Abstract
In order to improve dispersibility, polymerization characteristics, chemical stability, and magnetic flocculation performance, magnetic Fe3O4 is often assembled with multifarious polymers to realize a functionalization process. Herein, a typical three-dimensional configuration of hyperbranched amino acid polymer (HAAP) was employed to assemble it with Fe3O4, in which we obtained three-dimensional hyperbranched magnetic amino acid composites (Fe3O4@HAAP). The characterization of the Fe3O4@HAAP composites was analyzed, for instance, their size, morphology, structure, configuration, chemical composition, charged characteristics, and magnetic properties. The magnetic flocculation of kaolin suspensions was conducted under different Fe3O4@HAAP dosages, pHs, and kaolin concentrations. The embedded assembly of HAAP with Fe3O4 was constructed by the N–O bond according to an X-ray photoelectron energy spectrum (XPS) analysis. The characteristic peaks of –OH (3420 cm−1), C=O (1728 cm−1), Fe–O (563 cm−1), and N–H (1622 cm−1) were observed in the Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FTIR) spectra of Fe3O4@HAAP successfully. In a field emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM) observation, Fe3O4@HAAP exhibited a lotus-leaf-like morphological structure. A vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) showed that Fe3O4@HAAP had a relatively low magnetization (Ms) and magnetic induction (Mr); nevertheless, the ferromagnetic Fe3O4@HAAP could also quickly respond to an external magnetic field. The isoelectric point of Fe3O4@HAAP was at 8.5. Fe3O4@HAAP could not only achieve a 98.5% removal efficiency of kaolin suspensions, but could also overcome the obstacles induced by high-concentration suspensions (4500 NTU), high pHs, and low fields. The results showed that the magnetic flocculation of kaolin with Fe3O4@HAAP was a rapid process with a 91.96% removal efficiency at 0.25 h. In an interaction energy analysis, both the UDLVO and UEDLVO showed electrostatic repulsion between the kaolin particles in the condition of a flocculation distance of <30 nm, and this changed to electrostatic attraction when the separation distance was >30 nm. As Fe3O4@ HAAP was employed, kaolin particles could cross the energy barrier more easily; thus, the fine flocs and particles were destabilized and aggregated further. Rapid magnetic separation was realized under the action of an external magnetic field.
1. Introduction
In general, the turbidity of natural rivers and lakes increases as rainfall continuously scours their surfaces, which also greatly increases the risk of unsafe drinking water [1]. In addition, high turbidity also appears in the treatment process of waterworks [2], and agriculture and industry produce wastewater from paint [3], microplastic [4], dye [5], papermaking [6] beneficiation, and livestock and poultry breeding [7]. The colloidal particles in high-turbidity water usually exhibit the characteristics of electric charge, a small particle size, and a large specific surface area [8]; also, the particles carry harmful pollutants such as heavy metals, pathogens, and toxic organics [9,10]. Therefore, the treatment of high-turbidity water is essential and has enormous challenges.
For the treatment of high-turbidity water, the common methods mainly focus on physical, chemical, and biological methods. Physical methods mainly include centrifugation, filtration, gravity sedimentation, etc., which are usually time-consuming and energy-demanding; thus, they are difficult to use for large-scale applications.
Biological methods mainly select some filter-feeding fish or plankton, but their growth properties are difficult to control, as are the application effects [11]. In chemical methods, flocculation can be induced by chemicals, both inorganic and organic, or by microorganisms. The flocculation process can occur in response to environmental stress, certain pHs, nitrogen, and dissolved oxygen. In this process, the shape, size, and composition of flocs can be very dependent on the colloidal particles and flocculant [12,13]. Thus, selecting the appropriate and ideal flocculant is the key to obtaining a high flocculation efficiency in the treatment process.
Magnetic flocculation has emerged as a new technology, in which the separation process is achieved via the intrinsic paramagnetic movement of magnetic particles tagged with target colloidal particles. The magnetic flocculation process has the advantages of being convenient, maneuverable, environmentally friendly, quickly achieving separation, reducing or eliminating the leaching of pollutants, and facilitating its reuse [14,15,16]. During the application of magnetic flocculation, magnetic composites can react with the target pollutants through charge neutralization, adsorption bridge, double electric layer compression, and sweeping, so as to generate a high magnetic concentration and high-density composite flocs, which can achieve rapid settlement through the influence of gravity or an external magnetic field [17]. The core technology of magnetic flocculation mainly depends on the magnetic particles that are employed. Among magnetic particles, the common magnetic carriers are the magnetic particles of Fe3O4, which have the advantages of being available, inexpensive, and having a high magnetic responsiveness [18,19,20]. The flocculating materials for magnetic assembly are concentrated in selection from conventional flocculants. Recently, stereo-structured polymers have attracted wide attention because of their ability to overcome the structural instability of conventional linear or chain polymers, and hyperbranched polymers (HBPs) are typical examples among them.
HBPs applied as a new type of highly branched polymer have quickly attracted much attention, owing to their highly three-dimensional (3D) and highly branched topologies, high branches, and high density of surface functional groups [21,22,23]. Compared with normal linear polymers (LPs), the main characteristics of HBPs include a good solubility and low viscosity; special 3D topological structures that can prevent wounds and aggregation, resulting in some completely different properties from LPs; and numerous functional groups along the periphery of HBPs, with the properties of a higher solubility and easy modification/adjustment by changing the groups along the periphery [24]. The functional groups mainly include amine (–NH2), hydroxyl (–OH), and carboxyl (–COOH) groups, which increase the adsorption sites of HBPs [25]. Moreover, the branched chains and terminal functional groups of HBPs’ components are adjustable, which broadens their application range [26]. Up to now, there are several types of HBPs or modified substances, including polyamide amine (PAMAM) [27], hyperbranched pyridylphenylene polymer (PPP) [28], hyperbranched polyglycidol (HbPGL) [29], and hyper-branched polyethylenimines (HPEIs) [30], which are usually employed for assembling and fabricating in water treatment.
