Synthesis and Anti-Liver Fibrosis Research of Aspartic Acid Derivatives
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. The Modification Strategies of L-Asp
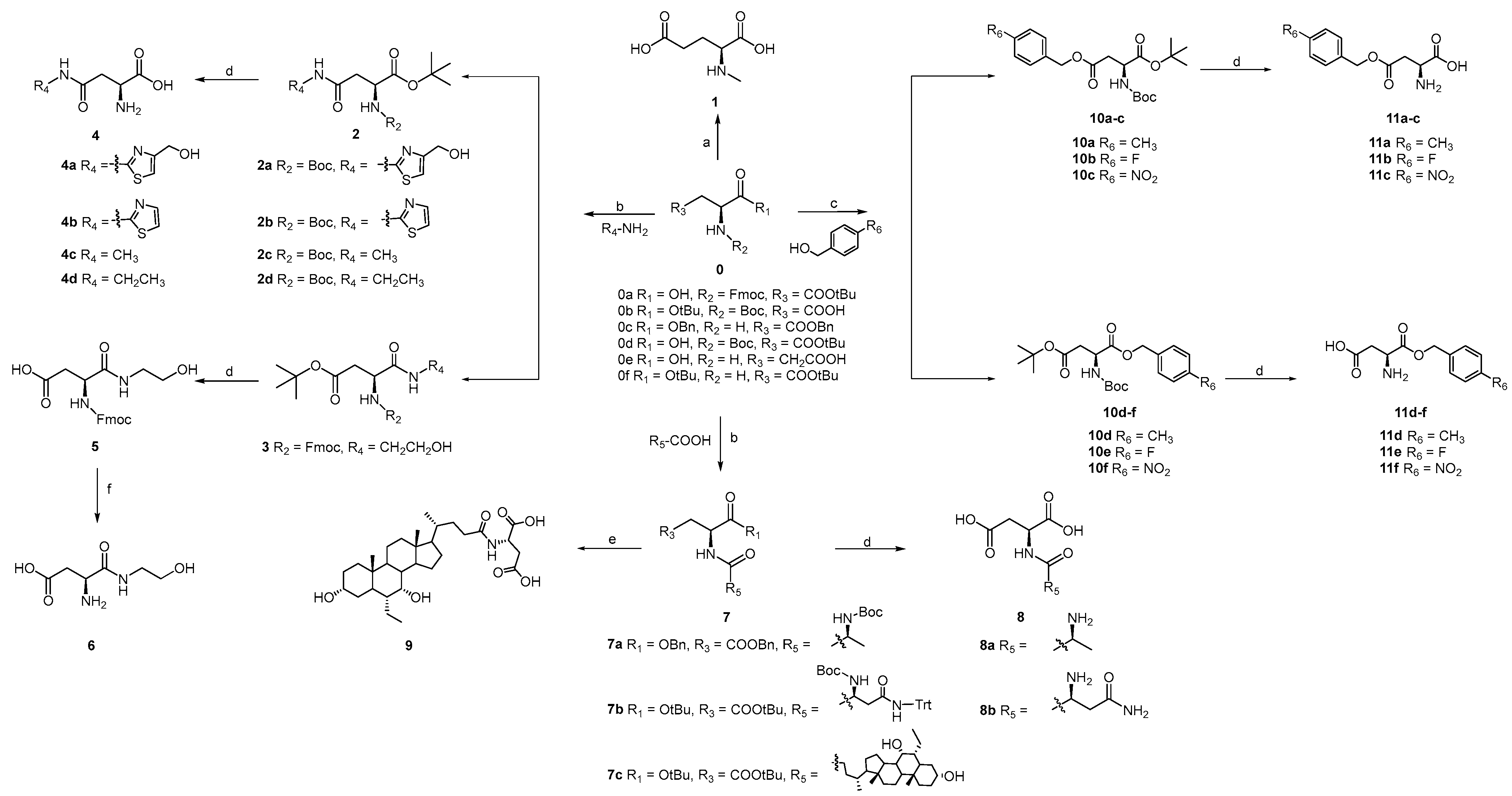
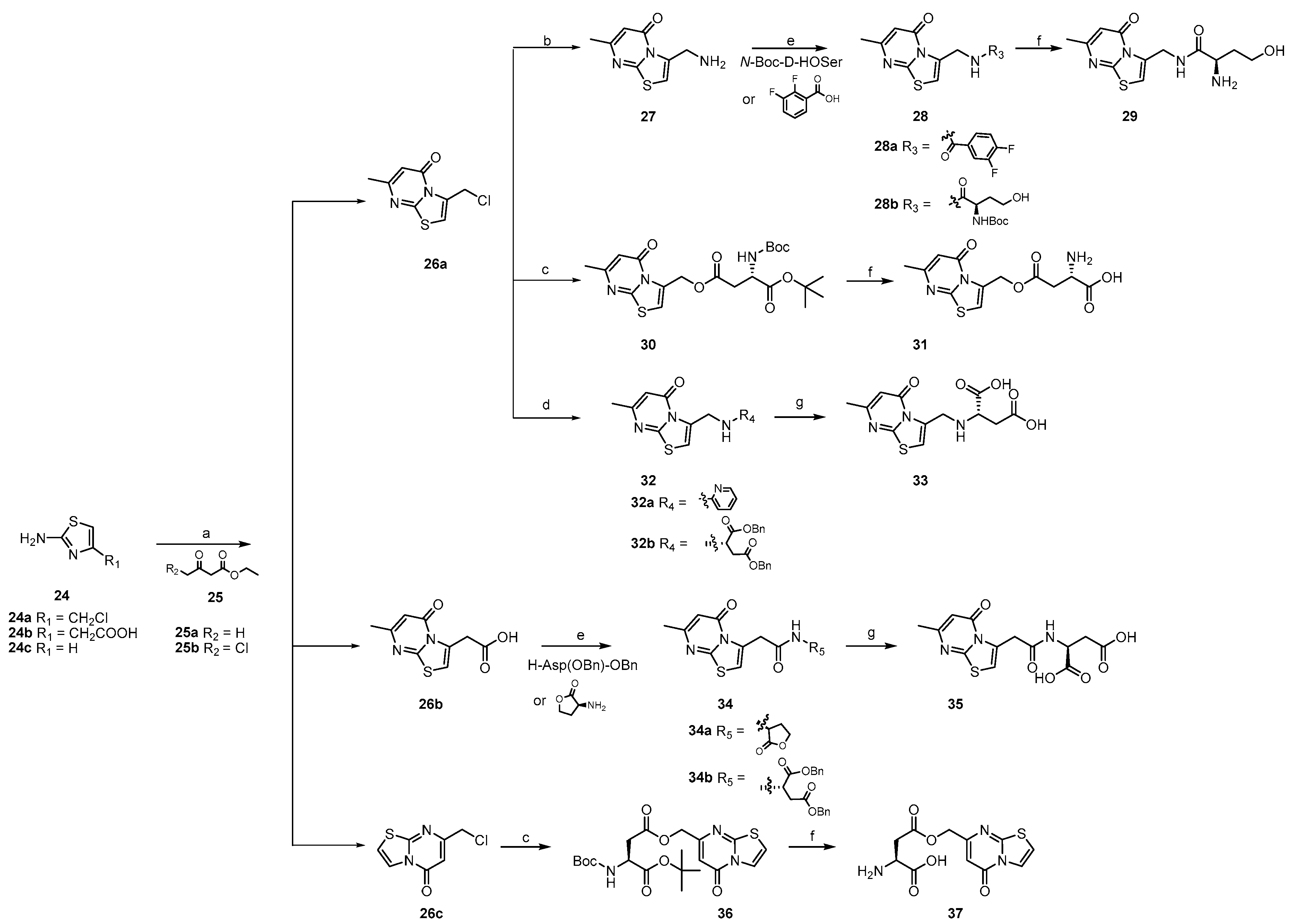
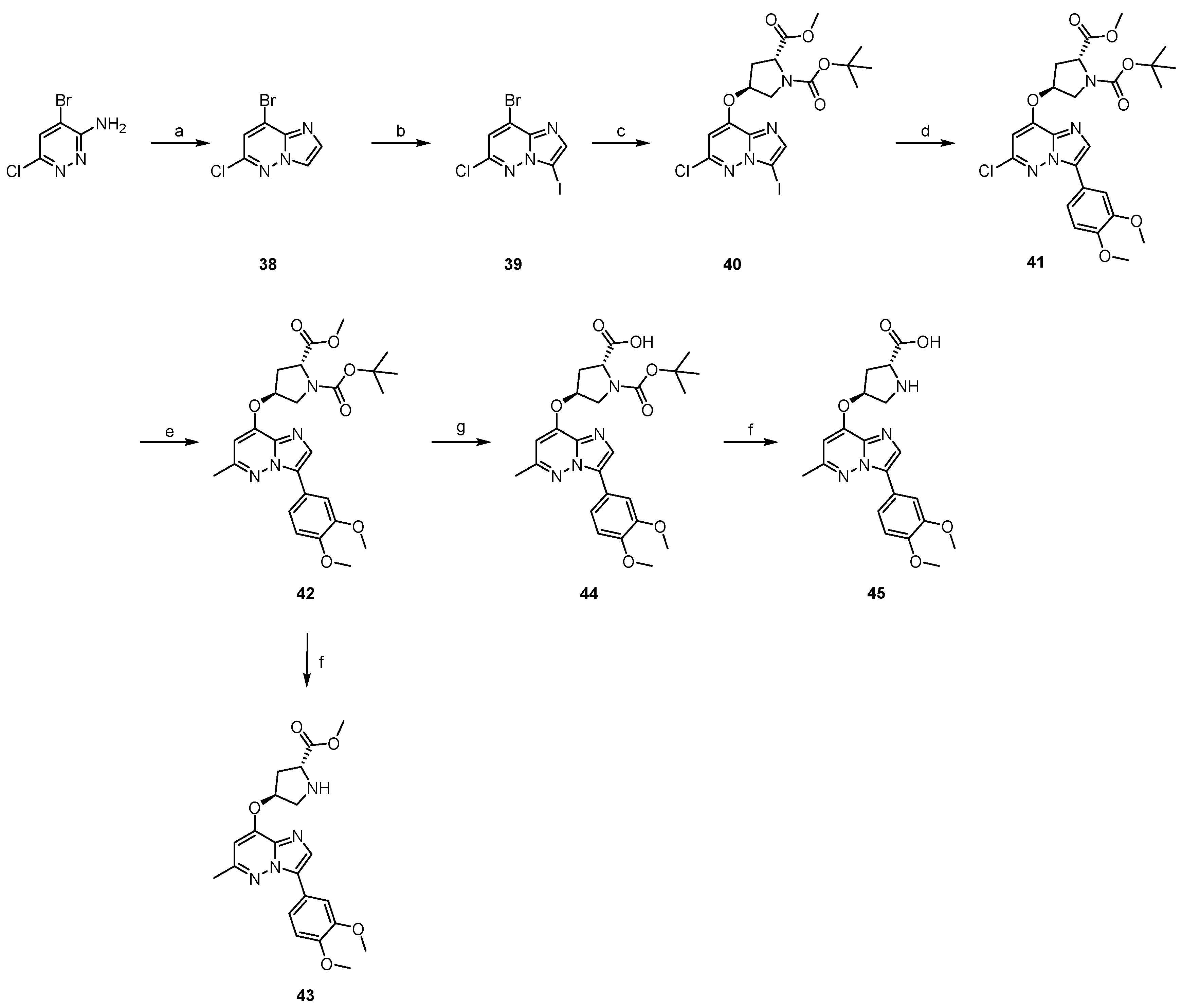
2.2. The Synthesis of Target Compounds
2.3. In Vitro Activity Evaluation and Structure—Activity Relationships (SAR) of Target Compounds
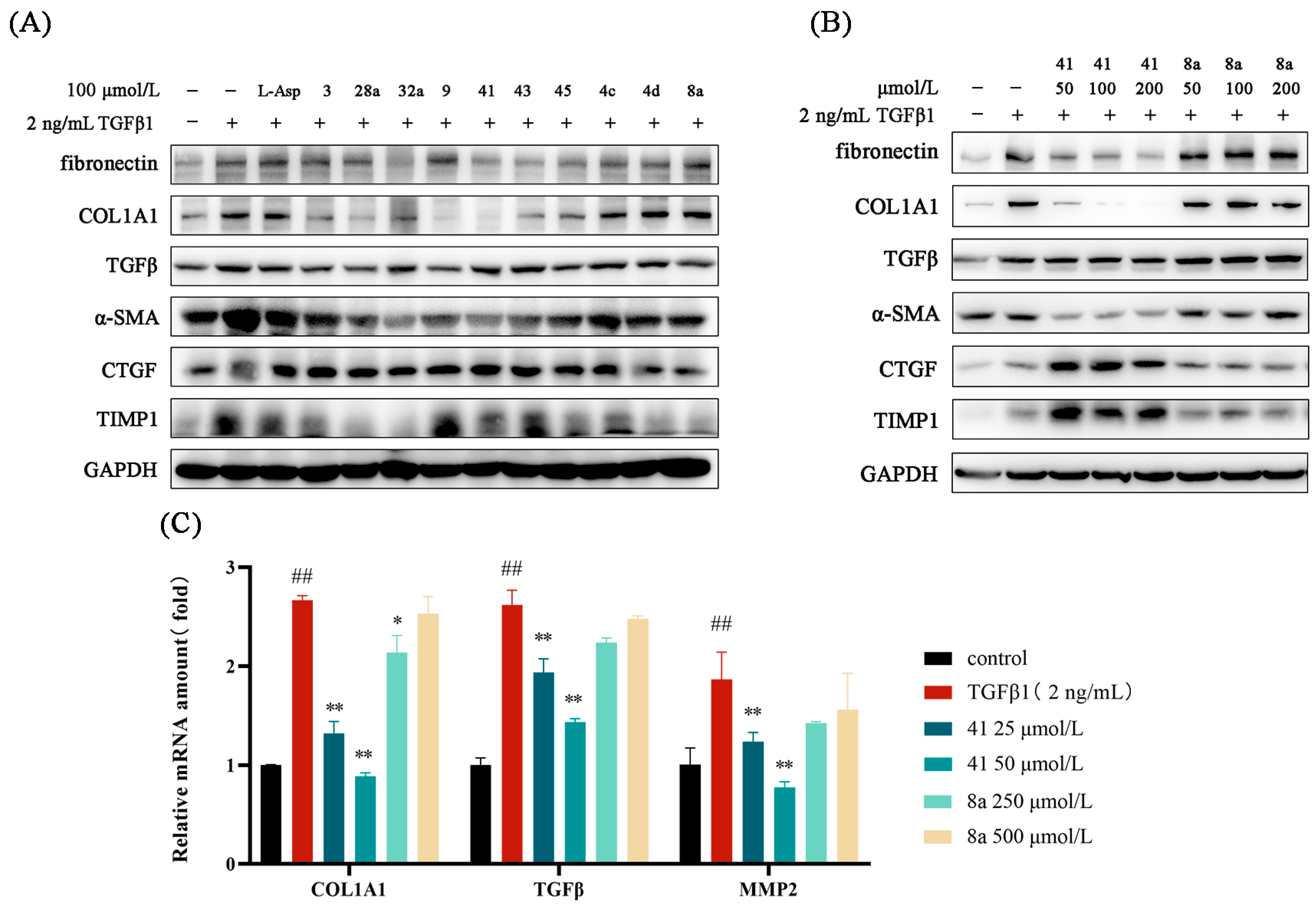
2.4. Effects of Key Compounds on the Expression of Fibro-Genic Genes
2.5. The Safety Profile of Representative Compounds in LX-2 Cells
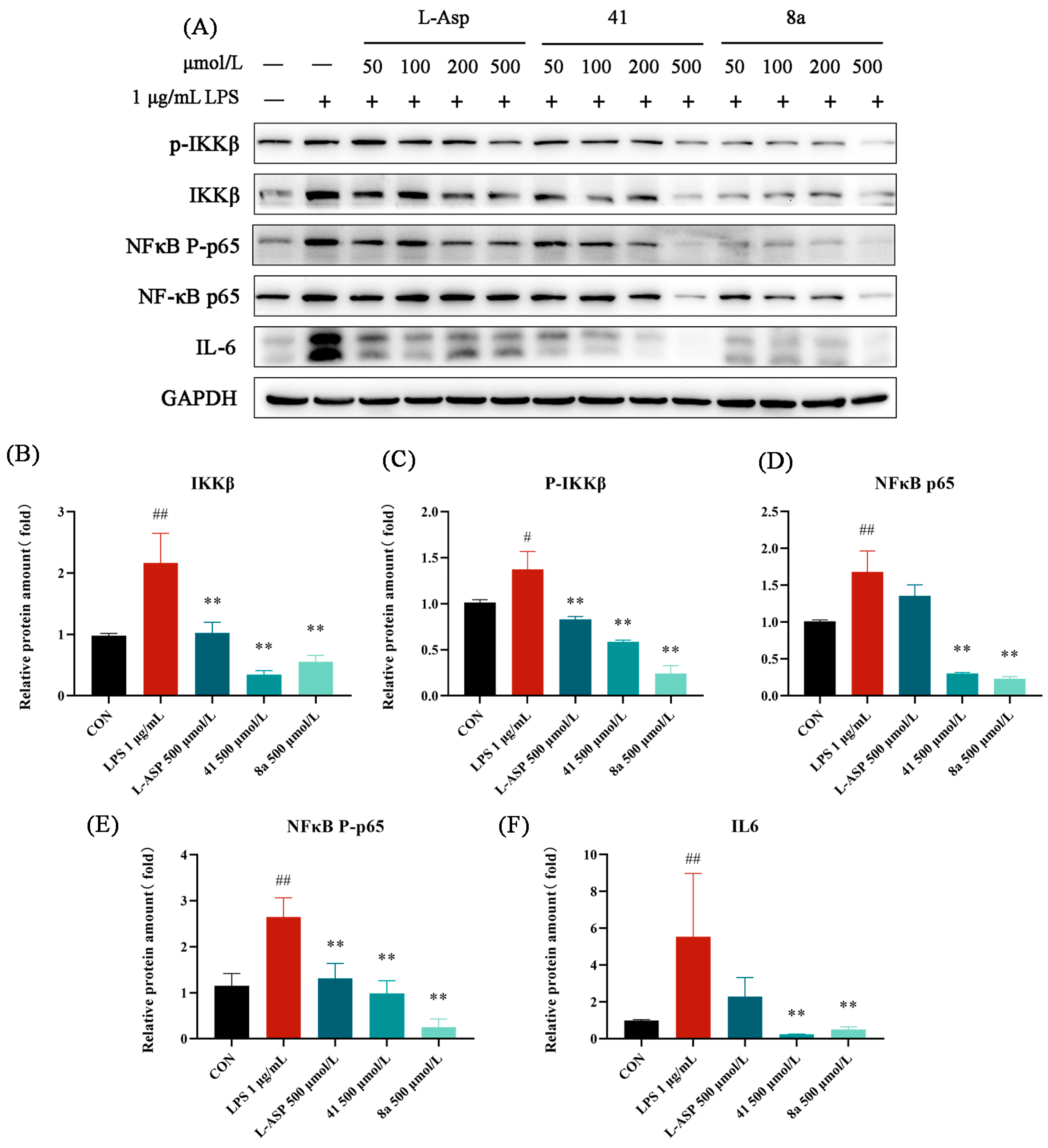
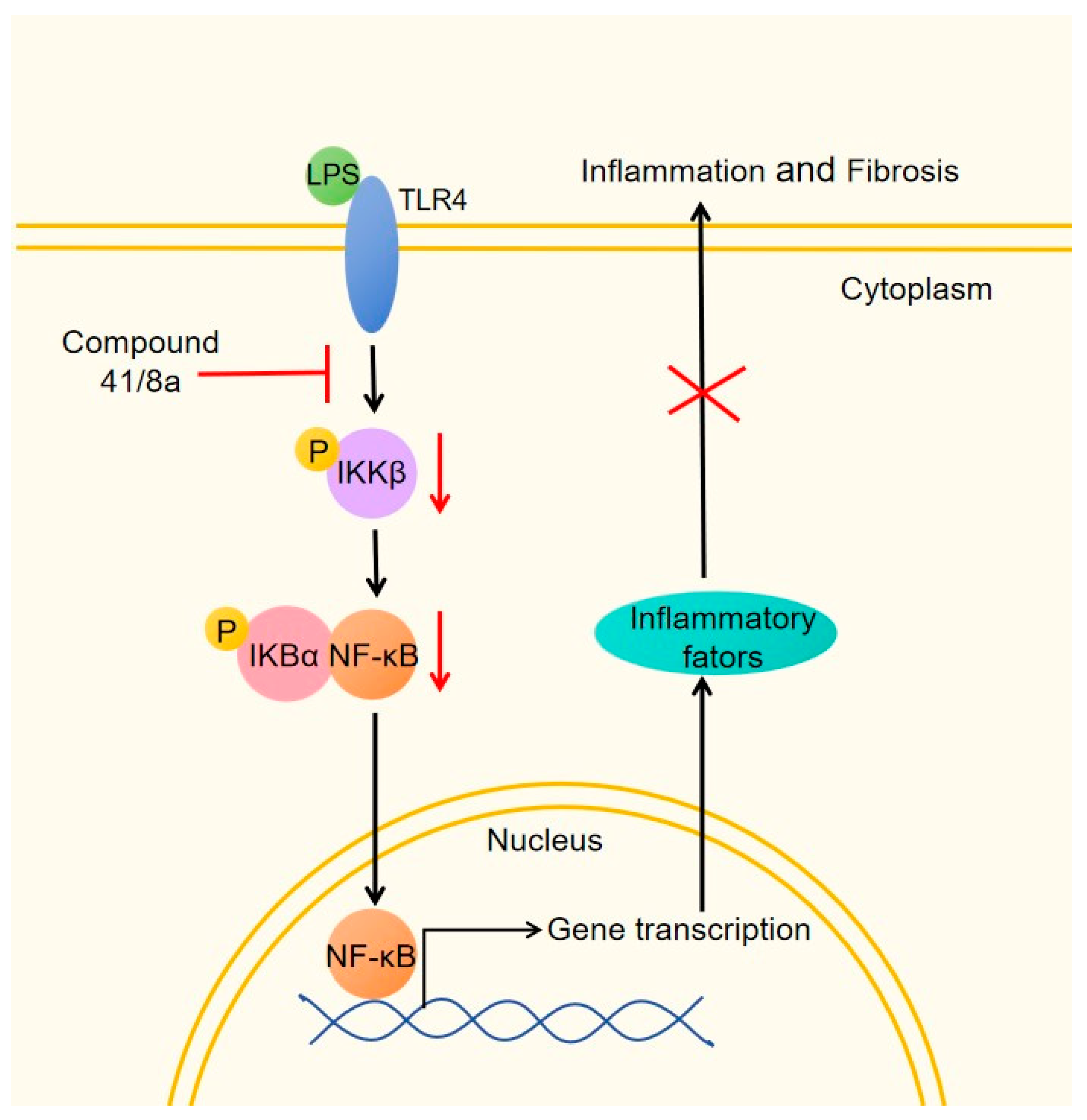
2.6. The Inhibitory Effect of 41 and 8a on LPS-Induced Inflammation in LX-2 Cells
2.7. The Inhibitory Effect of 41 and 8a on LPS-Induced Activation of LX-2 Cells
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. The Synthesis of 1
3.1.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 2a, 3 and 7c
3.1.3. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 4a–4d, 5 and 8a–8b
3.1.4. The Synthesis of 6
3.1.5. The Synthesis of 9
3.1.6. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 11a–11f
3.1.7. The Synthesis of 14
3.1.8. The Synthesis of 15a
3.1.9. The Synthesis of 15b
3.1.10. The Synthesis of 17
3.1.11. The Synthesis of 18a
3.1.12. The Synthesis of 19b
3.1.13. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 20a and 20b
3.1.14. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 22a and 22b
3.1.15. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 23a and 23b
3.1.16. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 26a–26c
