Inorganic Characterization of Feeds Based on Processed Animal Protein Feeds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. ICP-OES Analysis
2.2. Ionic Concentration in Samples: IC
3. Chemometric Data Processing
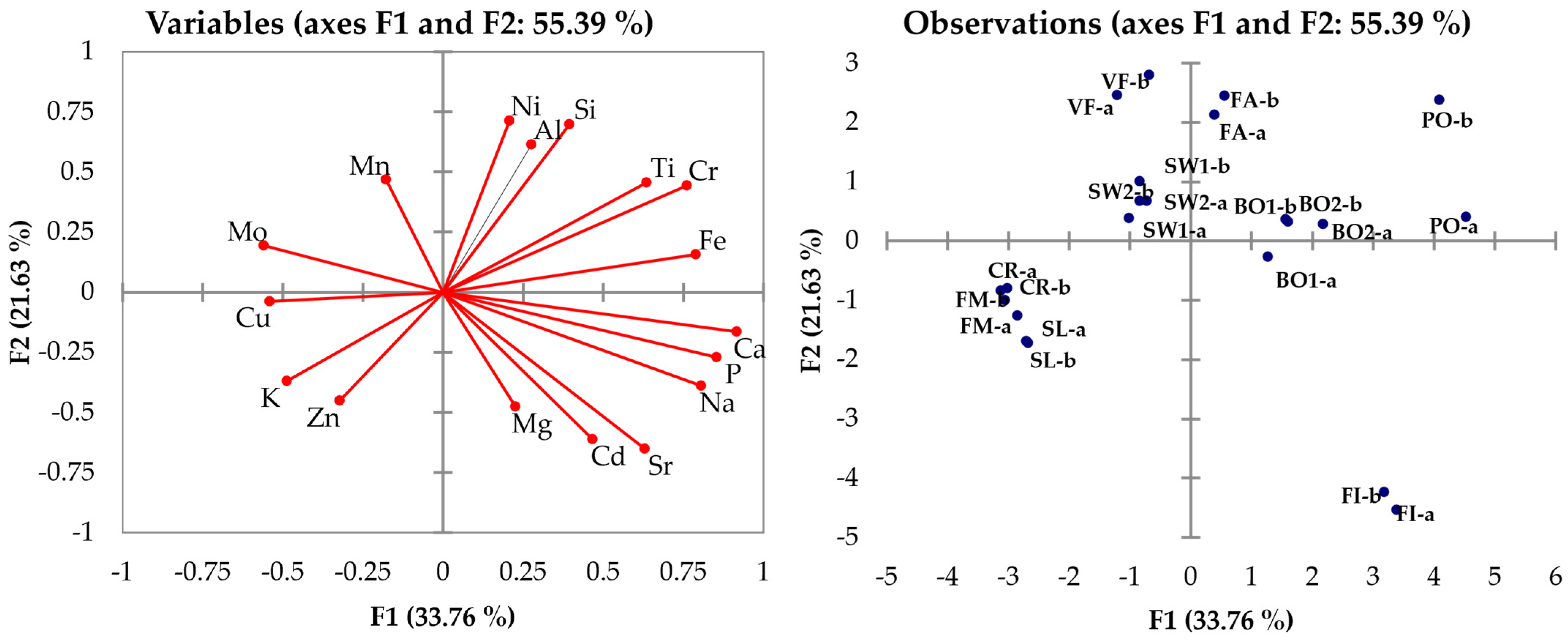
3.1. ICP-OES Data
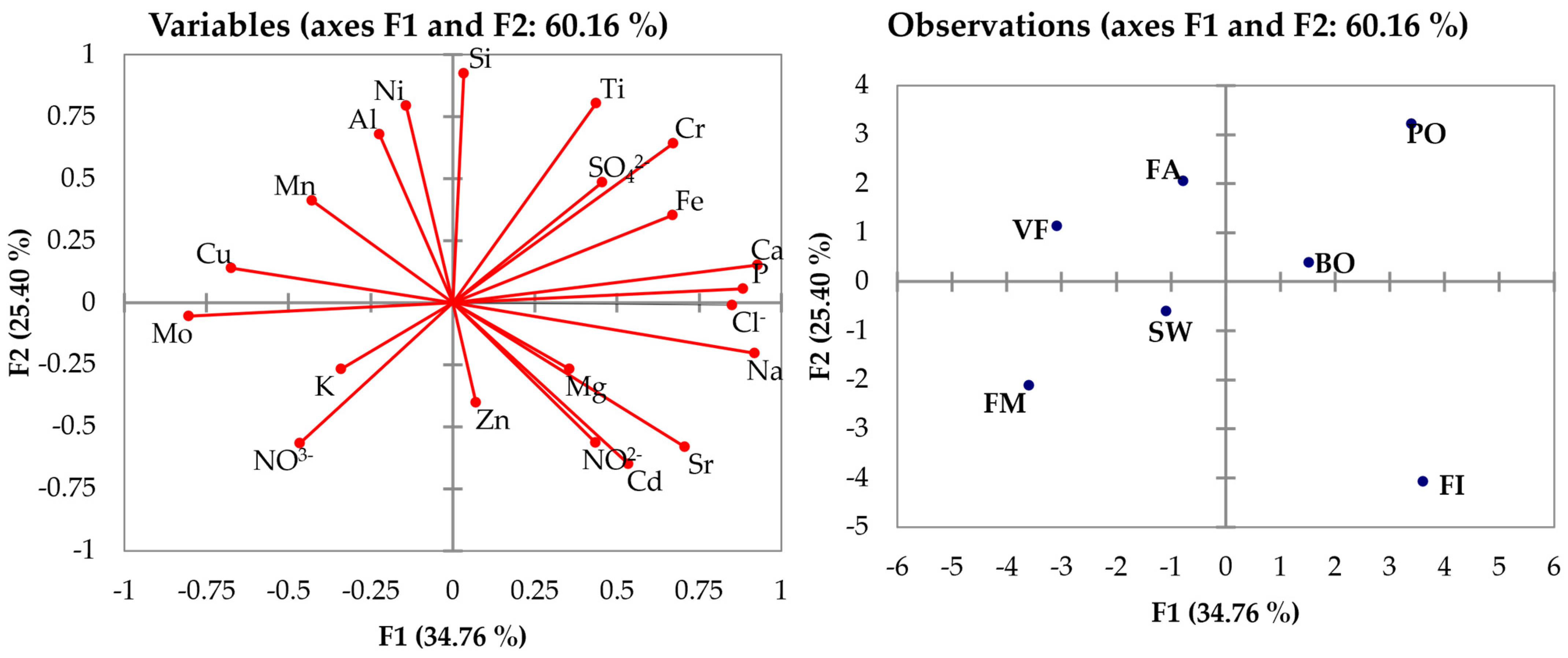
3.2. ICP-OES and IC Data
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Samples
4.2. Sample Pretreatment and Apparatus
4.3. Extraction and Ionic Chromatography
4.4. Chemometric Treatment
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en (accessed on 19 May 2024).
- Available online: https://www.alltech.com/press-release/2024-alltech-agri-food-outlook-shares-global-feed-production-survey-data-and (accessed on 28 November 2023).