Magnetic composites assembled from HBPs and magnetic materials improve the stability and reusable performance of HBPs, successfully making up for their shortcomings. Within these composites, magnetic Fe3O4 is evenly dispersed, and then the outer molecules are iteratively grafted to form a hyperbranched polymer, which ensures their magnetic response ability [31,32]. Meanwhile, the magnetic core and polymer are tightly bound together via a grafting reaction, and the hyperbranched carbon chains and terminal functional groups show a great ability in solid–liquid separation under the action of an external magnetic field [31]. It is known that flocculants with a high molecular weight and rich active groups are more effective in exhibiting the function of adsorption bridging ability [33,34]. Fortunately, magnetic hyperbranched polymers acquire the characteristics of both magnetic particles and dendritic macromolecular polymers.
In this research, a new type of three-dimensional hyperbranched magnetic composite (Fe3O4@HAAP) was obtained using a self-assembly strategy of hyperbranched amino acid polymer (HAAP) and naked Fe3O4 particles. Thus the magnetic flocculation properties and mechanisms were investigated. In order to explore the characteristics of Fe3O4@HAAP, the morphology, structure, configuration, chemical composition, charged characteristic, and magnetic and thermal properties were explored. The magnetic flocculation performance of Fe3O4@HAAP was evaluated in high-turbidity wastewater, taking into account factors like the dosage, pH, and kaolin concentration. In addition, the Derjaguin–Landau–Verwey–Overbeek (DLVO theory) was used to describe the interaction force between charged aggregates in order to discuss the reaction mechanism of the material.
2. Result and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of Fe3O4@HAAP
2.1.1. FTIR and XPS Spectra
The FTIR spectra of Fe3O4@HAAP, HAAP, and Fe3O4 are shown in Figure 1. An obvious Fe-O stretching vibration peak was observed at 578 cm−1. At 563 cm−1 of Fe3O4@HAAP, a comparable, slightly smaller peak can be seen. This verified that the HAAP had been successfully coated on the surface of Fe3O4 [35]. The peaks at 3420 cm−1, 1728 cm−1, and 1622 cm−1 are attributable to the stretching vibration of the –OH group, C=O band, and N–H band [36,37,38]. The weakening of these peaks also demonstrated the success of Fe3O4@HAAP assembly.
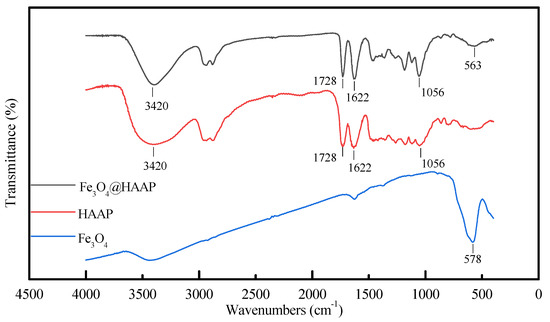
Figure 1.
The FTIR spectra of Fe3O4, HAAP, Fe3O4@HAAP.
The XPS spectra of Fe3O4@HAAP are presented in Figure 2. As to the Fe 2p high-resolution spectrum (Figure 2a), the two typical peaks at 724.6 and 710.8 eV correspond to Fe 2p1/2 and Fe 2p3/2. Specifically, the two peaks of Fe 2p3/2 and Fe 2p1/2 were deconvoluted into Fe3+ and Fe2+ ions. The small satellite peak at 733.3 eV could be assigned to Fe3+ [39]. Figure 2b shows the O 1s high-resolution spectra, with the four peaks at 532.9, 531.8, 532.3, and 529.8 eV attributed to O–C=O, O=C, O–C, and O–Fe, respectively [40,41,42]. In addition, three prominent peaks were observed at 286.4, 285.8, and 288.2 eV, corresponding to C–OH, C–C, and C=O (Figure 2c) [43,44]. Three peaks were identified in the N 1s spectrum (Figure 2d) at binding energies of 400.3, 401.5, and 399.8 eV, which belonged to N–H, N–O, and C–NH2 [21,42,45].
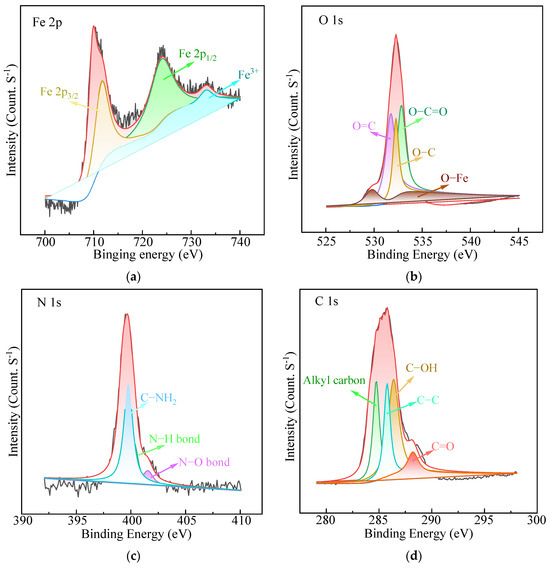
Figure 2.
The XPS spectra of Fe3O4@HAAP: (a) Fe 2p spectrum, (b) O 1s spectrum, (c) C 1s spectrum, (d) N 1s spectrum.
2.1.2. SEM and EDS
The morphology of Fe3O4@HAAP was examined by SEM, and the images at various magnifications are shown in Figure 3. The surface of Fe3O4@HAAP was covered by an oil-like film, and there were scattered patches (Figure 3a–c). This was due to the presence of the organic coating after the assembly of Fe3O4 and HAAP. In the ×50,000 observation, Fe3O4@HAAP exhibited a lotus leaf-like morphological structure (Figure 3d). Two points were randomly selected on the surface of the Fe3O4@HAAP for energy spectrum analysis, and the specific results can be observed in Table 1. Except for C and O elements, Fe element content was dominated by the others (16%). In addition, there was a small amount of Si element (3.2%), which came from the raw materials (tetraethylxysilane) in the Fe3O4@HAAP assembly process.
