Analysis of the Behavior of Deep Eutectic Solvents upon Addition of Water: Its Effects over a Catalytic Reaction
Abstract
1. Introduction
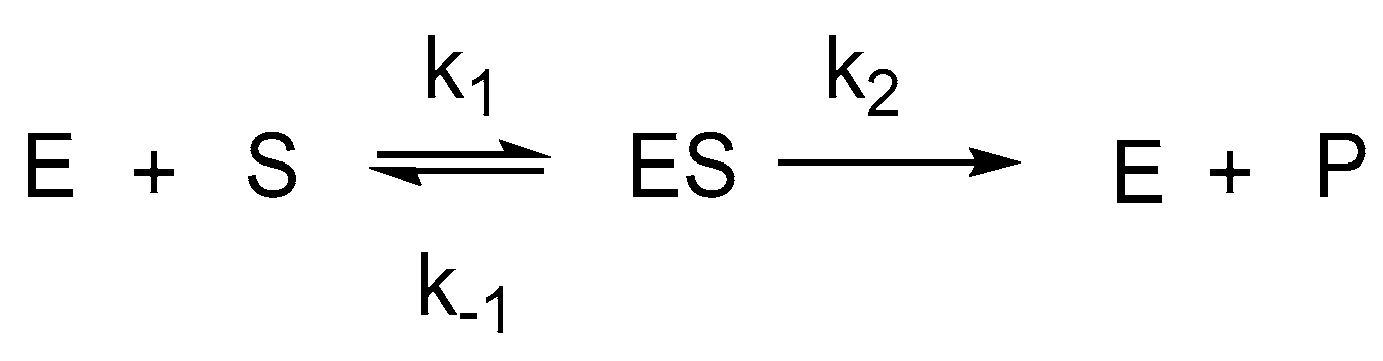
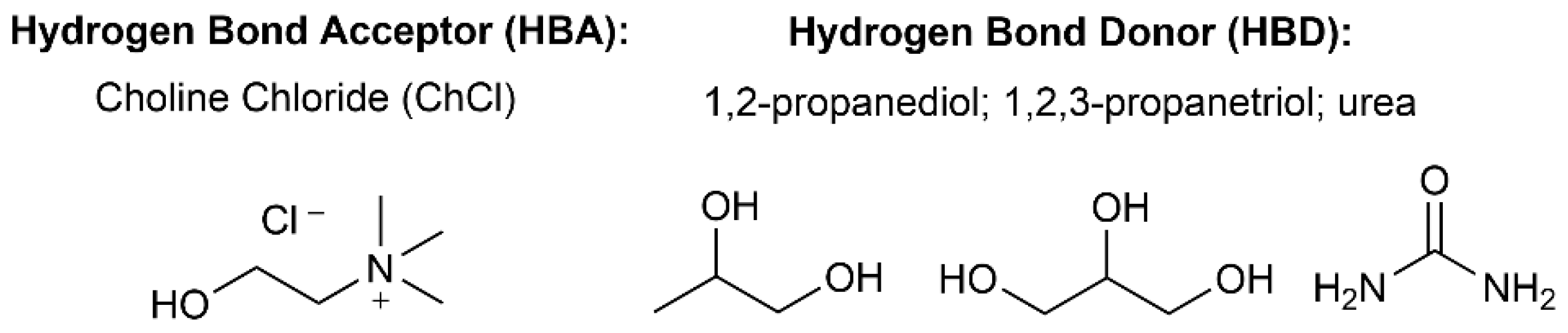
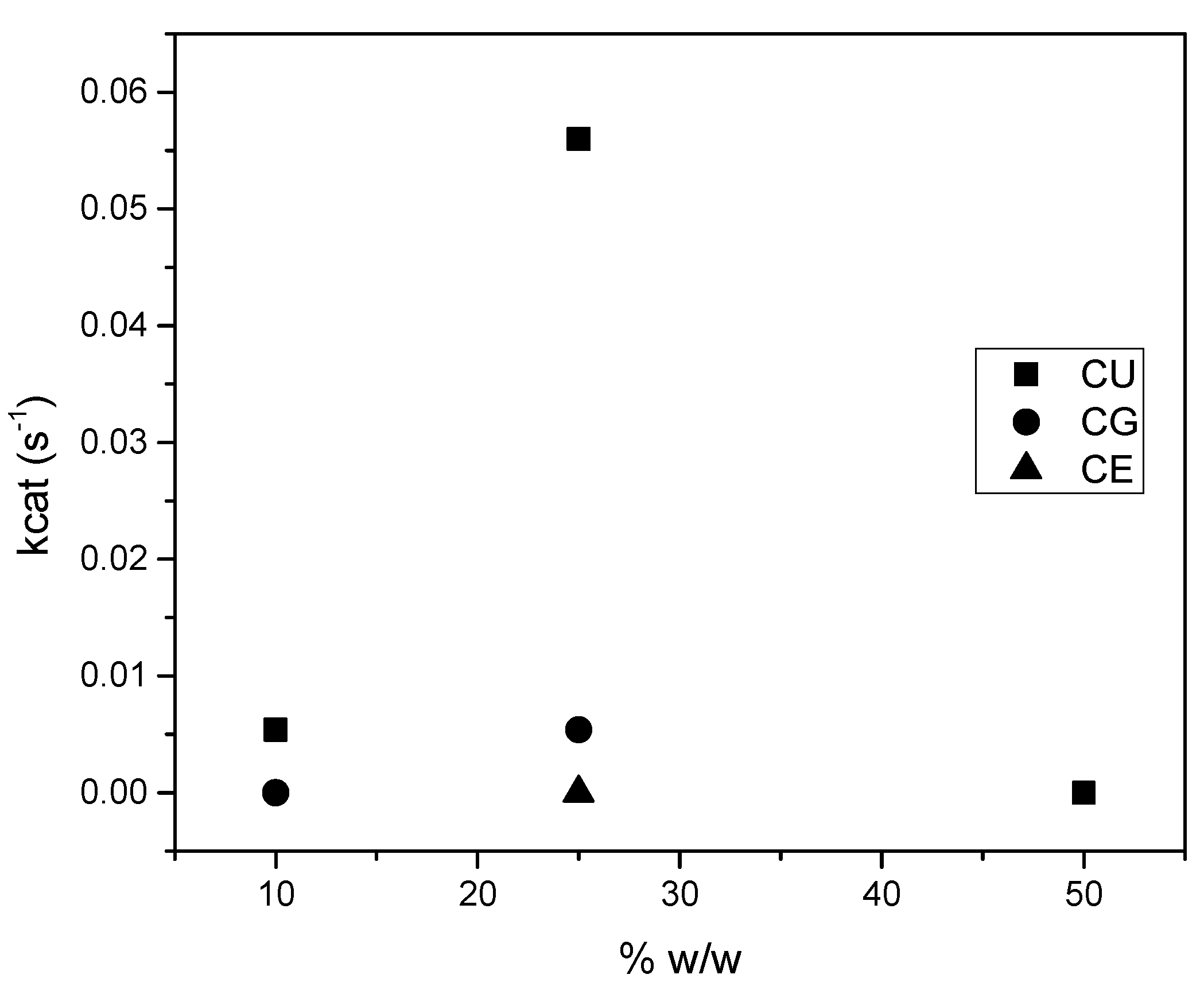
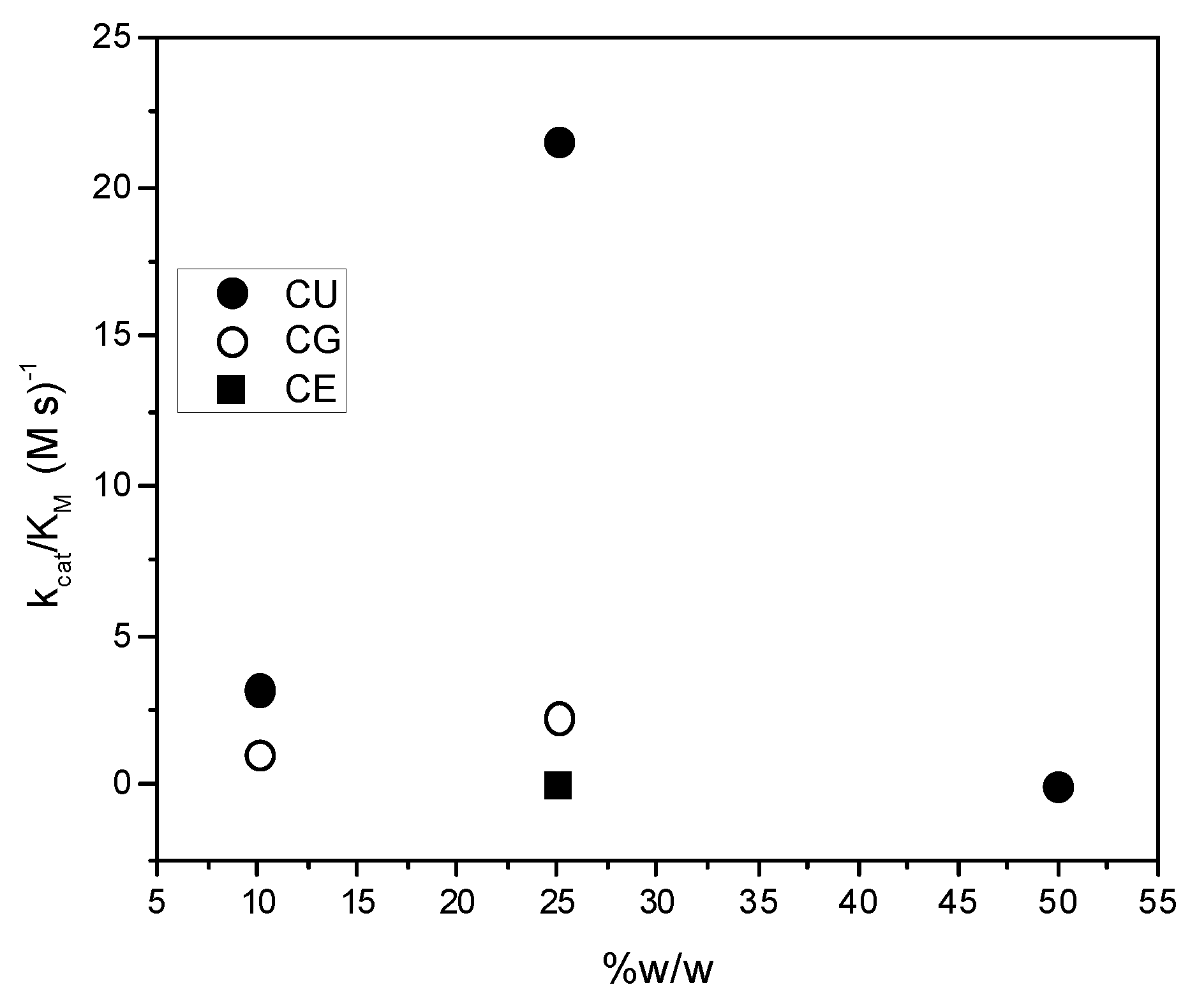
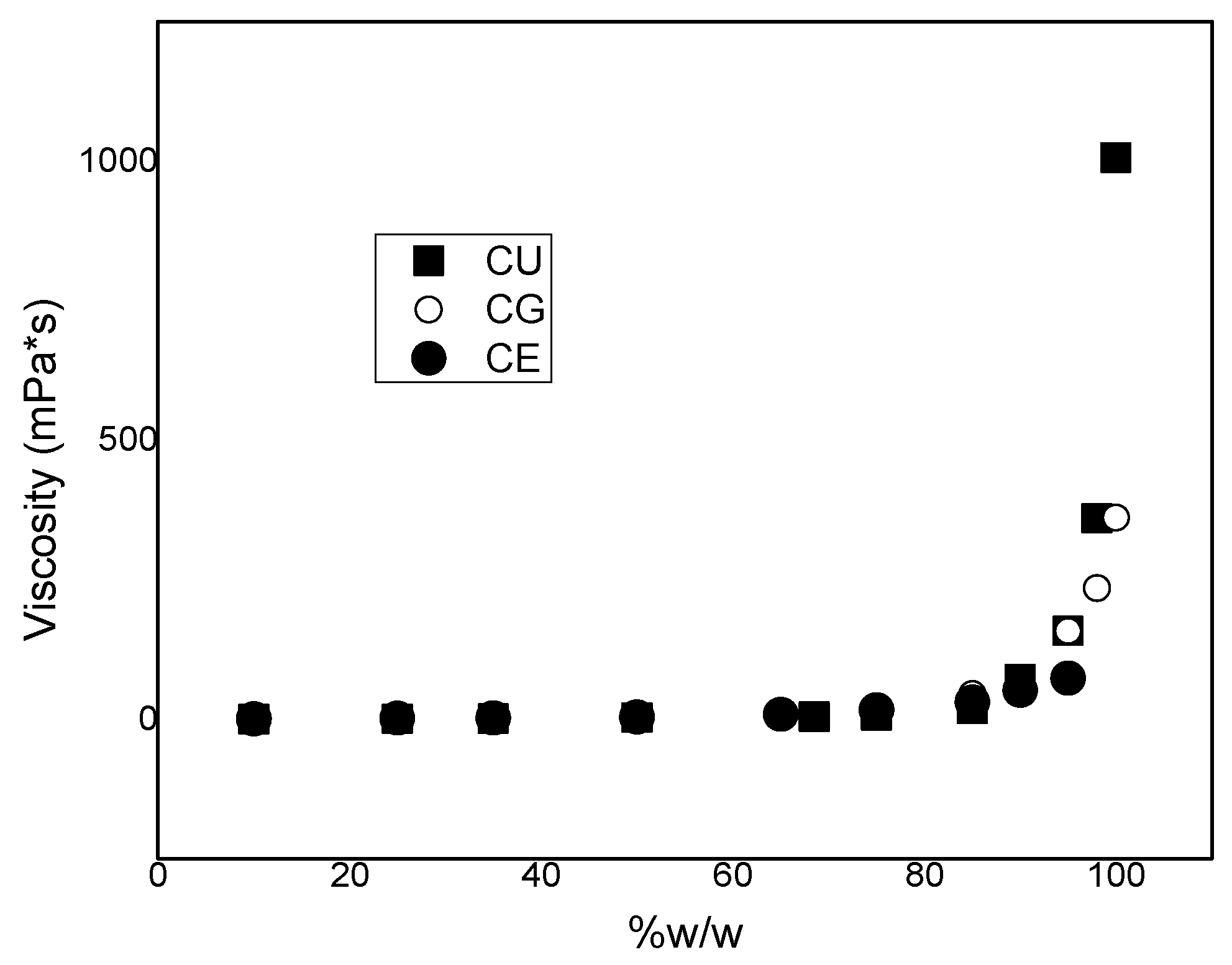
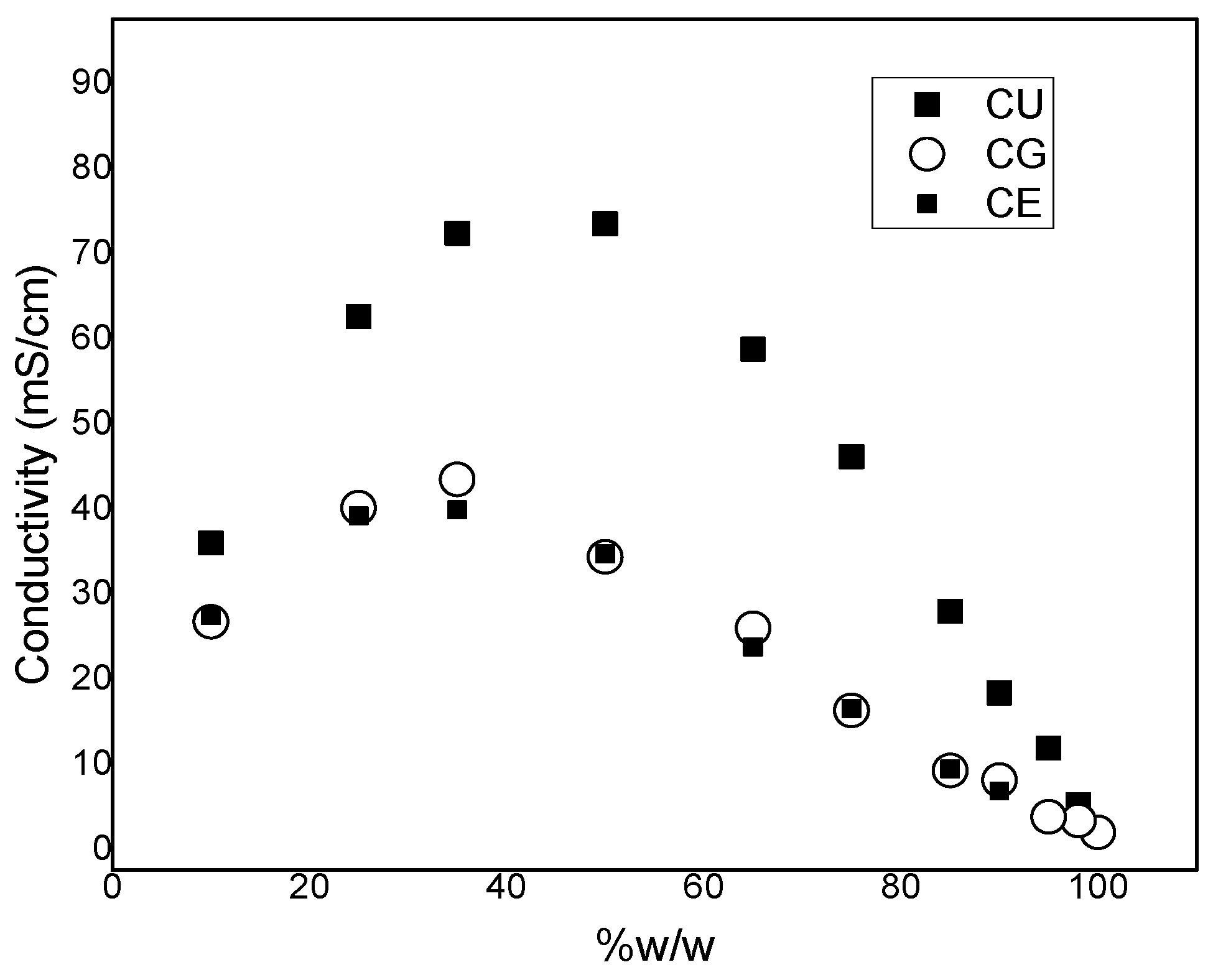
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Deep Eutectic Solvents
3.3. Mixtures
3.4. Lipase Activity Assays
3.5. Electric Conductivity Measurements
3.6. Viscosity Measurements
3.7. Acidity Measurements
3.8. Solvatochromic Solvent Parameters
3.9. Karl Fischer Method
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benkovic, S.J.; Hammes-Schiffer, S. A perspective on enzyme catalysis. Science 2003, 301, 1196–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenthaler, F.W. 100 Years “Schlüssel-Schloss-Prinzip”: What Made Emil Fischer Use this Analogy? Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1995, 33, 2364–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, E.F. Enzymes. By J.B.S. Haldane, M.A. Monographs on Biochemistry. Edited by R.H.A. Plimmer, D.Sc., and Sir F. G. Hopkins, M.A., M.B., D.Sc., F.R.S. Pp. vii+London: Longmans, Green & Co., Price 14s. J. Soc. Chem. Ind. 1930, 49, 919–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauling, L. Nature of forces between large molecules of biological interest. Nature 1948, 161, 707–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlsson, A.-C.C.; Scholfield, M.R.; Rowe, R.K.; Ford, M.C.; Alexander, A.T.; Mehl, R.A.; Ho, P.S. Increasing Enzyme Stability and Activity through Hydrogen Bond-Enhanced Halogen Bonds. Biochemistry 2018, 57, 4135–4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaelis, L.; Menten, M.L. Die Kinetik der Invertinwirkung. Biochem. Z. 1913, 49, 333–369. [Google Scholar]
- Juneidi, I.; Hayyan, M.; Hashim, M.A.; Hayyan, A. Pure and Aqueous Deep Eutectic Solvents for a Lipase-Catalysed Hydrolysis Reaction. Biochem. Eng. J. 2017, 117, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- English, B.P.; Min, W.; van Oijen, A.M.; Lee, K.T.; Luo, G.; Sun, H.; Cherayil, B.J.; Kou, S.C.; Xie, X.S. Ever-fluctuating single enzyme molecules: Michaelis-Menten equation revisited. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2006, 2, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, P. Biocatalysis in Green Solvents; Elsevier: London, UK, 2022; ISBN 9780323913065. [Google Scholar]
