Abstract
Phellinus is a precious perennial medicinal fungus. Its polysaccharides are important bioactive components, and their chemical composition is complex. The polysaccharides are mainly extracted from the fruiting body and mycelium. The yield of the polysaccharides is dependent on the extraction method. They have many pharmacological activities, such as antitumor, immunomodulatory, antioxidant, hypoglycemic, anti-inflammatory, etc. They are also reported to show minor toxic and side effects. Many studies have reported the anticancer activity of Phellinus polysaccharides. This review paper provides a comprehensive examination of the current methodologies for the extraction and purification of Phellinus polysaccharides. Additionally, it delves into the structural characteristics, pharmacological activities, and mechanisms of action of these polysaccharides. The primary aim of this review is to offer a valuable resource for researchers, facilitating further studies on Phellinus polysaccharides and their potential applications.
1. Introduction
Phellinus, often referred to as “forest gold”, is a valuable perennial medicinal fungus [1]. It belongs to the following family tree: Basidiomycotina → Hymenomycetes → Aphyllophorales → Hymenochaetaceae → Phellinus. There are mainly three types of Phellinus species: P. igniarius, P. linteus, and P. baumii Pilat [2,3]. Phellinus is parasitic and grows on the trunk of poplar, mulberry, willow, birch, and rhododendron. It is distributed in northeast, north, and northwest China, Sichuan, and Yunnan. Phellinus is widely used in Asian traditional medicine, and its medicinal use was first recorded in Li Shizhen’s Compendium of Materia Medica [4]. The recorded applications of Phellinus in ancient books are as follows: (1) promoting blood circulation, (2) relieving pain, (3) tonifying deficiency, (4) astringent hemostasis, (5) heat clearing, (6) detoxification, etc. [5]. Pharmacological studies have found that Phellinus has antitumor, immune-regulatory, antioxidant, hypoglycemic, and anti-inflammatory activities, etc. [6].
Polysaccharides are among the most significant components of fungi, playing a crucial role in immune regulation and exhibiting notable antitumor activity [7]. Over the past two decades, numerous pharmacologically active metabolites have been isolated and identified from Phellinus. Among these, polysaccharides have been recognized as the most active and significant components. [8]. The polysaccharides of Phellinus exhibit notable pharmacological effects, primarily extracted from the fruiting body and the mycelium. Their chemical composition is complex, and various extraction and purification methods can influence their pharmacological activities. Consequently, this review summarizes the extraction and purification techniques, structural characteristics, and pharmacological activities of polysaccharides obtained from P. igniarius and P. linteus. We believe this review will serve as a valuable educational resource for researchers, advancing the research and development of Phellinus polysaccharides.
Integrated efforts are essential for the study of antidiabetic drugs, with iminosugars and sugar derivatives playing a key role in this process [9]. Integrated efforts are essential for the study of antidiabetic drugs, with iminosugars and sugar derivatives playing a key role in this process [10]. Studies have shown that sugar-furan and n-butyl-substituted sugar-furan molecules are the most active and highly selective inhibitors [11]. These findings suggest that alternative methods for treating diabetes can be derived from this research, offering valuable insights for the development of new antidiabetic drugs utilizing these polysaccharides or their derivatives in the future.
2. Extraction of Phellinus Polysaccharides
Commonly used extraction methods for polysaccharides include solvent extraction, ultrasonic-wave-assisted extraction, microwave-assisted extraction, and enzyme-assisted extraction. The advantages and disadvantages of these methods are summarized in Table 1. The choice of extraction method significantly influences the properties of the polysaccharides. Traditional solvent extraction methods encompass hot water extraction, dilute acid extraction, and alkaline extraction [12]. The solvent extraction method is simple and requires very minimal equipment.

Table 1.
The advantages and disadvantages of extraction methods.
2.1. Hot Water Extraction
Hot water extraction is a traditional method for extracting water-soluble polysaccharides from plants, utilizing hot water in a safe and environmentally friendly manner. This method is widely used in current research due to its minimal impact on the chemical structure of the polysaccharides [13]. It is a simple technique that produces high yields of polysaccharides [14]. However, it requires longer extraction times [15].
The yield of polysaccharides is influenced by various factors, including temperature, time, number of cycles, and solid:liquid ratio. Yang et al. [16] optimized the experiment parameters for polysaccharides from P. igniarius using an orthogonal experiment, determining the optimal conditions as the temperature at 90 °C, extraction time of 2 h, 2 cycles, and a solid:liquid ratio of 1:50. Dou et al. [17] extracted polysaccharides from pulverized P. igniarius fruiting bodies by refluxing for 8 h, repeating the process three times, then combining, concentrating, and freeze-drying the filtrates. Xu et al. [18] optimized the solid:liquid ratio and extraction time at a constant temperature of 100 °C, finding the optimal solid:liquid ratio to be 1:45 with an extraction time of 3.5 h. Li et al. [19] conducted single-factor and orthogonal experiments to optimize the extraction process from P. igniarius, reporting the optimum conditions as temperature at 100 °C, extraction time of 2 h, 2 cycles, and a solid:liquid ratio of 1:15. Under these conditions, the reported yield was 6.64%.
2.2. Ultrasonic Wave-Assisted Extraction
The ultrasonic extraction method utilizes ultrasonic-assisted solvent extraction, which involves cavitation, vibration, crushing, and stirring. Ultrasonic waves disrupt the cell walls and enhance the penetration of the extraction solvent, allowing it to penetrate the cells of the medicinal materials more effectively. This improves the extraction rate and reduces the extraction time. Additionally, this method avoids the use of high temperatures and prolonged extraction periods, therefore minimizing the impact on the composition of the polysaccharides [20]. Guo et al. [21] investigated the optimum conditions for ultrasonic extraction using an orthogonal experiment, reporting the following optimal parameters: extraction power of 120 W, solid:liquid ratio of 1:40, temperature of 45 °C, and extraction time of 30 min. Under these conditions, the yield of polysaccharides from P. linteus mycelium was 107.324 mg/g. Fu et al. [22] reported the optimal conditions for extracting polysaccharides from P. igniarius mycelia as follows: extraction power of 210 W, solid:liquid ratio of 1:50, and extraction time of 60 min. The polysaccharide yield under these conditions was 12.78%.
Ultrasonic waves are often combined with other extraction methods, such as enzyme-assisted and microwave-assisted extraction [23,24,25]. Ying et al. [25] employed an ultrasonic-microwave-assisted method to extract polysaccharides from P. igniarius fruiting bodies, achieving a reported yield of 10.6%. Additionally, the antitumor and antioxidant activities of these polysaccharides were superior to those obtained using hot water extraction.
2.3. Microwave-Assisted Extraction
Microwave-assisted extraction is also a commonly used method. In this technique, low-energy microwaves disrupt the cell wall, releasing intracellular polysaccharides. The advantages of microwave-assisted extraction include high efficiency and selectivity. However, the primary disadvantage is the high cost associated with this method, making it unsuitable for large-scale industrial production [26,27].
Qin et al. [28] optimized the extraction conditions using the single-factor method, determining the optimal parameters as power at 540 W, a solid:liquid ratio of 1:41, and an extraction time of 51 min. Under these conditions, the yield was 4.18%. The influence of various factors was ranked as follows: microwave power > solid:liquid ratio > extraction time. Guo et al. [29] compared microwave-assisted extraction with hot water extraction, reporting a 20.5% increase in yield from P. igniarius using microwave-assisted extraction. Shi et al. [27] compared three kinds of extraction methods: hot water, microwave-assisted, and ultrasonic wave-assisted extraction. They found that the yield from microwave-assisted was twice as high as that from hot water extraction and 40% higher than that from ultrasonic wave-assisted extraction. Additionally, the extraction time for microwave-assisted extraction was significantly reduced.
2.4. Enzyme-Assisted Extraction
The enzyme-assisted extraction method utilizes enzymes such as cellulase, protease, and pectinase to accelerate the decomposition of plant tissue, therefore dissolving the intracellular polysaccharides in the solvent. This method offers higher extraction efficiency compared to hot water extraction, requiring mild conditions that do not alter the chemical composition of the polysaccharides. Often, enzyme-assisted extraction is combined with ultrasound wave-assisted methods, known as the ultrasonic compound enzyme method, to further enhance extraction efficiency.
Cheng et al. [30] combined ultrasonic waves and complex enzymes to extract the polysaccharides from the fruiting bodies of Phellinus. The material was treated with a combination of cellulase, pectinase, and protease. Using the response surface method to optimize the extraction parameters, the reported optimal conditions were power 360.6 W, solid:liquid ratio 1:32.5, and extraction time 32.7 min. Under these conditions, the yield was 3.31%. Xie et al. [24] employed a sequential extraction method using ultrasonic waves followed by enzyme treatment to extract the polysaccharides from P. linteus mycelia. The optimal ultrasonics were extraction time 20 min, solid:liquid ratio 1:25, and power 500 W. The subsequent enzyme treatment conditions were pH 6.5, temperature 50 °C, cellulase 2.5%, pectinase 2.5%, protease 1% and treatment time of 120 min. The polysaccharide yield obtained under these conditions was 6.619%.
2.5. Other Methods
Low temperature, low pressure, and alkaline water extraction methods have also been reported [31,32]. The yield and antioxidant activity (TEAC) of polysaccharides obtained from yellow mycelia were 4.41% and 6.33 mM, respectively, under the conditions of an extraction time of 1.8 h, pressure of 0.059 MPa, and liquid-to-material ratio of 52.5 mL/g [31]. During the extraction process, the alkaline solution effectively breaks the hydrogen bonds between cellulose and hemicellulose in the cell wall, allowing insoluble polysaccharides to be released and converted into soluble polysaccharides, significantly improving the extraction rate [32]. Leong et al. [33] examined the structural changes in polysaccharides isolated under acidic and alkaline extraction conditions. They found that, compared to acidic conditions, polysaccharides are more easily hydrolyzed under alkaline extraction conditions. This hydrolysis results in shorter side chains, reduced molecular weight, increased water solubility, and alterations in the molecular spatial arrangement of the extracted polysaccharides.
