Sorption of Iodine on Biochar Derived from the Processing of Urban Sludge and Garden Waste at Different Pyrolysis Temperatures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
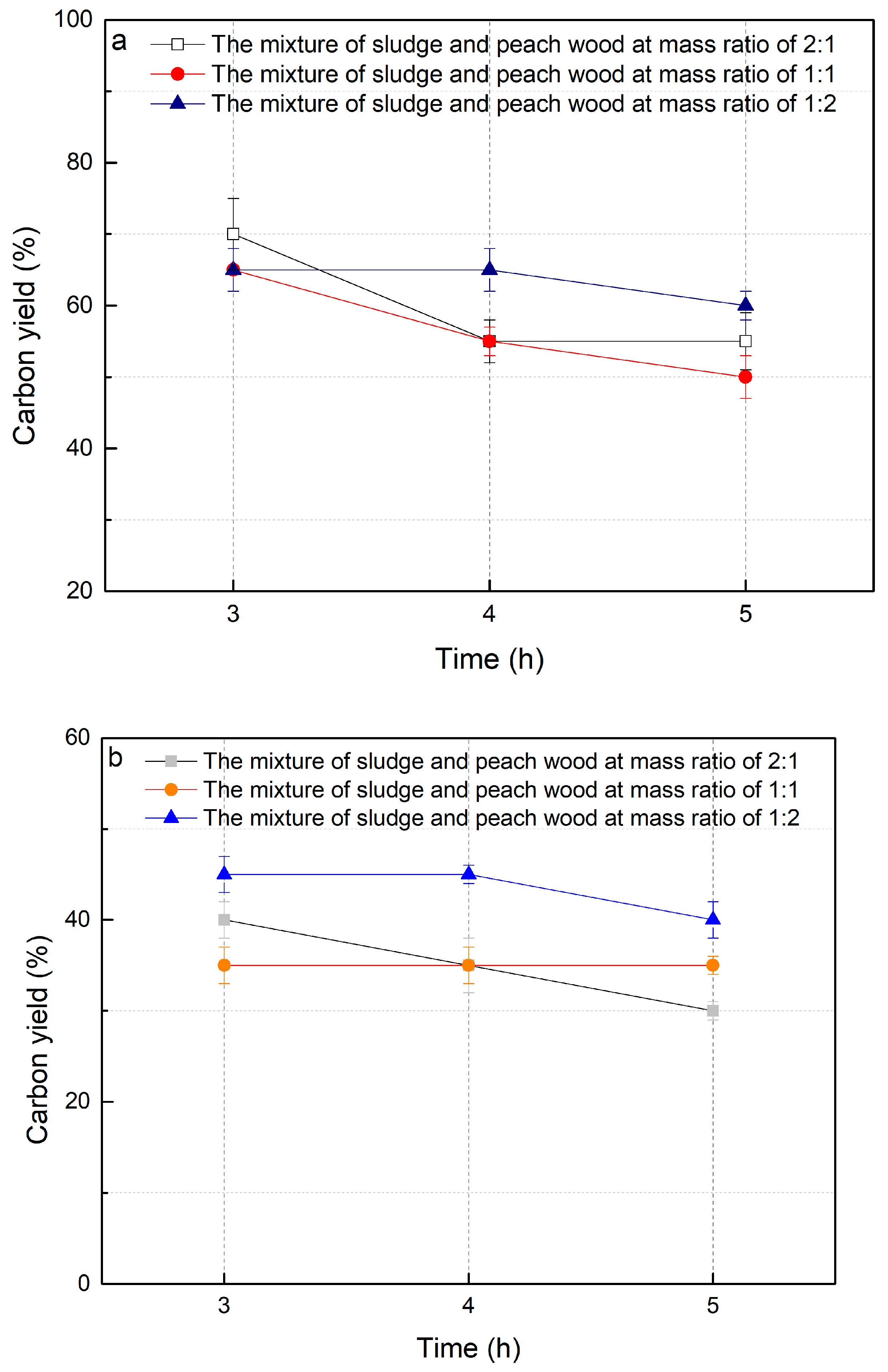
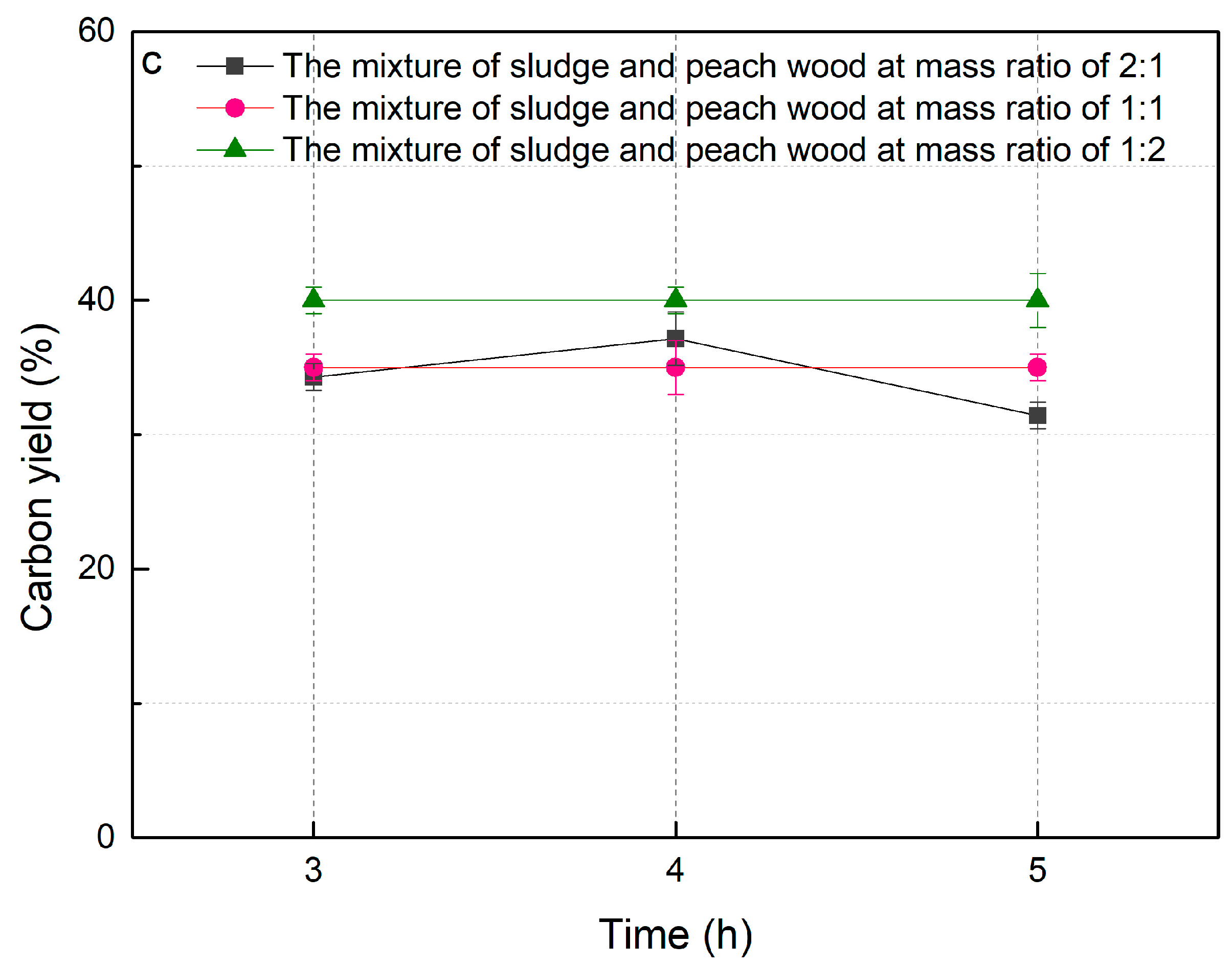
2.1. Optimal Reaction Conditions
2.2. Physicochemical Properties of Biochar
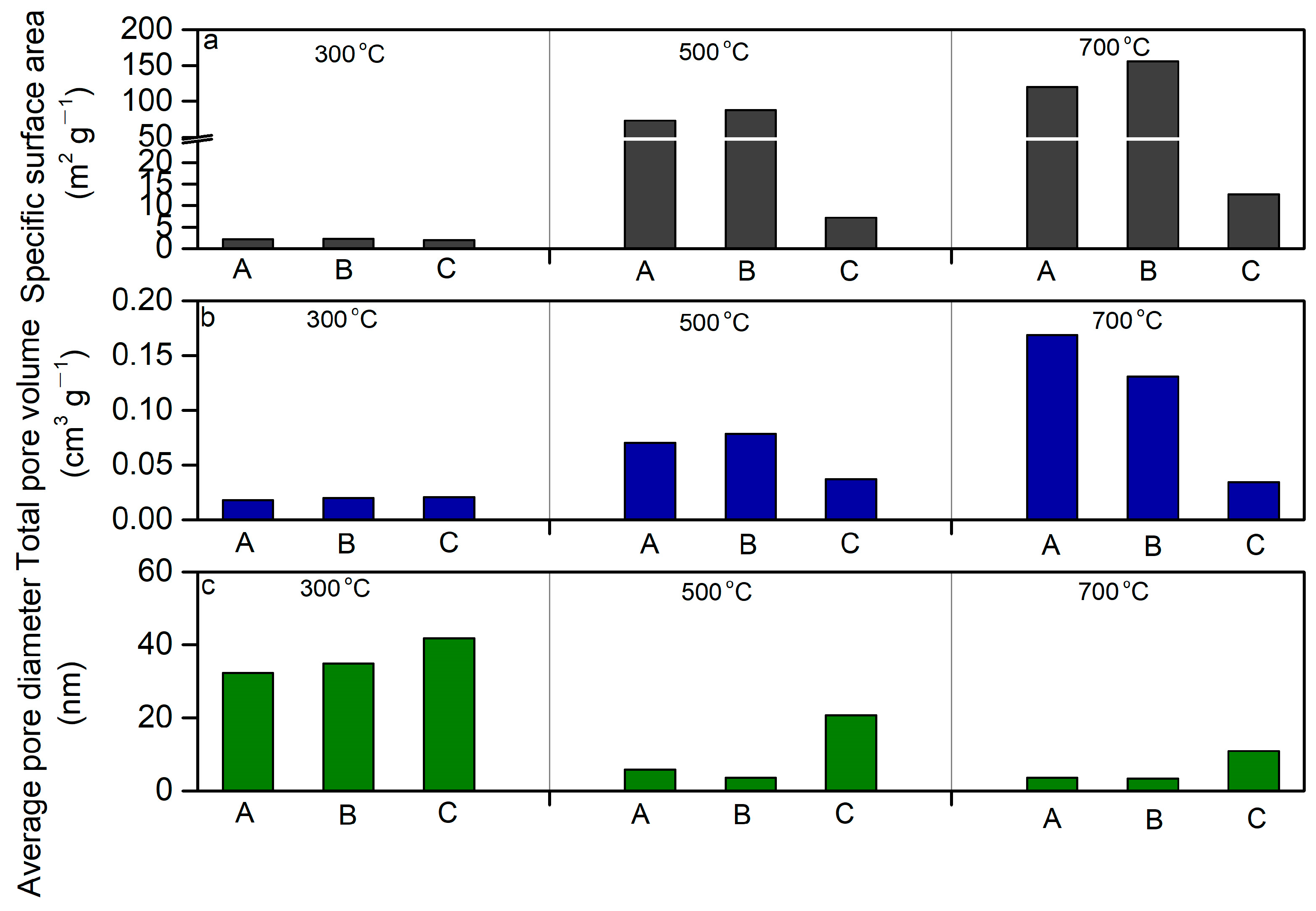
2.2.1. Specific Surface Area and Total Pore Volume
2.2.2. Pore Diameter
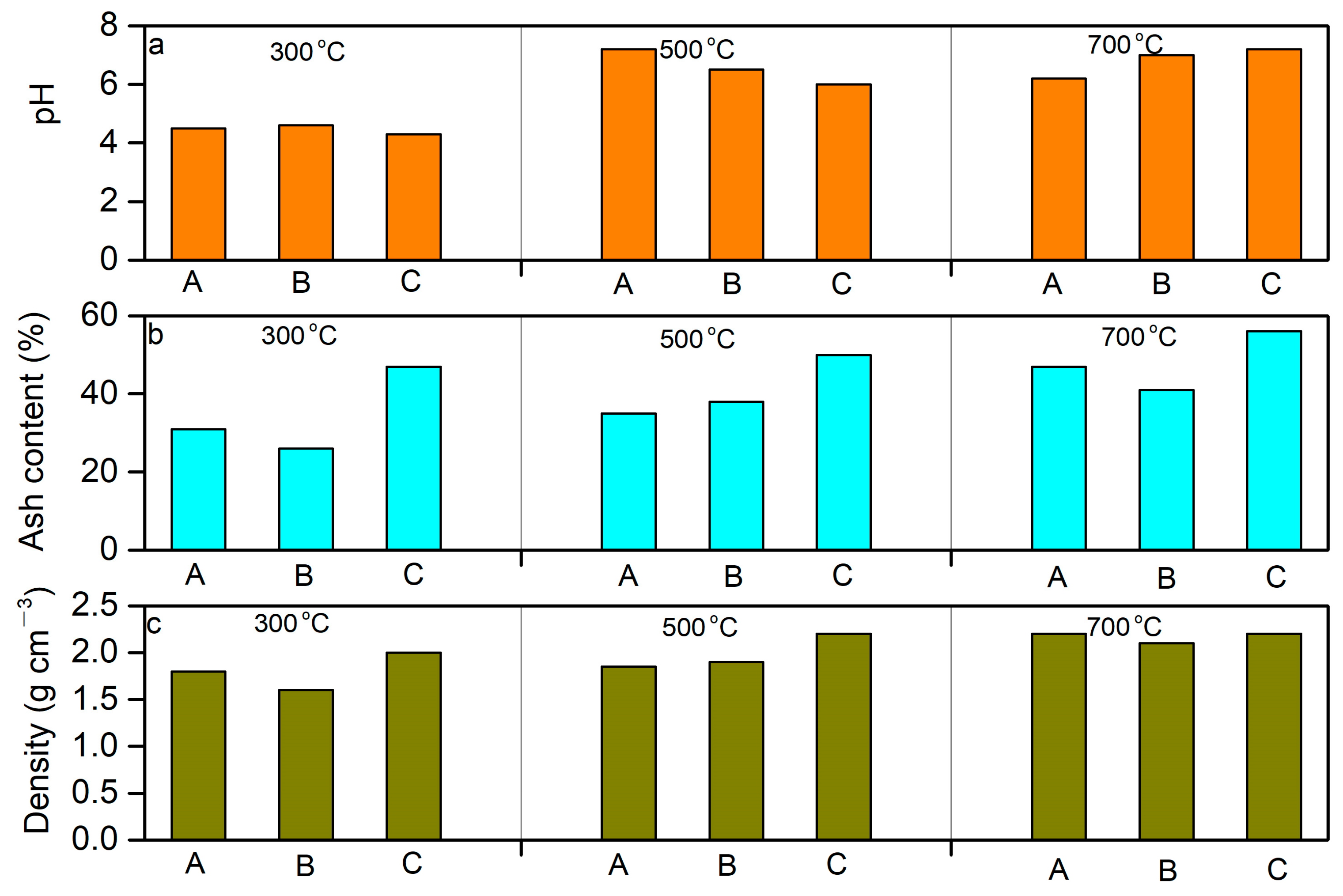
2.2.3. pH
2.2.4. Ash Content
2.2.5. Density
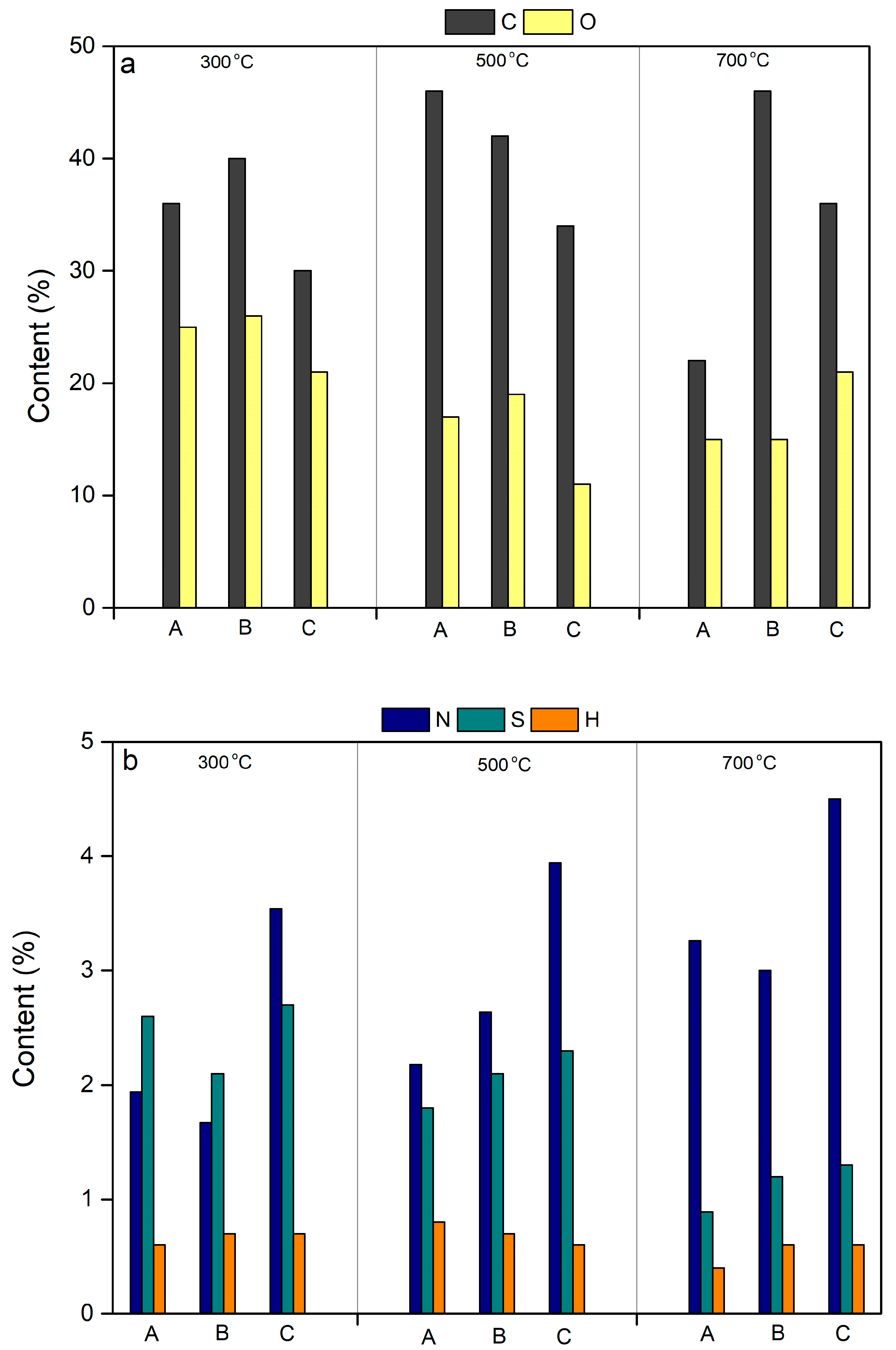
2.2.6. Elemental Composition
2.3. Adsorption Experiment
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of Biochar
3.2. Analysis of Biochar
3.3. Characterization of Biochar
3.4. Batch Experiment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.; Li, B.; Guo, D.; Munir, M.T.; Song, L.; Wu, X.; Huang, Y. Feasibility of using different hydrothermal processes for sewage sludge management in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Shao, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, G.; Qi, L.; Xu, X.; Liu, S. Current operation state of wastewater treatment plants in urban China. Environ. Res. 2021, 195, 110843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cai, W. Spatial and temporal evolution and drivers of GHG emissions from urban domestic wastewater treatment in China: A review at the provincial level. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 21028–21043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Xu, Z.; Dong, B. Occurrence, fate, and ecological risk of antibiotics in wastewater treatment plants in China: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 469, 133925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, P.H.; Morf, L.S. Waste to energy, indispensable cornerstone for circular economy: A mini-review. Waste Manag. Res. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Bou, L.; Gonzalez-Martinez, A.