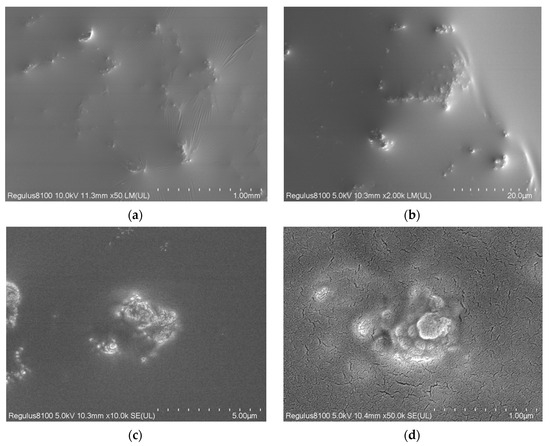
Figure 3.
SEM images of Fe3O4@HAAP: (a) ×50; (b) ×2000; (c) ×10,000; (d) ×50,000.

Table 1.
EDS values of Fe3O4@HAAP.
2.1.3. VSM and Zeta Potential
The hysteresis loop is a curve formed by the magnetic induction intensity of the sample with the change in the magnetic field, which represents the magnetic properties of the material. Figure 4 shows the magnetization hysteresis loops of Fe3O4 and Fe3O4@HAAP under varying magnetic field intensities. The saturation magnetization (Ms) of Fe3O4 and Fe3O4@HAAP was 66.13 emu/g and 17.1 emu/g, respectively. The reason for this phenomenon was that during the assembly of Fe3O4@HAAP, a non-magnetic shell was formed on the surface. In addition, the coercive force (Hc) and remanent magnetic induction (Mr) of Fe3O4 and Fe3O4@HAAP were 13.6 Oe, 1.35 emu/g and 17.49 Oe, 0.57 emu/g, respectively. The high value of Hc but low Mr showed that Fe3O4@HAAP exhibited superparamagnetic properties and was easily affected by magnetic fields, resulting in quick magnetic separation in application.
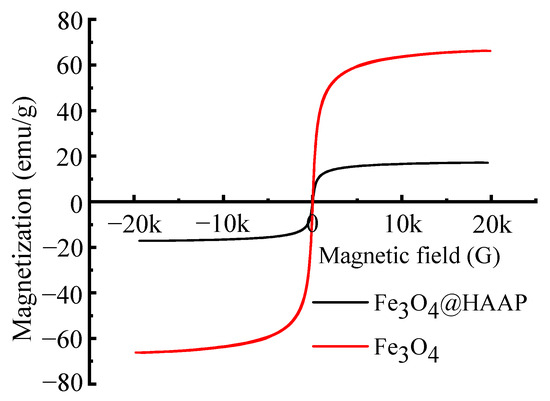
Figure 4.
The magnetization hysteresis loops of Fe3O4 and Fe3O4@HAAP.
The zeta potentials of kaolin solution, Fe3O4, HAAP, and Fe3O4@HAAP are displayed in Figure 5. The zeta potential of kaolin was negative and the absolute value increased with the increase in pH. Due to the crystal structure formed by the alternately arranged Si–O tetrahedral layer and Al–O octahedral layer and the active group type on the surface being O2−, the surface of kaolin has a negative charge. For Fe3O4@HAAP, the zeta potential was −5.39~1.58 mV and the isoelectric point was about 6. These values were all between Fe3O4 and HAAP, which, because of the successful assembly of two materials, resulted in a change in the zeta potential of Fe3O4@HAAP.
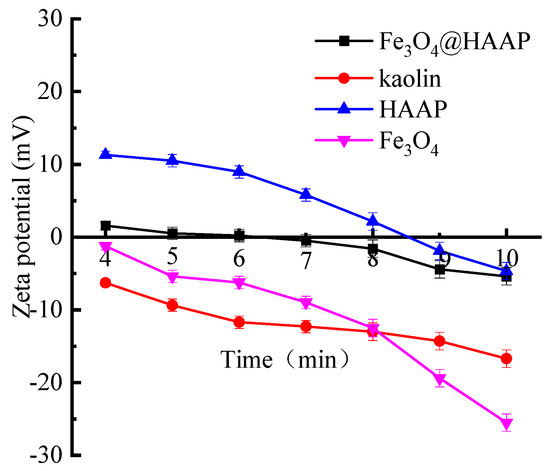
Figure 5.
Zeta potential of kaolin solution, Fe3O4, HAAP, and Fe3O4@HAAP.
2.2. Application in Wastewater Treatment
2.2.1. Simulated Wastewater
Fe3O4@HAAP was applied to treat kaolin simulated wastewater, and the different conditions were explored. The experimental results are shown in Figure 6. In order to compare the effects of different dosages, 0~120 mg/L of Fe3O4@HAAP was added to the wastewater, respectively. When the dosages were below 40 mg/L, the removing efficiency was less than 85% at 30 min. While the dosages further exceeded 50 mg/L, the removing efficiency was over 90% at 30 min. The removing efficiency reached 91.53% when the dosage was 50 mg/L (Figure 6a). Under acidic conditions, the zeta potential of Fe3O4@HAAP was positive and the surface was positively charged. The material could be combined with the negatively charged kaolin by electroneutralization to achieve the agglomeration. However, the low-dose flocculant was not enough to realize the electric neutralization mechanism, and reduced the possibility of collision, which caused the poor flocculation effect. In addition, the excessive dosage caused the contact site between the kaolin particles and the flocculant to be covered, the bridging effect was weakened, and the electrostatic repulsion between the floc was dominant, which made the floc unstable and was not conducive to the agglomeration of particles.
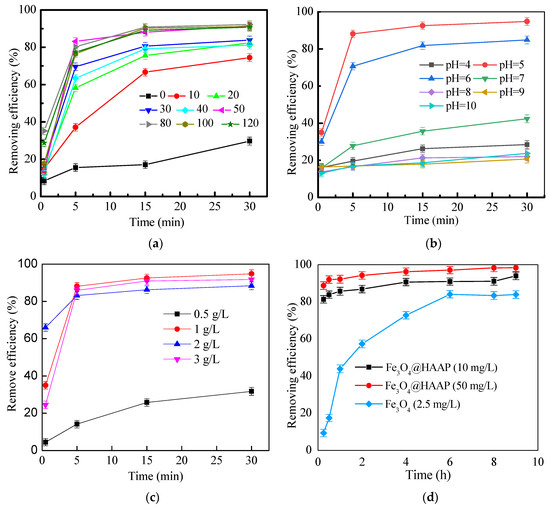
Figure 6.
