Synthetic Approaches and Clinical Application of Representative Small-Molecule Inhibitors of Cyclin-Dependent Kinase for Cancer Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
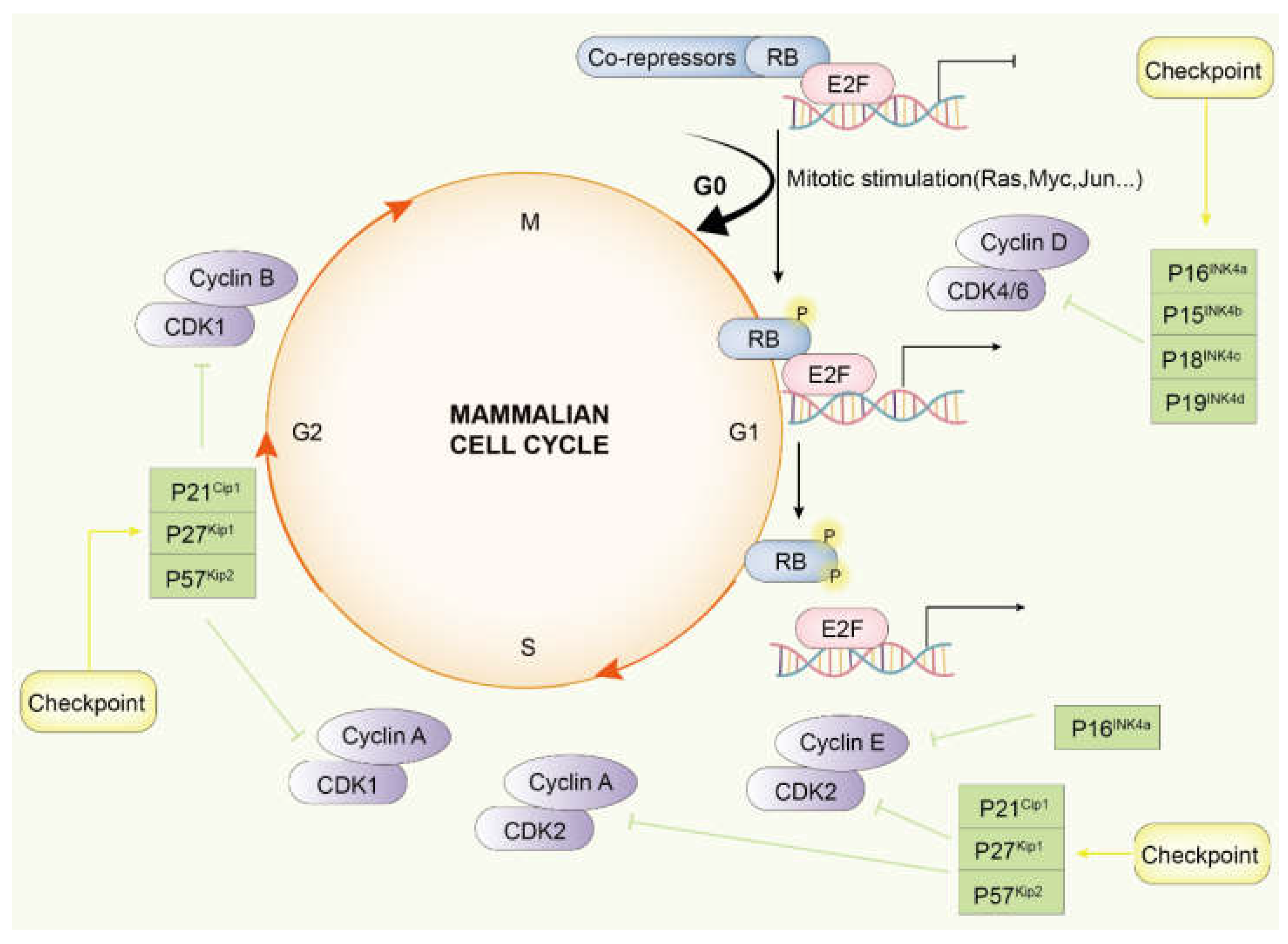
2. Signaling Pathway of CDK
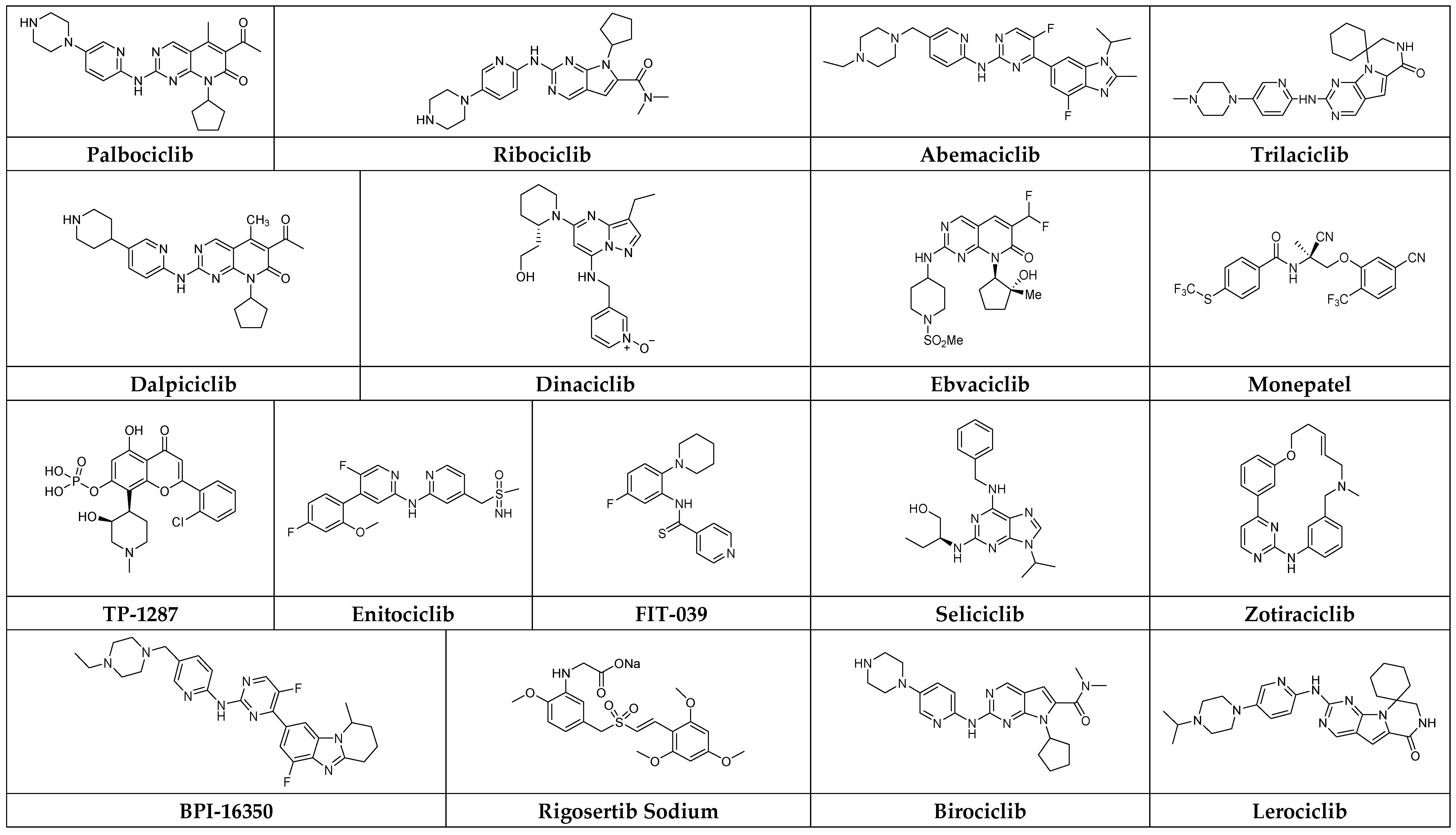
3. Representative Small-Molecule CDK Inhibitors in the Clinic
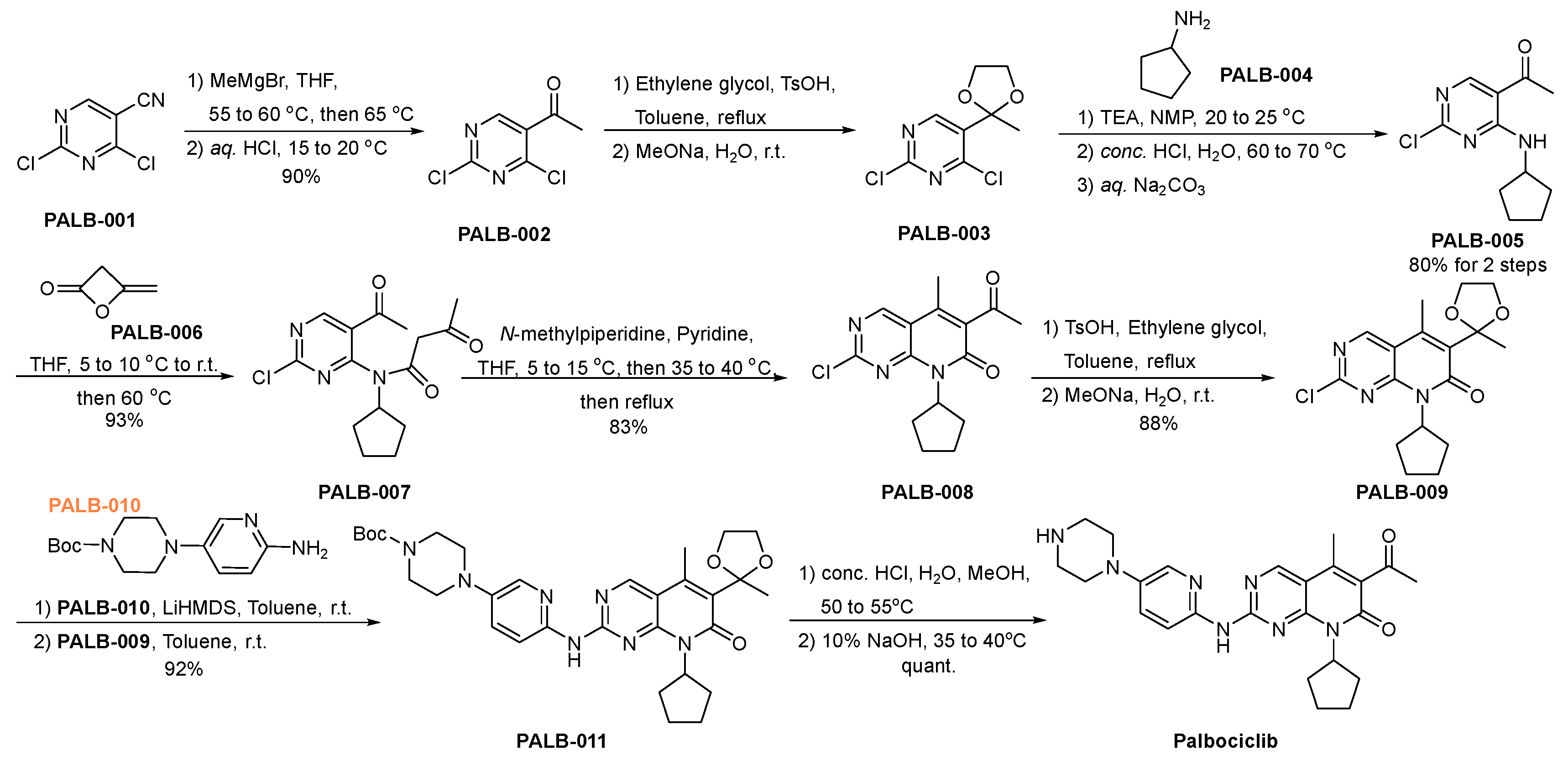
3.1. Palbociclib
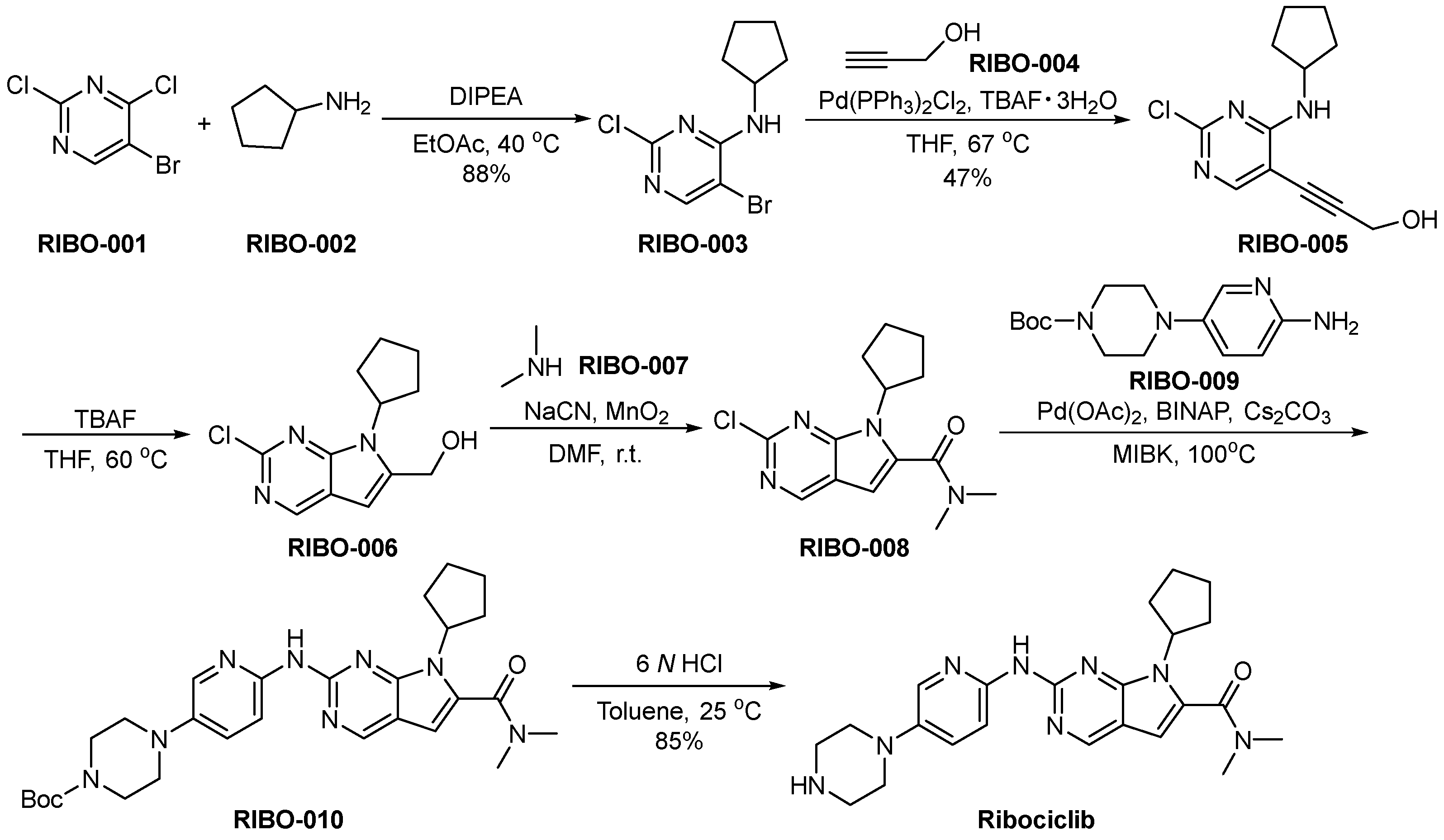
3.2. Ribociclib
3.3. Abemaciclib
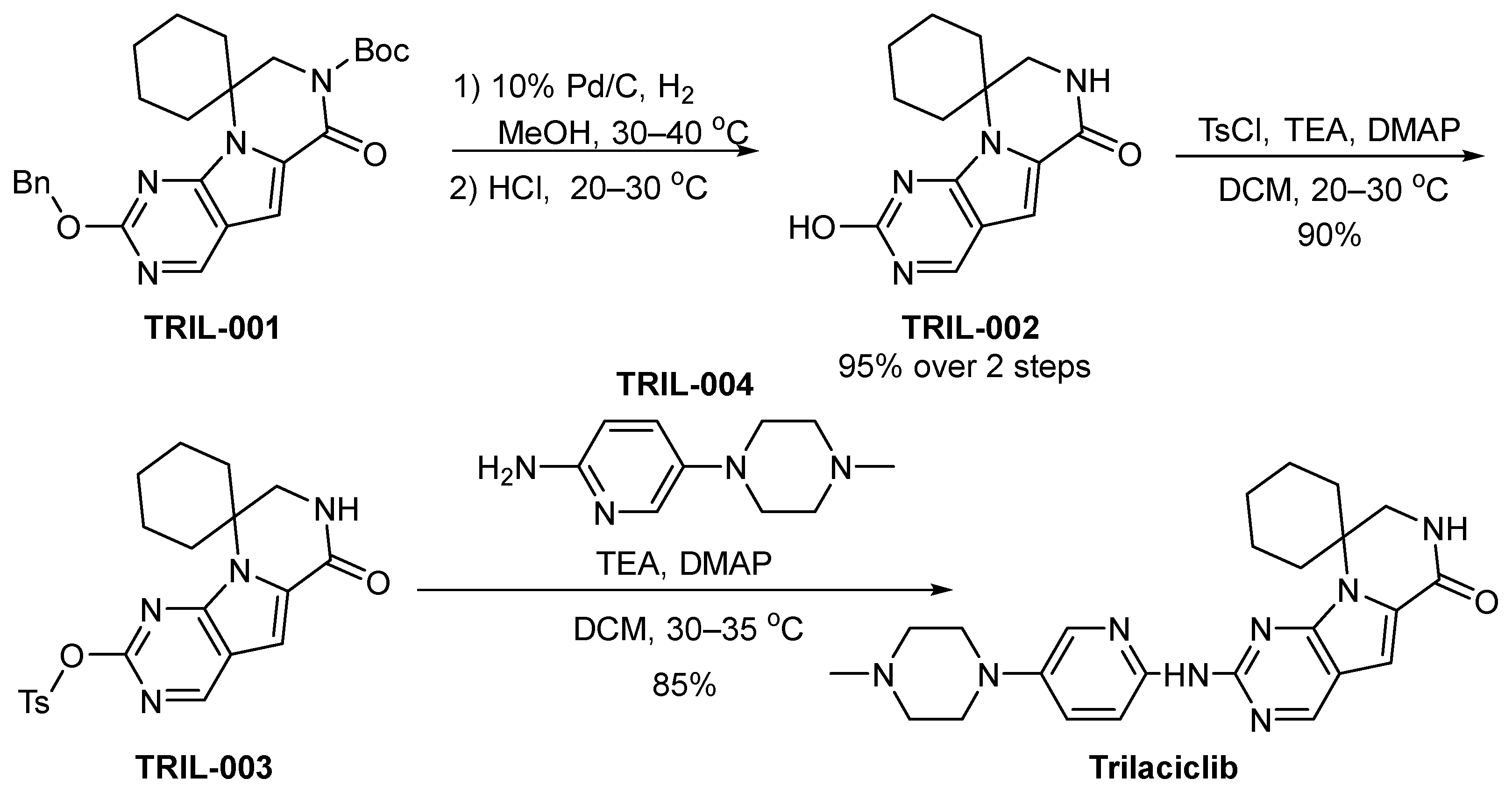
3.4. Trilaciclib
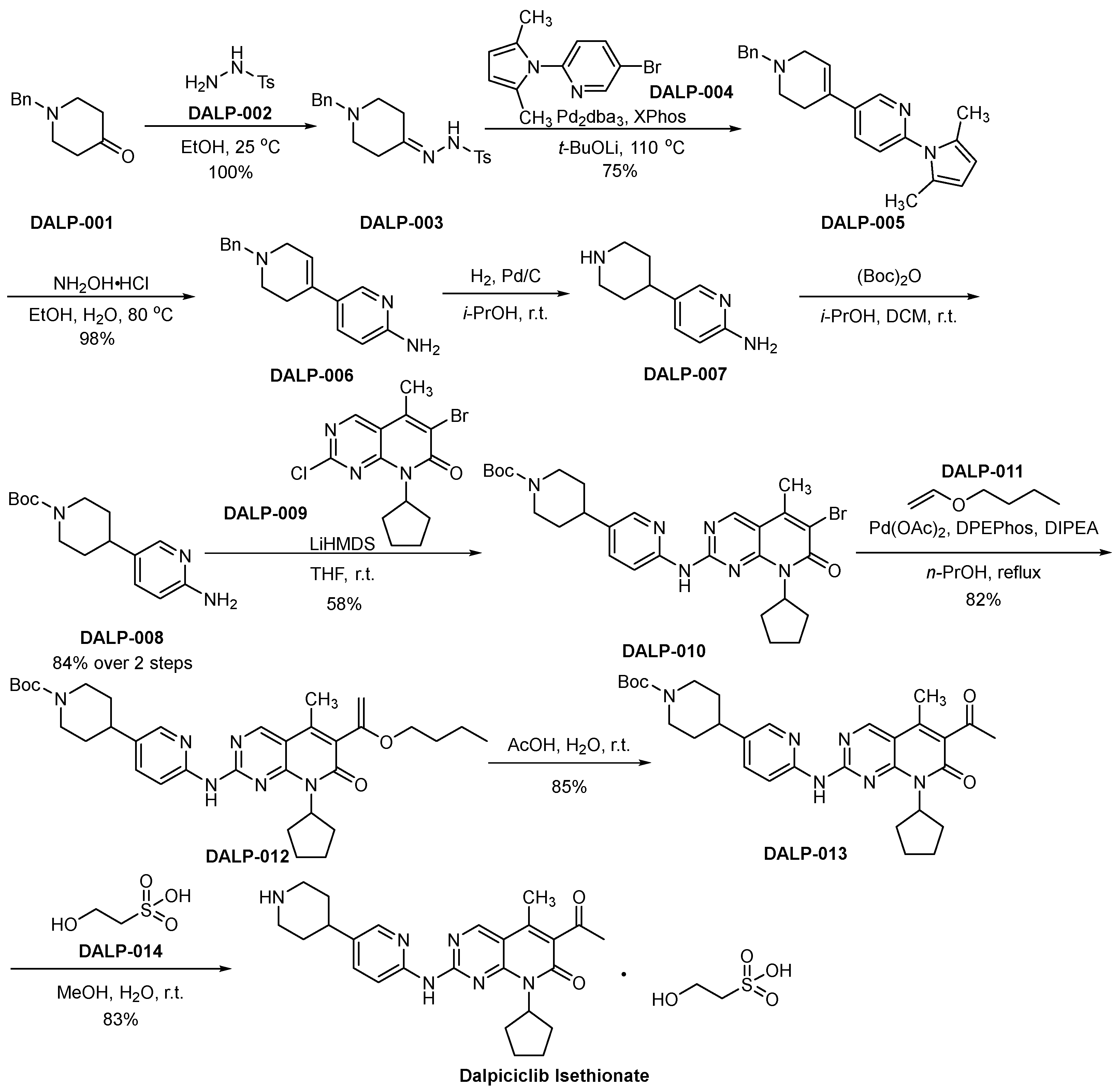
3.5. Dalpiciclib Isethionate
3.6. Dinaciclib
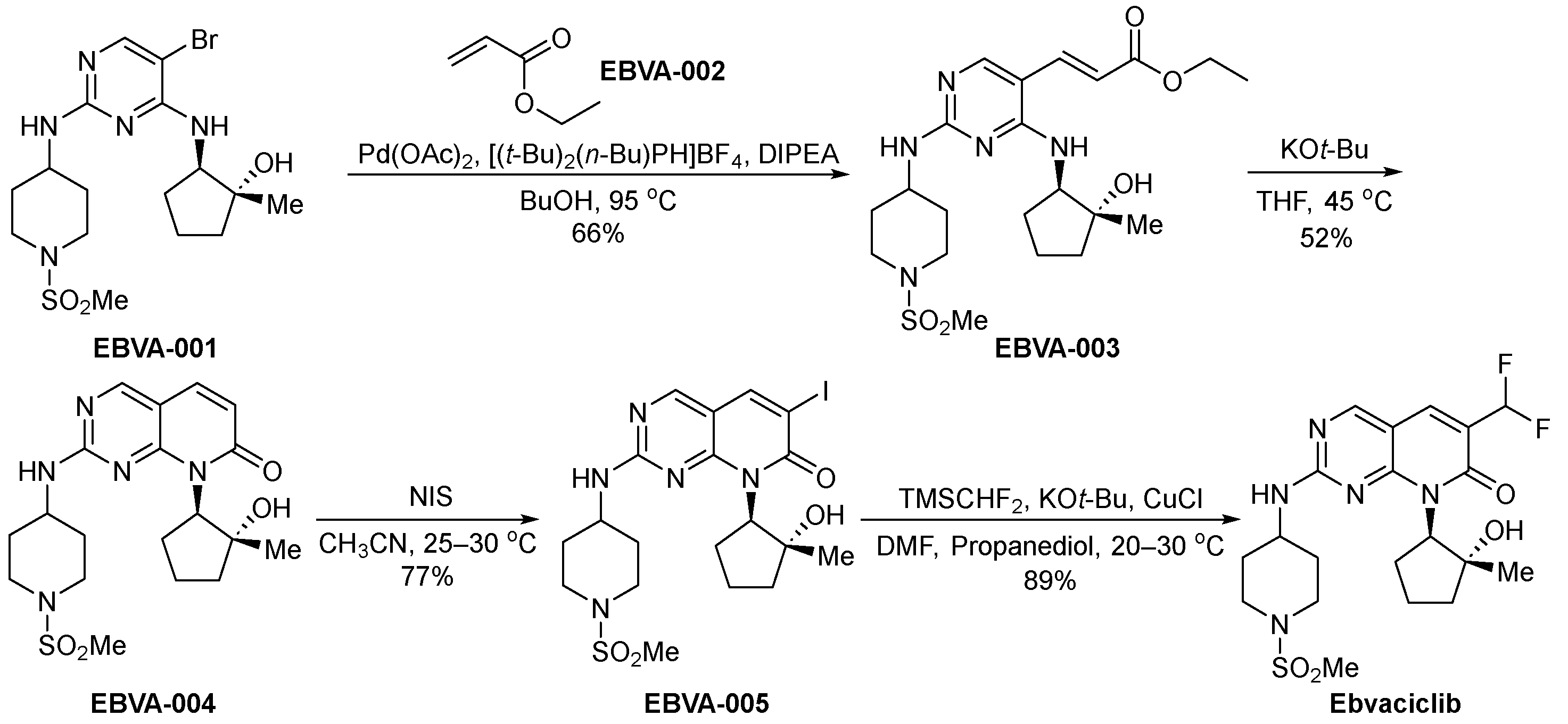
3.7. Ebvaciclib
3.8. Monepantel
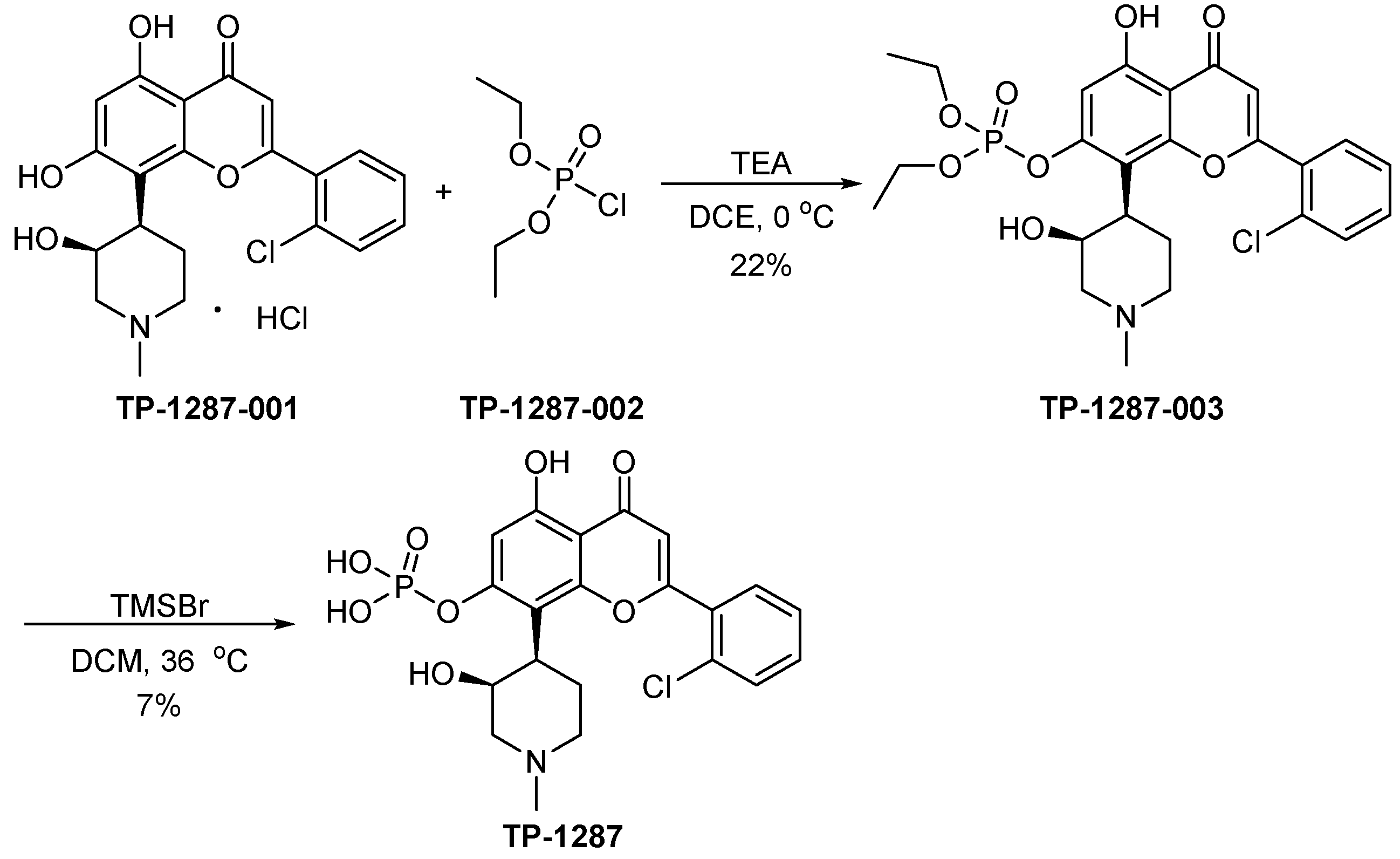
3.9. TP-1287
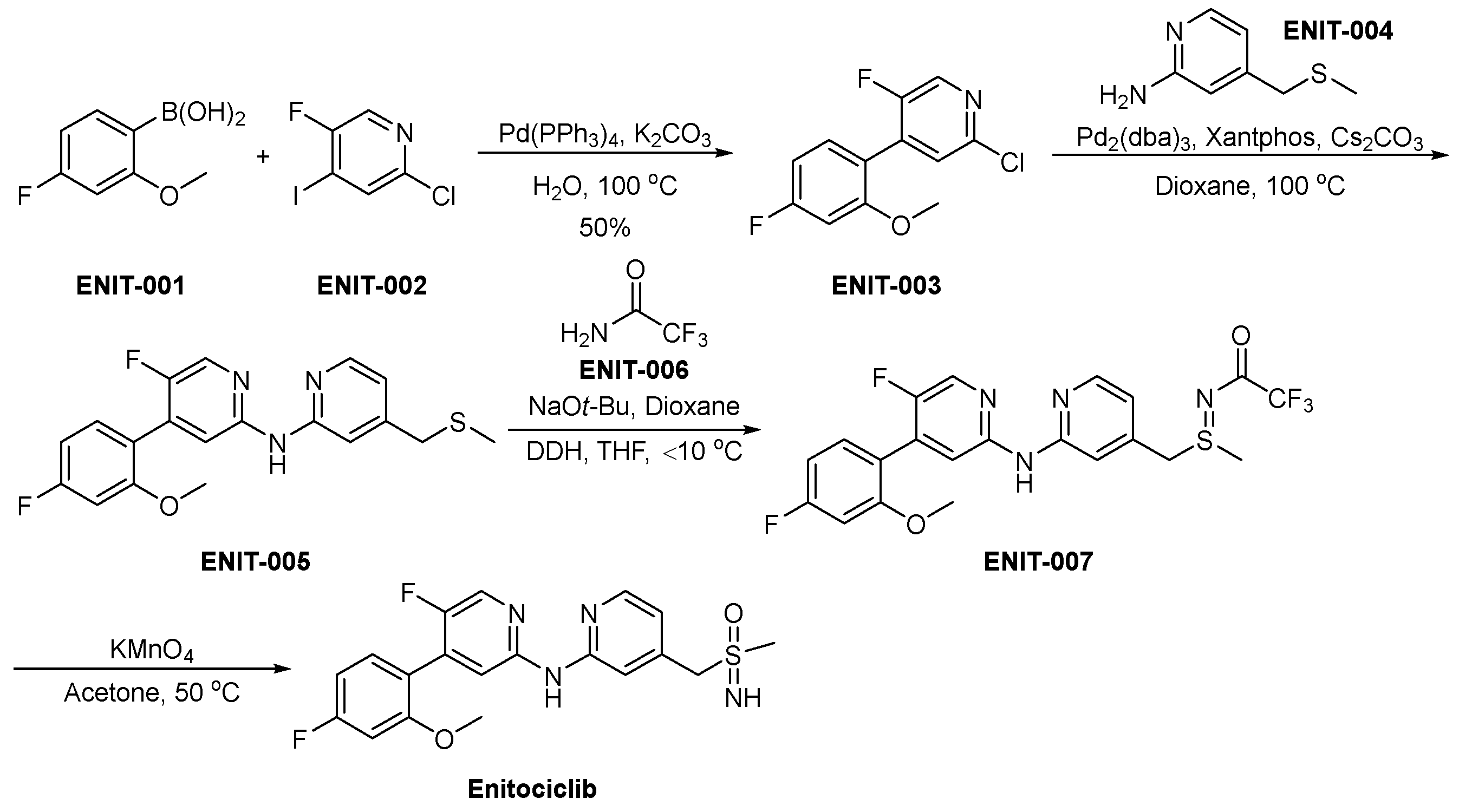
3.10. Enitociclib
3.11. FIT-039
3.12. Seliciclib
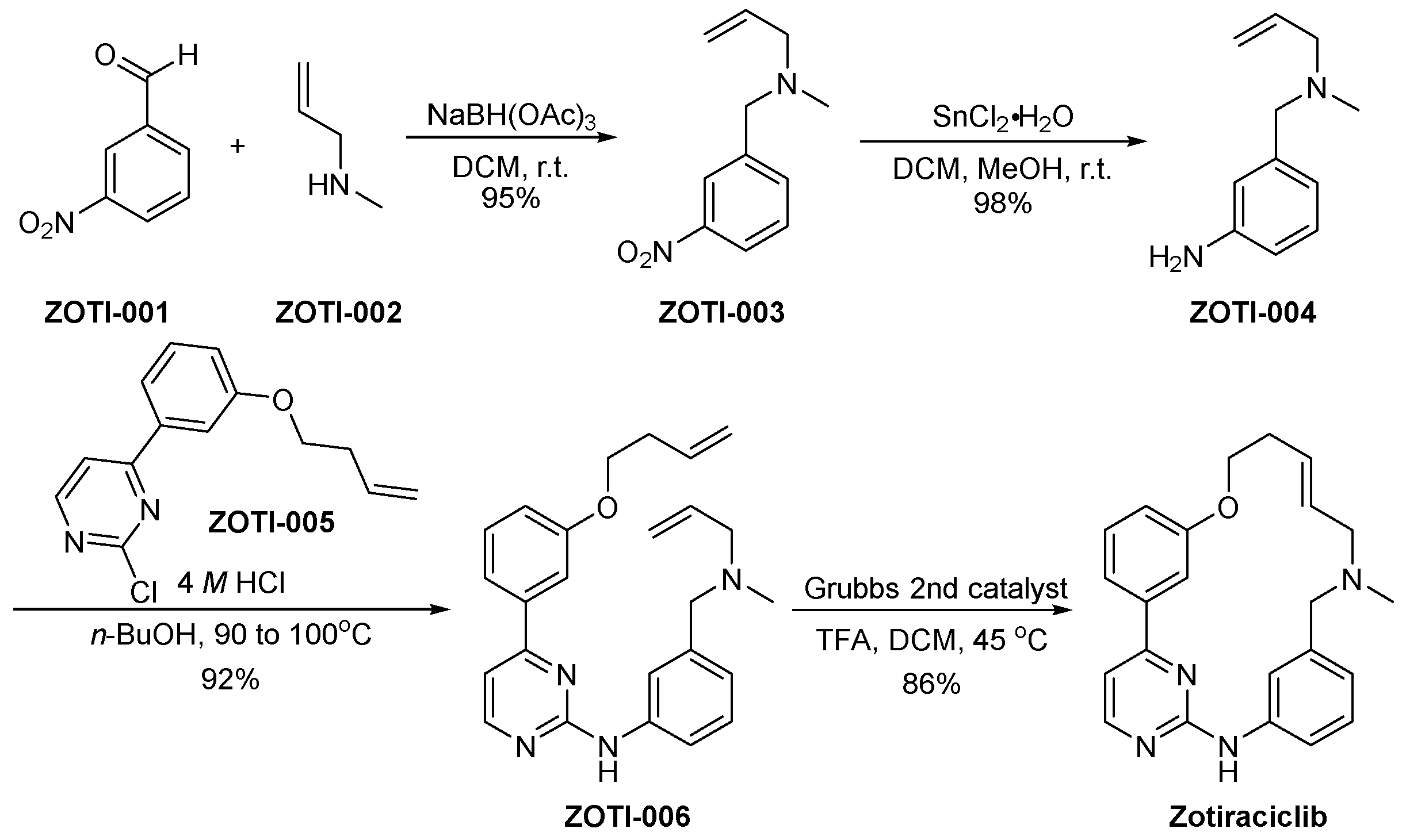
3.13. Zotiraciclib
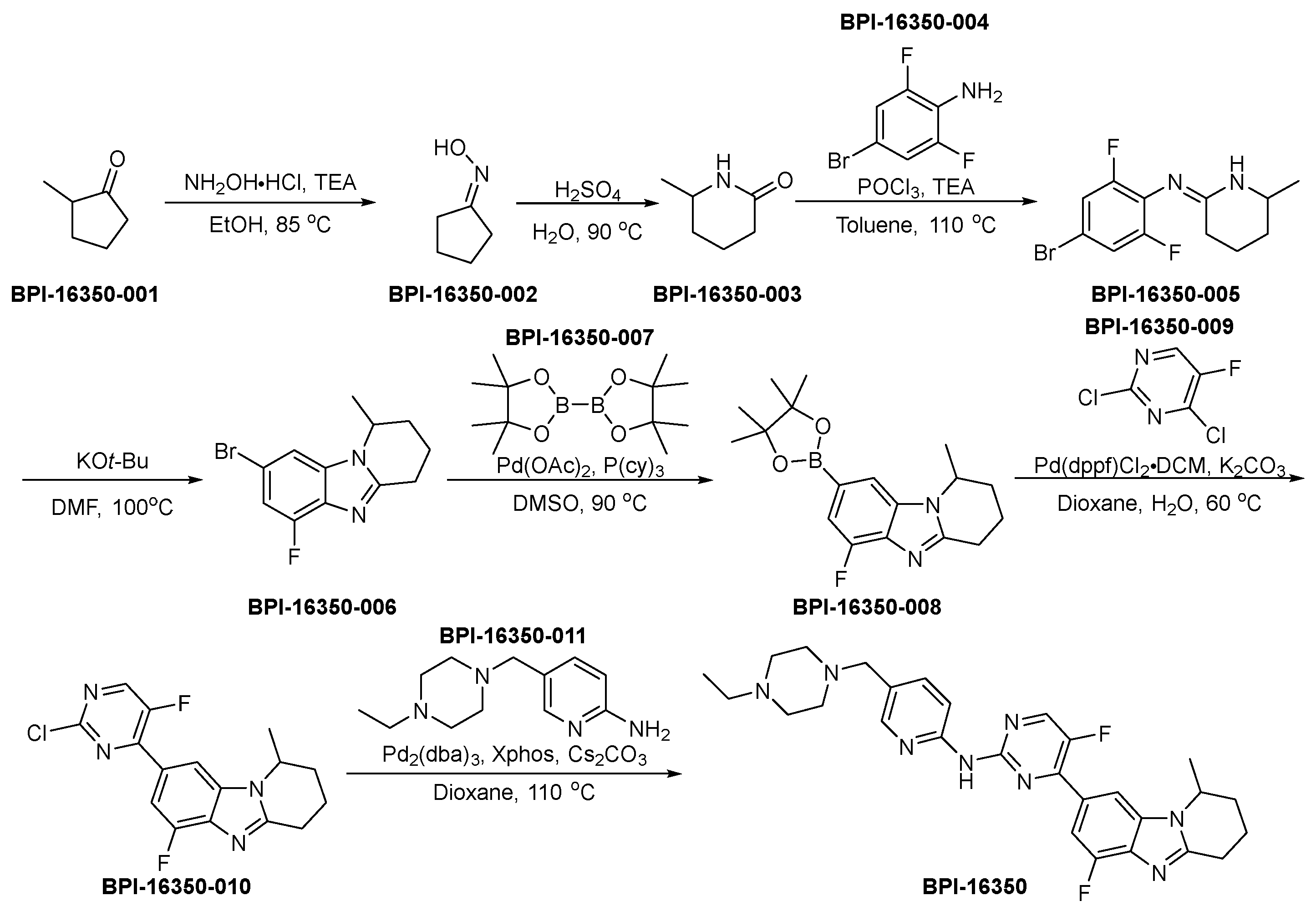
3.14. BPI-16350
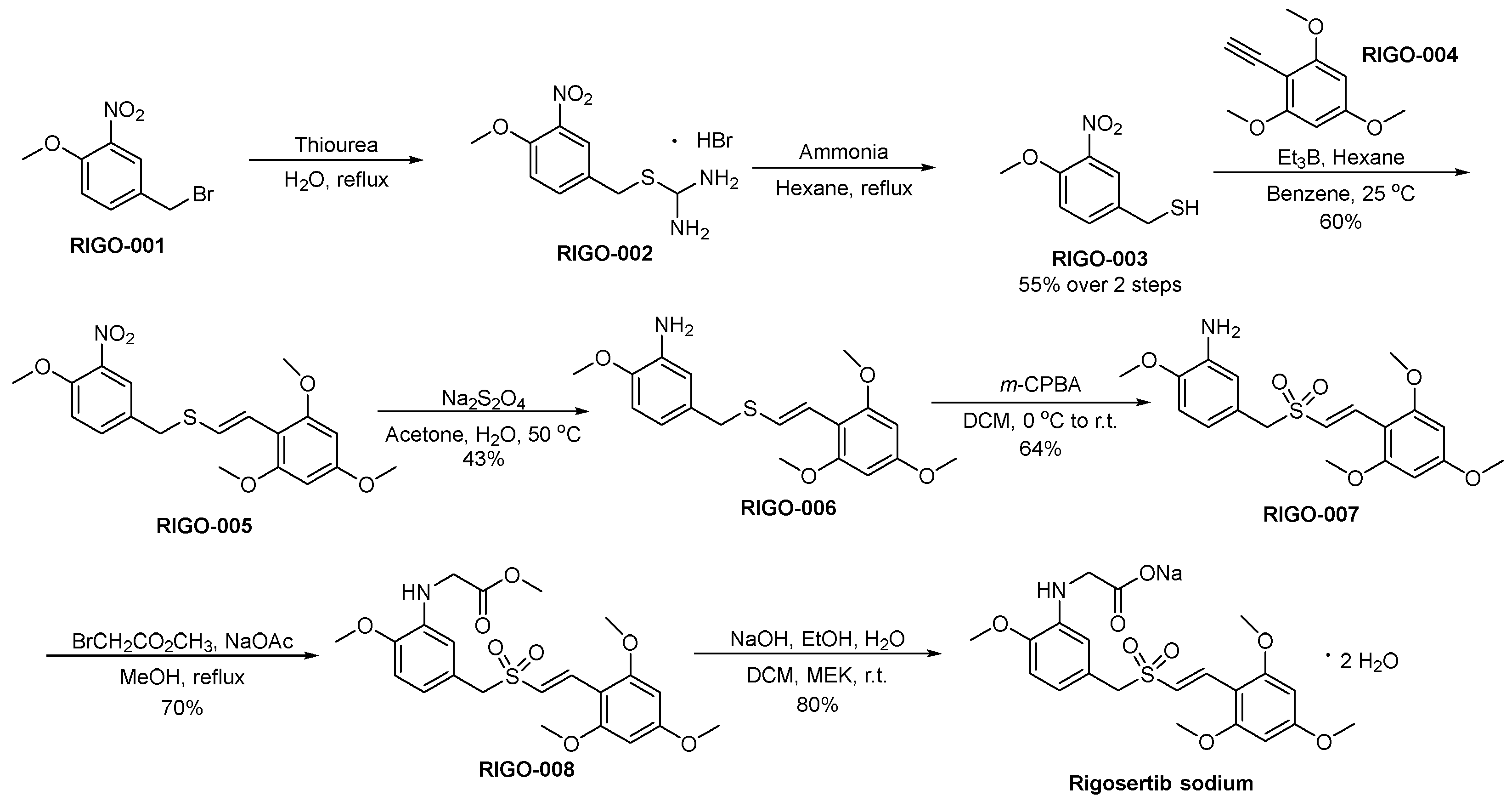
3.15. Rigosertib Sodium
3.16. Birociclib
3.17. Lerociclib
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malumbres, M. Cyclin-dependent kinases. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, L.; Hei, R.; Li, X.; Cai, H.; Wu, X.; Zheng, Q.; Cai, C. CDK inhibitors in cancer therapy, an overview of recent development. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 11, 1913–1935. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, G.I. Cyclin-dependent kinase pathways as targets for cancer treatment. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 1770–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z. Cell cycle progression and synchronization: An overview. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2579, 3–23. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Peng, Y.; Wei, W. Cell cycle on the crossroad of tumorigenesis and cancer therapy. Trends Cell Biol. 2022, 32, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bury, M.; Le Calvé, B.; Ferbeyre, G.; Blank, V.; Lessard, F. New Insights into CDK regulators: Novel opportunities for cancer therapy. Trends Cell Biol. 2021, 31, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.P.; Endicott, J.A.; Noble, M.E.M. Structure-based discovery of cyclin-dependent protein kinase inhibitors. Essays Biochem. 2017, 61, 439–452. [Google Scholar]
- Dhillon, S. Palbociclib: First global approval. Drugs 2015, 75, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, Y.Y. Ribociclib: First global approval. Drugs 2017, 77, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.S. Abemaciclib: First global approval. Drugs 2017, 77, 2063–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, S. Trilaciclib: First approval. Drugs 2021, 81, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdeldayem, A.; Raouf, Y.S.; Constantinescu, S.N.; Moriggl, R.; Gunning, P.T. Advances in covalent kinase inhibitors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 2617–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundar, V.; Vimal, S.; Mithlesh, M.S.S.; Dutta, A.; Tamizhselvi, R.; Manickam, V. Transcriptional cyclin-dependent kinases as the mediators of inflammation—A review. Gene 2021, 769, 145200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés, N.; Guzmán-Martínez, L.; Andrade, V.; González, A.; Maccioni, R.B. CDK5: A unique CDK and its multiple roles in the nervous system. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2019, 68, 843–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Tang, Y.D.; Zheng, C. When cyclin-dependent kinases meet viral infections, including SARS-CoV-2. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 2962–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, D.W.; Harvey, P.J.; Keller, P.R.; Elliott, W.L.; Meade, M.; Trachet, E.; Albassam, M.; Zheng, X.; Leopold, W.R.; Pryer, N.K.; et al. Specific inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 by PD 0332991 and associated antitumor activity in human tumor xenografts. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2004, 3, 1427–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.S.; Martin, M.; Rugo, H.S.; Jones, S.; Im, S.A.; Gelmon, K.; Harbeck, N.; Lipatov, O.N.; Walshe, J.M.; Moulder, S.; et al. Palbociclib and Letrozole in advanced breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1925–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shohdy, K.S.; Lasheen, S.; Kassem, L.; Abdel-Rahman, O. Gastrointestinal adverse effects of cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 inhibitors in breast cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ther. Adv. Drug Saf. 2017, 8, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Ju, L.; Qi, Y.; Li, X. Low-Cost Preparation Method for Palbociclib. CN104610254A, 1 January 2015. [Google Scholar]
- VanArsdale, T.; Boshoff, C.; Arndt, K.T.; Abraham, R.T. Molecular pathways: Targeting the cyclin D-CDK4/6 axis for cancer treatment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2905–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, D.; Bardia, A.; Sellers, W.R. Ribociclib (LEE011): Mechanism of action and clinical impact of this selective cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor in various solid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 3251–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, C.J.; Guang-Pei, C.; Baoqing, G.; Koteswara, K.P.; Vishal, S. Salt(s) of Cell Cycle Regulatory Protein Dependent Kinase Inhibitor and Methods of Making Thereof. WO2012064805A1, 18 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sledge, G.W., Jr.; Toi, M.; Neven, P.; Sohn, J.; Inoue, K.; Pivot, X.; Burdaeva, O.; Okera, M.; Masuda, N.; Kaufman, P.A.; et al. The effect of Abemaciclib plus Fulvestrant on overall survival in hormone receptor-positive, ERBB2-negative breast cancer that progressed on endocrine therapy-MONARCH 2: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelbert, L.M.; Cai, S.; Lin, X.; Sanchez-Martinez, C.; Del Prado, M.; Lallena, M.J.; Torres, R.; Ajamie, R.T.; Wishart, G.N.; Flack, R.S.; et al. Preclinical characterization of the CDK4/6 inhibitor LY2835219: In-vivo cell cycle-dependent/independent anti-tumor activities alone/in combination with gemcitabine. Investig. New Drugs 2014, 32, 825–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, S.; Sowers, A.; Choudhuri, R.; Wissler, M.; Gamson, J.; Mathias, A.; Cook, J.A.; Mitchell, J.B. Abemaciclib, a selective CDK4/6 inhibitor, enhances the radiosensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer in vitro and in vivo. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 3994–4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.A.; Shepherd, S.T.; Johnston, S.R. Abemaciclib, a potent cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 inhibitor, for treatment of ER-positive metastatic breast cancer. Future Oncol. 2019, 15, 3309–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederick, M.O.; Kjell, D.P. A synthesis of abemaciclib utilizing a Leuckart–Wallach reaction. Tetrahedron Lett. 2015, 56, 949–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisi, J.E.; Sorrentino, J.A.; Roberts, P.J.; Tavares, F.X.; Strum, J.C. Preclinical characterization of G1T28: A novel CDK4/6 inhibitor for reduction of chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Hart, L.; Owonikoko, T.K.; Aljumaily, R.; Lima, C.M.R.; Conkling, P.R.; Webb, R.T.; Jotte, R.M.; Schuster, S.; Edenfield, W.J.; et al. Trilaciclib dose selection: An integrated pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic analysis of preclinical data and Phase Ib/IIa studies in patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2021, 87, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, C.; Fan, Z. Preparation Method of Bone Marrow Protective Agent Trilaciclib. CN116693535A, 5 September 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Dong, X.; Ashby, C.R., Jr.; Chen, Z.-S.; Zhang, Y. Dalpiciclib. Cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 (CDK4/6) inhibitor, treatment of HR+/HER2− and HER2+ advanced breast cancer. Drug Future 2022, 47, 867–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Garcia, J.M.; Cortes, J.; Llombart-Cussac, A. CDK4/6 inhibitors in breast cancer: Spotting the difference. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1868–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, N.; Bi, K.; Sun, L.; Qiao, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Wang, D.; et al. Dalpiciclib partially abrogates ER signaling activation induced by pyrotinib in HER2(+)HR(+) breast cancer. eLife 2023, 12, e85246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, H.; Lingjian, Z.; Weifeng, T.; Yang, Z.; Bing, L. Preparation Method of Pyridopyrimidine Derivative and Intermediate Thereof. CN109384767A, 26 February 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gojo, I.; Sadowska, M.; Walker, A.; Feldman, E.J.; Iyer, S.P.; Baer, M.R.; Sausville, E.A.; Lapidus, R.G.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Clinical and laboratory studies of the novel cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor dinaciclib (SCH 727965) in acute leukemias. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2013, 72, 897–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, D.; Guzi, T.; Shanahan, F.; Davis, N.; Prabhavalkar, D.; Wiswell, D.; Seghezzi, W.; Paruch, K.; Dwyer, M.P.; Doll, R.; et al. Dinaciclib (SCH 727965), a novel and potent cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 2344–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paruch, K.; Dwyer, M.P.; Alvarez, C.; Brown, C.; Chan, T.Y.; Doll, R.J.; Keertikar, K.; Knutson, C.; McKittrick, B.; Rivera, J.; et al. Discovery of Dinaciclib (SCH 727965): A potent and selective inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman-Cook, K.D.; Hoffman, R.L.; Behenna, D.C.; Boras, B.; Carelli, J.; Diehl, W.; Ferre, R.A.; He, Y.A.; Hui, A.; Huang, B.; et al. Discovery of PF-06873600, a CDK2/4/6 inhibitor for the treatment of cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 9056–9077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ding, L.; Jiang, H.; Yuan, X.; Xiang, L.; Tang, C. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel pteridin-7(8H)-one derivatives as potent CDK2 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2023, 88, 129284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Wang, E.S.; Jenkins, R.W.; Li, S.; Dries, R.; Yates, K.; Chhabra, S.; Huang, W.; Liu, H.; Aref, A.R.; et al. CDK4/6 inhibition augments antitumor immunity by enhancing T-cell activation. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 216–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.R.; Desrosiers, J.-N.; Duan, S.; Hawkins, J.M.; Hayward, C.M.; Maloney, M.T.; Monfette, S.; Perfect, H.H.; Widlicka, D.W. Synthesis of Pyrido[2,3-D]pyrimidin-7(8H)-ones. CN113039178A, 25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bahrami, F.; Mekkawy, A.H.; Badar, S.; Morris, D.L.; Pourgholami, M.H. Monepantel antitumor activity is mediated through inhibition of major cell cycle and tumor growth signaling pathways. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 11, 3098–3110. [Google Scholar]
- Bahrami, F.; Morris, D.L.; Rufener, L.; Pourgholami, M.H. Anticancer properties of novel aminoacetonitrile derivative monepantel (ADD 1566) in pre-clinical models of human ovarian cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2014, 4, 545–557. [Google Scholar]
- Pourgholami, M.H.; Morris, D.L.; Aston, R. Compounds for the Treatment of Mtor Pathway Related Diseases. US9790176B2, 17 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tyagi, E.; Whatcott, C.; Foulks, J.M.; Siddiqui-Jain, A.; Bearss, D.J.; Warner, S.L. The oral CDK9 inhibitor, TP-1287, is active in non-clinical models of multiple myeloma. Blood 2018, 132, 3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Haws, H.; Peterson, P.; Whatcott, C.J.; Weitman, S.; Warner, S.L.; Bearss, D.J.; Siddiqui-Jain, A. Abstract 5133: TP-1287, an oral prodrug of the cyclin-dependent kinase-9 inhibitor alvocidib. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 5133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anshabo, A.T.; Milne, R.; Wang, S.; Albrecht, H. CDK9: A comprehensive review of its biology, and its role as a potential target for anti-cancer agents. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 678559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelzang, N.J.; George, B.; Ashenbramer, N.; Edenfield, W.J.; Richards, D.; Gross, M.E.; Fine, G.D.; Martinez, P. Abstract CT191: Phase 1, first-in-human, dose-escalation study of oral TP-1287, a cyclin dependent kinase 9 (CDK9) inhibitor, in patients (pts) with advanced solid tumors (ASTs). Cancer Res. 2022, 82, CT191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cote, G.M.; Wagner, A.J.; Charlson, J.A.; Hu, J.S.; Dickson, M.A.; D’Amato, G.Z.; Kabir, S.; Xu, B.; Lebedinsky, C.; Mehren, M.V. Phase 1 dose-expansion study of oral TP-1287, a cyclin-dependent kinase 9 (CDK9) inhibitor, in patients with Ewing sarcoma (EWS). J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, TPS11589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A.J.; Cote, G.M.; Richards, D.; Vogelzang, N.J.; Edenfield, W.J.; Gross, M.E.; Mar, L.; Fine, G.D.; Dow, E.; Charlson, J.A. Abstract A019: Phase 1, first-in-human, dose-expansion study of oral TP-1287, a cyclin dependent kinase 9 (CDK9) inhibitor, in patients with sarcoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, A019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui-Jain, A.; Bearss, D.J. Alvocidib Prodrugs Having Increased Bioavailability. US9758539B2, 12 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lucking, U.; Bohnke, N.; Scholz, A.; Lienau, P.; Siemeister, G.; Bomer, U.; Kosemund, D.; Bohlmann, R.; Zorn, L. 5-Fluoro-n-(pyridin-2-yl)pyridin-2-amine Derivatives Containing a Sulfoximine Group. US9877954B2, 30 January 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, D.; Desai, A.; Yan, F.; Gong, T.; Ye, H.; Ahmed, M.; Nomie, K.; Romaguera, J.; Champlin, R.; Li, S.; et al. Challenges and opportunities for high-grade B-cell lymphoma with MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6 rearrangement (double-hit lymphoma). Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 42, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigault, M.M.; Mithal, A.; Wong, H.; Stelte-Ludwig, B.; Mandava, V.; Huang, X.; Birkett, J.; Johnson, A.J.; Izumi, R.; Hamdy, A. Enitociclib, a selective CDK9 inhibitor, induces complete regression of MYC+ lymphoma by downregulation of RNA polymerase II mediated transcription. Cancer Res. Commun. 2023, 3, 2268–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Onogi, H.; Kii, I.; Yoshida, S.; Iida, K.; Sakai, H.; Abe, M.; Tsubota, T.; Ito, N.; Hosoya, T.; et al. CDK9 inhibitor FIT-039 prevents replication of multiple DNA viruses. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 3479–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagiwara, M. Methods for Controlling SR Protein Phosphorylation, and Antiviral Agents Whose Active Ingredients Comprise Agents That Control SR Protein Activity. US8816089B2, 26 August 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Siebert, S.; Pratt, A.G.; Stocken, D.D.; Morton, M.; Cranston, A.; Cole, M.; Frame, S.; Buckley, C.D.; Ng, W.F.; Filer, A.; et al. Targeting the rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblast via cyclin dependent kinase inhibition: An early phase trial. Medicine 2020, 99, e20458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, L.; Hery-Arnaud, G.; Leven, C.; Nowak, E.; Hillion, S.; Renaudineau, Y.; Durieu, I.; Chiron, R.; Prevotat, A.; Fajac, I.; et al. Safety and pharmacokinetics of Roscovitine (Seliciclib) in cystic fibrosis patients chronically infected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a randomized, placebo-controlled study. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2022, 21, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.A.; Ben-Shlomo, A.; Carmichael, J.D.; Wang, C.; Swerdloff, R.S.; Heaney, A.P.; Barkhoudarian, G.; Kelly, D.; Noureddin, M.; Lu, L.; et al. Treatment of cushing disease with pituitary-targeting Seliciclib. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 108, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, W.S.; Soo, R.; Peh, B.K.; Loh, T.; Dong, D.; Soh, D.; Wong, L.S.; Green, S.; Chiao, J.; Cui, C.Y.; et al. Pharmacodynamic effects of seliciclib, an orally administered cell cycle modulator, in undifferentiated nasopharyngeal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 1435–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, L.; Borgne, A.; Mulner, O.; Chong, J.P.; Blow, J.J.; Inagaki, N.; Inagaki, M.; Delcros, J.G.; Moulinoux, J.P. Biochemical and cellular effects of roscovitine, a potent and selective inhibitor of the cyclin-dependent kinases CDC2, CDK2 and CDK5. Eur. J. Biochem. 1997, 243, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.C.; Barnett, A.L.; McClue, S.J.; Green, S.R. Seliciclib, a cell-cycle modulator that acts through the inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2008, 3, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havlícek, L.; Hanus, J.; Veselý, J.; Leclerc, S.; Meijer, L.; Shaw, G.; Strnad, M. Cytokinin-derived cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors: Synthesis and CDC2 inhibitory activity of olomoucine and related compounds. J. Med. Chem. 1997, 40, 408–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Sun, J.F.; Nie, P.; Herdewijn, P.; Wang, Y.T. Synthesis and clinical application of small-molecule inhibitors of Janus kinase. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 261, 115848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- William, A.D.; Lee, A.C.; Goh, K.C.; Blanchard, S.; Poulsen, A.; Teo, E.L.; Nagaraj, H.; Lee, C.P.; Wang, H.; Williams, M.; et al. Discovery of kinase spectrum selective macrocycle (16E)-14-methyl-20-oxa-5,7,14,26-tetraazatetracyclo[19.3.1.1(2,6).1(8,12)]heptacosa-1(25),2(26),3,5,8(27),9,11,16,21,23-decaene (SB1317/TG02), a potent inhibitor of cyclin dependent kinases (CDKs), janus kinase 2 (JAK2), and fms-like tyrosine kinase-3 (FLT3) for the treatment of cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 169–196. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, R.; Gao, S.; Chen, W.; Han, X.; Ma, Y.; Ding, L.; Wang, J.; Lan, H.; Hu, X. BPI-16350, a novel promising CDK4/6 inhibitor for HR+/HER2- metastatic breast cancer (MBC): Results from a phase I study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, e13051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray-Coquard, I.; Monk, B.J.; Lorusso, D.; Mahdi, H.; Upadhyay, V.; Graul, R.; Husain, A.; Mirza, M.R.; Slomovitz, B. The promise of combining CDK4/6 inhibition with hormonal therapy in the first-line treatment setting for metastatic or recurrent endometrial adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2023, 33, 1943–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Ding, L. Benzoimidazole Derivatives, Manufacturing Methods and Their Uses. CN110234652A, 13 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.; Chen, T.; Yang, H.; Wen, X.; Sun, Y.; Liu, S.; Peng, T.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L. Synthesis and antitumor effects of novel benzyl naphthyl sulfoxide/sulfone derivatives derived from Rigosertib. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 37462–37471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, F.; Asgharzadeh, F.; Avan, A.; Barneh, F.; Parizadeh, M.R.; Ferns, G.A.; Ryzhikov, M.; Ahmadian, M.R.; Giovannetti, E.; Jafari, M.; et al. Rigosertib potently protects against colitis-associated intestinal fibrosis and inflammation by regulating PI3K/AKT and NF-κB signaling pathways. Life Sci. 2020, 249, 117470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; He, Q.; Li, X.; Chang, C.K.; Wu, L.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, L.; Shi, W.H.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, Y.S.; et al. Rigosertib as a selective anti-tumor agent can ameliorate multiple dysregulated signaling transduction pathways in high-grade myelodysplastic syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, M.V.; Venkatapuram, P.; Mallireddigari, M.R.; Pallela, V.R.; Cosenza, S.C.; Robell, K.A.; Akula, B.; Hoffman, B.S.; Reddy, E.P. Discovery of a clinical stage multi-kinase inhibitor sodium (E)-2-{2-methoxy-5-[(2′,4′,6′-trimethoxystyrylsulfonyl)methyl]phenylamino}acetate (ON 01910.Na): Synthesis, structure-activity relationship, and biological activity. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 6254–6276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallela, V.R.; Mallireddigari, M.R.; Cosenza, S.C.; Akula, B.; Subbaiah, D.R.; Reddy, E.P.; Reddy, M.V. Hydrothiolation of benzyl mercaptan to arylacetylene: Application to the synthesis of (E) and (Z)-isomers of ON 01910·Na (Rigosertib®), a phase III clinical stage anti-cancer agent. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, 1964–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, T.; Li, H.; Cheng, Y.; Li, H.; Tong, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, W.; Wu, X.; et al. A multicenter, single-arm, open-label trial of Birociclib, a CDK4/6 inhibitor, as a single agent, in patients with refractory HR+/HER2- metastatic breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Tian, L.; Qiang, T.; Li, J.; Xing, Y.; Ren, X.; Liu, C.; Liang, C. From structure modification to drug launch: A systematic review of the ongoing development of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors for mltiple cancer therapy. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 6390–6418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dr. Reddy’S Laboratories Limited. Process for the Preparation of Ribociclib and Salts Thereof. IN201821020528A, 6 December 2019.
- Bisi, J.E.; Sorrentino, J.A.; Jordan, J.L.; Darr, D.D.; Roberts, P.J.; Tavares, F.X.; Strum, J.C. Preclinical development of G1T38: A novel, potent and selective inhibitor of cyclin dependent kinases 4/6 for use as an oral antineoplastic in patients with CDK4/6 sensitive tumors. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 42343–42358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krastev, B.; Rai, R.; Bulat, I.; Maglakelidze, M.; Murias, C.; Arkenau, H.T.; Baird, R.D.; Wardley, A.M.; Roylance, R.; Crijanovschi, A.; et al. 278MO cfDNA analysis from phase I/II study of lerociclib (G1T38), a continuously dosed oral CDK4/6 inhibitor, with fulvestrant in HR+/HER2- advanced breast cancer patients. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, S351–S352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, Y.; Tong, Z.; Sun, T.; Shan, C.; Liu, X.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, B.; Wang, S.; et al. LEONARDA-1: Phase III randomized study of lerociclib plus fulvestrant in patients with HR+, HER2- locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer that has progressed on prior endocrine therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.; White, H.S.; Tavares, F.X.; Krasutsky, S.; Chen, J.-X.; Dorrow, R.L.; Zhong, H. Synthesis of N-(Heteroaryl)-pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-amines. WO2018005865A1, 4 January 2018. [Google Scholar]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.-T.; Jiang, S.-Q.; Zhang, S.-L. Synthetic Approaches and Clinical Application of Representative Small-Molecule Inhibitors of Cyclin-Dependent Kinase for Cancer Therapy. Molecules 2024, 29, 3029. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29133029
Wang Y-T, Jiang S-Q, Zhang S-L. Synthetic Approaches and Clinical Application of Representative Small-Molecule Inhibitors of Cyclin-Dependent Kinase for Cancer Therapy. Molecules. 2024; 29(13):3029. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29133029
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ya-Tao, Shi-Qi Jiang, and Shao-Lin Zhang. 2024. "Synthetic Approaches and Clinical Application of Representative Small-Molecule Inhibitors of Cyclin-Dependent Kinase for Cancer Therapy" Molecules 29, no. 13: 3029. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29133029
APA StyleWang, Y.-T., Jiang, S.-Q., & Zhang, S.-L. (2024). Synthetic Approaches and Clinical Application of Representative Small-Molecule Inhibitors of Cyclin-Dependent Kinase for Cancer Therapy. Molecules, 29(13), 3029. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29133029