- Pastor, E.; Otero, C.; Ballesteros, A. Enzymatic Preparation of Mono- and Di-Stearin by Glycerolysis of Ethyl Stearate and Direct Esterification of Glycerol in the Presence of a Lipase from Candida Antarctica (Novozym 435). Biocatal. Biotransformation 1995, 12, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastas, P.T.; Warner, J.C. Green Chemistry: Theory and Practice; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000; ISBN 9780198506980. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldon, R.A. The greening of solvents: Towards sustainable organic synthesis. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2019, 18, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, R.A.; Woodley, J.M. Role of Biocatalysis in Sustainable Chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 801–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campodónico, P.R.; Calderón, C.; Alcázar, J.J.; Olivares, B.; Jaldin, L.; Suárez-Rozas, C. Exploring the behavior of Candida antarctica lipase B in aqueous mixtures of an imidazolium ionic liquid and its surfactant analogue. Front. Chem. 2024, 11, 1289398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laszlo, J.A.; Compton, D.L. α-Chymotrypsin catalysis in imidazolium-based ionic liquids. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2001, 75, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halling, P.J. Thermodynamic predictions for biocatalysis in nonconventional media: Theory, tests, and recommendations for experimental design and analysis. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 1994, 16, 178–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón, C.; Contreras, R.; Campodónico, R. Surfactant-mediated enzymatic superactivity in water/ionic liquid mixtures, evaluated on a model hydrolytic reaction catalyzed by α-chymotrypsin. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 283, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; De Oliveira Vigier, K.; Royer, S.; Jérôme, F. Deep Eutectic Solvents: Syntheses, Properties and Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7108–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, M.A.R.; Pinho, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Insights into the nature of eutectic and deep eutectic mixtures. J. Solut. Chem. 2018, 48, 962–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.H.; van Spronsen, J.; Dai, Y.; Verberne, M.; Hollmann, F.; Arends, I.W.C.E.; Witkamp, G.