Optimization of Liquid Fermentation of Acanthopanax senticosus Leaves and Its Non-Targeted Metabolomics Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
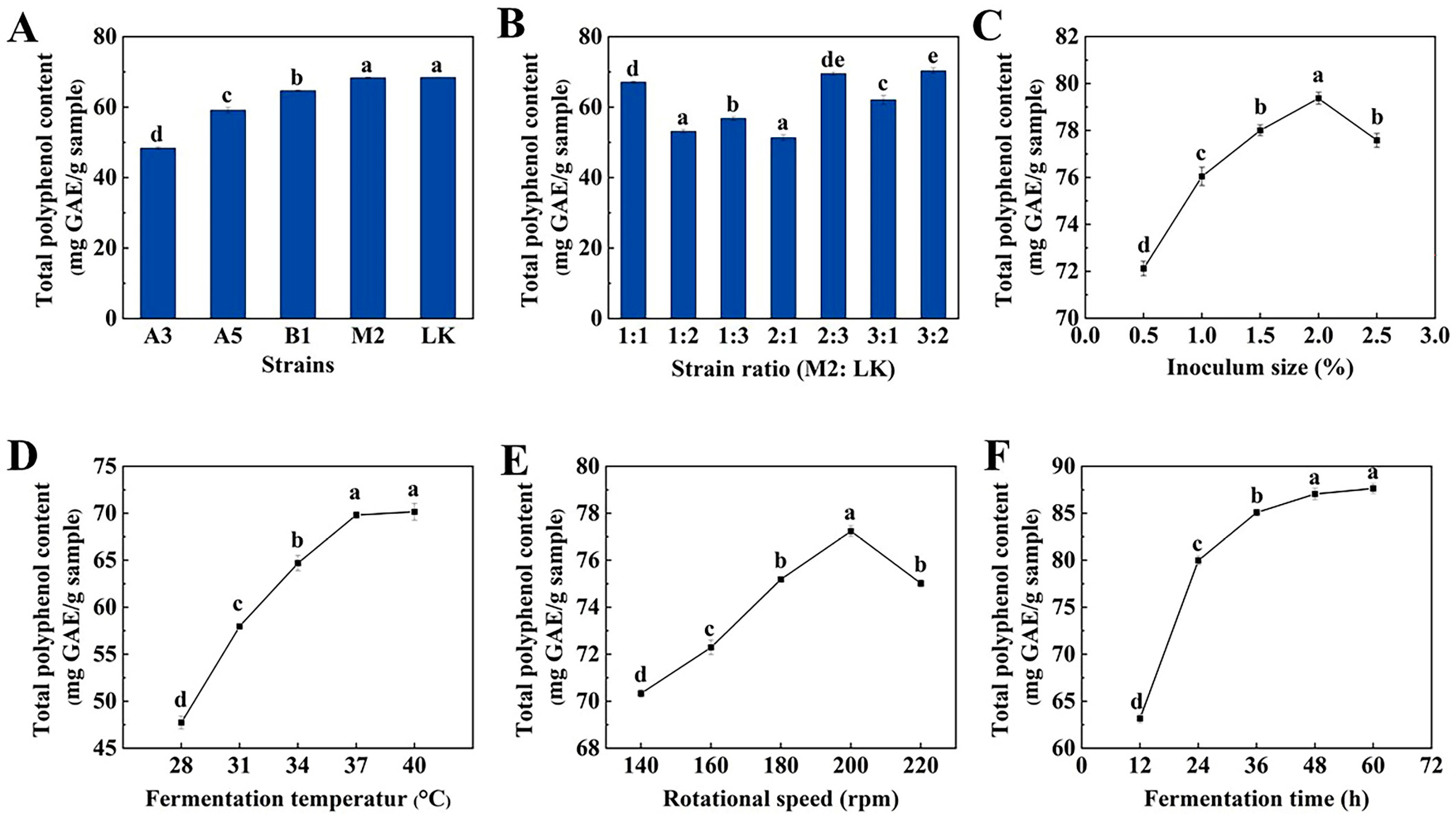
2.1. Results of Screening for Dominant Strains
2.2. Optimization of Strains Ratio
2.3. Single-Factor Test
2.4. Response Surface Methodology
2.5. Dynamic Changes of TPC and Total Flavonoid Content (TFC) at Different Fermentation Times
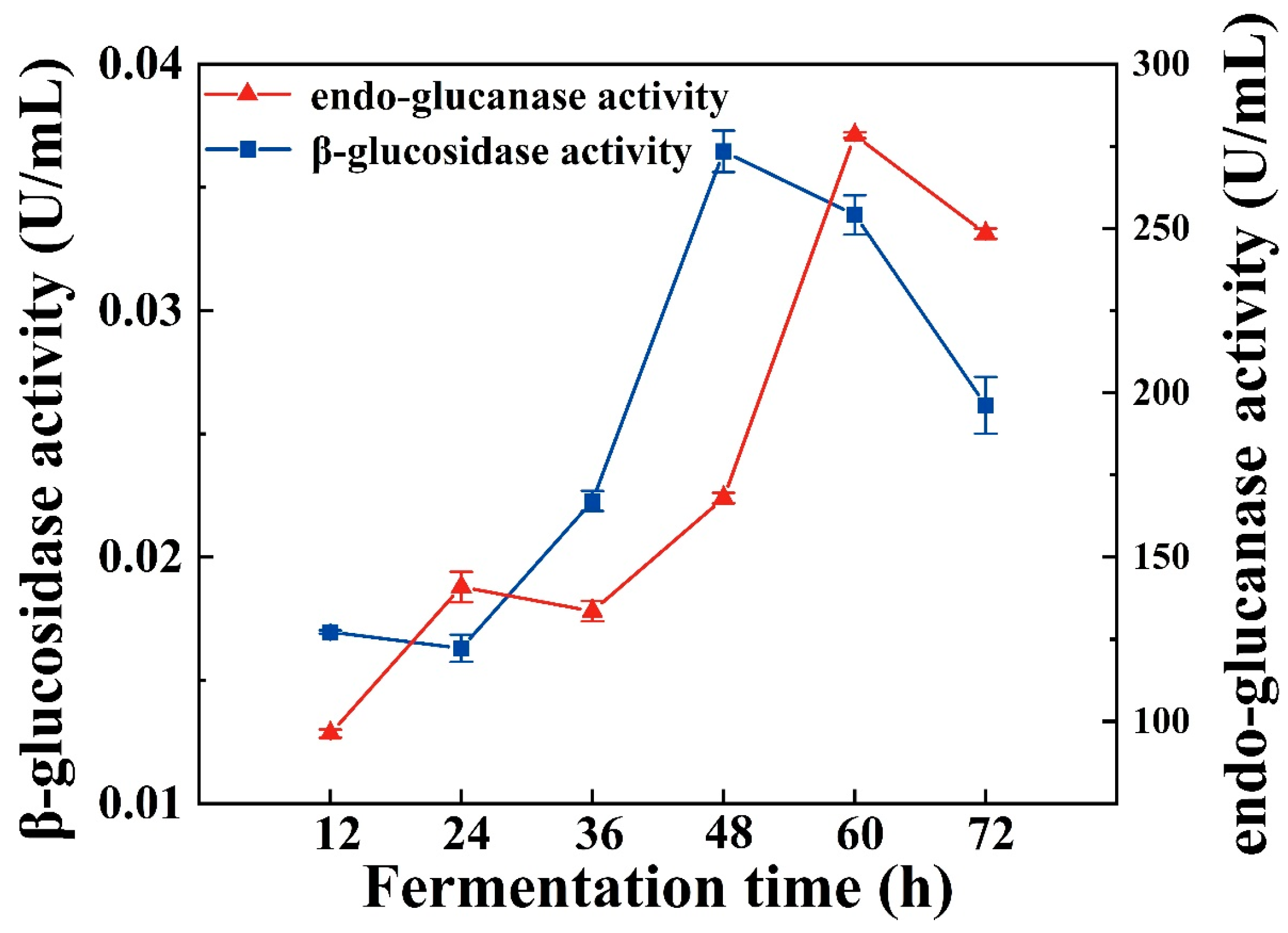
2.6. Enzyme Activity Assay
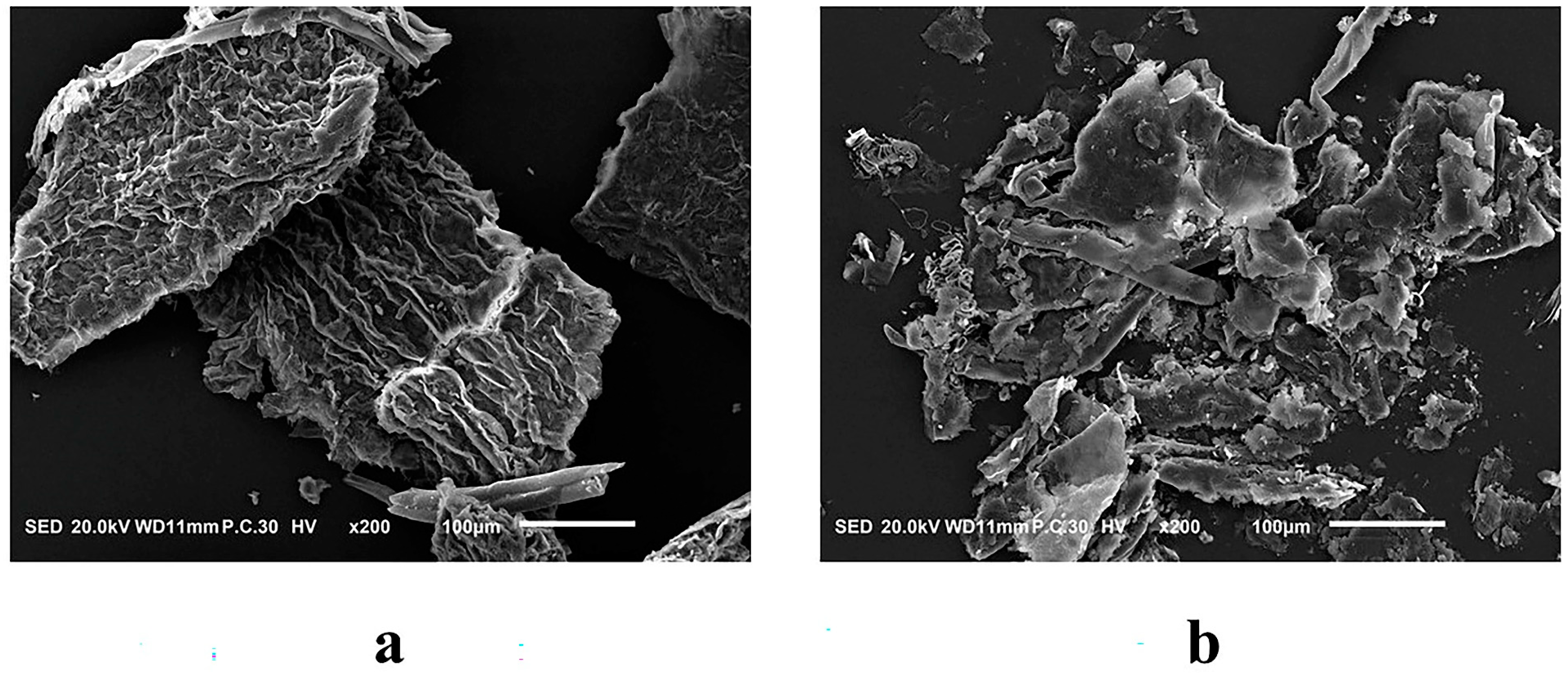
2.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
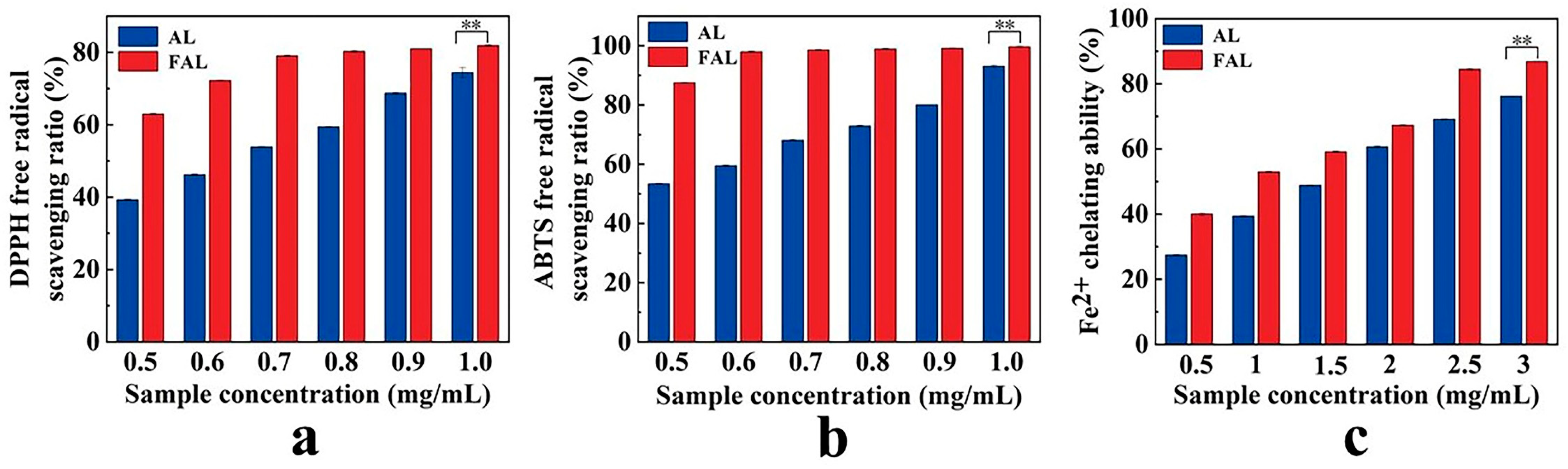
2.8. Antioxidant Activity Analysis
2.9. Non-Targeted Metabolomics
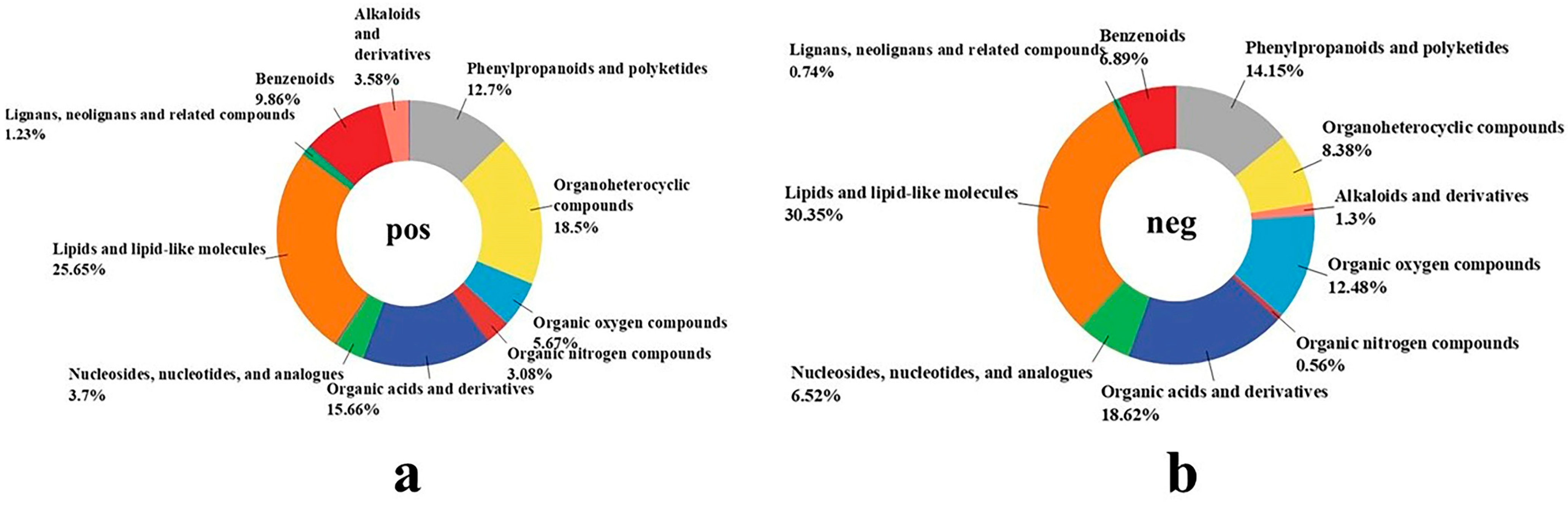
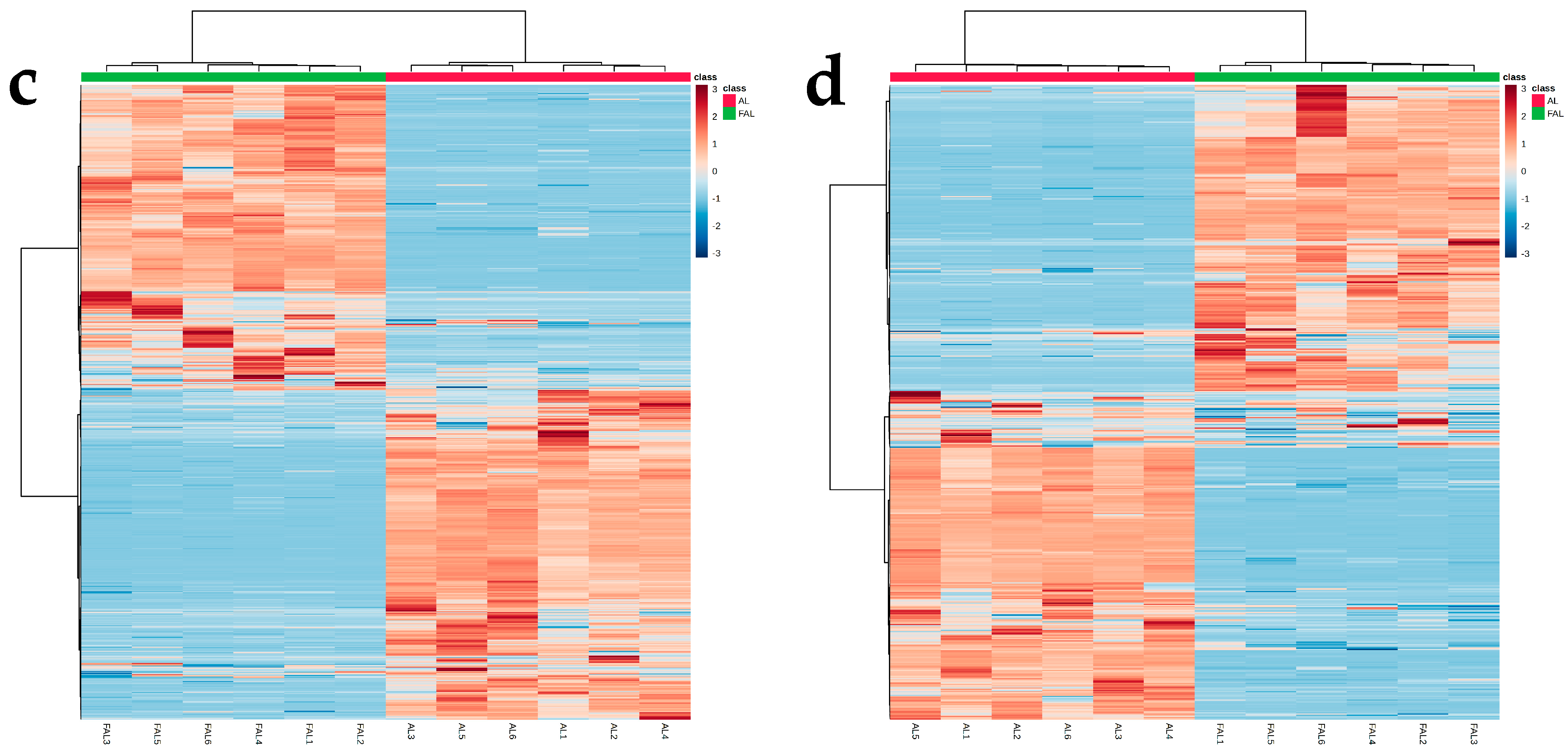
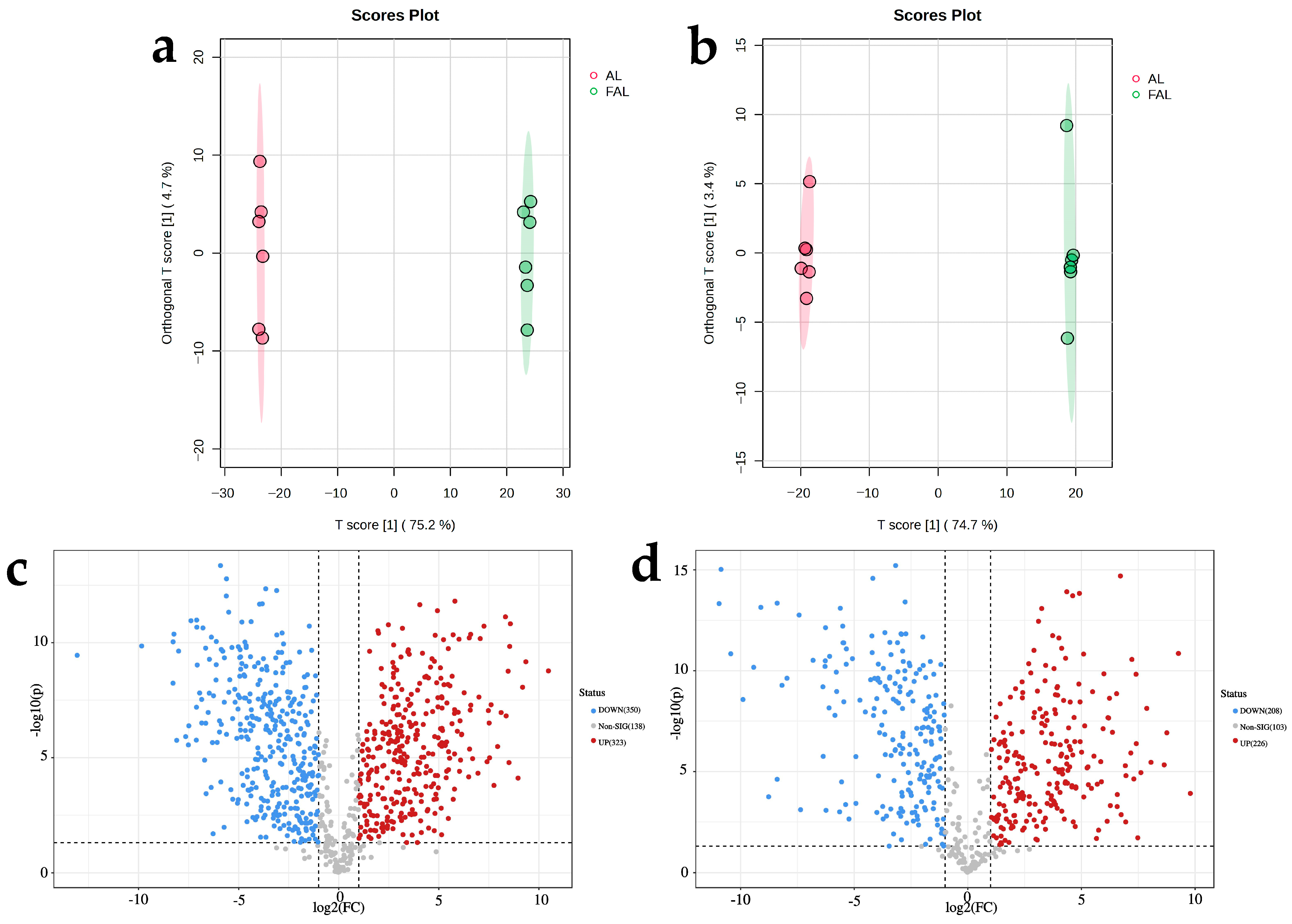
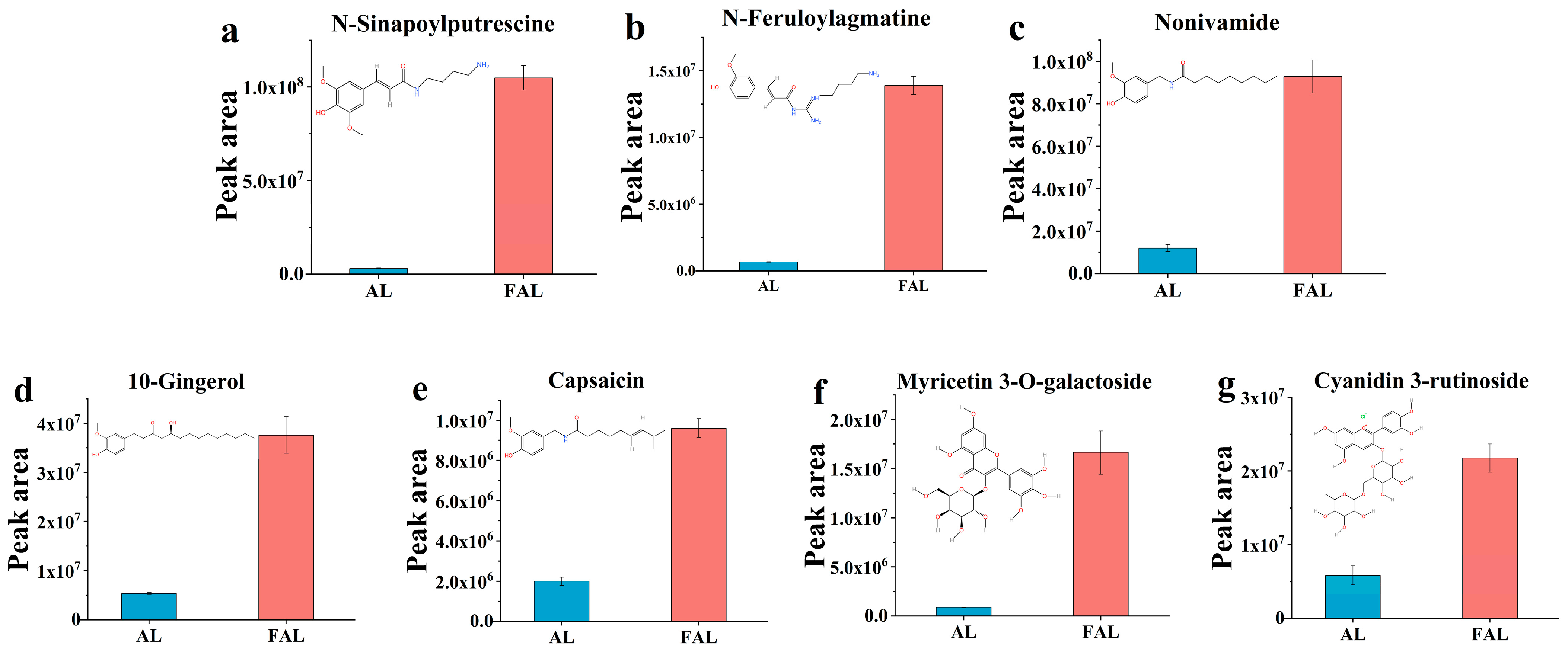
2.9.1. Effect of Fermentation with Mixture Probiotic on AL Metabolites
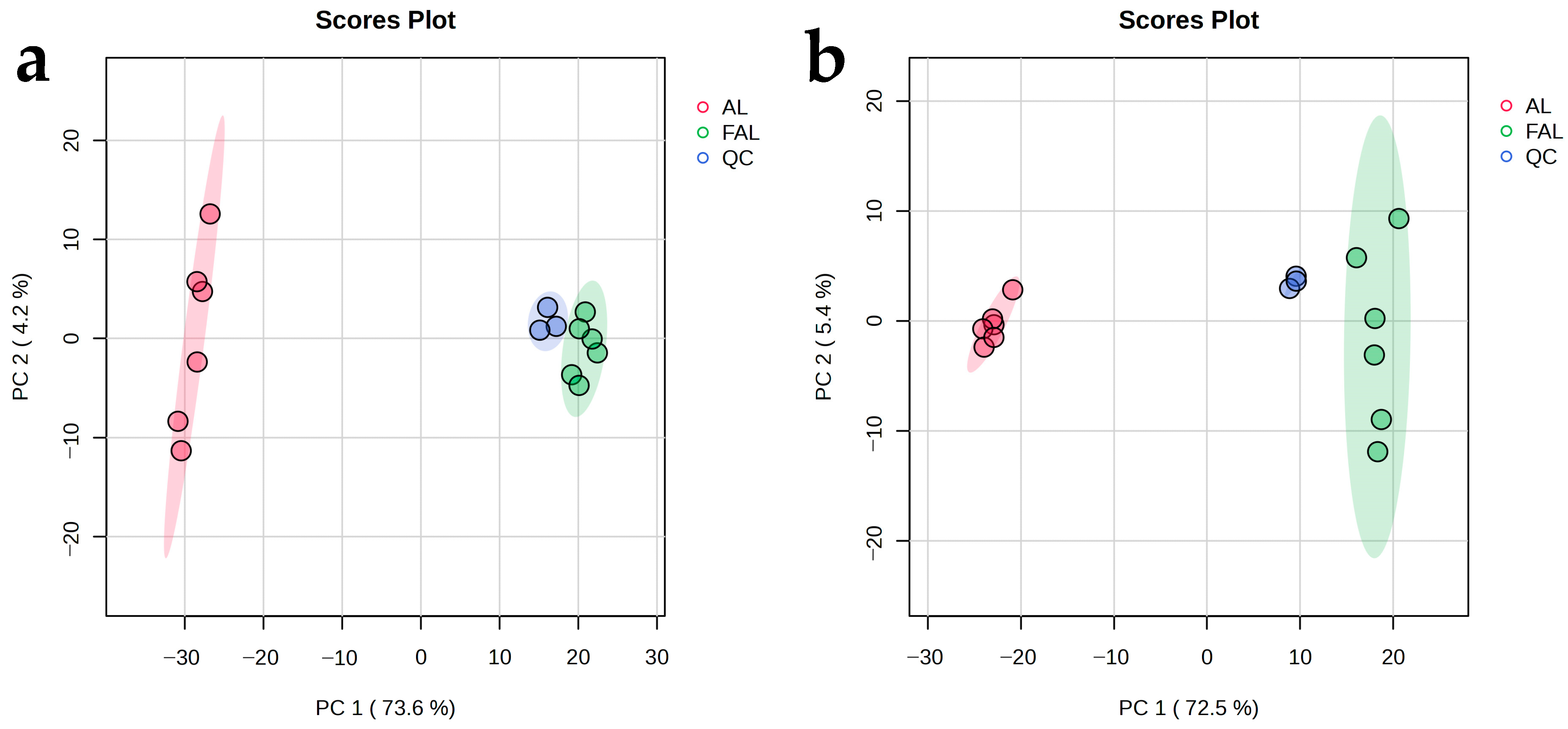
2.9.2. Differential Metabolite Analysis Based on Supervised Orthogonal Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis (OPLS-DA)
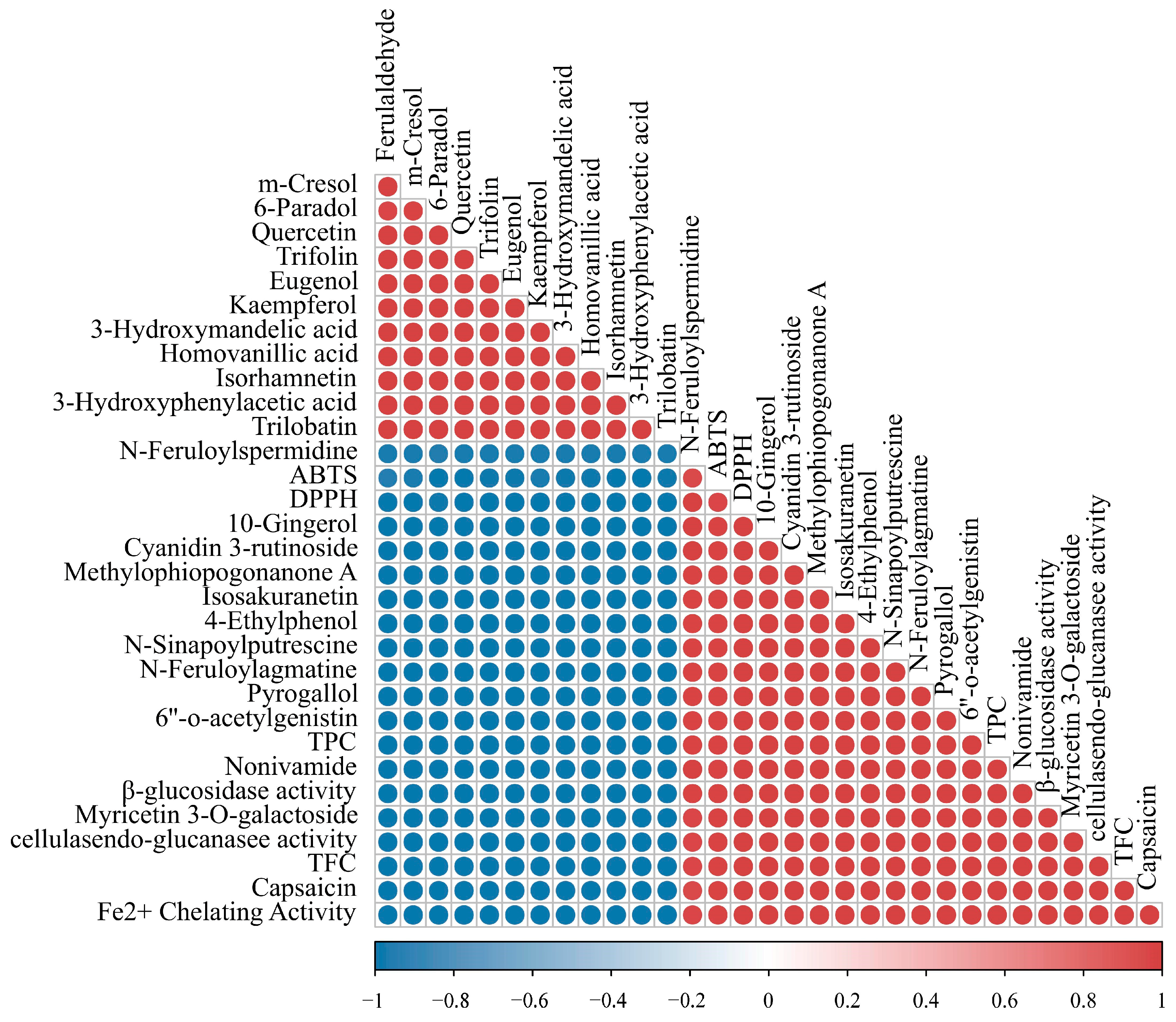
2.9.3. Correlation of Polyphenols and Flavonoids Differential Metabolites with Antioxidant Activity of AL and FAL
2.9.4. Correlation of Polyphenol and Flavonoid Differential Metabolites with Enzyme Activities
2.9.5. KEGG Enrichment Analysis of Differential Metabolites
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Chemicals
3.2. Fermentation Media and Strains
3.3. Screening of Probiotics
3.4. Optimization of Strain Ratio
3.5. Single-Factor Experiment
3.6. Response Surface Methodology Assay
3.7. Dynamic Observation during Fermentation
3.8. Determination of TPC and TFC
3.9. Enzyme Activity Assay
3.9.1. Endo-Glucanase Activity
3.9.2. β-Glucosidase Activity
3.10. SEM
3.11. Antioxidant Activity
3.12. Non-Targeted Metabolomics Analysis
3.13. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tohda, C.; Matsui, M.; Inada, Y.; Yang, X.; Kuboyama, T.; Kimbara, Y.; Watari, H. Combined Treatment with Two Water Extracts of Eleutherococcus senticosus Leaf and Rhizome of Drynaria fortunei Enhances Cognitive Function: A Placebo-Controlled, Randomized, Double-Blind Study in Healthy Adults. Nutrients 2020, 12, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nhiem, N.X.; Kim, K.C.; Kim, A.D.; Hyun, J.W.; Kang, H.K.; Van Kiem, P.; Van Minh, C.; Thu, V.K.; Tai, B.H.; Kim, J.A.; et al. Phenylpropanoids from the leaves of Acanthopanax koreanum and their antioxidant activity. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2011, 13, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.-G.; Huang, Y.-X.; Liang, J.; Kuang, H.