From Bioink to Tissue: Exploring Chitosan-Agarose Composite in the Context of Printability and Cellular Behaviour
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Physiochemical Properties of Chitosan–Agarose Composition
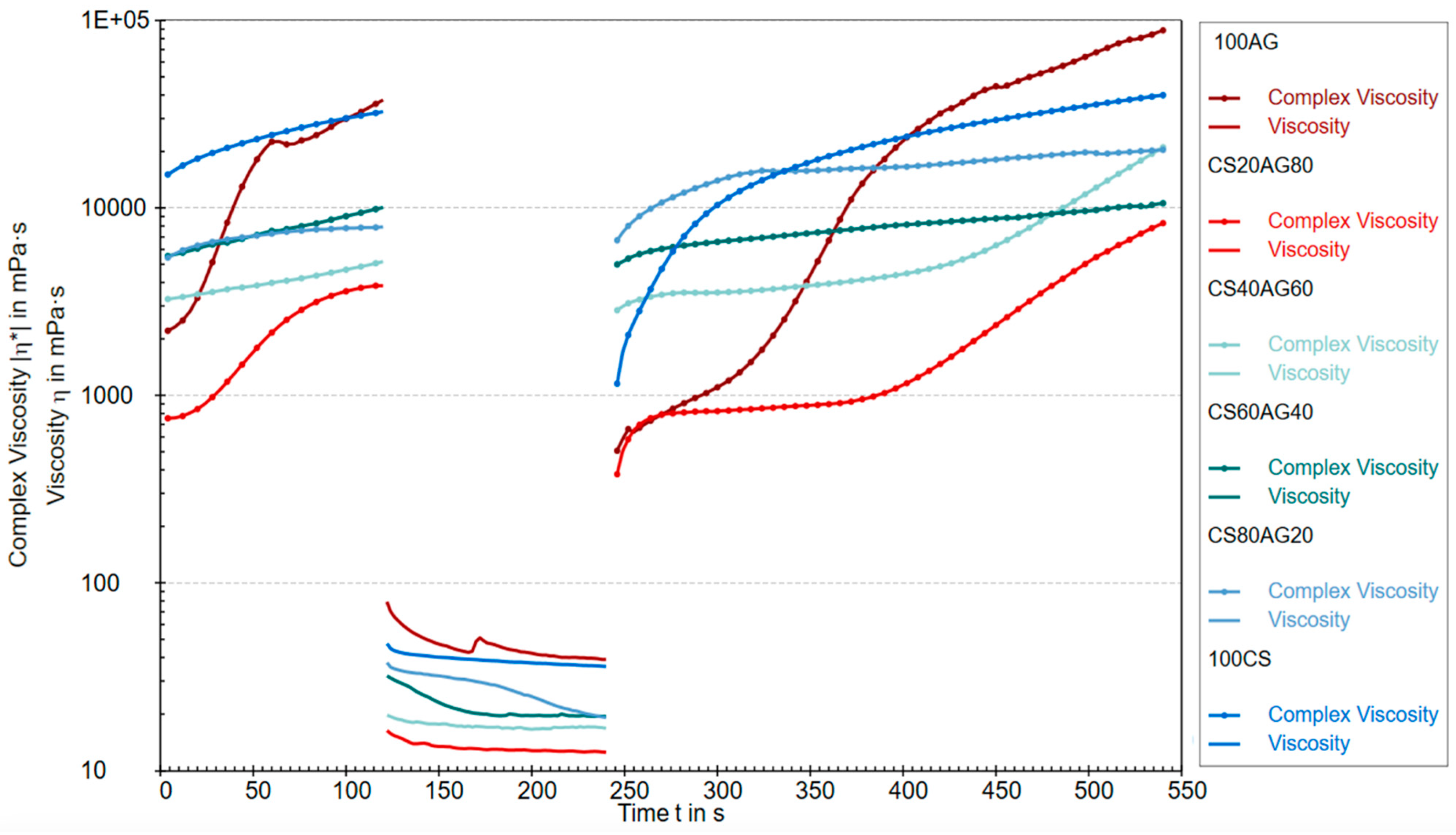
2.1.1. Rheological Properties
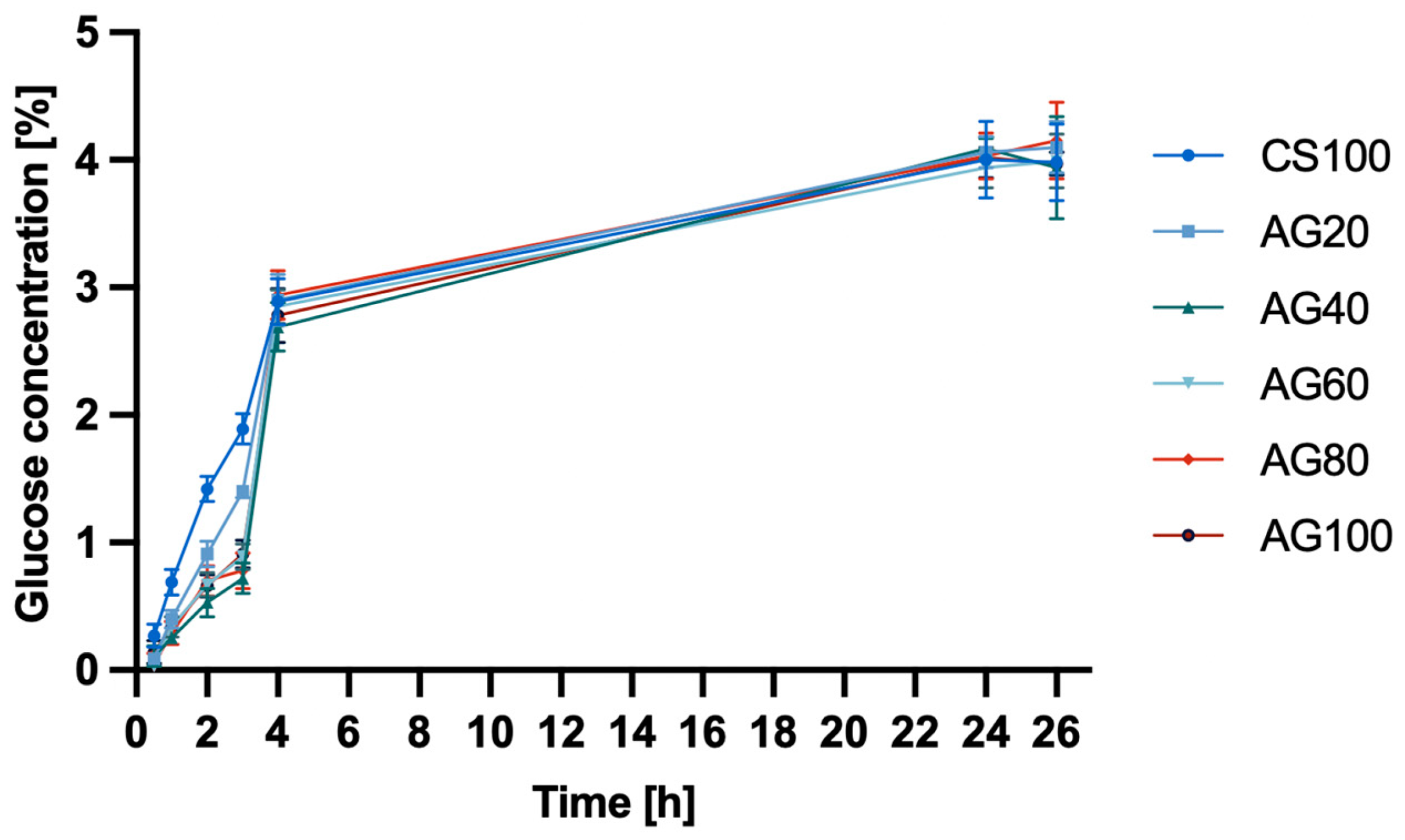
2.1.2. Permeability
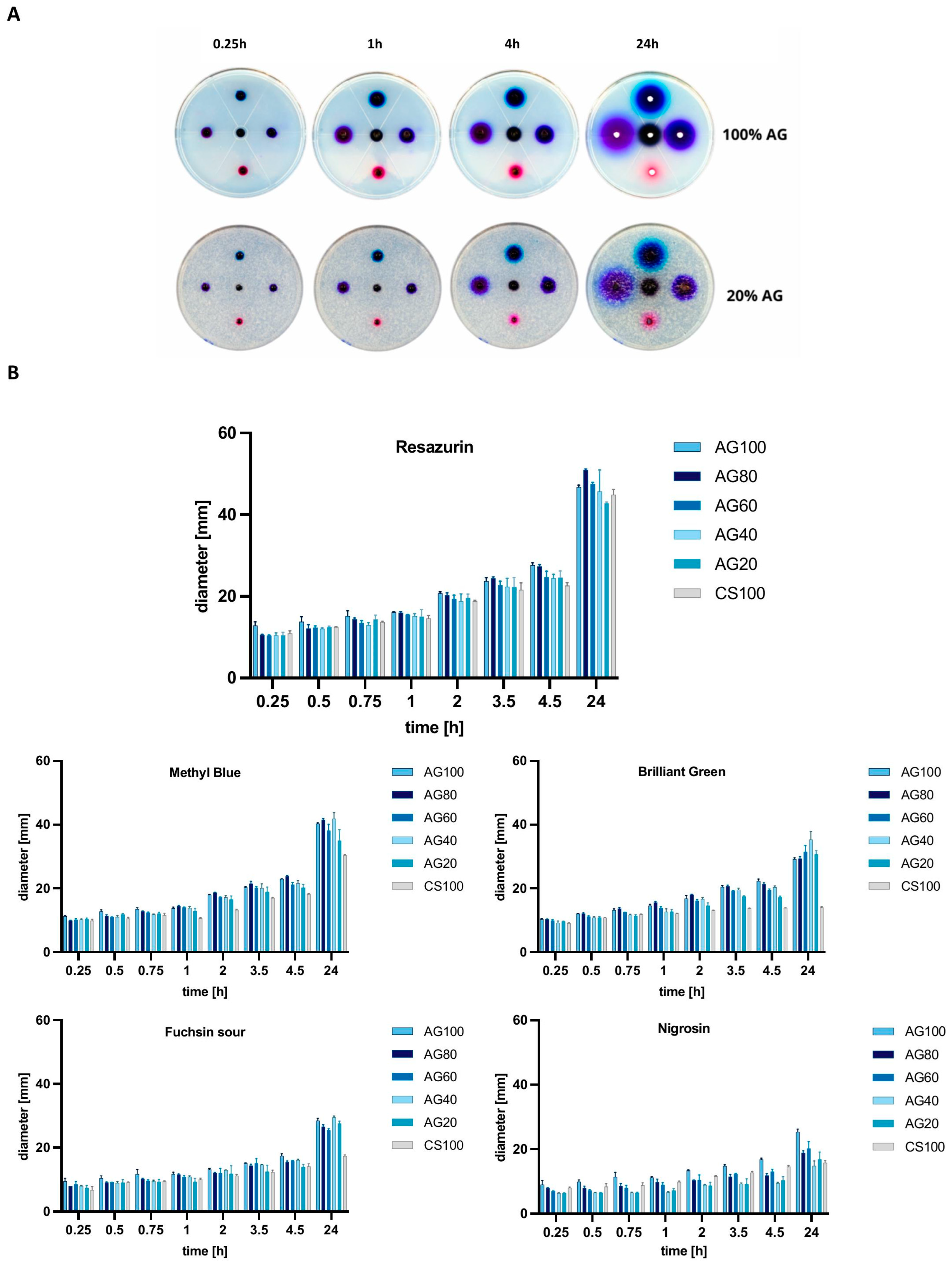
2.2. Biological Properties of Chitosan–Agarose Composition
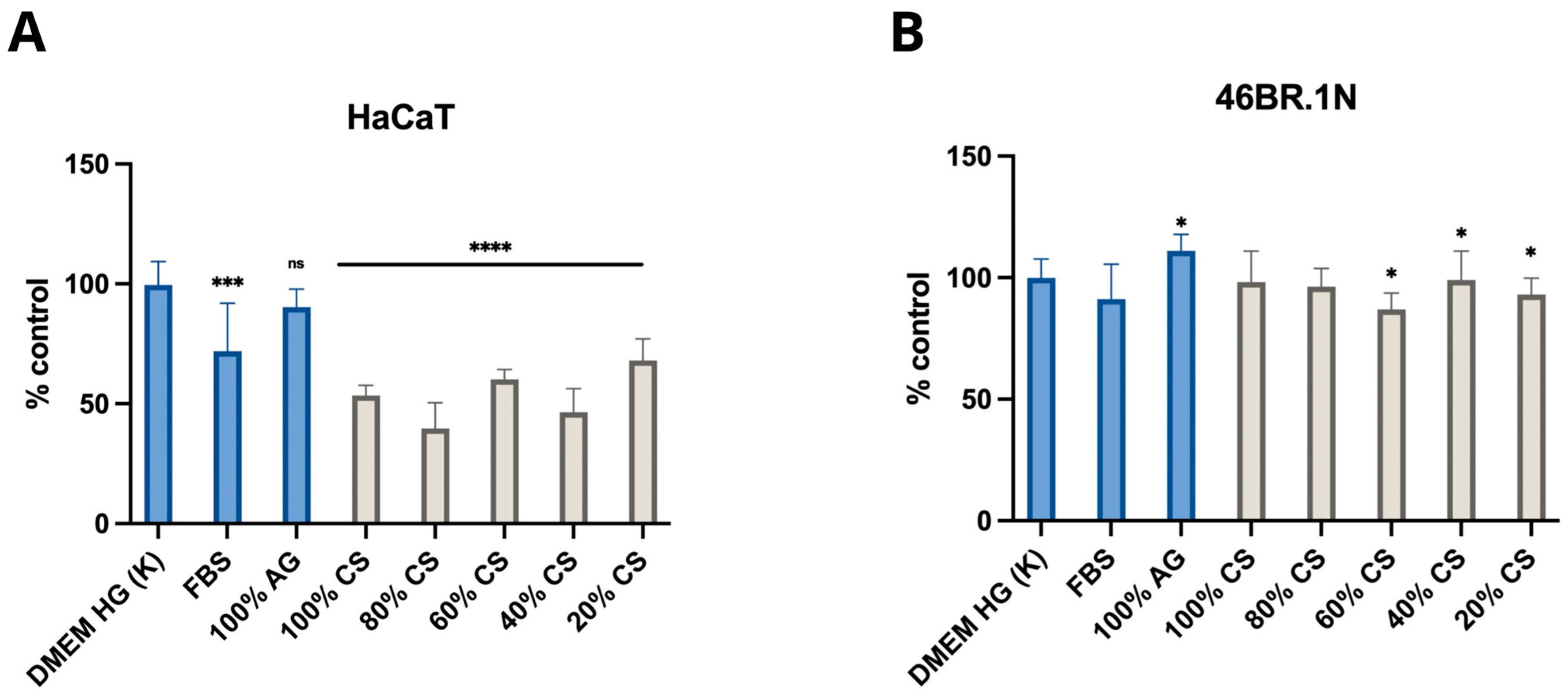
2.2.1. MTT Test
2.2.2. Migration Test
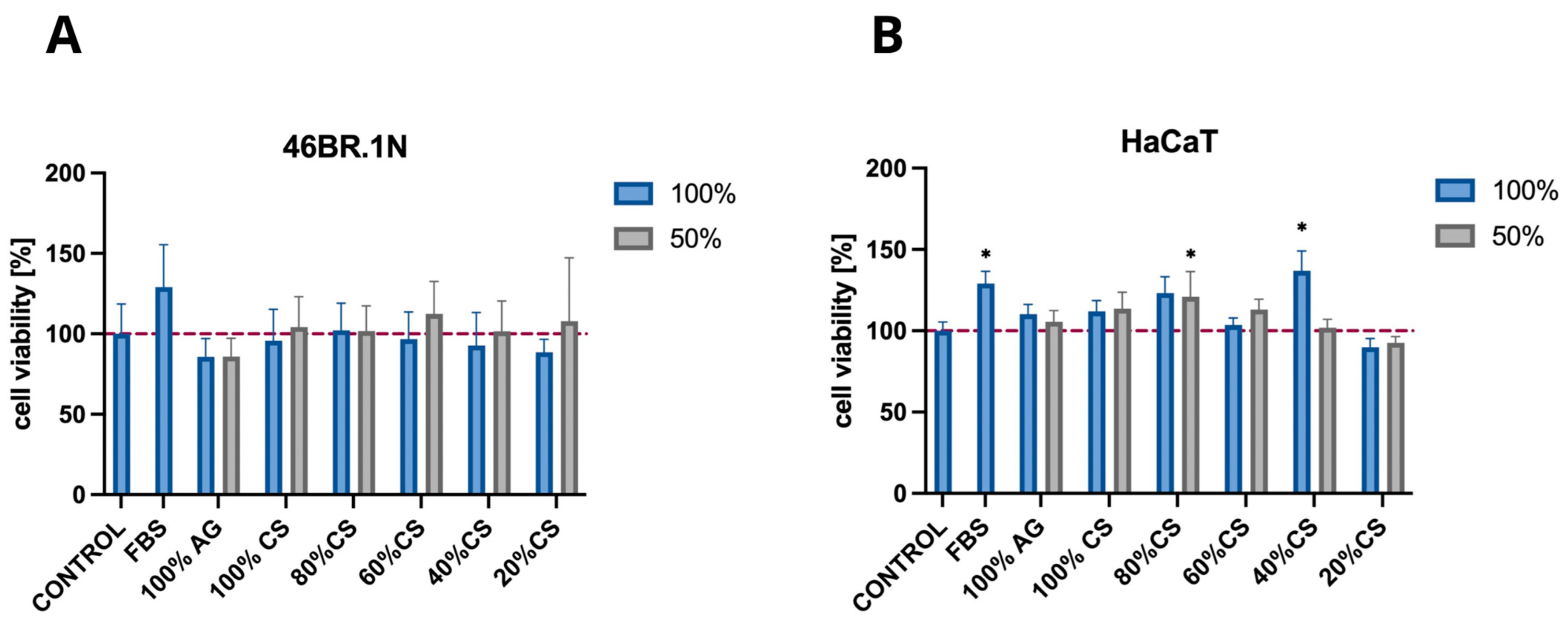
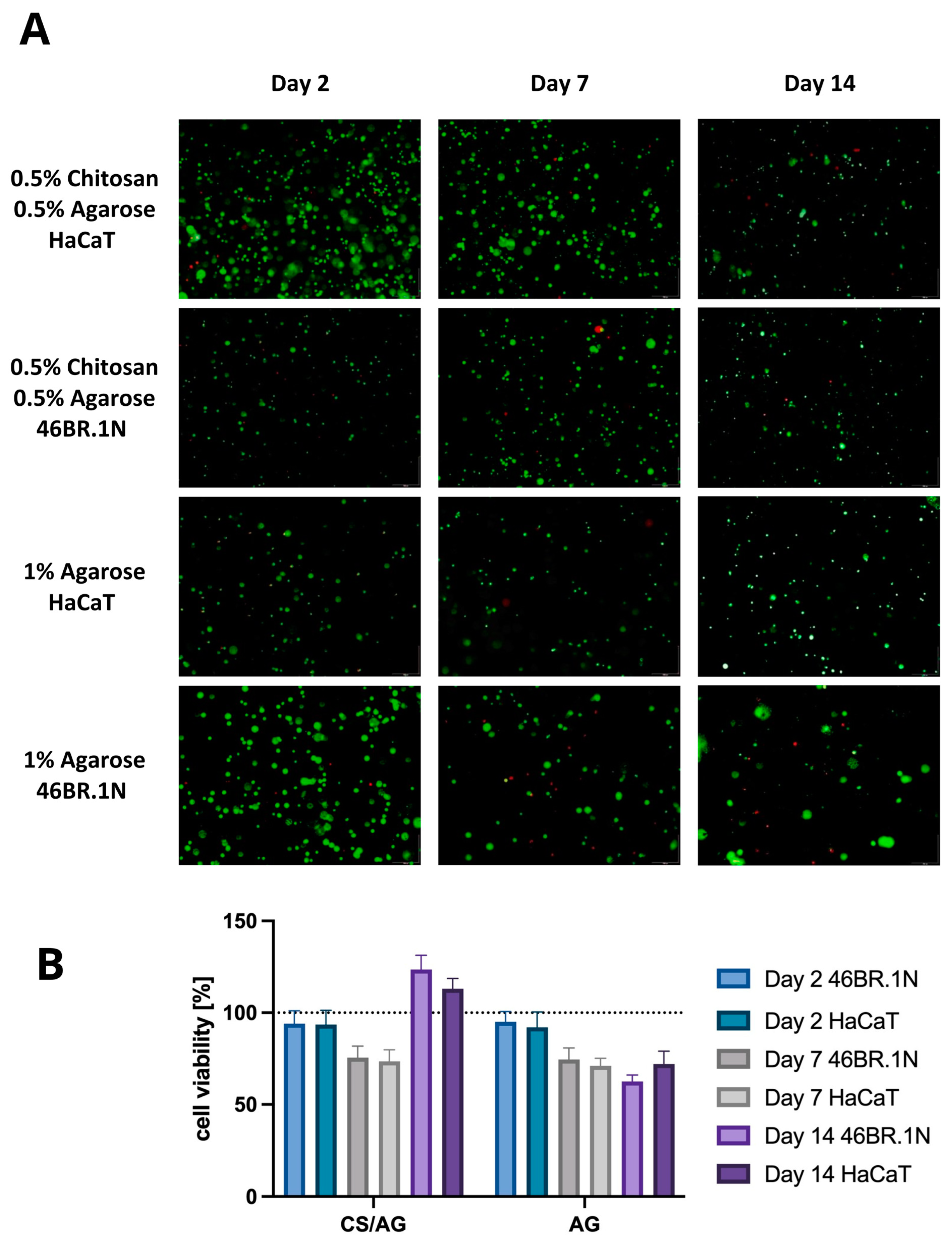
2.2.3. Cell Viability
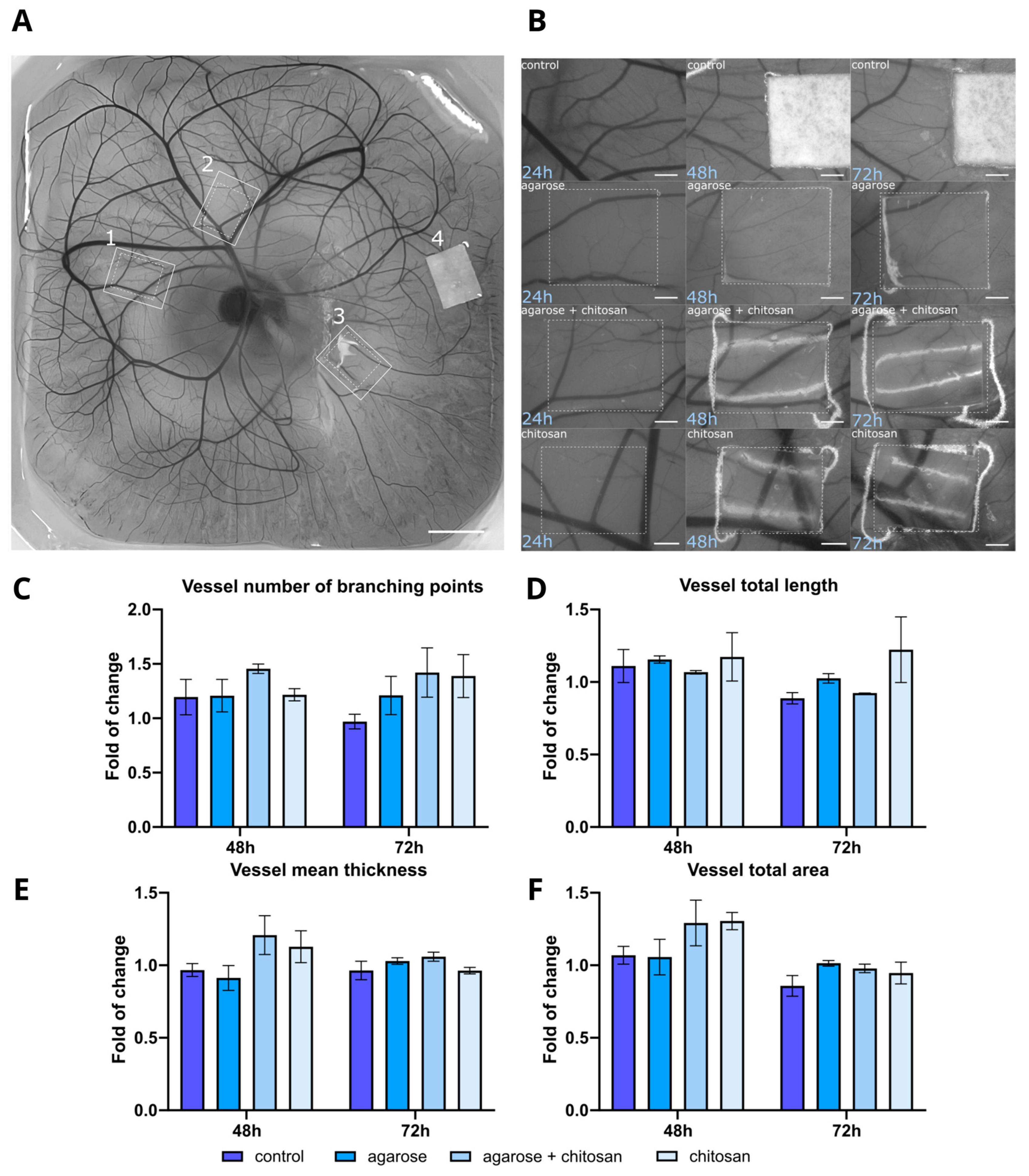
2.2.4. Angiogenesis
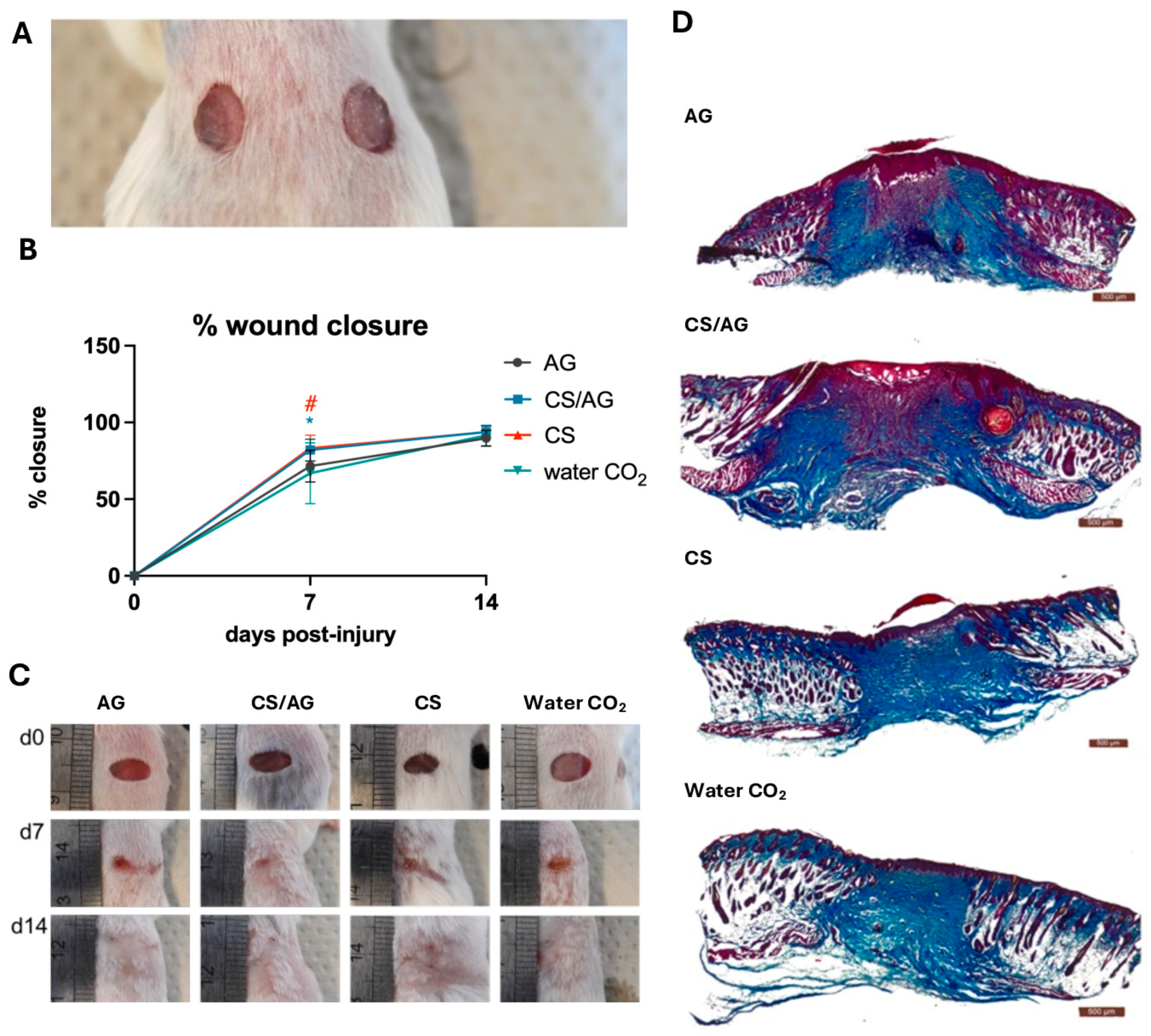
2.2.5. Wound Healing
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
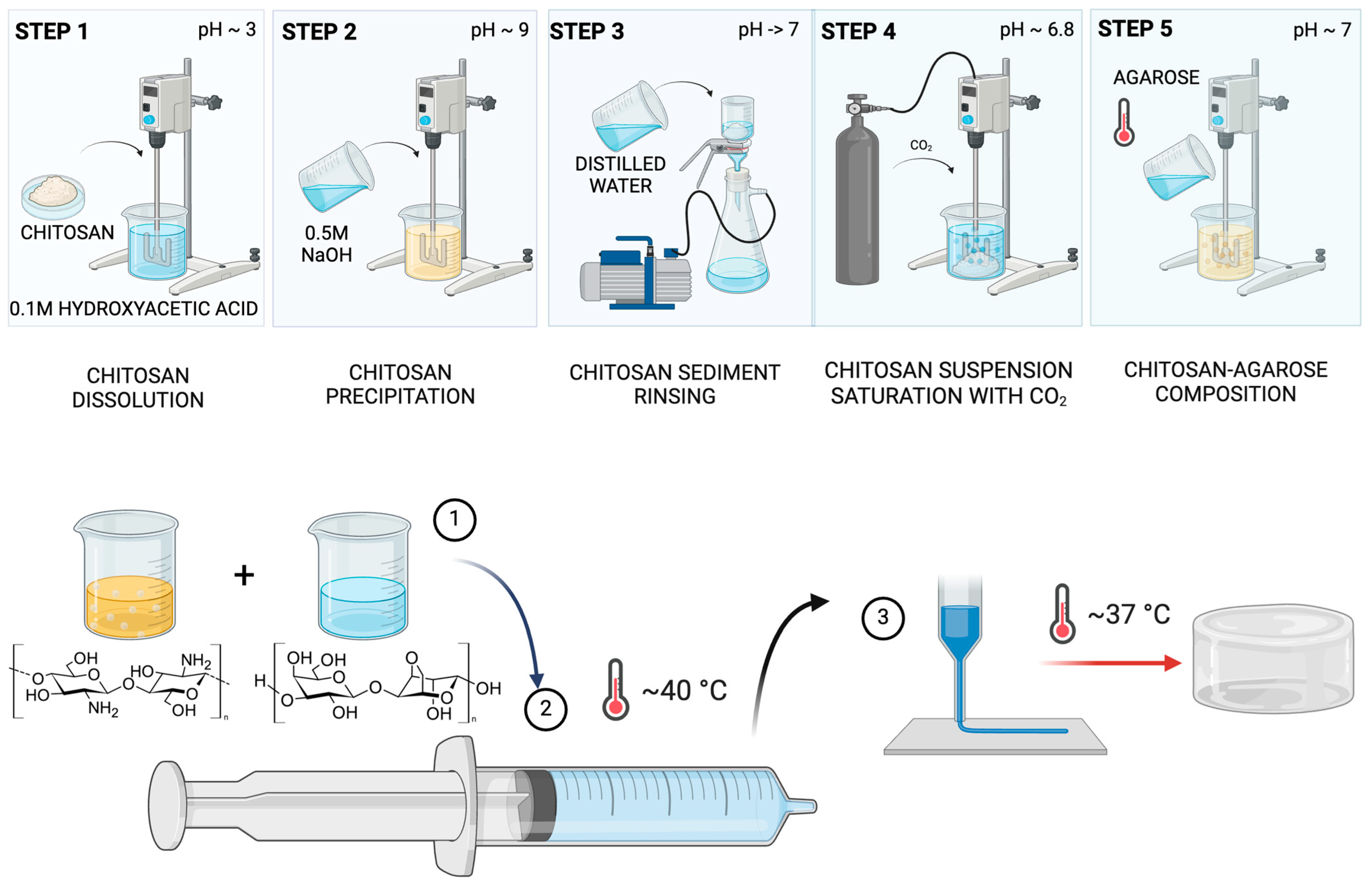
3.2. Hydrogel Preparation
3.3. Physiochemical Characterisation of Chitosan–Agarose Composition
3.3.1. Rheological Properties Assessment
3.3.2. Permeability Assessment
3.4. Biological Properties of Chitosan–Agarose Composition Assessment
3.4.1. Cell Culture Conditions
3.4.2. MTT
3.4.3. Cell Viability Assessment