Removing efficiency of Fe3O4@HAAP on kaolin solution under different conditions: (a) Fe3O4@HAAP dosage, (b) pH, (c) kaolin concentration, (d) reaction time.
Figure 6b shows the effect of different pHs on the removing efficiency. When pH was 5, the removing efficiency was optimal and the value was 88.11% at 5 min, while it reached 94.83% at 30 min. And there was a significant difference (p < 0.05) in the removing rate between the two periods, which indicates that the flocculation process is not in equilibrium at 5 min. When Fe3O4@HAAP was applied in the strong acid condition, H+ in the solution inhibited the dissociation of carboxyl groups, thus reducing the complex ability of the material and weakening the flocculation effect. However, –COO− ions could be ionized from the –COOH and become negatively charged under alkaline conditions. This caused the ionization of the carboxyl group on the surface of Fe3O4@HAAP, which resulted in its zeta potential becoming negative and the absolute value gradually increasing, thus increasing the electrostatic repulsion between Fe3O4@HAA and kaolin particles, and reducing the flocculation effect.
As shown in Figure 6c, the removing efficiency exhibited significant differences when Fe3O4@HAAP was used to treat kaolin suspension. When the kaolin concentration was 1.0 mg/L, Fe3O4@HAAP showed the best removal properties and the value was 94.83%. However, when the kaolin concentration was 0.5 mg/L, the removing efficiency was only 31.74%. The excessive concentration of kaolin also resulted in a slight decrease in the removing efficiency. The reason was that the amount of flocculant was higher than the pollutant, and then the spatial resistance of the polymer and the electrostatic repulsion between the floc caused the stability of the formed floc to deteriorate. The particle aggregation ability was also reduced, and the degree of fragmentation was increased, which resulted in a poor processing effect. However, excessive kaolin also led to a decline in treatment performance because of the insufficient binding site of the flocculant, resulting in the positive charge of Fe3O4@HAAP, which could not completely neutralize the negative charge of kaolin.
Different dosages of Fe3O4@HAAP were added to treat kaolin, and the results can be observed in Figure 6d. Fe3O4 was added for the control group. The results showed that the flocculation of kaolin with Fe3O4@HAAP was a rapid process, and that the removing efficiencies were 83.85% and 91.96% at 0.25 h when the dosages of Fe3O4@HAAP were 10 mg/L and 50 mg/L, respectively. After analysis, the flocculation kinetics conformed to the Smoluchowski classical model. In the experiment, the small kaolin particles first rapidly aggregate and then flocculate through bridging into larger flocs. But for Fe3O4@HAAP, the low dosage weakened the interaction between the flocculant and the kaolin. This was not only insufficient to produce a full collision between flocculant molecules and kaolin particles, but also insufficient to realize an electric neutralization mechanism. Moreover, appropriate addition made the positive charge of the magnetic material and the negative charge of kaolin electric neutralization particle collision sufficient, and combined with the adsorption bridge to achieve rapid flocculation [46]. However, with the excessive dosage, both the spatial resistance of the polymer and electrostatic repulsion between the flocs led to instability, reduced the particle aggregation degree, and increased the fragmentation degree, thus affecting the flocculation kinetics and flocculation performance [47].
2.2.2. Actual Water
In addition to the simulated wastewater samples, actual water at its natural pH and temperature conditions was used in determining the effects of Fe3O4@HAAP. An addition of Fe3O4 was used as a comparison. Different from the simulated water samples, there are a variety of complex substances, such as plankton, chemical components existing in nature, which may influence the results of experiments. Samples from two lakes were collected to verify the practicability of Fe3O4@HAAP, and the results are shown in Figure 7. Fe3O4@HAAP showed a significant removing effect in both lake samples (Figure 7a,b). The removing efficiencies were 95.6% and 92.7% at 30 min, respectively. The results indicated that Fe3O4@HAAP could overcome the influence of interfering substances in natural water and maintain an excellent magnetic flocculation effect.
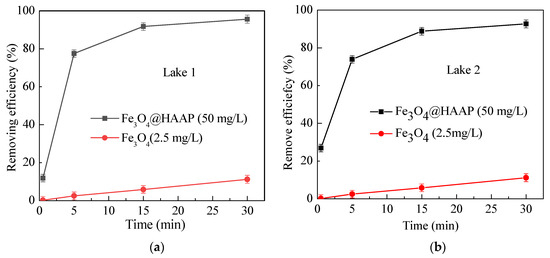
Figure 7.
Removing efficiency of Fe3O4@HAAP on actual water: (a) Lake 1, (b) Lake 2. The Fe3O4@HAAP dosage was 50 mg/L, pH = 5.
2.2.3. Recycling and Reuse
It is well known that the recyclability and reusability of materials are key factors in reducing costs. Fe3O4 and Fe3O4@HAAP were separated from solution by a magnet and the reuse performance was explored via treating kaolin solution. As shown in Figure 8a, the recycling efficiency of both Fe3O4 and Fe3O4@HAAP remains above 97% and there was no significant difference (p > 0.05) in the efficiency of each recycling efficiency with only a small amount of material loss, which may be due to incomplete material separation during the flocculation–separation process. In the kaolin treatment process, although Fe3O4@HAAP was repeatedly applied five times, the removing efficiency decreased slightly each time, with no significant difference (p > 0.05). Therefore, Fe3O4@HAAP maintained high removing efficiency even after five cycles, with a value of 92.6% (Figure 8b). The results showed that Fe3O4@HAAP had excellent stability, could be reused multiple times, and maintained excellent treatment effects, which made the material a potential candidate for the treatment of high-turbidity wastewater.
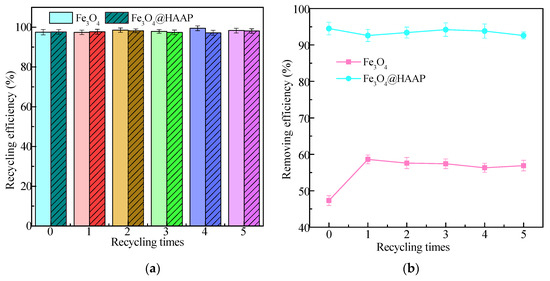
Figure 8.