3. Separation and Purification of Phellinus Polysaccharides
The separation of polysaccharides from proteins and pigments can be achieved through deproteinization and decolorization processes, respectively. The polysaccharides obtained from the extraction mentioned typically contain proteins and pigments. Common methods for removing proteins include the Sevag method, the trichloroacetic acid (TCA) method, and the alcohol precipitation method. [34,35,36]. Pigments can be removed using techniques such as carbon decolorization, macroporous resin adsorption, and flocculation [37].
Further purification is required to obtain highly pure homogeneous polysaccharides with stable and functional properties. The main purification techniques include graded alcohol precipitation, ultrafiltration, ion-exchange chromatography, and gel filtration [38,39]. Xie et al. [34] reported that the trichloroacetic acid (TCA) method is more effective than the Sevag method for removing proteins. The optimal conditions for the TCA method are a TCA concentration of 5%, a treatment time of 30 min, and three treatments. Ge et al. [36] compared the effects of alcohol precipitation and flocculation (using chitosan adsorbent) on the loss of polysaccharides from P. igniarius, finding that the flocculation method resulted in minimal polysaccharide loss. Xie et al. [40] used DEAE-52 cellulose ion-exchange chromatography and Sephadex G-100 gel filtration chromatography to obtain two homogeneous polysaccharides, Pmae 47000 and Pmae 8700. Ge et al. [41] employed DEAE-Sepharose for purification, developing Fast-Flow ion exchange and Sephacryl S-400 High-Resolution gel filtration methods to isolate pure polysaccharide PBF6. Wu et al. [42] utilized an aqueous two-phase system (ATPS) of choline chloride ([Chol] Cl) and K2HPO4 to purify the polysaccharides, demonstrating that the antioxidant activity of these polysaccharides was superior to those obtained via alcohol precipitation. The optimal parameters for this method were 68.9% K2HPO4, 20% [Chol] Cl, a temperature of 21.2 °C, and a treatment time of 30 min. The flow chart of extraction, separation, and purification of Phellinus polysaccharides is shown in Figure 1.
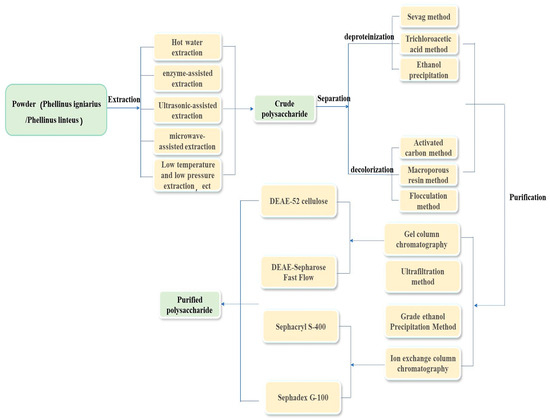
Figure 1.
Flow chart of extraction, separation, and purification of Phellinus polysaccharides.
4. Chemical Composition and Structure of Phellinus Polysaccharides
4.1. Structural Analysis of Phellinus Polysaccharides
The structure of fungal polysaccharides can be categorized into primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary levels, with the primary focus of current research being on elucidating the primary structure. The pharmacological activities of polysaccharides are highly dependent on their structures, making structural characterization crucial. Studies aimed at confirming the structure involve determining molecular weight, monosaccharide composition, main chain composition, glycosidic bond type, and more. Commonly used methods for analyzing polysaccharide structure include high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) for monosaccharide composition and molecular weight, gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) for determining monosaccharide composition after hydrolysis and derivation, as well as the type of glycosidic bonds [43,44,45,46,47]. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) is used to identify functional groups and the form of glycoside rings (pyran, furan) [48]. After hydrolysis and derivation, the monosaccharide composition is analyzed using HPLC, GC-MS, and high-performance anion-exchange chromatography (HPAEC) [49]. GC-MS analysis can also determine the type of glycosidic bonds. High-performance liquid and gel chromatography techniques are also commonly used to analyze the molecular weight of polysaccharides. Size exclusion chromatography (SEC) coupled with a multi-angle laser light scattering (MALLS) detector and a differential refractive index (RI) detector is employed to analyze molecular conformation and molecular weight [50]. UV-Vis spectroscopy is used to assess the purity of polysaccharides by scanning over the entire UV range [51]. GC-MS and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) can analyze the main and side-chain composition. NMR analyzes main and side-chain compositions, and combined with one-dimensional and two-dimensional spectra, it can infer the linkage and sequence of sugar residues [52]. Additionally, periodate oxidation and Smith degradation can be used to analyze the structure of polysaccharides [17]. These comprehensive techniques ensure a detailed understanding of the structural attributes of polysaccharides, which is essential for correlating their structure with their pharmacological activities.
4.2. Chemistry of Phellinus Polysaccharides
The chemical structure of Phellinus polysaccharides is extremely complex, with different polysaccharides being obtained from the same species using various culturing and extraction methods. Phellinus polysaccharides can be categorized into those derived from the fruiting body, mycelium, and extracellular sources (from fermentation broth). Research has primarily focused on the structure of polysaccharides from the fruiting body, particularly P. igniarius and P. linteus, while the structure of extracellular polysaccharides has received comparatively little attention. The monosaccharide composition of mycelium polysaccharides is more complex than that of the fruiting body, containing higher amounts of fucose and mannose. The molecular weight of polysaccharides from the fruiting body ranges from 104 to 106 Da, whereas polysaccharides from the extracellular matrix have molecular weights greater than 106 Da.
Polysaccharides from the fruiting body are mainly heterogeneous and composed mainly of glucose (50~70%). They also contain mannose, galactose, xylose, arabinose, and rhamnose. Its glycosidic linkages are (1→3), (1→6), or (1→3, 6). Its main chain is →3)-β-D-Glcp-(1→. A study has reported 3 (4)-O-methyl-hexose in P. igniarius polysaccharides. Ge et al. [53] reported the presence of mannose, glucose, galactose, and 3 (4)-O-methyl-hexose in a molar ratio of 0.64:1:1.94: 0.93 PIPF polysaccharide from P. igniarius. Kim et al. [54] derived a proteoglycan from the fruiting bodies of P. linteus containing mannose, galactose, glucose, arabinose, and xylose. The glycosidic linkages of this proteoglycan were α and β, with β-(1,3)-d-glucose as the backbone. Dou et al. [17] purified two neutral heteropolysaccharides (PL-A (14.2 × 103) and PL-B (22.2 × 103), from fruiting bodies of P. linteus. PL-A contains high glucose and low mannose amounts. PL-B is a proteoglycan containing rhamnose. The backbone of both is β-(1→3)—glucan. PL-A contains mannose in the branch and is connected to the backbone via (1→6) linkages. PL-B contains glucose, mannose, rhamnose, and amino acids in the branch that is connected to the backbone via (1→6) and (1→2).
The branches in polysaccharides from mycelium are mainly composed of mannose, galactose, and glucose. Their main chain is mainly composed of (1→3)-D-glucose. Tomoyuki et al. [55] extracted a protein-glucan complex from P. linteus mycelium containing 39.3% polysaccharide and connected to glucan via α-(1,3). Kim et al. [56] reported polysaccharide-protein complex (PPC) from the mycelium of P. linteus whose molecular weight is 73 KDa and contains mainly D-glucose and D-mannose in the molar ratio of 3:2. Song et al. [57] reported a proteoglycan PLC from P. linteus mycelium containing glucuronic acid (6.8%), neutral sugars are mannose (44.2%), galactose (24.1%), glucose (21.1%), arabinose (7.5%) and xylose (3.7%). Wu et al. [58] reported PIP1 polysaccharide (molecular weight, 1.7 × 104 Da) in the fermented mycelium of P. linteus, which contains glucose, galactose, and mannose (3.70:4.06:1.00). The glycosidic bond type of the polysaccharide is β. The main chain is (1→3)-glucose and (1→4)-mannose. In addition, Yuan et al. [43] reported high molecular weight (8.12 × 105 Da) heteropolysaccharide PIP-1 from P. igniarius fermented mycelium, which is composed of mannose, glucose, and galactose (2.41:87.74:3.86).
The extracellular polysaccharides of Phellinus are obtained from the fermentation broth, and the mycelium polysaccharides typically contain glucose, mannose, and galactose. Lee et al. [59] reported a heteroglycan-protein complex from P. linteus with molecular weights ranging from 9.4 × 103 Da to 15 × 103 Da, comprising glucose, galactose, mannose, arabinose, xylose, uronic acid, and amino sugars. Hwang, HJ et al. [47] isolated three components (KCTC6190: Fr-I, Fr-II, and Fr-III) from P. linteus with molecular weights of 43.43 × 104 Da, 3.14 × 104 Da, and 1.29 × 104 Da, respectively. These components primarily contain glucose, mannose, and galactose and do not have protein content. Jia et al. [48] reported the separation of a high molecular weight polysaccharide (HHM, 2.84 × 106 Da) and a low molecular weight polysaccharide (HLM, 5.33 × 104 Da) from the fermentation broth. HHM contains glucose, while HLM contains glucose and galactose. The structural characteristics of Phellinus polysaccharides are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
The structural characteristics of Phellinus polysaccharides.
