The Isolation, Structural Characterization and Anti-Inflammatory Potentials of Neutral Polysaccharides from the Roots of Isatis indigotica Fort.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Extraction, Isolation and Purification of Polysaccharide
2.2. Molecular Weight and Monosaccharide Composition
2.3. Methylation Analysis
2.4. FT-IR Spectra
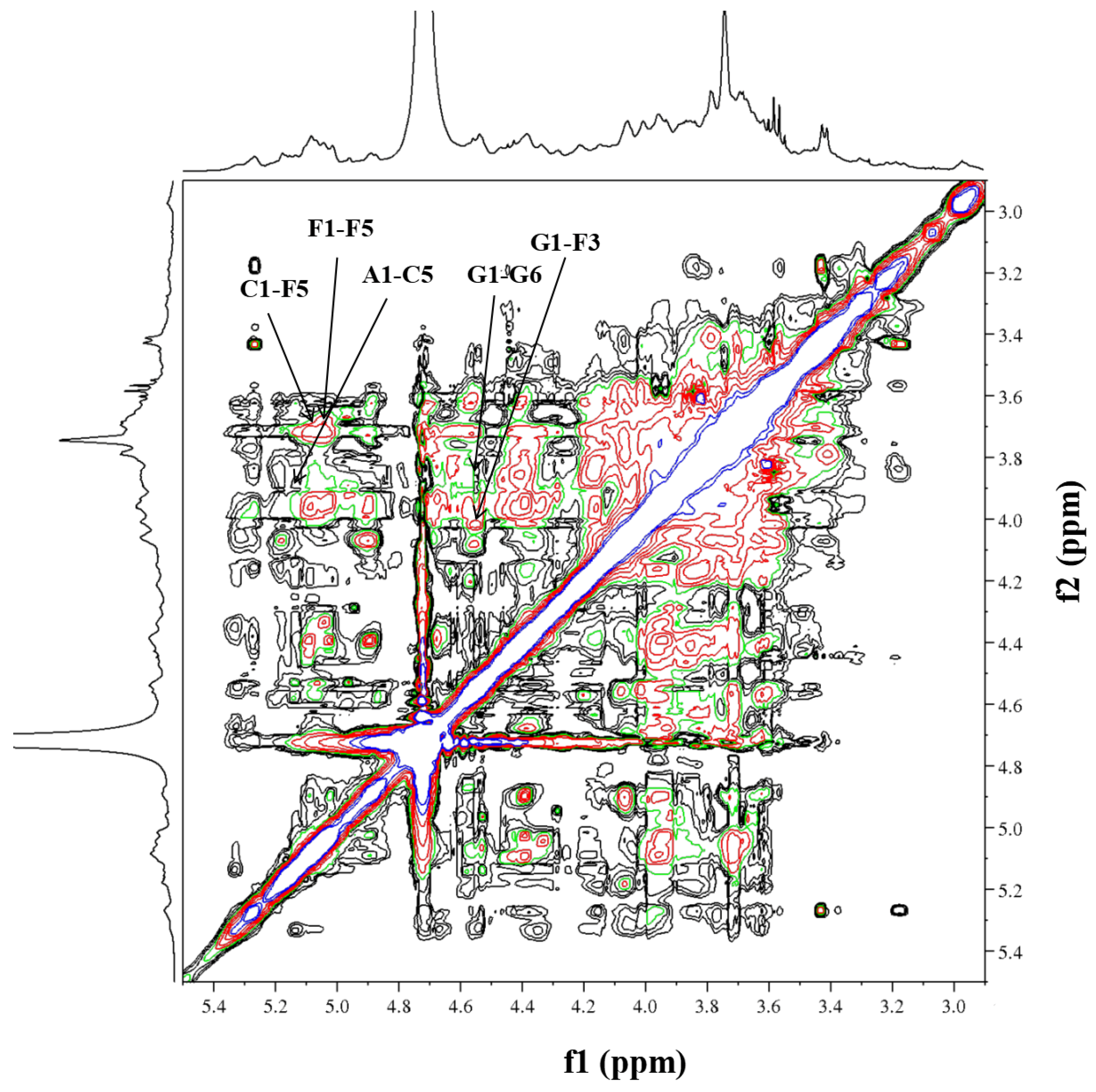
2.5. NMR Analysis of RIP-A1
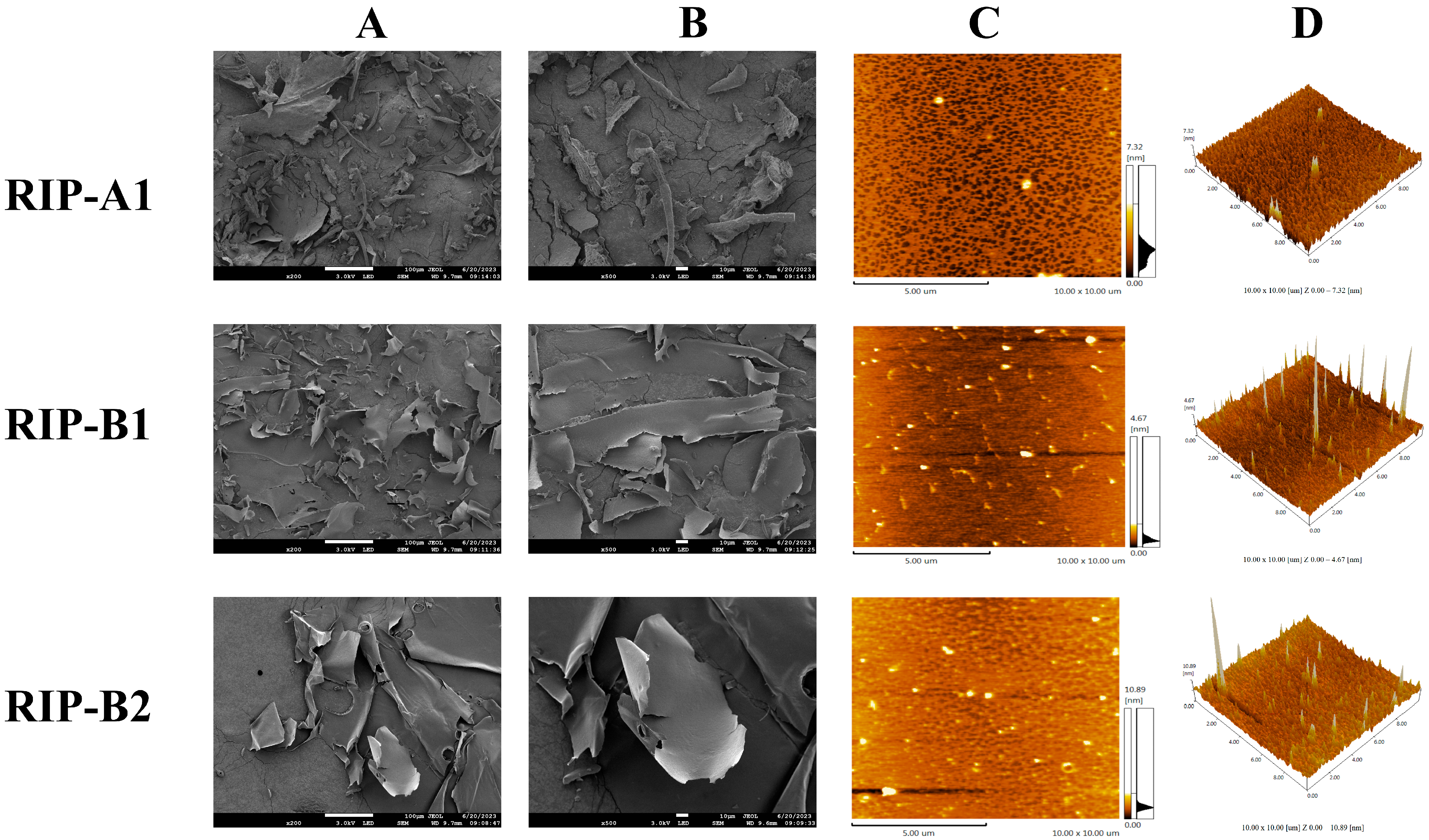
2.6. SEM and AFM Analysis
2.7. Anti-Inflammatory Activity Based on Raw 264.7 Cell Model
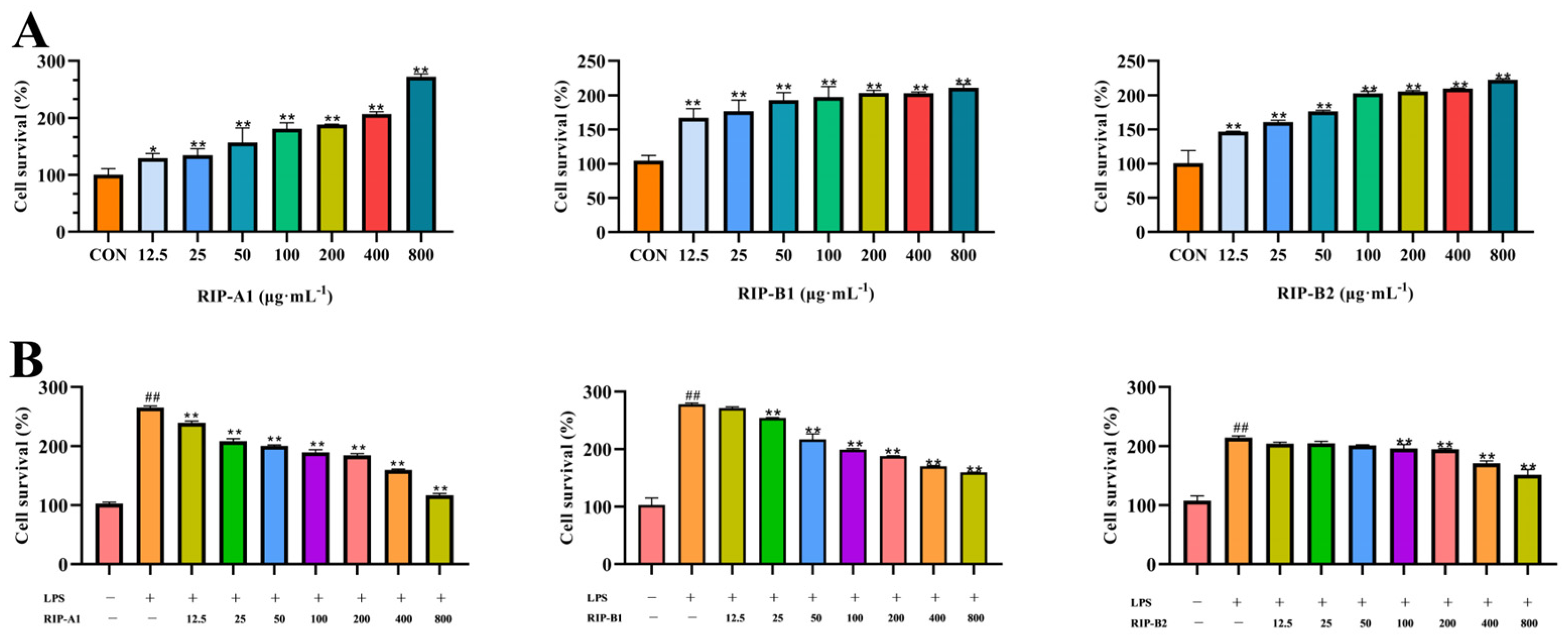
2.7.1. Determination of Cytotoxicity
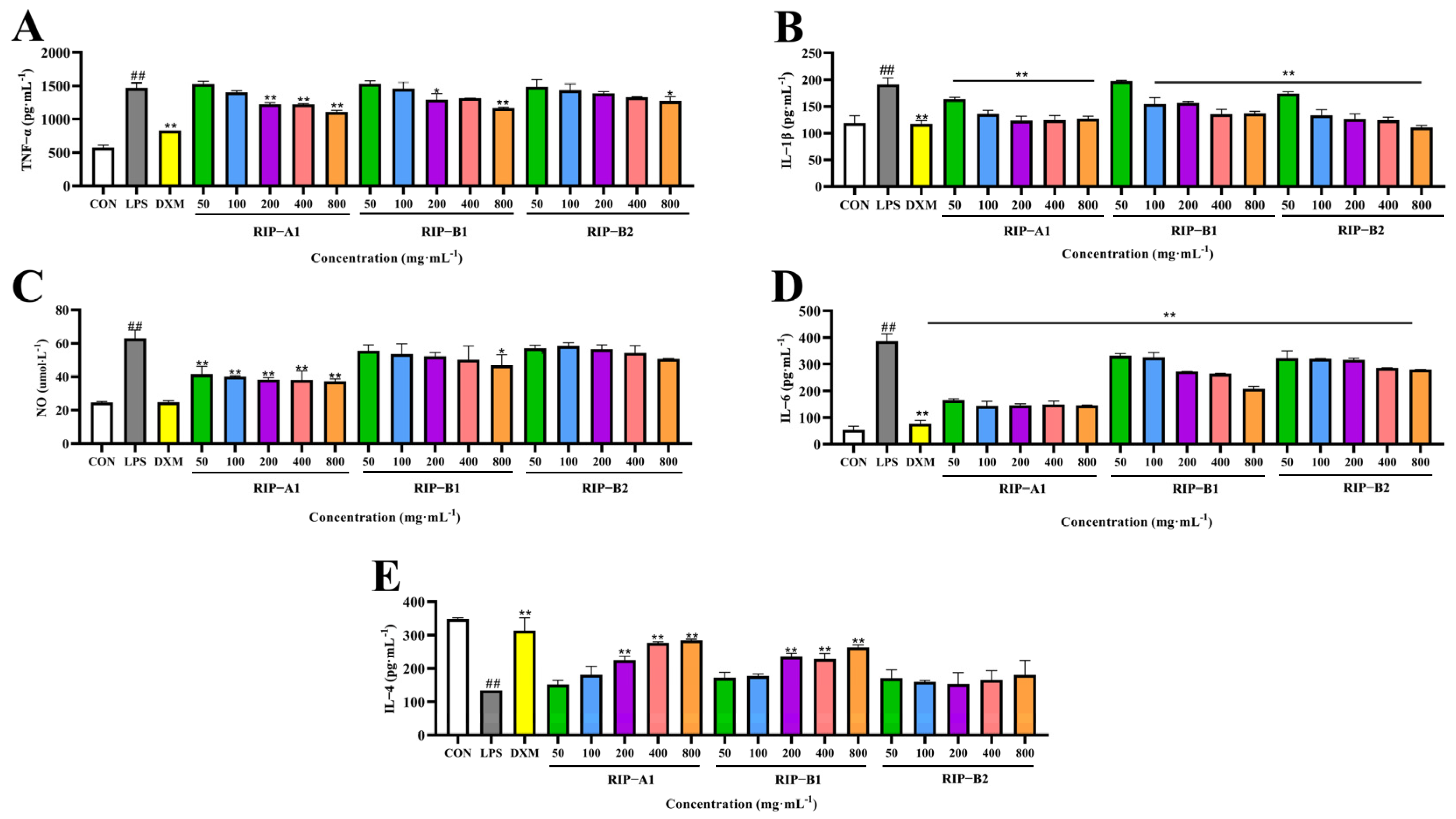
2.7.2. Screening of Anti-Inflammatory Activity of RIP-A1, RIP-B1 and RIP-B2
Effects of RIP-A1, RIP-B1 and RIP-B2 on RAW 264.7 Cell Activity Stimulated by LPS
IL-4, IL- 1β, NO, TNF-α and IL-6 Determination
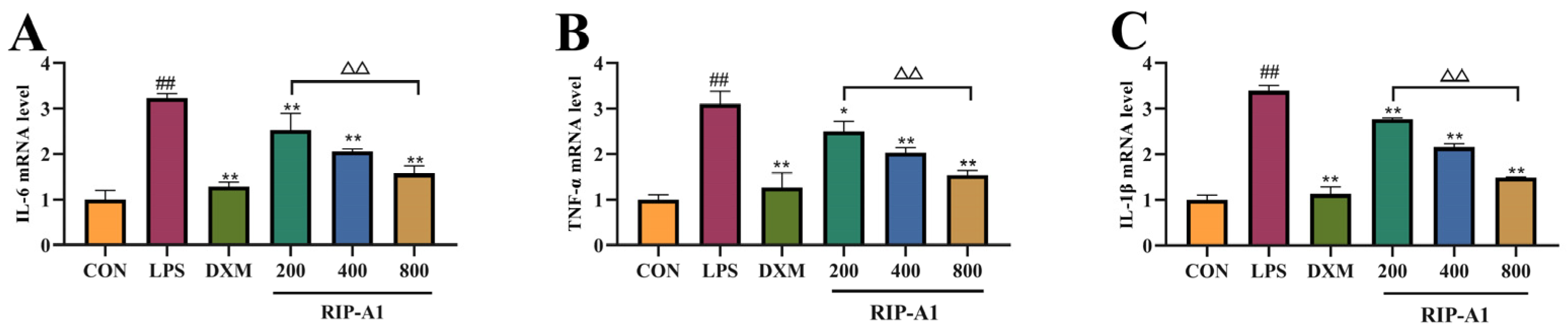
2.7.3. Effect of RIP-A1 on RAW 264.7 Cells’ mRNA Expression of IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α Caused by LPS
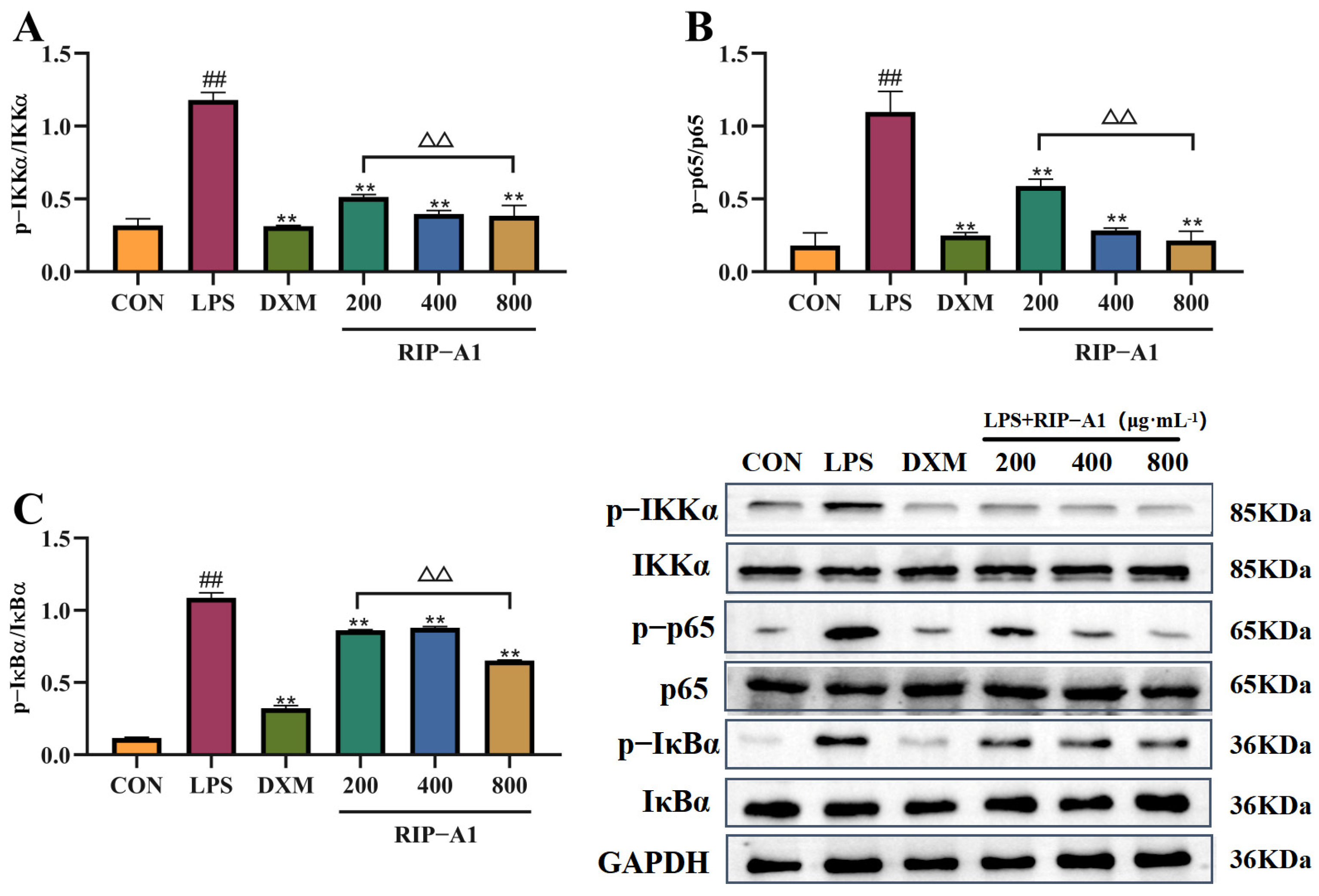
2.7.4. Effect of RIP-A1 on LPS-induced NF-κB Signaling Pathway in RAW 264.7 Cells
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Exaction and Isolation of Polysaccharides
3.3. Structural Analysis of Polysaccharides
3.3.1. Molecular Weight Determination
3.3.2. Monosaccharide Composition Analysis
3.3.3. Infrared Spectra (IR) Analysis
3.3.4. Methylation Analysis
3.3.5. NMR Analysis
3.3.6. SEM and AFM Analysis
3.4. Anti-Inflammatory Activity on RAW 264.7 Cells
3.4.1. Determination of Cytotoxicity
3.4.2. Screening of Anti-Inflammatory Activity of RIP-A1, RIP-B1 and RIP-B2
Effects of RIP-A1, RIP-B1 and RIP-B2 on LPS-Induced Activity of RAW 264.7 Cells
Effects of RIP-A1, RIP-B1 and RIP-B2 on LPS-induced IL-4, IL-1β, NO, TNF-α and IL-6 Production in RAW 264.7 Cells
3.4.3. qRT-PCR Analysis
3.4.4. Western Blotting Analysis
3.5. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Jin, M.Y.; Li, M.Y.; Huang, R.M.; Wu, X.Y.; Sun, Y.M.; Xu, Z.L. Structural features and anti-inflammatory properties of pectic polysaccharides: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 107, 284–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, T.; Lim, S.S. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1204–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, A.; Cilloniz, C.; Niederman, M.S.; Menéndez, R.; Chalmers, J.D.; Wunderink, R.G.; van der Poll, T. Pneumonia. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalski, S.; Karska, J.; Tota, M.; Skinderowicz, K.; Kulbacka, J.; Drąg-Zalesińska, M. Natural Compounds in Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer: Prevention and Treatment. Molecules 2024, 29, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Du, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, H.; Lu, L.; Wu, R.; Jin, C. The NLRP3 molecule is responsible for mediating the pyroptosis of intestinal mucosa cells and plays a crucial role in salmonellosis enteritis in chicks. Mol. Immunol. 2024, 168, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zeng, J.; Li, R.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, Y.; Hou, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Meng, X. Traditional Chinese medicine in regulating macrophage polarization in immune response of inflammatory diseases. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 325, 117838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, M.; Wang, H.; Qin, P.; Di, Y.; Jiang, S.; Li, Y.; Huang, L.; Jiao, N.; Yang, W. Glutamine attenuates bisphenol A-induced intestinal inflammation by regulating gut microbiota and TLR4-p38/MAPK-NF-κB pathway in piglets. