Abstract
Two water-soluble block copolymers composed of acrylic acid (AA), 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropane sulfonic acid (AMPS), and optionally maleic anhydride (MAH) were synthesized through ammonium persulfate-catalyzed free radical polymerization in water. The introduction of aluminum sulfate (AS) into the resulting mixtures significantly reduced the setting times of the paste and enhanced the mechanical strength of the mortar compared to both the additive-free control and experiments facilitated solely by pure AS. This improvement was primarily attributed to the inhibition of rapid Al3+ hydrolysis, which was achieved through coordination of the synthesized block copolymers, along with the formation of newly identified hydrolytic intermediates. Notably, the ternary copolymer (AA–AMPS–MAH) exhibited superior performance compared to that of the binary copolymer (AA–AMPS). In the early stages of cement setting, clusters of ettringite (AFt) were found to be immobilized over newly detected linkage phases, including unusual calcium silicate hydrate and epistilbite. In contrast to the well-documented role of polymers in retarding cement hydration, this study presents a novel approach by providing both accelerating and hardening agents for cement setting, which has significant implications for the future design of cement additives.
1. Introduction
To this day, cement remains one of the most widely used construction materials. Initially, it was hydrated into an inorganic hydrogel known as hydrated tricalcium silicate (C-S-H, 3CaO·SiO2·3H2O), which then bound together various concrete components, such as bricks, wood, and sand, tightly and permanently, ensuring the durability of the structures for many years [,].
The rapid setting and hardening of OPC (Ordinary Portland Cement, also known as Standard Cement in China)-based concrete was crucial in cold regions and for constructing tunnels, bridges, and roadways. Without it, these structures could fail quickly due to prolonged setting times and slow development of mechanical strength. To address this issue, sprayed concrete (shotcrete) was developed []. The primary difference between conventional and sprayed concrete lies in the use of accelerators. However, accelerators can sometimes lead to long-term strength loss (after 28 days) and result in issues, such as shrinkage and durability [].
Over time, three main series of accelerators have been developed for both market and engineering applications. The first series includes setting and hardening accelerators. Setting accelerators focus on reducing the hydration time of concrete while hardening accelerators are designed to enhance early strength []. The second series, addressing concerns about the corrosion of steel in concrete due to chloride ions, includes both chloride-containing and non-chloride accelerators. Chloride-based accelerators, such as CaCl2, NaCl, and LiCl, are effective in promoting early-stage hydration []. However, due to issues such as excessive dosage, high cost, and the corrosive effects on steel reinforcement [], their use has become less common. Consequently, non-chloride accelerators have gained prominence. For example, the combination of Ca(NO3)2 and NaNO3 has been effective in accelerating the cementing process while simultaneously improving early strength [].
Lastly, it was discovered that excessive amounts of alkaline metal ions could trigger alkali-aggregate reactions during cement setting, leading to expansion and a significant loss of strength []. As a result, alkali-free accelerators containing 1% or less alkaline content have become more popular in both market and engineering applications compared to their alkali-containing counterparts [].
In recent years, aluminum sulfate (AS, Al2(SO4)3·18H2O) has emerged as a prominent and widely used material in the field of alkali-free accelerators. During the hydration of Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC), the pH gradually increases, causing Al3+ ions from AS to hydrolyze into [Al(OH)4]−. This species then reacts with Ca2+ and SO42− ions, leading to the formation of C3A (tricalcium aluminate, 3CaO·Al2O3) []. Further hydration of C3A with gypsum (CaSO4·2H2O) results in the formation of AFt (ettringite, calcium sulfoaluminate hydrate, 3CaO·Al2O3·3CaSO4·32H2O), which plays a crucial role as an adhesive in enhancing mechanical strength []. In OPC-based concretes, C-S-H (calcium silicate hydrate) bound SiO2, lime, and other components, typically form a two-dimensional layered structure that is not as robust as desired. The formation of AFt significantly improves this linkage by strengthening the material in an additional dimension [].
However, while AS facilitates the hydration of C3A and the subsequent formation of AFt, the rapid and substantial accumulation of AFt on the surface of C3S can inhibit its hydration of C3S due to inadequate water dispersion []. During this process, the morphology of AFt transitions from rounded masses to prismatic needles []. Consequently, to prevent the agglomeration of AFt on the C3S surface, it is essential to regulate the rapid hydrolysis of pure AS into Al3+ and [Al(OH)4]− by incorporating functional additives [,,,].
The design and application of polymers in cement hydration have garnered ongoing interest due to their structural versatility and relatively low cost []. In practice, the most commonly used polymers function as retarders or water reducers. Their dispersion in water and subsequent attachment to the surfaces of cement particles inhibit rapid hydration while maintaining high fluidity in mortar, thereby enhancing castability []. For instance, the incorporation of rubber latexes as additives in paving cement has improved various properties, including workability, adhesion to substrates, anti-bleeding characteristics, flexural and tensile strength, ductility, cracking resistance, impermeability, and reduced shrinkage []. Currently, EVA (ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer) stands out as the most widely utilized polymer in concrete engineering, significantly enhancing the tensile bond strength, flexural strength, and toughness of hardened concrete [].
There are numerous examples of using polymers as retarders or superplasticizers in the cementing process. For instance, an amphoteric retarder derived from the copolymerization of AMPS (2-acrylamido-2-methylpropane sulfonic acid), IA (itaconic acid), DMC (2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyltrimethylammonium chloride), and TPEG (methylallyl polyethenoxy ether), has demonstrated an excellent retarding effect at high temperatures for long-standing cementing applications []. This makes it suitable for deep-well construction []. Additionally, PCE (polycarboxylate ether) superplasticizers have been found to enhance the initial dissolution rate of cement and subsequently inhibit hydration through complexation with Ca2+, thereby exhibiting significant plasticizing properties [].
There are notable examples of organic polymers being utilized as accelerators in cementing. For instance, the combination of lignosulfonate with CaCl2 has demonstrated significant accelerating effects on cement hydration, resulting in high compressive strength after 28 days. However, this accelerator did not effectively prevent the deterioration of the blended cement in corrosive environments []. Additionally, polyacrylamide, a linear water-soluble polymer, plays a crucial role when added to cement slurry. The molecules of polyacrylamide linked together and adsorbed onto two or more cement particles, forming bridges that facilitate the formation of a cohesive structure. This interaction increases resistance to particle movement, thereby enhancing the viscosity of the slurry and accelerating the cementing setting [,].
However, there is a strong demand for cementing solutions that offer both short setting times and high mechanical strength, especially in engineering applications, such as the use of sprayed concrete (shotcrete) under high pressure and velocity for tunnel construction. In this context, block copolymers composed of various monomers with different functional groups are of particular interest. Each functional group imparts unique properties, and their combination can lead to unexpected and highly effective improvements in the cementing performance.
Initially, the primary role of the AA (acrylic acid) monomer was attributed to its carboxyl group, which prevented the agglomeration of Ca2+ during cement hydration, thus demonstrating excellent salt tolerance []. Additionally, the carboxyl group creates an acidic environment that inhibits rapid and excessive hydrolysis of Al3+, thereby naturally accelerating the cementing process [].
Furthermore, AMPS (2-acrylamido-2-methylpropane sulfonic acid) contains both sulfonic acid and amide groups. The sulfonic acid group provides high water solubility and good thermal stability, while the amide group helps control fluid loss and can be hydrolyzed at high temperatures, thereby enhancing the rheological performance [].
