Abstract
Under-deposit corrosion is widely present in the pipelines of oil and gas production, causing significant corrosion damage. In this paper, a novel electrochemical cathodic-polarization method was carried out to accelerate the formation of CaCO3 scale on a X65 steel surface in a simulated solution containing scaling ions. Subsequently, pre-scaled X65 steel was placed in a high temperature and pressure autoclave to conduct corrosion weight-loss experiments and in situ electrochemical measurements. The study mainly compared the corrosion inhibition behavior of four quaternary ammonium salt corrosion inhibitors, pyridinium quaternary salt (BPC), quinolinium quaternary salt (BQC), 8-hydroxyquinolinium quaternary salt (BHQ) and pyridinium (1-chloromethyl naphthalene) quaternary salt (1-CPN), in a simulated oilfield scale under corrosive conditions. The results of the weight-loss experiments demonstrated that the inhibition efficiencies of the corrosion inhibitors from high to low were as follows: 1-CPN < BHQ < BQC < BPC. The in situ electrochemical measurements showed that the immersion time and type of corrosion inhibitor had a pronounced influence on the corrosion and corrosion inhibition behavior of X65 steel with CaCO3 coating. It was also proved using both EIS and PC that 1-CPN shows the best inhibition performance in all. Lastly, the inhibition mechanism of corrosion inhibitors at under-deposit conditions was analyzed via a surface morphology observation of SEM.
1. Introduction
The internal metallic pipelines and related facilities in industrial production often have a tendency to be coated with different types of deposits [1,2,3,4]. These deposits include corrosion products, mineral scales, and products from bacterial growth. Particularly in oil and gas production processes, downhole tubulars, ground processing procedures, long-distance pipeline transportation systems, and associated equipment facilities are prone to developing complicated deposits [5,6,7,8]. The interaction among corrosion, bacteria, and scaling frequently results in complex deposit formations [9,10,11,12,13]. The metal surfaces beneath these deposits are vulnerable to corrosive attack due to the specific occluded environment. This accelerates metal corrosion deterioration.
In order to mitigate internal corrosion attack in oil and gas exploitation, the application of corrosion inhibitors is a common measure [14,15,16,17,18,19,20]. Numerous commercial corrosion inhibitors have been developed and implemented for effective corrosion protection in production. Water-soluble or water-dispersible organic compounds containing N, O, S, or P groups are frequently employed as corrosion inhibitors for metal pipelines. Illustrative examples include imidazoline derivatives, pyridine quaternary ammonium salts, and amines [21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30]. In practical production processes, the primary agents of corrosion inhibitors are often synergistically combined with small organic molecules such as thiourea and mercaptoethanol to enhance the efficacy while simultaneously reducing costs. Corrosion inhibitors usually protect against corrosion by adsorbing to the surface of the metal to form a protective film, thereby preventing oxygen, water, or other aggressive agents from coming into contact with the metal surface. Despite the attached scale layer, the corrosion inhibitor can still change the electrochemical properties of the metal surface, making it more difficult to be affected by corrosion, thus extending the service life of the metal material. In addition, corrosion inhibitors can also form a protective film on the metal surface with a self-healing or regenerative function that, once damaged, will automatically repair to continue to play a protective role [31,32,33,34,35].
However, in practical production processes, it is frequently observed that corrosion inhibitor formulations exhibiting exceptional performance selected during laboratory assessments fail to meet expectations when implemented on-site. This discrepancy can be attributed primarily to the fact that laboratory evaluations of corrosion inhibitors are predominantly conducted on bare steel surfaces, whereas metal surfaces encountered in practical production processes are typically covered with scales. Consequently, certain conventional corrosion inhibitor products having superior effectiveness may not effectively protect metal from corrosion under such conditions [31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39]. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out investigation on evaluation diverse corrosion inhibitor molecules against under-deposit corrosion [40,41,42,43].