5. Pharmacological Activities of Phellinus Polysaccharides
5.1. Antitumor Activity
Phellinus is known to produce polysaccharides with significant antitumor activity, achieving a tumor inhibition rate of 96.7 % [63]. The primary mechanism of action involves blocking the cell cycle and inducing apoptosis [66,67]. Phellinus polysaccharides have demonstrated antitumor effects on various cancers, including liver, lung, colon, and breast cancers. The specific details of these effects are illustrated in Figure 2.
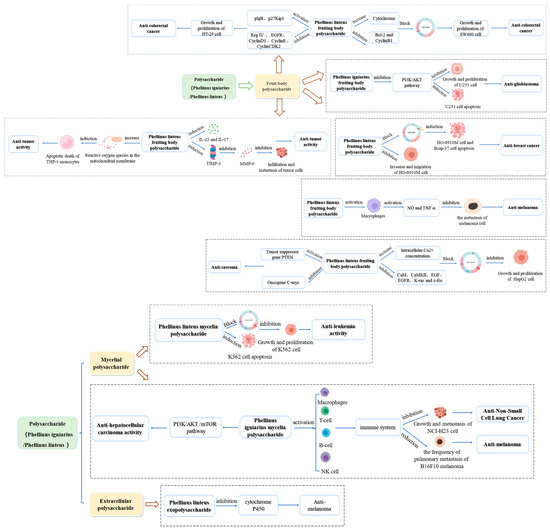
Figure 2.
Summary of the antitumor mechanisms of Phellinus Polysaccharides.
5.1.1. Antitumor Activity of Polysaccharides from Mycelium
Leukemia is a common malignant tumor of the blood system. It has been reported that intracellular polysaccharides from P. linteus significantly inhibit the proliferation of human leukemia cells (K562). The mechanism involves inducing apoptosis and blocking DNA synthesis during the S phase of cell division. However, there are currently no in vivo studies to confirm its activity in a biological system [68].
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common primary malignant tumor of the liver and ranks second among malignant tumors in terms of its serious impact on people’s health [69]. Currently, the primary therapeutic option for HCC is surgery, as there are no effective drugs available for its treatment. Zhao et al. [70] investigated the antitumor activity of mycelial polysaccharides from P. igniarius in a mouse model. The results demonstrated that these polysaccharides inhibit tumor proliferation and enhance the efficacy of cyclophosphamide while reducing its toxicity. The antitumor activity is mediated through the downregulation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and inflammatory factors such as TNF-α and IL-6. Wei et al. [71] investigated the antitumor activity of polysaccharides from P. igniarius mycelia at three different doses (100, 200, and 400 mg/kg) in hepatoma H22 tumor-bearing mice. The inhibition rates were 26.71%, 34.48%, and 56.65%, respectively. Additionally, the polysaccharides exhibited only mild side effects, and the weight of the mice was not affected.
Current chemotherapeutic agents often exhibit significant toxic effects and possess only limited efficacy against tumor growth and metastasis [71]. To enhance the efficacy of chemotherapeutic drugs, cytokines, and bacterial products have been utilized as immunochemotherapy agents. Han et al. [72] reported that polysaccharides from P. linteus mycelium prolonged the survival rate of B16F10 tumor-bearing mice and reduced the metastasis frequency of melanoma. Additionally, these polysaccharides inhibited tumor growth in the NCI-H23 lung cancer mouse model. It is postulated that P. linteus mycelium polysaccharides enhance the activity of T cells, macrophages, natural killer cells, and B cells, therefore inhibiting tumor growth and metastasis through immune system enhancement.
5.1.2. Antitumor Activity of Polysaccharide from Phellinus Fruiting Body
Zhao et al. [73] investigated the antitumor activity of polysaccharides from P. linteus fruiting bodies both in vitro and in vivo using a transplanted tumor model in nude mice. The polysaccharides inhibited the growth of breast tumors by 65.37 %. In vitro, they demonstrated inhibitory activity against highly metastatic ovarian cancer (HO-8910M) and breast cancer (Bcap-37) cells, with inhibition rates of 15.53% and 23.81%, respectively. The polysaccharides blocked the G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle, inhibited the adhesion of tumor cells to the extracellular matrix (ECM), and suppressed cell invasion and migration. Additionally, in vivo experiments showed that crude polysaccharides of Radix Corydalis had a significant inhibitory effect on the growth of Bcap-37 transplanted tumors in nude mice. It was found that P. linteus polysaccharides (PL) also directly killed HO-8910PM and Bcap-37 tumor cells cultured in vitro. The comparison of in vivo and in vitro results revealed that the inhibition rate of PL on the growth of transplanted tumors was 65.37%, while the highest inhibition rate on tumor cell proliferation was 23.81%. Furthermore, P. linteus polysaccharides inhibited the proliferation of human hepatoma (HepG2) cells. Zhong et al. [74] reported that P. linteus polysaccharides mediate their antitumor activity by increasing the intracellular Ca2+ concentration. This process down-regulates the expression of several critical genes, including Calmodulin (CaM), Ca2+/calmodulin dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII), Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF), epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), Kirsten ratsarcoma viral oncogene homolog (K-ras), and cellular oncogene fos (c-fos) genes. Additionally, they block the S phase of the cell cycle, contributing to its antitumor effects. Liu et al. [75] studied the in vitro and in vivo antitumor effects of polysaccharides from the P. linteus fruiting body using sarcoma S180 cells. The results demonstrated significant antitumor activity both in vitro and in vivo. This activity was attributed to the upregulation of the tumor suppressor gene phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome ten (PTEN) and the downregulation of the oncogene C-myc protein. LYU et al. [76] investigated the antitumor activity of polysaccharides from the P. igniarius fruiting body at doses of 1.25, 2.5, and 5 g/kg in S180 tumor-bearing mice. The results showed that the polysaccharides exhibited significant antitumor activity and increased the spleen index and thymus index, indicating an enhancement in immune function.
In addition, some studies have found that the antitumor mechanisms of polysaccharides from P. linteus fruiting body (CPP) are mediated through the regulation of Tissue Inhibitors of Metalloproteinase 1(TIMP-1), interleukin-23(IL-23), interleukin-17(IL-17), and matrix metallopeptidase 9 (MMP-9) [77]. The tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1) complexes with MMP-9 at a 1:1 ratio to inhibit MMP-9 activity [78]. The polysaccharides increased the TIMP-1 expression in RAW264.7 macrophages and mouse liver, contributing to their antitumor effects.
Apoptosis plays a critical role in the suppression of tumor development and can be initiated through external (death receptor-mediated) and internal (mitochondrial-mediated) pathways [79,80]. Griensven et al. [81] investigated the apoptosis of human leukemic mononuclear cells (THP-1) induced by polysaccharides from the fruiting bodies of P. linteus. The results demonstrated that these polysaccharides promote apoptosis in THP-1 cells by increasing reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the mitochondrial membrane. This increase in ROS leads to mitochondrial dysfunction, ultimately triggering apoptosis.
Glioblastoma (GBM) is a common primary intracranial tumor and a malignant tumor of the nervous system [82]. The current standard treatment involves surgery combined with radiotherapy and chemotherapy. However, these treatments often lead to immunosuppression, and, over time, chemotherapy can result in drug resistance, affecting the efficacy of the treatment. Wu et al. [83] studied the effects of P. igniarius polysaccharides on the proliferation and migration of glioma cells. Their results showed that P. igniarius polysaccharides inhibit the proliferation and migration of human glioma U251 cells and promote apoptosis. The underlying mechanism is believed to be related to the inhibition of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.
Colorectal cancer is a very common type of cancer. It has been found that P. linteus polysaccharide can inhibit the growth and invasion of SW480 colorectal cancer cells both in vivo and in vitro. The mechanism behind this effect is believed to be related to the inhibition of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway [84]. Other studies have found that the inhibitory effect of P. linteus polysaccharide on SW480 cell proliferation is achieved by inducing apoptosis, arresting the cell cycle at the G2/M phase, decreasing the B-cell lymphoma-2(Bcl-2) and cyclin B1 expression and increasing the cytochrome release [85]. This study lays the foundation for applying P. linteus polysaccharides as chemopreventive drugs and immune stimulants. To further explore the mechanism of antitumor activity of P. linteus polysaccharide, Li et al. [60] tested the anticancer activity of a purified proteoglycan P1 on HepG2, HT-29, NCI-H460 and MCF-7 cells. It was reported that P1 was effective in these cells, which had a certain degree of antitumor effect, and the best effect was on HT-29 cells. The authors found that P1 can up-regulate the expression of polymeric immunoglobulin receptor (pIgR) and down-regulate the expression of regenerating islet-derived family member 4(RegIV) and EGFR to inhibit cell mitosis and proliferation. Zhong et al. [86] found that P1 can arrest HT29 cells in the S phase of the cell cycle by up-regulating cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor (p27Kip1) and inhibiting cancer cell proliferation by downregulating cyclin D1 cyclin E and cyclin CDK2.
Due to the large differences in the polysaccharide structures of P. igniarius mycelium and fruiting bodies, their antitumor activities also differ. Studies have found that polysaccharides from P. igniarius fruiting bodies have significantly higher antitumor efficacy than polysaccharides from mycelium. Ying et al. [87] compared the in vitro and in vivo antitumor activity of P. igniarius mycelial polysaccharide and fruiting body polysaccharide. Cell Counting Kit-8(CCK-8) staining was used in in vitro experiments. In mice, the in vivo activity was tested by administering the polysaccharide intragastrically for 30 days. Both studies showed that polysaccharides from fruit and mycelium had an antitumor effect, which is more for polysaccharides from fruiting bodies.
