expands the structural diversity of azaphilones, but also provides inspiration for the discovery of antifungal leading compounds.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/molecules29020348/s1, Spectroscopic data of compounds 3–6; Table S1. Antibacterial activities of compounds 1–12 (MIC, µg/mL); Table S2. Antifungal activities of compounds 1–8, and 10–12 (MIC, µg/mL); Figure S1. HR-ESI-MS spectrum of compound 1; Figure S2. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CD3OD) spectrum of compound 1; Figure S3. 13C NMR (100 MHz, CD3OD) spectrum of compound 1; Figure S4. HMQC (CD3OD) spectrum of compound 1; Figure S5. 1H-1H COSY (CD3OD) spectrum of compound 1; Figure S6. HMBC (CD3OD) spectrum of compound 1; Figure S7. HR-ESI-MS spectrum of compound 2; Figure S8. 1H NMR (600 MHz, CD3OD) spectrum of compound 2; Figure edS9. 13C NMR (150 MHz, CD3OD) spectrum of compound 2; Figure S10. HMQC (CD3OD) spectrum of compound 2; Figure S11. 1H-1H COSY (CD3OD) spectrum of compound 2; Figure S12. HMBC (CD3OD) spectrum of compound 2; Figure S13. HR-ESI-MS spectrum of compound 7; Figure S14. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) spectrum of compound 7; Figure S15. 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) spectrum of compound 7; Figure S16. HMQC (CDCl3) spectrum of compound 7; Figure S17. 1H-1H COSY (CDCl3) spectrum of compound 7; Figure S18. HMBC (CDCl3) spectrum of compound 7; Figure S19. HR-ESI-MS spectrum of compound 8; Figure S20. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) spectrum of compound 8; Figure S21. 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) spectrum of compound 8; Figure S22. HMQC (DMSO-d6) spectrum of compound 8; Figure S23. 1H-1H COSY (DMSO-d6) spectrum of compound 8; Figure S24. HMBC (DMSO-d6) spectrum of compound 8.
Author Contributions
L.H. performed the experiments for the isolation, structure elucidation, bioactivity evaluation, and prepared the manuscript; Y.L., J.P., L.L. (Liuxia Lvand), J.Z., L.L. (Liqi Liang) and X.H. contributed to fungal fermentation, chemical extraction, part of the isolation and bioactivity evaluation; J.L. contributed to part of the structure determination; W.X. and R.Y. supervised the research work and revised the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the Guangxi Natural Science Foundation of China [Grant Nos. 2023GXNSFAA026228, 2021AC19424, and 2018GXNSFAA281169], the National Natural Science Foundation of China [Grant No. 21762007], the Project of State Key Laboratory for Chemistry and Molecular Engineering of Medicinal Resources (Guangxi Normal University) [CMEMR2018-C29].
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the Supplementary Materials or can be provided by the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Huang, X.; Zhang, W.; Tang, S.; Wei, S.; Lu, X. Collaborative biosynthesis of a class of bioactive azaphilones by two separate gene clusters containing four PKS/NRPSs with transcriptional crosstalk in fungi. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 132, 4379–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.M.; Yang, S.X.; Qin, J.C. Azaphilones: Chemistry and biology. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 4755–4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, K.; Greco, C.; Bailey, A.M.; Willis, C.L. Core steps to the azaphilone family of fungal natural products. ChemBioChem 2021, 22, 3027–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Kashef, D.H.; Youssef, F.S.; Hartmann, R.; Knedel, T.; Janiak, C.; Lin, W.; Reimche, I.; Teusch, N.; Liu, Z.; Proksch, P. Azaphilones from the red sea fungus Aspergillus falconensis. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Feng, X.; Xiao, Z.; Liu, L.; Li, H.; Ma, L.; Lu, Y.; Ju, J.; She, Z.; Lin, Y. Azaphilones and p-terphenyls from the mangrove endophytic fungus Penicillium chermesinum (ZH4-E2) isolated from the South China Sea. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.X.; Li, X.; Shi, L.Y.; Feng, L.; Wang, J.W.; Tan, N.H.; Wang, Z. Azaphilones with anti-colon cancer activities from the plant endophytic fungus Talaromyces primulinus WZ-883. Phytochem. Lett. 2023, 57, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.X.; Kusari, S.; Laatsch, H.; Golz, C.; Kusari, P.; Strohmann, C.; Kayser, O.; Spiteller, M. Antibacterial azaphilones from an endophytic fungus, Colletotrichum sp. BS4. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanokmedhakul, S.; Kanokmedhakul, K.; Nasomjai, P.; Louangsysouphanh, S.; Soytong, K.; Isobe, M.; Kongsaeree, P.; Prabpai, S.; Suksamrarn, A. Antifungal azaphilones from the fungus Chaetomium cupreum CC3003. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 891–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.J.; Zhang, Y.F.; Wu, K.; Xu, Y.X.; Meng, X.G.; Jiang, Z.T.; Ge, M.; Shao, L. New azaphilones, phomopsones A–C with biological activities from an endophytic fungus Phomopsis sp. CGMCC No. 5416. Fitoterapia 2020, 145, 104573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yang, J.; Liao, Y.Y.; Cheng, G.; Chen, J.; Cheng, X.D.; Qin, J.J.; Shao, Z. Cytotoxic nitrogenated azaphilones from the deep-sea-derived fungus Chaetomium globosum MP4-S01-7. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 1157–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.C.; Ke, T.Y.; Ko, Y.C.; Lin, J.J.; Chang, J.S.; Cheng, Y.B. Anti-inflammatory azaphilones from the edible alga-derived fungus Penicillium sclerotiorum. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Liao, Y.; Chen, R.; Hou, Y.; Ke, W.; Zhang, B.; Gao, M.; Shao, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, F. Chlorinated azaphilone pigments with antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities isolated from the deep sea derived fungus Chaetomium sp. NA-S01-R1. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Tao, H.; Chen, W.; Yang, B.; Zhou, X.; Luo, X.; Liu, Y. Recent advances in the chemistry and biology of azaphilones. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 10197–10220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, T.; Gu, Q.; Li, D. Penicyclones A–E, antibacterial polyketides from the deep-sea-derived fungus Penicillium sp. f23-2. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2699–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, T.; Inagaki, M.; Chai, H.B.; Wieboldt, T.; Rapplye, C.; Rakotondraibe, L.H. Halogenated compounds from directed fermentation of Penicillium concentricum, an endophytic fungus of the liverwort Trichocolea tomentella. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1397–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orfali, R.; Perveen, S.; Al-Taweel, A.; Ahmed, A.F.; Majrashi, N.; Alluhay, K.; Khan, A.; Luciano, P.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O. Penipyranicins A–C: Antibacterial methylpyran polyketides from a hydrothermal spring sediment Penicillium sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 3591–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.F.; Hou, X.M.; Yao, F.H.; Zheng, N.; Li, J.; Wang, C.Y.; Yang, R.Y.; Shao, C.L. Xylapeptide A, an antibacterial cyclopentapeptide with an uncommon L-pipecolinic acid moiety from the associated fungus Xylaria sp. (GDG-102). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.Y.; Huang, X.S.; Liu, X.B.; Mo, T.X.; Xu, Z.L.; Li, B.C.; Qin, X.Y.; Li, J.; Schäberle, T.F.; Yang, R.Y. Three new andrastin derivatives from the endophytic fungus Penicillium vulpinum. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 36, 3262–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, T.X.; Huang, X.S.; Zhang, W.X.; Scháberle, T.F.; Qin, J.K.; Zhou, D.X.; Qin, X.Y.; Xu, Z.L.; Li, J.; Yang, R.Y. A series of meroterpenoids with rearranged skeletons from an endophytic fungus Penicillium sp. GDGJ-285. Org. Chem. Front. 2021, 8, 2232–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.R.; Sena Filho, J.G.; Hoover, A.R.; King, J.B.; Ellis, T.K.; Powell, D.R.; Cichewicz, R.H. Chemical epigenetics alters the secondary metabolite composition of guttate excreted by an atlantic-forest-soil-derived Penicillium citreonigrum. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 942–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Son, S.; Kim, J.W.; Jeon, E.S.; Ko, S.K.; Ryoo, I.J.; Shin, K.S.; Hirota, H.; Takahashi, S.; Osada, H. Penidioxolanes A and B, 1, 3-dioxolane containing azaphilone derivatives from marine-derived Penicillium sp. KCB12C078. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2015, 21, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.B.; Tang, J.; Jiao, W.; Jiao, W.H.; Li, L.; Sun, F.; Wang, S.P.; Yang, F.; Lin, H.W. Azaphilone and isocoumarin derivatives from the sponge-derived fungus Eupenicillium sp. 6A-9. Tetrahedron Lett. 2018, 59, 3345–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Xu, W.; Fan, R.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Han, S.; Liu, W.; Pan, M.; Cheng, Z. Penithoketone and penithochromones A–L, polyketides from the deep-Sea-derived fungus Penicillium thomii YPGA3. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 2679–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.L.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Yang, T.; Yao, C.; Wu, L.W.; Li, G.Y. Azaphilone alkaloids with anti-inflammatory activity from fungus Penicillium sclerotiorum cib-411. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2019, 67, 2175–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Q.; Du, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, T.; Zhu, W. Azaphilones from the marine sponge-derived fungus Penicillium sclerotiorum OUCMDZ-3839. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Huang, Y.; Hong, J.; Wei, X.; Zeng, F.; Li, J.; Ye, G.; Yuan, J.; Long, Y. Preparation, COX-2 inhibition and anticancer activity of sclerotiorin derivatives. Mar. Drugs 2020, 19, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casillo, A.; Di Guida, R.; Carillo, S.; Chen, C.; Kamasaka, K.; Kawamoto, J.; Kurihara, T.; Corsaro, M.M. Structural elucidation of a novel lipooligosaccharide from the cold-adapted bacterium OMVs producer Shewanella sp. HM13. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Dong, L.; Zang, X.; Gu, Z.; He, X.; Yao, L.; Cao, L.; Qiu, J. A new azaphilone from the entomopathogenic fungus Hypocrella sp. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 2000–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Long, Y.; Lei, X.; Xu, J.; Huang, Z.; She, Z.; Lin, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, L. Azaphilones isolated from an alga-derived fungus Penicillium sp. ZJ-27. Phytochem. Lett. 2016, 18, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.F.; Ma, J.; Jing, Q.Q.; Cao, X.Z.; Chen, L.; Chao, R.; Zheng, J.Y.; Shao, C.L.; He, X.Y.; Wei, M.Y. Integrating activity-guided strategy and fingerprint analysis to target potent cytotoxic brefeldin a from a fungal library of the medicinal mangrove Acanthus ilicifolius. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, C.G.; Uppuluri, P.; Tristan, A.R.; Wormley, F.L.; Mowat, E.; Ramage, G.; Lopez-Ribot, J.L. A simple and reproducible 96-well plate-based method for the formation of fungal biofilms and its application to antifungal susceptibility testing. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1494–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Shafi, J.; Ji, M.S.; Bi, Y.H.; Yu, Z.G. Antimicrobial metabolites from Streptomyces sp. SN0280. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1015–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fromtling, R.A.; Galgiani, J.N.; Pfaller, M.A.; Espinel-Ingroff, A.; Bartizal, K.F.; Bartlett, M.S.; Body, B.A.; Frey, C.; Hall, G.; Roberts, G.D. Multicenter evaluation of a broth macrodilution antifungal susceptibility test for yeasts. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1993, 37, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.Y.; Li, C.Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Peng, G.T.; She, Z.G.; Zhou, S.N. Lactones from a brown alga endophytic fungus (No. ZZF36) from the South China Sea and their antimicrobial activities. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 4205–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).