Dual Gene Detection of H5N1 Avian Influenza Virus Based on Dual RT-RPA
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Establishment and Optimization of Dual RT-RPA Detection
2.2. Dual RT-RPA Sensitivity
2.3. Dual RT-RPA Specificity
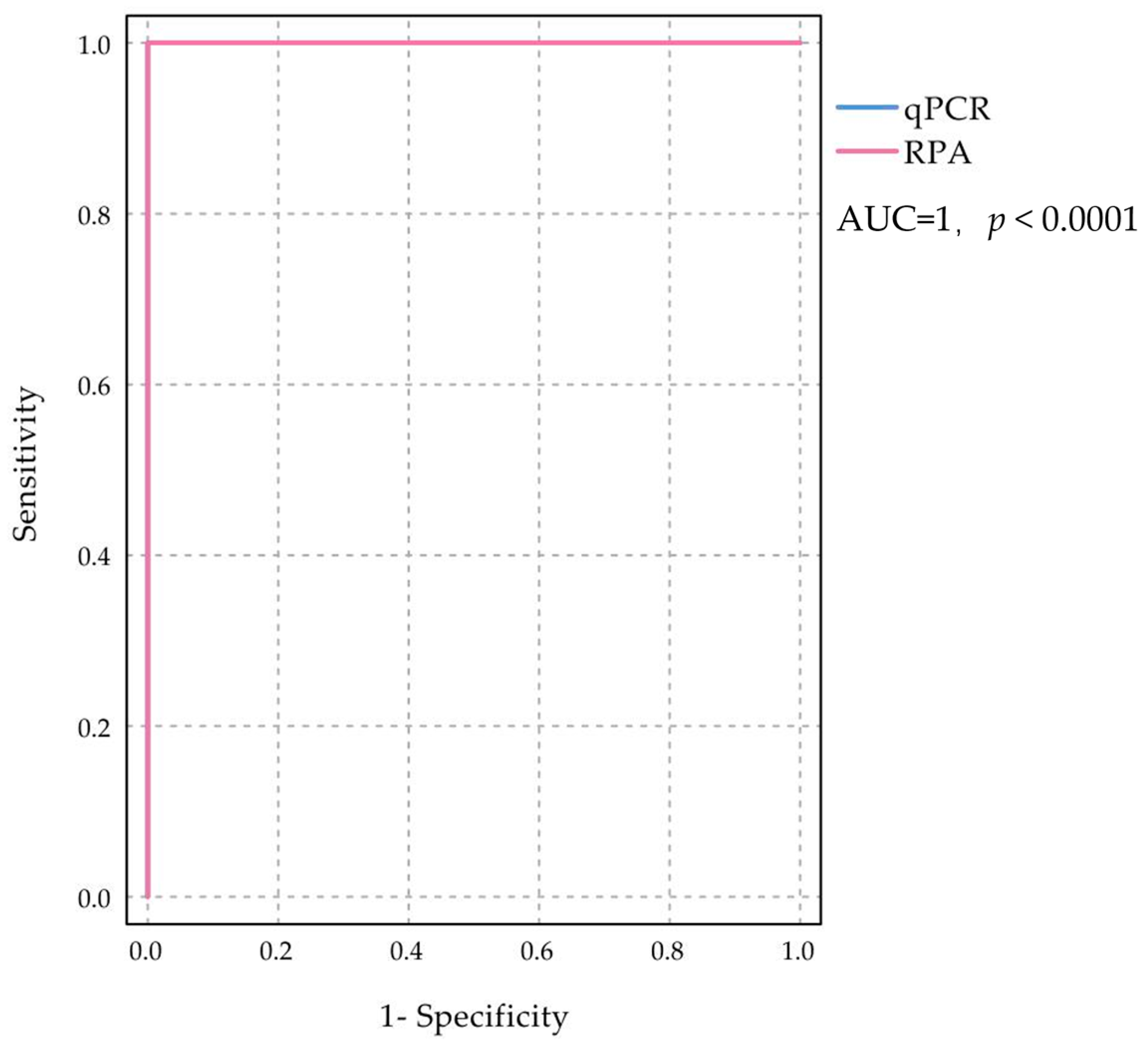
2.4. Detection and Evaluation of Clinical Samples
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethical Statement
4.2. Extraction of Samples and Viral Nucleic Acids
4.3. Construction of Standard Plasmid
4.4. Primer Design
4.5. Establishment of Dual RT-RPA Detection
4.6. Dual RT-RPA Sensitivity Analysis
4.7. Dual RT-RPA Specificity Analysis
4.8. Evaluation of Dual RT-RPA Detection Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neumann, G.; Noda, T.; Kawaoka, Y. Emergence and pandemic potential of swine-origin H1N1 influenza virus. Nature 2009, 459, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Wit, E.; Kawaoka, Y.; de Jong, M.D.; Fouchier, R.A. Pathogenicity of highly pathogenic avian influenza virus in mammals. Vaccine 2008, 26, D54–D58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouchier, R.A.M.; Munster, V.; Wallensten, A.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Herfst, S.; Smith, D.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Olsen, B.; Osterhaus, A.D.M.E. Characterization of a Novel Influenza A Virus Hemagglutinin Subtype (H16) Obtained from Black-Headed Gulls. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 2814–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaye, D.; Pringle, C.R. Avian Influenza Viruses and their Implication for Human Health. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 40, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Huang, B.; Ma, X.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, L.; Fan, Q.; Sun, Y.; Wang, K. Reverse transcription recombinase-aided amplification assay for H7 subtype avian influenza virus. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.-H.; Criado, M.F.; Swayne, D.E. Pathobiological Origins and Evolutionary History of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Viruses. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2021, 11, a038679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Goot, J.A.; van Boven, M.; Koch, G.; de Jong, M.C. Variable effect of vaccination against highly pathogenic avian influenza (H7N7) virus on disease and transmission in pheasants and teals. Vaccine 2007, 25, 8318–8325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Tran, K.; Gray, M.; Li, Y.; Ao, Z.; Yao, X.; Kobasa, D.; Kobinger, G.P. Evaluation of conserved and variable influenza antigens for immunization against different isolates of H5N1 viruses. Vaccine 2009, 27, 3083–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Cho, C.H.; Shin, J.H.; Yang, J.C.; Park, T.J.; Park, J.; Park, J.P. Highly sensitive and label-free detection of influenza H5N1 viral proteins using affinity peptide and porous BSA/MXene nanocomposite electrode. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1251, 341018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Subbarao, K.; Cox, N.J.; Guo, Y. Genetic Characterization of the Pathogenic Influenza A/Goose/Guangdong/1/96 (H5N1) Virus: Similarity of Its Hemagglutinin Gene to Those of H5N1 Viruses from the 1997 Outbreaks in Hong Kong. Virology 1999, 261, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbarao, K.; Klimov, A.; Katz, J.; Regnery, H.; Lim, W.; Hall, H.; Perdue, M.; Swayne, D.; Bender, C.; Huang, J.; et al. Characterization of an Avian Influenza A (H5N1) Virus Isolated from a Child with a Fatal Respiratory Illness. Science 1998, 279, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Tian, J.; Lin, T.; Shao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chang, H. Features of human-infecting avian influenza viruses and mammalian adaptations. J. Infect. 2016, 73, 95–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, D. Avian influenza. Vet. Rec. 2005, 157, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vries, E.; Guo, H.; Dai, M.; Rottier, P.J.; Van Kuppeveld, F.J.; De Haan, C.A. Rapid Emergence of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Subtypes from a Subtype H5N1 Hemagglutinin Variant. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 842–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Cumulative Number of Confirmed Human Cases† or Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Reported to WHO, 2003–2023; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- OIE. Avian Influenza in Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals; OIE: Paris, France, 2008; pp. 465–481. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.; Kim, E.; Lee, Y.; Yeo, S.; Park, C. Multiplex real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction for differential detection of H5, N1, and N8 genes of highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses. Vet. Med. 2017, 62, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, F.; Jiang, N.; Zhuang, Q.; Hou, G.; Jiang, L.; Yu, J.; Yu, X.; Liu, H.; et al. Reverse transcription recombinase-aided amplification assay for H5 subtype avian influenza virus. Virol. J. 2022, 19, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Shin, J.; Shin, S.; Chung, Y.-J. Development of reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification assays for point-of-care testing of avian influenza virus subtype H5 and H9. Genom. Inform. 2020, 18, e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bei, L.; Cheng, H.R.; Yan, Q.F.; Huang, Z.J.; Shen, G.F.; Zhang, Z.F.; Yinv, L.I.; Deng, Z.X.; Lin, M. Recombinase-Aid Amplification:a Novel Technology of in vitro Rapid Nucleic Acid Amplification. Sci. China Life Sci. 2010, 40, 983–988. [Google Scholar]