Polysaccharides from P. linteus fruiting body and mycelium showed different modes of action in inhibiting tumor cell metastasis. Macrophages are essential for maintaining homeostasis and host defense. Kim et al. [88] found that peritoneal macrophages (PM) cultured with mulberry fruiting body polysaccharides (PL) had a dose-dependent killing effect on B16 melanoma cells. At 200 μg/mL, the inhibition rate of PL on cell growth increased by 4 times. Nitric oxide (NO) is the main effector molecule produced by macrophages to destroy tumor cells. Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) is an important defense cytokine produced by macrophages against tumor cells. PL has no direct cytotoxicity and can stimulate macrophages to produce NO and TNF-α, thus producing an antitumor metastasis effect. Han et al. [89] found that polysaccharides from mulberry mycelium have two ways to prevent tumor metastasis. On the one hand, polysaccharides from P. linteus mycelium can activate host immunity to inhibit tumor metastasis. On the other hand, PL can directly inhibit the adhesion and invasion of tumor cells.
5.1.3. Antitumor Activity of Phellinus Exopolysaccharide
Chemoprevention is the use of chemical or natural substances to prevent cancer development. Chemical prophylaxis mainly acts on the stage of carcinogenesis, among which the conversion of carcinogens to metabolites by cytochrome P450 (CYP) plays an important role. Shon et al. [90] studied the effect of polysaccharides from the fermentation broth of P. linteus on the activity of cytochrome P450 isozymes in rat liver microsomes. The results showed that extracellular polysaccharides decreased the activity of Cytochrome P450 (CYP1A1) in a dose-dependent manner and had a strong inhibitory effect on CYP isozymes. It can be concluded that the extracellular polysaccharide of P. linteus has much potential to become a chemopreventive agent. However, the in vivo metabolism of extracellular polysaccharides of P. linteus remains to be studied.
5.2. Antioxidant Activity
Oxidative stress is a negative effect of free radicals in the body, which is an important factor leading to aging and disease [91]. Under normal circumstances, the production and clearance of free radicals in the human body are in a dynamic balance. Once this balance is broken, it will cause body damage and lead to various diseases. Therefore, the research on antioxidant activity mainly focuses on the scavenging of various free radicals. The antioxidant activity of the Phellinus polysaccharide is shown in Figure 3.
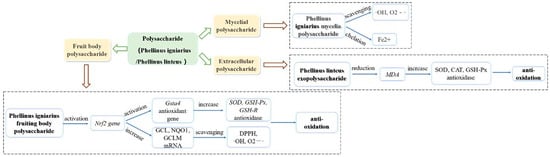
Figure 3.
Summary of the antitumor mechanisms of Phellinus Polysaccharides.
5.2.1. Antioxidant Activity of Polysaccharides from Phellinus Mycelium
Yan et al. [61] studied the antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from P. igniarius mycelium (IPS) through an in vitro antioxidant model. The results showed that IPS could scavenge ∙OH, O2− and chelated Fe2+. Wang et al. [92] analyzed the polysaccharides extracted using different methods (hot water, 1% (NH4)2C2O4, and 1.25 M NaOH/0.05% NaBH4) by TEAC and Ferric reducing/antioxidant power (FRAP) in vitro. The results showed that the polysaccharides extracted by the three methods showed a certain degree of antioxidant activity. Moreover, the antioxidant activity of these polysaccharides is positively correlated with the activation ability of uronic acid groups.
5.2.2. Antioxidant Activity of Polysaccharide from Phellinus Fruiting Body
Schistosoma japonicum can destroy the body’s antioxidant defense mechanism of the body. Zhang et al. [93] established a mouse model infected with Schistosoma japonicum to investigate the antioxidant activity of ethanol-extracted polysaccharides (PPI) from P. igniarius. The results showed that PPI could significantly improve the body’s antioxidant capacity, increase the content of glutathione (GSH), and restore the activities of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) and glutathione reductase (GSH-R). Its mechanism is related to activating the expression of the nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2(Nrf2) gene and promoting the expression of downstream antioxidant genes such as the glutathione transferase gene, Gsta4.
Hu et al. [4] found that polysaccharides from P. igniarius fruiting body can scavenge 1,1-diphenyl-2-picryhydrazyl (DPPH), superoxide anion, and hydroxyl radicals. Its mechanism regulates the Nrf2 pathway and increases the mRNA expression of glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic (GCLC), quinone acceptor oxidoreductase 1(NQO1), and glutamatecysteine ligase, modifier subunit (GCLM).
5.2.3. Antitumor Activity of Phellinus Exopolysaccharide
Yan et al. [65] studied the effects of PL-A11 on antioxidant enzymes in the serum and liver of aging mice. The results showed that PL-A11 could significantly reduce the level of malondialdehyde (MDA) and increase the activities of antioxidant enzymes (SOD, CAT, GSH-Px) in serum and liver. Zhu et al. [94] used a chemical simulation system to compare the antioxidant capacity of intracellular polysaccharides (IPS) and extracellular polysaccharides (EPS). The results showed that the antioxidant capacity of IPS was better than that of EPS. Moreover, the antioxidant capacity of P. linteus polysaccharides showed an obvious dose-effect relationship.
5.3. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
Inflammation is still one of the most common and serious complications of the disease. Excessive inflammation can lead to a variety of diseases. Few researchers [95] studied the anti-inflammatory activities of intracellular and extracellular polysaccharides of P. igniarius using xylene-induced ear inflammation (acute inflammation model) and glaucoma induced by a cotton ball (chronic inflammation model) in mice. The results showed that both intracellular and extracellular polysaccharides had anti-inflammatory effects to a certain extent. Xie et al. [96] showed that P. linteus polysaccharide decreased the expression of pro-inflammatory factors (TNF-α, IL-1 β, IL-2, IL-6, IL-12) and increased the expression of anti-inflammatory factors (IL-4, IL-10) in mouse macrophages, Mouse Abelson murine leukemia virus-transformed macrophages (RAW 264.7). NF-κB translocation was significantly inhibited in a dose-dependent manner. Its mechanism involves inhibiting the translocation of NF-κB from the cytoplasm to the nucleus and regulating the balance of anti-inflammatory and pro-inflammatory factors. However, this pathway has not been verified in animal models.
Abdominal infection is often accompanied by intraperitoneal fibrin deposition, leading to abscess and adhesion. Bae et al. [97] showed that P. linteus polysaccharides reduced abscess formation and adhesion in a rat model of peritonitis. Its mechanism was related to regulating the fibrinolytic ability of urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) and tissue-type plasminogen activator (tPA) produced by macrophages.
Colitis is a chronic, non-specific inflammation of the colon and rectum, which may cause colon cancer [98]. Hu et al. [99] used lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in RAW264.7 cells (in vitro) and sodium dextran sulfate-induced colitis in mice (in vivo) to the effect of polysaccharides from P. linteus mycelium. DAI score was used to evaluate the anti-inflammatory efficacy, DAI = (weight loss score + stool score + blood stool score)/3. The results showed that polysaccharides significantly reduced the phenotypic changes and improved the damage to the colon and spleen. Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPAR) signaling pathways are closely related to the inflammatory response. It was found that P. linteus polysaccharides regulated MAPK and PPAR signaling pathways to inhibit the expression of inflammatory cytokines. The mechanisms involved in the anti-inflammatory activity of Phellinus polysaccharides are shown in Figure 4.
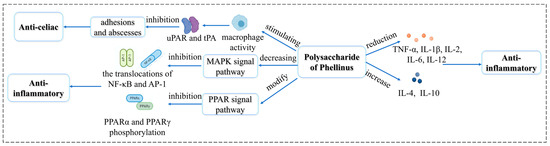
Figure 4.
Summary of the Anti-inflammatory mechanisms of Phellinus polysaccharides.
5.4. Immunomodulatory Activity
As an immunomodulator, Phellinus polysaccharide can significantly promote the proliferation of T cells and B cells, increase the production of macrophage secretory factors and NO, and regulate humoral and cellular immunity. The immunomodulatory effect of Phellinus polysaccharides is shown in Figure 5.
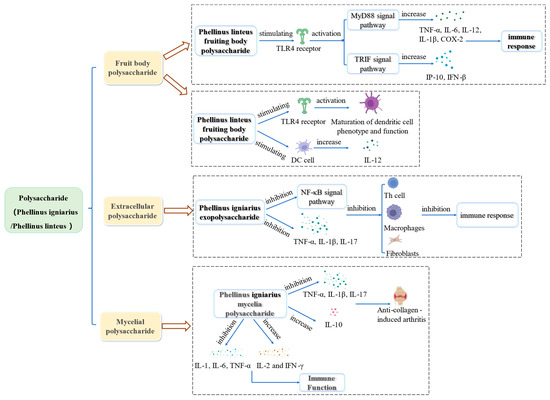
Figure 5.
Summary of the immunomodulatory mechanisms of Phellinus polysaccharides.
5.4.1. Immunomodulatory Activity of Phellinus Exopolysaccharide
Rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic autoimmune disease, and its main lesion is a joint deformity. At present, anti-inflammatory drugs such as glucocorticoids can relieve patients’ pain, but their use is associated with side effects [100]. Li et al. [101] used a collagen-induced arthritis rat model to evaluate extracellular polysaccharides’ efficacy from P. igniarius. The results showed a reduction in the degree of toe swelling, improved joint tissue’s pathological condition, and significantly reduced the expression of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-17 in serum. Its mechanism is related to the inhibition of the NF-κB signal pathway and the expression of inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL17). Thus, it reduces the immune response of helper T cells, macrophages, and fibroblasts.