Moreover, the MAH (maleic anhydride) monomer contributes to water reduction, which improves paste fluidity and accelerates the setting time []. Given the diverse properties of these functional monomers, it is intriguing to explore whether copolymerization of these groups could achieve both rapid setting and effective hardening in cementing applications.
To enhance the performance of AS-induced cement hydration, two block copolymers such as AA–AMPS and AA–AMPS–MAH were synthesized via (NH4)2S2O8-initiated free radical polymerization in an aqueous solution. These copolymers were then combined with AS to serve as accelerators in the hydration of Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC). This study involved measuring both the setting times of the paste and the mechanical properties of the mortar as well as exploring parameters such as the type and dosage of the accelerator. Additionally, characterization was conducted to understand the underlying mechanisms. This research aimed to contribute to the development of new accelerators with hardening effects, particularly in the context of sprayed concrete applications.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of Block Copolymers and Accelerators
Synthesis of block copolymers were shown in Figure 1. The X and α values of the prepared block copolymers are shown in Table 1. (NH4)2S2O8 seemed to be an effective initiator for the aqueous free radical polymerization of AA, AMPS, and MAH at moderate temperatures (Figure 1) [], and α stemmed from the polymerization of AA, AMPS, and MAH was slightly better than that of AA and AMPS (Table 1). It was previously reported that MAH showed high activity in copolymerization with olefinic compounds, leading to uniform polymeric microspheres [], which may promote the copolymerization of AA and AMPS in this work (Figure 1).
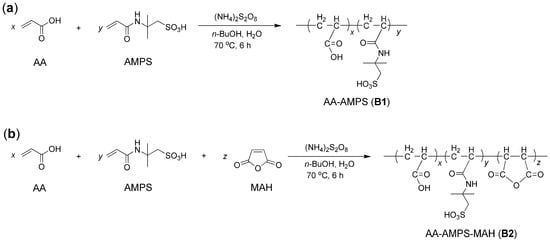
Figure 1.
Synthesis of block copolymers: (a) AA–AMPS (B1) and (b) AA–AMPS–MAH (B2).

Table 1.
The bromine number (X) and monomer conversion (α) of tested sample a.
The FT-IR spectra of all the block copolymers (B1 and B2, Section 3.3) and their corresponding accelerators (B1a and B2a, accordingly, Section 3.5) are presented in Figure 2. In Figure 2a, a moderate broadband at 3391 cm−1 for B1 corresponds to the O–H stretching vibrations of carboxyl groups from acrylic acid (AA) and sulfonic acid groups from AMPS []. It has been previously reported that hydrogen-bonded hydroxyl groups exhibit lower intensities and broader FT-IR peaks compared to non-hydrogen-bonded groups []. The peaks at 2974 and 2900 cm−1 were indicative of the anti-symmetric and symmetric stretching of the C–H bonds in the methyl groups of AMPS in B1, respectively []. Additionally, the peak at 2341 cm−1 was associated with the vibration of CO2 (due to air interference).
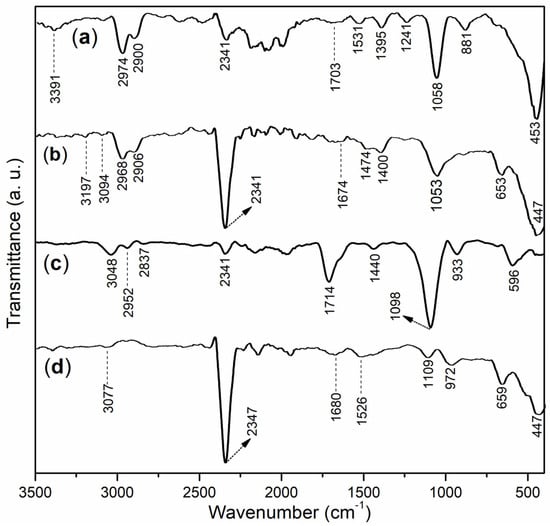
Figure 2.
FT-IR spectra of block copolymers and accelerators: (a) B1; (b) B1a; (c) B2; (d) B2a.
Furthermore, B1 showed a small band at 1703 cm−1, probably indicating C=O stretching of the carboxyl group on AA []. Meanwhile, the small band that occurred at 1531 cm−1 was characteristic of the C=O vibration of the amide group on AMPS []. Moreover, there was one small peak at 1395 cm−1, which could be ascribed to the C–H bending vibration of the B1 framework (Figure 1). The following two peaks appeared at 1241 and 1058 cm−1 and were attributed to the anti-symmetric and symmetric stretching vibrations of the sulfonic acid group on AMPS []. Additionally, B1 also showed peaks at 881 and 453 cm−1, which could be attributed to the residual effects of the sulfonic acid group on AMPS.
The small band observed at 3391 cm−1 in B1 notably diminished and shifted to 3197 cm−1 after B1 was mixed with AS, resulting in the formation of accelerator B1a (Figure 2b vs. Figure 2a). This shift suggested that the O–H units of the carboxyl and sulfonic acid groups in B1 coordinated with Al3+ []. Additionally, when comparing B1 with B1a, a weak peak at 1674 cm−1 was detected in B1a, which was significantly lower than the 1703 cm−1 peak observed in B1 (Figure 2b vs. Figure 2a). This change further indicated that the C=O unit of the carboxyl group in B1’s AA component also coordinated with Al3+ []. The same phenomenon was observed for the C=O unit of the amide on the AMPS of B1 (1474 vs. 1531 cm−1, Figure 2b vs. Figure 2a).
Moreover, the peak observed at 1058 cm−1 on B1 red-shifted to 1053 cm −1 (Figure 2b vs. Figure 2a), suggesting that the S=O unit of the amide group on AMPS was attached to Al3+. In addition, there was a new peak at 447 cm−1 on B1a, which was different from that at 453 cm−1 on B1 (Figure 2b vs. Figure 2a), which could be attributed to the Al–O stretching vibration of [Al(OH)4]− originating from the hydrolysis of Al3+ during the preparation of the accelerator (Section 2.5).
The B2 showed a moderate peak at 3028 cm−1 (Figure 2c), which summarized the effects of the O–H groups of both carboxyl groups on AA and sulfonic acid groups on AMPS. There were two following peaks occurred at 2952 and 2837 cm−1 (Figure 2c), mainly owing to anti-symmetric and symmetric stretching of the C–H bond of the methylene group on B2, which were different from those found at 2974 and 2900 cm−1 on B1, obviously due to the copolymerization of MAH (Figure 1b). The next peak appeared at 1714 cm−1, compared to 1703 cm−1 on B1 (Figure 2c vs. Figure 2a), reflecting the influence of C=O originating from the carboxyl group on AA, as well as that of the cyclic lactone on MAH on B2. Furthermore, B2 showed another weak peak at 1400 cm−1, indicating C–H bending of the B2 framework (Figure 1b). In addition, the larger peak formed at 1098 cm−1 clearly indicates the symmetric stretching of the sulfonic acid group on the AMPS of B2.
