Treatment and Resource Utilization of Gaseous Pollutants in Functionalized Ionic Liquids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Synthesis and Characterization of FILs
3. Treatment and Recycling of CO2
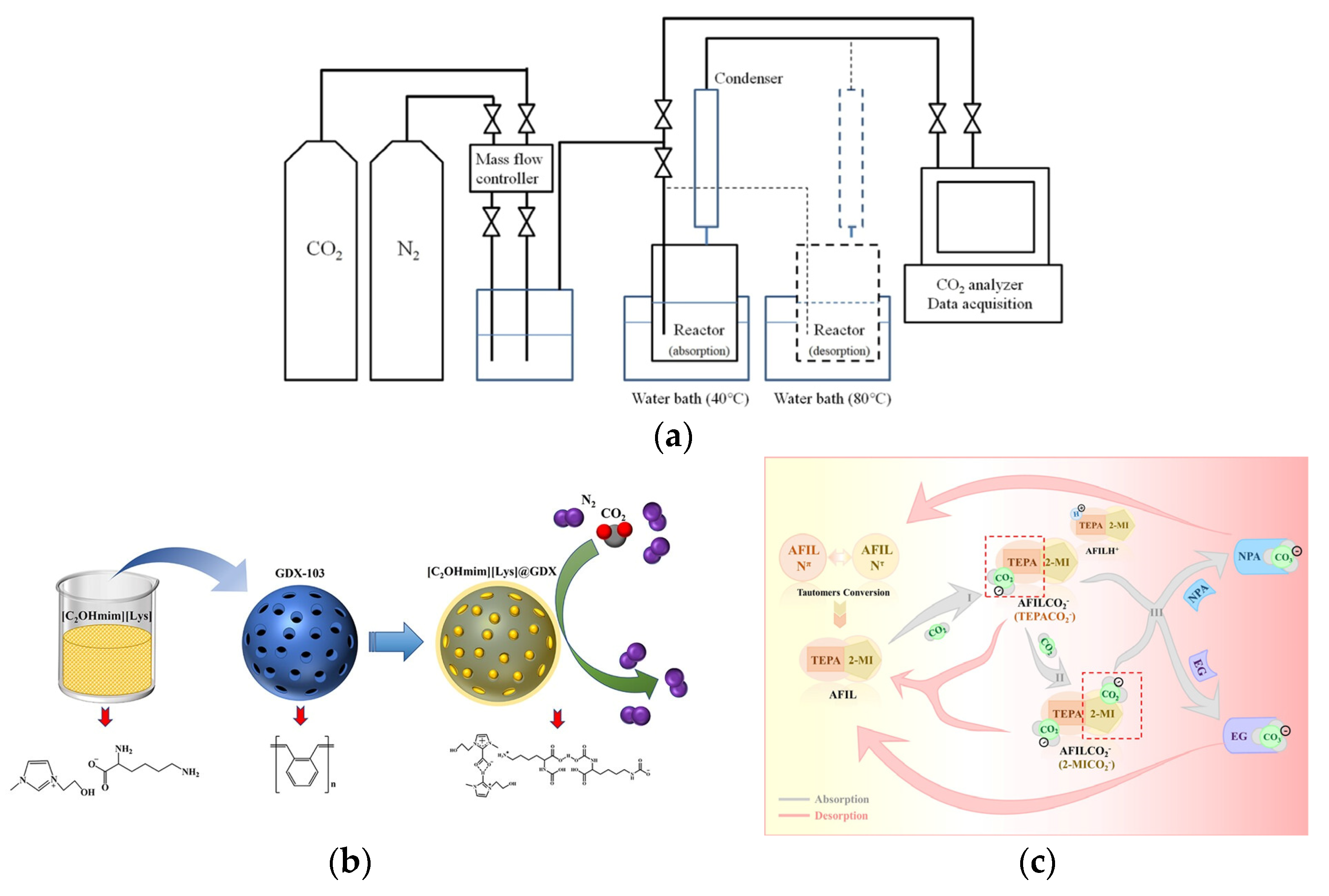
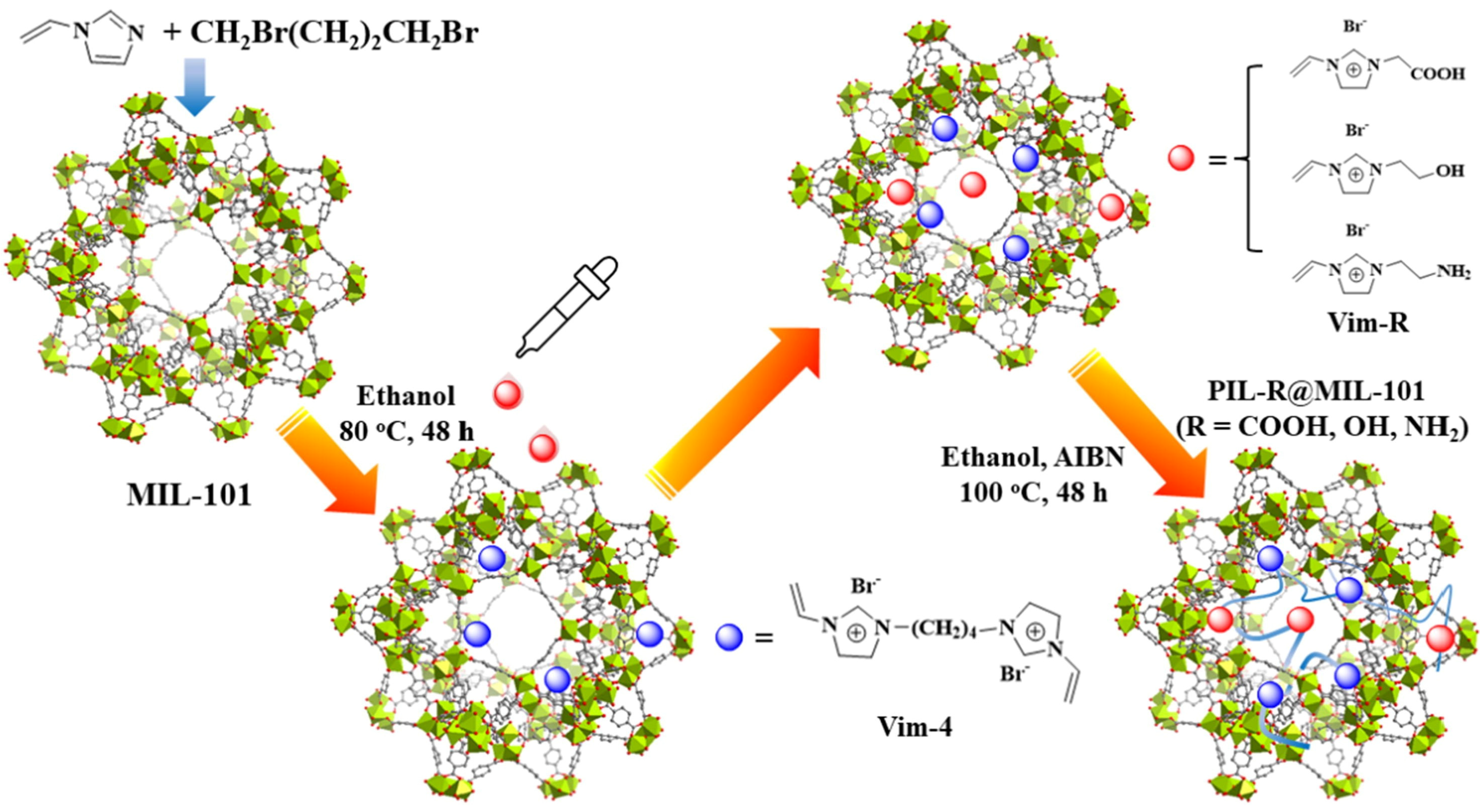
3.1. Absorption of CO2
| Ionic Liquids | Temperature K | Pressure Bar | Solubility mol/mol IL | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [Apaeim][OH] | 313.15 | 1 | 3.75 | [32] |
| [Eaeim][OH] | 2.19 | |||
| [Paeim][OH] | 2.15 | |||
| [Apaeim][gly] | 4.19 | |||
| [Apaeim][ala] | 4.72 | |||
| [Apaeim][val] | 4.44 | |||
| [Eaeim][gly] | 1.97 | |||
| [Eaeim][ala] | 2.44 | |||
| [Eaeim][val] | 2.9 | |||
| [Paeim][gly] | 2.45 | |||
| [Paeim][ala] | 2.67 | |||
| [Paeim][val] | 2.96 | |||
| [bmim][ARG] | 298 | 2 | 0.62 | [35] |
| [bmim][LYS] | 0.48 | |||
| [bmim][HIS] | 0.45 | |||
| [bmim][MET] | 0.42 | |||
| [bmim][LEU] | 0.38 | |||
| [bmim][GLY] | 0.38 | |||
| [bmim][VAL] | 0.39 | |||
| [bmim][ALA] | 0.39 | |||
| [bmim][PRO] | 0.32 | |||
| [Bmim][ATZ] | 298.15 | 1 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | [36] |
| 293.15 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | |||
| 298.15 | 2.04 ± 0.06 | |||
| 2 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | |||
| 323.15 | 1 | 0.08 ± 0.03 | ||
| 2 | 0.13 ± 0.02 | |||
| [Emim][ATZ] | 298.15 | 1 | 0.13 ± 0.01 | |
| 293.15 | 0.13 ± 0.01 | |||
| [4NH2-BA] | 203.15 | 0.8 | [37] | |
| [6NH2-NC] | 0.78 | |||
| [2NH2-NC] | 0.56 | |||
| [Me-Gly] | 0.9 | |||
| [Ac-Gly] | 0.49 | |||
| [Ac-PhO] | 1.2 |
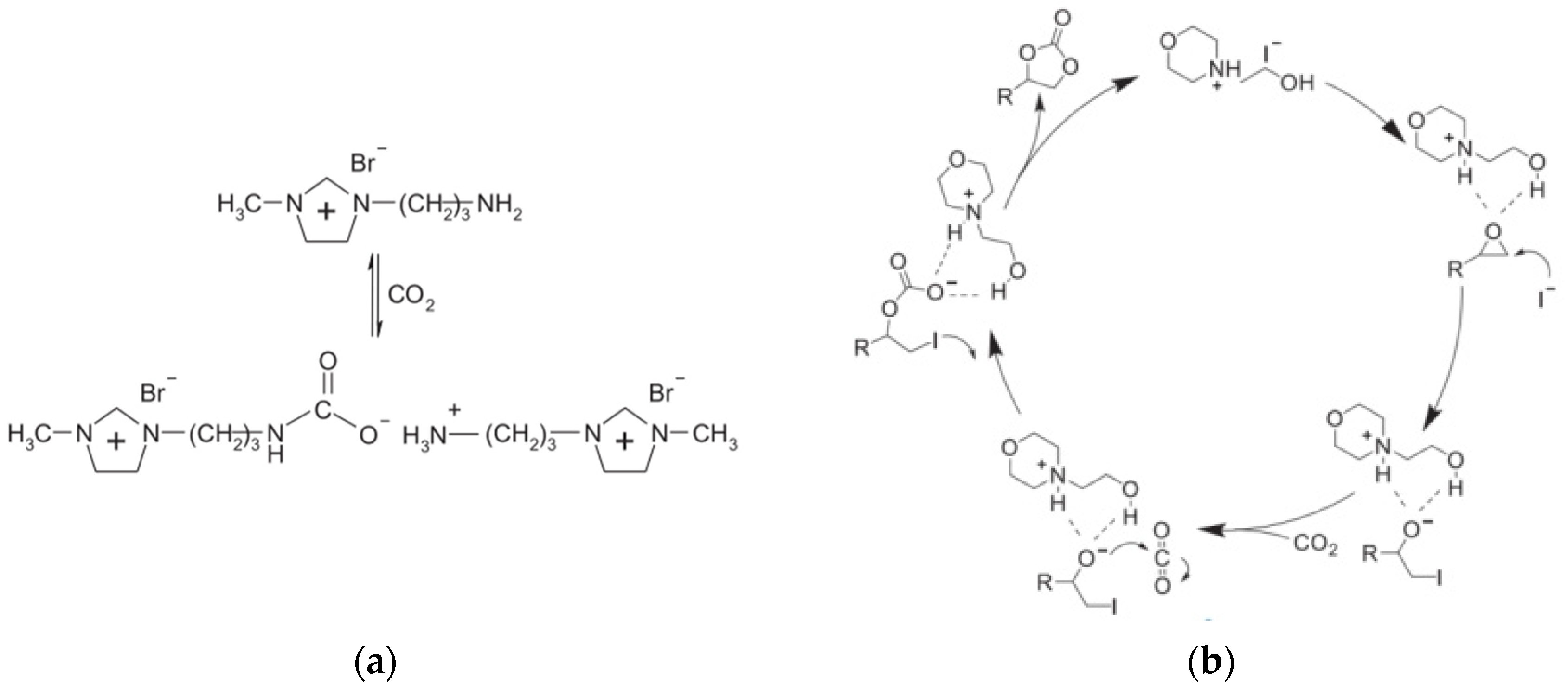