The recycling efficiency (a) and removing efficiency (b) of Fe3O4 and Fe3O4@HAAP on kaolin treatment under 5 recycling times, the colors correspond to different recycling times.
2.3. Interaction Energy Analysis
In the DLVO theory calculation model, the van der Waals force is the dipole between the molecules or the atoms of two particles, resulting in an interaction between the atoms or molecules of the two particles. Electrostatic force refers to the force generated by the interaction of double electric layers between particles. In DLVO theory, the total interaction energy between particles depends on the interaction potential energy generated by the van der Waals interaction (UVDW) and the electrostatic interaction force energy caused by the compression double layer (UEI) [48]. However, the extended DLVO (EDLVO) theory revises the classical DLVO theory by supplementing the Lewis acid–base polar (AB) force. There is a polar force between particles that can explain the repulsive force due to hydration and the electrostatic force at the hydrophilic and hydrophobic interfaces [49]. Therefore, in EDLVO theory, the total interaction energy between particles is determined by UVDW, UEI, and UAB [50].
The interaction potential energy between Fe3O4@HAAP and kaolin was analyzed via DLVO and EDLVO theory, and the results are shown in Figure 9. As observed in Figure 9a, for the two interacting kaolin particles, when the separation distance was less than 30 nm, the value of UDLVO between kaolin was positive, which indicated that the force between particles behaved as an electrostatic repulsion. However, when the separation distance was greater than 30 nm, the value turned negative, which meant the force between particles gradually changed to electrostatic attraction [51]. In addition, when the separation distance is in the range of 0–10 nm, there is a repulsive barrier between the interaction particles. The presence of the barrier meant that the repulsion potential of kaolin in the solution was greater than the kinetic energy of Braun movement, and kaolin in the solution was suspended, without instability or aggregation. Otherwise, the value of UEDLVO between particles was similar to that of UDLVO; this was because, in the kaolin solution, the mutual potential energy between the particles is still contributed by UEI.
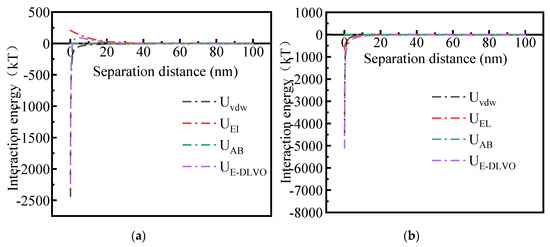
Figure 9.
The interaction energy between Fe3O4@HAAP and kaolin: (a) kaolin–kaolin; (b) Fe3O4@HAAP–kaolin. pH = 5.
Figure 9b shows the interaction potential energy of Fe3O4@HAAP–kaolin, represented by the dissociation curve, when Fe3O4@HAAP was added to the kaolin solution. The value of UDLVO between Fe3O4@HAAP and kaolin was negative, due to the same negative values of Uvdw and UEI, and the electrostatic force was manifested as an attractive force [52]. Hence, with the addition of Fe3O4@HAAP, the external magnetic field would cause the energy barrier of kaolin particles to be crossed, and the particles would be destabilized and aggregated. Using more accurate EDLVO theory, it is found that the value of UEDLVO in the system was also negative throughout the separation distance, and there was still no energy barrier. Based on the results, it was indicated that the influence of Lewis acid–base interaction energy UAB on the total interaction energy was negligible.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
All chemicals used in experiments are of analytical grade and available from commercial sources. Tetraethylxysilane (98.6%), diethanol amine (99%), methyl acrylate (98.5%), p-toluenesulfonic acid (99%), FeSO4·7H2O, and FeCl3·6H2O were all purchased from Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China.
3.2. Preparation of Fe3O4@HAAP
The Fe2+ and Fe3+ mixed solution was obtained by dissolving 2.7 g FeSO4·7H2O and 5.7 g FeCl3·6H2O into 100 mL deionized water. Ammonia water was added drop by drop into the solution and adjusted to a pH of 10. Then, the reaction lasted 30 min at 80 °C. The product (Fe3O4) was drawn out by a magnet and washed several times with ethanol and distilled water.
The prepared Fe3O4 was evenly dispersed in the mixture of ethanol and deionized water (volume ratio: 4:1). Ammonia water (28%) and tetraethylxysilane (98.6%) were added to the solution in turn and reacted for 6 h. Finally, Fe3O4@SiO2 was harvested by magnetic separation and freeze-drying.
Methyl N (10 mL) and n-dihydroxyethyl-3-aminopropionate (9.1 mL) were produced via mixing methyl alcohol, diethanolamine, and methyl acrylate adequately in a three-mouth flask with a reaction for 4 h at 35 °C, then heated up to 85 °C for 80 min. Trimethylolpropane (4.43 g) and p-toluenesulfonic acid (0.1 g) reacted with methyl N, n-dihydroxyethyl-3-aminopropionate to form hyperbranched amino acid polymer (HAAP) at specific conditions (120 °C for 3 h and then 100 °C for 1 h). With the addition of maleic anhydride (3.56 g) and p-toluenesulfonic acid (0.16 g), the target product Fe3O4@HAAP was obtained via the assembly of HAAP and Fe3O4@SiO2.
3.3. Characterization of Fe3O4@HAAP
The infrared spectrogram analysis of samples (Fe3O4, HAAP, and Fe3O4@HAAP) was carried out with a Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FTIR, IRTracer-100, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). The resolution was 1 cm−1, and the wavelength range was 400~4500 cm−1. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy of Fe3O4@HAAP was tested via an Escalab 250 Xi spectrometer (XPS, Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) with a monochromated source of X-rays (Al Kα, 1486.6 photo energy) as the excitation source. The surface morphology and element composition were observed with a scanning electron microscope (SEM) equipped with energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS, FlexSEM 1000, Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan) with an operating voltage of 3 kV. The magnetic property of Fe3O4@HAAP was examined using a vibrating-sample magnetometer (VSM, LakeShore 7404, Columbus, OH, USA) and the test magnetic moment range is 5 × 10−7 to 103 emu with the maximum magnetic field being 2.17 T. The zeta potential of Fe3O4@HAAP was detected by a zeta potential analyzer (2000HSA, Malvern, UK).
