Encapsulated Mn-Saturated Lactoferrin as a Safe Source of Manganese Ions for Restoring Probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
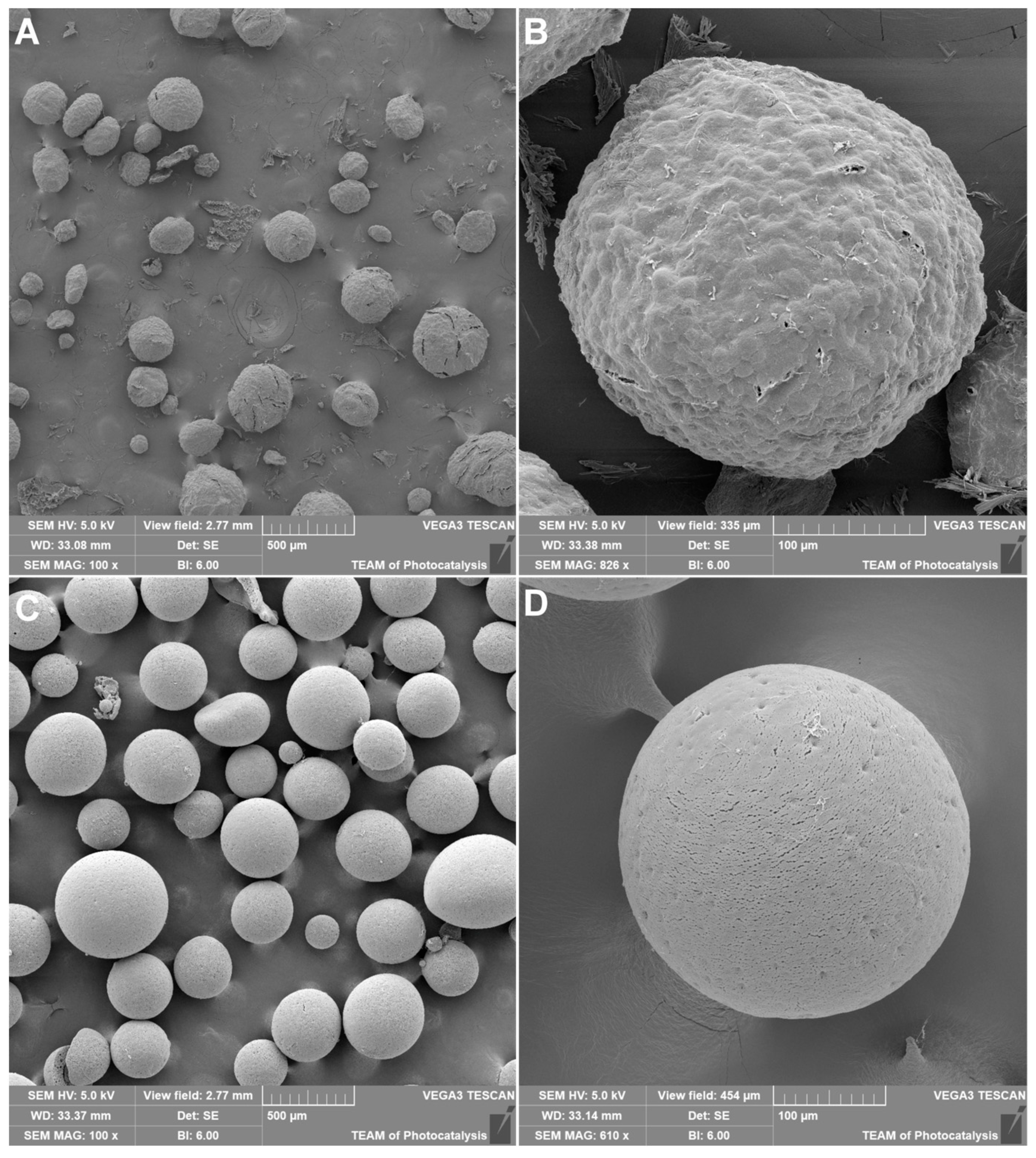
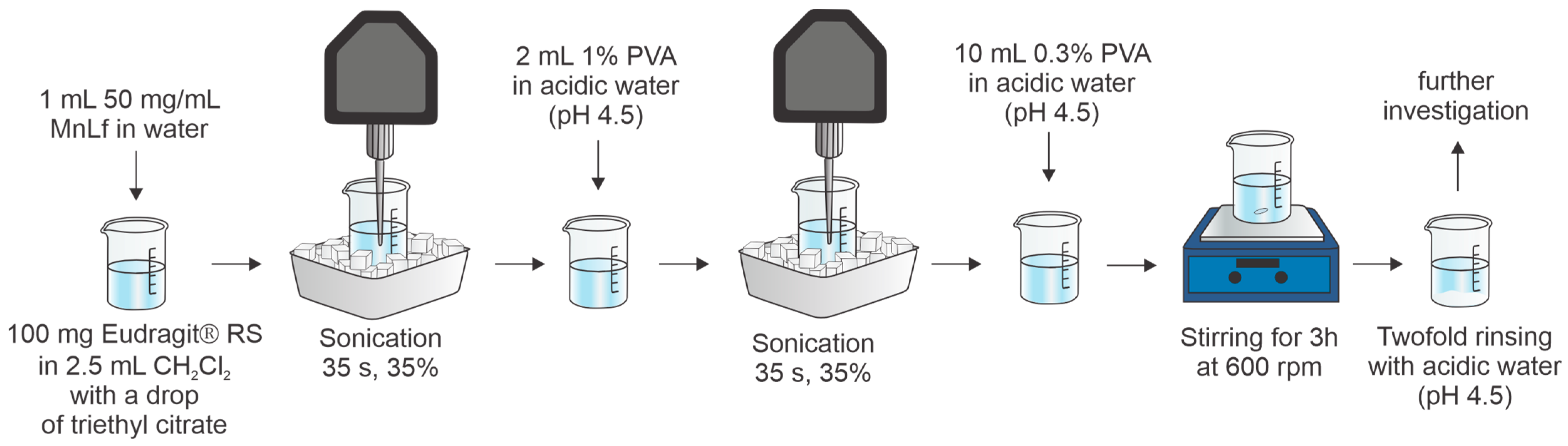
2.1. Protein Encapsulation in Microparticles
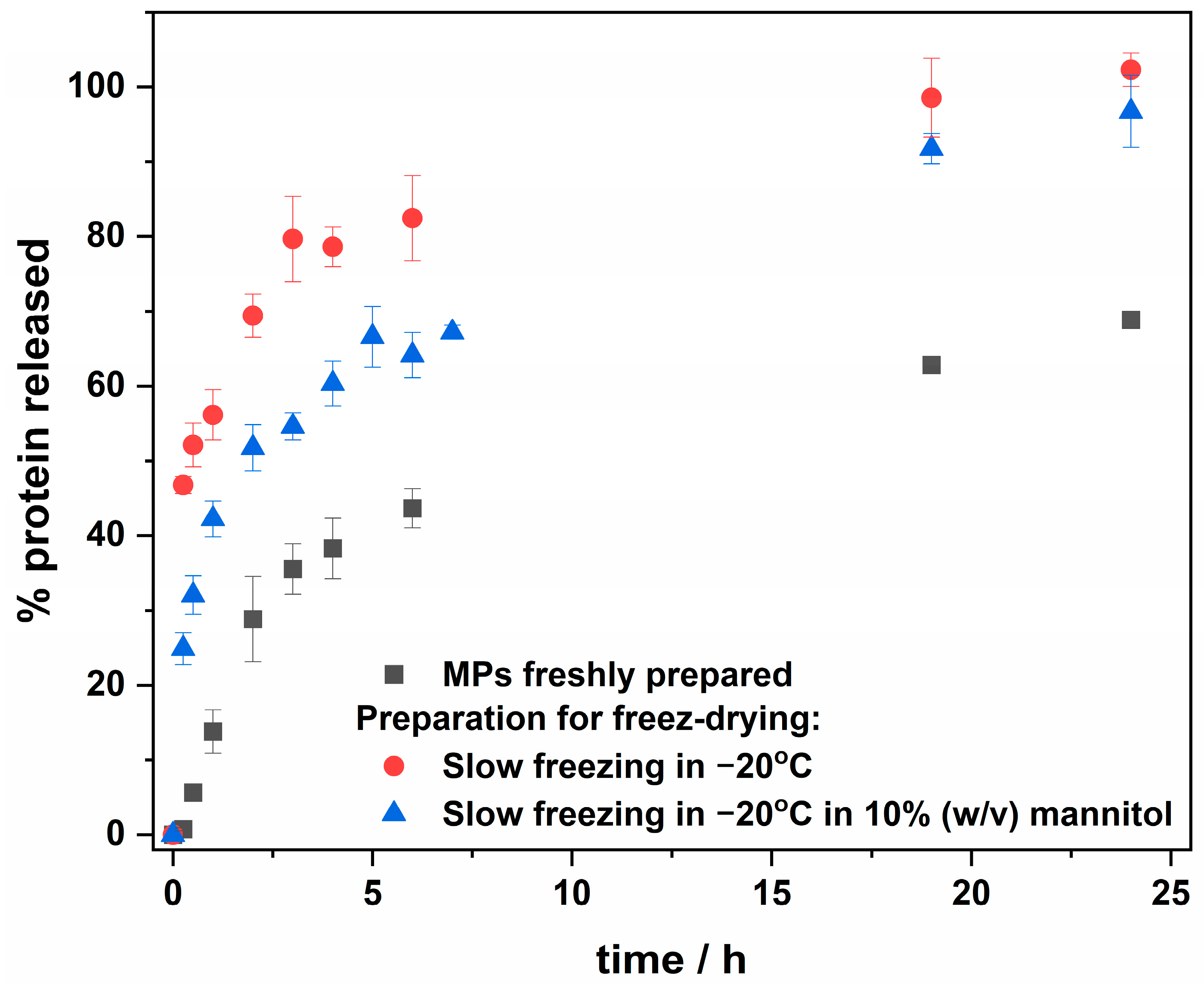
2.2. Release Profile—Freshly Prepared MPs vs. Lyophilized
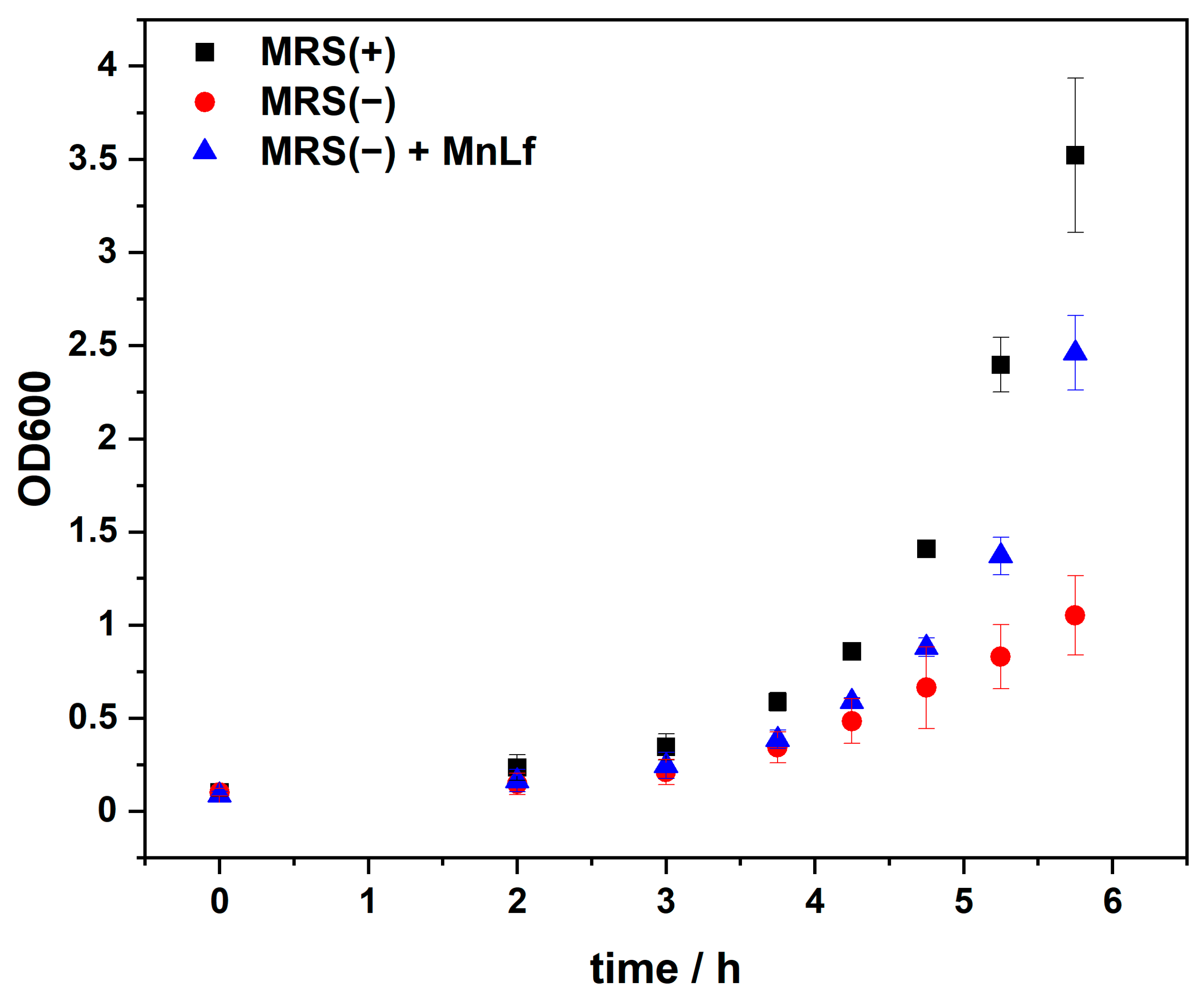
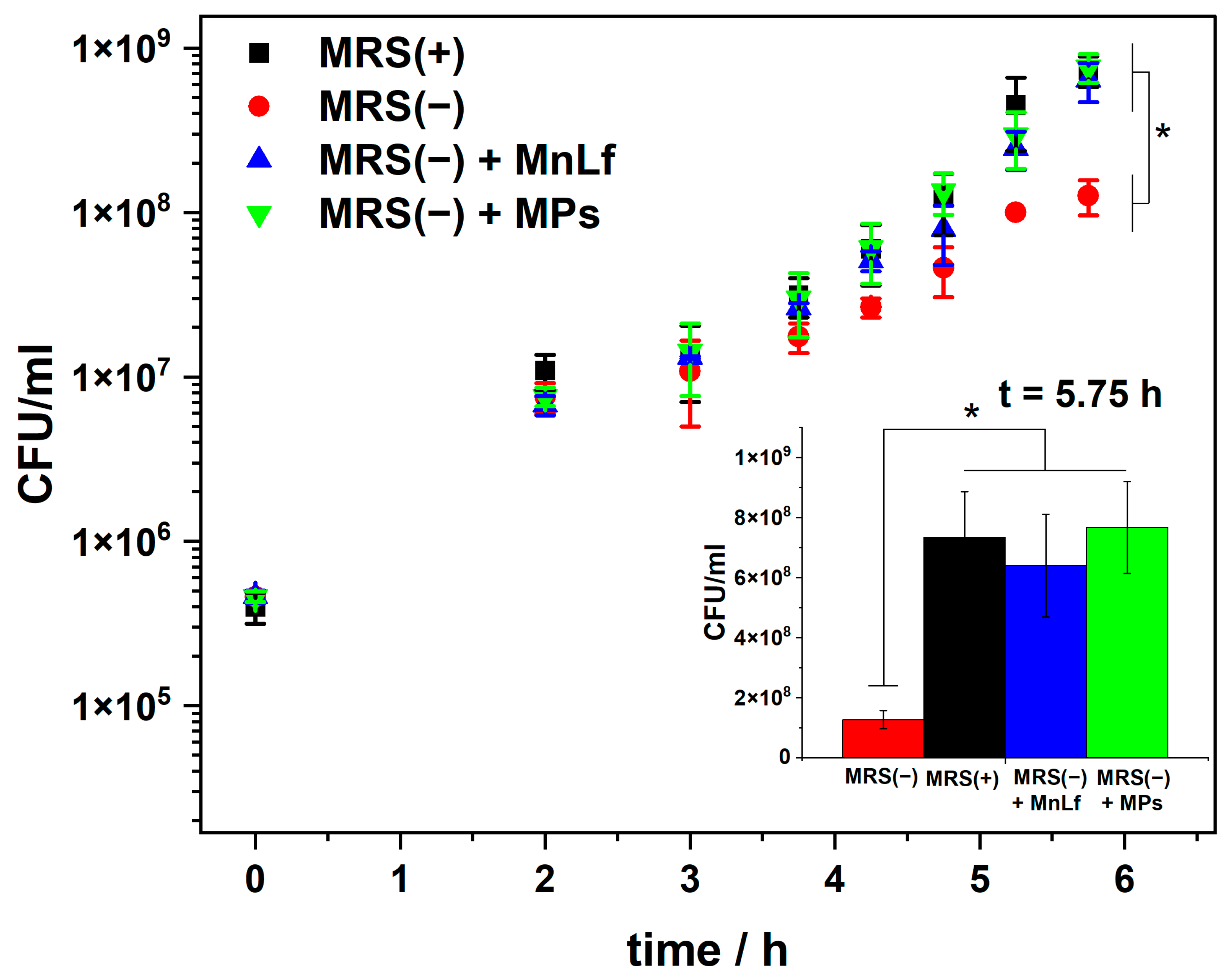
2.3. MPs Prebiotic Activity towards Lactobacillus Plantarum
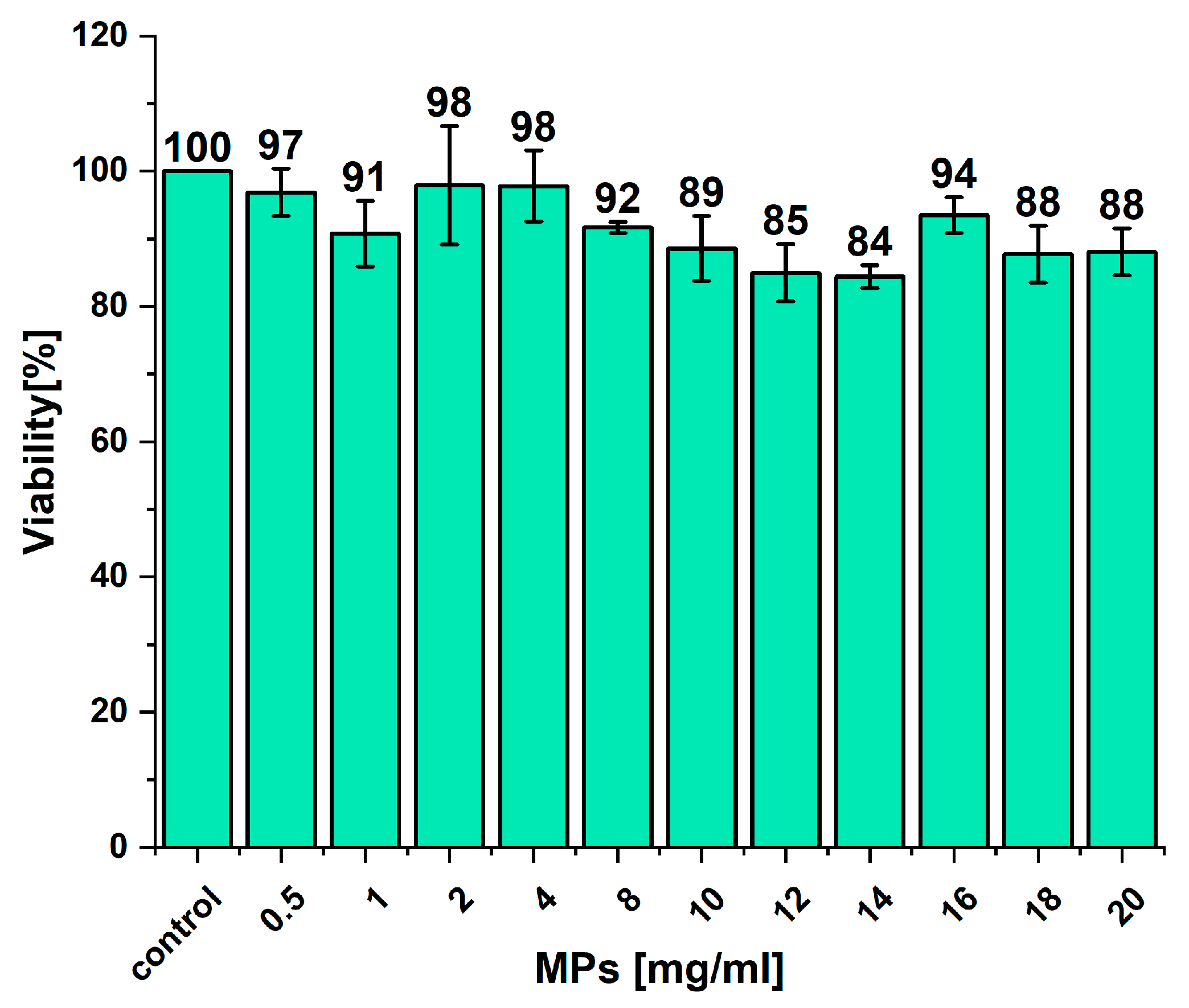
2.4. Toxicity of MPs—Preliminary Studies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Metal Content Determination
3.2. Saturation of Lactoferrin with Manganese (MnLf)
3.3. Protein Encapsulation
3.4. Protein Release Profile Investigation
3.5. Bacteria Cultivation
3.6. Toxicity Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guarner, F.; Malagelada, J.-R. Gut Flora in Health and Disease. Lancet 2003, 361, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimura, K.E.; Slusher, N.A.; Cabana, M.D.; Lynch, S.V. Role of the Gut Microbiota in Defining Human Health. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2010, 8, 435–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, S.L.; Patterson, A.D. The Gut Microbiome: An Orchestrator of Xenobiotic Metabolism. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 10, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, S.; Singh, A. Gut Microbiome and Human Health: Exploring How the Probiotic Genus Lactobacillus Modulate Immune Responses. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1042189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaser, M.J. The Microbiome Revolution. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 4162–4165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Rashidi, H.E. Gut Microbiota and Immunity Relevance in Eubiosis and Dysbiosis. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 1628–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, C.A.; Skaar, E.P. The Impact of Dietary Transition Metals on Host-Bacterial Interactions. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imbert, M.; Blondeau, R. On the Iron Requirement of Lactobacilli Grown in Chemically Defined Medium. Curr. Microbiol. 1998, 37, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posey, J.E.; Gherardini, F.C. Lack of a Role for Iron in the Lyme Disease Pathogen. Science 2000, 288, 1651–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, D.S.; Puntel, R.L.; Aschner, M. Manganese in Health and Disease; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 199–227. [Google Scholar]
- Ainscough, E.W.; Brodie, A.M.; Plowman, J.E. The Chromium, Manganese, Cobalt and Copper Complexes of Human Lactoferrin. Inorganica Chim. Acta 1979, 33, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.; Xu, T.; Luo, J.; Luo, Y.; An, P. Comparative Effects between Oral Lactoferrin and Ferrous Sulfate Supplementation on Iron-Deficiency Anemia: A Comprehensive Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials. Nutrients 2022, 14, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aisen, P.; Leibman, A.; Zweier, J. Stoichiometric and Site Characteristics of the Binding of Iron to Human Transferrin. J. Biol. Chem. 1978, 253, 1930–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Śpiewak, K.; Majka, G.; Pilarczyk-Żurek, M.; Nowak, P.M.; Woźniakiewicz, M.; Pietrzyk, P.; Korzeniak, T.; Stochel-Gaudyn, A.; Fyderek, K.; Strus, M.; et al. Mn3+-Saturated Bovine Lactoferrin Asa New Complex with Potential Prebiotic Activities for Dysbiosis Treatment and Prevention—On the Synthesis, Chemical Characterization and Origin of Biological Activity. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 38, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strus, M.; Stochel, G.; Brindell, M.; Pilarczyk-Żurek, M.; Śpiewak, K.; Majka, G.M. A Complex of Lactoferrin with Manganese Ions, a Method of Manufacturing Use and a Pharmaceutical Composition Comprising Complex of Lactoferrin with Manganese Ions. International Patent Application No. WO2017037641A1, 1 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Majka, G.; Pilarczyk-Zurek, M.; Baranowska, A.; Skowron, B.; Strus, M. Lactoferrin Metal Saturation—Which Form Is the Best for Neonatal Nutrition? Nutrients 2020, 12, 3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, X.; Bunt, C.; Cornish, J.; Quek, S.