3.4.4. Wound Healing Ibidi
3.4.5. Angiogenesis Assessment
3.4.6. Wound Healing Model in Mice
3.4.7. Tissue Isolation for Histological Analyses
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Summary and Conclusions
5. Further Action
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fornetti, E.; De Paolis, F.; Fuoco, C.; Bernardini, S.; Giannitelli, S.M.; Rainer, A.; Seliktar, D.; Magdinier, F.; Baldi, J.; Biagini, R.; et al. A Novel Extrusion-Based 3D Bioprinting System for Skeletal Muscle Tissue Engineering. Biofabrication 2023, 15, 025009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antezana, P.E.; Municoy, S.; Álvarez-Echazú, M.I.; Santo-Orihuela, P.L.; Catalano, P.N.; Al-Tel, T.H.; Kadumudi, F.B.; Dolatshahi-Pirouz, A.; Orive, G.; Desimone, M.F. The 3D Bioprinted Scaffolds for Wound Healing. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSimone, E.; Schacht, K.; Jungst, T.; Groll, J.; Scheibel, T. Biofabrication of 3D Constructs: Fabrication Technologies and Spider Silk Proteins as Bioinks. Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deptuła, M.; Karpowicz, P.; Wardowska, A.; Sass, P.; Sosnowski, P.; Mieczkowska, A.; Filipowicz, N.; Dzierżyńska, M.; Sawicka, J.; Nowicka, E.; et al. Development of a Peptide Derived from Platelet-Derived Growth Factor (PDGF-BB) into a Potential Drug Candidate for the Treatment of Wounds. Adv. Wound Care 2020, 9, 657–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banach-Kopeć, A.; Mania, S.; Pilch, J.; Augustin, E.; Gabriel, I.; Tylingo, R. A novel method of endotoxins removal from chitosan hydrogel as a potential bioink component obtained by CO2 saturation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Fu, J.; Lin, H.; He, Y. Development of 3D Bioprinting: From Printing Methods to Biomedical Applications. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 15, 529–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dell, A.C.; Wagner, G.; Own, J.; Geibel, J.P. 3D Bioprinting Using Hydrogels: Cell Inks and Tissue Engineering Applications. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, L.; Wang, C.; Deng, Y.; Shavandi, A. Bio-Inspired Hydrogels via 3D Bioprinting. In Biomimetics; Bio-Inspired Hydrogels via 3D Bioprinting; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.; Luo, Y.; Ke, C.; Qiu, H.