On the other hand, the comparison of B2a with B2 showed a very similar tendency to that of B1a with B1, similar to 3077 (weak and broad) vs. 3048, 1680 vs. 1714, and 972 vs. 1098 (Figure 2d vs. Figure 2c), clearly indicating that the O–H groups of carboxyl groups on AA and sulfonic acid groups on AMPS, C=O originating from carboxyl group on AA, C=O of cyclic lactone MAH, and S=O unit of amide group on AMPS were all attached to Al3+.
2.2. Effects of Accelerators
The IST and FST of the cement paste, along with the compressive and flexural strengths of the cement mortar, are summarized in Table 2. Above all, in the absence of any accelerator, the IST and FST of the cement paste were prolonged, and the compressive and flexural strengths of the mortar developed very slowly during 6 h, 24 h, and 28 d (entry 1, Table 2). When pure AS was introduced as an accelerator, both the IST and FST were shortened significantly, and the compressive and flexural strengths improved at 6 h, 24 h, and 28 d (entries 2 vs. 1, Table 2). However, the present IST and FST (18.75 and 36.74 min, entry 2, Table 2) could not match the requirements of Chinese standard GB/T 35159-2017 (IST ≤ 5 min, FST ≤ 12 min). The use of B1 as an accelerator could slightly decrease the setting times and concurrently improve the mechanical strength compared to the blank experiment (entries 3 vs. 1, Table 2), probably owing to the acidic nature of B1 in the cement setting, similar to the effect of inorganic acids as accelerators [].

Table 2.
Setting time of cement paste and mechanical strength of cement mortar under different accelerators a.
The application of B1a sharply decreased both the IST and FST of paste in comparison with those of AS and B1, and promoted the development of both compressive and flexural strengths (entries 4 vs. 2 and 3, Table 2). Actually, the same tendency was found in the utilization of B2a (entries 7 vs. 2 and 3, Table 2). Therefore, this series of accelerators promoted the setting and hardening of cement together.
Herein, coordination of the block copolymer to Al3+ may inhibit the agglomeration and hydrolysis of Al3+ into unreactive Al(OH)3 or Al2O3, subsequently stabilizing the formation of [Al(OH)4]−, which accelerates the occurrence of C3A (precursor of AFt), leading to faster setting [,]. At the same time, the block copolymers may act as structure-directing agents and contribute to the ordered arrangement of AFt on the surface of C3S [].
2.3. Effects of Maleic Anhydride Monomer and Accelerator Dosage
With the accelerator, the dosage was fixed at 7 wt.%, B2a showed similar IST as well as decreased FST than B1a, and both compressive and flexural strengths of mortar derived from B2a were much higher than those from B1a (entries 8 vs. 5, Table 2). Furthermore, B2a showed higher R28 and Rr, 90 values than those of B1a (Table 3). These results indicated that the incorporation of MAH into the AA–AMPSs chain may play a key role in the coordination between Al3+ and the block copolymer, which affected the formation and arrangement of C3A and the subsequent AFt. It was recently reported that MAH can be copolymerized with other olefinic compounds into uniform polymeric microspheres through self-stabilized precipitation polymerization []. Obviously, this unique property of MAH may contribute to the fast setting and strength development in cementing.

Table 3.
Comprehensive strength retention ratio after 28 and 90 days.
The accelerator dosage also facilitated cement setting. When B1a was used as an accelerator, a dosage of 7 wt.% performed much better than 6 wt.% and 8 wt.% (entries 5 vs. 4 and 6, Table 2), and the same tendency was found for the cementing accelerated by B2a (entries 8 vs. 7 and 9, Table 2). This result may be related to the presence of organic residues in the cement paste and mortar.
2.4. Analytical Insights into Cementing Process Facilitated by Accelerator
2.4.1. Composition of Cement and Accelerators
In order to further understand the cementing process facilitated by the accelerator, comprehensive characterizations were carried out to provide clear illustrations. First of all, Table 4 shows the composition and ignition loss of cement, corresponding to those of typical OPC []. For cement (raw material) and hydration products, XPS survey scans are listed in Figure 3, while binding energy and atomic composition are in Table 5. Most elements of cement detected by ICP–OES can be found on the cement surface through XPS (Figure 3a vs. Table 4), but the XPS signals of Fe, Na, and Mg were too weak to be collected (Figure 3a; entry cement, Table 5), mainly due to their low contents.

Table 4.
The composition of cement a.
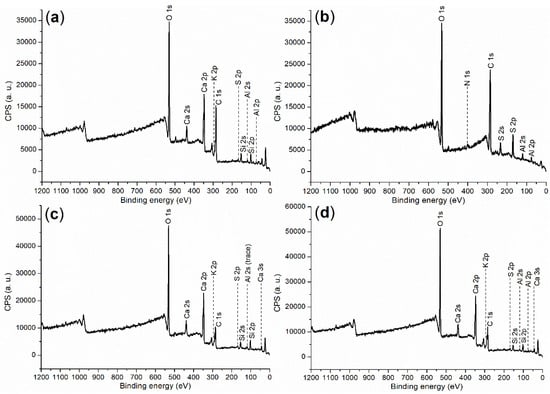

Table 5.
Binding energy and atomic composition of the elements on the sample surface (depth: 0–10 nm).
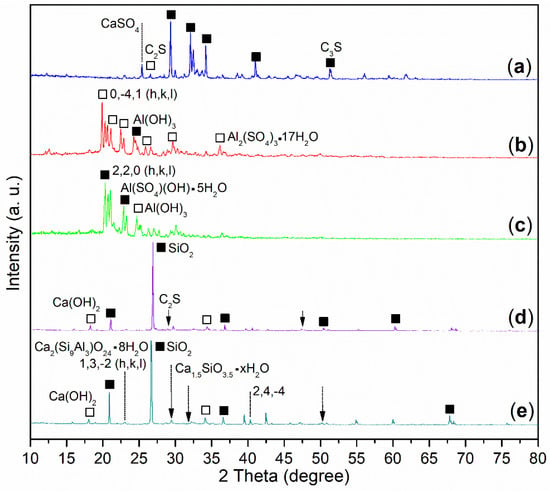
On the other hand, there were three phases in the wide-angle XRD of the cement, including C3S (dark cubes, Figure 4a; 3CaO·SiO2, PDF No. 31-0301), C2S (white cube, Figure 4a; 2CaO·SiO2, PDF No. 31-0302), and CaSO4 (dotted line, Figure 4a; PDF No. 37-0184).
Next, it seemed necessary to determine the chemical state of Al during cementing. The binding energy of the Al 2p photoelectron coming from fresh cement was centered at 74.0 eV as shown in Figure 5a, which is much higher than that of metallic Al (72.6 Â eV) [] but lower than the Al3+ of the Al2O3 phase (75.9 Â eV) [], probably characterizing the tetrahedral Al3+ of the Al(OH)3 phase in the cement.
