Biodegradable Acid-Based Fe2MnO4 Nanoparticles for Water Remediation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
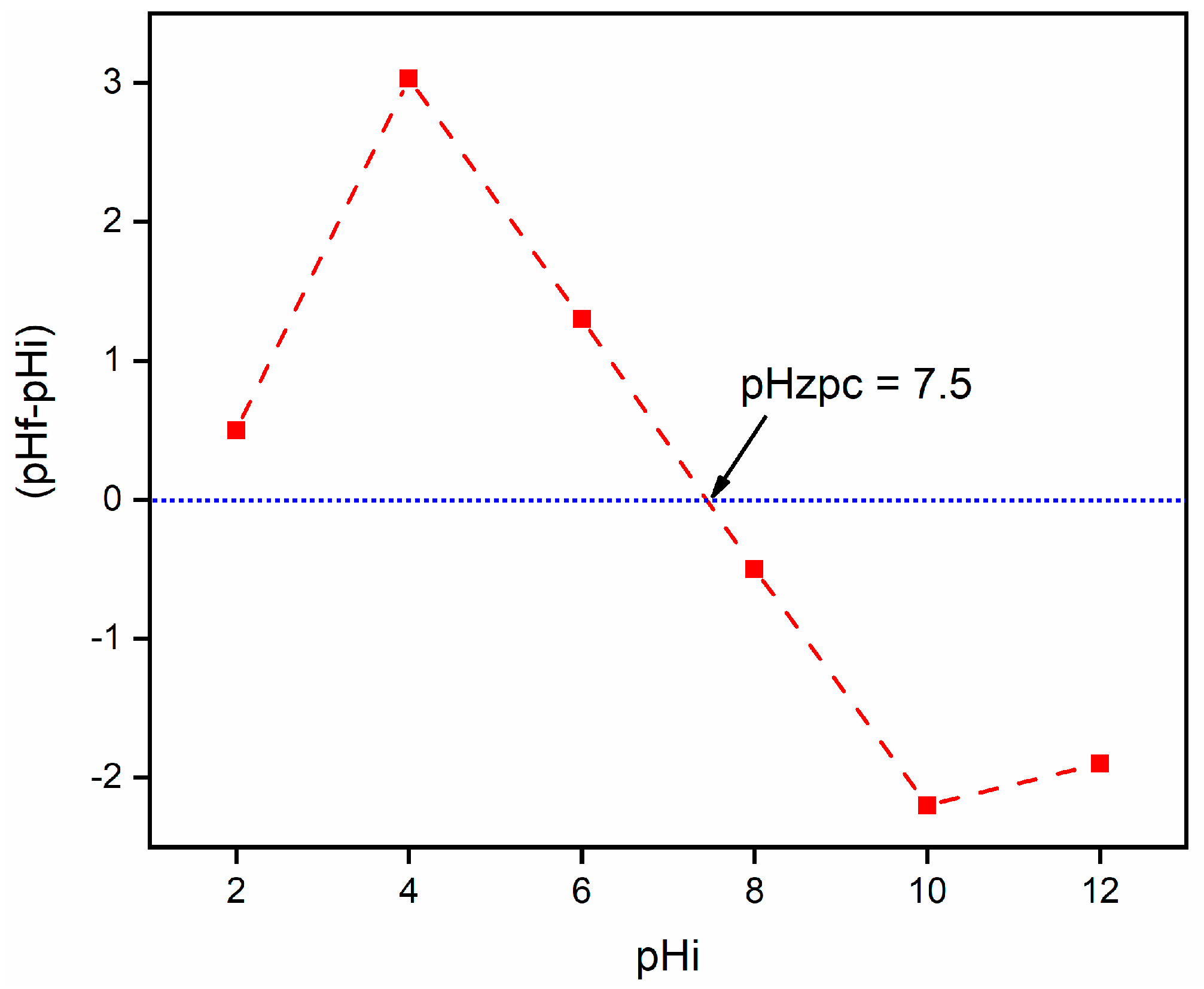
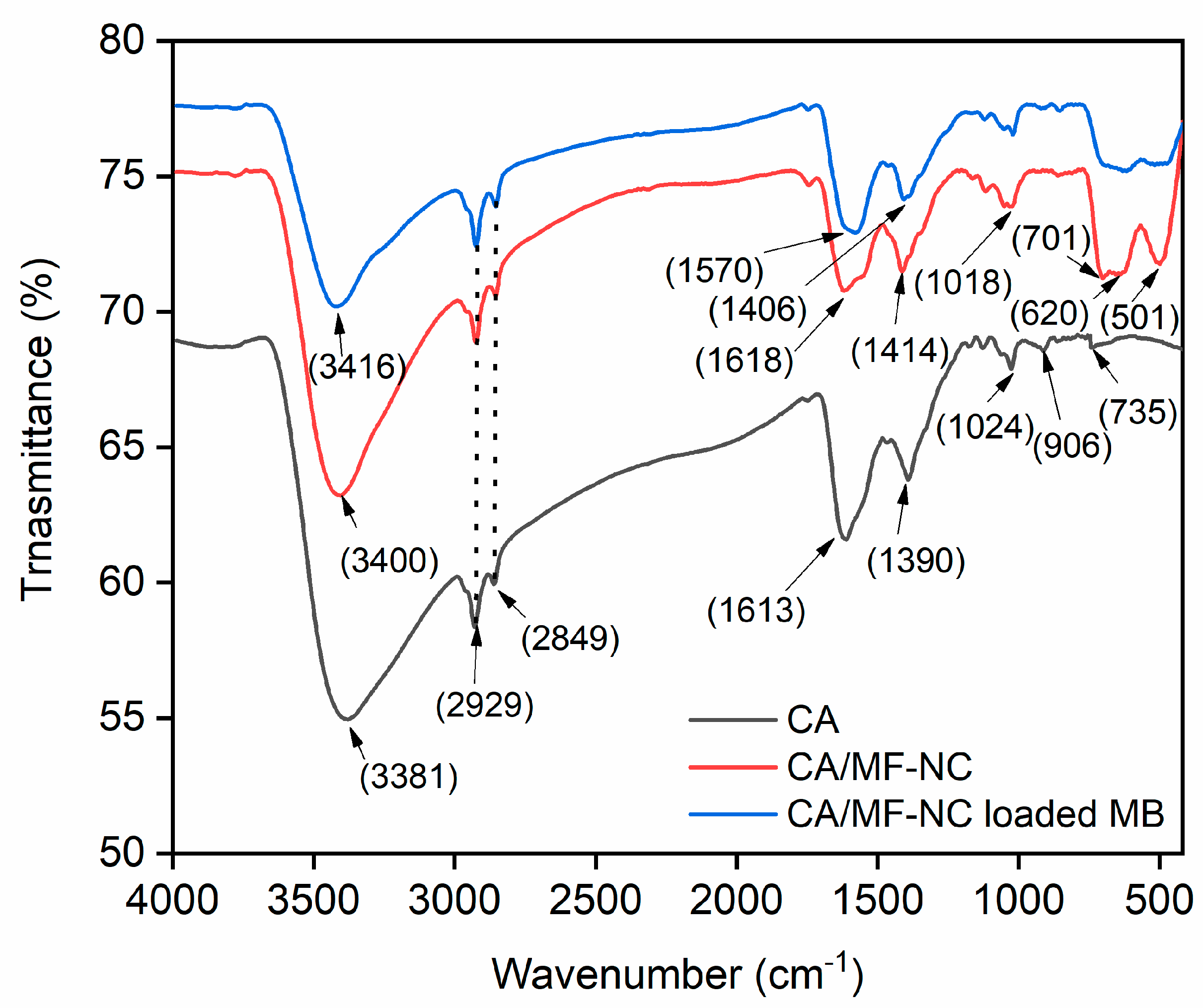
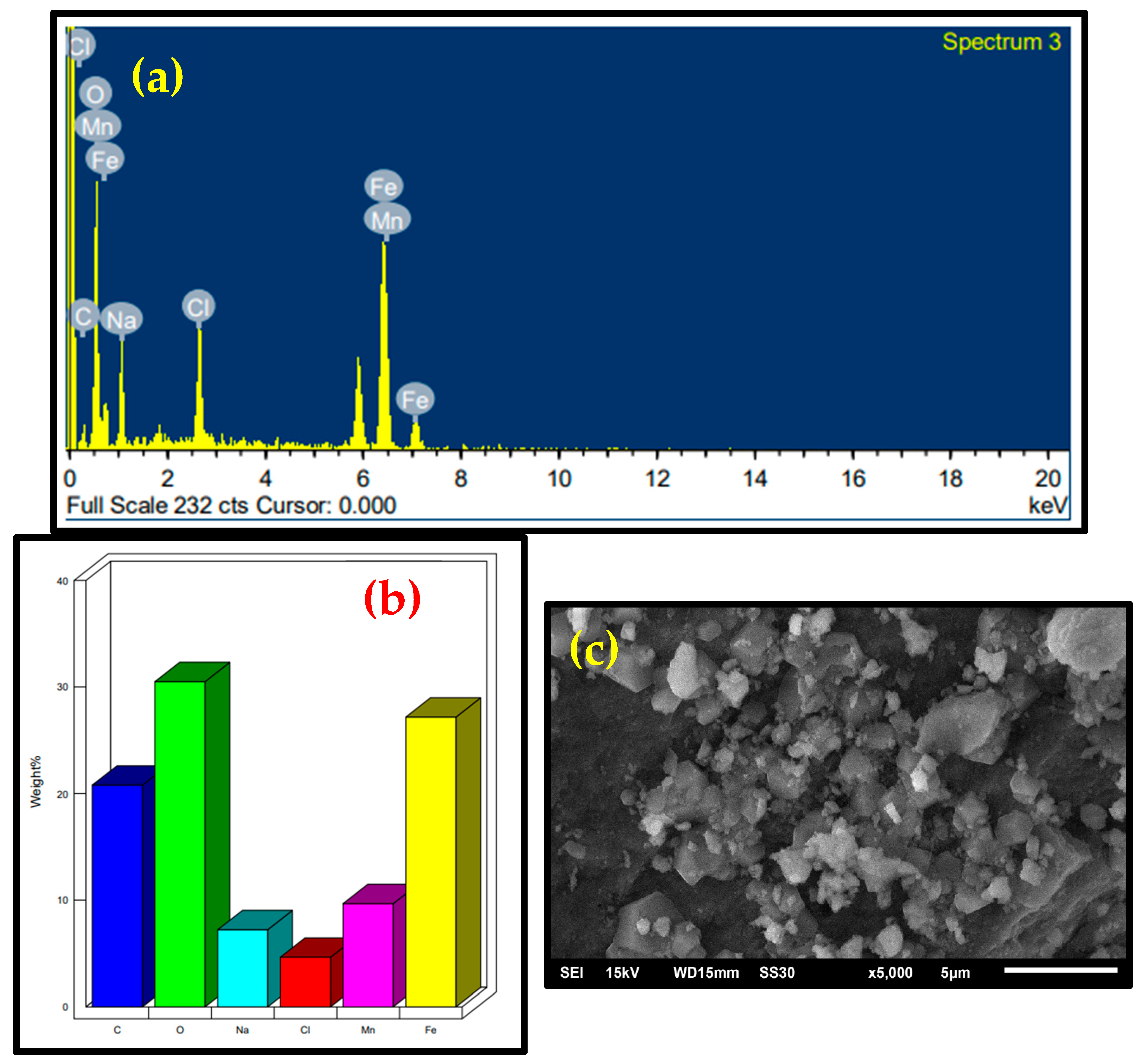
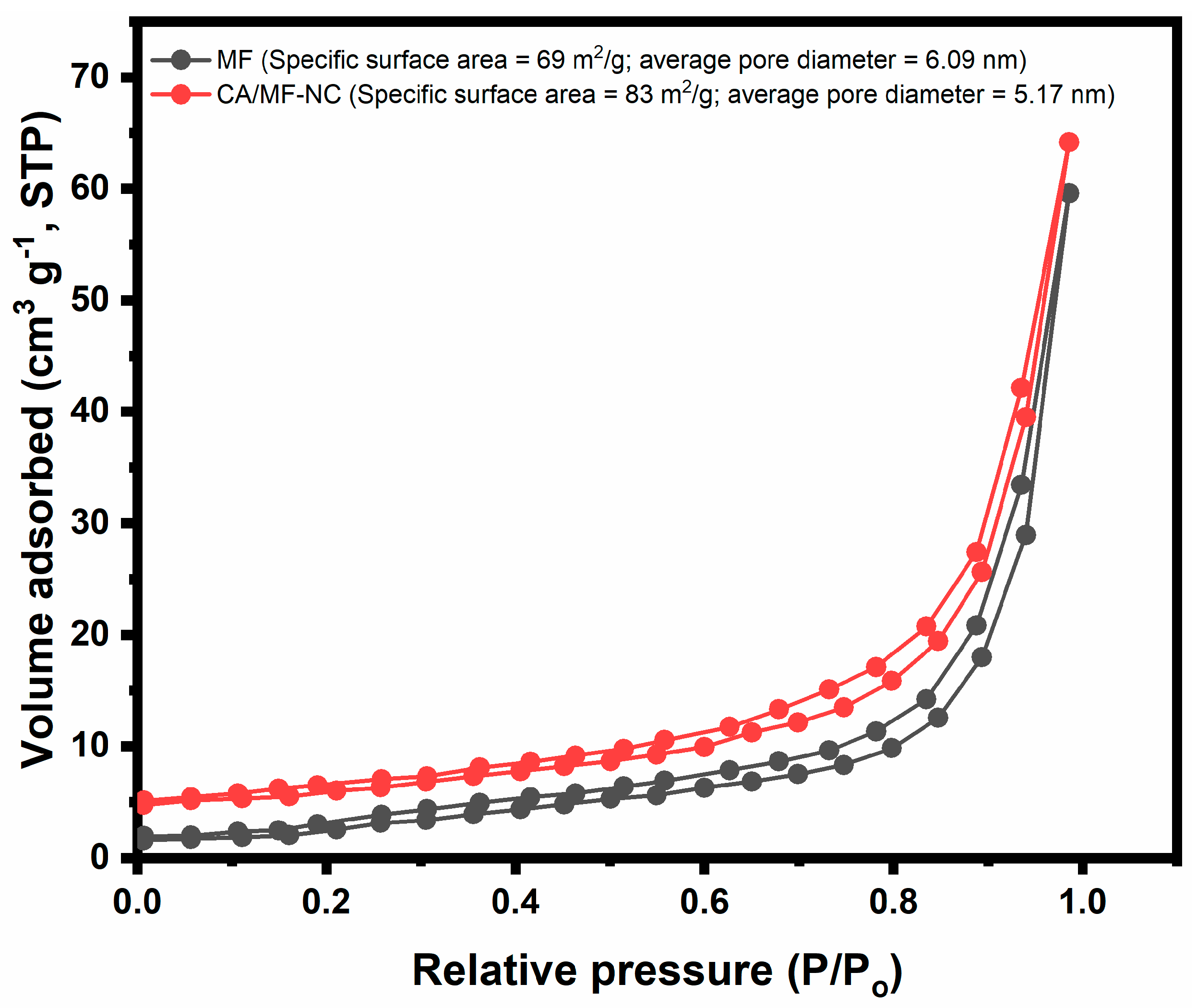
2.1. Characterization
2.2. Adsorption Analysis
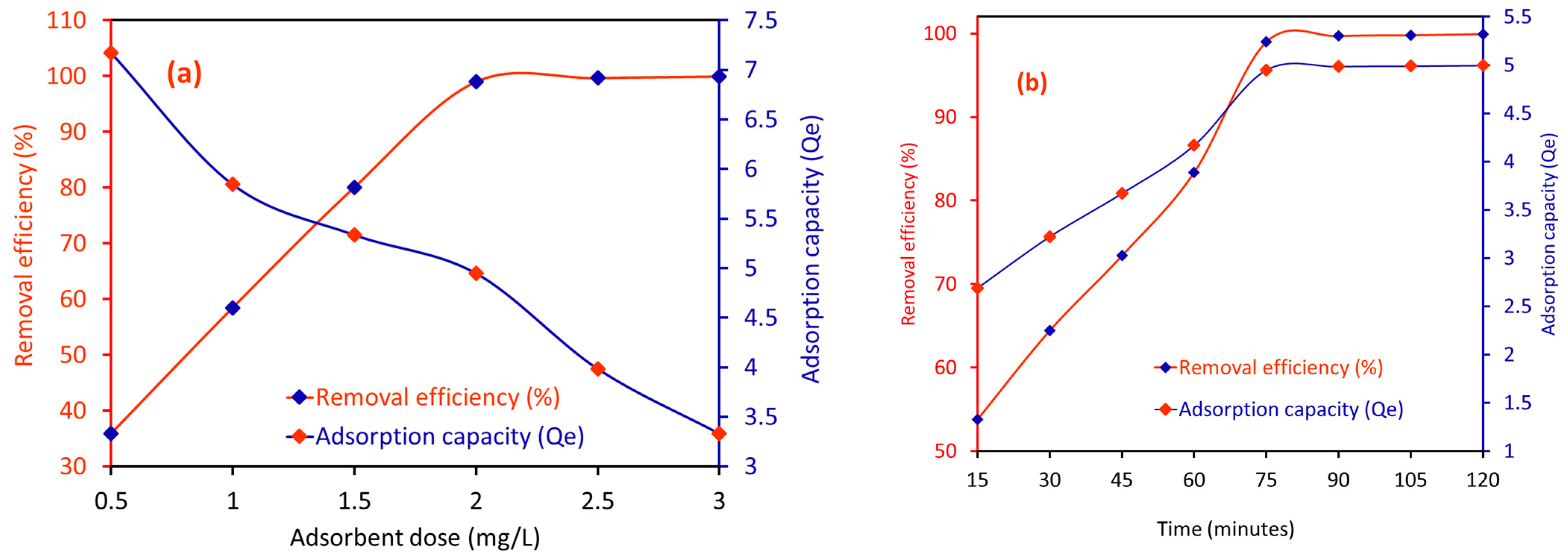
2.2.1. Effect of the Amount of CA/MF-NC on the RE (%) for MB Dye
2.2.2. Effect of Time on the RE (%) of CA/MF-NC for MB Dye
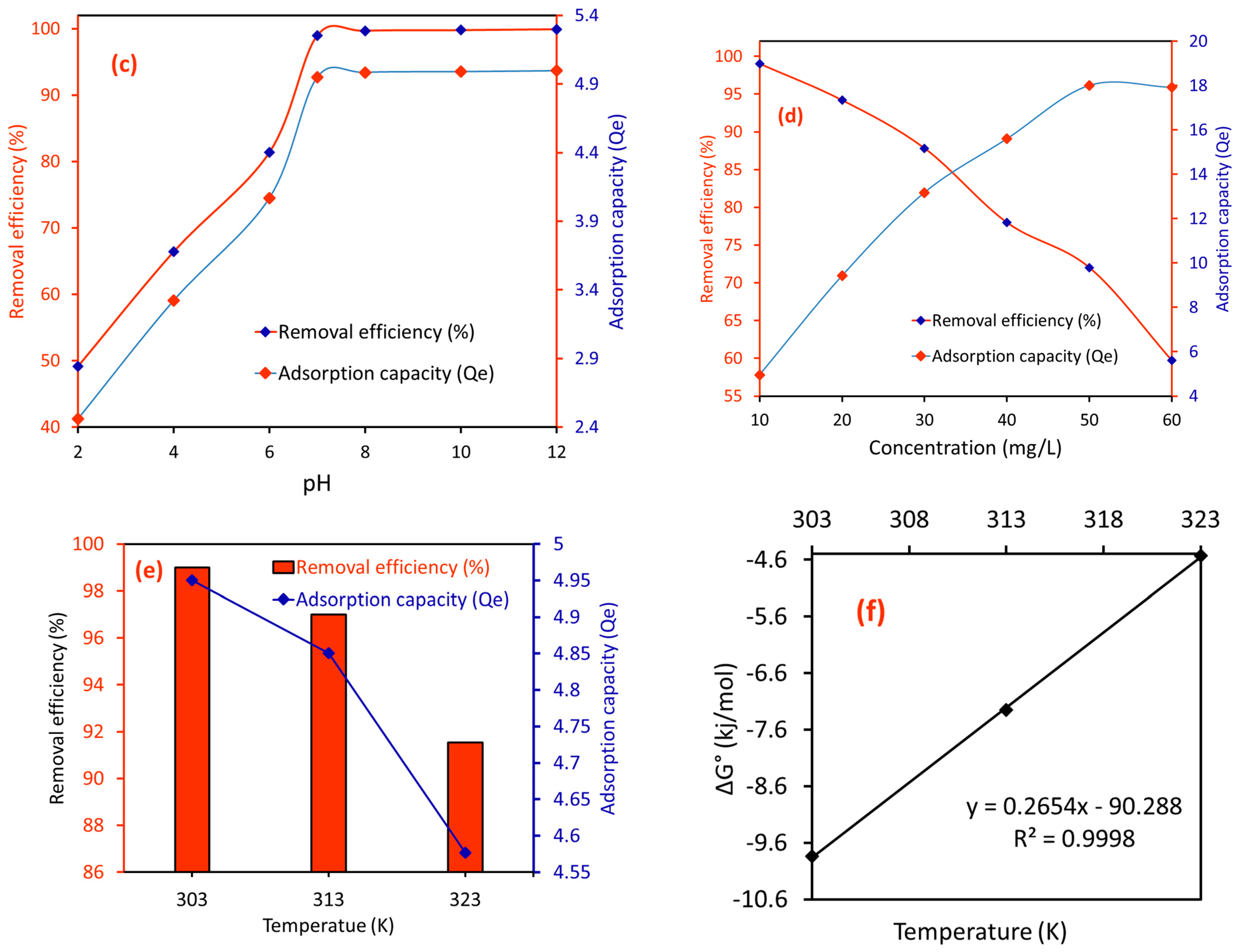
2.2.3. Effect of pH on the RE (%) of CA/MF-NC for MB Dye
2.2.4. Effect of MB Concentration on the RE (%) of CA/MF-NC for MB Dye
2.2.5. Effect of Temperature on the RE (%) of CA/MF-NC for MB Dye and Associated Thermodynamics
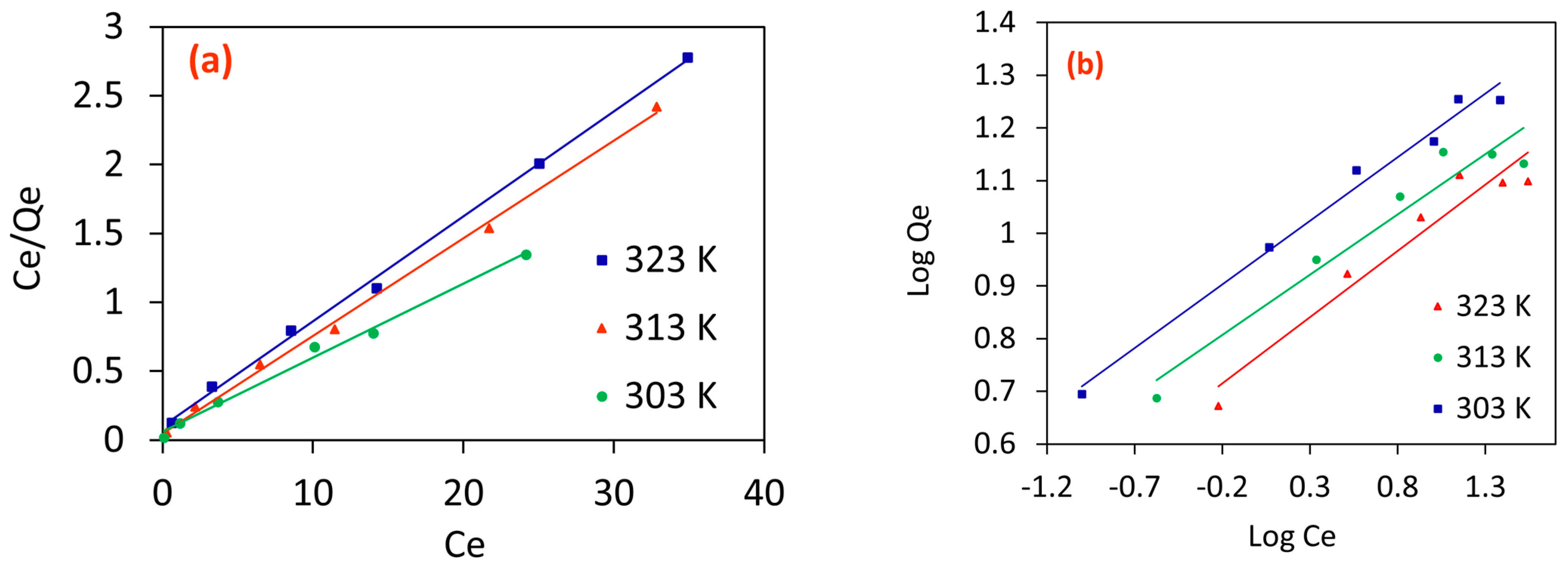
2.2.6. Adsorption Isotherm Analysis
Langmuir Isotherm
Freundlich Isotherm
2.2.7. Reusability Testing
2.2.8. Performance Evaluation and Comparative Analysis
3. Chemicals and Preparation
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Synthesis of CA/MF-NC
3.3. Development of the MB Stock Solution
3.4. Instrumentation and Characterization
3.5. Adsorption Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moondra, N.; Jariwala, N.D.; Christian, R.A. Integrated approach of phytoremediation in wastewater treatment: An insight. Water Conserv. Manag. 2021, 5, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moondra, N.; Jariwala, N.D.; Christian, R.A. Microalgal-bacterial consortia: An alluring and novel approach for domestic wastewater treatment. Water Conserv. Manag. 2020, 4, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Wu, S.; Yan, A.; Chen, Z.; Xu, J.; Gu, C.; Qi, Y.; Wu, S. Efficient recycling of sewage water in a polyester integrated industry: A case study. Desalin. Water Treat. 2024, 319, 100508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jiang, S.