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J.; Correa-Galeote, D. Promising bioprocesses for the efficient removal of antibiotics and antibiotic-resistance genes from urban and hospital wastewaters: Potentialities of aerobic granular systems. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 342, 123115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.H.; Yang, W.N.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.S.; Jin, P.K.; Dzakpasu, M.; Yang, S.J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.C.; Ao, D. Current status of urban wastewater treatment plants in China. Environ. Int. 2016, 92–93, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, D.; Chen, X.; Cheng, R.; Min, S.; Wang, J.; Xiao, Q.; Wang, J. Overview of membrane technology applications for industrial wastewater treatment in China to increase water supply. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 105, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Sun, Y.; Liu, J.; Chiu, Y.-h. Analysis of the circular economy efficiency of China’s industrial wastewater and solid waste—Based on a comparison before and after the 13th Five-Year Plan. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 881, 163435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Xuan, W.; Yan, S.; Wang, Q. Zeolites synthesized from industrial and agricultural solid waste and their applications: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sravan, J.S.; Matsakas, L.; Sarkar, O. Advances in Biological Wastewater Treatment Processes: Focus on Low-Carbon Energy and Resource Recovery in Biorefinery Context. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Duan, W.; Huang, X.; Zeng, D.; Hu, L.; Gui, W.; Zhu, G.; Jiang, J. Application of calcium peroxide in promoting resource recovery from municipal sludge: A review. Chemosphere 2024, 354, 141704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, N.; Wang, Y.-Z. Humic acid biosynthesis and bacterial community evolution during aerobic composting of rice straw. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 108, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, H.; Liu, L.; Song, B.; Liu, H.; Shi, H.; Zhu, Y. Mesophilic and thermophilic fermentation of activated sludge for volatile fatty acids production: Focusing on anaerobic degradation of carbohydrate and protein. Environ. Technol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Yuan, S.; Dai, X. Obtain high quality hydrochar from waste activated sludge with low nitrogen content using acids and alkali pretreatment by enhancing hydrolysis and catalyzation. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2024, 177, 106315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Cheng, K. Enhanced biogas production efficiency of kitchen waste by anaerobic co-digestion and pretreatment. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieślik, B.M.; Namieśnik, J.; Konieczka, P. Review of sewage sludge management: Standards, regulations and analytical methods. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 90, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucina, M.; Tacconi, C.; Ricci, A.; Pezzolla, D.; Sordi, S.; Zadra, C.; Gigliotti, G. Evaluation of benefits and risks associated with the agricultural use of organic wastes of pharmaceutical origin. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613–614, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallerman, J.; Itria, R.; Babay, P.; Saparrat, M.; Levin, L. Biodegradation of nonylphenol polyethoxylates by litter-basidiomycetous fungi. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.; Yadav, K.K.; Kumar, S.; Pandita, P.; Bhutto, J.K.; Alreshidi, M.A.; Ravindran, B.; Yaseen, Z.M.; Osman, S.M.; Cabral-Pinto, M.M.S. Review on biofuel production: Sustainable development scenario, environment, and climate change perspectives —A sustainable approach. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 111996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yameen, M.Z.; Naqvi, S.R.; Juchelková, D.; Khan, M.N.A. Harnessing the power of functionalized biochar: Progress, challenges, and future perspectives in energy, water treatment, and environmental sustainability. Biochar 