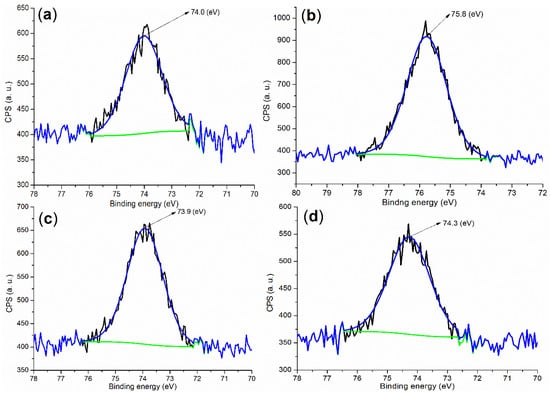
On the other hand, B2a showed the XPS peak of Al 2p at 75.8 eV (Figure 5b), a little lower than that of Al3+ of Al2O3 (75.9 eV) [], meaning some new Al3+-containing species occurred. In association with XRD, there were two phases, Al(SO4)(OH)·5H2O (black cubes, Figure 4c; rostite, PDF No. 41-1382; the peak at 100% intensity at 2θ = 20.860 ° with h, k, l of 2, 2, 0), and Al(OH)3 (white cube, Figure 4c; PDF No. 26-0025) on B2a. The first phase indicated that AS was hydrolyzed stepwise, while the second phase indicated that the remaining AS was completely hydrolyzed.
In comparison, B1a exhibited diffraction systems of Al2(SO4)3·17H2O (white cubes, Figure 4b; alunogen, PDF No. 26-1010; the peak of 100% intensity at 2θ = 19.906 ° with h, k, l of 0, −4, 1) and Al(OH)3 (dark cube, Figure 4b; PDF No. 37-1377). The former phase illustrated that AS was almost untouched, while the latter was characteristic of hydrolyzed Al3+.
Evidently, the roles of B1 and B2 appear to be different in the formation of the accelerator. Therefore, the incorporation of MAH as a monomer increased accelerator activity to a large extent (entries 8 vs. 5, Table 2). Additionally, Figure 5c,d showed two peaks at 73.9 and 74.3 eV, respectively, lower than 75.8 eV on B2a, indicating Al3+ may come into the Al2O3 phase rather than remain in the accelerator as cementing continued.
2.4.2. Composition of Hydrated Mortars
The TGA of the mortar may provide clues for illustrating the accelerating and hardening effects of the accelerators (Figure 6). At first, the red line was always located below the black line at 30–600 °C, indicating that the loading of pure AS as an accelerator resulted in more crystalline water and volatile species than in the blank experiment, but pure AS provided faster setting times and higher mechanical strengths (entries 2 vs. 1, Table 2).
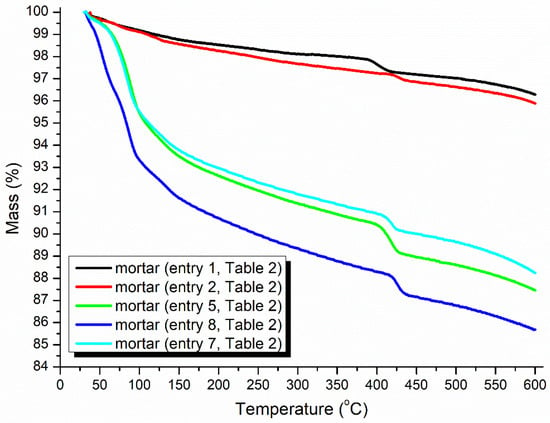
Figure 6.
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) of the mortars (24 h, Table 2).
Next, the use of B1a as an accelerator induced much more crystalline water and organic species in the mortar than AS (green vs. red, Figure 6), corresponding to a decreased setting time and enhanced strength (entries 5 vs. 2, Table 2). The blue line was continuously located below the green line at 30–600 °C (Figure 6), indicating that B2a introduced more crystalline water and organic species than B1a at the same dosage (7 wt.%).
The larger the dosage of the accelerator loaded, the more volatiles contained in the mortar (blue vs. slightly blue, Figure 6), leading to a better setting behavior (entries 8 vs. 7, Table 2). However, excessive loading of B2a depressed the setting conversely (entries 9 vs. 8, Table 2), indicating that the accelerator dosage was highly sensitive to the setting behavior.
Based on the data obtained thus far, there has been a growing interest in detecting organic residues in hydrated mortar. Initially, three distinct peaks were observed at 284.8, 285.9, and 289.2 eV in the cement, corresponding to carbons of the C (sp3 configuration, saturated)–H group, C–O bond, and carboxyl group, respectively (Figure 7a) []. These peaks can be attributed to the presence of small organic molecules residual in the cement. In contrast, B2a exhibited three C 1s peaks at 285.3, 286.6, and 289.2 eV (Figure 7b), which are associated with carbons from the C–O bond, C–N bond in amides, and carboxyl group []. These features primarily originated from the functional groups in the B2 backbone (Figure 1).
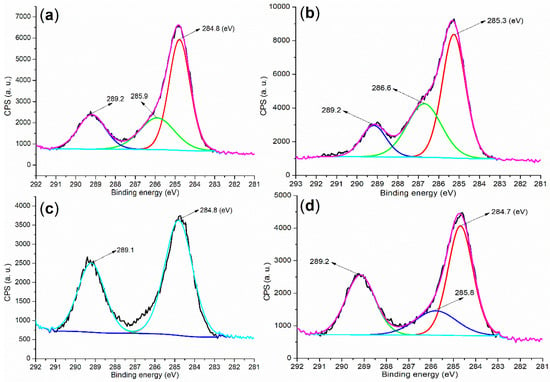
Furthermore, the mortar induced by B2a exhibited three peaks at 284.7, 285.8, and 289.2 eV (Figure 7d), which were significantly closer to those observed in cement than to those in B2a. Additionally, after hydration facilitated by B1a, the resulting mortar displayed two peaks at 284.8 and 289.1 eV (Figure 7c), which are also in close proximity to those found in cement, indicating the presence of saturated C–H and carboxyl groups. These observations suggested that most of the water-soluble block copolymer may have been washed away during hydration, while the remaining residues appeared to consist of small organic molecules.
Given that B2a, at the same dosage of 7 wt.% introduced more crystalline water and organic species compared to B1a (blue vs. green, Figure 6) and exhibited significantly shorter setting times and higher mechanical strengths in cementing (entries 8 vs. 5, Table 2), it appeared that B2 (the organic backbone of B2a) may function as an active template in mortar hydration.
In association with XRD, there were three components in the B1a-facilitated mortar (24 h), including SiO2 (dark tubes, Figure 4d; quartz low, PDF No. 65-0466), Ca(OH)2 (white tubes, Figure 4d; Portlandite, PDF No. 04-0733), and unreacted C2S (arrow, Figure 4d; 2CaO·SiO2, PDF No. 49-1672). It seemed that the weight loss of this mortar (TGA) originated from the dehydration of Ca(OH)2, as well as the release of organic B1 residues (green line, Figure 6).
However, the B2a-induced mortar (24 h) showed four phases: SiO2 (dark tubes, Figure 4e; quartz, PDF No. 46-1045), Ca(OH)2 (white cubes, Figure 4e; Portlandite, PDF No. 04-0733), Ca1.5SiO3.5·xH2O (dotted arrows, Figure 4e; calcium silicate hydrate, PDF No. 33-0306), and Ca2(Si9Al3)O24·8H2O (dotted lines, Figure 4e; epistilbite, PDF No. 39-1381) as well. The weight loss of the B2a-induced mortar (24 h) at 30–600 °C can be attributed to the dehydration of Ca(OH)2, Ca1.5SiO3.5·xH2O, and Ca2(Si9Al3)O24·8H2O (30–200 °C) along with the release of organic B2 residues (200–600 °C) [].