5.4.2. Immunomodulatory Activity of Polysaccharide from Phellinus Mycelium
Li et al. [102] also studied the immunomodulatory effect of polysaccharides from P. igniarius mycelium on collagen-induced arthritis in rats. The results showed that the effect of polysaccharides from P. igniarius mycelium is the same as that of extracellular polysaccharides. Both inhibited the expression of pro-inflammatory factors (TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-17). In addition, polysaccharides from P. igniarius mycelium can also promote the expression of anti-inflammatory IL-10 and play a therapeutic role in CIA rats.
Wei et al. [71] studied the effect of P. igniarius polysaccharides (100, 200, and 400 mg/kg) on the proliferation of T and B lymphocytes in hepatoma H22 tumor-bearing mice. T lymphocytes are mainly responsible for regulating cellular immunity, while B lymphocytes are mainly responsible for regulating humoral immunity. The results showed that polysaccharides promoted the proliferation of T and B lymphocytes in splenocytes, the body’s humoral immunity, and cellular immunity. The authors also studied the effect of liquid-fermented P. igniarius mycelium polysaccharide on the immune function of normal mice. It enhanced the carbon clearance in mice, increased the levels of IL-2 and Interferon-γ(IFN-γ), and decreased the levels of IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-α [103]. It can be seen that the mycelium polysaccharide of P. igniarius has the effect of an immune enhancer, which can significantly enhance the immune function of the body.
5.4.3. Immunomodulatory Activity of Polysaccharide from Phellinus Fruiting Body
Zhao et al. [104] studied the immunomodulatory effect of polysaccharides from P. igniarius fruiting body in the cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppressive rat model. The functional state of the spleen and thymus can reflect the immune function. The results showed that polysaccharides increased the spleen and thymus index in normal rats and resisted the spleen and thymus atrophy induced by cyclophosphamide.
Toll-like receptor 4 is a pathogen pattern recognition receptor located on the cell membrane of antigen-presenting cells (APC). It can recognize lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and activate innate and acquired immune responses [105,106]. Kim et al. [107] found that polysaccharides from the P. igniarius fruit body activate the Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and promote the maturation of dendritic cells. Wang et al. [108] studied the immunomodulatory effect of polysaccharides from the P. igniarius fruiting body on HEK-BlueTMhTLR4 cells (a kind of human cells). The authors found that polysaccharides from P. igniarius fruit body can be used as TLR4 agonists to activate the TLR and increase the expression of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-12, IL-1β, COX-2, etc. via MyD88 pathway. It also increased the expression of IFN-γ-inducible protein (IP-10) and IFN-β via the TIR domain-containing adaptor inducing interferon-β(TRIF) pathway. Wang et al. [109] reported the activation of TLR4 by polysaccharides from the fruiting body of P. igniarius in RAW264.7 cells and peritoneal macrophages. The authors found that P. igniarius fruit body polysaccharides improve the proliferation of OVA-specific antibodies and specific spleen cells in mouse serum. Thus, these polysaccharides can be considered safe and effective immune adjuvants.
Dendritic cells (DC) are specialized antigen-presenting cells. Mature dendritic cells can stimulate initial T cells [110,111]. The expression of IL-12 is a specific marker for activating DC [112,113]. Park et al. [114] found that polysaccharides from fruiting bodies of P. linteus can effectively promote the phenotypic and functional maturation of mouse dendritic cells and stimulate DC to secrete IL-12.
5.5. Other Pharmacological Activities
Phellinus polysaccharides have been found to promote hematopoiesis and exhibit antiallergic, antidiabetic, and antifatigue effects, as detailed in Table 3. Studies have demonstrated that Phellinus polysaccharides have significant hypoglycemic effects both in vitro and in vivo. For instance, in in vivo experiments using nonobese diabetic mice as a model, Phellinus polysaccharides were able to suppress the development of autoimmune diabetes, reduce blood glucose levels, and decrease pancreatic islet infiltration by regulating cytokine expression. After treatment with Phellinus polysaccharides, the mice showed a mean blood glucose level of 110 mg/dl and delayed splenocyte transfer [115]. Inhibition of α-amylase and α-glucosidase is an effective strategy to control diabetes by reducing glucose absorption. Zhang et al. [116] measured the in vitro hypoglycemic activity of purified polysaccharide from Phellinus baumii fruiting bodies and showed high α-glucosidase and α-amylase inhibition activities of 57.37% and 54.10%, respectively. In addition, it also has a strong glucose adsorption capacity, which has a significant inhibitory effect on glucose diffusion.

Table 3.
Other pharmacological activities of Phellinus polysaccharides.
6. Toxicity and Safety
Despite its various pharmacological activities, the toxicity and safety of Phellinus polysaccharides are important considerations. Reports indicate that Phellinus polysaccharides have a very high safety profile. Zhong et al. [86] observed a slight weight gain in Phellinus polysaccharide-treated tumor-bearing mice, with no significant increase in serum ALT and AST levels or lipid peroxide concentrations in the liver and kidney, suggesting that a dose of 200 mg/kg of Phellinus polysaccharides is not toxic to mammals. In recent years, cell chromosome aberration and micronucleus test tests have been used to assess the genotoxicity of drugs. One study found no significant difference (p > 0.05) in the chromosomal aberration rate and micronucleus rate of bone marrow cells across various dose groups (2.5 g/kg, 5.0 g/kg, 10.0 g/kg BW) compared to the blank control [126]. In addition, Lin et al. also demonstrated no reproductive toxicity of Phellinus polysaccharides in male mice using mouse sperm aberration and chromosome aberration tests in testicular cells [127].
7. Future Prospects
Phellinus polysaccharide has shown many pharmacological effects, including antitumor, immune regulation, hypoglycemic, anti-inflammatory, etc., with very few side effects. Thus, many research studies have been focused on exploring the therapeutic potential of Phellinus in cancer and inflammatory diseases. In recent years, researchers in China and worldwide have been evaluating the pharmacological effects and molecular mechanisms of Phellinus polysaccharides. So far, the research has mainly focused on the fruiting body and mycelium, and very few studies have been carried out on polysaccharides extracted from the culture medium. Moreover, the current research is limited to only in vitro and in vivo experiments. No clinical research was carried out. Although Phellinus polysaccharides have shown extensive pharmacological activities in multiple studies, their exact mechanism of action in vivo, including its absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and so on, is still poorly understood. Extensive further studies are needed to determine their specific targets and mode of action in vivo. Phellinus polysaccharides’ structures are complex and vary depending on extraction and purification techniques. Thus, there are still some challenges in confirming the secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures of Phellinus polysaccharides. Until now, the main focus was on the primary structures. In addition, studies on pharmacological activities were carried out on crude polysaccharides. There are only very limited studies elucidating the influence of the chemistry of polysaccharides on their pharmacological activities.
With the enhancement of people’s health awareness and the increase in market demand, the commercial application of Phellinus polysaccharides in medicine, healthcare products, food, and other fields has gradually shown great potential. Japan and South Korea were the first to carry out the cultivation of Phellinus in labs for mass production, and it was used in the manufacture of anticancer drugs and cosmetics [128]. China has great reserves of Phellinus and thus has a greater potential to improve its commercial value. Phellinus polysaccharides can be used in combination with other edible and medicinal mushrooms, such as Ganoderma lucidum and Cordyceps, and complement other health foods. The launch of skin care products with Phellinus polysaccharides as an ingredient is a new direction that can be developed in the future.
More attention must be paid to improving the culturing techniques for Phellinus, the accurate identification of polysaccharides, and understanding the structure-activity relationship of these polysaccharides. Computer-assisted liquid nuclear magnetic resonance analysis can be utilized to accurately determine the structures of polysaccharides. Additionally, molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation techniques have been widely employed for studying pharmacological activity and mechanisms [129]. For instance, molecular docking analysis has shown that the mycelium of P. linteus has the potential to resist paracetamol-induced liver injury [123]. Wu et al. used molecular dynamics simulation and rigid macromolecule docking, combined with spectroscopy, to elucidate the complex three-dimensional conformation of lentinan [130].
Good separation and purification technologies are the keys to improving the commercial and pharmacological application of polysaccharides. We should first concentrate on improving the separation and purification technologies, then technologies to confirm the chemistry of polysaccharides, their pharmacological activities, molecular mechanisms, and structure-activity relationship. In addition, large-scale randomized clinical trials of Phellinus polysaccharides involving a large number of participants, with randomization and double-blind design, are essential to ensure the efficacy and safety of Phellinus polysaccharides in the treatment of various diseases, therefore guiding clinical practice and developing treatment guidelines.
Enhancing separation and purification technologies is crucial for improving the commercial and pharmacological application of polysaccharides. Efforts should first focus on advancing these technologies, followed by refining methods to confirm the chemical properties of polysaccharides, their pharmacological activities, molecular mechanisms, and structure-activity relationships. Conducting large-scale randomized clinical trials on Phellinus polysaccharides is essential to confirm their efficacy and safety in treating various diseases. These trials should involve a significant number of participants and employ randomization and double-blind designs to ensure robust results. This approach will help guide clinical practice and the development of treatment guidelines based on the efficacy and safety of Phellinus polysaccharides.