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Hou, R.; Xu, L.; Wu, S. Chitosan-Based Functional Materials for Skin Wound Repair: Mechanisms and Applications. Front Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 650598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matica, M.A.; Aachmann, F.L.; Tøndervik, A.; Sletta, H.; Ostafe, V. Chitosan as a wound dressing starting material: Antimicrobial properties and mode of action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Huang, J.; Fang, Y.; Huang, H.; Wu, J. 1D, 2D, and 3D scaffolds promoting angiogenesis for enhanced wound healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 437, 134690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, H.M.; Naseri, E.; MacDonald, D.S.; Tasker, R.A.; Ahmadi, A. Investigation of rheology, printability, and biocompatibility of N, O-carboxymethyl chitosan and agarose bioinks for 3D bioprinting of neuron cells. Materialia 2021, 18, 101169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banach-Kopeć, A.; Mania, S.; Tylingo, R. Marine polymers in tissue bioprinting: Current achievements and challenges. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2024, 63, 20230180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reys, L.L.; Silva, S.S.; Soares da Costa, D.; Rodrigues, L.C.; Reis, R.L.; Silva, T.H. Building Fucoidan/Agarose-Based Hydrogels as a Platform for the Development of Therapeutic Approaches against Diabetes. Molecules 2023, 28, 4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owczarz, P.; Ziółkowski, P.; Modrzejewska, Z.; Kuberski, S.; Dziubiński, M. Rheo-Kinetic Study of Sol-Gel Phase Transition of Chitosan Colloidal Systems. Polymers 2018, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Liu, J.C.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Xu, C.X. A review on cell damage, viability, and functionality during 3D bioprinting. Mil. Med. Res. 2022, 9, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozbolat, I.T.; Hospodiuk, M. Current advances and future perspectives in extrusion-based bioprinting. Biomaterials 2016, 76, 321–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafezi, F.; Shorter, S.; Tabriz, A.G.; Hurt, A.; Elmes, V.; Boateng, J.; Douroumis, D. Bioprinting and Preliminary Testing of Highly Reproducible Novel Bioink for Potential Skin Regeneration. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gwak, M.A.