3.4. Application in Wastewater Treatment
In order to verify the flocculation property of Fe3O4@HAAP, kaolin suspension simulated wastewater was used as the treatment target. Different reaction conditions, such as Fe3O4@HAAP dosage, pH, and kaolin concentration, were explored. The Fe3O4@HAAP dosage range was 0~120 mg/L. The pH range was 4~10. The kaolin concentration range was 0.5~3 g/L. The reaction time was 0~30 min. In order to investigate the influence of reaction time and then discuss the flocculation kinetics, the reaction lasted for 9 h with timed sampling. In order to test the application effect in the actual water, Fe3O4@HAAP and Fe3O4 were added to the target water, respectively. The reaction was conducted under the conditions that the Fe3O4@HAAP dosage was 50 mg/L, pH = 5, and the reaction time was 30 min. Since the turbidity in the natural water was much lower than the experimental concentration, kaolin was added to the original water to bring the turbidity up to 1300~1450 NTU. In order to investigate the stability performance of Fe3O4@HAAP, the material was recycled and reused five times in kaolin treatment.
3.5. Interaction Energy Analysis of Fe3O4@HAAP and Kaolin
The Derjaguin–Landau–Verwey–Overbeek (DLVO) and extended DLVO (EDLVO) theories were used to analyze the mechanism of magnetic flocculation between Fe3O4@HAAP and kaolin. The interaction energies between magnetic aggregates include van der Waals (Uvdw), electrostatic interaction (UEI), and Lewis acid–base interaction (UAB) [7]. Herein, in the DLVO theory, the total interaction energy (UDLVO) between the surfaces of interacting particles was simulated by the sum of Uvdw and UEI. In the EDLVO theory, the total interaction energy (UEDLVO) was simulated by the sum of UDLVO and UAB. The relevant calculation formulae for computing the total interaction energies are as follows [36,53,54]:
where all the relevant parameters for equations are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
The parameters for DLVO and EDLVO equations [7,36].
3.6. Analysis Methods
The turbidity meter (WGZ-800, Shanghai Xinrui Instrument Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) was used to measure turbidity during the experiments and the removing efficiency was calculated with Equation (4):
After the experiments, the supernatant was removed from the suspensions. The magnetic particle–kaolin aggregates were collected and dispersed in deionized water (10 mL). The kaolin particles were detached from the Fe3O4 particles by employing an ultrasonic generator (50 Hz, 1200 W) for 5 min. The Fe3O4 particles were collected with a permanent (50 mm L × 50 mm W × 25 mm H, 0.38 T) and then washed three times with 10 mL deionized water. The collected Fe3O4 particles were vacuum-dried to obtain recycled Fe3O4 powder. The recycling efficiency of Fe3O4 or Fe3O4@HAAP was calculated using Equation (5):
where mo (g) and mi (g) are the initial quality of Fe3O4 or Fe3O4@HAAP, and the quality after recovery time i (i = 1, 2, 3… 5), respectively. The recovered Fe3O4 or Fe3O4@HAAP was employed in the fresh kaolin suspensions immediately without any pre-treatment.
3.7. Statistical Analysis
The significant differences in the experiment data were determined by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) via IBM SPSS 20 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). A value of p < 0.05 was considered to be significantly different.
4. Conclusions
A novel three-dimensional magnetic composite of Fe3O4@HAAP was assembled by hyperbranched amino acid composites and Fe3O4. Through characterization, it was found that the hyperbranched polymer successfully linked with Fe3O4 and exhibited a lotus leaf-like morphological structure at the micro level. The superparamagnetic properties still existed and were easily affected by magnetic fields. Fe3O4@HAAP exhibited excellent turbidity (kaolin) removing efficiency and the removing efficiency reached 94.83% when the Fe3O4@HAAP dosage was 50 mg/L, pH = 5, and the kaolin concentration was 1 g/L. The flocculation of kaolin with Fe3O4@HAAP was a rapid process; the removing efficiency was 83.85% and 91.96% at 0.25 h, as the dosages were 10 and 50 mg/L. Fe3O4@HAAP proved to have such high stability that the recycling and removing efficiency were over 97% and 92.6%, respectively, after five cycles. In DLVO and EDLVO theory analysis, the mutual potential energy of kaolin–kaolin particles were dominated by UEI, which showed electrostatic repulsion at short distances (<30 nm) and electrostatic attraction at long distances (>30 nm). When Fe3O4@HAAP was added to kaolin solution, an external magnetic field would cause the energy barrier of kaolin particles to be crossed, and the kaolin particles were destabilized and aggregated. The above results indicated that Fe3O4@HAAP would be more competitive in the treatment of ecological water due to its biodegradability and environmental friendliness in the future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Z., Q.F. and L.S.; methodology, Y.Z., Q.F. and L.S.; software, Y.L. and M.Z.; data analysis, M.Z., X.W. and J.L.; validation, Y.Z., Q.F. and L.S.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.Z., Q.F., L.S., Y.L. and M.Z.; writing—review and editing, Y.Z., Q.F., L.S., X.W. and J.L.; visualization, Y.L. and J.L.; supervision, M.Z. and X.W.; resources, Y.Z., Q.F. and L.S.; project administration and funding acquisition, Y.Z., Q.F. and L.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32300047), the Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province, China (212300410138), the Program of Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China (23KJB550004), the High-level Innovation and Entrepreneurship Talents Introduction Program of Jiangsu Province of China (JSSCBS20230419), the Intellectual Property Projects in Henan Province (HNGD2024011), and the Student Research and Training Program of Henan University of Science and Technology (No. 2023182; 2024188).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Shiyanjia lab (www.shiyanjia.com) for XPS and VSM analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Park, W.I.; Jeong, S.; Im, S.J.; Jang, A. High turbidity water treatment by ceramic microfiltration membrane: Fouling identification and process optimization. Environ. Technol. Inno. 2020, 17, 100578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Roos, A.J.; Gurian, P.L.; Robinson, L.F.; Rai, A.; Zakeri, I.; Kondo, M.C. Review of Epidemiological Studies of Drinking-Water Turbidity in Relation to Acute Gastrointestinal Illness. Environ. Health Persp. 2017, 125, 086003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, K.S.; Manu, B.; Azhoni, A. Sustainable treatment of paint industry wastewater: Current techniques and challenges. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 296, 113105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayarkhuu, B.; Byun, J. Optimization of coagulation and sedimentation conditions by turbidity measurement for nano- and microplastic removal. Chemosphere 2022, 306, 135572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, Y.M.; Shao, G.Y.; Zhang, W.J.; Chen, J.J.; Qu, Y.X.; Zhang, F.; Tian, S.C.