Temperature-Sensitive Sensors Modified with Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide): Enhancing Performance through Tailored Thermoresponsiveness
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
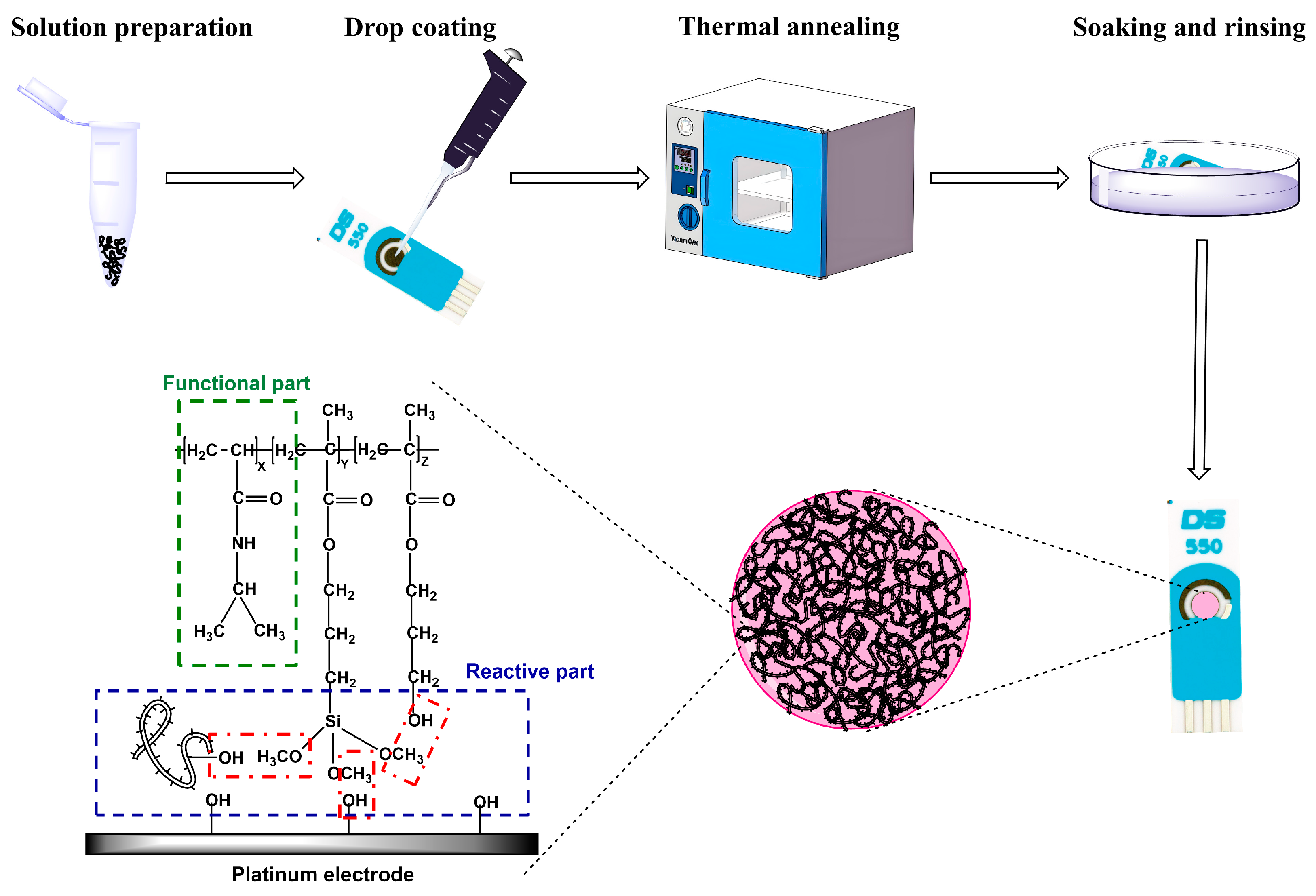
2.1. Preparation of P(NIPAM-co-TMSPMA-co-HPMA) Copolymer Film-Modified Platinum Working Electrode
2.2. Characterization of P(NIPAM-co-TMSPMA-co-HPMA) Copolymer Film Modified Platinum Working Electrode
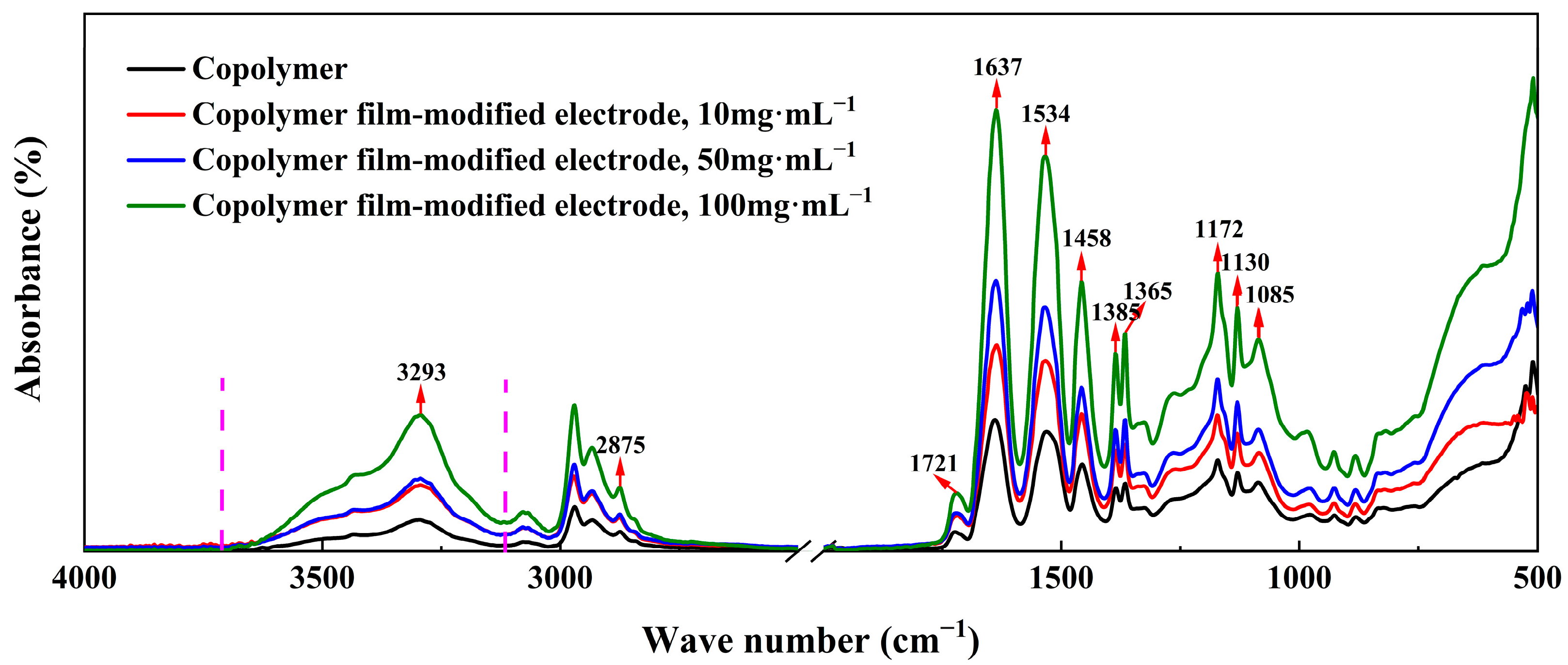
2.2.1. Chemical Composition
2.2.2. Grafting Density
2.2.3. Equilibrium Swelling
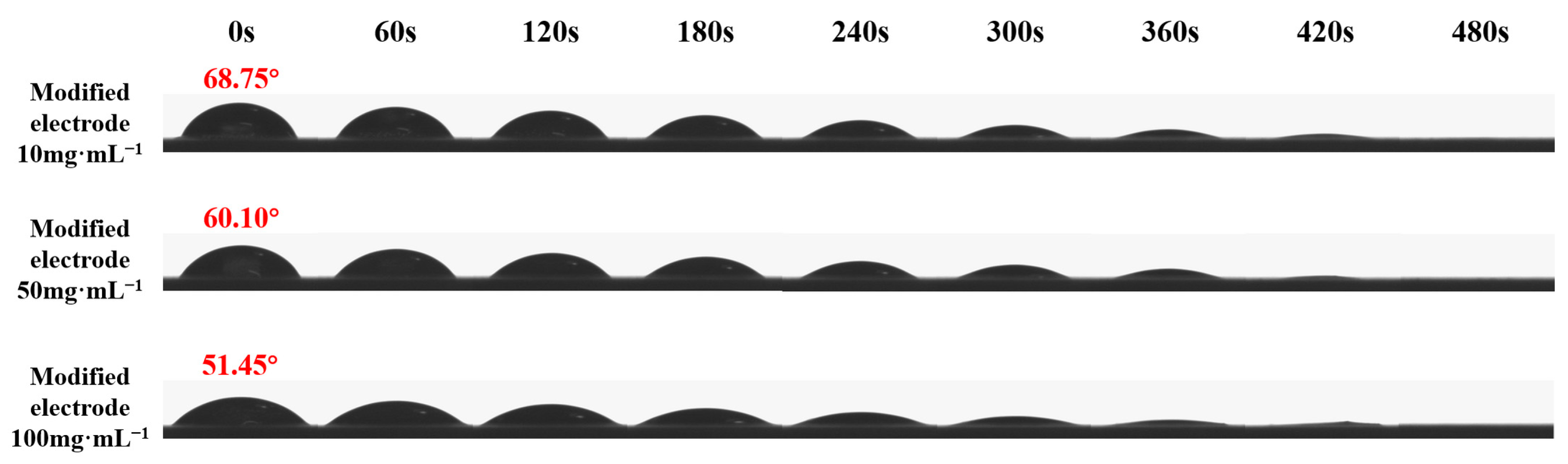
2.2.4. Surface Wettability
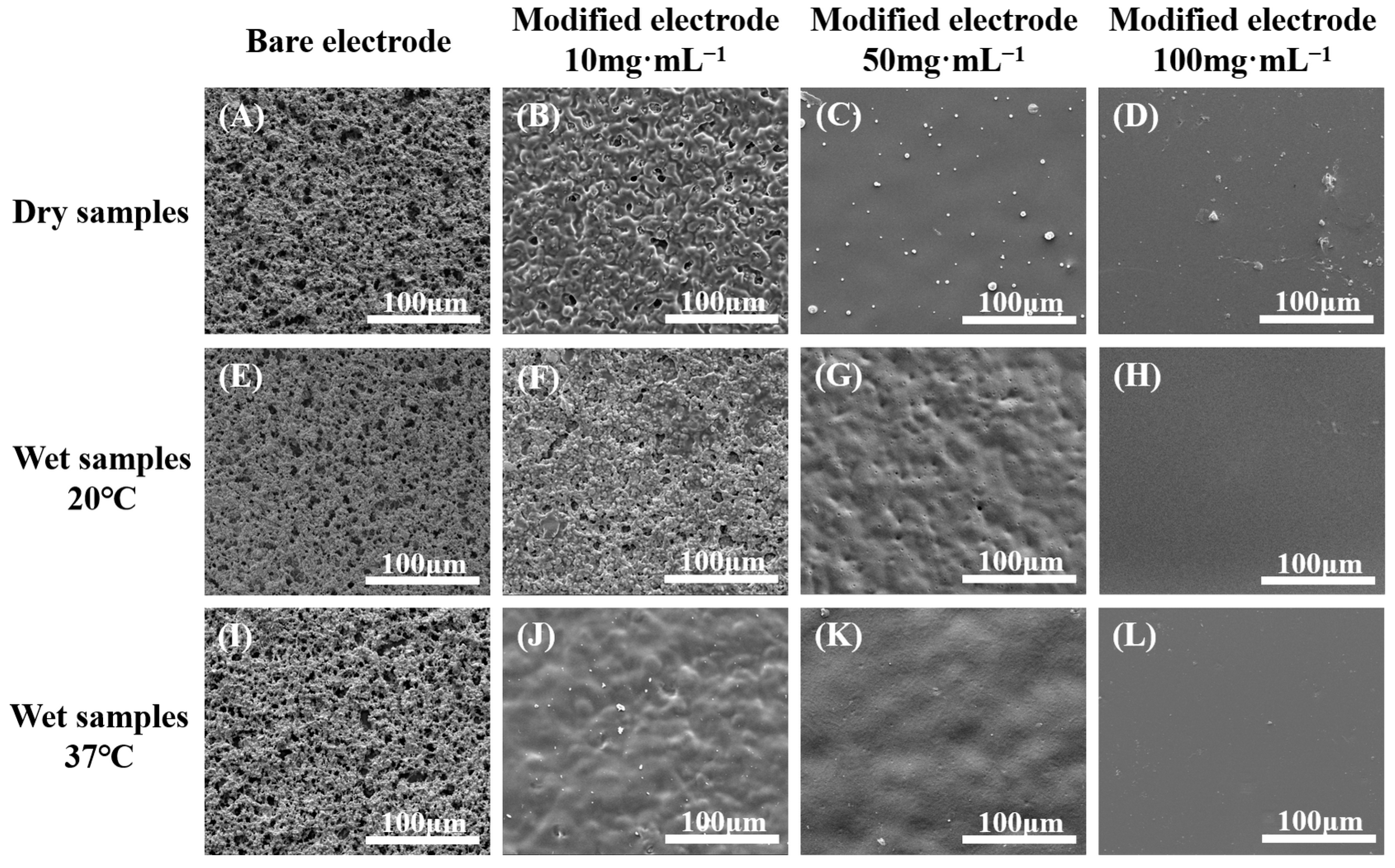
2.2.5. Surface Morphology
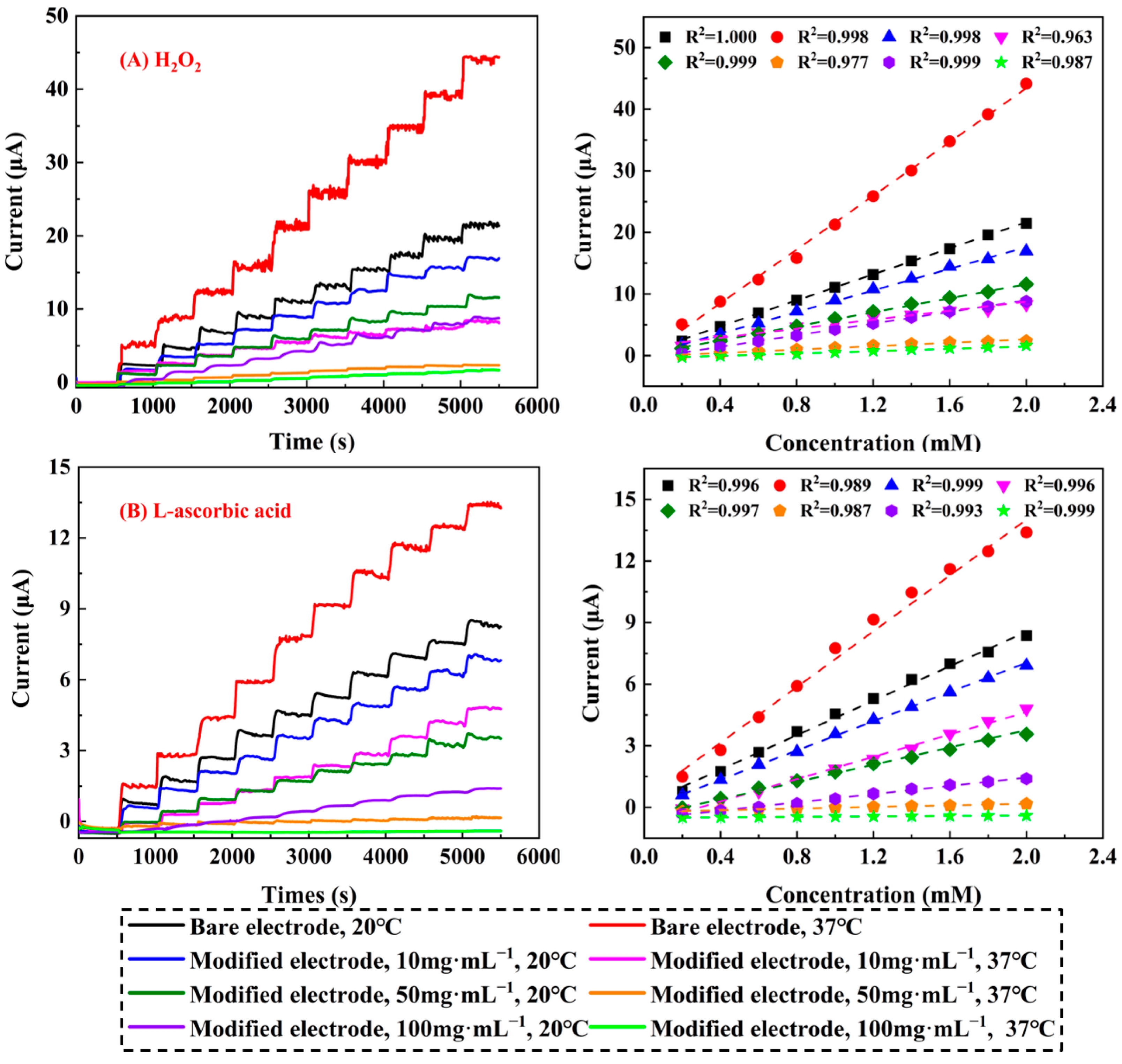
2.2.6. Amperometric Response
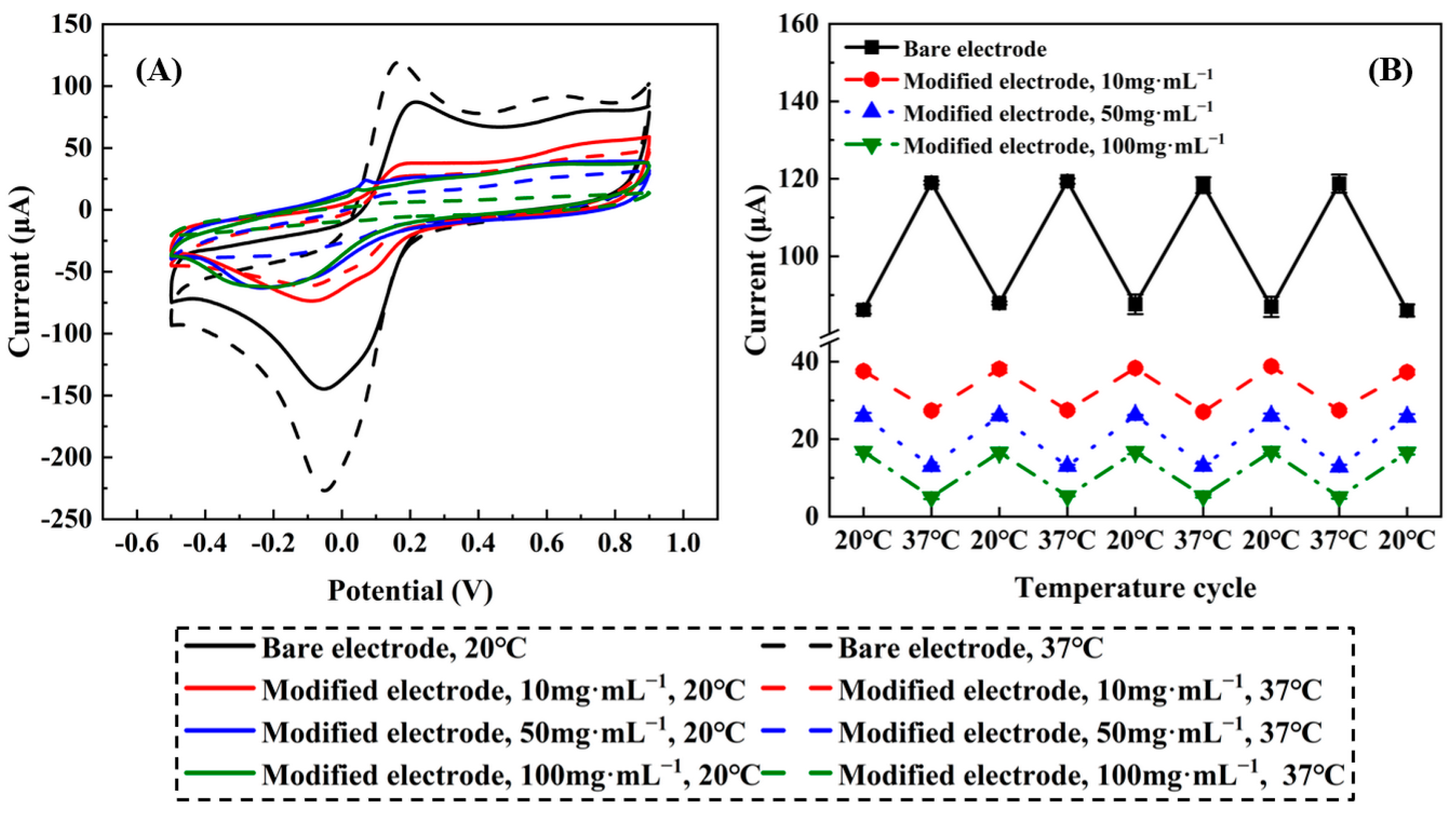
2.2.7. Cyclic Voltammograms
2.2.8. Stability, Repeatability and Selectivity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of P(NIPAM-co-TMSPMA-co-HPMA) Copolymer Film Modified Platinum Working Electrode
3.3. Characterization of P(NIPAM-co-TMSPMA-co-HPMA) Copolymer Film-Modified Platinum Working Electrodes
3.3.1. Chemical Composition
3.3.2. Grafting Density
3.3.3. Equilibrium Swelling
3.3.4. Surface Wettability
3.3.5. Surface Morphology
3.3.6. Amperometric Response
3.3.7. Cyclic Voltammograms
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, Y.X.; Wang, C.F.; Chang, C.J.; Lu, C.H.; Chen, J.K. Fabrication of scalable poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)/gold nanoparticles composite ring array as LSPR sensor for label-free biosensor application. Sens. Actuators B 2023, 375, 132875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polley, N.; Werner, P.; Balderas-Valadez, R.F.; Pacholski, C. Bottom, top, or in between: Combining plasmonic nanohole arrays and hydrogel microgels for optical fiber sensor applications. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 9, 2102312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahar, D.; Gholamhossein, S. A new approach for synthesis of cyclic poly(N-isopropylacrylamide), for applying in biomaterial applications. Polym. Bull. 2024, 81, 929–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Fan, X.; Wu, Z.; Wen, X.; Xie, W.