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 270, 115836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liang, J.; Fan, H.; Lei, K.; Li, H.; Liu, D.; Zheng, F.; He, M.; Chen, Y. Study on anti-inflammatory effect of Shangkehuangshui in vitro and in vivo based on TLR4/TLR2-NF-κB signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 323, 117709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.P.; Li, C.Y.; Peng, X.; Zou, Y.F.; Rise, F.; Paulsen, B.S.; Wangensteen, H.; Inngjerdingen, K.T. Polysaccharides from Aconitum carmichaelii leaves: Structure, immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory activities. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 291, 119655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Li, W.; Liang, M.; Li, G.; Wu, Z.; Long, J.; Yuan, C.; Mei, W.; Xia, X. Preparation, Characterization, and Antioxidant Activities of Extracts from Amygdalus persica L. Flowers. Molecules 2024, 29, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Chen, Y.; Lv, Z.; Taoerdahong, H.; Li, G.; Li, J.; Zhao, X.; Jin, X.; Chang, J. Structural characterization of a polysaccharide from Alhagi honey and its protective effect against inflammatory bowel disease by modulating gut microbiota dysbiosis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 259, 128957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cui, Y.; Feng, Y.; Jiao, F.; Jia, L. Lentinus edodes Polysaccharides Alleviate Acute Lung Injury by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Molecules 2022, 27, 7328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Li, A.; Li, X.; Sun, L.; Guo, Y. An overview of classifications, properties of food polysaccharides and their links to applications in improving food textures. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 102, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, J.R.; de Carvalho Junior, R.N. Polysaccharides obtained from natural edible sources and their role in modulating the immune system: Biologically active potential that can be exploited against COVID-19. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 108, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Zhao, P.; Li, X.; Guo, L.; Gao, W. The potential roles of natural plant polysaccharides in inflammatory bowel disease: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 277, 118821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.K.; Hao, Z.T.; Gao, Y.C.; Cai, X.; Tang, J.T.; Liao, X.J.; Tan, J.Q. Research progress on the hypoglycemic activity and mechanisms of natural polysaccharides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 252, 126199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Paulsen, B.S.; Fu, Y.P.; Huang, C.; Feng, B.; Li, L.X.; Chen, X.F.; Jia, R.Y.; Song, X.; et al. Prospects of Codonopsis pilosula polysaccharides: Structural features and bioactivities diversity. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 103, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Liu, M.; Wei, Y.; Tong, L.; Guo, S.; Kang, H.; Zhang, W.