- Nathanson, N.; Wilesmith, J.; Griot, C. Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE): Causes and Consequences of a Common Source Epidemic. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1997, 145, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union. Regulation (EC) No 999/2001 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 May 2001 Laying down Rules for the Prevention, Control and Eradication of Certain Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathies. Off. J. L 2001, 147, 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner, S.B. Prion Diseases and the BSE Crisis. Science 1997, 278, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, P. Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy and Variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease: Background, Evolution, and Current Concerns. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2001, 7, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union. Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 21 October 2009 Laying down Health Rules as Regards Animal by-Products and Derived Products Not Intended for Human Consumption and Repealing Regulation (EC) No 1774/2002 (Animal by-Products Regulation). Off. J. Eur. Union 2009, 300, 33. [Google Scholar]
- The European Commission. Commission Regulation (EU) No 142/2011 of 25 February 2011 Implementing Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council Laying down Health Rules as Regards Animal by-Products and Derived Products Not Intended for Human Consumption and Implementing Council Directive 97/78/EC as Regards Certain Samples and Items Exempt from Veterinary Checks at the Border under That Directive Text with EEA Relevance. Off. J. Eur. Union 2011, 54, 254. [Google Scholar]
- Woodgate, S.L.; Wan, A.H.L.; Hartnett, F.; Wilkinson, R.G.; Davies, S.J. The Utilisation of European Processed Animal Proteins as Safe, Sustainable and Circular Ingredients for Global Aquafeeds. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 14, 1572–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecrenier, M.-C.; Plasman, L.; Cordonnier, A.; Baeten, V. Preliminary Feed Sedimentation Step for the Sensitive and Specific Detection of Processed Animal Proteins by Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomics. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 15774–15784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecrenier, M.-C.; Veys, P.; Fumière, O.; Berben, G.; Saegerman, C.; Baeten, V. Official Feed Control Linked to the Detection of Animal Byproducts: Past, Present, and Future. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 8093–8103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.S. Discovery of Human Zinc Deficiency: Its Impact on Human Health and Disease. Adv. Nutr. 2013, 4, 176–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajarillo, E.A.B.; Lee, E.; Kang, D.-K. Trace Metals and Animal Health: Interplay of the Gut Microbiota with Iron, Manganese, Zinc, and Copper. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 7, 750–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pederiva, S.; Avolio, R.; Marchis, D.; Abete, M.C.; Squadrone, S. Preliminary Data on Essential and Non-Essential Element Occurrence in Processed Animal Proteins from Insects. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2023, 201, 4133–4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Commission. Commission Regulation (EU) No 56/2013 of 16 January 2013 Amending Annexes I and IV to Regulation (EC) No 999/2001 of the European Parliament and of the Council Laying down Rules for the Prevention, Control and Eradication of Certain Transmissible Spongiform encephalopathies Text with EEA Relevance. Off. J. Eur. Union 2013, 21, 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- The European Commission. Commission regulation (EU) 2017/ 893 of 24 May 2017 Amending Annexes I and IV to Regulation (EC) No 999/2001 of the European Parliament and of the Council and Annexes X, XIV and XV to Commission Regulation (EU) No 142/2011 as Regards the Provisions on Processed Animal Protein. Off. J. Eur. Union 2017, 138, 92–116. [Google Scholar]
- The European Commission. Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2021/1327 of 10 August 2021 Amending Annexes II, IX and XV to Implementing Regulation (EU) 2021/405 as Regards the Lists of Third Countries or Regions Thereof Authorised for the Entry into the Union of Fresh Meat of Wild Solipeds, Fishery Products from Aquaculture, and Insects, and Correcting Annex XI to That Implementing Regulation as Regards the List of Third Countries and Regions Thereof Authorised for the Entry into the Union of Frogs’ Legs and Snails. Off. J. Eur. Union 2021, 288, 28–36. [Google Scholar]
