Novel and Extremely Sensitive NiAl2O4-NiO Nanostructures on an ITO Sensing Electrode for Enhanced Detection of Ascorbic Acid
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Synthesis of NiAl2O4-NiO Nanostructures
2.2. Morphological and Structural Characterization
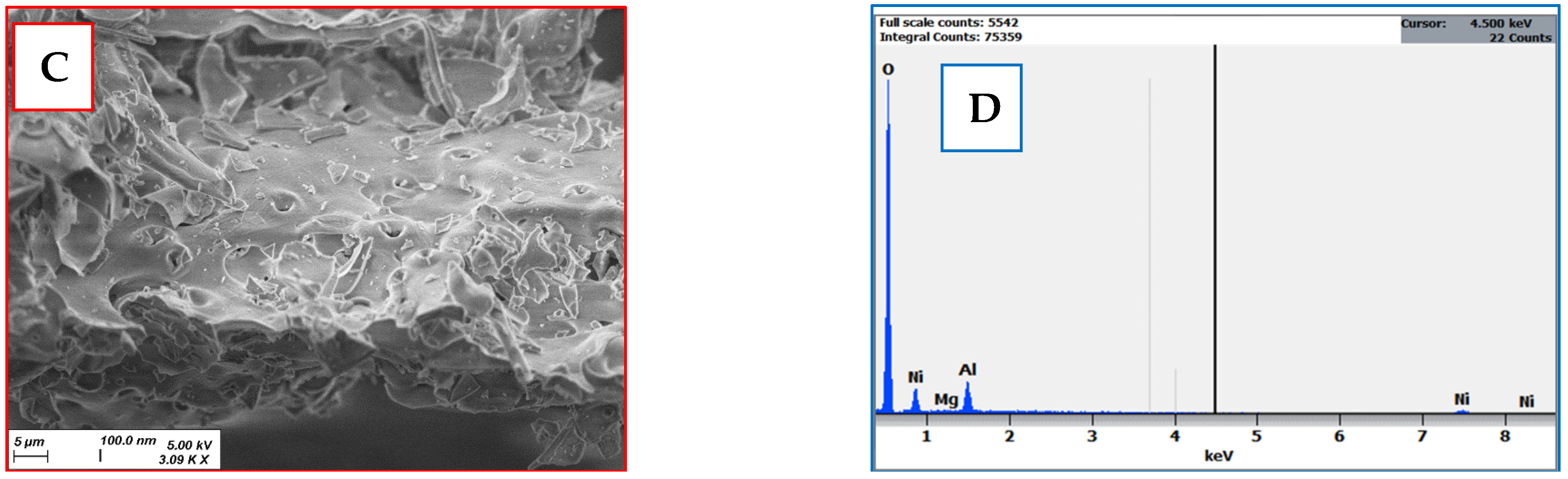
2.2.1. SEM Analysis
2.2.2. XRD Analysis
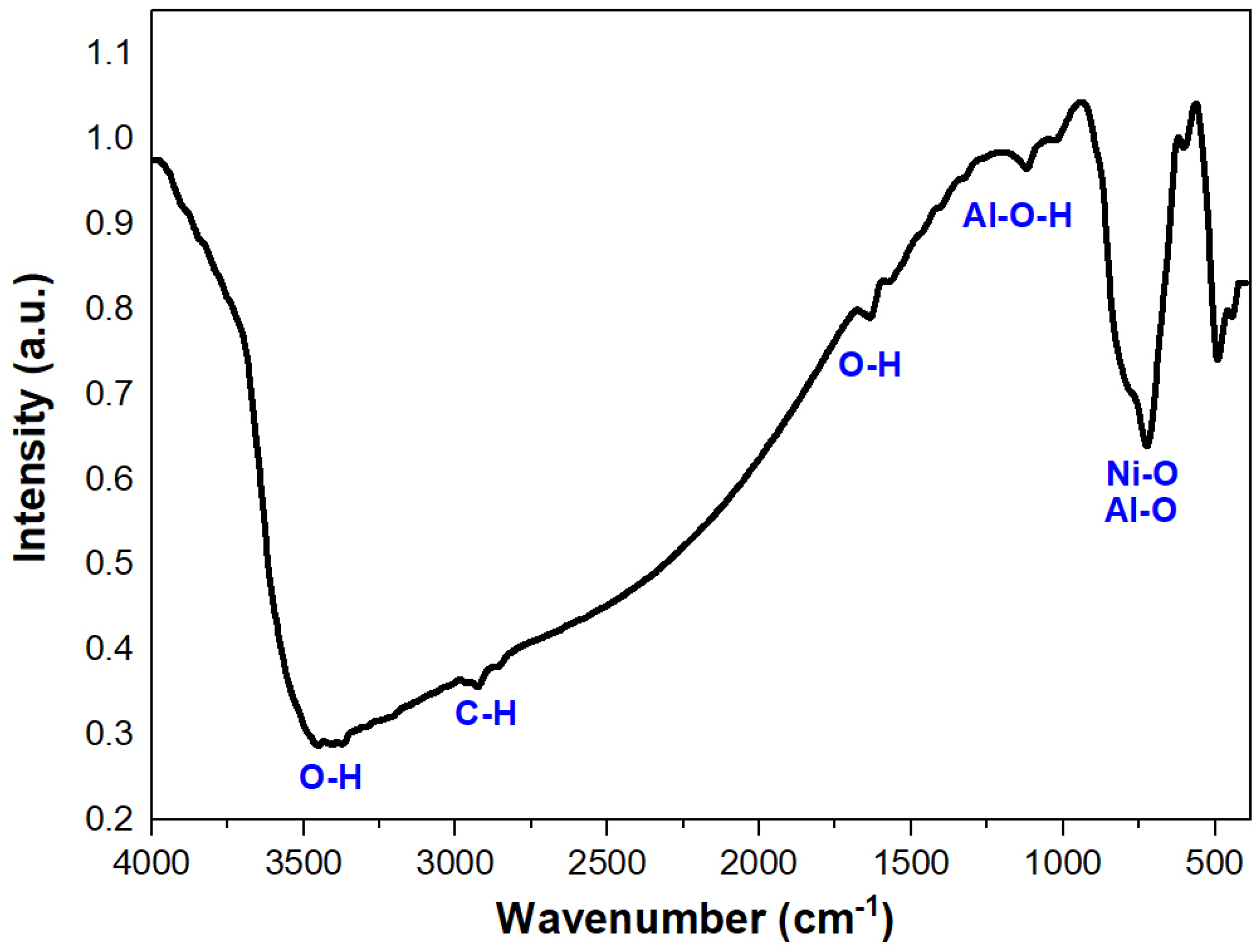
2.2.3. FT-IR Analysis
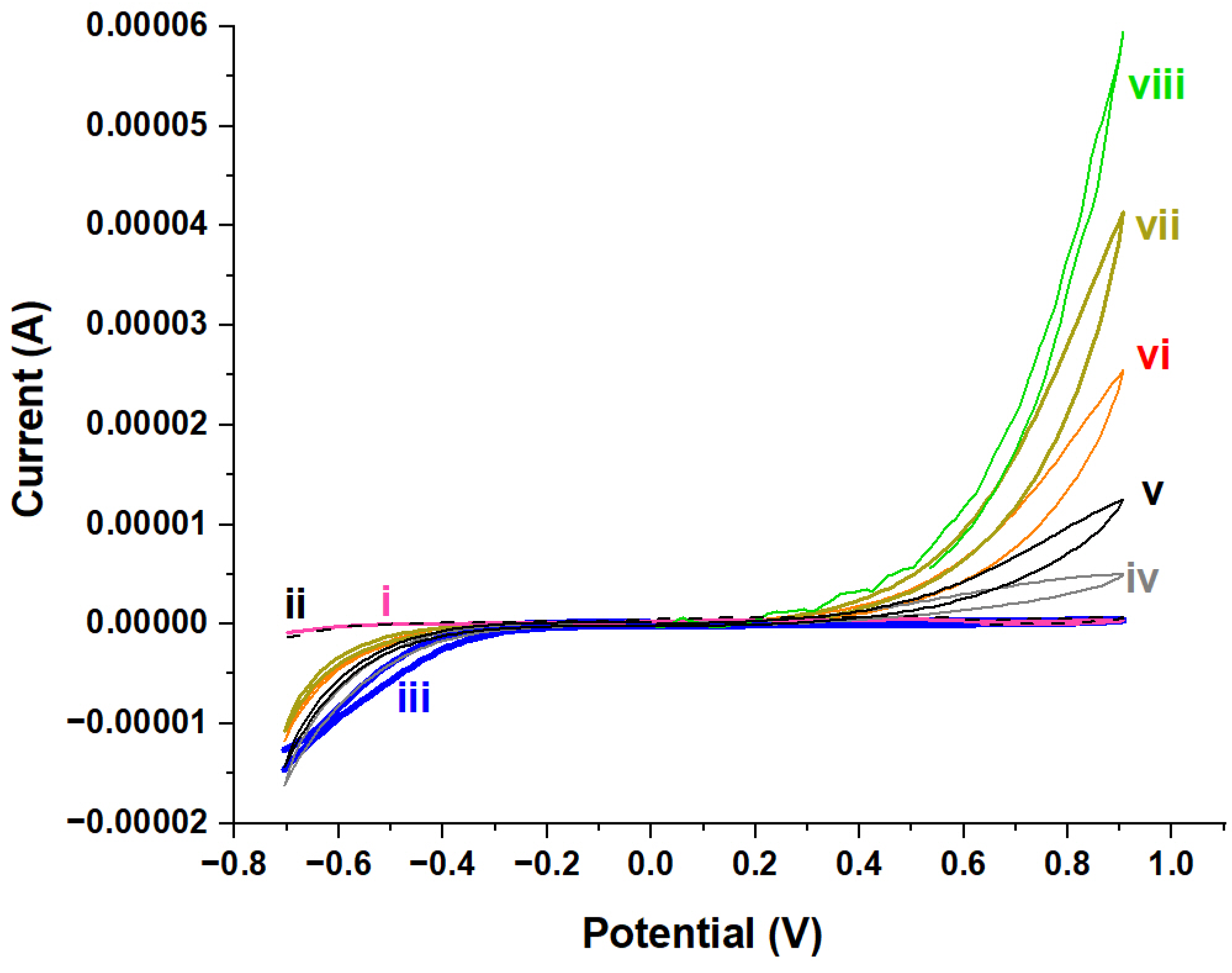
2.2.4. Electrochemical Characterization
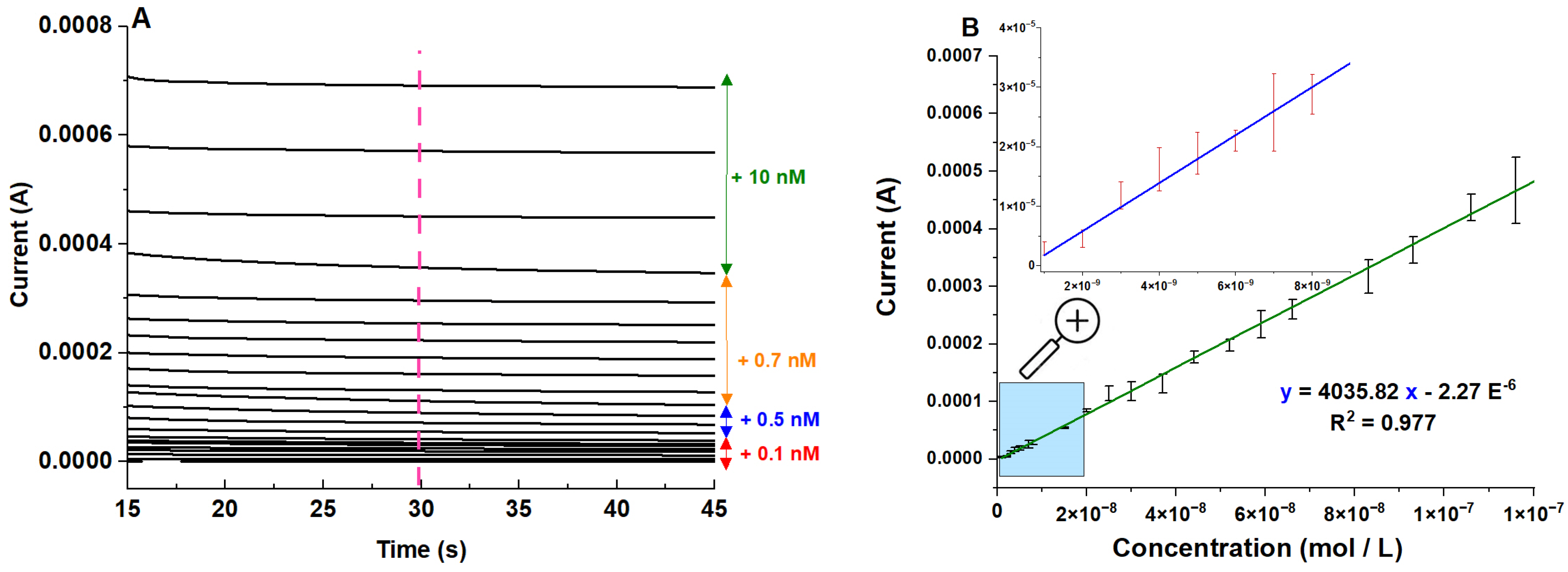
2.3. Electrochemical Performance of NiAl2O4-NiO/ITO Electrode
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sabatier, M.; Rytz, A.; Husny, J.; Dubascoux, S.; Nicolas, M.; Dave, A.; Singh, H.; Bodis, M.; Glahn, R.P. Impact of ascorbic acid on the in vitro iron bioavailability of a casein-based iron fortificant. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebling, E.J.; Sze, R.W.; Behrens, E.M. Vitamin C deficiency mimicking inflammatory bone disease of the hand. Pediatr. Rheumatol. 2020, 18, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, K.L.; Bragança, V.A.; Pacheco, L.V.; Ota, S.S.; Aguiar, C.P.; Borges, R.S. Essential features for antioxidant capacity of ascorbic acid (vitamin C). J. Mol. Model. 2022, 28, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, K.M.; Kwon, E.B.; Lee, B.; Kim, C.Y. Recent trends in controlling the enzymatic browning of fruit and vegetable products. Molecules 2020, 25, 2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agostoni, C.; Canani, R.B.; Fairweather-Tait, S.; Heinonen, M.; Korhonen, H.; La Vieille, S.; Verhagen, H. Scientific opinion on dietary reference values for selenium. EFSA J. 2014, 12, 3846. [Google Scholar]
