Novel Iridoid Derivatives Isolated from the Roots of Patrinia scabra with Potential Anti-Renal Fibrosis Activity In Vitro
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
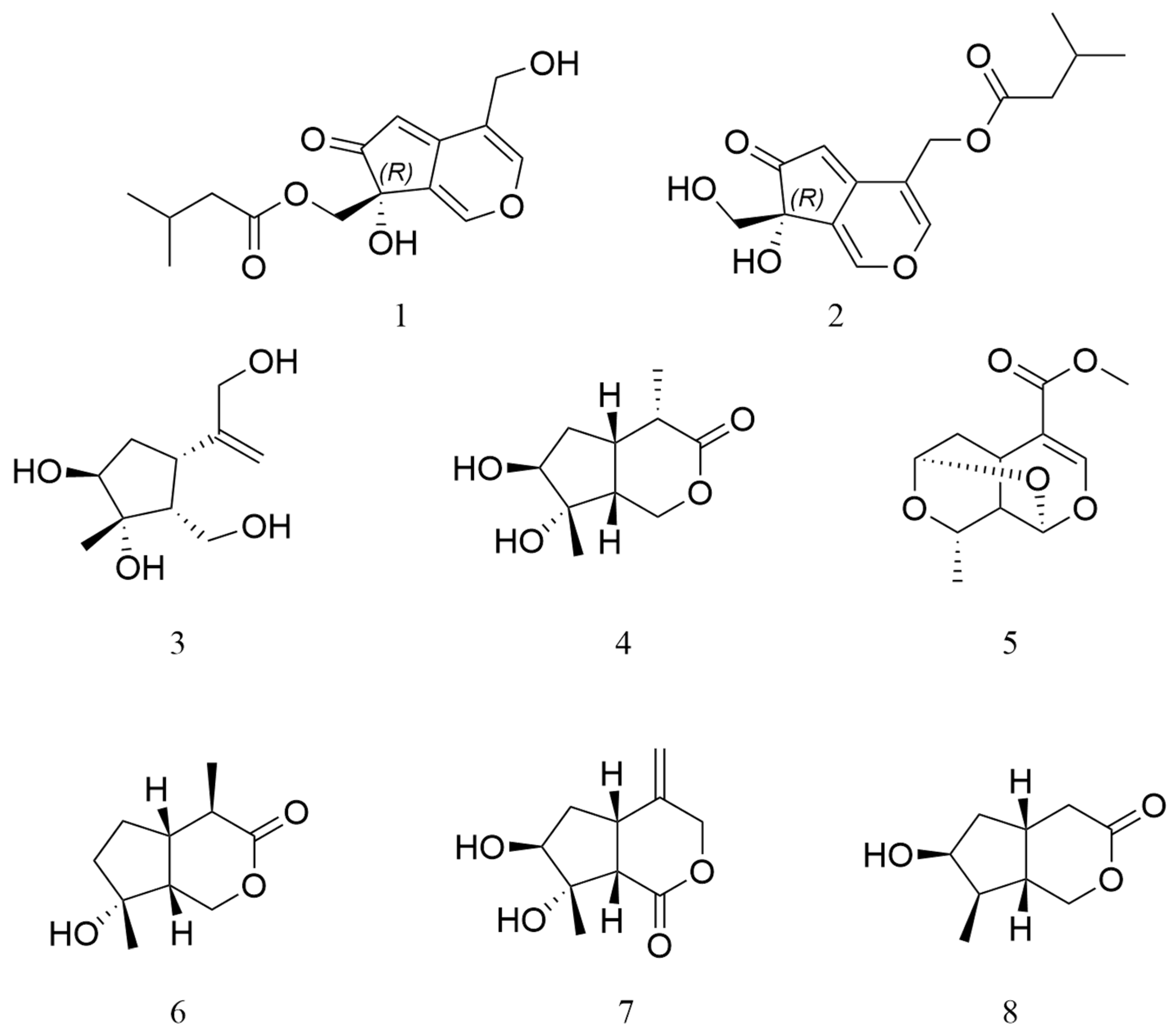
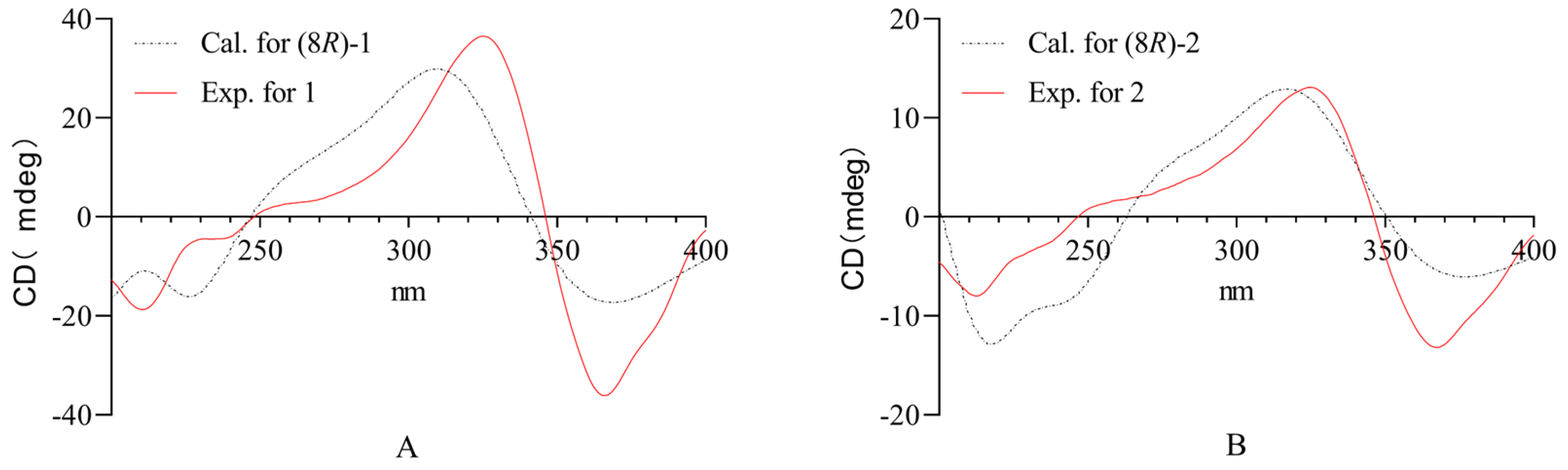
2.1. Structure Elucidation of the Compounds
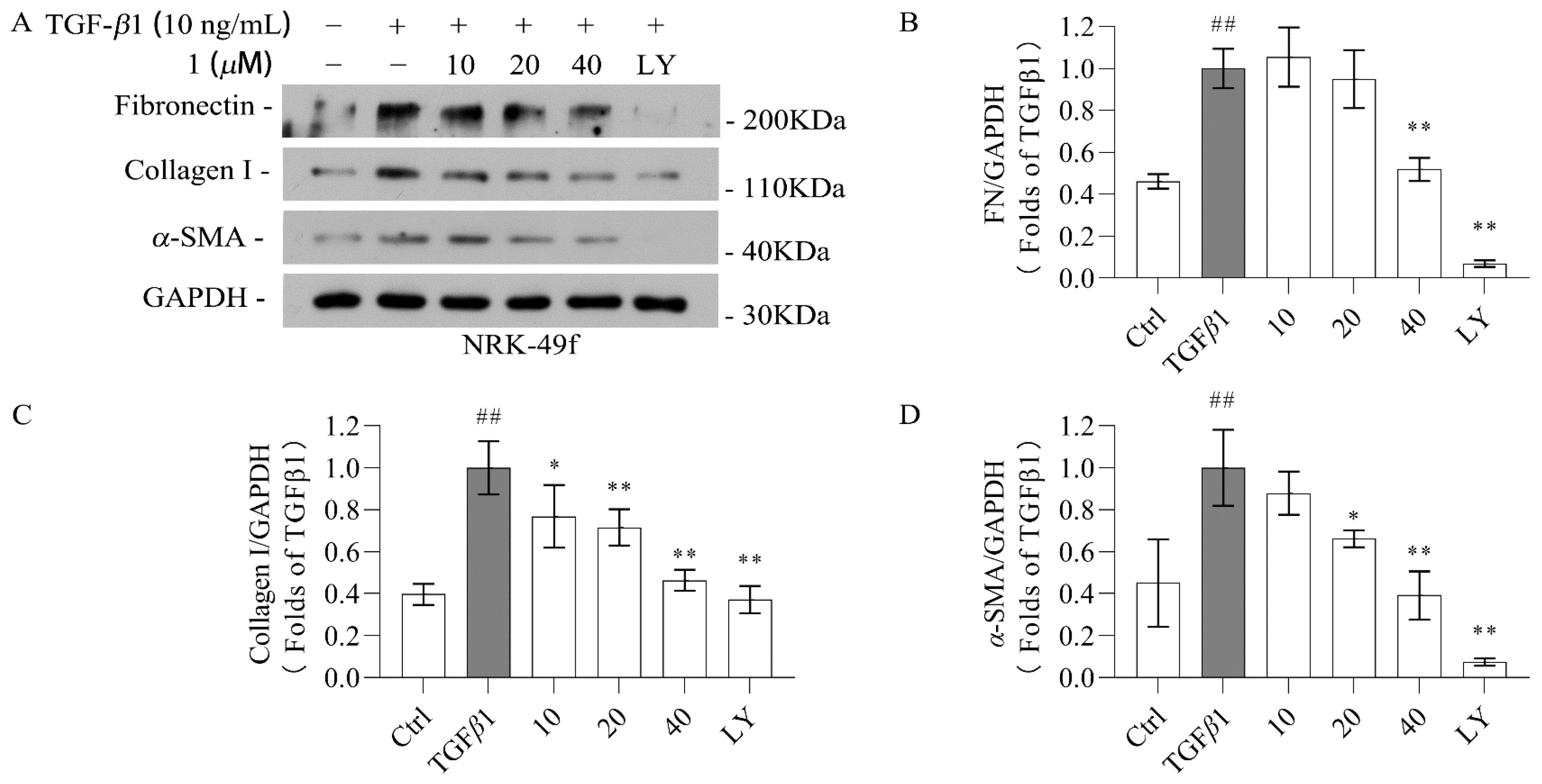
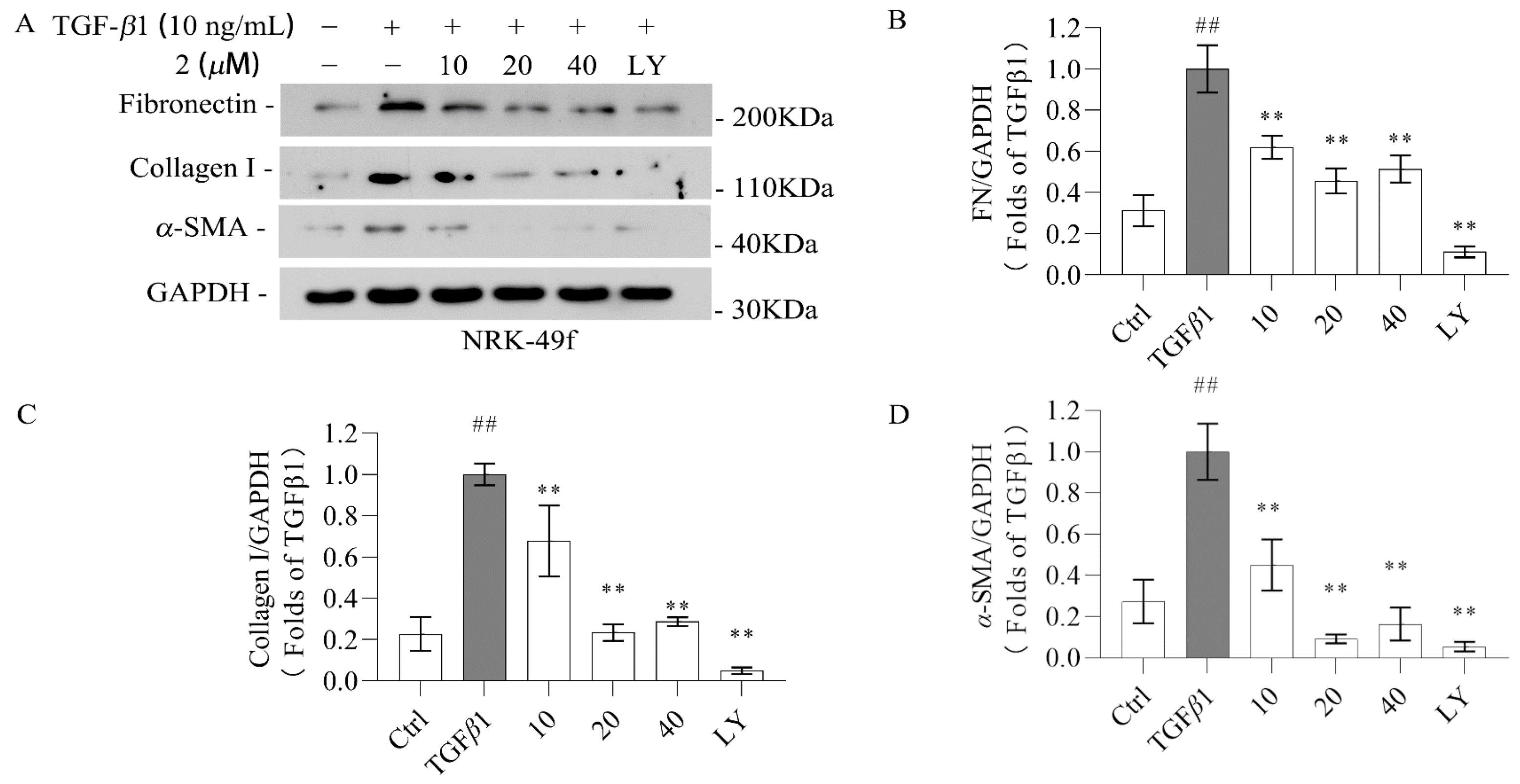
2.2. Biological Evaluation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Procedures, Materials, and Reagents
3.2. Plant Material
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Computational Methods
3.5. Anti-Fibrosis Activity
3.5.1. Cell Culture
3.5.2. Cell Viability Assay
3.5.3. Western Blotting
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shin, J.S.; Kang, S.Y.; Lee, H.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, D.H.; Jang, D.S.; Lee, K.T. Patriscabrin F from the roots of Patrinia scabra attenuatesLPS-induced inflammation by downregulating NF-kappaB, AP-1, IRF3, and STAT1/3 activation in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Phytomedicine 2020, 68, 153167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.H.; Shin, J.S.; Kang, S.Y.; Lee, S.B.; Lee, J.S.; Ryu, S.M.; Lee, K.T.; Lee, D.; Jang, D.S. Iridoids from the Roots of Patrinia scabra and Their Inhibitory Potential on LPS-Induced Nitric Oxide Production. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 1468–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.H.; Shin, J.S.; Lee, J.S.; Kang, S.Y.; Han, H.S.; Ryu, S.M.; Lee, K.T.; Lee, D.; Jang, D.S. Non-glycosidic iridoids from the roots of Patrinia scabra and their nitric oxide production inhibitory effects. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2019, 42, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Di, L.; Gao, W.C.; Wang, K.J.; Zu, L.B. Cytotoxic iridoids from the roots of Patrinia scabra. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1723–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Rui, M.J.; Xu, H.T.; Chou, G.X. Lignans, Monoterpenes and gamma-Pyrone Derivatives from Patrinia scabiosifolia with Cytotoxic Activity against HCT-116 Cells. Chem. Biodivers. 2020, 17, e2000397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.F.; Ma, H.M.; Chen, G.; Wang, H.F.; Xiang, Z.; Feng, Q.M.; Hua, H.M.; Pei, Y.H. A new sesquiterpene lactone glycoside and a new quinic acid methyl ester from Patrinia villosa. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 18, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, N.; Liu, J.Y.; Cai, P.L.; Yang, S.L. New triterpenoid saponins from Patrinia scabiosaefolia. Carbohydr. Res. 2011, 346, 2881–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, J.; Yoon, I.; Yun, H.; An, H.; Suh, Y.G. Divergent synthetic route to new cyclopenta[c]pyran iridoids: Syntheses of jatamanin A, F, G and J, gastrolactone and nepetalactone. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 1244–1251. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hwi-Ho, L.; Eungyeong, J.; Shin-Young, K.; Ji-Sun, S.; Hee-Soo, H.; Tae-Woo, K.; Da Hye, L.; Jang-Hoon, L.; Sik, J.D.; Kyung-Tae, L. Anti-inflammatory potential of Patrineolignan B isolated from Patrinia scabra in LPS-stimulated macrophages via inhibition of NF-κB, AP-1, and JAK/STAT pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 86, 106726. [Google Scholar]