- Yehia, N.; Eldemery, F.; Arafa, A.-S.; El Wahed, A.A.; El Sanousi, A.; Weidmann, M.; Shalaby, M. Reverse Transcription Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assay for Rapid Detection of Avian Influenza Virus H9N2 HA Gene. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, S.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, W.; Li, Z.; Qin, Y.; Chen, J.; et al. Development and Application of RAA Nucleic Acid Test Strip Assay and Double RAA Gel Electrophoresis Detection Methods for ASFV and CSFV. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 8, 811824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Tholoth, M.; Branavan, M.; Naveenathayalan, A.; Balachandran, W. Recombinase polymerase amplification–nucleic acid lateral flow immunoassays for Newcastle disease virus and infectious bronchitis virus detection. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 6391–6397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y. Pathogenicity and virulence of influenza. Virulence 2023, 14, 2223057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Chen, G.; Huang, S.; Wen, F. Receptor Binding Properties of Neuraminidase for influenza A virus: An Overview of Recent Research Advances. Virulence 2023, 14, 2235459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrando, V.A.; Friedrich, M.E.; Gandhi, S.; Mellmann, A.; Masemann, D.; Christersson, A.; Anhlan, D.; Brunotte, L.; Stoll, M.; Harder, T.; et al. Cell-intrinsic genomic reassortment of pandemic H1N1 2009 and Eurasian avian-like swine influenza viruses results in potentially zoonotic variants. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2023, 12, 2212809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.C.; Murale, D.P.; Jang, S.; Haque, M.; Seo, M.; Lee, S.; Woo, D.H.; Kwon, J.; Song, C.; Kim, Y.K.; et al. Discrimination of Avian Influenza Virus Subtypes using Host-Cell Infection Fingerprinting by a Sulfinate-based Fluorescence Superoxide Probe. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 9716–9721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sączyńska, V.; Florys-Jankowska, K.; Porębska, A.; Cecuda-Adamczewska, V. A novel epitope-blocking ELISA for specific and sensitive detection of antibodies against H5-subtype influenza virus hemagglutinin. Virol. J. 2021, 18, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, H.; Wang, R.; Hargis, B.; Lu, H.; Li, Y. A SPR Aptasensor for Detection of Avian Influenza Virus H5N1. Sensors 2012, 12, 12506–12518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, N.X.; Jin, J.H.; Chen, X.R. Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Technology and Its Application in Field of Life Sciences. Acta Agric. Jiangxi 2021, 33, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Wei, G. Research progress and application of recombinant polymerase amplification technology. Lab. Med. Clin. 2022, 19, 3145–3149. [Google Scholar]
- Behrmann, O.; Bachmann, I.; Hufert, F.; Dame, G. Schnellnachweis von SARS-CoV-2 mit recombinase polymerase amplification. BIOspektrum 2020, 26, 624–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.B.; Wu, Y.D.; Ma, J.G.; Zhu, X.Q.; Zhou, D.H. Recombinase polymerase amplification and its applications in parasite detection. Chin. J. Parasitol. Parasit. Dis. 2015, 33, 382–386. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Shen, H.; Jiang, G.; Dong, J.; Zhao, P.; Gao, S. A Real-Time Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Method for Rapid Detection of Vibrio vulnificus in Seafood. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 586981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Component | Volume (μL) |