The Si 2p regions of the cement and mortar provided valuable insights into the formation of new phases during hydration. Initially, cement exhibited two peaks at 102.6 eV and 101.4 eV (Figure 8a), which corresponded to silicon in SiO2 and C3S, respectively (Figure 4a) []. After 24 h of hydration under B1a, the Si 2p peak associated with Si in C3S significantly diminished and shifted by 0.2 eV compared to the peak observed in the cement (Figure 8b vs. Figure 8a). This shift indicated that a substantial portion of C3S was transformed into hydrated products, while C2S remained (Figure 4d).
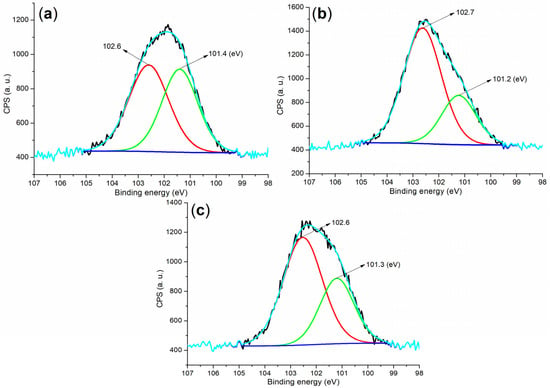
Furthermore, the Si 2p peaks observed in the B2a-facilitated mortar after 24 h, at 102.6 and 101.3 eV (Figure 8c), were similar to those found in the B1a-facilitated mortar in terms of binding energy and peak intensity. These peaks correspond to silicon in SiO2 and other silicon-containing phases, such as Ca1.5SiO3.5·xH2O and Ca2(Si9Al3)O24·8H2O (Figure 4e).
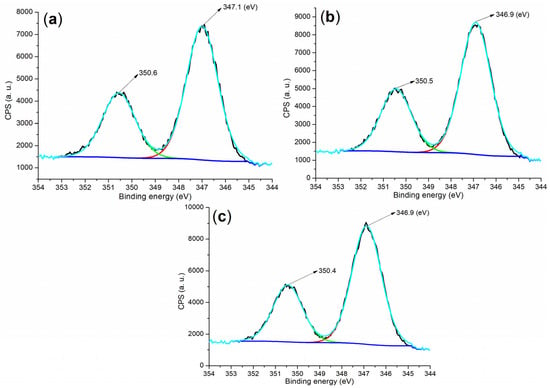
To further analyze the composition of the hydrated mortar, the Ca 2p regions of both the raw material and the hydrated mortar were examined. As depicted in Figure 9a, the cement displayed two peaks at 350.6 and 347.1 eV, corresponding to Ca 2p1/2 and 2p3/2 photoelectrons, respectively []. These peaks are characteristic of Ca2+ in C3S, C2S, and CaSO4 (Figure 4a). In contrast, both B1a- and B2a-facilitated mortars exhibited lower binding energies for the Ca 2p1/2 and 2p3/2 photoelectrons compared to the cement (Figure 9b,c vs. Figure 9a), indicating changes in the calcium-containing components (Figure 4d,e vs. Figure 4a).
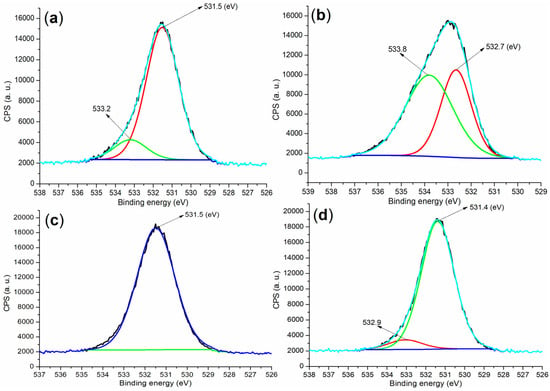
From the perspective of anions, XPS analysis of the O 1s regions in the raw materials and hydrated mortars can further corroborate the findings of cation detection. Specifically, the cement sample displayed two peaks at 533.2 eV and 531.5 eV (Figure 10a), which were attributed to the oxygens in CaSO4 and C2S (the former) and C3S (the latter) (Figure 4a) []. In contrast, the B2a showed peaks at 533.8 eV and 532.7 eV (Figure 10b), indicative of oxygens in OH− and H2O (the former) and SO42− (the latter) (Figure 4c). Post-hydration, the mortar prepared using B1a exhibited an O 1s peak at 531.5 eV (Figure 10c), predominantly corresponding to oxygen in the SiO2 phase (Figure 4d). However, the mortar produced with B2a presented an additional peak at 532.9 eV compared to the B1a sample (Figure 10d vs. Figure 10c), which aligned with the formation of new phases such as Ca1.5SiO3.5·xH2O and Ca2(Si9Al3)O24·8H2O (Figure 4e).
2.4.3. Morphology of Hydrated Mortars
From another point of view, the morphology of hydrated mortar may provide more information on the cementing process. In Figure 11a, the accelerator-free mortar shows a layered and porous appearance with a size of several square micrometers. When B1a was loaded as an accelerator, there were many clusters composed of fibers with lengths of 500–800 nm (Figure 11b), probably originating from AFt []. However, the fiber morphology of the mortar derived from B2a appeared much longer (about 500–2000 nm) and slimmer than that from B1a (Figure 11d vs. Figure 11b), owing to the different structures of B1 and B2 (Figure 1).

Figure 11.
SEM images of the mortar: (a) mortar of entry 1, Table 2 (24 h, magnification 20,000×); (b) mortar of entry 5, Table 2 (24 h, 20,000×); (c) mortar of entry 5, Table 2 (28 d, 10,000×); (d) mortar of entry 8, Table 2 (24 h, 20,000×); (e) mortar of entry 8, Table 2 (24 h, 20,000×); (f) mortar of entry 8, Table 2 (28 d, 10,000×).
Meanwhile, flower-like mesoporous structures were observed on the external surface of the fiber clusters of the mortar stemming from B2a (Figure 11e), which may be attributed to the formation of Ca1.5SiO3.5·xH2O and Ca2(Si9Al3)O24·8H2O (Figure 4e). These newly-formed phases may not only act as sturdy linkers, leading to better setting time and mechanical strength of the mortar (24 h, entries 8 vs. 5, Table 2), but also give a much denser mortar material after incubation for 28 days (Figure 11f vs. Figure 11c).
2.5. Proposed Mechanism for Cement Hydration Facilitated by Accelerator B2a
Based on the results obtained so far, the mechanism of cement hydration facilitated by B2a can be summarized in Figure 12. Initially, the AS was ionized in water and promptly coordinated by B2. This coordination was preferred over the direct hydrolysis of Al3+ into less reactive Al(OH)3 or Al2O3 due to the low solubility of AS (36.5 g AS vs. 100 g H2O at 20 °C) [].
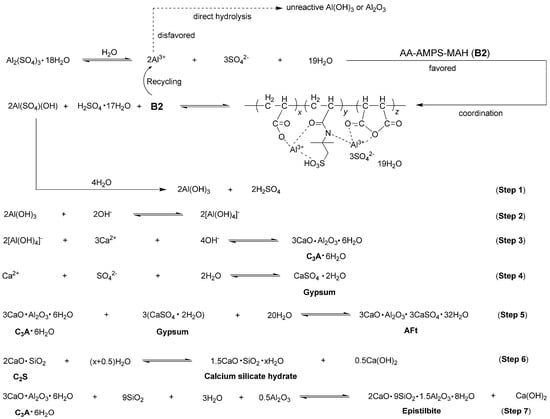
Figure 12.