Author Contributions
Y.Y. and X.S.: Conceptualization, writing-original draft; X.C., F.L., W.N. and B.L.: Investigation, writing-original draft; X.W. and M.R.: Supervision, Writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. ZR2021QH232) and Key R&D Projects of Shandong Province (No. 2020CXGC010505).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Li, J.; Wang, X.M.; Yang, C.J.; Liu, F. Effects of fagopyrumcymosum extracts on proliferation and apoptosis of lung cancer cell line A549. Chin. Remedies Clin. 2015, 15, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, P.K. NMR spectroscopy in the structural elucidation of oligosaccharides and glycosides. Phytochemistry 1992, 31, 3307–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, J.H.; Deng, K.J.; Peng, W.H.; Guo, Y.; Jia, D.H.; Gan, B.C. Molecular identification and genetic diversity analysis of Phellinus Phellinus fungi. Mycosystema 2010, 29, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.T.; Ye, Y.J.; Shi, G.; Zhao, N.X.; Gu, M.L.; Yan, Y.N.; Zhou, J.N.; An, L.P. Extraction of polysaccharides from fruiting bodies of Phellinus igniarius and its protective effect on D-Galactose induced 3T3 cell injury. Food Sci. 2020, 41, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.W.; Yu, Z.M.; Dong, Y.; Chen, L.J.; Li, H.Y.; Zhang, J.M.; Shou, D. Application records of Phellinus SPP in traditional Chinese medicine books and its modern advanced in studies. Chin. Arch. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2014, 32, 2249–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.D.C.; Jie, X.; Wu, D.M.; Ye, C.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Liu, W.H. Research progress on the pharmacological effects of active components of Phellinus linteus. Zhejiang J. Integr. Tradit. Chin. West. Med. 2018, 28, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Y. Fungal polysaccharides. Adv. Pharmacol. 2020, 87, 277–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapora, E.; Wolkowycki, M.; Bakier, S.; Zjawiony, J.K. Phellinus igniarius: A Pharmacologically Active Polypore Mushroom. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2016, 11, 1043–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Compain, P.; Martin, O.R. Iminosugars: From Synthesis to Therapeutic Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 187–298. [Google Scholar]
- Tseng, P.S.; Ande, C.; Moremen, K.W.; Crich, D. Influence of Side Chain Conformation on the Activity of Glycosidase Inhibitors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202217809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthyala, R.; Rajasekaran, P.; Ande, C.; Vankar, Y.D. Synthesis of (5,6 & 6,6)-oxa-oxa annulated sugars as glycosidase inhibitors from 2-formyl galactal using iodocyclization as a key step. Arkivoc 2022, 2022, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Mo, J.K.; Fan, D.Y.; Liu, G.Q. Resarch progress on pharmacological actions and extraction methods of polysaccharide from Phellinus igniarius. Biotechnol. Bull. 2018, 34, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L. Bioactivities, isolation and purification methods of polysaccharides from natural products: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 92, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glibowski, P.; Pikus, S.; Jurek, J.; Kotowoda, M. Factors affecting inulin crystallization after its complete dissolution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 110, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Zhou, X.; Sun, M. Comparison and optimization of extraction methods of Phellinus Phellinus mycelium polysaccharide. Edible Fungi 2009, 31, 62–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Yan, H.J.; Li, Y.H.; Wang, Q. Optimized extraction conditions for mycelia polysaccharides of Phellinus igniarius by orthogonal design. J. Guangdong Pharm. Univ. 2005, 21, 697–698, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Q.Q.; Ling, P.X.; Wang, H.Q. Purification and characterization of two new polysaccharides from fruiting body of Phellinus linteus. Food Drug 2009, 11, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q. Optimizing the extraction conditions of polysaccharides from Phellinus igniarius mycelium and analysis of the components of polysaccharides. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2014, 53, 4405–4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Yang, X.M.; Liu, L.; Guo, D.Z. Extraction of polysaccharides from Phellinus igniarius mycelium and research of its antioxidation activity in vitro. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2016, 37, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.L.; Zhao, M.S.; Yang, H. Research progress on ultrasonic-assisted extraction technology. J. Guangdong Pharm. Univ. 2012, 28, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.Z.; Ma, H.L.; Cao, Y.; Wang, W.X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.W. Ultrasonic wave-assisted extraction of active substances from Phellinus igniarius. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 15, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.Q.; Li, Y.; Fu, H.Y. Study on the extraction of polysaccharides from Phellinus linteus mycelium by ultrasonic method. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2012, 28, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Qin, J.Z.; Du, J.G.; Zhang, C.H. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted enzymatic extraction of polysaccharide from Phellinus igniarius. Mod. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 28, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.Y.; Wang, F.W.; Li, H.J.; Gan, B.C.; Peng, W.H.; Tan, W.; Huang, Z.Q. Ultrasonic pretreatment followed by enzymatic hydrolysis for extraction of polysaccharides from fermented mycelia of Phellinus linteus. Food Sci. 2010, 31, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, R.F.; Huang, M.G.; Wang, Y.S.; Wu, C.E.; Li, T.T.; Fan, G.J. Ultrasonic-microwave synergistic assisted extraction and activity of polysaccharides from Phellinus igniarius. Food Res. Dev. 2019, 40, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Qin, J.Z.; Du, J.G. Model establishment and kinetics analysis of the extraction of polysaccharide from the Fruits of Phellinus igniarius. Mod. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 513–518. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, D.F.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, Q. Study on the extraction method of crude polysaccharide from Phellinus linteus mycelium. J. Fungal Res. 2008, 6, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.Z.; Ren, J.M.; Yin, H. Optimization of microwave assisted the extraction of Phellinus polysaccharides using response surface methodology. J. Shanxi Univ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 32, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.F.; Cai, T.G.; Li, H.; Li, Y. Microwave-assisted technology for extracting polysaccharide from Phellinus igniarius fruitbodys. Spec. Wild Econ. Anim. Plant Res. 2008, 30, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.W.; He, L.; Wei, H.L.; Song, J.L.; Hu, Z.J.; Zhou, J.Q.; Li, H.B.; Jiang, Y.H. Ultrasonic-assisted enzymatic method extraction of polysaccharide from inonotus sanghuang. J. Zhejiang For. Sci. Technol. 2017, 37, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ma, Y.; Li, T.T.; Mu, X.P.; Wang, M.; Liu, T.; Ma, X.K. Extraction of active polysaccharide from Phellinus species by a low temperature and pressure method. Food Res. Dev. 2016, 37, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Ding, Z.C.; Pei, J.J.; Yan, J.K. Antioxidant activities of polysaccharides from Phellinus linteus mycelia by alkaline extraction. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2020, 41, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, Y.K.; Yang, F.C.; Chang, J.S. Extraction of polysaccharides from edible mushrooms: Emerging technologies and recent advances. Carbohyd. Polym. 2021, 251, 117006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.Y.; Peng, W.H.; Gan, B.C. Protein removing method and condition optimization in polysaccharide extraction from Phellinus baumii. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2011, 24, 363–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.Y.; Huang, F.; Zhao, C.; Yu, P.; Qin, D.; Song, A.R. Deproteinzation and antitumor activity of Phellinus igniarius crude polysaccharides. Chin. J. Bioprocess Eng. 2012, 10, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.R.; Cao, H.J.; Zhang, X.L.; Bian, J.; Jiang, S.H.; Ji, S.L.; Zhang, C.Y. Study on the optimum extraction and purification technology for polysaccharides from Phellinus igniarius. Food Res. Dev. 2009, 30, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.Z.; Cheng, W.; Du, J.G. Adsorption and desorption characteristics of microporous resins to pigments of Phellinus linteus polysaccharide extraction. J. Shanxi Univ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 31, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Tang, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Xia, W. Structural elucidation of a 3-O-methyl-D-galactose-containing neutral polysaccharide from the fruiting bodies of Phellinus igniarius. Carbohydr. Res. 2007, 342, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.T.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.F.; Bao, D.P. Preparation, structural characteristics and biological activities of Phellinus polysaccharides. Acta Edulis Fungi 2013, 20, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wu, X.; Peng, W.H.; Gan, B.C. Isolation, purification and physico-chemical characteristics analysis of mycelial polysaccharides from Phellinus baumii. Food Sci. 2011, 32, 143–147. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Q.; Mao, J.W.; Zhang, A.Q.; Sun, Q.L. Isolation, purification and structural identification of polysaccharides from Phellinus linteus fruiting bodies. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 38, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, Z.H.; Huang, D.Y.; Nong, L.Z.; Ning, Z.X.; Hu, Z.Z.; Xu, C.P.; Yan, J.K. Purification of polysaccharides from Phellinus linteus by using an aqueous two-phase system and evaluation of the physicochemical and antioxidant properties of polysaccharides in vitro. Prep. Biochem. Biotech. 2022, 52, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Q.; Zhao, L.; Li, Z.; Harqin, C.; Peng, Y.; Liu, J. Physicochemical analysis, structural elucidation and bioactivities of a high-molecular-weight polysaccharide from Phellinus igniarius mycelia. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120 Pt B, 1855–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suabjakyong, P.; Nishimura, K.; Toida, T.; Van Griensven, L.J. Structural characterization and immunomodulatory effects of polysaccharides from Phellinus linteus and Phellinus igniarius on the IL-6/IL-10 cytokine balance of the mouse macrophage cell lines (RAW 264.7). Food Funct. 2015, 6, 2834–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Ma, H.; Liu, W.; Pei, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Yan, J. Ultrasound enhanced production and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from mycelial fermentation of Phellinus igniarius. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 113, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Pan, J.Z.