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, M.; Guo, J. Effects of Na+/H2O2 on nitrogen removal and sludge activity: Performance and mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Qian, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, F.; Ma, J.; Zhang, X.; Lin, H. Biodegradation of sulfametoxydiazine by Alcaligenes aquatillis FA: Performance, degradation pathways, and mechanisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 452, 131186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdrashitova, R.N.; Bozhenkova, G.S.; Ponomarev, A.A.; Gilya-Zetinov, A.G.; Markov, A.A.; Zavatsky, M.D. Synthesis of ZnO doped multi walled carbon nanotubes (mwnts) for dyes degradation and water purification. Water Conserv. Manag. 2023, 7, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyan, S.M.; Prabhu, S.V.; Sissay, T.T.; Getahun, A.A. Sugarcane bagasse based activated carbon preparation and its adsorption efficacy on removal of BOD and COD from textile effluents: RSM based modeling, optimization and kinetic aspects. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2021, 14, 100664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naser, J.A.; Ahmed, Z.W.; Ali, E.H. Nanomaterials usage as adsorbents for the pollutants removal from wastewater; a review. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 42, 2590–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade-Guel, M.; Cabello-Alvarado, C.; Bartolo-Pérez, P.; Medellin-Banda, D.I.; Ávila-Orta, C.A.; Cruz-Ortiz, B.; Espinosa-Muñoz, A.; Pliego, G.C. Surface modification of TiO2/ZnO nanoparticles by organic acids with enhanced methylene blue and rhodamine B dye adsorption properties. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 28494–28504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, S.J.; Mahmood, W.M. Review on magnetic spinel ferrite (MFe2O4) nanoparticles: From synthesis to application. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, A.; Kaida, T.; Desai, H.B.; Ghosh, S.; Bhatt, R.P.; Tanna, A.R. Dye degradation and antimicrobial applications of manganese ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by plant extracts. Chem. Phys. Imp. 2022, 5, 100098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamdab, U.; Wetchakun, K.; Kangwansupamonkon, W.; Wetchakun, N. Effect of a pH-controlled co-precipitation process on rhodamine B adsorption of MnFe2O4 nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 6709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yao, Q.; Wang, C.; Fan, B.; Sun, Q.; Jin, C.; Xiong, Y.; Chen, Y. A simple, one-step hydrothermal approach to durable and robust superparamagnetic, superhydrophobic and electromagnetic wave-absorbing wood. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35549–35558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivashankar, R.; Sivasubramanian, V.; Kishore, K.A.; Sathya, A.B.; Thirunavukkarasu, A.; Nithya, R.; Deepanraj, B. Metanil Yellow dye adsorption using green and chemical mediated synthesized manganese ferrite: An insight into equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamics. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 136218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, M.; Kumar, A.; Singh, K.P.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, V.; Srivastava, C.M.; Rawat, V.; Rao, G.; Kumari, S.; Sharma, P.; et al. Graphene oxide-manganese ferrite (GO-MnFe2O4) nanocomposite: One-pot hydrothermal synthesis and its use for adsorptive removal of Pb2+ ions from aqueous medium. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 315, 113769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ding, Z.; Cai, M.; Jian, H.; Zeng, Z.; Li, F.; Liu, J.P. Synthesis and high-efficiency methylene blue adsorption of magnetic PAA/MnFe2O4 nanocomposites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 346, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Liang, H.; Wang, Z. MnFe2O4/chitosan nanocomposites as a recyclable adsorbent for the removal of hexavalent chromium. Mater. Res. Bull. 2013, 48, 3910–3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derakhshani, E.; Naghizadeh, A.; Mortazavi-Derazkola, S. Biosynthesis of MnFe2O4@TiO2 magnetic nanocomposite using oleaster tree bark for efficient photocatalytic degradation of humic acid in aqueous solutions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 3862–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naz, S.; Rasheed, T.; Naqvi, S.T.R.; Hussain, D.; Fatima, B.; Haq, M.N.U.; Majeed, S.; Shafi, S.; Rizwan, K.; Ibrahim, M. Polyvinylpropyllidone decorated manganese ferrite based cues for the efficient removal of heavy metals ions from waste water. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2020, 599, 412559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Mou, F.; Li, X.; Deng, Z.; Sun, J.; Xua, L.; Guan, J. Multifunctional magnetic oleic acid-coated MnFe2O4/polystyrene Janus particles for water treatment. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 11768–11774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xue, K.; Wang, B.; Ren, W.; Sun, D.; Shao, C.; Sun, R. Advances in lignin-based biosorbents for sustainable wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 395, 130347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momina; Ahmad, K.; Rafatullah, M. Chapter 15–Applications of biodegradable polymer nanocomposites in water and wastewater treatment. In Biodegradable and Biocompatible Polymer Nanocomposites; Deshmukh, K., Pandey, M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 515–553. [Google Scholar]