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, P.; et al. Phase transition behaviors of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) nanogels with different compositions induced by (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate and ethyl gallate. Molecules 2023, 28, 7823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Song, X.; Chen, D.; Qu, R.; Zhao, Y. Self-powered multifunctional organic hydrogel based on poly(acrylic acid-N-isopropylacrylamide) for flexible sensing devices. Langmuir 2023, 39, 6151–6159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dan, X.; Li, R.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Wang, G.; Li, Z. Thermal-switchable sensor based on palladium-graphene composite and poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) for electrochemical detection of 4-nitrophenol. Microchem. J. 2022, 172, 106970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Feng, L.; Gu, X.; Zhang, C. Electro-conductive and temperature-sensitive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) composite hydrogels with improved mechanical properties. Appl. Nanosci. 2020, 10, 2189–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogenboom, R.; Thijs, H.M.L.; Jochems, M.J.H.C.; Van Lankvelt, B.M.; Fijten, M.W.M.; Schubert, U.S. Tuning the LCST of poly(2-oxazoline)s by varying composition and molecular weight: Alternatives to poly(N-isopropylacrylamide). Chem. Commun. 2008, 44, 5758–5760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yim, H.; Kent, M.S.; Mendez, S.; Lopez, G.P.; Satija, S.; Seo, Y. Effects of grafting density and molecular weight on the temperature-dependent conformational change of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) grafted chains in water. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 3420–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.W.; Hsu, C.W.; Hsieh, C.C. Numerical design and experimental realization of a PNIPAM-based micro thermosensor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 8591–8600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rullyani, C.; Singh, M.; Li, S.H.; Sung, C.F.; Lin, H.C.; Chu, C.W. Stimuli-responsive polymer as gate dielectric for organic transistor sensors. Org. Electron. 2020, 85, 105818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrinho, J.A.; Júnior, G.A.B.; Mazali, I.O.; Sigoli, F.A. Water-soluble poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) nanoparticles grafted to trivalent lanthanide complexes as highly sensitive ratiometric nanothermometers. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 8068–8075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuguchi, M.; Fujii, S. HCl gas sensor coating based on poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) nanoparticles prepared from water-methanol binary solvent. Sensors 2018, 18, 3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Q. Detection of the self-assembly of poly-(N-isopropylacrylamide) on gold based on microcantilever sensor. Acta Phys. Sin. 2009, 58, 6122–6127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gant, R.M.; Abraham, A.A.; Hou, Y.; Cummins, B.M.; Grunlan, M.A.; Coté, G.L. Design of a self-cleaning thermoresponsive nanocomposite hydrogel membrane for implantable biosensors. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 2903–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ting, Z.; Liu, G.; Leong, W.; Liu, C.; Kwok, M.H.; Ngai, T.; Liu, R. Hybrid nanodiamond quantum sensors enabled by volume phase transitions of hydrogels. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Huo, C.; Ji, Y.; Xu, S.; Zhang, C.; Xia, C.; Liu, H.; Zhang, R.; Jin, Y.; Miao, Z. A molecularly imprinted sensor based on thermo-responsive calcium alginate nanohydrogels for lysozyme detection. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2023, 301, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirel, G.; Rzaev, Z.; Patir, S.; Pişkin, E. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) layers on silicon wafers as smart DNA-sensor platforms. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2009, 9, 1865–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuguchi, M.; Takaoka, K.; Kai, H. HCl gas adsorption/desorption properties of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) brushes grafted onto quartz resonator for gas-sensing applications. Sens. Actuators B 2015, 208, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Li, X.; Serpe, M.J. Stimuli-responsive microgel-based surface plasmon resonance transducer for glucose detection using a competitive assay with concanavalin A. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2019, 1, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culver, H.R.; Sharma, I.; Wechsler, M.E.; Anslyn, E.V.; Peppas, N.A. Charged poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) nanogels for use as differential protein receptors in a turbidimetric sensor array. Analyst 2017, 142, 3183–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Pan, F.; Zhao, X.; Yaseen, M.; Padia, F.; Coffey, P.; Freund, A.; Yang, L.; Liu, T.; Ma, X.; et al. Thermoresponsive copolymer nanofilms for controlling cell adhesion, growth, and detachment. Langmuir 2010, 26, 17304–17314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Wu, L.; Yang, L. Fabrication and characterization of thermoresponsive composite carriers: PNIPAAm-grafted glass spheres. e-Polymers 2021, 21, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Lei, J.; Gu, S.; Leng, X.; Liu, C.; Yang, L. Regulation of thermoresponsive PNIPAAm copolymers with enhanced hydrophilicity via NVP moieties. Mater. Rep. 2023, 37, 21100186-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyiranshuti, L.; Andrews, E.R.; Povolotskiy, L.I.; Gomez, F.M.; Bartlett, N.R.; Royappa, A.T.; Rheingold, A.L.; Seitz, W.R.; Planalp, R.P. Development of a ratiometric fluorescent Cu(II) indicator based on poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) thermal phase transition and an aminopyridyl Cu(II) ligand. Molecules 2023, 28, 7097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Gu, S.; Wu, L.; Yang, L. Preparation