3.1.17. The Synthesis of 27
3.1.18. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 28a, 28b and 34a, 34b
3.1.19. The Synthesis of 29
3.1.20. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 31 and 37
3.1.21. The Synthesis of 32a
3.1.22. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 33 and 35
3.1.23. The Synthesis of 38
3.1.24. The Synthesis of 39
3.1.25. The Synthesis of 40
3.1.26. The Synthesis of 41
3.1.27. The Synthesis of 42
3.1.28. The Synthesis of 44
3.1.29. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 43 and 45
3.2. Biology
3.2.1. Reagents
3.2.2. Cell Culture
3.2.3. COL1A1 Promoter Inhibition Rate Assay
3.2.4. Sulfor-Hodamine B (SRB) Assay
3.2.5. RT–qPCR Assay
3.2.6. Western Blot
3.2.7. Statistics
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Devarbhavi, H.; Asrani, S.K.; Arab, J.P.; Nartey, Y.A.; Pose, E.; Kamath, P.S. Global burden of liver disease: 2023 update. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 516–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.A.; Wallace, M.C.; Friedman, S.L. Pathobiology of liver fibrosis: A translational success story. Gut 2015, 64, 830–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiskirchen, R.; Tacke, F. Liver Fibrosis: From Pathogenesis to Novel Therapies. Dig. Dis. 2016, 34, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, S.L. Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 1655–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, A.J.; Patel, K. Antifibrotic therapies: Will we ever get there? Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2010, 12, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novo, E.; Parola, M. The role of redox mechanisms in hepatic chronic wound healing and fibrogenesis. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 2012, 5 (Suppl. S1), S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roehlen, N.; Crouchet, E.; Baumert, T.F. Liver Fibrosis: Mechanistic Concepts and Therapeutic Perspectives. Cells 2020, 9, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhouri, N.; LaCerte, C.; Edwards, J.; Poordad, F.; Lawitz, E.; Lee, L.; Karan, S.; Sawhney, S.; Erickson, M.; MacConell, L.; et al. Safety, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of obeticholic acid in subjects with fibrosis or cirrhosis from NASH. Liver Int. 2024, 44, 966–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francque, S.M.; Bedossa, P.; Ratziu, V.; Anstee, Q.M.; Bugianesi, E.; Sanyal, A.J.; Loomba, R.; Harrison, S.A.; Balabanska, R.; Mateva, L.; et al. A Randomized, Controlled Trial of the Pan-PPAR Agonist Lanifibranor in NASH. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 21, 1547–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Hu, Y.; Xu, L.; Liu, C.; Liu, P. Effect of Fuzheng Huayu formula and its actions against liver fibrosis. Chin. Med. 2009, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, V.J.; Belle, S.H.; D’Amato, M.; Adfhal, N.; Brunt, E.M.; Fried, M.W.; Reddy, K.R.; Wahed, A.S.; Harrison, S.; Silymarin in NASH and C Hepatitis (SyNCH) Study Group. Silymarin in non-cirrhotics with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled trial. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221683. [Google Scholar]