-X. Comparable studies of two polysaccharides from leaves of Acanthopanax senticosus: Structure and antioxidation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 147, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Xing, J.; Liu, S.; Song, F.; Cai, Z.; Pi, Z.; Liu, Z.; Liu, S. Screening and determination for potential α-glucosidase inhibitors from leaves of Acanthopanax senticosus harms by using UF-LC/MS and ESI-MS(n). Phytochem. Anal. 2012, 23, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.H.; Cha, Y.S.; Rhee, S.J. Effects of the Cellcultured Acanthopanax senticosus Extract on Antioxidative Defense System and Membrane Fluidity in the Liver of Type 2 Diabetes Mouse. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2009, 45, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leem, K.H.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.K. Extrusion Process Enhances the Anti-inflammatory Effect of Acanthopanax senticosus Leaves. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 23, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sithisarn, P.; Jarikasem, S. Antioxidant Activity of Acanthopanax trifoliatus. Med. Princ. Pract. 2009, 18, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.B.; Tanikawa, T.; Hayashi, K.; Asagi, M.; Kasahara, Y.; Hayashia, T. Characterization and biological effects of two polysaccharides isolated from Acanthopanax sciadophylloides. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 116, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Liang, Z.; Li, T.; Hao, Q.; Xiang, H.; Xie, Q. Metabolome and microbiome analyses of the anti-fatigue mechanism of Acanthopanax senticosus leaves. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 3791–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.P.; Wu, D.; Sun, Y.P.; Zhao, H.Q.; Wang, Y.Y.; Zhang, W.S.; Su, F.Z.; Yang, B.Y.; Wang, Q.H.; Kuang, H.X. Comprehensive Analysis of Eleutherococcus senticosus (Rupr. & Maxim.) Maxim. Leaves Based on UPLC-MS/MS: Separation and Rapid Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 865586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beh, B.K.; Mohamad, N.E.; Yeap, S.K.; Ky, H.; Boo, S.Y.; Chua, J.Y.H.; Tan, S.W.; Ho, W.Y.; Sharifuddin, S.A.; Long, K.; et al. Anti-obesity and anti-inflammatory effects of synthetic acetic acid vinegar and Nipa vinegar on high-fat-diet-induced obese mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, N.T.; Van Camp, J.; Smagghe, G.; Raes, K. Improved release and metabolism of flavonoids by steered fermentation processes: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 19369–19388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robledo-Márquez, K.; Ramírez, V.M.; González-Córdova, A.F.; Ramírez-Rodríguez, Y.; García-Ortega, L.; Trujillo, J. Research opportunities: Traditional fermented beverages in Mexico. Cultural, microbiological, chemical, and functional aspects. Food Res. Int. 2021, 147, 110482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendangnaro, J.; Chitta Ranjan, D. Biochemical Characterization of Three Vegetable Based Fermented Food Products (Hungrii, Rhujuk and Tsutuocie) of Nagaland, India. Nat. Resour. 2021, 13, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Xu, X.; Wu, Y.; Niu, T.