|---|---|
| HA-RPA-F Primer (10 μM) | 2.4 |
| HA-RPA-R Primer (10 μM) | 2.4 |
| M2-RPA-F Primer (10 μM) | 2.4 |
| M2-RPA-R Primer (10 μM) | 2.4 |
| Buffer | 29.5 |
| template | 2 |
| DEPC H2O | 6.4 |
| 280 mM MgOAc | 2.5 |
| Total | 50 |
| RT-RPA | Total | Kappa | Confidence Interval | p Value | Sensitivity % | Specificity % | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | Upper Limit | Lower Limit | |||||||
| RT-qPCR | Positive | 28 | 0 | 28 | 1 | 0.041 | 0 | <0.05 | 100 | 100 |
| Negative | 0 | 44 | 44 | |||||||
| Total | 28 | 44 | 72 | |||||||
| Gene | Name | Primer Sequence (5′–3′) | Product Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HA | HA-RPA-F | TCTAGTATGCCATTCCACAACATACACCCCC | 193 |
| HA | HA-RPA-R | AACCATCTACCATTCCCTGCCATCCTCCCTC | |
| M2 | M2-RPA-F | AGCTATACAAGAAGCTGAAAAGAGAAATAAC | 167 |
| M2 | M2-RPA-R | CTGCTCACAAGTGGCACACACTAGGCCAAAA | |
| HA | HA-qPCR-F | TCAAACTCCAATGGGGGCG | 249 |
| HA | HA-qPCR-R | CCCTGCTCATTGCTATGGTG | |
| M2 | M2-qPCR-F | GGGATTTTAGGATTTGTG | 350 |
| M2 | M2-qPCR-R | CTGATTAGTGGGTTGGTG |
| Sample | Virus | Subtype | Pathogenicity | Dual RT-RPA Assay | RT-qPCR |
| K144(2.3.2.1) | AIV | H5N1 | high | + | + |
| S1322(2.3.2) | AIV | H5N1 | high | + | + |
| MK2 | AIV | H5N1 | high | + | + |
| BBVM | AIV | H5N1 | high | + | + |
| 390 | AIV | H1N1 | low | − | − |
| s1069 | AIV | H7N9 | high | − | − |
| X1330 | AIV | H3N2 | low | − | − |
| A32 | AIV | H9N2 | low | − | − |
| NX2006016 | NDV | / | / | − | − |
| JS1816 | NDV | / | / | − | − |
| M41 | IBV | / | / | − | − |
| H52 | IBV | / | / | − | − |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Q.; Wu, S.; Shuai, J.; Li, Y.; Fu, X.; Zhang, M.; Yu, X.; Ye, Z.; Ma, B. Dual Gene Detection of H5N1 Avian Influenza Virus Based on Dual RT-RPA. Molecules 2024, 29, 2801. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122801
Wang Q, Wu S, Shuai J, Li Y, Fu X, Zhang M, Yu X, Ye Z, Ma B. Dual Gene Detection of H5N1 Avian Influenza Virus Based on Dual RT-RPA. Molecules. 2024; 29(12):2801. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122801
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Qian, Shiwen Wu, Jiangbing Shuai, Ye Li, Xianshu Fu, Mingzhou Zhang, Xiaoping Yu, Zihong Ye, and Biao Ma. 2024. "Dual Gene Detection of H5N1 Avian Influenza Virus Based on Dual RT-RPA" Molecules 29, no. 12: 2801. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122801
APA StyleWang, Q., Wu, S., Shuai, J., Li, Y., Fu, X., Zhang, M., Yu, X., Ye, Z., & Ma, B. (2024). Dual Gene Detection of H5N1 Avian Influenza Virus Based on Dual RT-RPA. Molecules, 29(12), 2801. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122801







