Biochemical Modulators of Tight Junctions (TJs): Occludin, Claudin-2 and Zonulin as Biomarkers of Intestinal Barrier Leakage in the Diagnosis and Assessment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Progression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patients’ Characteristics
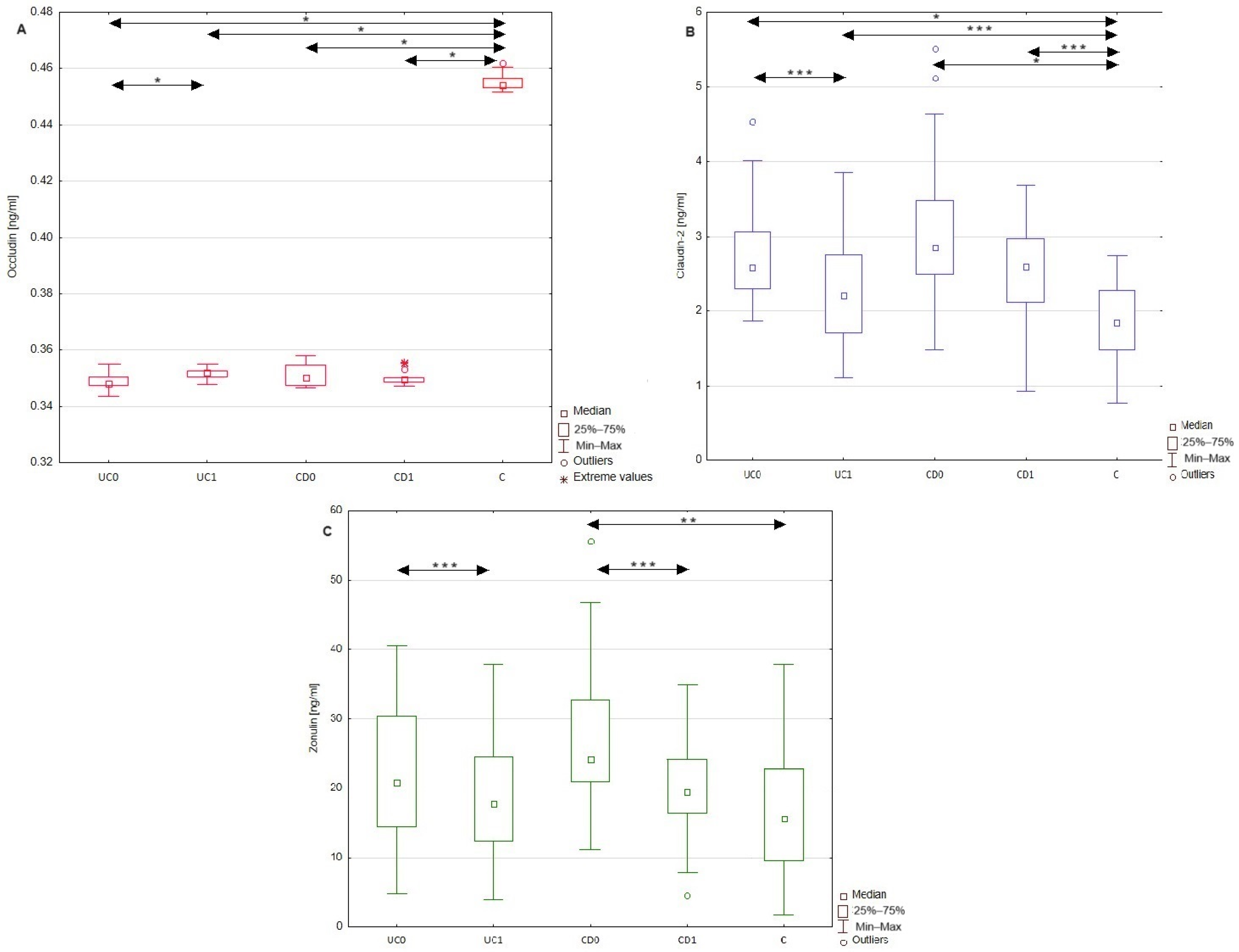
2.2. Differences in Occludin, Claudin-2, and Zonulin Serum Profiles between Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Healthy Individuals
2.3. ROC Analysis of Occludin, Claudin-2, and Zonulin Levels for Diagnosis of Ulcerative Colitis and Chron’s Disease
2.4. Usefulness of Occludin, Claudin-2, and Zonulin as Biomarkers Evaluating Disease Activity
2.5. Influence of Anti-Inflammatory Treatment on the Serum Profile of Occludin, Cludin-2, and Zonulin in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn’s Disease
3. Discussion
3.1. Usefulness of Occludin, Claudin-2, and Zonulin as Diagnostic Markers in Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn’s Disease
3.2. Influence of Anti-Inflammatory Treatment on the Serum Profile of Occludin, Claudin-2, and Zonulin in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn’s Disease
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population
4.2. Measurements of Tight Junction Proteins (Occludin, Claudin-2, and Zonulin) by ELISA
4.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALT | alanine aminotransferase |
| AUC | area under curve |
| AST | aspartate aminotransferase |
| BMI | body mass index |
| CRP | c-reactive protein |
| CD0 | patients with Crohn’s disease before treatment |
| CD1 | patients with Crohn’s disease after treatment |
| CDAI | Crohn’s disease activity index |
| EGFR | epidermal growth factor receptor |
| IBD | inflammatory bowel disease |
| IFN-γ | interferon-γ |
| IL-6 | interleukin-6 |
| IL-23 | interleukin-23 |
| IECs | intestinal epithelial cells |
| MMPs | metalloproteinases |
| Na | sodium |
| NPV | negative predictive value |
| PPV | positive predictive value |
| K | potassium |
| PAR | protease-activated receptor |
| ROC | receiver-operating characteristic |
| TJs | tight junctions |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor α |
| UC0 | patients with ulcerative colitis before treatment |
| UC1 | patients with ulcerative colitis after treatment |
References
- Guan, Q. A Comprehensive Review and Update on the Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 7247238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, G.P.; Papadakis, K.A. Mechanisms of Disease: Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2019, 94, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabla, B.S.; Schwartz, D.A. Assessing Severity of Disease in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 49, 671–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narula, N.; Pray, C.; Wong, E.C.L.; Colombel, J.F.; Marshall, J.K.; Daperno, M.; Reinisch, W.; Dulai, P.S. Categorising Endoscopic Severity of Crohn’s Disease Using the Modified Multiplier SES-CD [MM-SES-CD]. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2022, 16, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.R.; Rodriguez, J.R. Clinical presentation of Crohn’s, ulcerative colitis, and indeterminate colitis: Symptoms, extraintestinal manifestations, and disease phenotypes. Semin. Pediatr. Surg. 2017, 26, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.C.; Shi, H.Y.; Hamidi, N.; Underwood, F.E.; Tang, W.; Benchimol, E.I.; Panaccione, R.; Ghosh, S.; Wu, J.C.Y.; Chan, F.K.L.; et al. Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century: A systematic review of population-based studies. Lancet 2017, 390, 2769–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaser, C.; Sturm, A.; Vavricka, S.R.; Kucharzik, T.; Fiorino, G.; Annese, V.; Calabrese, E.; Baumgart, D.C.; Bettenworth, D.; Borralho Nunes, P.; et al. ECCO-ESGAR Guideline for Diagnostic Assessment in IBD Part 1: Initial diagnosis, monitoring of known IBD, detection of complications. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2019, 13, 144–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soubières, A.A.; Poullis, A. Emerging role of novel biomarkers in the diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease. World J. Gastrointest. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 7, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelakkot, C.; Ghim, J.; Ryu, S.H. Mechanisms regulating intestinal barrier integrity and its pathological implications. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landy, J.; Ronde, E.; English, N.; Clark, S.K.; Hart, A.L.; Knight, S.C.; Ciclitira, P.J.; Al-Hassi, H.O. Tight junctions in inflammatory bowel diseases and inflammatory bowel disease associated colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 3117–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, W.T.; Odenwald, M.A.; Turner, J.R.; Zuo, L. Tight junction proteins occludin and ZO-1 as regulators of epithelial proliferation and survival. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2022, 1514, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummins, P.M. Occludin: One protein, many forms. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 32, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capaldo, C.T. Claudin Barriers on the Brink: How Conflicting Tissue and Cellular Priorities Drive IBD Pathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Hernandez, V.; Quiros, M.; Nusrat, A. Intestinal epithelial claudins: Expression and regulation in homeostasis and inflammation. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2017, 1397, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serek, P.; Oleksy-Wawrzyniak, M. The Effect of Bacterial Infections, Probiotics and Zonulin on Intestinal Barrier Integrity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veres-Székely, A.; Szász, C.; Pap, D.; Szebeni, B.; Bokrossy, P.; Vannay, Á. Zonulin as a Potential Therapeutic Target in Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis Disorders: Encouraging Results and Emerging Questions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharzik, T.; Walsh, S.V.; Chen, J.; Parkos, C.A.; Nusrat, A. Neutrophil transmigration in inflammatory bowel disease is associated with differential expression of epithelial intercellular junction proteins. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 159, 2001–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.Q.; Wang, J.; Sheng, J.Y.; Zha, J.M.; Graham, W.V.; Turner, J.R. Contributions of Myosin Light Chain Kinase to Regulation of Epithelial Paracellular Permeability and Mucosal Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, R.F.; Caetano, M.A.F.; Magalhães, H.I.R.; Castelucci, P. Study of tumor necrosis factor receptor in the inflammatory bowel disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 29, 2733–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubowska, K.; Pryczynicz, A.; Iwanowicz, P.; Niewiński, A.; Maciorkowska, E.; Hapanowicz, J.; Jagodzińska, D.; Kemona, A.; Guzińska-Ustymowicz, K. Expressions of Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMP-2, MMP-7, and MMP-9) and Their Inhibitors (TIMP-1, TIMP-2) in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2016, 2016, 2456179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.R.; Nalle, S.C.; Tretiakova, M.; Rubin, D.T.; Turner, J.R. Claudin-1 and claudin-2 expression is elevated in inflammatory bowel disease and may contribute to early neoplastic transformation. Lab. Investig. 2008, 88, 1110–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Yoshinaga, N.; Tanabe, S. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) regulates claudin-2 expression and tight junction permeability in intestinal epithelium. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 31263–31271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, S.; Mingrino, R.; Kaukinen, K.; Hayes, K.L.; Powell, R.M.; MacDonald, T.T.; Collins, J.E. Inflammatory processes have differential effects on claudins 2, 3 and 4 in colonic epithelial cells. Lab. Investig. 2005, 85, 1139–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, M.; Pohin, M.; Powrie, F. Cytokine Networks in the Pathophysiology of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Immunity 2019, 50, 992–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushlinskii, N.E.; Gershtein, E.S.; Zybina, N.N.; Tsarapaev, P.V.; Salyanova, E.P.; Korotkova, E.A.; Nikonov, E.L.; Mamedli, Z.Z.; Bozhenko, V.K.; Stilidi, I.S. Blood Serum Zonulin in Colorectal Cancer, Autoimmune Bowel Diseases, and Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2022, 173, 376–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caviglia, G.P.; Dughera, F.; Ribaldone, D.G.; Rosso, C.; Abate, M.L.; Pellicano, R.; Bresso, F.; Smedile, A.; Saracco, G.M.; Astegiano, M. Serum zonulin in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: A pilot study. Minerva Med. 2019, 110, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Asmar, R.; Panigrahi, P.; Bamford, P.; Berti, I.; Not, T.; Coppa, G.V.; Catassi, C.; Fasano, A. Host-dependent zonulin secretion causes the impairment of the small intestine barrier function after bacterial exposure. Gastroenterology 2002, 123, 1607–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Elamin, E.; Elizalde, M.; Bours, P.P.H.A.; Pierik, M.J.; Masclee, A.A.M.; Jonkers, D.M.A.E. Modulation of Intestinal Epithelial Permeability by Plasma from Patients with Crohn’s Disease in a Three-dimensional Cell Culture Model. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billmeier, U.; Dieterich, W.; Neurath, M.F.; Atreya, R. Molecular mechanism of action of anti-tumor necrosis factor antibodies in inflammatory bowel diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 9300–9313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlén, R.; Strid, H.; Lundgren, A.; Isaksson, S.; Raghavan, S.; Magnusson, M.K.; Simrén, M.; Sjövall, H.; Öhman, L. Infliximab inhibits activation and effector. Scand. J. Immunol. 2013, 78, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringheanu, M.; Daum, F.; Markowitz, J.; Levine, J.; Katz, S.; Lin, X.; Silver, J. Effects of infliximab on apoptosis and reverse signaling of monocytes from healthy individuals and patients with Crohn’s disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2004, 10, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegh, C.A.M.; de Roos, N.M.; Hovenier, R.; Meijerink, J.; Besseling-van der Vaart, I.; van Hemert, S.; Witteman, B.J.M. Intestinal Permeability Measured by Urinary Sucrose Excretion Correlates with Serum Zonulin and Faecal Calprotectin Concentrations in UC Patients in Remission. J. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 2019, 2472754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Uzzau, S.; Goldblum, S.E.; Fasano, A. Human zonulin, a potential modulator of intestinal tight junctions. J. Cell Sci. 2000, 113 Pt 24, 4435–4440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pierro, M.; Lu, R.; Uzzau, S.; Wang, W.; Margaretten, K.; Pazzani, C.; Maimone, F.; Fasano, A. Zonula occludens toxin structure-function analysis. Identification of the fragment biologically active on tight junctions and of the zonulin receptor binding domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 19160–19165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Patients with Ulcerative Colitis | Patients with Crohn’s Disease | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Treatment UC0 | After Treatment UC1 | p UC0 vs. UC1 | Before Treatment CD0 | After Treatment CD1 | p CD0 vs. CD1 | |
| Number of patients | 31 | n.a. | 18 | n.a. | ||
| Sex [females/males] | 12/19 | n.a. | 8/10 | n.a. | ||
| Age [years] | 33.4 ± 12.8 | n.a. | 32.1 ± 9.6 | n.a. | ||
| BMI [kg/m2] | 24.3 ± 3.6 | 24.5 ± 4.2 | >0.05 | 20.6 ± 3.4 | 19.8 ± 2.8 | >0.05 |
| Mayo score | 3 (2–3) | 2 (1–3) | <0.001 | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. |
| CDAI score | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | 303.4 ± 52.5 | 270.8 ± 44.3 | <0.05 |
| CRP [mg/L] | 14.1 ± 24.1 | 7.9 ± 13.3 | <0.05 | 20.9 ± 21.1 | 15.8 ± 11.4 | >0.05 |
| Serum calprotectin [ng/mL] | 3337.1 ± 1775.3 | 2708.3 ± 890.9 | >0.05 | 3537.5 ± 1893.8 | 2915.3 ± 1325.9 | >0.05 |
| Albumin [g/L] | 42 (40–46) | 43 (40–48) | >0.05 | 43.5 (42–47.3) | 43.5 (42–49) | >0.05 |
| Creatinine [μmol/L] | 77.8 (68.5–87.9) | 74.7 (63.4–87.1) | >0.05 | 81.3 ± 14.1 | 86.6 ± 13.2 | >0.05 |
| Glucose [mmol/L] | 4.9 ± 0.7 | 4.8 ± 0.8 | >0.05 | 5.1 ± 0.9 | 4.9 ± 0.4 | >0.05 |
| AST [U/L] | 19.0 (14–46) | 19 (15–23) | >0.05 | 21.5 (18.5–24.3) | 21 (16.8–23.5) | >0.05 |
| ALT [U/L] | 15 (10–26) | 16 (10–25) | >0.05 | 24 (16.3–29) | 21.5 (14.5–31) | >0.05 |
| Na [mmol/L] | 140 (138–142) | 140.00 (138–141) | >0.05 | 138.2 ± 2.9 | 138.4 ± 3.9 | >0.05 |
| K [mmol/L] | 4.2 ± 0.4 | 3.9 ± 0.3 | <0.05 | 4.4 (4.2–4.5) | 4.4 (4.2–4.5) | >0.05 |
| Hemoglobin [g/dL] | 12.8 ± 2.3 | 13.5 ± 2.3 | <0.01 | 11.6 ± 2.3 | 12.4 ± 1.9 | >0.05 |