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Ren, Z.Q. The degradation of printing and dyeing wastewater by manganese-based catalysts. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 828, 154390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, R.; Nicu, R.; Latour, I.; Lupei, M.; Bobu, E.; Blanco, A. Efficiency of chitosans for the treatment of papermaking process water by dissolved air flotation. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 231, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Du, S.; Cheng, P.; Liang, W. Magnetic coagulation and flocculation of kaolin suspension using Fe3O4 with plant polyphenol self-assembled flocculants. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, K.; Brighu, U.; Choudhary, A. Pilot-scale coagulation of organic and inorganic impurities: Mechanisms, role of particle concentration and scale effects. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, X.Y.; Qin, L.L.; Li, H.J.; Liang, W.Y. Magnetic coagulation and flocculation of a kaolin suspension using Fe3O4 coated with SiO2. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abirhire, O.; Davies, J.M.; Guo, X.L.; Hudson, J. Understanding the factors associated with long-term reconstructed turbidity in Lake Diefenbaker from Landsat-imagery. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 724, 138222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.H.; Ge, Z.H.; Liu, K.X.; Wang, C.; Wu, T.; Zhang, J.B. Application of calcium peroxide for efficient treatment of surface water turbidity: Mechanisms and microbial community responses. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhou, W.B.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Peng, C.; Peng, Y. Study on the preparation of polysilicate ferric flocculant and its treatment of high turbidity tailings water. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 44, 102457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiavola, A.; Di Marcantonio, C.; D’Agostini, M.; Leoni, S.; Lazzazzara, M. A combined experimental-modeling approach for turbidity removal optimization in a coagulation-flocculation unit of a drinking water treatment plant. J. Process Contr. 2023, 130, 103068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.Y.; Fu, K.; Fu, X.; Guan, Q.Q.; Ding, L.; Shi, J.; Zhu, G.C.; Zhang, X.X.; Zhang, S.H.; Jiang, L.Y. Flocculation properties and kinetic investigation of polyacrylamide with different cationic monomer content for high turbid water purification. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 182, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.H.; He, X.W.; Wei, M.; Li, F.Q.; Hou, P.; Zhang, C.H. Magnetic Flocculation Treatment of Coal Mine Water and a Comparison of Water Quality Prediction Algorithms. Mine Water Environ. 2019, 38, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.J.; Hou, J.; Pan, Z.G.; Wu, M.; Zhang, M.Z.; Yin, X.X.; Wu, J.; Miao, L.Z.; Liu, Q.D. A novel La(OH)3 decorated co-graft tannin and polyethyleneimine co-coating magnetic adsorbent for effective and selective phosphate removal from natural water and real wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 369, 133345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Yao, Y.X.; Wang, J.; Li, B.; Dou, L.P.; Wei, L.F.; Zhuo, B.; Zhang, W.; Hu, X.Y. Effective dewatering and resourceful utilization of high-viscosity waste slurry through magnetic flocculation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 425, 136014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.K.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, I.; Jeon, H. Efficient separation performance of suspended soil and strontium from aqueous solution using magnetic flocculant. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, T.; Zhang, S.; Qi, D.M.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, H.T. Enhanced demulsification from aqueous media by using magnetic chitosan-based flocculant. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2018, 518, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.J.; Agbakpe, M.; Wu, Z.Y.; Kuang, L.Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.Q. Influences of Surface Coating, UV Irradiation and Magnetic Field on the Algae Removal Using Magnetite Nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1190–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Fan, Q.L.; Liu, Y.H.; Wang, S.W.; Guo, X.D.; Guo, L.J.; Zhu, M.C.; Wang, X. Preparation and Application of Amino-Terminated Hyperbranched Magnetic Composites in High-Turbidity Water Treatment. Molecules. 2023, 28, 6787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.F.; Xu, Z.J.; Zhang, D.H. Synthesis and application of epoxy-ended hyperbranched polymers. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 343, 283–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.K.; Xu, Q.Q.; Yan, C.; Li, J.; Zhou, W.F.; Gao, H.X.; Zhang, S.B.; Lu, R.H. Hyperbranched aromatic polyamide modified magnetic nanoparticles for the extraction of benzoylurea insecticides. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 1939–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Tang, R.; Li, Q.; Li, Z. Functional hyperbranched polymers with advanced optical, electrical and magnetic properties. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 3997–4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, D.; Yan, P.; Nie, J.; Sharma, V.K.; Wang, C.Y. Highly efficient and selective removal of mercury ions using hyperbranched polyethylenimine functionalized carboxymethyl chitosan composite adsorbent. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 358, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavand, A.; Anton, N.; Vandamme, T.; Serra, C.A.; Chan-Seng, D. Synthesis and functionalization of hyperbranched polymers for targeted drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2020, 321, 285–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Qu, R.J.; Xu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, C.M.; Ji, C.N.; Wang, Y. Fabrication of Triethylenetetramine Terminal Hyperbranched Dendrimer-Like Polymer Modified Silica Gel and Its Prominent Recovery Toward Au (III). Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuchkina, N.V.; Haskell, A.K.; Sorokina, S.A.; Torozova, A.S.; Nikoshvili, L.Z.; Sulman, E.M.; Stein, B.D.; Morgan, D.G.; Bronstein, L.M.; Shifrina, Z.B. Pd Catalyst Based on Hyperbranched Polypyridylphenylene Formed In Situ on Magnetic Silica Allows for Excellent Performance in Suzuki-Miyaura Reaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 22170–22178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosecki, M.; Urbaniak, M.; Martinho, N.; Gosecka, M.; Zloh, M. Evaluation of Encapsulation Potential of Selected Star-Hyperbranched Polyglycidol Architectures: Predictive Molecular Dynamics Simulations and Experimental Validation. Molecules 2023, 28, 7308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, L.; Liu, J.S.; Liu, X.Y.; Chen, C.H.; Li, G.Y.; Meng, Y.F. Graphene oxides cross-linked with hyperbranched polyethylenimines: Preparation, characterization and their potential as recyclable and highly efficient adsorption materials for lead(II) ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 285, 698–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, S.Y.; Liu, Q.W.; Fan, Z.Z.; Tong, Q.L.; Cai, L.; Fu, Y.F. Magnetic Hyperbranched Molecular Materials for Treatment of Oily Sewage Containing Polymer in Oilfield Compound Flooding. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 865832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.C.; Wang, Z.W.; Yue, R.R.; Gao, F.; Ren, R.L.; Wei, J.F.; Wane, X.L.; Kong, Z.Y. Functional group-rich hyperbranched magnetic material for simultaneous efficient removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Wang, X.Y.; Du, S.C.; Liang, W.Y. Synthesis of chitosan-based grafting magnetic flocculants for flocculation of kaolin suspensions. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 139, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Xu, X.J.; Nie, R.; Feng, L.; Li, X.H.; Liu, B.Z. Chitosan Modified Cationic Polyacrylamide Initiated by UV-H2O2 for Sludge Flocculation and New Insight on the Floc Characteristics Study. Polymers 2020, 12, 2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.Y.; Fu, X.; Xia, W.; Zhang, R.; Fu, K.; Wu, G.Y.; Jia, B.T.; Li, S.; Li, J.C. Removal of emulsified oil from water by using recyclable chitosan based covalently bonded composite magnetic flocculant: Performance and mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.Y.; Liu, C.; Qin, L.L.; Liang, W.Y. Self-assembly of Fe3O4 with natural tannin as composites for microalgal harvesting. Fuel 2022, 321, 124038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demircan, D.; Zhang, B.Z. Facile synthesis of novel soluble cellulose-grafted hyperbranched polymers as potential natural antimicrobial materials. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 1913–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.J.; Jin, Y.J.; Wang, B.; Tian, H.F.; Kang, K.; Men, S.; Weng, Y.X. High-toughening modification of polylactic acid by long-chain hyperbranched polymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 51295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, S.; Sardar, M.; Satpati, B.; Kumar, S.; Banerjee, S. Magnetization Enhancement of Fe3O4 by Attaching onto Graphene Oxide: An Interfacial Effect. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 21356–21365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Wang, H.F.; Shao, J.W.; Zhang, K.F.; Wu, J.; Yan, L.F. S4-Containing hyperbranched polymer modified graphene oxide as strong linker for both rubber and carbon black to enhance the crosslinking and mechanical properties of nitrile butadiene rubber. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 129336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Aal, M.; Said, A.A.; Goda, M.N.; Zeid, E.F.A.; Ibrahim, S.M. Fe3O4@CMC-Cu magnetic nanocomposite as an efficient catalyst for reduction of toxic pollutants in water. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 385, 122317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Luo, Y.; Bian, M.; Guo, X.; Zhang, N. Synthesis of easily renewable and recoverable magnetic PEI-modified Fe3O4 nanoparticles and its application for adsorption and enrichment of tungsten from aqueous solutions. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 330, 121703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.N.; Han, P.; Gu, Z. Grafting of a novel hyperbranched polymer onto carbon fiber for interfacial enhancement of carbon fiber reinforced epoxy composites. Mater. Design. 2021, 200, 109456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.C.; Song, G.J.; Zhang, X.C.; Zhou, S.F.; Liu, Y.Q.; Zhang, L.Y. Attaching SiO2 nanoparticles to GO sheets via amino-terminated hyperbranched polymer for epoxy composites: Extraordinary improvement in thermal and mechanical properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 157, 110677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.Y.; Chen, Z.X.; Li, Z.H.; Hu, M.Q.; Dong, X.Y.; Xia, Q.H. Controlled synthesis of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol-imprinted amino-functionalized nano-Fe3O4-polymer magnetic composite for highly selective adsorption. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 481, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.Y.; Zou, Y.H.; Sun, Q.; Liu, S.; Sun, M.L.; Zheng, H.L.; Li, H. Copolymers functionalized with quaternary ammonium compounds under template chain exhibit simultaneously efficient bactericidal and flocculation properties: Characterization, performance and mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, R.; Ghorai, S.; Pal, S. Flocculation characteristics of polyacrylamide grafted hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose: An efficient biodegradable flocculant. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 229, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Zhou, X.T.; Xi, H.P.; Sun, J.X.; Liang, X.L.; Wei, J.; Xiao, X.; Liu, Z.G.; Li, S.W.; Liang, Z.S.; et al. Interpretation of adhesion behaviors between bacteria and modified basalt fiber by surface thermodynamics and extended DLVO theory. Colloid Surf. B. 2019, 177, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanudjaja, H.J.; Chew, J.W. Assessment of oil fouling by oil-membrane interaction energy analysis. J. Membrane. Sci. 2018, 560, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paula, F.L.O.; Castro, L.L.; Cassiano, T.S.A.; dos Santos, S.G.; Gomide, G.; Depeyrot, J.; Campos, A.F.C. pH-dependent phase transitions in ferrofluids: A Monte Carlo simulation study using an extended DLVO model. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 658, 130578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Li, Y.B.; Liu, J.X.; Ying, H.W.; Han, H.F.; Chen, X. Enhanced dispersing properties of kaolin due to high-strength kneading process. Appl. Clay. Sci. 2024, 247, 107218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, D.; Qv, M.; Liu, D.Y.; Tang, C.M.; Wang, W.; Wu, Q.R.; Yin, Z.H.; Zhu, L.D. Structural insights into mechanisms of rapid harvesting of microalgae with pH regulation by magnetic chitosan composites: A study based on E-DLVO model and component fluorescence analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 456, 141071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbakpe, M.; Ge, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Kobylarz, P. Algae harvesting for biofuel production: Influences of UV irradiation and polyethylenimine (PEI) coating on bacterial biocoagulation. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 166, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.A.; Kim, S.B. DLVO and XDLVO calculations for bacteriophage MS2 adhesion to iron oxide particles. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2015, 181, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).