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Du, G.; Liu, L. Advances and prospects of Bacillus subtilis cellular factories: From rational design to industrial applications. Metab. Eng. 2018, 50, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Zhang, A.H.; Miao, J.H.; Sun, H.; Han, Y.; Yan, G.L.; Wu, F.F.; Wang, X.J. Metabolomics biotechnology, applications, and future trends: A systematic review. Rsc Adv. 2019, 9, 37245–37257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Liu, Z.; Song, F.; Xing, J.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, S. A Strategy for Identification and Structural Characterization of Compounds from Plantago asiatica L. by Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Combined with Ion Mobility Spectrometry. Molecules 2022, 27, 4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.J.; Park, J.G.; Ahn, S.K.; Kim, K.W.; Choi, J.; Kim, H.Y.; Ha, S.H.; Seo, W.D.; Kim, J.K. Discrimination of Adzuki Bean (Vigna angularis) Geographical Origin by Targeted and Non-Targeted Metabolite Profiling with Gas Chromatography Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Metabolites 2020, 10, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, W.K.; Tan, Y.X.; Lyu, X.M.; Chen, W.N. Effects of submerged liquid fermentation of Bacillus subtilis WX-17 using okara as sole nutrient source on the composition of a potential probiotic beverage. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 3119–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, T.T.; Chen, M.X.; Zu, Z.Q.; Chen, Q.; Lu, H.Q.; Yue, P.X.; Gao, X.L. Untargeted and targeted metabolomics reveal changes in the chemical constituents of instant dark tea during liquid-state fermentation by Eurotium cristatum. Food Res. Int. 2021, 148, 110623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.S.; Wu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, C.G.; Xiong, Z.Y.; Eweys, A.S.; Zhou, H.B.; Dong, Y.; Xiao, X. Metabolomics strategy for revealing the components in fermented barley extracts with Lactobacillus plantarum dy-1. Food Res. Int. 2021, 139, 109808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.W.; Yan, D.; Singh, R.; Liu, J.; Lu, X.; Ucmak, D.; Lee, K.; Afifi, L.; Fadrosh, D.; Leech, J.; et al. Alteration of the cutaneous microbiome in psoriasis and potential role in Th17 polarization. Microbiome 2018, 6, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Liu, H.N.; Ma, A.M.; Zhou, J.Z.; Xia, X.D. Synergetic effects of Lactobacillus plantarum and Rhizopus oryzae on physicochemical, nutritional and antioxidant properties of whole-grain oats (Avena sativa L.) during solid-state fermentation. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 154, 112687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Yang, T.; Shen, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L. Study on the properties of Dendrobium officinale fermentation broth as functional raw material of cosmetics. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 21, 1216–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heng, X.Y.; Chen, H.Y.; Lu, C.X.; Feng, T.; Li, K.Y.; Gao, E.B. Study on synergistic fermentation of bean dregs and soybean meal by multiple strains and proteases. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 154, 112626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, G.; Yang, H.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Q.; Tian, Y. Effect of incubation time, inoculum size, temperature, pasteurization time, goat milk powder and whey powder on ACE inhibitory activity in fermented milk by L. plantarum LP69. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2015, 14, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lu, J.; Ma, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Diao, M.; Xie, N. A Green Route for High-Yield Production of Tetramethylpyrazine From Non-Food Raw Materials. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 792023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Guo, Y.; Wu, P.; Liu, S.; Gu, C.; Yolandani; Wu, M.; Ma, H.; He, R. Enhancement of Polypeptide Yield Derived from Rapeseed Meal with Low-Intensity Alternating Magnetic Field. Foods 2022, 11, 2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, E.Y.; Sun, W.J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.Y.; Xu, B.C.; Chen, X.G.; Hao, K.Y.; He, L.Z.; Si, H.B. Optimization of Ultrasonic-Assisted Extraction of Total Flavonoids from Abrus Cantoniensis (Abriherba) by Response Surface Methodology and Evaluation of Its Anti-Inflammatory Effect. Molecules 2022, 27, 2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, D.; Yu, C.; Yao, L.; Chen, Z.; Tao, Y.; Cao, W. Phytochemical Analysis, Antioxidant and Analgesic Activities of Incarvillea compacta Maxim from the Tibetan Plateau. Molecules 2019, 24, 1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.B.; Lei, Y.T.; Li, Q.Z.; Li, Y.C.; Deng, Y.; Liu, D.Y. Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus acidophilus fermentation on antioxidant activity and metabolomic profiles of loquat juice. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 171, 114104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isas, A.S.; Celis, M.S.M.; Correa, J.R.P.; Fuentes, E.; Rodríguez, L.; Palomo, I.; Mozzi, F.; Van Nieuwenhove, C. Functional fermented cherimoya (Annona cherimola Mill.) juice using autochthonous lactic acid bacteria. Food Res. Int. 2020, 138, 109729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.X.; Jin, X.M.; Zhang, X.C.; Xie, X.; Tu, Z.C.; He, X.H. From Function to Metabolome: Metabolomic Analysis Reveals the Effect of Probiotic Fermentation on the Chemical Compositions and Biological Activities of Perilla frutescens Leaves. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 933193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Song, M.; Wang, N.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; An, X.; Qi, J. The effects of solid-state fermentation on the content, composition and in vitro antioxidant activity of flavonoids from dandelion. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Liu, H.N.; Liu, C.Q.; Zhou, J.Z.; Liu, X.L.; Zhang, H.Z. Hulless Black Barley as a Carrier of Probiotics and a Supplement Rich in Phenolics Targeting Against H2O2-Induced Oxidative Injuries in Human Hepatocarcinoma Cells. Front. Nutr. 2022, 8, 790765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bano, S.; Qader, S.A.U.; Aman, A.; Syed, M.N.; Durrani, K. High production of cellulose degrading endo-1,4-β-d-glucanase using bagasse as a substrate from Bacillus subtilis KIBGE HAS. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 91, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meannui, N.; Riebroy, S.; Tangwatcharin, P.; Hong, J.H.; Sumpavapol, P.; Chaijan, M. β-glucosidase Producing Bacillus Isolated from Thua-nao, an Indigenous Fermented Soybean Food in Thailand. Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2017, 44, 1257–1269. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, F.; Chao, J.P.; Zhao, X.X.; Betchem, G.; Ding, Y.H.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.L.; Ma, H.L. Enhancing protease activity of Bacillus subtilis using UV-laser random mutagenesis and high-throughput screening. Process. Biochem. 2022, 119, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stodolak, B.; Starzynska-Janiszewska, A.; Mika, M.; Wikiera, A. Rhizopus oligosporus and Lactobacillus plantarum Co-Fermentation as a Tool for Increasing the Antioxidant Potential of Grass Pea and Flaxseed Oil-Cake Tempe. Molecules 2020, 25, 4759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.; Pothula, R.; Abdelgaffar, H.; Bashir, S.; Jurat-Fuentes, J.L. Identification and functional characterization of a β-glucosidase from Bacillus tequelensis BD69 expressed in bacterial and yeast heterologous systems. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, S.A.; Vishwakarma, R.A.; Ashraf, N. Functional Characterization of CsBGlu12, a β-Glucosidase from Crocus sativu, Provides Insights into Its Role in Abiotic Stress through Accumulation of Antioxidant Flavonols. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 4700–4713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Hu, K.K.; Haritos, V.S. Enzymatic production of cello-oligosaccharides with potential human prebiotic activity and release of polyphenols from grape marc. Food Chem. 2024, 435, 137562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, S.B.; Wang, O.; Wu, W.; Zhu, S.J.; Zhou, F.; Ji, B.P.; Gao, F.Y.; Zhang, D.; Liu, J.; Cheng, Q. Comparative Study of the Effects of Solid-State Fermentation with Three Filamentous Fungi on the Total Phenolics Content (TPC), Flavonoids, and Antioxidant Activities of Subfractions from Oats (Avena sativa L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- On, J.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.M.; Park, S.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, C.H.; Kim, S.K. Effects of Fermented Artemisia annua L. and Salicornia herbacea L. on Inhibition of Obesity In Vitro and In Mice. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernacka, K.; Bednarska, K.; Starzec, A.; Mazurek, S.; Fecka, I. Antioxidant and Antiglycation Effects of Cistus x incanus Water Infusion, Its Phenolic Components, and Respective Metabolites. Molecules 2022, 27, 2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouahhoud, S.; Khoulati, A.; Kadda, S.; Bencheikh, N.; Mamri, S.; Ziani, A.; Baddaoui, S.; Eddabbeh, F.E.; Lahmass, I.; Benabbes, R.; et al. Antioxidant Activity, Metal Chelating Ability and DNA Protective Effect of the Hydroethanolic Extracts of Crocus sativus Stigmas, Tepals and Leaves. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbe, A.; Ramé, C.; Mellouk, N.; Estienne, A.; Bongrani, A.; Brossaud, A.; Riva, A.; Guérif, F.; Froment, P.; Dupont, J. Effects of Grape Seed Extract and Proanthocyanidin B2 on In Vitro Proliferation, Viability, Steroidogenesis, Oxidative Stress, and Cell Signaling in Human Granulosa Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Wang, L.; Liu, B.; Wang, J.; Su, H.; Zhang, T.; Huang, Z. Analysis of the Metabolic Characteristics of Serum Samples in Patients with Multiple Myeloma. Front. Pharmacol 2018, 9, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Zeng, Y.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, L.; Shu, Y. LC-MS-Based Untargeted Metabolomics Reveals Early Biomarkers in STZ-Induced Diabetic Rats with Cognitive Impairment. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 665309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, X.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Liu, R.; Lu, Q. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of rape bee pollen after fermentation and their correlation with chemical components by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time of flight mass spectrometry-based untargeted metabolomics. Food Chem. 2023, 409, 135342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlNeyadi, S.S.; Amer, N.; Thomas, T.G.; Al Ajeil, R.; Breitener, P.; Munawar, N. Synthesis, Characterization, and Antioxidant Activity of Some 2-Methoxyphenols derivatives. Heterocycl. Commun. 2020, 26, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Jiang, W.; Yang, X.Y.; He, C.H.; Wang, W.; Xing, J.G. Pretreatment with Total Flavonoid Extract from Dracocephalum Moldavic L. Attenuates Ischemia Reperfusion-induced Apoptosis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobhy, E.S.; Abdo, E.; Shaltout, O.; Abdalla, A.; Zeitoun, A. Nutritional Evaluation of Beetroots (Beta vulgaris L.) and Its Potential Application in a Functional Beverage. Plants 2020, 9, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; He, C.; Chen, Y.; Ho, C.T.; Wu, X.; Huang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Hou, A.; Li, Z.; Wang, W.; et al. UPLC–QQQ–MS/MS-based widely targeted metabolomic analysis reveals the effect of solid-state fermentation with Eurotium cristatum on the dynamic changes in the metabolite profile of dark tea. Food Chem. 2022, 378, 131999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, V.Q.; Anh, H.; Quan, N.V.; Xuan, T.D.; Hanamura, I.; Uchino, K.; Karnan, S.; Takami, A. Cytotoxicity of Callerya speciosa Fractions against Myeloma and Lymphoma Cell Lines. Molecules 2022, 27, 2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yuan, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Cao, X.