and characterization of thermoresponsive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) copolymers with enhanced hydrophilicity. e-Polymers 2020, 20, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, S.; Zolali, A.M.; Jalali, A.; Park, C.B. Strong, highly hydrophobic, transparent, and super-insulative polyorganosiloxane-based aerogel. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 413, 127488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dam, X.T.; Dao, P.H.; Nguyen, A.H.; Pham, T.T.G.; Nguyen, T.H.; Nguyen, T.C.; Ly, T.N.L.; Thai, H. Enhancing anticorrosive performance of epoxy-based zno nanocomposite coatings via 3-(trimethoxysilyl)propyl methacrylate modification. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2024, 141, e55466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Chen, Q.; Hempenius, M.A.; Vancso, G.J. Polymer brushes: Probing the collapse dynamics of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) brushes by AFM: Effects of co-nonsolvency and grafting densities. Small 2011, 7, 1440–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhu, Y. Facile method to prepare smooth and homogeneous polymer brush surfaces of varied brush thickness and grafting density. Langmuir 2009, 25, 13448–13455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, I.; Bae, J.W.; Jee, K.S.; Lee, J.W.; Park, K.D.; Yuk, S.H. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-N-vinylpyrrolidone) as a novel implant materials: Preparation and thermo-gelling behavior. Macromol. Res. 2002, 10, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Liu, J.; Fryxell, G.E.; Young, J.S.; Engelhard, M.H.; Alford, K.L.; Rieke, P.C. Surfaces with reversible hydrophilic/hydrophobic characteristics on cross-linked poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels. Langmuir 2000, 16, 8016–8023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Wei, J.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Chen, X.; Song, X.; Chen, J. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-vinyl acetate)/poly(L-lactic acid) composite with thermoresponsive wettability. Colloids Surf. A 2022, 636, 128179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, Y.G.; Aoki, T.; Sanui, K.; Ogata, N.; Sakurai, Y.; Okano, T. Temperature-modulated platelet and lymphocyte interactions with poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-grafted surfaces. Biomaterials 1995, 16, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.Q. Preparation and thermosensitivity of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels with graded structure. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 568, 400–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagase, K.; Matsuda, J.; Takeuchi, A.; Ikemoto, Y. Hydration and dehydration behaviors of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)- grafted silica beads. Surf. Interfaces 2023, 40, 103058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, M.; Lopes, I.C.; Vadgama, P. A preliminary electrochemical study of crosslinked albumin and collagen membranes as diffusion barriers for potentially degradable chronic wound biosensors. Electrochem. Sci. Adv. 2022, 2, e2100132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacanovska, A.; Rong, Z.; Schmidt, M.; Russell, P.S.J.; Vadgama, P. Bio-sensing using recessed gold-filled capillary amperometric electrodes. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398, 1687–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poh, C.K.; Lim, S.H.; Pan, H.; Lin, J.; Lee, J.Y. Citric acid functionalized carbon materials for fuel cell applications. J. Power Sources 2008, 176, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, X.; Tian, J. Electrocatalytic oxidation of methanol at 2-aminophenoxazin-3-one- functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes supported PtRu nanoparticles. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 7114–7120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricoli, A.; Bo, R. Nanoparticle-based biomedical sensors. Front. Nanosci. 