-J.; Verpoorte, R. Are natural deep eutectic solvents the missing link in understanding cellular metabolism and physiology? Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 1701–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mero, A.; Koutsoumpos, S.; Giannios, P.; Stavrakas, I.; Moutzouris, K.; Mezzetta, A.; Guazzelli, L. Compar-ison of physicochemical and thermal properties of choline chloride and betaine-based deep eutectic solvents: The influence of hydrogen bond acceptor and hydrogen bond donor nature and their molar ratios. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 377, 121563–121583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Xue, Z.; Mu, T. Deep eutectic solvents as a green toolbox for synthesis. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2022, 3, 100809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, B.; Campodónico, P.R.; Contreras, R. Gutmann’s Donor and Acceptor Numbers for Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 861379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapeña, D.; Errazquin, D.; Lomba, L.; Lafuente, C.; Giner, B. Ecotoxicity and biodegradability of pure and aqueous mixtures of deep eutectic solvents: Glyceline, ethaline, and reline. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 8812–8821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanches, M.V.; Freitas, R.; Oliva, M.; Mero, A.; De Marchi, L.; Cuccaro, A.; Fumagalli, G.; Mezzetta, A.; Dugoni, G.C.; Ferro, M.; et al. Are natural deep eutectic solvents always a sustainable option? A bioassay-based study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 17268–17279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.X.; Mubarak, N.M.; Mazari, S.A.; Jatoi, A.S.; Ahmad, A.; Khalid, M.; Walvekar, R.; Abdullah, E.; Karri, R.R.; Siddiqui, M.; et al. A review on the properties and applications of chitosan, cellulose and deep eutectic solvent in green chemistry. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 104, 362–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nian, B.; Cao, C.; Liu, Y. How Candida antarctica lipase B can be activated in natural deep eutectic solvents: Experimental and molecular dynamics studies. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2020, 95, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clouthier, C.M.; Pelletier, J.N. Expanding the organic toolbox: A guide to integrating biocatalysis in synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 1585–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paiva, A.; Craveiro, R.; Aroso, I.; Martins, M.; Reis, R.L.; Duarte, A.R.C. Natural deep eutectic solvents–Solvents for the 21st century. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorke, J.T.; Srienc, F.; Kazlauskas, R.J. Hydrolase-catalyzed biotransformations in deep eutectic solvents. Chem. Commun. 2008, 10, 1235–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Baker, G.A.; Holmes, S. New eutectic ionic liquids for lipase activation and enzymatic preparation of biodiesel. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 1908–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, S.P.M.; Santos, L.D.F.; Saraiva, J.A.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Ionic liquids microemulsions: The key to Candida antarctica lipase B superactivity. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 1620–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshjou, S.; Khodaverdian, S.; Dabirmanesh, B.; Rahimi, F.; Daneshjoo, S.; Ghazi, F.; Khajeh, K. Improvement of chondroitinases ABCI stability in natural deep eutectic solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 227, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, A.; Bornscheuer, U.; Capewell, A.; Combes, D.; Condoret, J.-S.; Koenig, K.; Kolisis, F.N.; Marty, A.; Menge, U.; Scheper, T.; et al. Review Article Enzymes in Non-Conventional Phases. Biocatal. Biotransformation 1995, 13, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Q.; Shi, J.; Shao, Q. Effects of Water on the Solvation and Structure of Lipase in Deep Eutectic Solvents Containing a Protein Destabilizer and Stabilizer. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2021, 23, 23372–23379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maugeri, Z.; de María, P.D. Whole-Cell Biocatalysis in Deep-Eutectic-Solvents/Aqueous Mixtures. ChemCatChem 2014, 6, 1535–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.B.; Spittle, S.; Chen, B.; Poe, D.; Zhang, Y.; Klein, J.M.; Horton, A.; Adhikari, L.; Zelovich, T.; Doherty, B.W.; et al. Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Review of Fundamentals and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2020, 121, 1232–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pätzold, M.; Siebenhaller, S.; Kara, S.; Liese, A.; Syldatk, C.; Holtmann, D. Deep Eutectic Solvents as Efficient Solvents in Biocatalysis. Trends Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 943–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lousa, D.; Baptista, A.M.; Soares, C.M. A Molecular Perspective on Nonaqueous Biocatalysis: Contributions from Simulation Studies. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 13723–13736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Zheng, G.-W.; Zong, M.-H.; Li, N.; Lou, W.-Y. Recent Progress on Deep Eutectic Solvents in Biocatalysis. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2017, 4, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jančíková, V.; Jablonský, M.; Voleková, K.; Šurina, I. Summarizing the Effect of Acidity and Water Content of Deep Eutectic Solvent-like Mixtures—A Review. Energies 2022, 15, 9333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, O.S.; Bowron, D.T.; Edler, K.J. The Effect of Water upon Deep Eutectic Solvent Nanostructure: An Unusual Transition from Ionic Mixture to Aqueous Solution. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 9782–9785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durand, E.; Lecomte, J.; Baréa, B.; Piombo, G.; Dubreucq, E.; Villeneuve, P. Evaluation of Deep Eutectic Solvents as New Media for Candida antarctica B Lipase Catalyzed Reactions. Process Biochem. 2012, 47, 2081–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, D.; de la Fuente Revenga, M.; Widersten, M. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) Are Viable Cosolvents for Enzyme-Catalyzed Epoxide Hydrolysis. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 147, 169–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, A.P.; Cullis, P.M.; Gibson, M.J.; Harris, R.C.; Raven, E. Extraction of Glycerol from Biodiesel into a Eutectic Based Ionic Liquid. Green Chem. 2007, 9, 868–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Baker, G.A.; Holmes, S. Protease Activation in Glycerol-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2011, 72, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Meng, X.; Zhou, H.; Liu, Y.; Secundo, F.; Liu, Y. Enzyme Stability and Activity in Non-Aqueous Reaction Systems: A Mini Review. Catalysts 2016, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolasco, M.M.; Pedro, S.N.; Vilela, C.; Vaz, P.D.; Ribeiro-Claro, P.; Rudić, S.; Parker, S.F.; Freire, C.S.; Freire, M.G.; Silvestre, A.J.D. Water in Deep Eutectic Solvents: New Insights from Inelastic Neutron Scattering Spectroscopy. Front. Phys. 2022, 10, 834571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Ha, S.H.; Sethaphong, L.; Koo, Y.