- Feng Feng Xi-Yu, X.U.; Fu-Lei LI, U.; Wen-Yuan LI, U.; Ning XI, E. Triterpenoid saponins from Patrinia scabra. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2014, 12, 43–46. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Z.; Chen, X.; Yang, G.; Li, T.; Liu, W.; Zhang, W. Studies on immunocompetent constituents of Patrinia scabra Bunge. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2002, 25, 178–180. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, L.; Zhao, Y.; Ji, X.; Li, W.; Jiang, W.; Li, Q.; Zhu, L.; Luo, Y. The therapeutic effect of Picroside II in renal ischemia-reperfusion induced acute kidney injury: An experimental study. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 967, 176391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong-yi, Z.; Na, T.; Liu, L.; Rong, Y. Iridoids modulate inflammation in diabetic kidney disease: A review. J. Integr. Med. 2024, 22, 210–222. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.; Geng, R.; Guo, J.; Kang, S.G.; Huang, K.; Tong, T. Oleuropein Supplementation Ameliorates Long-Course Diabetic Nephropathy and Diabetic Cardiomyopathy Induced by Advanced Stage of Type 2 Diabetes in db/db Mice. Nutrients 2024, 16, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.L.; Zhou, Y.T.; Yan, Y.M.; Cheng, Y.X. Sesquiterpenoid-Chromone Heterohybrids from Agarwood of Aquilaria sinensis as Potent Specific Smad3 Phosphorylation Inhibitors. J. Org. Chem. 2022, 87, 