- Gasco, L.; Acuti, G.; Bani, P.; Dalle Zotte, A.; Danieli, P.P.; De Angelis, A.; Fortina, R.; Marino, R.; Parisi, G.; Piccolo, G.; et al. Insect and Fish By-Products as Sustainable Alternatives to Conventional Animal Proteins in Animal Nutrition. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 19, 360–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Scientific Committee. Risk Profile Related to Production and Consumption of Insects as Food and Feed. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 4257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Huis, A.; Oonincx, D.G.A.B. The Environmental Sustainability of Insects as Food and Feed. A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 37, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soren, A.D.; Choudhury, K.; Sapruna, P.J.; Sarma, D. Nutrient and Toxic Heavy Metal Assessment of Tarbinskiellus Portentosus and Schizodactylus Monstrosus Consumed by the Bodo Tribe in Assam, India. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2021, 41, 2001–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselmo, A.; Veys, P.; Fumière, O.; Lecrenier, M.-C.; Cordonnier, A.; Michez, D.; Baeten, V. Challenges Related to the Application of Analytical Methods to Control Insect Meals in the Context of European Legislation. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2023, 40, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veys, P.; Baeten, V. Protocol for the Isolation of Processed Animal Proteins from Insects in Feed and Their Identification by Microscopy. Food Control 2018, 92, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Han, L.; Veys, P.; Baeten, V.; Jiang, X.; Dardenne, P. An Overview of the Legislation and Light Microscopy for Detection of Processed Animal Proteins in Feeds. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2011, 74, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Raamsdonk, L.W.D.; von Holst, C.; Baeten, V.; Berben, G.; Boix, A.; de Jong, J. New Developments in the Detection and Identification of Processed Animal Proteins in Feeds. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2007, 133, 63–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedzwiecka, A.; Boucharef, L.; Hahn, S.; Zarske, M.; Steinhilber, A.; Poetz, O.; Zagon, J.; Seidler, T.; Braeuning, A.; Lampen, A. A Novel Antibody-Based Enrichment and Mass Spectrometry Approach for the Detection of Species-Specific Blood Peptides in Feed Matrices. Food Control 2019, 98, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumière, O.; Dubois, M.; Baeten, V.; Von Holst, C.; Berben, G. Effective PCR Detection of Animal Species in Highly Processed Animal Byproducts and Compound Feeds. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 385, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecrenier, M.C.; Planque, M.; Dieu, M.; Veys, P.; Saegerman, C.; Gillard, N.; Baeten, V. A Mass Spectrometry Method for Sensitive, Specific and Simultaneous Detection of Bovine Blood Meal, Blood Products and Milk Products in Compound Feed. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchis, D.; Altomare, A.; Gili, M.; Ostorero, F.; Khadjavi, A.; Corona, C.; Ru, G.; Cappelletti, B.; Gianelli, S.; Amadeo, F.; et al. LC-MS/MS Identification of Species-Specific Muscle Peptides in Processed Animal Proteins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 10638–10650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecrenier, M.-C.; Marien, A.; Veys, P.; Belghit, I.; Dieu, M.; Gillard, N.; Henrottin, J.; Herfurth, U.M.; Marchis, D.; Morello, S.; et al. Inter-Laboratory Study on the Detection of Bovine Processed Animal Protein in Feed by LC-MS/MS-Based Proteomics. Food Control 2021, 125, 107944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Wu, S.; Yuan, Z.; Hu, W.; Yu, X.; Kang, N.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, M.; Xia, K.; Yang, W.; et al. Pharmacokinetics, Tissue Distribution, and Excretion Characteristics of a Radix Polygoni Multiflori Extract in Rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 827668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmasso, A.; Fontanella, E.; Piatti, P.; Civera, T.; Rosati, S.; Bottero, M.T. A Multiplex PCR Assay for the Identification of Animal Species in Feedstuffs. Mol. Cell. Probes 2004, 18, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gizzi, G.; von Holst, C.; Baeten, V.; Berben, G.; van Raamsdonk, L. Determination of Processed Animal Proteins, Including Meat and Bone Meal, in Animal Feed. J. AOAC Int. 2004, 87, 1334–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepanova, M.V.; Sotnikova, L.F.; Zaitsev, S.Y. Relationships between the Content of Micro- and Macroelements in Animal Samples and Diseases of Different Etiologies. Animals 2023, 13, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco-Fuentes, E.; Moity, N.; Ramírez-González, J.; Andrade-Vera, S.; Hardisson, A.; González-Weller, D.; Paz, S.; Rubio, C.; Gutiérrez, Á.J. Metals in Commercial Fish in the Galapagos Marine Reserve: Contribution to Food Security and Toxic Risk Assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 286, 112188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behie, S.W.; Bidochka, M.J. Insects as a Nitrogen Source for Plants. Insects 2013, 4, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, C.M.; Farrell, A.P.; Brauner, C.J. Fish Physiology: Homeostasis and Toxicology of Essential Metals; Academis Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Galindo-Riaño, M.D.; Oliva, M.; Jurado, J.A.; Sales, D.; Granado-Castro, M.D.; López-Aguayo, F. Comparative Baseline Levels of Heavy Metals and Histopathological Notes in Fish from Two Coastal Ecosystems of South-West of Spain. Int. J. Environ. Resour. 2015, 9, 163–178. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: http://www.Lenntech.Com/Periodic/Water/Strontium/Strontium-and-Water.Htm (accessed on 28 October 2020).