Proposed mechanism for cement hydration facilitated by accelerator B2a.
Furthermore, the coordination intermediate decomposed into Al(SO4)(OH), which was then hydrolyzed to form active Al(OH)3 (Step 1, Figure 12). Al(OH)3 was formed through the successive substitution of SO42− with OH− from Al(SO4)(OH), thereby preventing the agglomeration and precipitation of Al3+. Subsequently, the resulting Al(OH)3 reacted with OH− to produce [Al(OH)4]−, which then reacted with Ca2+ to form C3A (Steps 2–3, Figure 12). Upon the formation of gypsum, C3A and gypsum underwent hydrolysis together, ultimately leading to the formation of AFt (Steps 4–5, Figure 12).
Moreover, the C2S phase of cement (2CaO·SiO2, white cube, Figure 4a) hydrated into calcium silicate hydrate (Ca1.5SiO3.5·xH2O, dotted arrows, Figure 4e) and Ca(OH)2 (white cubes, Figure 4e), as illustrated in Step 6 of Figure 12. Concurrently, C3A·6H2O from Step 4 further reacted with SiO2, H2O, and Al2O3 to form epistilbite (Ca2(Si9Al3)O24·8H2O, dotted lines, Figure 4e) along with additional Ca(OH)2 (white cubes, Figure 4e), as depicted in Step 7 of Figure 12.
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Starting Materials
The AS (aluminum sulfate, Al2(SO4)3·18H2O, 99%) was purchased from Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). The AA (acrylic acid, 99%), AMPS (2-acrylamido-2-methylpropane sulfonic acid, 98%), MAH (maleic anhydride, 99%), (NH4)2S2O8 (ammonium persulfate, 98%), and n-BuOH (n-butanol, 99%) were purchased from Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). H2SO4 (concentrated sulfuric acid, 98%), KBrO3 (potassium bromate, 99.5%), KBr (potassium bromide, 99%), HgSO4 (mercuric sulfate, 99%), NaCl (sodium chloride, 99.5%), KI (potassium iodide, 99%), as well as Na2S2O3 (sodium thiosulfate, 99%) were commercially available from Alfa Aesar, Thermo Fisher Scientific (China) Co. Ltd., Shanghai, China. Cement (P·O 42.5) was purchased from the China National Academy of Building Materials Science Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China), while the Chinese ISO standard sand produced according to GB/T 17671 to measure mortar strength was commercially obtained from Xiamen ISO Standard Sand Co. Ltd., Xiamen, China. Distilled water was prepared in our laboratory.
3.2. Instruments
The cement and additives were mixed using a cement paste mixer, NJ-160A. Both the initial setting time (IST) and final setting time (FST) of cement paste were tested on a Vicat apparatus. Cement mortar was prepared using a cement mortar mixer, JJ-5. The three instruments were all manufactured by Wuxi Xiyi Building Material Instrument Factory (Wuxi, China).
Both the compressive and flexural strengths of the cement mortar were tested using a fully automatic anti-folding and compression testing machine (WAY-300B) equipped with an automatic pressure testing machine control system (EHC-2300), with a maximum power of 300 kN and a pressing speed of 48 N s−1. The cement mortar was incubated in a numerical control standard cement conservation box (HBY-40B) at a temperature of 20 °C and a humidity of 90%. The two machines were manufactured by Wuxi Xiyi Building Material Instrument Factory.
FT-IR spectra were obtained using KBr pellets on a Bruker Tensor 27 spectrometer (Billerica, MA, USA). X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was carried out on a Kratos Axis Ultra DLD (Kratos Co., Ltd., Manchester, UK), using monochromatic Al-Kα X-rays (1486.6 eV) as a lighting source. The binding energy scale was calibrated by setting the C 1s peak to 284.8 eV as standard. The peaks were fitted using the Gaussian–Lorentz (G/L) product function with a 30% Lorentzian ratio. The wide-angle (2θ = 10–80°) X-ray diffractions of samples were obtained on a Philips X’Pert Pro diffractometer (PANalytical B.V. Co., Ltd., Almelo, The Netherlands) with Cu-Kα radiation (λ = 1.5418 Å), in association with an interval of 0.05° s−1, was used as the X-ray source.
Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometer (ICP–OES) was performed on Agilent 5110 (Santa Clara, CA, USA), with pump rate of 60 r min−1, plasma gas of 12.0 L min−1, nebulizer flow of 0.70 L min−1, stable time of 20 s, auxiliary gas of 1.0 L min−1, reading access time of 5 s, sample flush time of 20 s, RF power of 1250 w. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) of the prepared sample was performed on a NETZSH TG 209C (Haimhausen, Germany), featuring a TASC 414/4 controller under N2 protection, where a heating rate of 10 °C min−1 was selected at 30–600 °C. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was carried out using Zeiss Sigma300 (Jena, Germany).
3.3. Synthesis of Block Copolymers
As shown in Figure 1a, AA (100 g, 1.38 mol), AMPS (100 g, 0.48 mol), and n-BuOH (200 mL, 162.96 g, 2.19 mol) were combined with distilled H2O (400 mL) into a three-necked bottle (1 L) having condenser, addition funnel and magnetic stirrer. Under vigorous stirring at 25 °C, (NH4)2S2O8 solution (2 g, 8.6 mmol, dissolved in 100 mL of distilled H2O) was added slowly through an addition funnel (within 1 h). Then, the temperature was slowly increased to 70 °C under continuous stirring, and the resulting mixture was stirred at 70 °C for 6 h. After cooling in air, the solvent was completely removed by rotary evaporation, and the remaining slightly yellow oil was obtained as AA–AMPS (B1).
As shown in Figure 1b, AA (100 g, 1.38 mol), AMPS (100 g, 0.48 mol), MAH (100 g, 1.01 mol), and n-BuOH (200 mL, 162.96 g, 2.19 mol) were combined with distilled H2O (400 mL) into a three-necked bottle (1 L) featuring condenser, addition funnel and magnetic stirrer. The subsequent process was the same as that for B1. The resulting AA, –AMPS–MA (B2), was also a slightly yellow oil.
3.4. Determination of Monomer Conversion of Block Copolymers
The bromine concentration (X, mg g−1, bromine consumption per gram of sample) was determined using the Chinese standard GB/T 10535-1997. In principle, Br2 (generated in situ) was covalently added to the unpolymerized monomers in the tested sample. The excessive Br2 would react with KI solution that was added subsequently, and the precipitated I2 was determined by the standard Na2S2O3 titration.
In practice, B1 (or B2, 0.5000 g) was added to a volumetric flask (250 mL), and distilled H2O was added to a fixed volume. The resulting solution (25.00 mL) was transferred to an iodine flask (250 mL), and then a KBrO3–KBr mixed solution (10 mL, prepared by mixing 5.5 g of KBrO3 and 20.0 g of KBr with enough distilled H2O in a brown volumetric flask of 1000 mL was added. After shaking for 5 min, H2SO4 solution (20 mL, 3 mol L−1) was introduced, and HgSO4 solution (5 mL, prepared by mixing 15 g of HgSO4 with 14 mL of concentrated H2SO4 into 475 mL of distilled H2O) was further added. The resulting solution was shaken well and then stored in a dark place for 30 min at 0–20 °C.