3.2. Recycling of CO2
4. Treatment and Recycling of H2S
4.1. Absorption of H2S
| Ionic Liquids | Temperature K | Pressure Bar | Solubility mol/mol IL | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [TETAH][HCOO]-EG | 303.15 | 1 | 0.897 | [65] |
| [TETAH][BF4]-EG | 1.018 | |||
| [TETAH]Br-EG | 1.003 | |||
| [DETAH][Im] | 298.2 | 0.1 | 1.31 | [66] |
| [TETAH][Im] | 1.49 | |||
| [TEPAH][Im] | 1.6 | |||
| [BDMAEE][AcO] | 298.2 | 1.044 | [69] | |
| 1.004 | ||||
| 1.073 | ||||
| 0.95 | ||||
| [TDMAPAH][Ac] | 313.2 | 1 | 1.92 | [73] |
| [PMDPTAH][Ac] | 1.15 | |||
| [TMDAPH][Ac] | 0.65 | |||
| [P4444][MSA] | 303.2 | 1 | 0.9 | [71] |
| [P4444][2-MPA] | 0.84 | |||
| [N2224][2-MPA] | 0.75 | |||
| [N2224][MSA] | 0.49 |
4.2. Recycling of H2S
5. Treatment and Recycling of SO2
5.1. Absorption of SO2
| Ionic Liquid | Temperature K | Pressure Bar | Solubility mol/mol IL | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [Na(PEG400)][Triz] | 303.15 | 1 | 0.93 | [93] |
| [Na(PEG400)][Bentriz] | 0.93 | |||
| [Na(PEG400)][3-Br-Triz] | 0.86 | |||
| [Na(PEG400)][4-NO2-Im] | 0.77 | |||
| [Na(PEG400)][Tetz] | 0.66 | |||
| [Na(PEG400)][SCN] | 0.047 | |||
| [Na(PEG400)][Tetz] | 0.66 | |||
| [Na(PEG300)][Tetz] | 0.81 | |||
| [Na(mPEG4-OH)2][Tetz] | 0.78 | |||
| PEG400 | 0.0078 | |||
| [E3MIm2][Tf2N] | 323.15 | 1 | 1.213 | [91] |
| 293.15 | 3.307 | |||
| [E1MIm2][Tf2N]2 | 313.15 | 1.291 | ||
| [E2MIm2][Tf2N]2 | 1.506 | |||
| [E3MIm2][Tf2N]2 | 1.62 | |||
| [E2Py]Clb | 293.15 | 1 | 3.924 | [100] |
| [E3Mim]Clb | 4.367 | |||
| [E3Py]Clb | 4.289 | |||
| [E4Py]Clb | 4.594 | |||
| [E3Py]Clb | 353.15 | 1.581 | ||