2020, 15, 247–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, N.; Karawdeniya, B.I.; Dutt, S.; Zhou, T.; Afrin, N.; Moazzam, P.; Tricoli, A.; Kluth, P. Advancements in the performance of nanopore sensing and its implications towards the identification of biomarkers. Biophys. J. 2023, 122, 1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biazar, E.; Khorasani, M.T.; Joupari, M.D. Cell adhesion and surface properties of polystyrene surfaces grafted with poly(N-isopropylacrylamide). Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2013, 31, 1509–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daumann, K.; Frost, S.; Ulbricht, M. Tunable and switchable nanoparticle separation with thermo-responsive track-etched membranes prepared by controlled surface-initiated polymerization of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide). RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 21028–21038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, B.Y.; Wei, H.L.; Hu, C.W.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Yang, S.; Wang, G.; Shen, Y.M.; Li, J.J. Preparation of ph/temperature-sensitive semi-interpenetrating network hydrogel adsorbents from sodium alginate via photopolymerization for removing methylene blue. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 21, 227–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheswari, B.; Jagadeesh Babu, P.E.; Agarwal, M. Role of N-vinyl 2-pyrrolidinone on the thermoresponsive behavior of PNIPAm hydrogel and its release kinetics using dye and vitamin-B12 as model drug. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2014, 25, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample | Wf—W0 (mg) | Wwet,20°C—Wdry,20°C (mg) | Wwet,37°C—Wdry,37°C (mg) | dg (mg·cm−2) | ESR20°C | ESR37°C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modified electrode, 10 mg·mL−1 | 0.31 ± 0.02 | 1.59 ± 0.07 | 0.52 ± 0.11 | 2.53 ± 0.16 | 5.13 ± 0.23 | 1.68 ± 0.35 |
| Modified electrode, 50 mg·mL−1 | 0.51 ± 0.03 | 1.73 ± 0.13 | 0.72 ± 0.08 | 4.16 ± 0.24 | 3.39 ± 0.25 | 1.41 ± 0.16 |
| Modified electrode, 100 mg·mL−1 | 0.73 ± 0.08 | 2.21 ± 0.16 | 0.97 ± 0.10 | 5.95 ± 0.65 | 3.03 ± 0.22 | 1.33 ± 0.14 |