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Duan, J.A. Structural characteristics and structure-activity relationship of four polysaccharides from Lycii fructus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, M.; Padmavathy, T.K.; Mani, S.; Malarvizhi, R.; Sali, V.K.; Vasanthi, H.R. Sulfated polysaccharide from Turbinaria ornata suppress lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 4299–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezerra, I.d.L.; Caillot, A.R.C.; Palhares, L.C.G.F.; Santana-Filho, A.P.; Chavante, S.F.; Sassaki, G.L. Structural characterization of polysaccharides from Cabernet Franc, Cabernet Sauvignon and Sauvignon Blanc wines: Anti-inflammatory activity in LPS stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 186, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Tong, L.; Han, Q.; Ren, B.; Guo, D. Anti-inflammatory activity of Boletus aereus polysaccharides: Involvement of digestion and gut microbiota fermentation. Food Chem. X 2024, 21, 101052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Ding, Y.; Tian, Y.; Yang, R.; Quan, M.; Tong, Z.; Zhang, X.; Luo, D.; Chi, Z.; Liu, C. Hydrolyzed low-molecular-weight polysaccharide from Enteromorpha prolifera exhibits high anti-inflammatory activity and promotes wound healing. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 133, 112637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Lai, Z.; Hu, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Gao, M.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Q.; et al. Effect of monosaccharide composition and proportion on the bioactivity of polysaccharides: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 254, 127955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, G.; Dang, T.; Deng, Y.; Han, J.; Zou, Z.; Jing, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Huang, L.; Wang, Z. Physicochemical properties and biological activities of polysaccharides from Lycium barbarum prepared by fractional precipitation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.H.; Su, C.H.; Liu, S.C.; Ng, L.T. Isolation, Anti-Inflammatory Activity and Physicochemical Properties of Bioactive Polysaccharides from Fruiting Bodies of Cultivated Cordyceps cicadae (Ascomycetes). Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2019, 21, 995–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Q.; Liu, W.; Hao, W.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Li, H.; Shui, M.; Wu, D.T.; Wang, S. Glycosidic linkages of fungus polysaccharides influence the anti-inflammatory activity in mice. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 1232, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, Z.; Gao, T.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Q.; Fu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, F.; Liao, W. Isatidis Radix and Isatidis Folium: A systematic review on ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 283, 114648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Zhou, L.; Li, H.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Chen, D. Intestinal microbiota metabolizing Houttuynia cordata polysaccharides in H1N1 induced pneumonia mice contributed to Th17/Treg rebalance in gut-lung axis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 221, 288–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, D.G.; Kim, M.C.; Park, M.; Park, K.M.; Quan, F.S.; Song, J.M.; Wee, J.J.; Wang, B.Z.; Cho, Y.K.; Compans, R.W.; et al. Protective Effect of Ginseng Polysaccharides on Influenza Viral Infection. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 33678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, D.; Tian, Y.; Chen, X.; Lan, J.; Wei, F.; Li, Y.; Luo, Y.; Sun, X. Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides ameliorate lipopolysaccharide-induced acute pneumonia via inhibiting NRP1-mediated inflammation. Pharm. Biol. 2022, 60, 2201–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lai, Y.; Dong, L.; Kang, S.; Chen, X. Polysaccharides from Citrus grandis L. Osbeck suppress inflammation and relieve chronic pharyngitis. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 113, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Zheng, C.; Li, J.; Yang, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, R. Separation and Quantification of Four Main Chiral Glucosinolates in Radix Isatidis and Its Granules Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Diode Array Detector Coupled with Circular Dichroism Detection. Molecules 2018, 23, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, L.X.; Wu, Y.L.; Dai, Z.; Ma, S.C. Antiviral activity of Isatidis Radix derived glucosinolate isomers and their breakdown products against influenza A in vitro/ovo and mechanism of action. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 251, 112550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, P.; Yan, Z.; Chen, M.; Li, P.; Wang, D.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Z.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Li, C.; et al. Effects of dietary supplementation with Radix Isatidis polysaccharide on egg quality, immune function, and intestinal health in hens. Res. Vet. Sci. 2024, 166, 105080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.L.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; He, L.Y.; Huang, Q.W.; Peng, W.; Wu, C.J. Processing methods and mechanisms for alkaloid-rich Chinese herbal medicines: A review. J. Integr. Med. 2021, 19, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Li, L.; Zhou, H.; Zeng, L.; Chen, T.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, B.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Hu, P.; et al. Radix isatidis Polysaccharides Inhibit Influenza a Virus and Influenza A Virus-Induced Inflammation via Suppression of Host TLR3 Signaling In Vitro. Molecules 2017, 22, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, X.; Zhuo, Y.; Si, C.; Yang, L.; Meng, L.; Zhu, B. Antiviral activity of a polysaccharide from Radix Isatidis (Isatis indigotica Fortune) against hepatitis B virus (HBV) in vitro via activation of JAK/STAT signal pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 257, 112782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wang, D.N.; Zhang, W.Y.; Sun, T.T.; Feng, Y.T.; Liu, M.X.; Li, J.P. Protective effects of Radix Isatidis polysaccharide ameliorates obesity via promotion AMPK pathway in high-fat-diet-induced obese rats and 3T3-L1 adipocyte cells. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2022, 74, 1170–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Li, P. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of Radix Isatidis polysaccharide in murine alveolar macrophages. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 58, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, U.; Yu, Y.; Ning, X.; Ho, C.; Ji, L.; Mayo, K.H.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, L. Comparative study of water-soluble polysaccharides isolated from leaves and roots of Isatis indigotica Fort. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 206, 642–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ruan, S.; Gu, X.; Zhu, B. Antiviral activities of Radix Isatidis polysaccharide against type II herpes simplex virus in vitro. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 38, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, H.; Pang, X.; Yao, W.; Gao, X. Characterization and antioxidant activity of two low-molecular-weight polysaccharides purified from the fruiting bodies of Ganoderma lucidum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2010, 46, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Yan, X.; Liang, J.; Li, S.; He, H.; Xiong, Q.; Lai, X.; Hou, S.; Huang, S. Comparison of different extraction methods for polysaccharides from Dendrobium officinale stem. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 198, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.G.; Wang, T.L.; Sun, H.M.; Liang, J.; Kuang, H.X. Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry-based trimethylsilyl-alditol derivatives for quantitation and fingerprint analysis of Anemarrhena asphodeloides Bunge polysaccharides. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 198, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.P.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, W.Y.; Jiang, Z.; Hu, T.J.; Fenga, Y.T.; Liu, M.X. Effect of Radix isatidis polysaccharide on alleviating insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus cells and rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2018, 71, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Zhu, X.; Yang, G.; Zhang, J.; Wang, R.; Shen, Y.; Li, H.; Gatasheh, M.K.; Abbasi, A.M.; Yang, X. Ultrasonic extraction of Moringa oleifera seeds polysaccharides: Optimization, purification, and anti-inflammatory activities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 258, 128833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Luo, Y.; Sang, Y.; Kan, J. Isolation, purification, structural characterization, and hypoglycemic activity assessment of polysaccharides from Hovenia dulcis (Guai Zao). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 208, 1106–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lei, Z.; Zhao, M.; Wu, C.; Wang, L.; Xu, Y. Microwave-assisted extraction of an acidic polysaccharide from Ribes nigrum L.: Structural characteristics and biological activities. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2020, 147, 112249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebada, D.; Hefnawy, H.T.; Gomaa, A.; Alghamdi, A.M.; Alharbi, A.A.; Almuhayawi, M.S.; Alharbi, M.T.; Awad, A.; Al Jaouni, S.K.; Selim, S.; et al. Characterization of Delonix regia Flowers’ Pigment and Polysaccharides: Evaluating Their Antibacterial, Anticancer, and Antioxidant Activities and Their Application as a Natural Colorant and Sweetener in Beverages. Molecules 2023, 28, 3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Zheng, Q.; Duan, Y.; Cai, M.; Zhang, H. Effect of subcritical water temperature on the structure, antioxidant activity and immune activity of polysaccharides from Glycyrrhiza inflata Batalin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 261, 129591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, F.; Chen, W.; He, P.; Zhan, Q.; Wang, Q.; Wu, H.; Zhang, M. Structural characterization of polysaccharides with potential antioxidant and immunomodulatory activities from Chinese water chestnut peels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 246, 116551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Guo, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liang, J.; Kuang, H.X.; Xia, Y.G. Structure and immunological activity of an arabinan-rich acidic polysaccharide from Atractylodes lancea (Thunb.) DC. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 199, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; An, L.; Zhang, S.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Cui, J.; Zhang, J.; Jin, D.-Q.; Tuerhong, M.; Abudukeremu, M.; et al. A heteropolysaccharide purified from leaves of Ilex latifolia displaying immunomodulatory activity in vitro and in vivo. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 245, 116469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brecker, L.; Wicklein, D.; Moll, H.; Fuchs, E.C.; Becker, W.-M.; Petersen, A. Structural and immunological properties of arabinogalactan polysaccharides from pollen of timothy grass (Phleum pratense L.). Carbohydr. Res. 2005, 340, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; An, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Shi, L.; Bao, J.; Lan, X.; Zhang, E.; Lall, N.; et al. Structural elucidation of an immunological arabinan from the rhizomes of Ligusticum chuanxiong, a traditional Chinese medicine. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 170, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yue, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liang, L.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Peng, M.; Yang, M.; Zhao, M.; et al. Structural characterization and anti-inflammatory effects of an arabinan isolated from Rehmannia glutinosa Libosch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 303, 120441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Xiang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Mao, G.; Feng, W.; Chen, Y.; Li, Q.; Wu, X.; Yang, L.; Zhao, T. Purification, structural elucidation and physicochemical properties of a polysaccharide from Abelmoschus esculentus L (okra) flowers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 740–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Yao, J.; Du, Z.; Wang, P.; Ding, K. Structural elucidation and immune-enhancing activity of an arabinogalactan from flowers of Carthamus tinctorius L. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 202, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Xie, Y.; Guo, T.; Dai, W.; Nan, L.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Lan, W.; Wang, Z.; Huang, L.; et al. A new perspective on structural characterisation and immunomodulatory activity of arabinogalactan in Larix kaempferi from Qinling Mountains. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 265, 130859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, P.-z.; Shen, J.-w.; Qian, Y.-y.; Liu, M.; Ruan, Y.; Wang, X.-g.; Zhang, S.-n.; Ma, B.-j. Physicochemical properties and bioactivities of original and Se-enriched polysaccharides with different molecular weights extracted from Pleurotus ostreatus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 141, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Li, Q.; Liang, W. Polysaccharides from Radix Peucedani: Extraction, Structural Characterization and Antioxidant Activity. Molecules 2023, 28, 7845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Kong, H.; Wang, Y.; Gao, P.; Guo, M.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; et al. Structural characteristics of a novel Bletilla striata polysaccharide and its activities for the alleviation of liver fibrosis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 313, 120781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posé, S.; Kirby, A.R.; Mercado, J.A.; Morris, V.J.; Quesada, M.A. Structural characterization of cell wall pectin fractions in ripe strawberry fruits using AFM. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 882–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zheng, G.; You, L.; Wen, L.; Li, C.; Fu, X.; Zhou, L. Structural characterization and macrophage immunomodulatory activity of a polysaccharide isolated from Gracilaria lemaneiformis. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 33, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Sun, J.; Zhou, B.; Jin, C.; Liu, J.; Gou, Y.; Chen, H.; Kan, J.; Qian, C.; Zhang, N. Immunomodulatory effects of polysaccharides from purple sweet potato on lipopolysaccharide treated RAW 264.7 macrophages. J. Food Biochem. 2018, 42, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.-F.; Fu, Y.-P.; Chen, X.-F.; Austarheim, I.; Inngjerdingen, K.T.; Huang, C.; Lei, F.-Y.; Song, X.; Li, L.; Ye, G.; et al. Polysaccharides with immunomodulating activity from roots of Gentiana crassicaulis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 172, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, X.; Pan, W.; Shen, X.; He, Y.; Yin, H.; Zhou, K.; Zou, L.; Chen, S.; Liu, S. Exopolysaccharides produced by yogurt-texture improving Lactobacillus plantarum RS20D and the immunoregulatory activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 121, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Xu, L.; Zeng, Y.; Gong, F. Effect of gut microbiota on LPS-induced acute lung injury by regulating the TLR4/NF-kB signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 91, 107272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.R.; Qi, C.H.; Cheng, J.P.; Liu, G.; Huang, L.J.; Wang, Z.F.; Zhou, W.X.; Zhang, Y.X. Lycium barbarum polysaccharide LBPF4-OL may be a new Toll-like receptor 4/MD2-MAPK signaling pathway activator and inducer. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 19, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.J.; Hu, T.T.; Chen, Y.Y.; Wang, S.; Kang, Y.F. Analysis of the polysaccharide fractions isolated from pea (Pisum sativum L.) at different levels of purification. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, 13248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Liang, J.; Guo, Y.-L.; Li, Y.; Kuang, H.-X.; Xia, Y.-G. Ultrafiltration isolation, structures and anti-tumor potentials of two arabinose- and galactose-rich pectins from leaves of Aralia elata. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 255, 117326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Li, Y.; Pi, Y.; Yue, X. Effects of almond (Armeniaca Sibirica L. Lam) polysaccharides on gut microbiota and anti-inflammatory effects on LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 263, 130098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuBois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.G.; Wang, T.L.; Yu, S.M.; Liang, J.; Kuang, H.X. Structural characteristics and hepatoprotective potential of Aralia elata root bark polysaccharides and their effects on SCFAs produced by intestinal flora metabolism. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 207, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Huang, X.; Dou, M.; Tang, S.; Wang, G.; Fan, Y.; Luo, A.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y. Structural Characterization and Immunoenhancing Properties of Polysaccharide CPTM-P1 from Taxus media. Molecules 2024, 29, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yin, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, B.; Lu, J.; Wang, X. Structural Characteristics, Antioxidant, and Immunostimulatory Activities of an Acidic Polysaccharide from Raspberry Pulp. Molecules 2022, 27, 4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

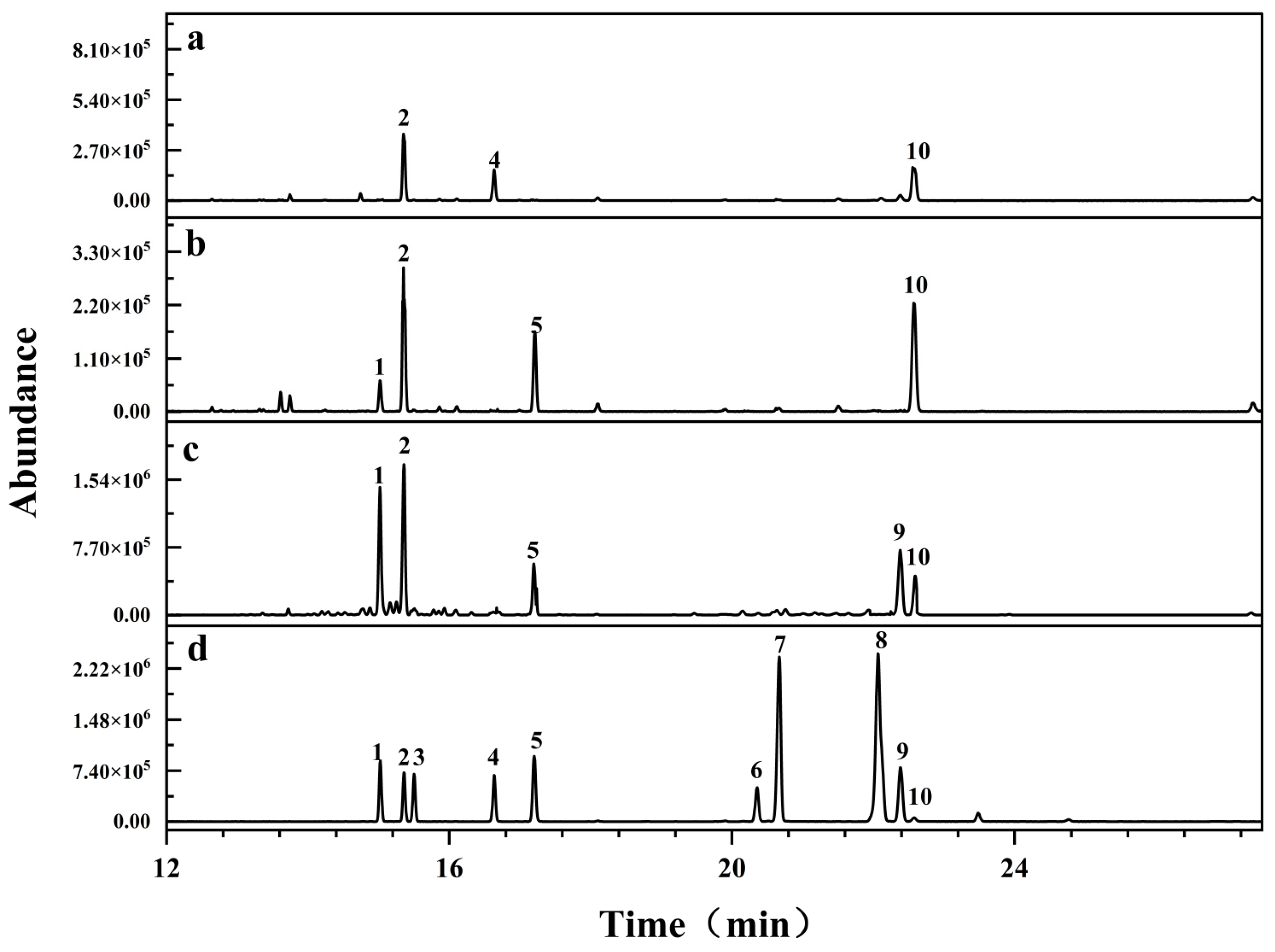
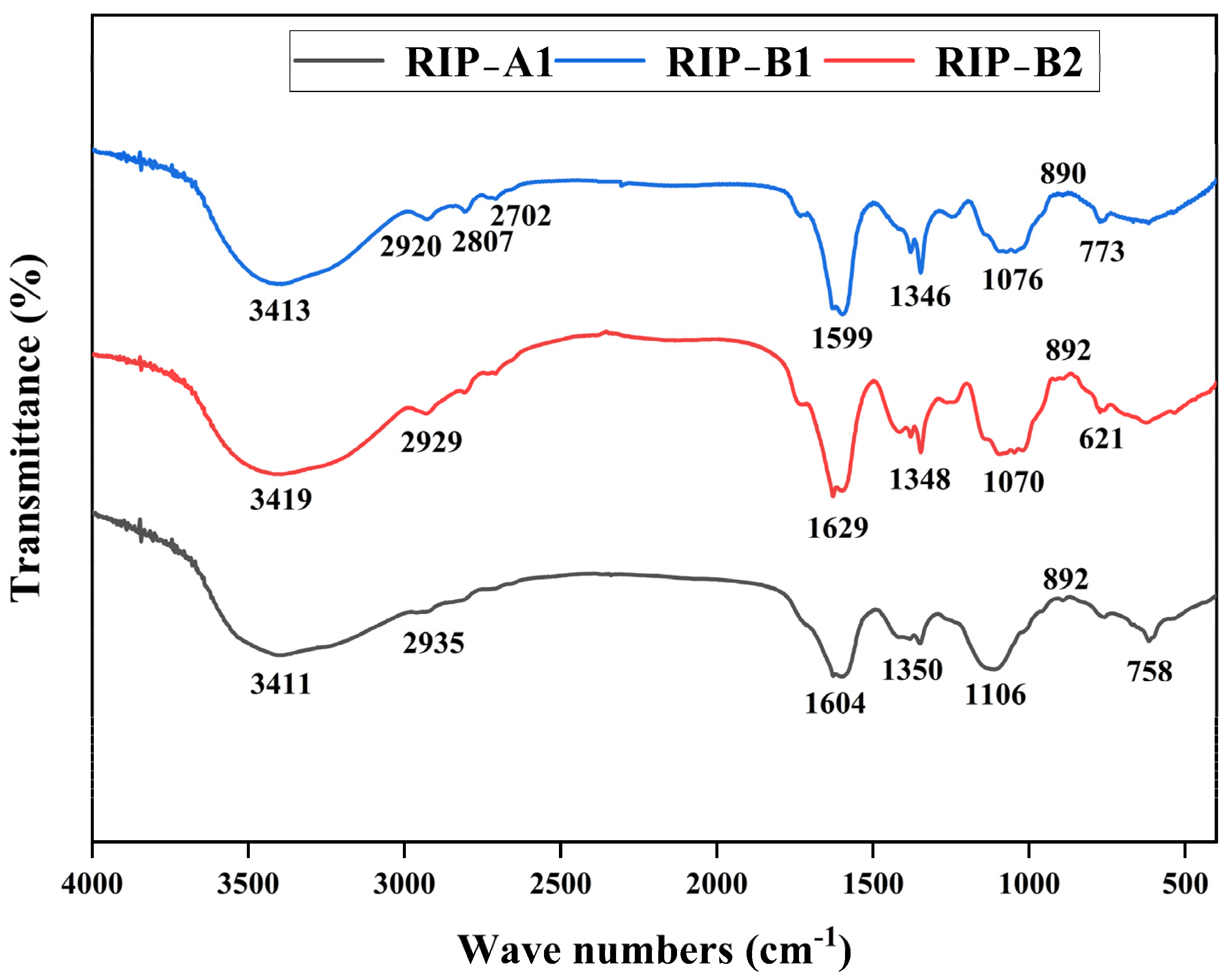
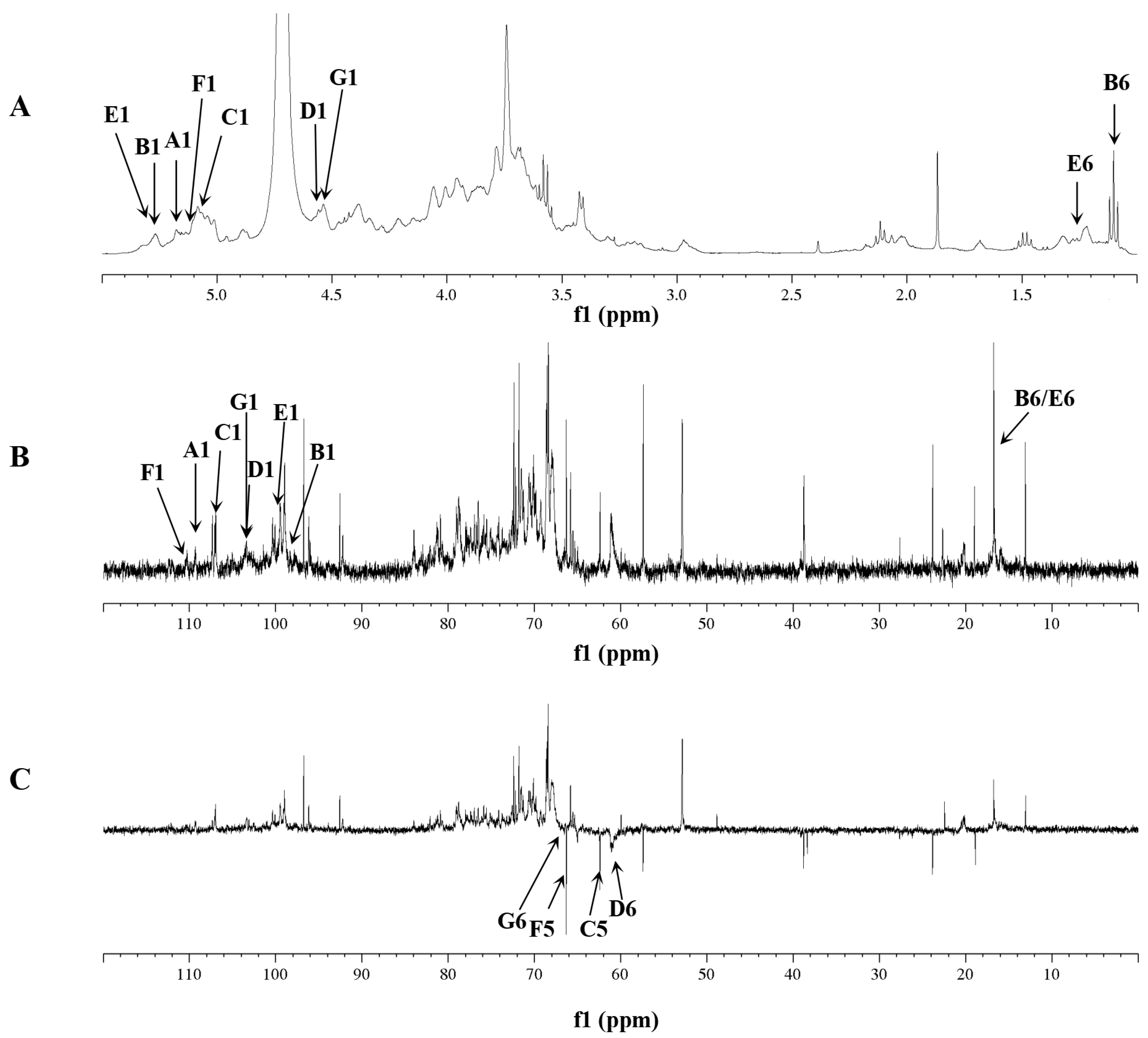


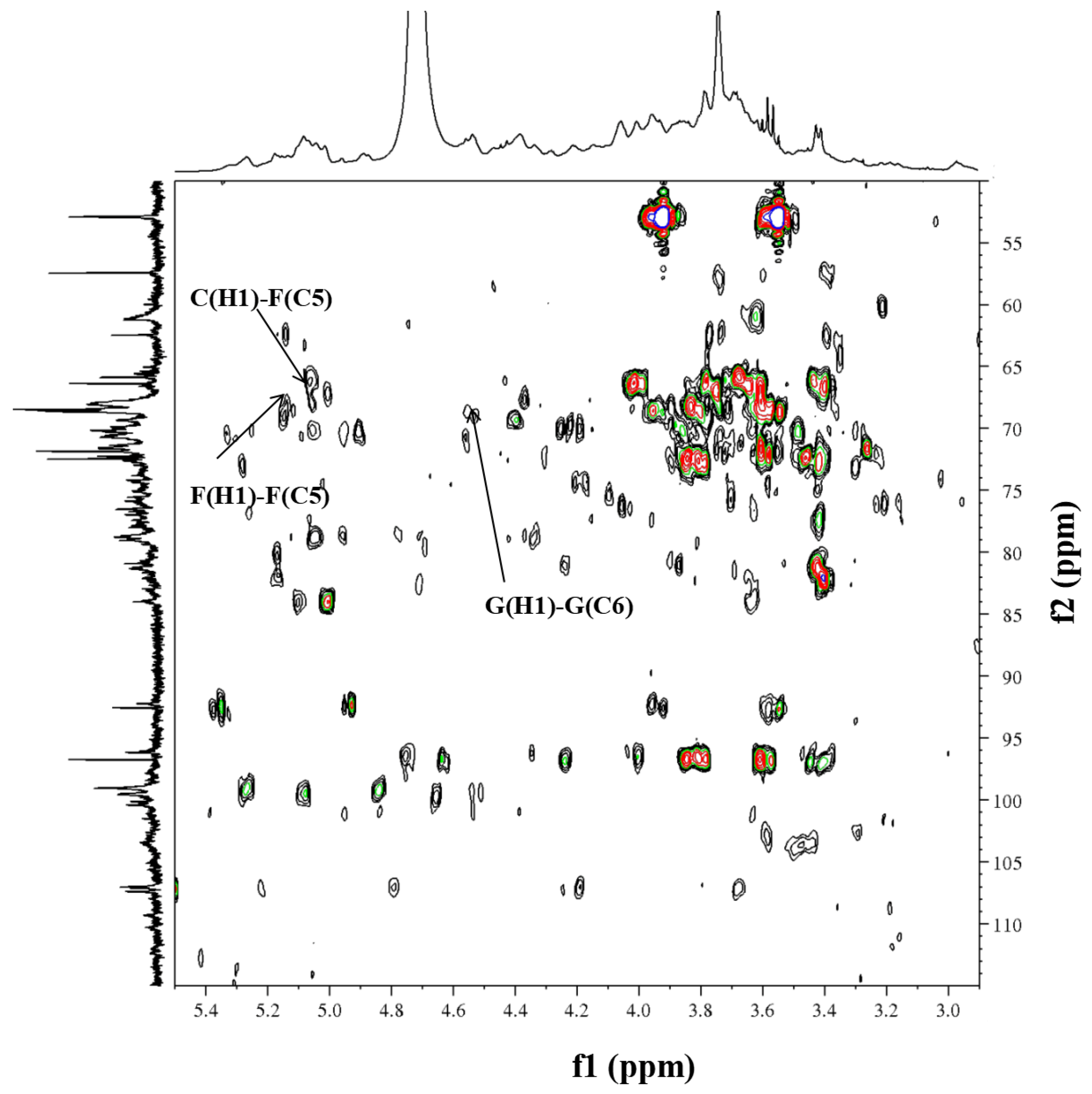

| Type of Glycosidic Bond | PMAA | Mass Fragments (m/z) | Mol (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RIP-A1 | RIP-B1 | RIP-B2 | |||
| T-Arap | 1,5-di-O-Ac-2,3,4-tri-O-Me Ara | 59, 71, 87, 102, 118, 129, 145 | 0.33 | 3.2 | 0.30 |