| White blood cell count [×103/μL] | 7.9 (3.9–13.7) | 7.1 ± 3.2 | >0.05 | 6.7 ± 2.1 | 6.7 ± 2.1 | >0.05 |
| Platelet count [×109/L] | 375.9 ± 108.8 | 342 ± 101.7 | <0.05 | 356.5 (277.5–396) | 232.2 (134.2–309.1) | >0.05 |
| Parameter | UC0 | UC1 | p UC0 vs. UC1 | CD0 | CD1 | p CD0 vs. CD1 | C | p UC0 vs. C | p CD0 vs. C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Occludin [ng/mL] | 0.349 ± 0.003 | 0.351 ± 0.002 | <0.001 | 0.353 (0.349–0.357) | 0.350 (0.349–0.353) | >0.05 | 0.454 (0.453–0.457) | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Claudin-2 [ng/mL] | 2.72 ± 0.66 | 2.24 ± 0.76 | <0.05 | 3.17 ± 1.12 | 2.51 ± 0.75 | >0.05 | 1.88 ± 0.48 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Zonulin [ng/mL] | 21.92 ± 9.29 | 18.85 ± 8.04 | <0.05 | 27.19 ± 11.38 | 19.2 ± 7.65 | <0.05 | 17.06 ± 10.15 | >0.05 | <0.01 |
| Patients | Parameter | AUC | Cut-Off | Youden Index | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UC | Occludin | 0.959 (95% CI 0.907–1) | 0.45 ng/mL | 0.90 | 95% | 90% | 100% | 100% | 91% |
| Claudin-2 | 0.864 (95% CI 0.776–0.952) | 2.33 ng/mL | 0.57 | 79% | 73% | 84% | 79% | 76% | |
| Zonulin | 0.634 (95% CI 0.495–0.774) | 17.52 ng/mL | 0.32 | 66% | 71% | 61% | 65% | 68% | |
| CD | Occludin | 0.948 (95% CI 0.879–1) | 0.36 ng/mL | 0.82 | 93% | 88% | 90% | 100% | 91% |
| Claudin-2 | 0.896 (95% CI 0.792–0.999) | 2.49 ng/mL | 0.69 | 85% | 77% | 90% | 81% | 88% | |
| Zonulin | 0.740 (95% CI 0.598–0.881) | 20.78 ng/mL | 0.46 | 70% | 81% | 65% | 54% | 87% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Górecka, A.; Jura-Półtorak, A.; Koźma, E.M.; Szeremeta, A.; Olczyk, K.; Komosińska-Vassev, K. Biochemical Modulators of Tight Junctions (TJs): Occludin, Claudin-2 and Zonulin as Biomarkers of Intestinal Barrier Leakage in the Diagnosis and Assessment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Progression. Molecules 2024, 29, 4577. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194577
Górecka A, Jura-Półtorak A, Koźma EM, Szeremeta A, Olczyk K, Komosińska-Vassev K. Biochemical Modulators of Tight Junctions (TJs): Occludin, Claudin-2 and Zonulin as Biomarkers of Intestinal Barrier Leakage in the Diagnosis and Assessment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Progression. Molecules. 2024; 29(19):4577. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194577
Chicago/Turabian StyleGórecka, Aleksandra, Agnieszka Jura-Półtorak, Ewa M. Koźma, Anna Szeremeta, Krystyna Olczyk, and Katarzyna Komosińska-Vassev. 2024. "Biochemical Modulators of Tight Junctions (TJs): Occludin, Claudin-2 and Zonulin as Biomarkers of Intestinal Barrier Leakage in the Diagnosis and Assessment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Progression" Molecules 29, no. 19: 4577. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194577
APA StyleGórecka, A., Jura-Półtorak, A., Koźma, E. M., Szeremeta, A., Olczyk, K., & Komosińska-Vassev, K. (2024). Biochemical Modulators of Tight Junctions (TJs): Occludin, Claudin-2 and Zonulin as Biomarkers of Intestinal Barrier Leakage in the Diagnosis and Assessment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Progression. Molecules, 29(19), 4577. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194577