2024, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, Z.; Makara, A.; Kulczycka, J.; Generowicz, A.; Kwaśnicki, P.; Ciuła, J.; Gronba-Chyła, A. Conversion of Sewage Sludge into Biofuels via Different Pathways and Their Use in Agriculture: A Comprehensive Review. Energies 2024, 17, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Lai, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, M.; Han, W.; Zhang, M.; Ji, H. Synthesis and environmental applications of biochar-supported nano-zero-valent iron composites: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2024, 22, 1345–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Du, C.; Zhou, L.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zou, H.; Yu, G.; Wu, H. Biochar from phytoremediation plant residues: A review of its characteristics and potential applications. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 16188–16205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrow, C.J. Biochar: Potential for countering land degradation and for improving agriculture. Appl. Geogr. 2012, 34, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucheta, A.R.; Cannavan, F.d.S.; Tsai, S.M.; Kuramae, E.E. Amazonian Dark Earth and Its Black Carbon Particles Harbor Different Fungal Abundance and Diversity. Pedosphere 2017, 27, 832–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Wang, L.; Song, Y.; Zhu, J.; Qin, M.; Wu, L.; Hu, P.; Li, F.; Fang, L.; Chen, C.; et al. Integrated Life Cycle Assessment for Sustainable Remediation of Contaminated Agricultural Soil in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 12032–12042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.; Peng, A.; Chu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Huang, H.; Mi, Y.; Xia, D.; Wu, X.; Ye, Z.; Tao, Y.; et al. Sustainable remediation of Cr(VI)-contaminated soil by soil washing and subsequent recovery of washing agents using biochar supported nanoscale zero-valent iron. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 921, 171107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Ma, Q.