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Gai, S. Metabolomics analysis reveals Embden Meyerhof Parnas pathway activation and flavonoids accumulation during dormancy transition in tree peony. BMC Plant. Biol. 2020, 20, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.T.; Zhang, H.L.; Wei, X.B.; Ye, X.Q.; Tian, J.H. Phytochemicals and Antioxidant Capacities of Young Citrus Fruits Cultivated in China. Molecules 2022, 27, 5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamy, D.; Huang, Y.Y.; Akpabli-Tsigbe, N.D.K.; Battino, M.; Chen, X.M. Valorization of Citrus Reticulata Peels for Flavonoids and Antioxidant Enhancement by Solid-State Fermentation Using Aspergillus niger CGMCC 3.6189. Molecules 2022, 27, 8949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, V.; Farkas, C.; Riyad, O.; Bujna, E.; Kilin, A.; Sipiczki, G.; Sharma, M.; Usmani, Z.; Gupta, V.K.; Nguyen, Q.D. Enhancement of the enzymatic hydrolysis efficiency of wheat bran using the Bacillus strains and their consortium. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 343, 126092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Xue, P.; Chen, Y.; Xie, J.; Peng, G.; Tian, S.; Chang, C.; Yu, Q. Effect of Soluble Dietary Fiber of Navel Orange Peel Prepared by Mixed Solid-State Fermentation on the Quality of Jelly. Foods 2023, 12, 1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, J.K.S.; Denadai, M.; de Oliveira, C.S.; Nunes, M.L.; Narain, N. Evaluation of bioactive compounds potential and antioxidant activity of brown, green and red propolis from Brazilian northeast region. Food Res. Int. 2017, 101, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, Y.A.; Chung, S.W.; Kim, S.C.; Lee, Y.J. Comprehensive Assessment of Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Papaya Extracts. Foods 2022, 11, 3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Su, Y.; Su, J.; Xue, J.; Zhang, R.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Ding, Y.; Chu, X. Optimization of Enzyme-Assisted Aqueous Extraction of Polysaccharide from Acanthopanax senticosus and Comparison of Physicochemical Properties and Bioactivities of Polysaccharides with Different Molecular Weights. Molecules 2023, 28, 6585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
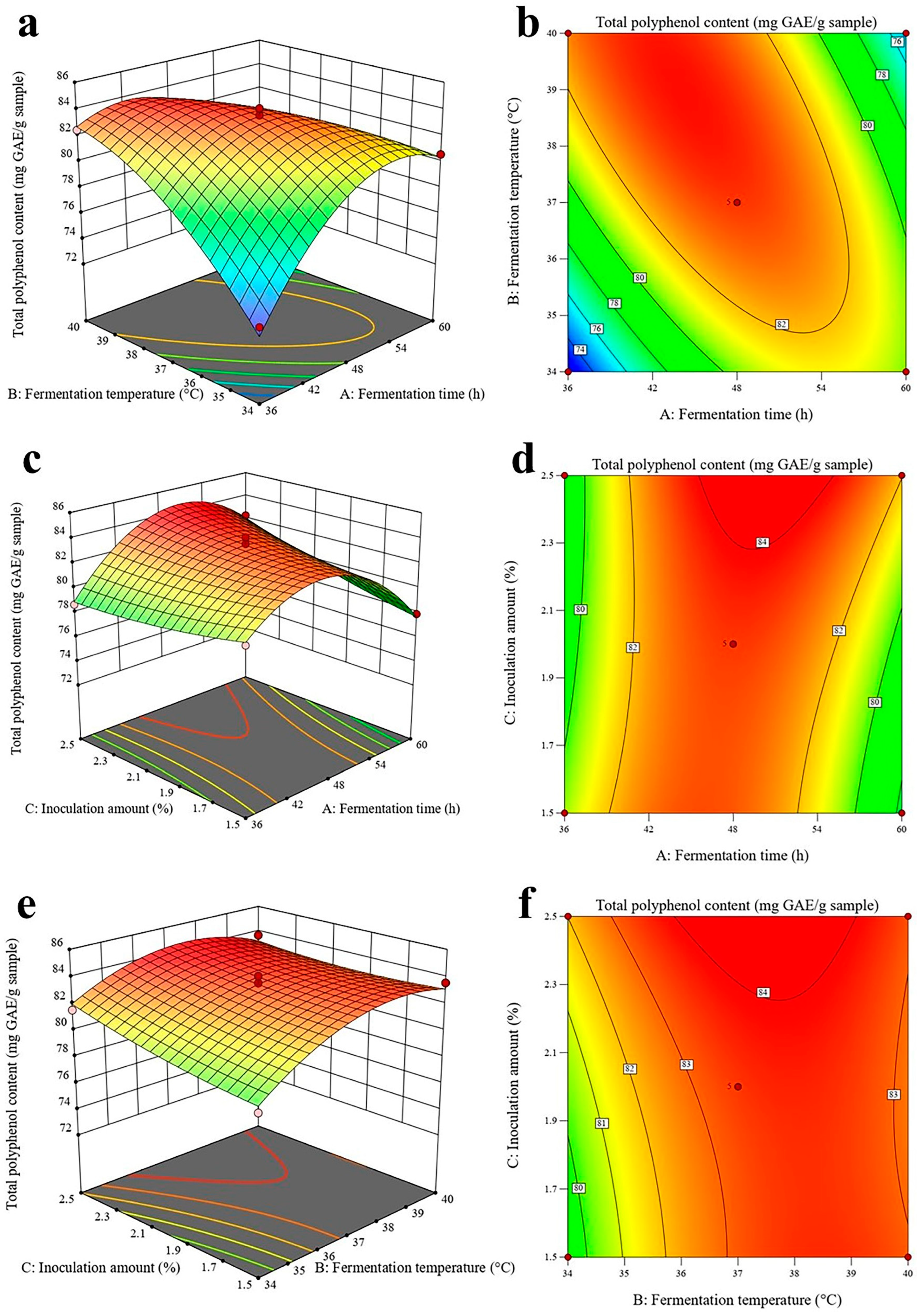


| Number | A Fermentation Time (h) | B Fermentation Temperature (°C) | C Inoculation Amount (%) | Total Polyphenol Content (mg GAE/g Sample) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 83.12 |
| 2 | 1 | −1 | 0 | 80.6 |
| 3 | 0 | −1 | −1 | 78.94 |