- Carr, A.C.; Rosengrave, P.C.; Bayer, S.; Chambers, S.; Mehrtens, J.; Shaw, G.M. Hypovitaminosis C and vitamin C deficiency in critically ill patients despite recommended enteral and parenteral intakes. Crit. Care 2017, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabiee, N.; Ahmadi, S.; Rahimizadeh, K.; Chen, S.; Veedu, R.N. Metallic nanostructure-based aptasensors for robust detection of proteins. Nanoscale Adv. 2024, 6, 747–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Ren, Q.; Jiang, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, M. A triple-aptamer tetrahedral DNA nanostructures based carbon-nanotube-array transistor biosensor for rapid virus detection. Talanta 2024, 266, 124973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, L.; Tan, M.; Su, W. Recent Progress in Photoelectrochemical Sensing of Pesticides in Food and Environmental Samples: Photoactive Materials and Signaling Mechanisms. Molecules 2024, 29, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gayathri, R.C.; Elakkiya, V.; Sumathi, S. Effect of method of preparation on the photocatalytic activity of NiAl2O4. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2021, 129, 108634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, S.G.; Swart, H.C. Microwave-assisted synthesis of blue-green NiAl2O4 nanoparticle pigments with high near-infrared reflectance for indoor cooling. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 819, 152991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunkumar, M.; Nesaraj, A.S. One pot chemical synthesis of ultrafine NiAl2O4 nanoparticles: Physico-chemical properties and photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes under visible light irradiation. Inorg. Nano-Met. Chem. 2021, 51, 910–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataramana, C.; Botsa, S.M.; Shyamala, P.; Muralikrishna, R. Photocatalytic degradation of polyethylene plastics by NiAl2O4 spinels-synthesis and characterization. Chemosphere 2021, 265, 129021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebretinsae, H.G.; Tsegay, M.G.; Nuru, Z.Y. Biosynthesis of nickel oxide (NiO) nanoparticles from cactus plant extract. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 36, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepa, J.; Šišoláková, I.; Vojtko, M.; Trnková, L.; Nagy, G.; Maskaľová, I.; Oriňaková, R. NiO nanoparticles for electrochemical insulin detection. Sensors 2021, 21, 5063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Liu, B.; Xu, Z.; Liu, J. NiO nanoparticles for exceptionally stable DNA adsorption and its extraction from biological fluids. Langmuir 2018, 34, 9314–9321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivakumar, M.; Pandi, K.; Chen, S.M.; Yadav, S.; Chen, T.W.; Veeramani, V. Highly sensitive detection of gallic acid in food samples by using robust NiAl2O4 nanocomposite materials. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, B29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, H.E.; Medetalibeyoglu, H.; Polat, I.; Yola, B.B.; Atar, N.; Yola, M.L. Graphene quantum dots incorporated NiAl2O4 nanocomposite based molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor for 5-hydroxymethyl furfural detection in coffee samples. Anal. Methods 2023, 15, 1932–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangcharoen, T.; T-Thienprasert, J.; Kongmark, C. Effect of calcination temperature on structural and optical properties of MAl2O4 (M = Ni, Cu, Zn) aluminate spinel nanoparticles. J. Adv. Ceram. 2019, 8, 352–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadeeshwaran, C.; Murugaraj, R. Structural, Optical, Magnetic, and Electrical Properties of Ni0.5Co0.5Al2O4 System. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2020, 33, 1765–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurita-Mendez, N.N.; Carbajal-De la Torre, G.; Cadenas, E.; Liu, H.; Espinosa-Medina, M.A. Synthesis and characterization of nickel aluminate nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 6, 