7643–7648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouno, I.; Yasuda, I.; Mizoshiri, H.; Tanaka, T.; Marubayashi, N.; Yang, D.M. Two new iridolactones and their glycosides from the roots of Patrinia scabra. Phytochemistry 1994, 37, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.Y.; Chang, C.P.; Yin, W.K.; Chang, N.C. Total Synthesis of (+/−)-Sarracenin. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khera, S.; Woldemichael, G.M.; Singh, M.P.; Suarez, E.; Timmermann, B.N. A novel antibacterial iridoid and triterpene from Caiophora coronata. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 1628–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, B.; Li, Y.; Di, L.; Cheng, R.; Liu, L.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Tang, Z.; Yan, Y.; Lu, T.; et al. A naturally derived small molecule compound suppresses tumor growth and metastasis in mice by relieving p53-dependent repression of CDK2/Rb signaling and the Snail-driven EMT. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2024, 22, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Position | 13C NMR of 1 | 13C NMR of 2 | 1H NMR of 1 | 1H NMR of 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 141.93, CH | 141.46, CH | 7.46 (s) | 7.44 (s) |
| 3 | 150.53, CH | 152.98, CH | 7.53 (s) | 7.64 (s) |
| 4 | 120.64, C | 116.03, C | ||
| 5 | 161.20, C | 160.82, C | ||
| 6 | 106.06, CH | 106.86, CH | 5.44 (s) | 5.41 (s) |
| 7 | 204.88, C | 206.36, C | ||
| 8 | 75.32, C | 77.77, C | ||
| 9 | 129.62, C | 130.48, C | ||
| 10 | 66.72, CH2 | 66.26, CH2 | Ha: 4.39 (d, 10.90) Hb: 4.04 (d, 10.92) | Ha: 3.70 (d, 11.09) Hb: 3.54 (d, 11.12) |