| [C10Py]Cl | 1.334 | |||
| [C3O1Mim][H3CSO3] | 298.15 | 1 | 2.621 | [98] |
| [C5O2Mim][H3CSO3] | 3.106 | |||
| [C7O3Mim][H3CSO3] | 3.453 | |||
| [P4442][TFSI] | 293.15 | 1 | 1.43 | [97] |
| [P4442][HFA] | 2.8 | |||
| [P4442][BTFA] | 4.27 | |||
| [P4442][TTFA] | 4.05 | |||
| [MDEAH][MOAc] | 313.2 | 1 | 1.17 | [84] |
| [MDEAH][EOAc] | 1.2 | |||
| [BDEAH][MOAc] | 1.29 | |||
| [BDEAH][EOAc] | 1.27 | |||
| [P66614][6-BrC5H10COO] | 298.15 | 1 | 4.34 | [85] |
| [P66614][6-ClC5H10COO] | 4.28 | |||
| [P66614][2-BrC5H10COO] | 3.97 | |||
| [P66614][C5H11COO] | 3.82 | |||
| [P66614][BrCH2COO]d | 3.89 | |||
| [P66614][CH3COO]d | 3.48 | |||
| [NEt2C2Py][SCN] | 293.15 | 1 | 3.958 | [83] |
| [C4CNPy][SCN] | 2.917 | |||
| [C4OPy][SCN] | 2.956 | |||
| [K(TX-7)][SCN] | 293.15 | 1.01325 | 3.96 | [95] |
| [Na(TX-7)][SCN] | 3.74 | |||
| [Li(TX-7)][SCN] | 3.51 | |||
| [Li(TX-4)][SCN] | 2.45 | |||
| [Li(TX-10)][SCN] | 4.75 | |||
| [Na(TX-10)][Tf2N] | 3.71 | |||
| [Na(TX-10)][SCN] | 4.89 | |||
| [Na(TX-10)][PhO] | 5.4 | |||
| [Na(TX-10)][Im] | 6.65 | |||
| TX-4 | 1.92 | |||
| TX-7 | 3.15 | |||
| TX-10 | 4.52 |
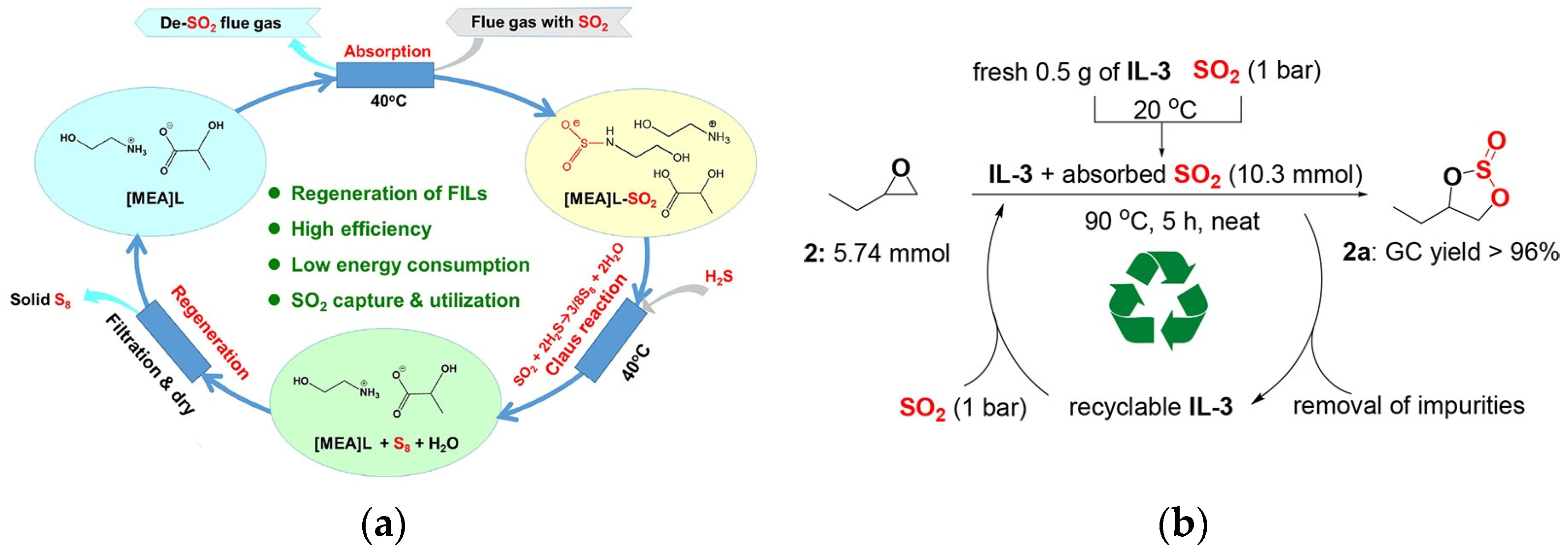
5.2. Recycling of SO2
6. Treatment and Recycling of NH3
7. Treatment and Recycling of VOCs
8. Summary and Future Outlook
- (1)
- Research and development of new functional ionic liquids: By designing more efficient functional groups and optimizing the structure of ionic liquids, it can improve its adsorption capacity, kinetic performance, and selective recognition of gaseous pollutants, so as to achieve a more efficient and highly selective absorption process of gaseous pollutants.