- Quicke, D.L.J.; Wyeth, P.; Fawke, J.D.; Basibuyuk, H.H.; Vincent, J.F.V. Manganese and Zinc in the Ovipositors and Mandibles of Hymenopterous Insects. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 1998, 124, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montowska, M.; Kowalczewski, P.Ł.; Rybicka, I.; Fornal, E. Nutritional Value, Protein and Peptide Composition of Edible Cricket Powders. Food Chem. 2019, 289, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlisle, E.M. Silicon: An Essential Element for the Chick. Science 1972, 178, 619–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrows, J. Plant Nutrition—From Genetic Engineering to Field Practice. In Proceedings of the 12th International Plant Nutrition Colloquium, Perth, Australia, 21–26 September 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Millaleo, R.; Reyes-Diaz, M.; Ivanov, A.G.; Mora, M.L.; Alberdi, M. Manganese as essential and toxic element for plants: Transport, accumulation and resistance mechanisms. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2010, 10, 470–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunmodede, O.T.; Adewole, E.; Adeniran, O.A.; Adewale, O.B.; Adewumi, F. Contents of Nitrosamine and Its Precursors in Some Roasted Nigerian Food Grains, Tubers and Animals and Their Potential Ingestion in the Diet. Arch. Appl. Sci. Res. 2012, 4, 285–291. [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos, D.K.; Lattos, A.; Chatzigeorgiou, I.; Tsaballa, A.; Ntinas, G.K.; Giantsis, I.A. The Influence of Water Nitrate Concentration Combined with Elevated Temperature on Rainbow Trout Oncorhynchus Mykiss in an Experimental Aquaponic Setup. Fishes 2024, 9, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Analytical Research Labs, Inc. Available online: https://arltma.com/ (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Kourkoumelis, N.; Balatsoukas, I.; Tzaphlidou, M. Ca/P Concentration Ratio at Different Sites of Normal and Osteoporotic Rabbit Bones Evaluated by Auger and Energy Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy. J. Biol. Phys. 2012, 38, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huis, A. Van Edible Insects: Future Prospects for Food and Feed Security; FAO forestry paper; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2013; ISBN 978-92-5-107595-1. [Google Scholar]