- Olugbenga, O.S.; Adeleye, P.G.; Oladipupo, S.B.; Adeleye, A.T.; John, K.I. Biomass-derived biochar in wastewater treatment- a circular economy approach. Waste Manag. Bull. 2024, 1, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalska, K.; Goszkiewicz, A.; Skalska, K.; Kołodziejczyk, E.; Markiewicz, J.; Majzer, R.; Siedlecki, M. Treatment of Industrial Wastewaters and Liquid Waste by Fungi. In Encyclopedia of Mycology; Zaragoza, Ó., Casadevall, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 662–682. [Google Scholar]
- Rathi, G.; Singh, V.; Chaudhry, S.A. Alysicarpus Vaginalis Plant-Based Antioxidant Hybrid Nanocomposite-MnFe2O4/AV for Water Treatment. Chem. Select 2023, 8, e202302199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podder, M.S.; Majumder, C.B. Sequestering of As(III) and As(V) from wastewater using a novel neem leaves/MnFe2O4 composite biosorbent. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2016, 18, 1237–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tara, N.; Abomuti, M.A.; Alshareef, F.M.; Abdullah, O.; Allehyani, E.S.; Chaudhry, S.A.; Oh, S. Nigella sativa-Manganese Ferrite-Reduced Graphene Oxide-Based Nanomaterial: A Novel Adsorbent for Water Treatment. Molecules 2023, 28, 5007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, L.; Mi, N.; Yao, Y.R.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, S.G.; He, H.; Hu, X.; Li, S.Y.; Ni, L.X. Efficient removal of Cr(VI) by tannic acid-modified FeS nanoparticles: Performance and mechanisms. Water Sci. Eng. 2021, 14, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudeja, I.; Mankoo, R.K.; Singh, A.; Kaur, J. Citric acid: An ecofriendly cross-linker for the production of functional biopolymeric materials. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2023, 36, 101307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, I.; Pooja, N.; Govindaraju, I.; Managuli, V.; Banik, S.; Mahato, K.K.; Mazumder, N. Preparation and characterization of citric acid crosslinked starch based bioplastic. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 55, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payan, C.; Gancel, A.-L.; Jourdes, M.; Christmann, M.; Teissedre, P.-L. Wine acidification methods: A review. OENO One 2023, 57, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.I.; Chaudhry, S.A. Nigella sativa plant based nanocomposite-MnFe2O4/BC: A 936 non-toxic, antibacterial material for water purification application. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 200, 996–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabkhani, P.; Javadian, H.; Asfaram, A.; Hosseini, S.N. A reusable mesoporous adsorbent for efficient treatment of hazardous triphenylmethane dye wastewater: RSM-CCD optimization and rapid microwave-assisted regeneration. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulla, N.K.; Siddiqui, S.I.; Fatima, B.; Sultana, R.; Tara, N.; Hashmi, A.A.; Ahmad, R.; Mohsin, M.; Nirala, R.K.; Linh, N.T. Silver based hybrid nanocomposite: A novel antibacterial material for water cleansing. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 284, 124746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebeia, N.; Jabli, M.; Ghith, A.; Saleh, T.A. Eco-friendly synthesis of Cynomorium coccineum extract for controlled production of copper nanoparticles for sorption of methylene blue dye. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 4263–4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, W.; Farooq, U.; Ahmad, M.; Athar, M.; Khan, M.A. Potential biosorbent, Haloxylon recurvum plant stems, for the removal of methylene blue dye. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S1512–S1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Kushwaha, A.K.; Chattopadhyaya, M.C. Application of potato (Solanum tuberosum) plant wastes for the removal of methylene blue and malachite green dye from aqueous solution. Arab. J. Chem. 2016, 9 (Suppl. S1), S707–S716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.I.; Zohra, F.; Chaudhry, S.A. Nigella sativa seed based nanohybrid composite-Fe2O3–SnO2/BC: A novel material for enhanced adsorptive removal of methylene blue from water. Environ. Res. 2019, 178, 108667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, T.; Dabwan, A.H.A.; Furukawa, M.; Tateishi, I.; Katsumata, H.; Kaneco, S. Development of Carbon Nanotube as Highly Active Photocatatlytic Adsorbent for Treatment of Acid Red 88 Dye. Water Conserve. Manage. 2021, 5, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Order | Temperature, (K) | ∆G° | ∆H° | ∆S° |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 303 | −9.838 | −90.288 | −0.265 |
| 2. | 313 | −7.251 | ||
| 3. | 323 | −4.529 |
| Order | Temperature, (K) | Langmuir Isotherm | Freundlich Isotherm | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qmax, (mg/g) | β (L/mg) | RL | R2 | KF (mg/g) (L/mg)1/n | N | R2 | ||
| 1. | 303 | 18.587 | 0.895 | 0.100 | 0.992 | 9.939 | 4.135 | 0.985 |
| 2. | 313 | 14.124 | 1.407 | 0.066 | 0.997 | 7.133 | 4.370 | 0.935 |
| 3. | 323 | 13.140 | 0.746 | 0.118 | 0.998 | 5.830 | 3.976 | 0.933 |
| Order | Temperature, °C | Reuse Cycle | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First | Second | Third | Forth | Fifth | ||
| 1. | 100 | 84 | 73 | 62 | 56 | 43 |
| 2. | 200 | 90 | 77 | 66 | 59 | 48 |
| 3. | 300 | 86 | 71 | 61 | 54 | 47 |
| 4. | 400 | 78 | 64 | 56 | 50 | 43 |
| Order | Adsorbent | Adsorbent Dose (g/L) | Contact Time (min) | Solution pH | Temperature (°C) | Initial Concentration (mg/L) | Equilibrium Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | Removal Efficiency (%) | PC (L/g) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | MnFe2O4/BC | 3.0 | 45.0 | 7.0 | 27.0 | 10.0 | 3.3 | 99.4 | 52.6 | [32] |
