The Synthesis of SNAC Phenolate Salts and the Effect on Oral Bioavailability of Semaglutide
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Salts Synthesis
2.1.1. SNAC-Na Salt
2.1.2. SNAC–Choline Salt
2.1.3. SNAC–Phosphatidylcholine Salt
2.2. Formulation Preparation
2.3. In Vivo Study
2.4. Sample Analysis
2.5. LC-MS Analytical Method
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
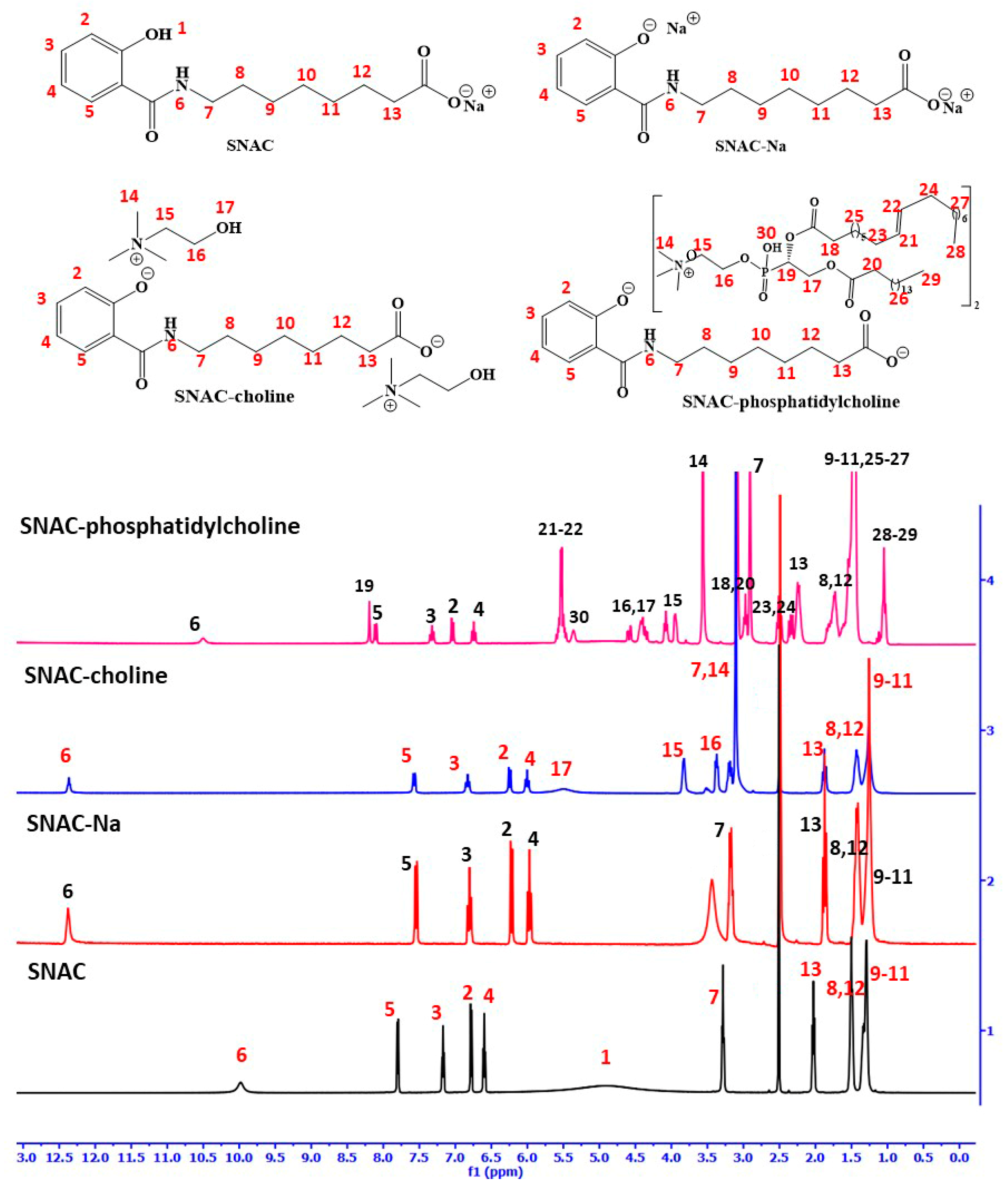
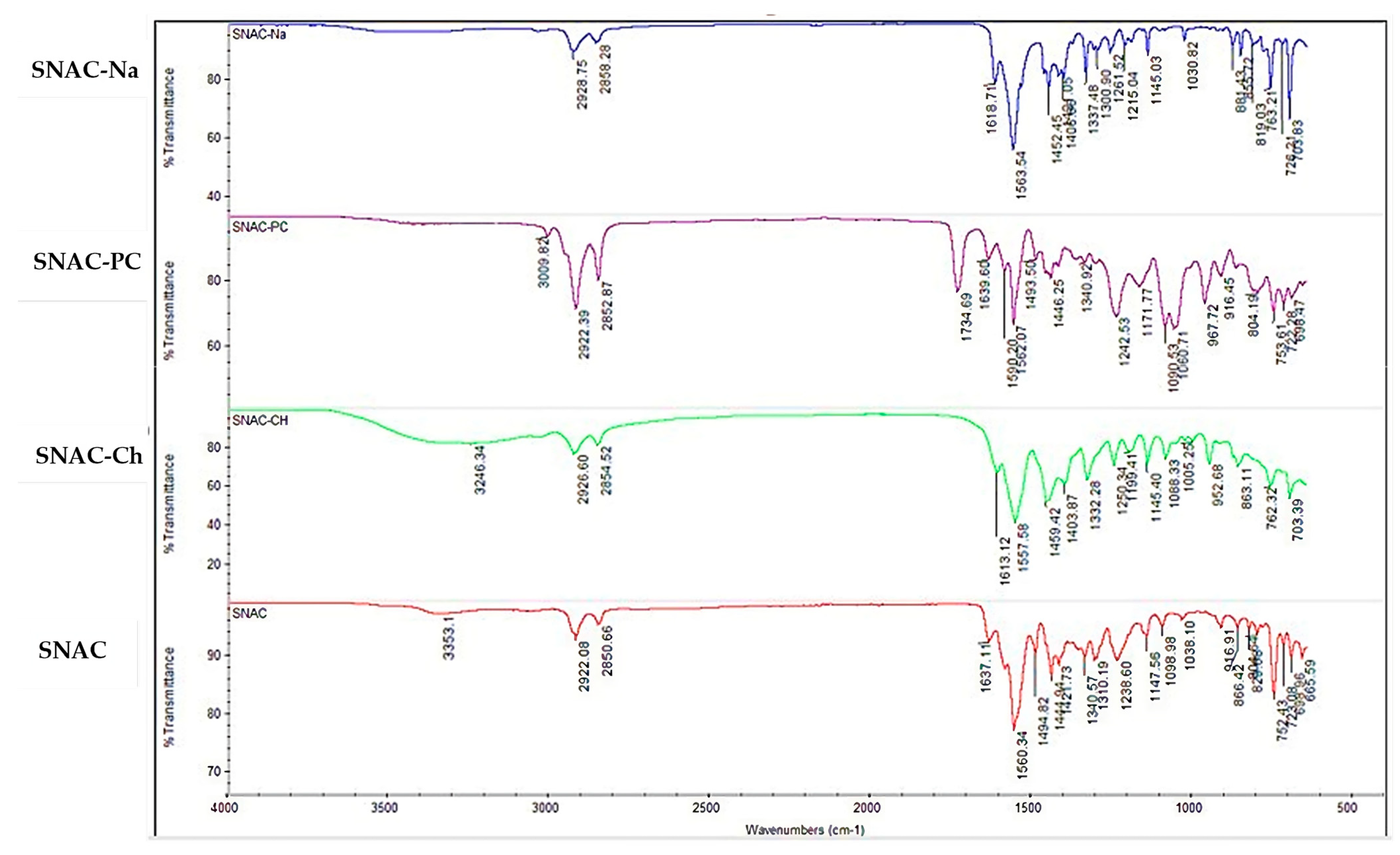
3.1. SNAC Salts’ Synthesis and Characterization
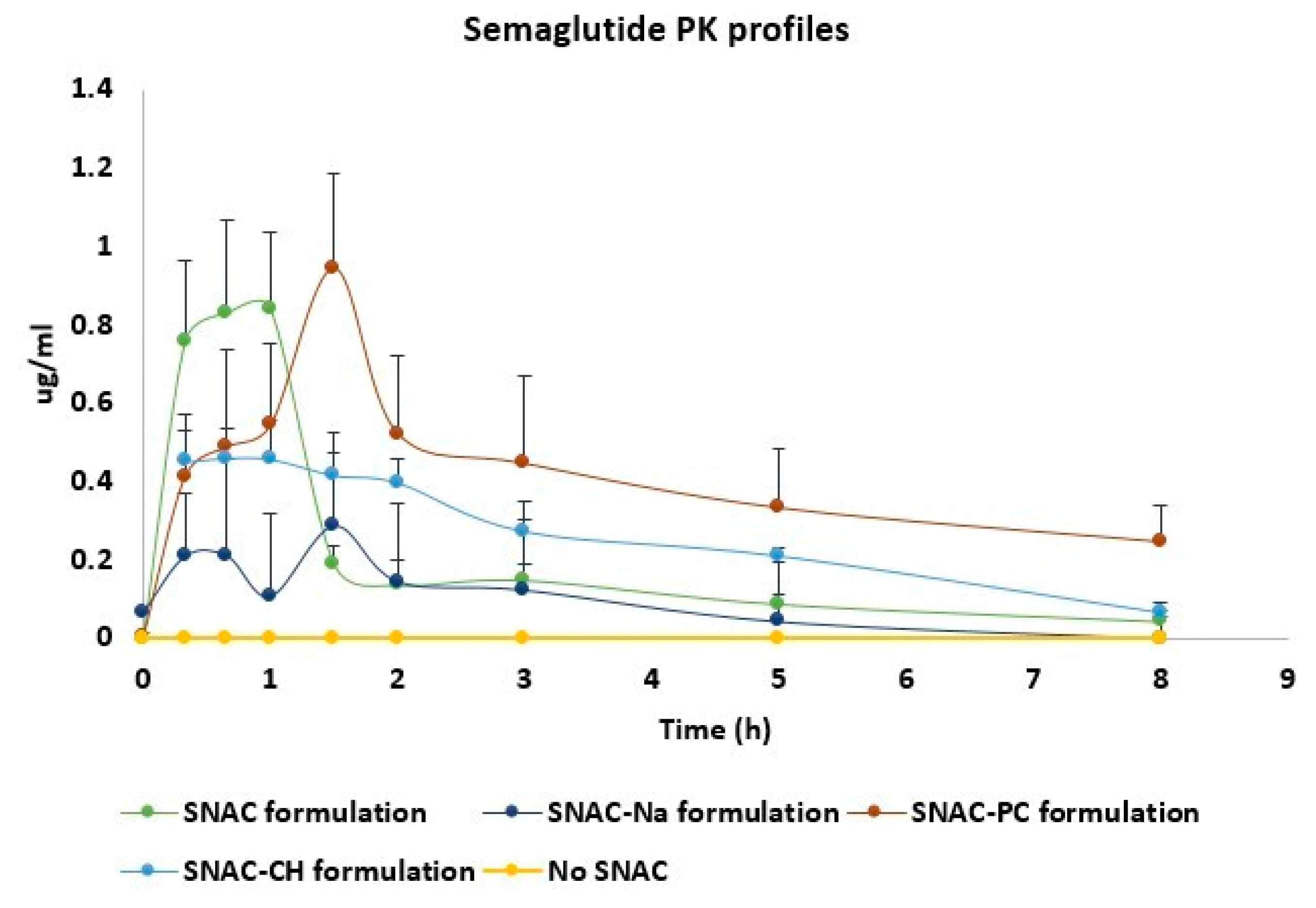
3.2. In Vivo PK Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kommineni, N.; Sainaga Jyothi, V.G.S.; Butreddy, A.; Raju, S.; Shapira, T.; Khan, W.; Angsantikul, P.; Domb, A.J. SNAC for Enhanced Oral Bioavailability: An Updated Review. Pharm. Res. 2022, 40, 633–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guruprasad Reddy, P.; Bar-Hai, A.; Hoffman, A.; Marc Feldmann, S.; Domb, A.J. Novel phenolate salts of bioactive agents: Cannabidiol phenolate salts. Bioorg. Chem. 2023, 141, 106914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarveiya, V.; Templeton, J.F.; Benson, H.A.E. Ion-pairs of ibuprofen: Increased membrane diffusion. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2004, 56, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Bhatia, D.; Dave, V.; Sutariya, V.; Varghese Gupta, S. Salts of Therapeutic Agents: Chemical, Physicochemical, and Biological Considerations. Molecules 2018, 23, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, P.G.; Domb, A.J. Bioactive Phenolate Salts: Thymol Salts. ChemMedChem 2023, 18, e202300045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saal, C.; Becker, A. Pharmaceutical salts: A summary on doses of salt formers from the Orange Book. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 49, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, J.L.; Dunn, M.K. Therapeutic peptides: Historical perspectives, current development trends, and future directions. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 2700–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aroda, V.R.; Blonde, L.; Pratley, R.E. A new era for oral peptides: SNAC and the development of oral semaglutide for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2022, 23, 979–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castelli, M.C.; Wong, D.F.; Friedman, K.; Riley, M.G.I. Pharmacokinetics of oral cyanocobalamin formulated with sodium N-[8-(2-hydroxybenzoyl)amino]caprylate (SNAC): An open-label, randomized, single-dose, parallel-group study in healthy male subjects. Clin. Ther. 2011, 33, 934–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twarog, C.; Fattah, S.; Heade, J.; Maher, S.; Fattal, E.; Brayden, D.J. Intestinal Permeation Enhancers for Oral Delivery of Macromolecules: A Comparison between Salcaprozate Sodium (SNAC) and Sodium Caprate (C10). Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malkov, D.; Angelo, R.; Wang, H.; Flanders, E.; Tang, H.; Gomez-Orellana, I. Oral delivery of insulin with the eligen (®) technology: Mechanistic studies. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2005, 2, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohley, M.; Leroux, J.-C. Gastrointestinal Permeation Enhancers Beyond Sodium Caprate and SNAC—What is Coming Next? Adv. Sci. 2024, 2400843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, S.T.; Bækdal, T.A.; Vegge, A.; Maarbjerg, S.J.; Pyke, C.; Ahnfelt-Rønne, J.; Madsen, K.G.; Schéele, S.G.; Alanentalo, T.; Kirk, R.K.; et al. Transcellular stomach absorption of a derivatized glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, aar7047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overgaard, R.V.; Navarria, A.; Ingwersen, S.H.; Bækdal, T.A.; Kildemoes, R.J. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Oral Semaglutide: Analyses of Data from Clinical Pharmacology Trials. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2021, 60, 1335–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craik, D.J.; Fairlie, D.P.; Liras, S.; Price, D. The future of peptide-based drugs. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2013, 81, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, M. Kunjappu, J. Characteristic Features of Surfactants. In Surfactants and Interfacial Phenomena; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 1–38. ISBN 9781118228920. [Google Scholar]
- Castelli, M.C.; Wong, D.F.; Tiano, D.; Bhargava, P.; Majuru, S.; Romero, F.; Kragie, L. SNAC co-formulation produces significant enhancement of oral vitamin B12 bioavailability in rats. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkov, D.; Wang, H.-Z.; Dinh, S.; Gomez-Orellana, I. Pathway of oral absorption of heparin with sodium N-[8-(2-hydroxybenzoyl)amino] caprylate. Pharm. Res. 2002, 19, 1180–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA. OZEMPIC® (Semaglutide) Injection, for Subcutaneous Use. Prescribing Information. 2021. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/209637s008lbl.pdf (accessed on 13 August 2024).