- Inaudi, P.; Giacomino, A.; Malandrino, M.; La Gioia, C.; Conca, E.; Karak, T.; Abollino, O. The Inorganic Component as a Possible Marker for Quality and for Authentication of the Hazelnut’s Origin. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollons, H.M.; Barraclough, P.B. Inorganic Orthophosphate for Diagnosing the Phosphorus Status of Wheat Plants. J. Plant Nutr. 1997, 20, 641–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Tomato Leaves SRM 1537a | A | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | 71.2 ± 6.40 | 74.7 ± 1.96 | 63.2 ± 5.94 | 92.0 ± 2.21 |
| Ba | 65.2 ± 1.06 | 66.5 ± 2.04 | 63.0 ± 0.32 | 72.2 ± 1.47 |
| Ca | 96.2 ± 2.19 | 93.9 ± 1.76 | 93.4 ± 9.00 | 96.2 ± 1.48 |
| Cd | 66.9 ± 0.94 | 69.8 ± 2.79 | 67.2 ± 1.82 | 94.2 ± 1.72 |
| Co | 80.8 ± 3.33 | 77.2 ± 7.24 | 73.1 ± 1.82 | 74.0 ± 14.7 |
| Cr | 54.0 ± 0.93 | 50.6 ± 2.72 | 64.7 ± 1.80 | 75.8 ± 2.84 |
| Cu | 95.3 ± 8.70 | 72.8 ± 3.15 | 53.6 ± 8.78 | 81.4 ± 5.71 |
| Fe | 76.3 ± 0.52 | 78.0 ± 0.87 | 75.4 ± 1.96 | 71.7 ± 4.49 |
| K | 100 ± 1.75 | 100 ± 5.62 | 82.0 ± 10.6 | 100 ± 3.50 |
| Mg | 86.3 ± 1.79 | 86.4 ± 1.83 | 85.2 ± 8.72 | 87.3 ± 4.66 |
| Mn | 78.7 ± 1.34 | 77.2 ± 0.88 | 78.7 ± 0.92 | 90.7 ± 0.83 |
| Na | 91.6 ± 1.39 | 88.0 ± 8.19 | 67.9 ± 1.27 | 90.6 ± 3.00 |
| P | 90.2 ± 1.57 | 90.1 ± 0.15 | 83.7 ± 0.42 | 94.0 ± 0.73 |
| Sr | 61.2 ± 1.91 | 79.6 ± 2.09 | 76.9 ± 2.35 | 87.0 ± 0.63 |
| V | 59.7 ± 3.71 | 61.6 ± 0.66 | 49.8 ± 6.64 | 72.2 ± 16.2 |
| Zn | 77.6 ± 2.86 | 64.8 ± 0.38 | 63.4 ± 1.63 | 78.3 ± 1.53 |
| Mean | 78.2 | 76.9 | 71.3 | 84.8 |
| Median | 78.1 | 77.2 | 70.5 | 87.1 |
| Bovine Liver CRM 185 | A | B | C | D |
| Ca | 91.9 ± 11.7 | 90.5 ± 2.70 | 90.4 ± 3.61 | 92.1 ± 1.92 |
| Cu | 79.5 ± 8.2 | 72.7 ± 0.92 | 88.1 ± 1.69 | 88.8 ± 1.34 |
| Fe | 86.6 ± 1.12 | 81.5 ± 1.05 | 85.0 ± 1.13 | 87.0 ± 0.71 |
| K | 100 ± 1.41 | 100 ± 7.10 | 100 ± 3.59 | 100 ± 11.6 |
| Mg | 84.2 ± 1.35 | 79.2 ± 1.04 | 71.5 ± 0.88 | 76.0 ± 0.18 |
| Mn | 86.7 ± 11.1 | 80.9 ± 1.16 | 77.0 ± 1.74 | 90.6 ± 0.90 |
| Na | 90.8 ± 10.8 | 84.1 ± 0.98 | 83.7 ± 1.11 | 85.2 ± 0.50 |
| P | 100 ± 11.2 | 99.0 ± 1.53 | 100 ± 4.08 | 100 ± 9.61 |
| Pb | 100 ± 15.3 | 100 ± 14.6 | 69.0 ± 14.9 | 100 ± 12.4 |
| Se | 85.1 ± 19.9 | 88.0 ± 15.6 | 62.9 ± 26.1 | 74.7 ± 17.1 |
| Zn | 74.5 ± 1.61 | 72.8 ± 0.39 | 83.5 ± 0.56 | 87.9 ± 0.58 |
| Mean | 89.0 | 86.2 | 82.8 | 89.3 |
| Median | 86.7 | 84.1 | 83.7 | 88.8 |