| 2. | Ag-Ag2O/ZrO2/GL | 2.0 | 30.0 | 7.0 | 27.0 | 10.0 | 4.9 | 99.0 | 50.6 | [34] |
| 3. | CuO | 2.5 | 30.0 | 6.0 | 22.0 | 25.0 | 5.5 | 54.7 | 0.5 | [35] |
| 4. | Haloxylon recurvum plant stems | 4.0 | 40.0 | 8.0 | 25.0 | 20.0 | 4.8 | 96.4 | 6.7 | [36] |
| 5. | Solanum tuberosum plant leaves | 2.0 | 24.0 | 7.0 | 30.0 | 10.0 | 3.9 | 79.0 | 1.9 | [37] |
| 6. | Fe2O3-SnO2/BC | 2.0 | 90.0 | 7.0 | 27.0 | 10.0 | 4.9 | 97.9 | 23.9 | [38] |
| 7. | MF NPs | 2.0 | 75.0 | 7.0 | 27.0 | 10.0 | 2.8 | 55.5 | 20.7 | Present study |
| 8. | CA/MF-NC | 2.0 | 75.0 | 7.0 | 27.0 | 10.0 | 5.0 | 99.2 | 64.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmad, R.; Alzahrani, E.A.; Dwivedi, P.; Hafeez, S.; Deswal, J.; Fatima, B.; Siddiqui, S.I.; Oh, S. Biodegradable Acid-Based Fe2MnO4 Nanoparticles for Water Remediation. Molecules 2024, 29, 3867. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163867
Ahmad R, Alzahrani EA, Dwivedi P, Hafeez S, Deswal J, Fatima B, Siddiqui SI, Oh S. Biodegradable Acid-Based Fe2MnO4 Nanoparticles for Water Remediation. Molecules. 2024; 29(16):3867. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163867
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmad, Rabia, Elham A. Alzahrani, Poonam Dwivedi, Sumbul Hafeez, Jyoti Deswal, Bushra Fatima, Sharf Ilahi Siddiqui, and Seungdae Oh. 2024. "Biodegradable Acid-Based Fe2MnO4 Nanoparticles for Water Remediation" Molecules 29, no. 16: 3867. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163867
APA StyleAhmad, R., Alzahrani, E. A., Dwivedi, P., Hafeez, S., Deswal, J., Fatima, B., Siddiqui, S. I., & Oh, S. (2024). Biodegradable Acid-Based Fe2MnO4 Nanoparticles for Water Remediation. Molecules, 29(16), 3867. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163867