| 1,5-Araf | 1,4,5-tri-O-Ac-2,3-di-O-Me Ara | 59, 71, 87, 102, 118, 129, 142, 189 | 1.02 | 0.36 | 0.01 |
| 1,3,5-Araf | 1,3,4,5-tet-O-Ac-2-O-Me Ara | 74, 85, 99, 118, 127, 141, 159, 173 | 11.41 | 8.9 | 0.80 |
| 1,2-Rhap | 1,2,5-tri-O-Ac-3,4-di-O-Me Man | 57, 85, 115, 131, 190, 281, 304 | 0.12 | - | - |
| 1,2,4-Rhap | 1,2,4,5-tet-O-Ac-3-O-Me Man | 59, 74, 88, 101, 130, 143, 190, 203 | 0.45 | - | - |
| T-Galp | 1,5-di-O-Ac-2,3,4,6-tet-O-Me Gal | 59, 74, 88, 101, 130, 143, 190, 203 | 0.09 | - | - |
| 1,6-Galp | 1,5,6-tri-O-Ac-2,3,4-tri-O-Me Gal | 59, 71, 88, 99, 117, 129, 157 | 10.23 | 9.6 | 4.60 |
| T-Xylp | 1,5-di-O-Ac-2,3,4-tri-O-Me Xyl | 59, 73, 87, 101, 115, 129 | - | 2.8 | 0.77 |
| 1,4-Fucp | 1,4,5-tri-O-Ac-2,3-di-O-Me Gal | 59, 72, 87, 101, 118, 129, 143 | - | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| 1,4-Glcp | 1,4,5-tri-O-Ac-2,3,6-tri-O-Me Glc | 59, 71, 99, 117, 129, 142 | - | - | 7.51 |
| Sugar Residues | Chemical Shifts, δ (ppm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H-1/C-1 | H-2/C-2 | H-3/C-3 | H-4/C-4 | H-5/C-5 | H-6/C-6 | |
| (A) T-α-Araf-(1→ | 5.16/109.4 | 4.15/81.3 | 3.65/80.4 | 3.75/75.8 | 3.66/64.4 | |
| (B) →2)-α-Rhap-(1→ | 5.26/98.4 | 4.06/76.7 | 3.56/69.7 | 3.18/75.8 | 3.53/75.7 | 1.10/16.7 |
| (C) →5)-α-Araf-(1→ | 5.07/106.9 | 4.53/78.1 | 3.92/76.7 | 4.24/78.0 | 3.86/65.1 | |
| (D) T-β-Galp-(1→ | 4.56/103.4 | 3.63/72.7 | 3.81/73.0 | 4.11/74.3 | 3.80/75.7 | 3.67, 3.78/61.0 |
| (E) →2,4)-α-Rhap-(1→ | 5.27/99.7 | 4.04/74.1 | 3.88/76.6 | 3.50/72.7 | 3.52/71.8 | 1.25/16.7 |
| (F) →3,5)-α-Araf-(1→ | 5.13/110.5 | 4.05/81.1 | 3.99/84.1 | 3.83/81.1 | 3.70/66.5 | |
| (G) →6)-β-Galp-(1→ | 4.55/103.5 | 3.63/72.9 | 3.81/72.0 | 4.16/66.7 | 3.8075.7 | 3.85, 3.78/68.4 |
| Gene | Primary Sequence |
|---|---|
| IL-6 | Forward:5′-CCAAGAGGTGAGTGCTTCCC-3′ |
| Reverse:5′-CTGTTGTTCAGACTCTCTCCCT-3′ | |
| IL-1β | Forward:5′-GACGTGGAACTGGCAGAAGAG-3 |
| Reverse:5′-TTGGTGGTTTGTGAGTGTGAG-3 | |
| TNF-α | Forward:5′-GCAACTGTTCCTGAACTCAACT-3 |
| Reverse:5′-ATCTTTTGGGGTCCGTCAACT-3 | |
| β-action | Forward:5′-GTGCTATGTTGCTCTAGACTTCG-3 |
| Reverse:5′-ATGCCACAGGATTCCA-TACC-3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, Y.; Wu, S.; Song, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, H.; Wu, L.; Zhao, H.; Qiu, H.; Zhang, Y. The Isolation, Structural Characterization and Anti-Inflammatory Potentials of Neutral Polysaccharides from the Roots of Isatis indigotica Fort. Molecules 2024, 29, 2683. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112683
Shen Y, Wu S, Song M, Zhang H, Zhao H, Wu L, Zhao H, Qiu H, Zhang Y. The Isolation, Structural Characterization and Anti-Inflammatory Potentials of Neutral Polysaccharides from the Roots of Isatis indigotica Fort. Molecules. 2024; 29(11):2683. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112683
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Yu, Shihao Wu, Mingming Song, Huiming Zhang, Hong Zhao, Lili Wu, Hongbo Zhao, Hongbin Qiu, and Yu Zhang. 2024. "The Isolation, Structural Characterization and Anti-Inflammatory Potentials of Neutral Polysaccharides from the Roots of Isatis indigotica Fort." Molecules 29, no. 11: 2683. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112683
APA StyleShen, Y., Wu, S., Song, M., Zhang, H., Zhao, H., Wu, L., Zhao, H., Qiu, H., & Zhang, Y. (2024). The Isolation, Structural Characterization and Anti-Inflammatory Potentials of Neutral Polysaccharides from the Roots of Isatis indigotica Fort. Molecules, 29(11), 2683. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112683