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Meng, Q.L.; Wang, Q. Endo-polysaccharide of Phellinus igniarius exhibited anti-tumor effect through enhancement of cell mediated immunity. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2011, 11, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, H.J.; Kim, S.W.; Choi, J.W.; Yun, J.W. Production and characterization of exopolysaccharides from submerged culture of Phellinus linteus KCTC 6190. Enzyme Microb. Tech. 2003, 33, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.B.; Li, X.Q.; Yang, W.; Zhang, H. Segregation and purification of polysaccharides from Phellinus igniarius and structure appraisal of this fraction. Food Sci. 2006, 27, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.B.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Liu, Y.F.; Zhang, J.S.; Tang, Q.J.; Feng, N.; Wu, D. Comparison of chemical compositions and vitro immunological activities of eight kinds of crude polysaccharides from Phellinus sp. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2010, 22, 873–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.X.; Wu, S.S.; Deng, K.; Xu, C.P. Molecular structure and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Phellinus vaninii Ljup. J. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 37, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, J.F.; Ding, X.H.; Wen, C.P.; Fan, Y.S. Separation, purification and structure identification of polysaccharides from Phellinus igniarius mycelium. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Med. Res. 2017, 37, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.Y.Y.; Wang, J.Q.; Yin, J.Y.; Nie, S.P.; Xie, M.Y. A review of NMR analysis in polysaccharide structure and conformation: Progress, challenge and perspective. Food Res. Int. 2021, 143, 110290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Q.; Zhang, A.Q.; Sun, P.L. Isolation, Purification and Monosaccharide Composition Analysis of Polysaccharide from Fruiting Bodies of Phellinus igniarius (L.ex.Fr.) Quel. Food Sci. 2008, 29, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.Y.; Park, H.S.; Nam, B.H.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, J.D. Purification and characterization of acidic proteo-heteroglycan from the fruiting body of Phellinus linteus (Berk. & MA Curtis) Teng. Bioresour. Technol. 2003, 89, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Matsugo, S.; Uzuka, Y.; Matsuo, S.; Kawagishi, H. Fractionation and anti-tumor activity of the mycelia of liquid-cultured Phellinus linteus. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2004, 68, 868–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, J.O.; Ryu, C.H.; Choi, B.T.; Jeong, Y.K.; Lee, K.W.; Jeong, S.C.; Choi, Y.H. Partial characterization and immunostimulatory effect of a novel polysaccharide-protein complex extracted from Phellinus linteus. Biosci. Biotech. Bioch. 2006, 70, 1218–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, K.S.; Cho, S.M.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.M.; Han, S.B.; Ko, K.S.; Yoo, I.D. B-lymphocyte-stimulating polysaccharide from mushroom Phellinus linteus. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 1995, 43, 2105–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.J.; Jiang, D.Z.; Liu, T.M.; Zhang, L.P. Structural analysis of water-soluble polysaccharide PIP1 extracted from the cultured mycelium of Phellinus igniarius. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2006, 22, 708–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Baek, S.J.; Bang, K.W.; Kim, Y.S.; Ha, I.S. Characteristics of polysaccharide isolated from the fruit body and cultured mycelia of Phellinus linteus IY001. Korean J. Mycol. 1999, 6, 424–429. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.G.; Ji, D.F.; Zhong, S.; Zhu, J.X.; Chen, S.; Hu, G.Y. Anti-tumor effects of proteoglycan from Phellinus linteus by immunomodulating and inhibiting Reg IV/EGFR/Akt signaling pathway in colorectal carcinoma. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 48, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.K.; Ma, H.L.; Zhu, Z.P.; Zheng, H.H.; Yang, X.M.; Liu, W.M. Physico-chemical properties and antioxidant activity in virto of intracellular polysaccharides from Phellinus igniarius. Food Sci. 2012, 33, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Mei, Y.X.; Zhu, H.; Hu, Q.M.; Liu, Y.Y.; Zhao, S.M.; Peng, N.; Liang, Y.X. A novel polysaccharide from mycelia of cultured Phellinus linteus displays antitumor activity through apoptosis. Carbohyd. Polym. 2015, 124, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikekawa, T.; Nakanishi, M.; Uehara, N.; Chihara, G.; Fukuoka, F. Antitumor action of some Basidiomycetes, especially Phllinus inteus. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1968, 59, 155–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.J.; Wang, Z.B.; Ma, H.L.; Yan, J.K. Structural features and antitumor activity of a novel polysaccharide from alkaline extract of Phellinus linteus mycelia. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 115, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.K.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, Z.B.; Ma, H.L.; Pei, J.J.; Wu, J.Y. Structure and antioxidative property of a polysaccharide from an ammonium oxalate extract of Phellinus linteus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamet-Payrastre, L.; Li, P.; Lumeau, S.; Cassar, G.; Dupont, M.A.; Chevolleau, S.; Gasc, N.; Tulliez, J.; Terce, F. Sulforaphane, a naturally occurring isothiocyanate, induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in HT29 human colon cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 1426–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, A.W. Recycling the cell cycle: Cyclins revisited. Cell 2004, 116, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.Q.; Chen, Y.S.; Wei, Z.; Ma, J.B. Inhibitory effects of Phellinus linteus intracellular polysaccharide on the proliferation of leukemic cells K562. Carcinog. Teratog. Mutagen. 2007, 19, 440–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Jiang, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.W.; Yang, L.X.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.M. Research progress on the mechanism of multidrug resistance in primary liver cancer. Chin. J. Clin. Oncol. Rehabil. 2018, 25, 1020–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.H.; Zhou, J.N.; Qi, Y. Phellinus linteus polysaccharide regulates PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway to inhibit liver cancer and ascites tumor-bearing mice and its attenuating and synergistic effect on chemotherapy. Chin. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 25, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, J.F.; Wen, C.P.; Fan, Y.S.; Ding, X.H. Therapeutic effect of Phellinus linteus polysaccharides on hepatocellular carcinoma H22 tumor-bearing mice. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2016, 39, 2868–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.B.; Lee, C.W.; Jeon, Y.J.; Hong, N.D.; Yoo, I.D.; Yang, K.H.; Kim, H.M. The inhibitory effect of polysaccharides isolated from Phellinus linteus on tumor growth and metastasis. Immunopharmacology 1999, 41, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, H.F. Inhibitory effects of polysaccharides extracted from Phellinus linteus on the proliferation and metastasis of HO-8910PM and Bcap-37. J. East China Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. 2008, 2008, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Li, Y.G.; Lin, T.B.; LYU, Z.Q.; Ji, D.F. Effects of Phellinus linteus polysaccharide P1 on HepG2 cell cycle and calmodulin signaling pathway in liver cancer. Chin. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2015, 29, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Liu, H.Y.; Chang, J.; Dang, H.Q. Antitumor effect of Phellinus linteus polysaccharide on sarcoma S180 cells in vivo and in vitro. China Pharm. 2017, 28, 3069–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LYU, H. Phellinus igniarius and flavonoids and their antitumor activity. Acta Chin. Med. 2018, 33, 27–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.K.; Sung, S.K.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, H.W. Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1) and IL-23 Induced by Polysaccharide of the Black Hoof Medicinal Mushroom, Phellinus linteus (Agaricomycetes). Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2017, 19, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heppner, K.J.; Matrisian, L.M.; Jensen, R.A.; Rodgers, W.H. Expression of most matrix metalloproteinase family members in breast cancer represents a tumor-induced host response. Am. J. Pathol. 1996, 149, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkenazi, A.; Holland, P.; Eckhardt, S.G. Ligand-based targeting of apoptosis in cancer: The potential of recombinant human apoptosis ligand 2/Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (rhApo2L/TRAIL). J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 3621–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulda, S.; Debatin, K.M. Extrinsic versus intrinsic apoptosis pathways in anticancer chemotherapy. Oncogene 2006, 25, 4798–4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Griensven, L.J.; Verhoeven, H.A. Phellinus linteus polysaccharide extracts increase the mitochondrial membrane potential and cause apoptotic death of THP-1 monocytes. Chin. Med. 2013, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.J.; Yang, Y.S.; Fang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, P.; Xu, S. Expression of p110α in glioma SHG44 and its effect on cell proliferation and metastasis. Chin. J. Cancer Prev. Treat. 2019, 26, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.H.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, X.W.; Shan, Q.; Wang, X.J. Mechanism of inhibitory effect of Phelinus linteus polysaccharide on glioma vell proliferation and migration through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Chin. J. Cancer Prev. Treat. 2020, 27, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.S.; Li, G.; Kim, J.S.; Jing, K.P.; Kim, T.D.; Kim, J.P.; Seo, S.B.; Yoo, J.K.; Park, H.D.; Hwang, B.D.; et al. Protein-bound polysaccharide from Phellinus linteus inhibits tumor growth, invasion, and angiogenesis and alters Wnt/beta-catenin in SW480 human colon cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, T.D.; Park, B.J.; Park, H.D.; Park, J.I.; Na, M.K.; Kim, H.C.; Hong, N.D.; Lim, K.; et al. Protein-bound polysaccharide from Phellinus linteus induces G2/M phase arrest and apoptosis in SW480 human colon cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2004, 216, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, S.; Ji, D.F.; Li, Y.G.; Lin, T.B.; Lv, Z.Q.; Chen, H.P. Activation of P27kip1-cyclin D1/E-CDK2 pathway by polysaccharide from Phellinus linteus leads to S-phase arrest in HT-29 cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2013, 206, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, R.F.; Wu, C.E.; Huang, H.G.; Wang, Y.S. Anti-tumor activity of polysaccharides from Phellinus igniarius fruiting body and mycelium. China Food Addit. 2017, 12, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, G.Y.; Choi, G.S.; Lee, S.H.; Park, Y.M. Acidic polysaccharide isolated from Phellinus linteus enhances through the up-regulation of nitric oxide and tumor necrosis factor-alpha from peritoneal macrophages. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 95, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.B.; Lee, C.W.; Kang, J.S.; Yoon, Y.D.; Lee, K.H.; Lee, K.; Park, S.K.; Kim, H.M. Acidic polysaccharide from Phellinus linteus inhibits melanoma cell metastasis by blocking cell adhesion and invasion. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2006, 6, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shon, Y.H.; Nam, K.S. Inhibition of cytochrome P450 isozymes in rat liver microsomes by polysaccharides derived from Phellinus linteus. Biotechnol. Lett. 2003, 25, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.G.; Huang, M.; Xin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, G.; Liu, S.; Wan, J.; Ahmadi, A.R.; Sun, Z.; et al. The epigenetic regulator SIRT6 protects the liver from alcohol-induced tissue injury by reducing oxidative stress in mice. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 960–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.B.; Pei, J.J.; Ma, H.L.; Cai, P.F.; Yan, J.K. Effect of extraction media on preliminary characterizations and antioxidant activities of Phellinus linteus polysaccharides. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 109, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.N.; Qu, H.Y.; Zhang, J.M.; Feng, J.M.; Song, W.J.; Yuang, F.H. Polysaccharide from Phellinus igniarius alleviates oxidative stress and hepatic fibrosis in Schistosoma japonicum? infected mice. Chin. J. Schistosomiasis Control 2019, 31, 615–621. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.P.; Li, N. Antioxidant properties of polysaccharides from Phellinus igniarius in vitro. Food Sci. 2011, 32, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.L.; Chen, L.; Pan, J.Z.; Liu, F.S.; Wang, Q. Study on the anti-inflammatory effects of intracellular and extracellular polysaccharides in Phellinus linteus. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Med. Res. 2011, 22, 1130–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Qian, N.; Shen, G.; Chen, L. Anti-inflammatory activity of polysaccharides from Phellinus linteus by regulating the NF-kappaB translocation in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 129, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, J.S.; Ahn, S.J.; Yim, H.; Jang, K.H.; Jin, H.K. Prevention of intraperitoneal adhesions and abscesses by polysaccharides isolated from Phellinus spp in a rat peritonitis model. Ann. Surg. 2005, 241, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Fuentes, E.; Guzman-Jofre, L.; Moore-Carrasco, R.; Palomo, I. Role of PPARs in inflammatory processes associated with metabolic syndrome (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 8, 1611–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, T.; Lin, Q.L.; Guo, T.; Yang, T.; Zhou, W.H.; Deng, X.F.; Yan, J.K.; Luo, Y.; Ju, M.M.; Luo, F.J. Polysaccharide isolated from Phellinus linteus mycelia exerts anti-inflammatory effects via MAPK and PPAR signaling pathways. Carbohyd. Polym. 2018, 200, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, H.C.; Ding, X.H.; Ma, Z.L.; Wen, C.P.; Ding, Z.S.; Chen, Z.Z.; Fan, Y.S. Immunomodulatory effect of Qishe water extract on adjuvant arthritis rats. China J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Pharm. 2012, 27, 2676–2678. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.F.; Cai, G.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shui, B.J.; Fan, Y.S.; Ding, X.H. Immunoregulatory effects of Phellinus igniarius extracellular polysaccharide on collagen-induced arthritis rats. Shanghai J. Tradit Chin. Med. 2014, 48, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.F.; Yuan, J.J.; Zhang, Y.; Shui, B.J.; Fan, Y.S.; Ding, X.H. Therapeutic Effects of Phellinus igniarius mycelium polysaccharide on collagen-induced arthritis rats. Shanghai J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2014, 38, 526–530. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Chen, L.; Deng, Y.J.; Zou, X.; Xu, X.R. Effect of polysaccharides from Phellinus igniarius by liquid fermentation technology on mouse’s immunity function. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2016, 37, 344–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.Z.; Wang, X.J.; Yu, Z.M. Influence of Phellinus igniarius polysaccharides on growth and peripheral blood cells of rats treated by cyclophosphamide. Chin. J. Mod. Appl. Pharm. 2017, 34, 832–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Wang, W.; Sun, W.; Wang, M.; Zhang, N.; Yu, S. Antitumor and immunomodulating activities of six Phellinus igniarius polysaccharides of different origins. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 4627–4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shi, G.; An, L.P. Study on the immunoregulatory effect of Phellinus igniarius acid polysaccharide on D-galactose-induced mice. Chin. J. Immunol. 2022, 38, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.Y.; Han, M.G.; Song, Y.S.; Shin, B.C.; Shin, Y.I.; Lee, H.J.; Moon, D.O.; Lee, C.M.; Kwak, J.Y.; Bae, Y.S.; et al. Proteoglycan isolated from Phellinus linteus induces toll-like receptors 2- and 4-mediated maturation of murine dendritic cells via activation of ERK, p38, and NF-kappaB. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 27, 1656–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yao, L.; Jin, Y.W.; Jin, C.Y.; Dong, Y.; Shou, D.; Wang, Y.Q. Activation effect of human TLR4 signaling pathway by polysaccharide from Phellinus igniarius. Chin. J. Mod. Appl. Pharm. 2019, 36, 1178–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Mao, J.B.; Zhou, M.Q.; Jin, Y.W.; Lou, C.H.; Dong, Y.; Shou, D.; Hu, Y.; Yang, B.; Jin, C.Y.; et al. Polysaccharide from Phellinus igniarius activates TLR4-mediated signaling pathways in macrophages and shows immune adjuvant activity in mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 123, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinman, R.M. The dendritic cell system and its role in immunogenicity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1991, 9, 271–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austyn, J.M.; Kupiec-Weglinski, J.W.; Hankins, D.F.; Morris, P.J. Migration patterns of dendritic cells in the mouse. Homing to T cell-dependent areas of spleen, and binding within marginal zone. J. Exp. Med. 1988, 167, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosca, P.J.; Hobeika, A.C.; Clay, T.M.; Nair, S.K.; Thomas, E.K.; Morse, M.A.; Lyerly, H.K. A subset of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells expresses high levels of interleukin-12 in response to combined CD40 ligand and interferon-gamma treatment. Blood 2000, 96, 3499–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapointe, R.; Toso, J.F.; Butts, C.; Young, H.A.; Hwu, P. Human dendritic cells require multiple activation signals for the efficient generation of tumor antigen-specific T lymphocytes. Eur. J. Immunol. 2000, 30, 3291–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.K.; Kim, G.Y.; Lim, J.Y.; Kwak, J.Y.; Bae, Y.S.; Lee, J.D.; Oh, Y.H.; Ahn, S.C.; Park, Y.M. Acidic polysaccharides isolated from Phellinus linteus induce phenotypic and functional maturation of murine dendritic cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 312, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.M.; Kang, J.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, S.K.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Yun, J.; Hong, J.T.; Kim, Y.; Han, S.B. Evaluation of antidiabetic activity of polysaccharide isolated from in non-obese diabetic mouse. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2010, 10, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Lv, G.Y.; Cheng, J.W.; Cai, W.M.; Fan, L.F.; Miao, L.X. Characterization and biological activities of polysaccharides from artificially cultivated. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 129, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, H.; Jin, G.R.; Jin, G.Y.; Yan, G.H. Effect of polysaccharides from Phellinus linteus on degranulation of mast cell. Chin. J. Hosp. Pharm. 2011, 31, 1532–1534. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.P.; Zhao, S.M.; Ma, S.P.; Liang, Y.X. Effect of Phellinus linteus polysaccharide on anti-fatigue and enhancing anoxia endurance function. Edible Fungi China 2012, 31, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C. Anti-fatigue effect of fermentation broth polysaccharose of Phellinus igniarius. Edible Fungi China 2020, 39, 46–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Lin, P.H.; Wang, M.A.; Chen, H.Q.; Zheng, D.D.; Huang, Q.H.; Zhang, S.P.; Shi, Z.L. Phellinus linteus polysaccharides against renal interstitial fibrosis in diabetic mice through P311/TGF-β1/Snail1 pathway. Pharmacol. Clin. Chin. Mater. Med. 2019, 35, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, X.; Guo, X.; Sun, M. pH control strategy in a shaken minibioreactor for polysaccharide production by medicinal mushroom Phellinus linteus and its anti-hyperlipemia activity. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2009, 32, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.Y.; Roh, S.I.; Park, S.K.; Ahn, S.C.; Oh, Y.H.; Lee, J.D.; Park, Y.M. Alleviation of experimental septic shock in mice by acidic polysaccharide isolated from the medicinal mushroom Phellinus linteus. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 26, 1418–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Liu, X.; Qi, S.; Dias, A.C.; Yan, J.; Zhang, X. Hepatoprotective effect of Phellinus linteus mycelia polysaccharide (PL-N1) against acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mouse. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 154, 1276–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Li, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Mei, Y. Phellinus linteus polysaccharide extract improves insulin resistance by regulating gut microbiota composition. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 1065–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.; Zhang, S.; Wan, J.M.; Gui, L.; Ruan, M.; Li, N.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H. Polysaccharides extracted from Phellinus linteus ameliorate high-fat high-fructose diet induced insulin resistance in mice. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 200, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H. Effect of the Phellinus Linteus Polysaccharides on Chromosome and Mi-cronucleus of Murine Bone Marrow. Strait Pharm. J. 2014, 26, 16–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.W.; Lin, Y.Q. Study on the PoIysaccharides from Phellinus linteus on Sperm AbnormaIity and Chromosome Aberration in TesticIe CeII of Mice. Strait Pharm. J. 2017, 29, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, M.Z.; Zeng, P.; Liu, M.M.; Xie, H.Q.; Li, X.T.; Shi, L.G. Research progress on polysaccharide from Phellinus baumii. Bull. Seric. 2017, 48, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zhang, C.; Gao, X.; Cui, F.; Zhang, J.; Jia, M.; Jia, S.; Jia, L. Enzymatic and acidic degradation effect on intracellular polysaccharide of Flammulina velutipes SF-08. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 73, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.C.; Zheng, Z.M.; Guo, T.T.; Wang, K.P.; Zhang, Y. Molecular dynamics simulation of lentinan and its interaction with the innate receptor dectin-1. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 171, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).