- (2)
- Reduction of the preparation cost: Through process optimization, technological innovation and seeking economical and efficient raw material sources, effectively reduce the preparation cost of functional ionic liquids, so as to promote its popularization and promotion in large-scale industrial applications and achieve a win–win situation of economic and environmental benefits.
- (3)
- Expansion of the application field: The FILs are applied to more types of gas pollutants in the treatment and resource recycling process, in order to give full play to their comprehensive advantages in improving pollution control efficiency, promoting resource recycling and reducing environmental burden, and then enhance their overall benefits and application value in the field of environmental protection.
- (4)
- Development of new resource products: At present, the catalytic conversion of CO2 and H2S mostly focuses on the synthesis of carbonates and sulfate compounds. In order to expand the application field and meet the diversified industrial needs, further research is needed to explore and develop new high value-added catalytic products, such as fine chemicals containing oxygen or sulfur, functional materials, or new energy materials. The development of these new products will inject new impetus into the development of the environmentally friendly chemical industry.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raymond, P.A.; Hartmann, J.; Lauerwald, R.; Sobek, S.; McDonald, C.; Hoover, M.; Butman, D.; Striegl, R.; Mayorga, E.; Humborg, C.; et al. Global Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Inland Waters. Nature 2013, 503, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jion, M.M.M.F.; Jannat, J.N.; Mia, M.Y.; Ali, M.A.; Islam, M.S.; Ibrahim, S.M.; Pal, S.C.; Islam, A.; Sarker, A.; Malafaia, G.; et al. A Critical Review and Prospect of NO2 and SO2 Pollution over Asia: Hotspots, Trends, and Sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 876, 162851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behera, S.N.; Sharma, M.; Aneja, V.P.; Balasubramanian, R. Ammonia in the Atmosphere: A Review on Emission Sources, Atmospheric Chemistry and Deposition on Terrestrial Bodies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 8092–8131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, C.; Gupta, P.; Cribb, M. Ground-Level Gaseous Pollutants (NO2, SO2, and CO) in China: Daily Seamless Mapping and Spatiotemporal Variations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 1511–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Patil, R.S.; Dikshit, A.K.; Kumar, R. Assessment of Spatial Ambient Concentration of NH3 and Its Health Impact for Mumbai City. Asian J. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 13, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhai, S.; Kong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Song, G.; Song, H.; Liang, L.; Liu, X.; Jiang, X.; Wu, L. Synergistic Effects of Gaseous Pollutants on Hospital Admissions for Cardiovascular Disease in Liuzhou, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 9841–9851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, M.; Zhan, C.; Wu, W.; Guo, D.; Song, Y. Acute Gaseous Air Pollution Exposure and Hospitalizations for Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Time-Series Analysis in Tianjin, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchherr, J.; Reike, D.; Hekkert, M. Conceptualizing the Circular Economy: An Analysis of 114 Definitions. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 127, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morseletto, P. Targets for a Circular Economy. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 153, 104553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, A.J.; Jacquemin, J.; Hardacre, C. Industrial Applications of Ionic Liquids. Molecules 2020, 25, 5207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smiglak, M.; Pringle, J.M.; Lu, X.; Han, L.; Zhang, S.; Gao, H.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Rogers, R.D. Ionic Liquids for Energy, Materials, and Medicine. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 9228–9250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vekariya, R.L. A Review of Ionic Liquids: Applications towards Catalytic Organic Transformations. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 227, 44–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pârvulescu, V.I.; Hardacre, C. Catalysis in Ionic Liquids. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2615–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gohil, H.; Yadav, S.; Rajpurohit, D.; Bhojani, G.; Chatterjee, S.; Paital, A.R. Sensing vs Extraction: Functionalized Ionic Liquid as a Single Platform for Dual Applications with Biological Implications. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 13096–13105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, Z.; Xia, C. Alkyl Sulfonate Functionalized Ionic Liquids: Synthesis, Properties, and Their Application in Esterification. Chin. J. Catal. 2011, 32, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fareghi-Alamdari, R.; Nadiri Niri, M.; Hazarkhani, H. Synthesis and Characterization of a New Hydroxyl Functionalized Diacidic Ionic Liquid as Catalyst for the Preparation of Diester Plasticizers. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 227, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.Y.; Wang, R.; Liu, G.H.; Xu, L.Q.; Zhang, B.; Wu, X.Q. Synthesis of Multi-Hydroxyl and Sulfonyl Dual-Functionalized Room Temperature Ionic Liquids. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2007, 18, 633–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Li, Z.; Deng, Y. Synthesis and Characterization of Sulfonyl-Functionalized Ionic Liquids. Synth. Commun. 2005, 35, 1343–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Guo, C.; Wu, W.; Tong, J. Synthesis and Characterization of Physicochemical Properties of Two New Hydroxyl-Functionalized Ionic Liquids. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2023, 176, 106909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, B.; Hong, M.; Kong, Y.-X.; Tong, J.; Xu, W.-G. Synthesis and Characterization of Physicochemical Properties of New Ether-Functionalized Amino Acid Ionic Liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 304, 112718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondal, H.Y.; Mumtaz, S.; Abbaskhan, A.; Mumtaz, N.; Cano, I. New Alkoxymethyl-Functionalized Pyridinium-Based Chiral Ionic Liquids: Synthesis, Characterization and Properties. Chem. Pap. 2020, 74, 2951–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Xiang, W.; Wang, R.; Ding, F.; Hong, P.; Gao, B. Straw and Wood Based Biochar for CO2 Capture: Adsorption Performance and Governing Mechanisms. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 287, 120592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boer, D.G.; Langerak, J.; Pescarmona, P.P. Zeolites as Selective Adsorbents for CO2 Separation. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2023, 6, 2634–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Shen, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Lu, Y. Phase Change Solvents for Post-Combustion CO2 Capture: Principle, Advances, and Challenges. Appl. Energy 2019, 239, 876–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmad, S.; Mikkola, J.; Ji, X. Carbon Dioxide Capture with Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents: A New Generation of Sorbents. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 324–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Ho, W.S.W. Polymeric Membranes for CO2 Separation and Capture. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 628, 119244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yang, H.B.; Hung, S.; Ding, J.; Cai, W.; Liu, L.; Gao, J.; Li, X.; Ren, X.; Kuang, Z.; et al. Elucidating the Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction Reaction over a Model Single-Atom Nickel Catalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 798–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Küngas, R. Review—Electrochemical CO2 Reduction for CO Production: Comparison of Low- and High-Temperature Electrolysis Technologies. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 044508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zareiekordshouli, F.; Lashani-zadehgan, A.; Darvishi, P. Thermophysical Properties and CO2 Absorption Studies of the Amine Functionalized [Amim][Tf2N] and the Non-Functionalized Counterpart [Bmim][Tf2N] Ionic Liquids. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2016, 53, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Xia, C.; Zhou, X. Synthesis of Novel Amino-Functionalized Ionic Liquids and Their Application in Carbon Dioxide Capture. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 6859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Vijayaraghavan, R.; Zhou, F.; Kar, M.; Li, H.; Wang, C.; MacFarlane, D.R. Enhanced CO2 Uptake by Intramolecular Proton Transfer Reactions in Amino-Functionalized Pyridine-Based ILs. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 5950–5953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.; Chung, Y.G.; Kang, J.H.; Song, H. CO2 Absorption Characteristics of Amino Group Functionalized Imidazolium-Based Amino Acid Ionic Liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 297, 111825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yang, Z.; Xie, J.; Zhu, P.; Wei, J.; Jin, R.; Yang, H. Porous Polymer Supported Amino Functionalized Ionic Liquid for Effective CO2 Capture. Langmuir 2023, 39, 2729–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Shen, Y.; Shen, L.; Sun, C.; Chen, L.; Wang, Q.; Li, S.; Li, W. Novel Amino-Functionalized Ionic Liquid/Organic Solvent with Low Viscosity for CO2 Capture. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3520–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sistla, Y.S.; Khanna, A. CO2 Absorption Studies in Amino Acid-Anion Based Ionic Liquids. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 273, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L.; He, L.; Yuan, W.-L.; Xu, D.; Tao, G.-H. Is It Always Chemical When Amino Groups Come Across CO2? Anion–Anion-Interaction-Induced Inhibition of Chemical Adsorption. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 6536–6542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.Y.; Fan, X.; Shi, G.L.; Li, H.R.; Wang, C.M. Decreasing the Viscosity in CO2 Capture by Amino-Functionalized Ionic Liquids through the Formation of Intramolecular Hydrogen Bond. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 2807–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakubo, M.; Makino, T.; Taniguchi, T.; Nokami, T.; Itoh, T. CO2 Solubility in Ether Functionalized Ionic Liquids on Mole Fraction and Molarity Scales. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Y.; Yang, H.; Bi, H. Highly Efficient and Reversible CO2 Capture by Imidazolate-Based Ether-Functionalized Ionic Liquids with a Capture Transforming Process. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 69, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Dong, H.; Zeng, S.; Umair Ahmad, M.; Khurum Shehzad, F.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Y. Investigation Uncovered the Impact of Anions on CO2 Absorption by Low Viscous Ether Functionalized Pyridinium Ionic Liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 336, 116362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, B.; Xia, Y.; Shi, Y.; Liu, N.; Li, W.; Li, S. A Novel Hydrophilic Amino Acid Ionic Liquid [C2OHmim][Gly] as Aqueous Sorbent for CO2 Capture. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2016, 46, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, R.; Lemus, J.; Moya, C.; Moreno, D.; Alonso-Morales, N.; Palomar, J. Encapsulated Ionic Liquids to Enable the Practical Application of Amino Acid-Based Ionic Liquids in CO2 Capture. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 14178–14187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhao, J.; Cai, Q. Electrochemical Conversion of CO2 into Dimethyl Carbonate in a Functionalized Ionic Liquid. J. CO2 Util. 2013, 3–4, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gao, H.; Ding, T.; Ji, L.; Zhang, J.Z.H.; Gao, G.; Xia, F. Mechanistic Studies of CO2 Cycloaddition Reaction Catalyzed by Amine-Functionalized Ionic Liquids. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.-Y.; Chen, M.-J.; Yang, L.; Zhao, B.; Xia, T.; Chang, G.-G. Hollow MOF Capsule Encapsulated Amino-Functionalized Ionic Liquid for Excellent CO2 Catalytic Conversion. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 40, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, F.; Zhao, T.; Gu, J.; Chen, P.; Chen, T. Highly Efficient CO2 Fixation into Cyclic Carbonate by Hydroxyl-Functionalized Protic Ionic Liquids at Atmospheric Pressure. Mol. Catal. 2021, 511, 111756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Xiao, B.; Sun, J.; Dong, K.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, S.; Ng, F.T.T. Effect of Hydrogen Bond of Hydroxyl-Functionalized Ammonium Ionic Liquids on Cycloaddition of CO2. Tetrahedron Lett. 2015, 56, 1416–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Qu, H.; Song, X.; Zang, S.; Deng, G. Hydroxy Acid-Functionalized Ionic Liquids as Green Alternatives for the Efficient Catalytic Conversion of Epoxides to Cyclic Carbonates under Solvent and Co-Catalyst-Free Conditions. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2021, 11, 6999–7008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, P.; Jin, X.; Zhang, J.; He, H.; Zhang, S. Mechanism of Fixation of CO2 in the Presence of Hydroxyl-Functionalized Quaternary Ammonium Salts. J. CO2 Util. 2015, 10, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Ma, Y.; Jiang, J.; Zhu, X.; Fan, B.; Yu, G.; Li, N.; Wang, S.; Ren, T.; Wang, L.; et al. Hydroxyl-Functionalized Pyrazolium Ionic Liquids to Catalyze Chemical Fixation of CO2: Further Benign Reaction Condition for the Single-Component Catalyst. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 293, 111479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, D.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, J. Hydrogen Bond Donor Functionalized Poly(Ionic Liquids)@MIL-101 for the CO2 Capture and Improving the Catalytic CO2 Conversion with Epoxide. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 618, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, F.; Ren, T.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J. Synergistic Effect of Carboxylmethyl Group and Adjacent Methylene Substitution in Pyrazolium Ionic Liquid Promote the Conversion of CO2 under Benign Condition. J. CO2 Util. 2019, 34, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Geng, W.; Yue, C.; Wu, W.; Xiao, L. Multilayered Supported Ionic Liquids Bearing a Carboxyl Group: Highly Efficient Catalysts for Chemical Fixation of Carbon Dioxide. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2565–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Gunaratne, H.Q.N.; Jin, L. Design and Synthesis of Pyridinamide Functionalized Ionic Liquids for Efficient Conversion of Carbon Dioxide into Cyclic Carbonates. J. CO2 Util. 2022, 58, 101930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, N.; Chen, C.; Li, D.J.; Hu, Y.L. Cobalt Nanoparticles Embedded over Periodic Mesoporous Organosilica Functionalized with Benzotriazolium Ionic Liquid for Efficient and Heterogeneous Catalytic Transformation of Carbon Dioxide to Cyclic Carbonates. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Chen, K.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, C. Highly Efficient Synthesis of Quinazoline-2,4(1 H,3 H)-Diones from CO2 by Hydroxyl Functionalized Aprotic Ionic Liquids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5760–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tang, Y.; Qu, S.; Da, J.; Hao, Z. H2S-Selective Catalytic Oxidation: Catalysts and Processes. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 1053–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, S. Global Reaction Scheme for Partial Oxidation of Pure H2S and H2S + CH4 Mixture in Claus Conditions. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 6478–6492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Yousaf, M.; Cai, W.; Zhao, Z.-P. Enhanced H2S Removal from Diverse Fuels by a Coupled Absorption and Biological Process Uses CO2 as Carbon Resource for Microbial Ecosystem. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 310, 123182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, M.; Talakesh, M.M.; Arabi Shamsabadi, A.; Soroush, M. Novel Application of a Polyurethane Membrane for Efficient Separation of Hydrogen Sulfide from Binary and Ternary Gas Mixtures. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 3302–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokorna-Krayzelova, L.; Bartacek, J.; Vejmelkova, D.; Alvarez, A.A.; Slukova, P.; Prochazka, J.; Volcke, E.I.P.; Jenicek, P. The Use of a Silicone-Based Biomembrane for Microaerobic H2S Removal from Biogas. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 189, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petukhov, D.I.; Komkova, M.A.; Eliseev, A.A.; Poyarkov, A.A.; Eliseev, A.A. Nanoporous Polypropylene Membrane Contactors for CO2 and H2S Capture Using Alkali Absorbents. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2022, 177, 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirfendereski, S.M.; Niazi, Z.; Mohammadi, T. Selective Removal of H2S from Gas Streams with High CO2 Concentration Using Hollow-Fiber Membrane Contractors. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2019, 42, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.S.; Tsapatsis, M.; Siepmann, J.I. Hydrogen Sulfide Capture: From Absorption in Polar Liquids to Oxide, Zeolite, and Metal–Organic Framework Adsorbents and Membranes. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 9755–9803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Dong, B.; Wu, Y.; Hu, H.; Huang, H. Mechanism Study on H2S Capture of Ionic Liquids Based on Triethylenetetramine Blended with Ethylene Glycol. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 368, 120704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhang, P.; Chang, Y.; Chen, X. Highly Efficient Capture and Removal of H2S by Multi-Amine Functionalized Ionic Liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 392, 123501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Shi, M.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, W.; Hu, X.; Tu, Z.; Wu, Y. Facilitated Transport Separation of CO2 and H2S by Supported Liquid Membrane Based on Task-Specific Protic Ionic Liquids. Green Chem. Eng. 2022, 3, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Cai, D.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Z. Dual Lewis Base Functionalization of Ionic Liquids for Highly Efficient and Selective Capture of H2S. ChemPlusChem 2014, 79, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Hu, X.-B.; Wu, Y.-T. Absorption of H2S and CO2 in Aqueous Solutions of Tertiary-Amine Functionalized Protic Ionic Liquids. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 14060–14069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, J.M.M.V.; Sintra, T.E.; Ferreira, A.G.M.; Carvalho, P.J.; Fonseca, I.M.A. Solubility of H2S in Ammonium-Based Ionic Liquids. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2021, 154, 106336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Geng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lu, R.; Xu, Y.; Liu, C.; Xu, Y. Highly Efficient and Reversible H2S Capture by Mercapto Carboxylic Anion Functionalized Ionic Liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 343, 116975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Li, W.; Wu, T.; Ma, X.; Jiang, K.; Jin, X. Monoethanolamine-Enabled Electrochemical Detection of H2S in a Hydroxyl-Functionalized Ionic Liquid. Electrochem. Commun. 2018, 88, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Wu, D.; Feng, X.; Hu, J.; Zhang, F.; Wu, Y.-T.; Hu, X.-B. Low Viscous Protic Ionic Liquids Functionalized with Multiple Lewis Base for Highly Efficient Capture of H2S. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 263, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedhosseini, B.; Izadyar, M.; Housaindokht, M.R. A Computational Exploration of H2S and CO2 Capture by Ionic Liquids Based on α-Amino Acid Anion and N7,N9-Dimethyladeninium Cation. J. Phys. Chem. A 2017, 121, 4352–4362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, W.; Shi, M.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hu, X.; Tu, Z.; Wu, Y. Efficient Conversion of H2S into Mercaptan Alcohol by Tertiary-Amine Functionalized Ionic Liquids. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 50, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Shi, M.; Zhang, X.; Tu, Z.; Hu, X.; Wu, Y. The Efficient Conversion of H2S into Mercaptan Alcohols Mediated in Protic Ionic Liquids under Mild Conditions. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 7969–7975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminuddin, M.S.; Khalil, M.A.B.; Abdullah, B. Metal Chloride Anion Based Ionic Liquids: Synthesis, Characterization and Evaluation of Performance in Hydrogen Sulfide Oxidative Absorption. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 11906–11912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Guan, J.; Han, J.; Liang, W.; Wang, K.; Duan, E.; Guo, B. Absorption and Oxidation of H2S in Triethylamine Hydrochloride · Ferric Chloride Ionic Liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 209, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, R. Efficient Removal of H2S at High Temperature Using the Ionic Liquid Solutions of [C4Mim]3PMo12O40-An Organic Polyoxometalate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 331, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, K.; Liu, Z.; Dong, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, W.; Niu, S.; Jin, Z. [Bmim]FeCl4 Efficient Catalytic Oxidative Removal of H2S by Cu2+ Synergistic Reinforcement. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2022, 45, 1867–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córdoba, P. Status of Flue Gas Desulphurisation (FGD) Systems from Coal-Fired Power Plants: Overview of the Physic-Chemical Control Processes of Wet Limestone FGDs. Fuel 2015, 144, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Zhang, D.; Yan, J.; Zhao, S.; Liu, J. Process Development of Flue Gas Desulphurization Wastewater Treatment in Coal-Fired Power Plants towards Zero Liquid Discharge: Energetic, Economic and Environmental Analyses. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 261, 121144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; He, H.; Gao, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, S. Improving SO2 Capture by Tuning Functional Groups on the Cation of Pyridinium-Based Ionic Liquids. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 2470–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Z.; Xie, Q.; Fan, Z.; Sun, W.