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Guo, P.; Zhang, J.; Duan, G.; Lin, A.; Zhang, T.; Li, S. Efficient remediation of different concentrations of Cr-contaminated soils by nano zero-valent iron modified with carboxymethyl cellulose and biochar. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 147, 474–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Chen, H.; Mei, B.; Jia, L.; Zhang, Y. Construction of camphor leaves-derived biochar@bismuth for the capture of gaseous iodine. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2023, 281, 119205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorasani, A.C.; Satvati, P.R. Reusable cellulose-based biosorbents for efficient iodine adsorption by economic microcrystalline cellulose production from walnut shell. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 256, 128432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Gong, H.; Liu, X.; Luo, J.; Zhu, N. Target-prepared sludge biochar-derived synergistic Mn and N/O induces high-performance periodate activation for reactive iodine radicals generation towards ofloxacin degradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 460, 132362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Dissanayake, P.D.; Sun, M.; Tao, Z.; Han, W.; An, N.; Gu, Q.; Xia, D.; Tian, B.; Ok, Y.S.; et al. Adsorption and visible-light photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants by functionalized biochar: Role of iodine doping and reactive species. Environ. Res. 2021, 197, 111026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouedraogo Angelika, S.; Yuzhu Fu, G.; Yunus Ahmed, I. Treatment of Highway Stormwater Runoff Using Sustainable Biochar: A Review. J. Environ. Eng. 2023, 149, 03122005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premarathna, K.S.D.; Biswas, J.K.; Kumar, M.; Varjani, S.; Mickan, B.; Show, P.L.; Lau, S.Y.; Novo, L.A.B.; Vithanage, M. Biofilters and bioretention systems: The role of biochar in the blue-green city concept for stormwater management. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2023, 9, 3103–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, S.; Miller, S.A. Predicting biochar properties and pyrolysis life-cycle inventories with compositional modeling. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 399, 130551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Wei, K.H.; Dai, P.S. Effect of biochar on mechanical and permeability properties of concrete exposed to elevated temperature. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 234, 117338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streletskiy, O.A.; Zavidovskiy, I.A.; Nuriahmetov, I.F.; Khaidarov, A.A.; Pavlikov, A.V.; Minnebaev, K.F. The Field-Effect Transistor Based on a Polyyne–Polyene Structure Obtained via PVDC Dehydrochlorination. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werdin, J.; Fletcher, T.D.; Rayner, J.P.; Williams, N.S.G.; Farrell, C. Biochar made from low density wood has greater plant available water than biochar made from high density wood. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Tian, S.; Schauer, J.J. Penetration of submicron amino-functionalized graphene quantum dots in plant stomata, implication for the depollution of atmospheric soot particles. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023, 21, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Ma, A.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, N.; Fan, S.; Wang, Y. The Removal of Tetracycline from Aqueous Solutions Using Peanut Shell Biochars Prepared at Different Pyrolysis Temperatures. Sustainability 2023, 15, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutradhar, S.; Mondal, A.; Kuehne, F.; Krueger, O.; Rakshit, S.K.; Kang, K. Comparison of Oil-Seed Shell Biomass-Based Biochar for the Removal of Anionic Dyes—Characterization and Adsorption Efficiency Studies. Plants 2024, 13, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jang, H.M. Comparative study on characteristics and mechanism of levofloxacin adsorption on swine manure biochar. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 351, 127025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, T.; Hakeem, I.G.; Gupta, A.B.; Joshi, J.; Shah, K.; Vuppaladadiyam, A.K.; Sharma, A. Parametric influence of process conditions on thermochemical techniques for biochar production: A state-of-the-art review. J. Energy Inst. 2024, 113, 101559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Mao, S.; Shan, Y.; Gao, W.; Wang, S.; Malghani, S. Impact of iron-modified biochars on soil nitrous oxide emissions: Variations with iron salts and soil fertility. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 356, 120571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, S.; Radha; Sharma, K.; Dhumal, S.; Senapathy, M.; Deshmukh, V.P.; Kumar, S.; Madhu; Anitha, T.; Balamurugan, V.; et al. Unlocking the potential of cotton stalk as a renewable source of cellulose: A review on advancements and emerging applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 261, 129456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Ji, Z.; Bei, Y. Surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization of polyamine grafting from magnetic iron oxide submicroparticles for high adsorption capacity of cadmium in aqueous solution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 394, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keiluweit, M.; Nico, P.S.; Johnson, M.G.; Kleber, M. Dynamic Molecular Structure of Plant Biomass-Derived Black Carbon (Biochar). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1247–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Schauer, J.J. Quantifying the levels and oxidative potential of submicron carbon black in plant leaves. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2024, 15, 101954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vinh, N.; Zafar, M.; Behera, S.K.; Park, H.S. Arsenic(III) removal from aqueous solution by raw and zinc-loaded pine cone biochar: Equilibrium, kinetics, and thermodynamics studies. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 1283–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, S.; Jiang, X.; Jiang, X.; Xing, Z.; Guan, Y. Simultaneous Determination of PMS, PDS, and H2O2 Concentrations with Multi-Step Iodometry. Water 2023, 15, 2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