| 4 | −1 | −1 | 0 | 72.98 |
| 5 | −1 | 0 | −1 | 80.31 |
| 6 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 74.25 |
| 7 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 78.69 |
| 8 | −1 | 1 | 0 | 82.44 |
| 9 | 0 | −1 | 1 | 81.56 |
| 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 83.41 |
| 11 | 1 | 0 | −1 | 77.92 |
| 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 84.06 |
| 13 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 83.67 |
| 14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 83.12 |
| 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 83.55 |
| 16 | 0 | 1 | −1 | 83.57 |
| 17 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 82.27 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 174.97 | 9 | 19.44 | 51.63 | <0.0001 | significant |
| A | 0.0481 | 1 | 0.0481 | 0.1276 | 0.7315 | |
| B | 12.13 | 1 | 12.13 | 32.21 | 0.0008 | *** |
| C | 3.71 | 1 | 3.71 | 9.86 | 0.0164 | * |
| AB | 62.49 | 1 | 62.49 | 165.95 | <0.0001 | *** |
| AC | 8.91 | 1 | 8.91 | 23.66 | 0.0018 | ** |
| BC | 1.59 | 1 | 1.59 | 4.22 | 0.0791 | |
| A2 | 67.74 | 1 | 67.74 | 179.90 | <0.0001 | *** |
| B2 | 14.78 | 1 | 14.78 | 39.25 | 0.0004 | *** |
| C2 | 0.5351 | 1 | 0.5351 | 1.42 | 0.2721 | |
| Residual | 2.64 | 7 | 0.3765 | |||
| Lack of Fit | 2.03 | 3 | 0.6781 | 4.51 | 0.0899 | not significant |
| Pure Error | 0.6015 | 4 | 0.1504 | |||
| Cor Total | 177.60 | 16 |
| Factors | Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0 | 1 | |
| A. Fermentation time (h) | 36 | 48 | 60 |
| B. Fermentation temperature (°C) | 34 | 37 | 40 |
| C. Inoculation amount (%) | 1.5 | 2 | 2.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, R.; Wang, X.; Xue, J.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Ding, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Su, J.; Chu, X. Optimization of Liquid Fermentation of Acanthopanax senticosus Leaves and Its Non-Targeted Metabolomics Analysis. Molecules 2024, 29, 4749. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194749
Zhang R, Wang X, Xue J, Li X, Li Y, Ding Y, Feng Y, Zhang X, Su J, Chu X. Optimization of Liquid Fermentation of Acanthopanax senticosus Leaves and Its Non-Targeted Metabolomics Analysis. Molecules. 2024; 29(19):4749. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194749
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Rui, Xueyan Wang, Jiaojiao Xue, Xiaoli Li, Ying Li, Yi Ding, Yichao Feng, Xueping Zhang, Jianqing Su, and Xiuling Chu. 2024. "Optimization of Liquid Fermentation of Acanthopanax senticosus Leaves and Its Non-Targeted Metabolomics Analysis" Molecules 29, no. 19: 4749. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194749
APA StyleZhang, R., Wang, X., Xue, J., Li, X., Li, Y., Ding, Y., Feng, Y., Zhang, X., Su, J., & Chu, X. (2024). Optimization of Liquid Fermentation of Acanthopanax senticosus Leaves and Its Non-Targeted Metabolomics Analysis. Molecules, 29(19), 4749. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194749