015036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangcharoen, T.; T-Thienprasert, J.; Kongmark, C. Optical properties and versatile photocatalytic degradation ability of M Al2O4 (M = Ni, Cu, Zn) aluminate spinel nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 8995–9006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.K.; Ghose, R. Synthesis and characterization of nanocrystalline zinc aluminate spinel powder by sol–gel method. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 3209–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahinroosta, M.; Allahverdi, A. Production of nanostructured γ-alumina from aluminum foundry tailing for catalytic applications. Int. Nano Lett. 2018, 8, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, A.; Raouafi, N.; Mirsky, V.M. Electrically controlled Michael addition: Addressing of covalent immobilization of biological receptors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 121, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Xie, A.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, K.; Su, Z.; Song, N.; Luo, S. Three-dimensional g-C3N4/MWNTs/GO hybrid electrode as electrochemical sensor for simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1211, 339907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varatharajan, P.; Maruthupandi, M.; Ponnusamy, V.K.; Vasimalai, N. Purpald-functionalized biosensor for simultaneous electrochemical detection of ascorbic acid, uric acid, L-cysteine and lipoic acid. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 17, 100458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, N.; Verma, R.; Ram, R.; Singh, J.; Sarkar, A. Development of a biodegradable microfluidic paper-based device for blood-plasma separation integrated with non-enzymatic electrochemical detection of ascorbic acid. Talanta 2024, 266, 125019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaya, E.; Menendez, N.; Mazario, E.; Herrasti, P. Fe3O4-nanoparticle-modified sensor for the detection of dopamine, uric acid and ascorbic acid. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Electrode Material | Linear Range | Detection Limit | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| gC3N4/MWNTs/GO 1 | 0.2 to 7.5 mM | 96 μM | Wang et al. (2022) [26] |
| p-Purpald@GCE 2 | 33.2 to 76.9 µM | 392 nM | Varatharajan et al. (2024) [27] |
| n-MgF/SPE/EμPAD 3 | 0 to 80 μM | 2.44 μM | Gautam et al. (2024) [28] |
| Fe3O4/GCE 4 | 1050 to 2300 µM | 95 µM | Gaya et al. (2024) [29] |
| NiAl2O4-NiO/ITO | 3.96 × 10−9 nM to 10 mM | 1.2 × 10−9 nM | Present work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hammami, A.; Bardaoui, A.; Eissa, S.; Elgaher, W.A.M.; Chtourou, R.; Messaoud, O. Novel and Extremely Sensitive NiAl2O4-NiO Nanostructures on an ITO Sensing Electrode for Enhanced Detection of Ascorbic Acid. Molecules 2024, 29, 2837. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122837
Hammami A, Bardaoui A, Eissa S, Elgaher WAM, Chtourou R, Messaoud O. Novel and Extremely Sensitive NiAl2O4-NiO Nanostructures on an ITO Sensing Electrode for Enhanced Detection of Ascorbic Acid. Molecules. 2024; 29(12):2837. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122837
Chicago/Turabian StyleHammami, Asma, Afrah Bardaoui, Shimaa Eissa, Walid A. M. Elgaher, Radhouane Chtourou, and Olfa Messaoud. 2024. "Novel and Extremely Sensitive NiAl2O4-NiO Nanostructures on an ITO Sensing Electrode for Enhanced Detection of Ascorbic Acid" Molecules 29, no. 12: 2837. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122837
APA StyleHammami, A., Bardaoui, A., Eissa, S., Elgaher, W. A. M., Chtourou, R., & Messaoud, O. (2024). Novel and Extremely Sensitive NiAl2O4-NiO Nanostructures on an ITO Sensing Electrode for Enhanced Detection of Ascorbic Acid. Molecules, 29(12), 2837. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122837