| 11 | 59.06, CH2 | 61.09, CH2 | 4.38 (s) | 4.92 (s) |
| 1′ | 173.98, C | 174.24, C | ||
| 2′ | 43.91, CH2 | 43.96, CH2 | 2.18 (d, 7.16) | 2.22 (m) |
| 3′ | 26.79, CH | 26.91, CH | 2.00 (m) | 2.06 (m) |
| 4′ | 22.60, CH3 | 22.65, CH3 | 0.90 (d, 1.88, overlap) | 0.94 (overlap) |
| 5′ | 22.60, CH3 | 22.65, CH3 | 0.91 (d, 1.88, overlap) | 0.94 (overlap) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Xu, Y.; Sun, X.; Fan, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Ren, F.; Li, N.; Di, L. Novel Iridoid Derivatives Isolated from the Roots of Patrinia scabra with Potential Anti-Renal Fibrosis Activity In Vitro. Molecules 2024, 29, 4419. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29184419
Li Z, Xu Y, Sun X, Fan Z, Zhou Z, Ren F, Li N, Di L. Novel Iridoid Derivatives Isolated from the Roots of Patrinia scabra with Potential Anti-Renal Fibrosis Activity In Vitro. Molecules. 2024; 29(18):4419. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29184419
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ziran, Yang Xu, Xu Sun, Zhangrui Fan, Ziling Zhou, Fucai Ren, Ning Li, and Lei Di. 2024. "Novel Iridoid Derivatives Isolated from the Roots of Patrinia scabra with Potential Anti-Renal Fibrosis Activity In Vitro" Molecules 29, no. 18: 4419. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29184419
APA StyleLi, Z., Xu, Y., Sun, X., Fan, Z., Zhou, Z., Ren, F., Li, N., & Di, L. (2024). Novel Iridoid Derivatives Isolated from the Roots of Patrinia scabra with Potential Anti-Renal Fibrosis Activity In Vitro. Molecules, 29(18), 4419. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29184419