- Keam, S.J. Resmetirom: First Approval. Drugs 2024, 84, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydın, M.M.; Akçalı, K.C. Liver fibrosis. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 29, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muriel, P. NF-kappaB in liver diseases: A target for drug therapy. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2009, 29, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, A.; Schoonhoven, R.; Tuvia, S.; Brenner, D.A.; Rippe, R.A. Nuclear factor kappaB in proliferation, activation, and apoptosis in rat hepatic stellate cells. J. Hepatol. 2000, 33, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, J.; Chen, S.; Lu, S.; Shen, F.; Huang, Z. Triptolide dysregulates glucose uptake via inhibition of IKKβ-NF-κB pathway by p53 activation in cardiomyocytes. Toxicol. Lett. 2020, 318, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinz, M.; Scheidereit, C. The IκB kinase complex in NF-κB regulation and beyond. EMBO Rep. 2014, 15, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qiu, H.; Yao, S.; Li, Q.; Ding, Y.; Cao, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhu, X. Geniposide exerts protective effects on spinal cord injury in rats by inhibiting the IKKs/NF-κB signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 100, 108158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Xu, X.; Meng, B.; Wang, L.; Zhu, B.; Guo, B.; Zhang, J.; Xiang, L.; Dong, J.; Liu, M.; et al. Myeloid-derived growth factor alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease alleviates in a manner involving IKKβ/NF-κB signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heida, A.; Gruben, N.; Catrysse, L.; Koehorst, M.; Koster, M.; Kloosterhuis, N.J.; Gerding, A.; Havinga, R.; Bloks, V.W.; Bongiovanni, L.; et al. The hepatocyte IKK:NF-κB axis promotes liver steatosis by stimulating de novo lipogenesis and cholesterol synthesis. Mol. Metab. 