| BO1 | BO2 | SW1 | SW2 | FI | PO | FA | VF | FM | SL | CR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg/kg | |||||||||||
| Al | 84.0 ± 2.5 | 100 ± 23 | 4.60 ± 0.35 | 3.10 ± 0.17 | <0.30 | 49.4 ± 7.7 | 113 ± 33 | 118 ± 3 | 15.9 ± 0.29 | 0.52 ± 0.07 | 22.1 ± 0.5 |
| Cd | <0.30 | <0.30 | <0.30 | <0.30 | 1.20 ± 0.05 | <0.30 | <0.30 | <0.30 | <0.30 | <0.30 | <0.30 |
| Cr | 1.33 ± 0.51 | 1.90 ± 0.32 | 1.60 ± 0.09 | 1.89 ± 0.03 | 1.91 ± 0.09 | 4.09 ± 1.02 | 2.21 ± 0.08 | 1.76 ± 0.24 | <0.48 | <0.48 | 0.62 ± 0.19 |
| Cu | 6.09 ± 2.54 | 5.87 ± 2.93 | 2.71 ± 0.08 | 4.13 ± 0.37 | 4.54 ± 3.05 | 7.71 ± 0.21 | 11.2 ± 2.8 | 11.3 ± 0.27 | 15.7 ± 2.3 | 8.93 ± 6.70 | 26.9 ± 1.8 |
| Fe | 301 ± 12 | 288 ± 2 | 53.8 ± 7.7 | 53.4 ± 1.4 | 228 ± 0.89 | 246 ± 6 | 279 ± 6 | 136 ± 1 | 69.3 ± 2.0 | 22.3 ± 1.54 | 84.0 ± 4.9 |
| Mn | 8.19 ± 4.69 | 8.19 ± 4.54 | 0.73 ± 0.15 | 0.81 ± 0.87 | 4.19 ± 0.07 | 16.6 ± 3.57 | 23.1 ± 2.15 | 71.4 ± 18.4 | 7.96 ± 5.42 | 10.1 ± 0.15 | 31.1 ± 4.4 |
| Mo | 0.45 ± 0.15 | 0.59 ± 0.19 | 0.32 ± 0.62 | 0.26 ± 0.03 | 0.15 ± 0.45 | 0.43 ± 0.65 | 0.57 ± 2.06 | 1.20 ± 11.5 | 1.78 ± 0.2 | 0.59 ± 0.17 | 0.74 ± 1.51 |
| Ni | <0.10 | <0.10 | 1.54 ± 0.65 | 1.15 ± 0.05 | <0.10 | 1.67 ± 0.27 | 1.15 ± 0.58 | 1.14 ± 2.48 | 0.47 ± 0.07 | 0.31 ± 0.11 | 0.28 ± 0.11 |
| Si | 228 ± 20 | 248 ± 1 | 71.0 ± 38.9 | 119 ± 1 | 63.7 ± 4.10 | 320 ± 40 | 266 ± 15 | 271 ± 4 | 133 ± 1 | 123 ± 4 | 133 ± 3 |
| Sr | 24.7 ± 4.8 | 27.8 ± 8.0 | 2.88 ± 0.07 | 2.63 ± 1.66 | 228 ± 7 | 56.6 ± 20.4 | 13.9 ± 8.5 | 7.54 ± 7.51 | 4.12 ± 5.62 | 1.35 ± 0.4 | 3.01 ± 0.7 |
| Ti | 8.20 ± 0.33 | 6.22 ± 0.38 | 0.38 ± 0.91 | 0.37 ± 27.2 | 0.22 ± 0.13 | 32.2 ± 11.0 | 14.8 ± 3.4 | 5.49 ± 1.00 | 1.36 ± 0.17 | 0.24 ± 0.08 | 1.76 ± 0.50 |
| Zn | 71.5 ± 0.8 | 74.1 ± 0.28 | 42.2 ± 0.03 | 43.9 ± 2.4 | 131 ± 1 | 83.6 ± 4.6 | 120 ± 2 | 72.2 ± 9.0 | 129 ± 2.01 | 125 ± 21 | 211 ± 18 |
| g/kg | |||||||||||
| Ca | 49.1 ± 1.73 | 57.1 ± 6.10 | 5.98 ± 0.08 | 5.76 ± 0.01 | 73.2 ± 5.98 | 101 ± 44.6 | 15.4 ± 2.56 | 12.0 ± 7.21 | 0.40 ± 1 × 10−3 | 0.91 ± 0.01 | 1.35 ± 0.29 |
| K | 6.21 ± 0.03 | 6.17 ± 0.28 | 0.93 ± 0.01 | 0.94 ± 0.01 | 3.24 ± 0.01 | 3.73 ± 0.40 | 1.48 ± 0.01 | 4.51 ± 4.29 | 10.1 ± 0.02 | 11.1 ± 0.09 | 8.75 ± 0.07 |
| Mg | 1.49 ± 3 × 10−3 | 1.64 ± 0.11 | 0.31 ± 4 × 10−3 | 0.31 ± 1 × 10−3 | 2.37 ± 0.15 | 2.53 ± 0.50 | 0.74 ± 0.03 | 1.20 ± 0.64 | 2.57 ± 0.07 | 2.70 ± 0.07 | 0.65 ± 0.03 |