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Xu, Y. Investigation of Tertiary Amine-Based PILs for Ideal Efficient SO2 Capture from CO2. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, F.; Wang, J. Highly Efficient and Reversible SO2 Capture by Halogenated Carboxylate Ionic Liquids. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 60975–60982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Zheng, J.; Luo, X.; Lin, W.; Ding, F.; Li, H.; Wang, C. Tuning Anion-Functionalized Ionic Liquids for Improved SO2 Capture. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 10620–10624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siami, H.; Razmkhah, M.; Moosavi, F. Cation Functional Group Effect on SO2 Absorption in Amino Acid Ionic Liquids. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 1113394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, A.; Balasubramanian, S. Molecular Dynamics Investigation of Efficient SO2 Absorption by Anion-Functionalized Ionic Liquids. J. Chem. Sci. 2017, 129, 859–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Wang, C.; Zheng, J.; Guo, Y.; Luo, X.; Li, H. Highly Efficient SO2 Capture by Dual Functionalized Ionic Liquids through a Combination of Chemical and Physical Absorption. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Kang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Yan, Z.; Sheng, K. Chemically Tunable DILs: Physical Properties and Highly Efficient Capture of Low-Concentration SO2. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 240, 116572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, B.; Li, X.; Ge, X.; Wang, J. Ether-Functionalized Ionic Liquids with Low Viscosity for Efficient SO2 Capture. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 16335–16340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morganti, J.D.; Hoher, K.; Ribeiro, M.C.C.; Ando, R.A.; Siqueira, L.J.A. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Acidic Gases at Interface of Quaternary Ammonium Ionic Liquids. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 22012–22020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Pan, M.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Z.; Tao, H.; Lin, W.; Li, H.; Shi, G.; Wang, C. Tunable and Facile Preparation of Chelate-Based Ionic Liquids for Highly Efficient SO2 Separation under Low Concentration in Flue Gas. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 318, 123979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Lin, W.; Yu, X.; Luo, X.; Ding, F.; He, X.; Li, H.; Wang, C. Designing of Anion-functionalized Ionic Liquids for Efficient Capture of SO2 from Flue Gas. AIChE J. 2015, 61, 2028–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Zheng, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, K.; Cui, G.; Li, H.; Wang, C. Highly Efficient and Reversible SO2 Capture by Surfactant-Derived Dual Functionalized Ionic Liquids with Metal Chelate Cations. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 18568–18574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, X.; Huang, Y.; Xuan, X.; Wang, J. Acylamido-Based Anion-Functionalized Ionic Liquids for Efficient SO2 Capture through Multiple-Site Interactions. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2264–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Zhao, N.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, J. Limited Number of Active Sites Strategy for Improving SO2 Capture by Ionic Liquids with Fluorinated Acetylacetonate Anion. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 7985–7992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Jiang, H.; Hu, Y. Desulfurization Performance of Ether-Functionalized Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids Supported on Porous Silica Gel. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 1941–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.-Q.; Wu, X.-L.; Li, Z.-M.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, W.; Tao, D.-J. Sulfate Ionic Liquids Impregnated 2D Boron Nitride Nanosheets for Trace SO2 Capture with High Capacity and Selectivity. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 270, 118824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zeng, S.; Bai, L.; Gao, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S. Novel Ether-Functionalized Pyridinium Chloride Ionic Liquids for Efficient SO2 Capture. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 16832–16839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Hou, Y.; Ren, S.; Zhang, K.; Wu, W. Efficient Regeneration of SO2 -Absorbed Functional Ionic Liquids with H2S via the Liquid-Phase Claus Reaction. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 10931–10936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Hu, X. Efficient SO2 Capture and Fixation to Cyclic Sulfites by Dual Ether-Functionalized Protic Ionic Liquids without Any Additives. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 10886–10895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Yu, J.; Qazi, A.B.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X. Metal-Based Ionic Liquids in Oxidative Desulfurization: A Critical Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 1419–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zheng, L.; Ma, Y.; Cai, Z.; Cao, Y.; Huang, K.; Jiang, L. A Mini-Review on NH3 Separation Technologies: Recent Advances and Future Directions. Energy Fuels 2022, 36, 14516–14533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, K.; Jiang, L. Highly Efficient and Selective Separation of Ammonia by Deep Eutectic Solvents through Cooperative Acid-Base and Strong Hydrogen-Bond Interaction. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 337, 116463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-L.; Zhong, F.-Y.; Zhou, L.-S.; Tian, Z.-Q.; Huang, K. Deep Eutectic Solvents Formed by N -Methylacetamide and Heterocyclic Weak Acids for Highly Efficient and Reversible Chemical Absorption of Ammonia. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 2060–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, F.-Y.; Peng, H.-L.; Tao, D.-J.; Wu, P.-K.; Fan, J.-P.; Huang, K. Phenol-Based Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvents for Highly Efficient and Reversible Absorption of NH3. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 3258–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Li, Q.; Fang, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Cai, Z.; Huang, K.; Jiang, L. Ethanolammonium Chloride-Glycerol Deep Eutectic Solvents for Efficient and Reversible Absorption of NH3 through Multiple Hydrogen-Bond Interaction. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 393, 123583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Lan, X.; Yu, D.; Fu, H.; Liu, Z.; Mu, T. Deep Eutectic-Solvothermal Synthesis of Nanostructured Fe3S4 for Electrochemical N2 Fixation under Ambient Conditions. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 13010–13013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.-J.; Zhong, F.-Y.; Zhou, L.-S.; Peng, H.-L.; Fan, J.-P.; Huang, K. Chemical Dual-Site Capture of NH3 by Unprecedentedly Low-Viscosity Deep Eutectic Solvents. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 2399–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Dong, H.; Zhang, X.; Gao, H.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Wang, C. Efficient Absorption of Ammonia with Hydroxyl-Functionalized Ionic Liquids. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 81362–81370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Zhang, X.; Ren, B.; Yang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Bai, L.; Gao, H.; Zeng, S. Dual-functionalized Protic Ionic Liquids for Efficient Absorption of NH 3 through Synergistically Physicochemical Interaction. J. Chem. Tech. Biotech. 