- McCartney, F.; Gleeson, J.P.; Brayden, D.J. Safety concerns over the use of intestinal permeation enhancers: A mini-review. Tissue Barriers 2016, 4, e1176822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, S.; Rotshild, V.; Hoffman, A. Investigation of the enhancing mechanism of sodium N-[8-(2-hydroxybenzoyl)amino]caprylate effect on the intestinal permeability of polar molecules utilizing a voltage clamp method. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. Off. J. Eur. Fed. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 25, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Time (min) | Phase A, % | Phase B, % |
|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 40 | 60 |
| 3.5 | 20 | 80 |
| 8.0 | 20 | 80 |
| 8.2 | 40 | 60 |
| 14.0 | 40 | 60 |
| Compound | Molecular Ion [(M + 4H)]4+ (m/z) | Fragment (m/z) | DP (Volts) | CE (Volts) | CXP (Volts) | Retention Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Semaglutide | 1029.2 | 1237.9 (quantifier) | 120 | 43 | 35 | 6.0 |
| 136.0 (qualifier) | 120 | 137 | 14 |
| O–H Stretching (cm−1) | C–H Stretching (cm−1) | Amide C=O Stretching (cm−1) | Carboxylate Carbonyl Stretching (cm−1) | C-N Stretching (cm−1) | C=C Stretching (cm−1) | C-O Stretching (cm−1) | C–C Bending (cm−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNAC | 3353 | 2992–2850 | 1637 | 1560 | 1495 | 1444–1421 | 1340–1310–1238–1147 | 1098–1038 |
| SNAC-Na | -- | 2928–2858 | 1618 | 1568 | 1452 | 1424–1406 | 1337–1300–1261–1215–1145 | 1030 |
| SNAC-Ch | 3246 | 2926–2854 | 1613 | 1557 | 1459 | 1403–1332 | 1250–1199–1145 | 1088–1055 |
| SNAC-PC | -- | 2982–2852 | 1639 | 1590 | 1493 | 1446–1340 | 1242–1171 | 1090–1060 |
| Name of the Sample | Molecular Formula | Type | %C | %H | %N | %O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNAC | Na[C15H20O4N] | Theory | 59.80 | 6.69 | 4.65 | 21.24 |
| Experimental | 58.35 | 6.69 | 4.48 | 20.83 | ||
| Na salt of SNAC | Na3[C15H18O4N] 2H2O | Theory | 47.25 | 5.82 | 3.67 | 25.17 |
| Experimental | 46.71 | 5.91 | 3.43 | 25.52 | ||
| Choline salt of SNAC | (C5H14NO) (Na)[C15H19O4N] H2O | Theory | 56.86 | 8.35 | 6.63 | 22.72 |
| Experimental | 55.39 | 7.96 | 5.76 | 22.62 | ||
| Phosphatidylcholine salt of SNAC | (C44H85NO8P)2 [C15H19O4N] | Theory | 64.97 | 6.91 | 5.05 | 23.08 |
| Experimental | 62.95 | 9.53 | 2.50 | 17.34 |
| Mean ± SEM | SNAC (n = 3) | Na (n = 3) | CH (n = 3) | PC (n = 3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC0−8 (ng*h/mL) | 1626 ± 427 | 1039 ± 221 | 2031 ± 193 | 5083 ± 1478 * |
| AUC0−∞# (ng*h/mL) | 1904 ± 492 | 1183 ± 196 | 2281 ± 197 | 7729 ± 2928 * |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 867 ± 218 | 323 ± 73 | 494 ± 63 | 945 ± 295 |
| Fabs$ (%) | 0.095 ± 0.024 | 0.059 ± 0.01 | 0.113 ± 0.01 | 0.38 ± 0.15 * |
| (Absolute bioavailability) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shapira-Furman, T.; Bar-Hai, A.; Hoffman, A.; Domb, A.J. The Synthesis of SNAC Phenolate Salts and the Effect on Oral Bioavailability of Semaglutide. Molecules 2024, 29, 3909. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163909
Shapira-Furman T, Bar-Hai A, Hoffman A, Domb AJ. The Synthesis of SNAC Phenolate Salts and the Effect on Oral Bioavailability of Semaglutide. Molecules. 2024; 29(16):3909. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163909
Chicago/Turabian StyleShapira-Furman, Tovi, Ayala Bar-Hai, Amnon Hoffman, and Abraham J. Domb. 2024. "The Synthesis of SNAC Phenolate Salts and the Effect on Oral Bioavailability of Semaglutide" Molecules 29, no. 16: 3909. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163909
APA StyleShapira-Furman, T., Bar-Hai, A., Hoffman, A., & Domb, A. J. (2024). The Synthesis of SNAC Phenolate Salts and the Effect on Oral Bioavailability of Semaglutide. Molecules, 29(16), 3909. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163909