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, D.; Park, S.A.; Park, W.H. Highly gallol-substituted, rapidly self-crosslinkable, and robust chitosan hydrogel for 3D bioprinting. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 227, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Fei, F.; Li, X.; Nie, Z.; Zhou, D.; Liu, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Fei, Z.; Xu, T. A facile, versatile hydrogel bioink for 3D bioprinting benefits long-term subaqueous fidelity, cell viability and proliferation. Regen Biomater. 2021, 8, rbab026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, N.; Sawadkar, P.; Ho, S.; Sharma, V.; Snow, M.; Powell, S.; Woodruff, M.A.; Hook, L.; García-Gareta, E. Pre-screening the intrinsic angiogenic capacity of biomaterials in an optimised ex ovo chorioallantoic membrane model. J. Tissue Eng. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banach-Kopeć, A.; Mania, S.; Tylingo, R.; Wawrzynowicz, A.; Pawłowska, M.; Czerwiec, K.; Pikuła, M. Thermosensitive composite based on agarose and chitosan saturated with carbon dioxide. Preliminary study of requirements for production of new CSAG bioink. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 336, 122120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jan, H. Kirby-Bauer Disk Diffusion Susceptibility Test Protocol. Am. Soc. Microbiol. 2009, 15, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Boukamp, P.; Popp, S.; Altmeyer, S.; Hülsen, A.; Fasching, C.; Cremer, T.; Fusenig, N.E. Sustained nontumorigenic phenotype correlates with a largely stable chromosome content during long-term culture of the human keratinocyte line HaCaT. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 1997, 19, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukamp, P.; Petrussevska, R.T.; Breitkreutz, D.; Hornung, J.; Markham, A.; Fusenig, N.E. Normal keratinisation in a spontaneously immortalised aneuploid human keratinocyte cell line. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 106, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mania, S.; Banach-Kopeć, A.; Maciejewska, N.; Czerwiec, K.; Słonimska, P.; Deptuła, M.; Baczyński-Keller, J.; Pikuła, M.; Sachadyn, P.; Tylingo, R. From Bioink to Tissue: Exploring Chitosan-Agarose Composite in the Context of Printability and Cellular Behaviour. Molecules 2024, 29, 4648. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194648
Mania S, Banach-Kopeć A, Maciejewska N, Czerwiec K, Słonimska P, Deptuła M, Baczyński-Keller J, Pikuła M, Sachadyn P, Tylingo R. From Bioink to Tissue: Exploring Chitosan-Agarose Composite in the Context of Printability and Cellular Behaviour. Molecules. 2024; 29(19):4648. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194648
Chicago/Turabian StyleMania, Szymon, Adrianna Banach-Kopeć, Natalia Maciejewska, Katarzyna Czerwiec, Paulina Słonimska, Milena Deptuła, Jakub Baczyński-Keller, Michał Pikuła, Paweł Sachadyn, and Robert Tylingo. 2024. "From Bioink to Tissue: Exploring Chitosan-Agarose Composite in the Context of Printability and Cellular Behaviour" Molecules 29, no. 19: 4648. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194648
APA StyleMania, S., Banach-Kopeć, A., Maciejewska, N., Czerwiec, K., Słonimska, P., Deptuła, M., Baczyński-Keller, J., Pikuła, M., Sachadyn, P., & Tylingo, R. (2024). From Bioink to Tissue: Exploring Chitosan-Agarose Composite in the Context of Printability and Cellular Behaviour. Molecules, 29(19), 4648. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194648