2020, 95, 1815–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Gao, H.; Jiang, H.; Zeng, S.; Li, T.; Ren, B.; Zhang, X. Experimental and Thermodynamic Analysis of NH3 Absorption in Dual-Functionalized Pyridinium-Based Ionic Liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 323, 114601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, G.; Zeng, S.; Yuan, L.; Bai, L.; Zhang, X. Ultra-High NH3 Absorption by Triazole Cation-Functionalized Ionic Liquids through Multiple Hydrogen Bonding. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 307, 122825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, T.; Kanakubo, M. NH 3 Absorption in Brønsted Acidic Imidazolium- and Ammonium-Based Ionic Liquids. New. J. Chem. 2020, 44, 20665–20675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, D.; Zeng, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Bai, L.; Dong, H. Highly Efficient and Reversible Absorption of NH3 by Dual Functionalised Ionic Liquids with Protic and Lewis Acidic Sites. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 312, 113411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Yang, W.; Wang, C.; Xiong, S.; Cao, X.; Peng, Y.; Si, W.; Weng, Y.; Xue, M.; Li, J. Roles of Oxygen Vacancies in the Bulk and Surface of CeO2 for Toluene Catalytic Combustion. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 12684–12692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Ho, S.; Lu, Y.; Niu, R.; Xu, L.; Cao, J.; Lee, S. Removal of Indoor Volatile Organic Compounds via Photocatalytic Oxidation: A Short Review and Prospect. Molecules 2016, 21, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Zhang, M.; Toyota, K. Biodegradation of Volatile Organic Compounds and Their Effects on Biodegradability under Co-Existing Conditions. Microbes Environ. 2017, 32, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Gao, B.; Ok, Y.S.; Dong, L. Integrated Adsorption and Photocatalytic Degradation of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) Using Carbon-Based Nanocomposites: A Critical Review. Chemosphere 2019, 218, 845–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, B.; Creamer, A.E.; Cao, C.; Li, Y. Adsorption of VOCs onto Engineered Carbon Materials: A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 338, 102–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, W.; Zhang, X.; Chen, K.; Fang, J.; He, F.; Hu, X.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Ok, Y.S.; Gao, B. Enhanced Adsorption Performance and Governing Mechanisms of Ball-Milled Biochar for the Removal of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs). Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 123842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Shen, D.; Luo, K.H. A Critical Review on VOCs Adsorption by Different Porous Materials: Species, Mechanisms and Modification Methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 122102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-H.; Gao, K.-X.; Meng, Y.-N.; Wu, X.-K.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Z.-X. Solution Thermodynamics of Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids and Volatile Organic Compounds: Benzene and Acetone. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2015, 60, 1600–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Mu, M.; Li, J.; Wu, B.; Xu, R.; Liu, N.; Chen, B.; Dai, C. Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids Introduced into π-Electron Donors: Highly Efficient Toluene Capture. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 9058–9069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, Z.; Xu, X.; Gong, S.; Zhou, Y. The Molecular Behavior of Pyridinium/Imidazolium Based Ionic Liquids and Toluene Binary Systems. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2021, 23, 13300–13309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichowska-Kopczyńska, I.; Aranowski, R. Use of Pyridinium and Pyrrolidinium Ionic Liquids for Removal of Toluene from Gas Streams. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 298, 112091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.; Zhuang, H.; Wen, Y.; Han, F.; Yang, Q.; Yang, L.; Li, Z.; Xia, C. Efficient Thiolation of Alcohols Catalyzed by Long Chained Acid-Functionalized Ionic Liquids under Mild Conditions. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 2019, 3012–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Lu, B.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Cai, Q. A Functionalized Basic Ionic Liquid for Synthesis of Dimethyl Carbonate from Methanol and CO2. Fuel Process. Technol. 2013, 115, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Lu, B.; Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, J.; Cai, Q. Hydroxyl-Functionalized Ionic Liquid for Activation and Conversion of CO2 and Methanol into Dimethyl Carbonate. J. CO2 Util. 2015, 12, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahri, F.; Bacha, K.; Chiki, F.F.; Mbakidi, J.-P.; Panda, S.; Bouquillon, S.; Fourmentin, S. Air Pollution: New Bio-Based Ionic Liquids Absorb Both Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic Volatile Organic Compounds with High Efficiency. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 1403–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Catalyst | Reaction Temperature °C | Initial Pressure MPa | Catalyst Dosage mol% | Reaction Time h | Productivity % | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HEEPzBr | 110 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 91.2 | [50] |
| PIL-COOH@MIL-101 | 70 | 1 | 2.5 | 92.7 | [51] | |
| CMEPzBR | 110 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 99.4 | [52] |
| PS-ImEIMECOOHI2 | 120 | 2 | 0.87 | 2 | 99.4 ± 1.6 | [53] |
| PAIL-3 | 60 | 0.5 | 5 | 3 | 96.1 | [54] |
| [APbim][Lac] | 80 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 12 | 97 | [48] |
| Ionic Liquid | Temperature K | Pressure Bar | Solubility mol/mol IL | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [1, 2, 3-TrizH2][NO3]2 | 303.15 | 1 | 4.19 | [114] |
| [1, 2, 4-TrizH2][NO3]2 | 4.14 | |||
| [1, 2, 3-TrizH2][CF3SO3]2 | 6.52 | |||
| [1, 2, 4-TrizH2][CF3SO3]2 | 6.17 | |||
| [1, 2, 3-TrizH2][NO3]2 | 313.15 | 3.64 | ||
| [1, 2, 4-TrizH2][NO3]2 | 3.59 | |||
| [1, 2, 3-TrizH2][CF3SO3]2 | 5.69 | |||
| [1, 2, 4-TrizH2][CF3SO3]2 | 5.21 | |||
| [EtOHim][NTf2] | 313.15 | 1 | 3.11 | [112] |
| [EtOHim][BF4] | 2.47 | |||
| [EtOHim][SCN] | 2.23 | |||
| LiNTf2 | 313.1 | 1 | 3.92 | [116] |
| [Im][NTF2] | 3.46 | |||
| [2-Mim][NTf2] | 3.04 | |||
| [EIM][Li(NTf2)2] | 6.62 | |||
| [2-Mim][Li(NTf2)2] | 7.01 | |||
| [4-MeOHPy][NTf2] | 313.15 | 1 | 3.43 | [113] |
| [2-EtOHPy][NTf2] | 3.33 | |||
| [2-MeOHPy][NTf2] | 3.27 | |||
| [2-EtOHPy][SCN] | 2.33 | |||
| [2-EtOHPy][NO3] | 1.97 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Wang, R. Treatment and Resource Utilization of Gaseous Pollutants in Functionalized Ionic Liquids. Molecules 2024, 29, 3279. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143279
Wang J, Wang R. Treatment and Resource Utilization of Gaseous Pollutants in Functionalized Ionic Liquids. Molecules. 2024; 29(14):3279. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143279
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jiayu, and Rui Wang. 2024. "Treatment and Resource Utilization of Gaseous Pollutants in Functionalized Ionic Liquids" Molecules 29, no. 14: 3279. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143279
APA StyleWang, J., & Wang, R. (2024). Treatment and Resource Utilization of Gaseous Pollutants in Functionalized Ionic Liquids. Molecules, 29(14), 3279. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143279