2021, 54, 101349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holeček, M. Aspartic Acid in Health and Disease. Nutrients. 2023, 15, 4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooq, A.; Hoque, R.; Ouyang, X.; Farooq, A.; Ghani, A.; Ahsan, K.; Guerra, M.; Mehal, W.Z. Activation of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor downregulates inflammasome activity and liver inflammation via a β-arrestin-2 pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2014, 307, G732–G740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Zhao, J.; Han, M.; Ma, A.; Yang, S.; Zeng, Y.; Cheng, J. Aspartate Reduces Liver Inflammation and Fibrosis by Suppressing the NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway via Upregulating NS3TP1 Expression. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, F.J.; Martínez, G.S.; Blanco-Aparicio, C.; García, C.F.; Cebriá, G.A. Thiazolopyrimidones as inhibitors of DDR1/2 and therapeutic uses thereof. WO 2022/157166 A1, 28 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Mejdrová, I.; Chalupská, D.; Placková, P.; Muller, C.; Sála, M.; Klíma, M.; Nencka, R. Rational Design of Novel Highly Potent and Selective Phosphatidylinositol 4-Kinase IIIβ (PI4KB) Inhibitors as Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Agents and Tools for Chemical Biology. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 100–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Niu, T.; Zhu, J.; Mei, Y.; Shi, Y.; Meng, R.; Song, D. Evolution and Discovery of Matrine Derivatives as a New Class of Anti-Hepatic Fibrosis Agents Targeting Ewing Sarcoma Breakpoint Region 1 (EWSR1). J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 7969–7987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Fan, T.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; Bao, Y.; Ma, X.; Song, D. Discovery and development of palmatine analogues as anti-NASH agents by activating farnesoid X receptor (FXR). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 245 Pt 1, 114886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.N.; Shan, Q.; Hu, S.J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, G.N.; Zhu, M.; He, H.W. Discovery of 1,8-naphthalidine derivatives as potent anti-hepatic fibrosis agents via repressing PI3K/AKT/Smad and JAK2/STAT3 pathways. Bioorg Med. Chem. 2021, 49, 116438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.K.; Zhang, C.X.; Zhao, S.S.; Zhang, S.H.; Zhang, H.; Cai, S.Y.; He, H.W. The anti-fibrotic effects of epigallocatechin-3-gallate in bile duct-ligated cholestatic rats and human hepatic stellate LX-2 cells are mediated by the PI3K/Akt/Smad pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2015, 36, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammerich, L.; Tacke, F. Hepatic inflammatory responses in liver fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 20, 633–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellicoro, A.; Ramachandran, P.; Iredale, J.P.; Fallowfield, J.A. Liver fibrosis and repair: Immune regulation of wound healing in a solid organ. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Shen, X.; Wu, Z.; Dong, Y.; Cheng, J.C.H. MicroRNA-146a-5p Negatively Regulates Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Secretion and Cell Activation in Lipopolysaccharide Stimulated Human Hepatic Stellate Cells through Inhibition of Toll-Like Receptor 4 Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, N.; Wang, C.; Dai, X.; Zhou, M.; Gong, L.; Yu, L.; Li, Y. Phillygenin inhibits LPS-induced activation and inflammation of LX2 cells by TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 248, 112361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Gong, H.; Liu, Y.; Tao, X.; Zhang, H. Calcipotriol attenuates liver fibrosis through the inhibition of vitamin D receptor-mediated NF-κB signaling pathway. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 2658–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huh, J.Y.; Saltiel, A.R. Roles of IκB kinases and TANK-binding kinase 1 in hepatic lipid metabolism and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 1697–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Compound | Inhibitory Rate (%) | Compound | Inhibitory Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | / a | 11f | 20.62 ± 14.30 |
| 3 | 81.54 ± 5.62 | 20a | 17.91 ± 10.07 |
| 4a | 14.92 ± 8.45 | 20b | 24.02 ± 6.38 |
| 4b | 31.18 ± 14.30 | 23a | 27.88 ± 1.16 |
| 4c | 35.54 ± 18.11 | 23b | 34.60 ± 1.75 |
| 4d | 33.14 ± 19.03 | 28a | 43.91 ± 6.36 |
| 5 | 23.98 ± 15.44 | 29 | 33.20 ± 33.32 |
| 6 | / | 31 | 14.63 ± 3.11 |
| 8a | 49.34 ± 13.28 | 32a | 47.69 ± 4.81 |
| 8b | 23.82 ± 4.57 | 33 | 6.39 ± 7.06 |
| 9 | 97.44 ± 3.53 | 34a | 15.46 ± 16.61 |