-M.; Yingling, Y.G. The relationship between enhanced enzyme activity and structural dynamics in ionic liquids: A combined computational and experimental study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 2944–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Achkar, T.; Fourmentin, S.; Greige-Gerges, H. Deep Eutectic Solvents: An overview on their interactions with water and biochemical compounds. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 288, 111028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, C.; Harris, R.C.; Abbott, A.P.; Gladden, L.F.; Mantle, M.D. Molecular Motion and Ion Diffusion in Choline Chloride Based Deep Eutectic Solvents Studied by 1H Pulsed Field Gradient NMR Spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 21383–21391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negishi, S.; Shirasawa, S.; Arai, Y.; Suzuki, J.; Mukataka, S. Activation of Powdered Lipase by Cluster Water and the Use of Lipase Powders for Commercial Esterification of Food Oils. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2003, 32, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Witkamp, G.-J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Tailoring Properties of Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents with Water to Facilitate Their Applications. Food Chem. 2015, 187, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shehata, M.; Unlu, A.; Sezerman, U.; Timucin, E. Lipase and Water in a Deep Eutectic Solvent: Molecular Dynamics and Experimental Studies of the Effects of Water-In-Deep Eutectic Solvents on Lipase Stability. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 8801–8810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriele, F.; Chiarini, M.; Germani, R.; Tiecco, M.; Spreti, N. Effect of Water Addition on Choline Chloride/Glycol Deep Eutectic Solvents: Characterization of Their Structural and Physicochemical Properties. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 291, 111301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’anna, F.; La Marca, S.; Noto, R. p-Nitrophenolate: A Probe for Determining Acid Strength in Ionic Liquids. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 1952–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichardt, C. Polarity of Ionic Liquids Determined Empirically by Means of Solvatochromic Pyridinium N-phenolate Betaine Dyes. Green Chem. 2005, 7, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taft, R.W.; Kamlet, M.J. The Solvatochromic Comparison Method. 2. The.Alpha.-Scale of Solvent Hydrogen-Bond Donor (HBD) Acidities. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1976, 98, 2886–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamlet, M.J.; Taft, R.W. The Solvatochromic Comparison Method. I. The.Beta.-Scale of Solvent Hydrogen-Bond Acceptor (HBA) Basicities. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1976, 98, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilani, A.G.; Moghadam, M.; Zakerhamidi, M. Solvatochromism of Nile Red in Anisotropic Media. Dye. Pigment. 2012, 92, 1052–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Park, S.; Yu, H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Yang, Y.-H.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, K.J.; Kan, E.; Lee, S.H. Effect of Deep Eutectic Solvent Mixtures on Lipase Activity and Stability. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2016, 128, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppenberg, J.; Hansen, M.T.; Patkar, S.; Jones, T. The sequence, crystal structure determination and refinement of two crystal forms of lipase B from Candida antarctica. Structure 1994, 2, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bank, R.P.D. Rcsb Pdb—1tca: The Sequence, Crystal Structure Determination and Refinement of Two Crystal Forms of Lipase b from Candida antarctica. Available online: https://www.rcsb.org/structure/1tca (accessed on 4 June 2024).
- Guajardo, N.; de María, P.D.; Ahumada, K.; Schrebler, R.A.; Ramírez-Tagle, R.; Crespo, F.A.; Carlesi, C. Water as Cosolvent: Nonviscous Deep Eutectic Solvents for Efficient Lipase-Catalyzed Esterifications. ChemCatChem 2017, 9, 1393–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guajardo, N.; Ahumada, K.; de María, P.D.; Schrebler, R.A. Remarkable stability of Candida antarctica lipase B immobilized via cross-linking aggregates (CLEA) in deep eutectic solvents. Biocatal. Biotransformation 2018, 37, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, V.G.; Stock, R.I.; Reichardt, C. PyridiniumN-Phenolate Betaine Dyes. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 10429–10475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santana, A.P.; Mora-Vargas, J.A.; Guimarães, T.G.; Amaral, C.D.; Oliveira, A.; Gonzalez, M.H. Sustainable Synthesis of Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents (NADES) by Different Methods. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 293, 111452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramón, D.J.; Guillena, G. Deep Eutectic Solvents: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KgaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcón-Espósito, J.; Contreras, R.; Campodónico, P.R. Iso-Solvation Effects in Mixtures of Ionic Liquids on the Kinetics of a Model SNAr Reaction. N. J. Chem. 2017, 41, 13435–13441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares, B.; Martínez, F.A.; Ezquer, M.; Morales, B.J.; Fuentes, I.; Calvo, M.; Campodónico, P.R. Betaine-urea deep eutectic solvent improves imipenem antibiotic activity. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 350, 118551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashworth, C.R.; Matthews, R.P.; Welton, T.; Hunt, P.A. Doubly ionic hydrogen bond interactions within the choline chloride-urea deep eutectic solvent. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 18145–18160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Campodónico, P.R.; Alarcón-Espósito, J.; Alcázar, J.J.; Olivares, B.; Suárez-Rozas, C. Analysis of the Behavior of Deep Eutectic Solvents upon Addition of Water: Its Effects over a Catalytic Reaction. Molecules 2024, 29, 3296. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143296
Campodónico PR, Alarcón-Espósito J, Alcázar JJ, Olivares B, Suárez-Rozas C. Analysis of the Behavior of Deep Eutectic Solvents upon Addition of Water: Its Effects over a Catalytic Reaction. Molecules. 2024; 29(14):3296. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143296
Chicago/Turabian StyleCampodónico, Paola R., Jazmín Alarcón-Espósito, Jackson J. Alcázar, Belén Olivares, and Cristian Suárez-Rozas. 2024. "Analysis of the Behavior of Deep Eutectic Solvents upon Addition of Water: Its Effects over a Catalytic Reaction" Molecules 29, no. 14: 3296. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143296
APA StyleCampodónico, P. R., Alarcón-Espósito, J., Alcázar, J. J., Olivares, B., & Suárez-Rozas, C. (2024). Analysis of the Behavior of Deep Eutectic Solvents upon Addition of Water: Its Effects over a Catalytic Reaction. Molecules, 29(14), 3296. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143296