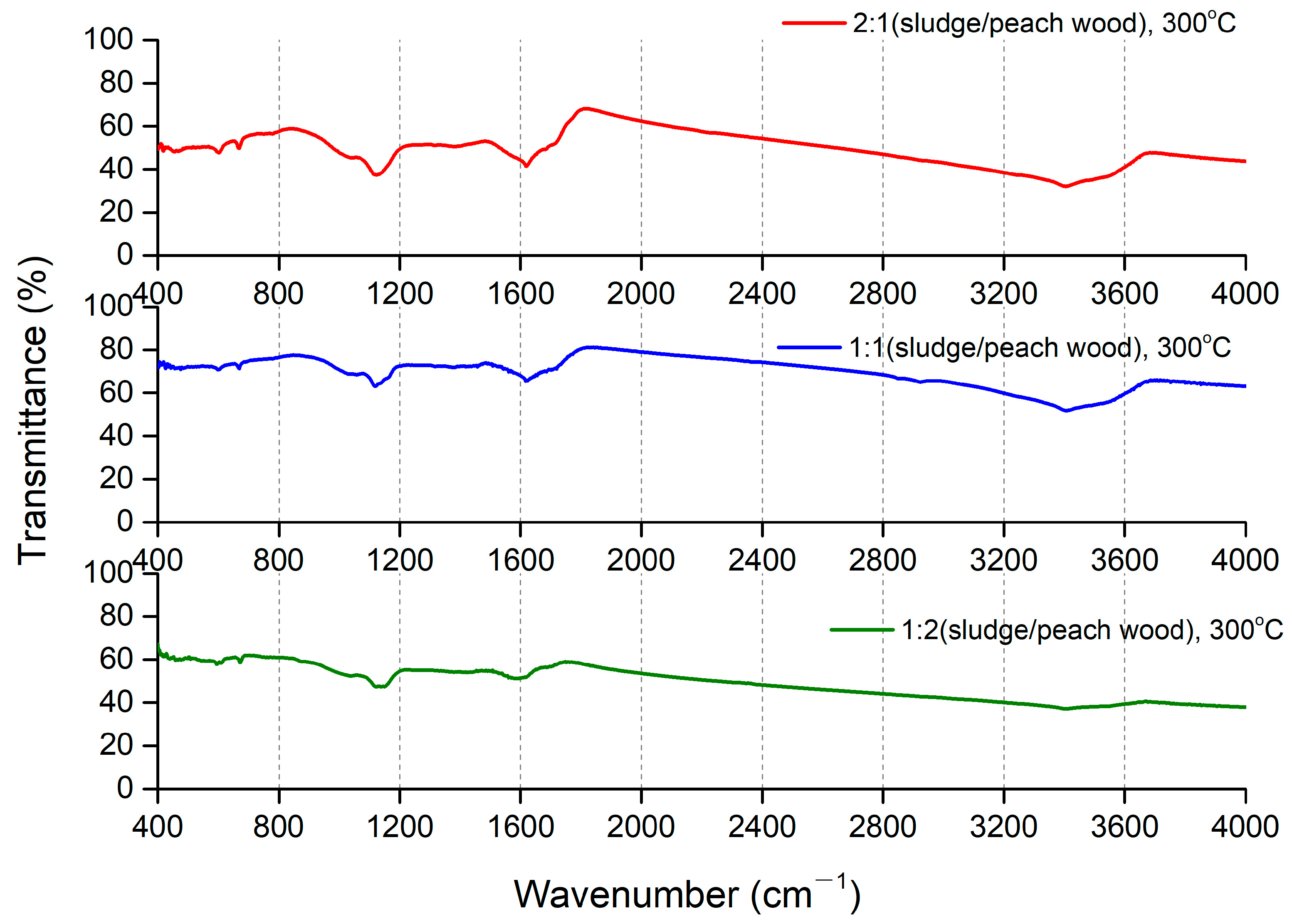

| Item | C (%) | O (%) | N (%) | S (%) | H (%) | Ash Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sludge | 18 | 21 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 39 |
| Peach wood | 50 | 45 | 0.1 | n.d. | 5 | 6 |
| Pyrolysis Temperature (°C) | Mass Ratio between Sludge and Peach Wood | Amounts (mg g−1) |
|---|---|---|
| 2:1 | 32.9 | |
| 300 | 1:1 | 223.3 |
| 1:2 | 78.6 | |
| 2:1 | 63.4 | |
| 500 | 1:1 | 131.9 |
| 1:2 | 74.2 | |
| 2:1 | 40.6 | |
| 700 | 1:1 | 86.3 |
| 1:2 | 55.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, B.; Liu, Q.; Li, H.; Liu, D.; Wang, H.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Z.; Yao, J. Sorption of Iodine on Biochar Derived from the Processing of Urban Sludge and Garden Waste at Different Pyrolysis Temperatures. Molecules 2024, 29, 3007. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29133007
Bai B, Liu Q, Li H, Liu D, Wang H, Zhang C, Yang Z, Yao J. Sorption of Iodine on Biochar Derived from the Processing of Urban Sludge and Garden Waste at Different Pyrolysis Temperatures. Molecules. 2024; 29(13):3007. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29133007
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Bing, Qingyang Liu, He Li, Dan Liu, Haichao Wang, Chengliang Zhang, Zheng Yang, and Jingjing Yao. 2024. "Sorption of Iodine on Biochar Derived from the Processing of Urban Sludge and Garden Waste at Different Pyrolysis Temperatures" Molecules 29, no. 13: 3007. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29133007
APA StyleBai, B., Liu, Q., Li, H., Liu, D., Wang, H., Zhang, C., Yang, Z., & Yao, J. (2024). Sorption of Iodine on Biochar Derived from the Processing of Urban Sludge and Garden Waste at Different Pyrolysis Temperatures. Molecules, 29(13), 3007. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29133007