| Na | 6.68 ± 0.15 | 6.91 ± 0.02 | 0.92 ± 4 × 10−3 | 0.94 ± 0.01 | 9.06 ± 0.02 | 7.04 ± 0.14 | 1.11 ± 0.01 | 1.20 ± 0.12 | 1.13 ± 3 × 10−3 | 0.08 ± 4 × 10−3 | 3.60 ± 0.02 |
| P | 27.8 ± 1.02 | 31.7 ± 2.47 | 4.78 ± 0.02 | 4.71 ± 0.01 | 40.9 ± 2.94 | 57.7 ± 9.20 | 2.40 ± 0.41 | 3.71 ± 1.46 | 8.79 ± 0.04 | 8.62 ± 0.10 | 6.50 ± 0.09 |
| Anion | BO1 | SW1 | PO | FI | FA | FM | VF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cl− | 3.02 | 1.78 | 4.00 | 3.06 | 1.26 | 1.95 | 0.77 |
| NO2− | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | 0.12 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| NO3− | 0.22 | 0.36 | 0.30 | 0.59 | 0.44 | 0.64 | 0.57 |
| SO42− | 0.30 | <0.2 | 0.38 | 0.24 | 0.65 | <0.2 | <0.2 |
| Code | Type of PAP |
|---|---|
| BO1 | Bovine |
| BO2 | Bovine |
| SW1 | Swine |
| SW2 | Swine |
| FI | Fish |
| PO | Poultry |
| FA | Feathers |
| VF | Vegetal feed |
| CR | Cricket |
| SL | Silkworm |
| FM | Flour moth |
| Mixture Code | Reagents |
|---|---|
| A | 6 mL HNO3 + 1 mL H2O2 |
| B | 6 mL HNO3 + 1 mL HCl |
| C | 6 mL HNO3 + 1 mL H2O2 + 1.5 mL H2O |
| D | 6 mL HNO3 + 1 mL H2O2 + 2 mL H2O + 2 mL HF |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Inaudi, P.; Mercurio, L.M.; Marchis, D.; Bosusco, A.; Malandrino, M.; Abollino, O.; Favilli, L.; Bertinetti, S.; Giacomino, A. Inorganic Characterization of Feeds Based on Processed Animal Protein Feeds. Molecules 2024, 29, 3845. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163845
Inaudi P, Mercurio LM, Marchis D, Bosusco A, Malandrino M, Abollino O, Favilli L, Bertinetti S, Giacomino A. Inorganic Characterization of Feeds Based on Processed Animal Protein Feeds. Molecules. 2024; 29(16):3845. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163845
Chicago/Turabian StyleInaudi, Paolo, Luca Maria Mercurio, Daniela Marchis, Andrea Bosusco, Mery Malandrino, Ornella Abollino, Laura Favilli, Stefano Bertinetti, and Agnese Giacomino. 2024. "Inorganic Characterization of Feeds Based on Processed Animal Protein Feeds" Molecules 29, no. 16: 3845. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163845
APA StyleInaudi, P., Mercurio, L. M., Marchis, D., Bosusco, A., Malandrino, M., Abollino, O., Favilli, L., Bertinetti, S., & Giacomino, A. (2024). Inorganic Characterization of Feeds Based on Processed Animal Protein Feeds. Molecules, 29(16), 3845. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163845