-Y.; Wen, J. Stability of Bovine Lactoferrin in Luminal Extracts and Mucosal Homogenates from Rat Intestine: A Prelude to Oral Absorption. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2014, 84, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Timilsena, Y.P.; Blanch, E.; Adhikari, B. Mild Thermal Treatment and In-Vitro Digestion of Three Forms of Bovine Lactoferrin: Effects on Functional Properties. Int. Dairy J. 2017, 64, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimoni, G.; Shani Levi, C.; Levi Tal, S.; Lesmes, U. Emulsions Stabilization by Lactoferrin Nano-Particles under In Vitro Digestion Conditions. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 33, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David-Birman, T.; Mackie, A.; Lesmes, U. Impact of Dietary Fibers on the Properties and Proteolytic Digestibility of Lactoferrin Nano-Particles. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 31, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosvenor, A.J.; Haigh, B.J.; Dyer, J.M. Digestion Proteomics: Tracking Lactoferrin Truncation and Peptide Release during Simulated Gastric Digestion. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 2699–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troost, F.J.; Saris, W.H.M.; Brummer, R.-J.M. Orally Ingested Human Lactoferrin Is Digested and Secreted in the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract In Vivo in Women with Ileostomies. J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 2597–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwata, H.; Yamauchi, K.; Teraguchi, S.; Ushida, Y.; Shimokawa, Y.; Toida, T.; Hayasawa, H. Functional Fragments of Ingested Lactoferrin Are Resistant to Proteolytic Degradation in the Gastrointestinal Tract of Adult Rats. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 2121–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furlund, C.B.; Ulleberg, E.K.; Devold, T.G.; Flengsrud, R.; Jacobsen, M.; Sekse, C.; Holm, H.; Vegarud, G.E. Identification of Lactoferrin Peptides Generated by Digestion with Human Gastrointestinal Enzymes. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, F.; Shi, P.; Chen, H.; Tu, M.; Wang, Z.; Lu, W.; Du, M. Identification and Availability of Peptides from Lactoferrin in the Gastrointestinal Tract of Mice. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajda-Morszewski, P.; Poznańska, A.; Yus, C.; Arruebo, M.; Brindell, M. Encapsulation of Iron-Saturated Lactoferrin for Proteolysis Protection with Preserving Iron Coordination and Sustained Release. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troost, F.J.; Steijns, J.; Saris, W.H.M.; Brummer, R.-J.M. Gastric Digestion of Bovine Lactoferrin In Vivo in Adults. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 2101–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gracia, R.; Yus, C.; Abian, O.; Mendoza, G.; Irusta, S.; Sebastian, V.; Andreu, V.; Arruebo, M. Enzyme Structure and Function Protection from Gastrointestinal Degradation Using Enteric Coatings. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 119, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Timilsena, Y.P.; Blanch, E.; Adhikari, B. Drying and Denaturation Characteristics of Three Forms of Bovine Lactoferrin. Dry. Technol. 2017, 35, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreedhara, A.; Flengsrud, R.; Langsrud, T.; Kaul, P.; Prakash, V.; Vegarud, G.E. Structural Characteristic, PH and Thermal Stabilities of Apo and Holo Forms of Caprine and Bovine Lactoferrins. BioMetals 2010, 23, 1159–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, N.A.; Sahlin, J.J. A Simple Equation for the Description of Solute Release. III. Coupling of Diffusion and Relaxation. Int. J. Pharm. 1989, 57, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molin, G.; Jeppsson, B.; Johansson, M.-L.; Ahrné, S.; Nobaek, S.; Ståhl, M.; Bengmark, S. Numerical Taxonomy of Lactobacillus spp. Associated with Healthy and Diseased Mucosa of the Human Intestines. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1993, 74, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, M.L.; Molin, G.; Jeppsson, B.; Nobaek, S.; Ahrné, S.; Bengmark, S. Administration of Different Lactobacillus Strains in Fermented Oatmeal Soup: In Vivo Colonization of Human Intestinal Mucosa and Effect on the Indigenous Flora. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasband, W.S. ImageJ, version 1.53e; National Institutes of Health: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 Years of Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gajda-Morszewski, P.; Poznańska, A.; Federyga, E.; Ściuk, A.; Brindell, M. Encapsulated Mn-Saturated Lactoferrin as a Safe Source of Manganese Ions for Restoring Probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum. Molecules 2024, 29, 2735. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122735
Gajda-Morszewski P, Poznańska A, Federyga E, Ściuk A, Brindell M. Encapsulated Mn-Saturated Lactoferrin as a Safe Source of Manganese Ions for Restoring Probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum. Molecules. 2024; 29(12):2735. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122735
Chicago/Turabian StyleGajda-Morszewski, Przemysław, Anna Poznańska, Eryk Federyga, Anna Ściuk, and Małgorzata Brindell. 2024. "Encapsulated Mn-Saturated Lactoferrin as a Safe Source of Manganese Ions for Restoring Probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum" Molecules 29, no. 12: 2735. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122735
APA StyleGajda-Morszewski, P., Poznańska, A., Federyga, E., Ściuk, A., & Brindell, M. (2024). Encapsulated Mn-Saturated Lactoferrin as a Safe Source of Manganese Ions for Restoring Probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum. Molecules, 29(12), 2735. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122735