| Sample | L20°C (cm) | L37°C (cm) | t0.5,20°C (s) | t0.5,37°C (s) | D20°C (cm2·s−1) | D37°C (cm2·s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modified electrode, 10 mg·mL−1 | 0.0017 | 0.0010 | 12.67 | 23.40 | 3.166 × 10−8 | 5.932 × 10−9 |
| Modified electrode, 50 mg·mL−1 | 0.0035 | 0.0018 | 68.18 | 90.50 | 2.494 × 10−8 | 4.969 × 10−9 |
| Modified electrode, 100 mg·mL−1 | 0.0047 | 0.0022 | 145.24 | 164.47 | 2.111 × 10−8 | 4.085 × 10−9 |
| Sample | EASA20°C (m2·g−1) | EASA37°C (m2·g−1) |
|---|---|---|
| Bare electrode | 117.78 ± 4.76 | 162.66 ± 5.66 |
| Modified electrode, 10 mg·mL−1 | 64.26 ± 2.48 | 46.79 ± 0.95 |
| Modified electrode, 50 mg·mL−1 | 44.33 ± 1.49 | 28.68 ± 1.23 |
| Modified electrode, 100 mg·mL−1 | 22.17 ± 0.19 | 8.64 ± 0.86 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, L.; Qiu, G.; Sun, Y.; Sun, L.; Fan, X.; Han, Q.; Li, Z. Temperature-Sensitive Sensors Modified with Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide): Enhancing Performance through Tailored Thermoresponsiveness. Molecules 2024, 29, 3327. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143327
Yang L, Qiu G, Sun Y, Sun L, Fan X, Han Q, Li Z. Temperature-Sensitive Sensors Modified with Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide): Enhancing Performance through Tailored Thermoresponsiveness. Molecules. 2024; 29(14):3327. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143327
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Lei, Guangwei Qiu, Yuanyuan Sun, Luqiao Sun, Xiaoguang Fan, Qiuju Han, and Zheng Li. 2024. "Temperature-Sensitive Sensors Modified with Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide): Enhancing Performance through Tailored Thermoresponsiveness" Molecules 29, no. 14: 3327. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143327
APA StyleYang, L., Qiu, G., Sun, Y., Sun, L., Fan, X., Han, Q., & Li, Z. (2024). Temperature-Sensitive Sensors Modified with Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide): Enhancing Performance through Tailored Thermoresponsiveness. Molecules, 29(14), 3327. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143327