Next, NaCl solution (15 mL, 116 g L−1) and KI solution (10 mL, 100 g L−1) were added, and the resulting solution was shaken well and stored in a bright place for 5 min at room temperature. Then, distilled H2O (20 mL) was added. The solution obtained so far was titrated with standard Na2S2O3 solution (0.1 mol L−1) until the solution color became slightly yellow. Then, a starch indicator solution (1 mL, 10 g/L) was added, and titration was continued until the color of the solution changed from blue to colorless. The bromine number (w, mg g−1) was calculated according to Equation (1):
where X is the bromine number (mg g−1), c is the real concentration of the standard Na2S2O3 solution (mol L−1); V0, consumed volume of the standard Na2S2O3 solution in the sample blank experiment, V, is the consumed volume of the standard Na2S2O3 solution in the regular experiment; 0.0799, is the bromine (Br) mass (g) derived from the consumption of the ideal Na2S2O3 solution (1 mL, 1.000 mol L−1), and m, is the mass of the tested sample.
The monomer conversion (α, %) of the tested sample was calculated according to Equation (2):
where α is the monomer conversion of the tested sample; X is the bromine number (mg g−1); m0, m1, m2, m3, corresponding to the masses of all monomers, AA, AMPS, MA (blank for B1), respectively; and M, M1, M2, and M3 are the relative molecular weights of Br, AA, AMPS, and MA (blank for B1).
3.5. Synthesis of Setting Accelerators
At room temperature (20–30 °C), B1 (or B2, 100 g) and AS (350 g) were mixed with distilled water (150 g) in a three-necked bottle (1 L) with mechanical stirring equipment. After vigorous stirring at room temperature for 1 h, the resulting white emulsion was decanted and stored for future use, corresponding to the accelerators B1a and B2a.
3.6. Measurement of Setting Time
On the basis of the Chinese standard JC 477-2005, both the IST and FST of cement paste were measured on a Vicat apparatus as follows. At first, cement (400 g) was combined with distilled H2O (148 g for an accelerator dosage of 6 wt.% over cement, 144 g for that of 7 wt.%, 140 g for that of 8 wt.%) into a cement paste mixer, which was first stirred at low speed for 30 s. Second, the accelerator (B1 or B2; 24 g, dosage of 6 wt.% over cement; 28 g, 7 wt.%; 32 g, 8 wt.%) was introduced, which was initially stirred at low speed for 5 s, then at high speed for 15 s. Furthermore, the total cement paste was quickly poured into a round mold, crushed, and then slightly vibrated. The paste surface was further smoothed by using a scraper.
Both the IST and FST were measured every 10 s over the Vicat apparatus by penetrating a needle of a fixed cross-section into the cement paste under constant force. The IST was derived from the time between releasing the needle in a free fall manner and the needle reaching the preset depth (4 ± 1 mm from the bottom). The FST was calculated as the time between the endpoint of the IST and the moment at which the needle could no longer drop.
3.7. Measurement of Compressive and Flexural Strengths
The compressive and flexural strengths of the cement mortar were also tested according to the Chinese standard JC 477-2005. First of all, cement (900 g) and distilled H2O (468 g at an accelerator dosage of 6 wt.% over cement, 459 g for 7 wt.%, 450 g for 8 wt.%) were combined into a mixing bowl, which was immediately stirred at low speed for 30 s over the assorted cement mortar mixer (JJ-5). After further stirring at a low speed for 30 s, Chinese ISO standard sand (1350 g) was added gradually. Next, the resulting mixture was mechanically stirred at a high speed for 30 s, paused for 90 s, and stirred again at a high speed for 30 s. Instantly after stirring, the accelerator (B1 or B2; 54 g, dosage of 6 wt.% over cement; 63 g, 7 wt.%; 72 g, 8 wt.%) was introduced, and the resulting mixture was further stirred at low speed for 5 s, then at high speed for 15 s. Furthermore, the cement mortar was immediately transferred into a mold with the size of 40 mm × 40 mm × 160 mm (trial mold for cement mortar soft scouring), and then stored in a cement conservation box at 20 °C with a humidity of 90% for a pre-set incubation time (6 h, 24 h, 28 d, and 90 d).
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, the use of aluminum sulfate coordinated by binary and ternary water-soluble block copolymer appeared to be an efficient accelerator with a hardening effect for cement setting. The main conclusions are summarized as follows:
- (1)
- The two block copolymers were prepared with high efficiency through ammonium persulfate-catalyzed free radical polymerization in an aqueous solution. The ternary block copolymer having monomers such as AA (acrylic acid), AMPS (2-acrylamido-2-methylpropane sulfonic acid), and MAH (maleic anhydride) showed higher monomer conversion than the binary copolymer featuring AA and AMPS units.
- (2)
- The combination of aluminum sulfate with two synthesized block copolymers can significantly shorten the initial and final setting times of the cement paste and improve the compressive and flexural strengths of the mortar. The conjunction of aluminum sulfate with a ternary block copolymer (AA–AMPS–MAH) performed even better than that with a binary copolymer (AA–AMPS) in cementing.
- (3)
- The role of synthesized block copolymers lay in the inhibition of Al3+ hydrolysis into unreactive Al(OH)3 or Al2O3. In particular, Al(SO4)(OH), derived from the mixing of Al3+ with AA–AMPS–MAH, was detected as an unexpected and highly active intermediate for optimizing cement hydration.
- (4)
- The use of aluminum sulfate associated with AA–AMPS–MAH would produce two new phases, including Ca1.5SiO3.5·xH2O and Ca2(Si9Al3)O24·8H2O in cement mortar after 24 h incubation compared to that with AA–AMPS, which actually acted as a great linker to enhance the mechanical strength of the mortar. Furthermore, the combination of aluminum sulfate with AA–AMPS–MAH produced a much denser mortar (28 d) with better mechanical strength than that with AA–AMPS.