| 11a | 11.42 ± 18.53 | 35 | / |
| 11b | / | 37 | 8.46 ± 8.16 |
| 11c | / | 41 | 66.72 ± 1.96 |
| 11d | 19.85 ± 4.99 | 43 | 38.23 ± 3.28 |
| 11e | 27.93 ± 5.81 | 45 | 69.64 ± 8.48 |
| L-Asp | 11.33 ± 0.35 | EGCG | 36.46 ± 4.64 |
| Code | IC50 (μmol/L) a | CC50 (μmol/L) b | SI c |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 327.1 ± 17.1 | 659.7 ± 24.61 | 2.01 |
| 9 | 269.9 ± 47.9 | 351.0 ± 19.4 | 1.30 |
| 41 | 30.6 ± 0.3 | 510.5 ± 51.5 | 16.68 |
| 45 | 297.9 ± 51.7 | 632.2 ± 11.2 | 2.12 |
| 8a | 1054.4 ± 111.2 | 13,871.0 ± 968.7 | 13.16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, M.; Guo, S.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Yi, H.; He, H.; Li, Z. Synthesis and Anti-Liver Fibrosis Research of Aspartic Acid Derivatives. Molecules 2024, 29, 4774. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194774
Lv M, Guo S, Yang H, Wang Y, Li Y, Li Y, Yi H, He H, Li Z. Synthesis and Anti-Liver Fibrosis Research of Aspartic Acid Derivatives. Molecules. 2024; 29(19):4774. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194774
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Miao, Simin Guo, Hexian Yang, Yongjian Wang, Yiming Li, Yang Li, Hong Yi, Hongwei He, and Zhuorong Li. 2024. "Synthesis and Anti-Liver Fibrosis Research of Aspartic Acid Derivatives" Molecules 29, no. 19: 4774. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194774
APA StyleLv, M., Guo, S., Yang, H., Wang, Y., Li, Y., Li, Y., Yi, H., He, H., & Li, Z. (2024). Synthesis and Anti-Liver Fibrosis Research of Aspartic Acid Derivatives. Molecules, 29(19), 4774. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194774