This work will contribute to the advancement of cement accelerators, particularly in their combined application in the engineering of sprayed concrete (shotcrete) for tunnel and roadway construction.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft preparation, Z.S.; formal analysis, S.C.; methodology, Z.B.; formal analysis, Y.W.; Conceptualization, Q.J.; funding acquisition, X.L.; methodology, W.O.; supervision, Y.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi Province (No. 2017JM2016).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Zhiyuan Song was employed by Shanxi Jiawei New Material Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Wei, T.; Xiao, J.; Cheng, X.; Gong, P.; Mei, K.; Hou, Z.; Wu, X. Improving the mechanical properties of cement-based materials under high temperature: Reducing the C3S/C2S ratio. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 421, 135741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phair, J.W. Green chemistry for sustainable cement production and use. Green Chem. 2006, 8, 763–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trussell, N.; Nordtug, P.Ø.; Asadi, I.; Kristoffersen, M.; Jacobsen, S. Water transport in cracks controlled by digital image correlation in wet sprayed concrete with and without an EVA based co-polymer admixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 400, 132423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, C.; Ma, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, Y. Accelerators for shotcrete–Chemical composition and their effects on hydration, microstructure and properties of cement-based materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 281, 122557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanahan, N.; Sedaghat, A.; Zayed, A. Effect of cement mineralogy on the effectiveness of chloride-based accelerator. Cement Concr. Comp. 2016, 73, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; He, T.; Ma, X. The influence of calcium nitrate/sodium nitrate on the hydration process of cement paste mixed with alkali free liquid accelerator. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 347, 128555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, M.; Li, G.; Zhang, J.; Cao, L. Preparation of alkali-free liquid accelerator based on aluminum sulfate and its accelerating mechanism on the hydration of cement pastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 253, 119246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; He, T.; Yang, R.; Ma, X. Effect of simulated different concentrations of sulfate on early properties of mineral admixture-cement-liquid accelerator system. J. Water Process. Eng. 2022, 47, 102829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qi, H.; Zhang, J.; Deng, X.; Li, M.; Jian, S.; Yang, H.; Tan, H. Effects of AFt and steel slag on the performance of beta-hemihydrate phosphogypsum-based cementitious materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 434, 136749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djobo, J.N.Y.; Stephan, D.; Elimbi, A. Setting and hardening behavior of volcanic ash phosphate cement. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 31, 101427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.G.; Sung, S.K.; Park, C.G.; Won, J.P. Influence of a C12A7 mineral-based accelerator on the strength and durability of shotcrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezania, M.; Moradnezhad, H.; Panahandeh, M.; Kami, M.J.R.; Rahmani, A.; Hosseini, B.V. Effects of Diethanolamine (DEA) and Glass Fibre Reinforced Polymer (GFRP) on setting time and mechanical properties of shotcrete. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 31, 101343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, G.; He, Y.; Sun, Z. New insight into the combined effect of aluminum sulfate and triethanolamine on cement hydration. Cem. Concr. Res. 2024, 181, 107547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Ge, S.; Wang, H.; Chen, R. Study on the improvement of water resistance and water absorption of magnesium oxychloride cement using long-chain organosilane-nonionic surfactants. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 306, 124872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoodia, S.; Al-Shargabi, M.; Wood, D.A.; Rukavishnikov, V.S. Recent advances in polymers as additives for wellbore cementing applications: A review. Fuel 2024, 357, 129692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuffrey, J.; Siwseng, P.; Laksanakit, C.; Chusilp, N. Enhancing the performance of waste paper pulp-cement composites, through the incorporation of natural rubber latex: A sustainable approach for high-performance construction materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 430, 136345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanka, S.T.; Moses, N.G.A.; Suppiah, R.R.; Maulianda, B.T. Physio-chemical interaction of Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate copolymer on bonding ability in the cementing material used for oil and gas well. Petrol. Res. 2022, 7, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Yu, X.; Hu, A.; Yan, H.; Dong, Z.; Yang, H.; Su, G. Amphoteric retarder for long-standing cementing: Preparation, properties and working mechanism. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 223, 211524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Feng, Q.; Luo, Q.; Bai, X.; Chen, K.; Lin, X. Effect of a specific PCE superplasticizer on the initial dissolution and early hydration of Portland cement. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 46, 103786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.B.; Singh, V.D.; Rai, S.; Chaturvedi, S. Effect of lignosulfonate, calcium chloride and their mixture on the hydration of RHA-blended portland cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2002, 32, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Tan, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, J.; Wang, J. Preparation and application of low rebound liquid alkali-free accelerator for shotcrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 367, 130220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garba, M.J.; Tian, Y.; Xie, Z.; Yu, C.; Hu, C.; Chen, L.; Yuan, Q. Effect of accelerators on the long-term performance of shotcrete and its improvement strategies: A review. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 89, 109364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiemeyer, C.; Plank, J. Synthesis, characterization, and working mechanism of a synthetic high temperature (200 °C) fluid loss polymer for oil well cementing containing allyloxy-2-hydroxy propane sulfonic (AHPS) acid monomer. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 128, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Liu, G.; Dong, Z.; Miao, X.; Hu, M.; Guo, J. Effect of poly(AMPS/DMAA/IA/SSS) intercalated Mg/Al layered double hydroxides on reducing fluid loss at 240 °C and improving early strength of oil well cement. Appl. Clay Sci. 2022, 229, 106658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Chen, D.; Wang, L.; Yang, W. A novel approach to methoxy polyethylene glycol-grafted sulfonated poly(maleic anhydride-alt-styrene) as superplasticizers in cement pastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 370, 130598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarza, S.; Wesołowska-Piętaka, A.; Konefał, R.; Świergosz, T. Persulfate initiated free-radical polymerization of itaconic acid: Kinetics, end-groups and side products. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 106, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.; Song, C.; Yang, L.; Wang, C.; Chen, D.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.; Yang, W. Self-stabilized precipitation polymerization of vinyl chloride and maleic anhydride. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 3612–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.M.; Zhang, L.; Gerritsen, G.; Abbenhuis, H.C.L.; van Santen, R.A.; Li, C. Enantioselective epoxidation epoxidation of β-methylstyrene catalyzed by immobilized Mn(salen) catalysts in different mesoporous silica supports. J. Catal. 2008, 256, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, Y.S.; Koparal, S.; Tekin, N.; Ömür, N. New approach: Solvent effects of benzaldehyde in aliphatic alcohol solvents with FT-IR spectroscopy and augmented vertex-adjacency matrices. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1321, 139815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Fan, C.; Yu, H.; Ma, J.; Pan, C.; Zhang, D.; Zheng, A.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y. Sol-gel preparation of helical silicate containing palladium oxide nanoparticles and the application for nitration of aromatic compound. Mol. Catal. 2018, 446, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Yang, S.; Xiao, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; E, T. Bovine hide collagen/tannin extract composite: A revelation of the selective structure-activity relationship between phenolic hydroxyls and Cu(II) and study on adsorption properties. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 682, 132886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharani, S.; Kalaiarasi, G.; Lynch, V.M.; Shankar, R.; Prabhakaran, R. Unpredicted coordination of hydrogen chloride in organoruthenium(II) pyrazolone complex: Synthesis, spectral and structural characterization. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 153, 110849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S. Microstructure and composition characterisation of three 20-year-old GGBS-OPC blended pastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 123, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivani; Sharma, N.; Kumar, M.; Kumar, M. Low resistance ohmic contact of multi-metallic Mo/Al/Au stack with ultra-wide bandgap Ga2O3 thin film with post-annealing and its in-depth interface studies for next-generation high-power devices. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 46, 103937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chubar, N. XPS determined mechanism of selenite (HSeO3−) sorption in absence/presence of sulfate (SO42−) on Mg-Al-CO3 Layered double hydroxides (LDHs): Solid phase speciation focus. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109669. [Google Scholar]
- Haselbach, L.M.; Ma, S. Potential for carbon adsorption on concrete: Surface XPS Analyses. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5329–5334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Gu, Q.; Low, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J. Recycling metal-organic framework residues (MOFRs) as bifunctional additives in fabricating porous ceramic membranes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 114105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iatsunskyi, I.; Gottardi, G.; Micheli, V.; Canteri, R.; Coy, E.; Bechelany, M. Atomic layer deposition of palladium coated TiO2/Si nanopillars: ToF-SIMS, AES and XPS characterization study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 542, 148603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korin, E.; Froumin, N.; Cohen, S. Surface Analysis of nanocomplexes by x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, M.; Matsubayashi, N.; Shimada, H. Catalytically active oxygen species in La1−xSrxCoO3−δ studied by XPS and XAFS spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 7348–7353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincon, J.; Camarillo, R.; Martín, A. Solubility of aluminum sulfate in near-critical and supercritical water. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2012, 57, 2084–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).