K. Chokshi et al. [44] investigated the precipitation process of ferrous carbonate scale and the interaction between corrosion inhibitors and ferrous carbonate deposition, as well as their impact on corrosion rate. The experiments were conducted in an electrolytic cell at 80 °C with a range of ferrous carbonate supersaturation from 7 to 150. A general imidazoline inhibitor was added at different stages to inhibit the formation of iron carbonate scale. The corrosion rate and precipitation rate were measured using electrochemical and weight-loss methods, respectively, and the scales were analyzed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The study found that the precipitation rate of iron carbonate was overestimated under the previously used method based on dissolved ferrous ion concentration. Although no antagonistic effect was observed under other test conditions, it can be seen that the addition of corrosion inhibitors delayed the growth of iron carbonate scale. J. E. Wong et al. [45] studied the effect of corrosion inhibitor active components on the growth of iron carbonate scale under CO2 conditions. It is debated whether the scale is necessary for the adsorption of the corrosion inhibitor. The author proved through experiments that quaternized amines accelerated the precipitation process of iron carbonate and promoted the existant protective passivation layer. Aiming to study the impact of surface scale deposition caused by supersaturated saline water, as well as the unknown mechanism of its subsequent effect on the corrosion process, M. Ciolkowski et al. [46] proposed a range of laboratory measurements to evaluate the impact of brines on corrosion and scale on both inhibited and uninhibited conditions.
In this paper, the pre-scaling of the CaCO3 layer was performed using cathodic polarization on X65 steel. The weight-loss and in situ electrochemical measurements were also carried out to investigate the corrosion behavior and inhibition efficiencies of four quaternary ammonium salts at under-deposit conditions. The top-view and cross-sectional morphologies of X65 steel before and after under-deposit corrosion were observed using SEM at all conditions to analyze the mechanism of corrosion and corrosion inhibition.
2. Experimental Methods and Materials
2.1. Material Preparation
X65 steel was used in the experiments as the specimen with the chemical composition shown in Table 1. The corrosion experiments were carried out at temperature of 40 °C, total pressure of 1 MPa, CO2 partial pressure of 0.5 MPa (total pressure of 1 MPa), and immersion time of 72 h. For the weight-loss experiment, X65 steel samples were prepared at a size of 40 mm × 13 mm × 2 mm and polished gradually using sandpaper ranging from 240# to 1000#. After rinsing with deionized water and degreasing with acetone, they were finally washed with alcohol and dried before being weighed three times. The specimens were sealed using silicone glue with exposed area of 5.2 cm2 for accelerated scaling before corrosion experiments in the autoclave (1308550, Dalian Kemao Experimental Equipment Co, Dalian, China). Cylindrical X65 steel samples were used in electrochemical experiments (CS350 in COM3, Wuhan Crest Instruments, Wuhan, China)with exposed area of 1 cm2 which underwent the same treatment as in the weight-loss experiment. The solution for pre-scaling treatment consisted of 0.555 g/L CaCl2, 0.84 g/L NaHCO3 and 34.415 g/L NaCl. The solution for weight-loss experiments in the autoclave consisted of 50 g/L NaCl, 0.406 g/L MgCl2·6 H2O, 0.852 g/L Na2SO4, 0.444 g/L CaCl2 and 0.0336 g/L NaHCO3.

Table 1.
Chemical composition of X65 steel (wt%).
Corrosion inhibitors were synthesized using pyridine, quinoline, 8-hydroxyquinoline, benzyl chloride, and 1-chloromethylnaphthalene. All chemical reagents used were analytical grade reagents provided by Chengdu Kelong Chemical Co., Chengdu, China. All solutions were prepared using deionized water.
2.2. Synthesis of Corrosion Inhibitors
By using pyridine, quinoline, and 8-hydroxyquinoline with benzyl chloride in a molar ratio of 1:1 at 110 °C for a duration of four hours, the corrosion inhibitors of (a) pyridinium quaternary salt (BPC), (b) quinolinium quaternary salt (BQC), and (c) 8-hydroxyquinolinium quaternary salt (BHQ) was achieved. Similarly, by subjecting pyridine to a reaction with 1-chloromethyl naphthalene in equimolar proportions at 110 °C for four hours, the formation of pyridinium (1-chloromethyl naphthalene) quaternary salt (d, 1-CPN) was synthesized. The crude product thus obtained by removing the solvent was purified using column chromatographic separation with ethyl acetate and methanol (5:1, v/v) as eluent. Yields obtained were the following: BPC (67%), BQC (67%), BHQ (67%) and 1-CPN (40%) [47]. The chemical structures of each corrosion inhibitor are shown in Figure 1.
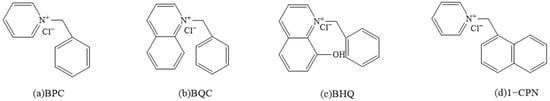
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of four synthesized corrosion inhibitors.
2.3. Pre-Scaling
By utilizing the technique of electrochemical cathodic-polarization, CaCO3 deposits are generated in situ on the metal surface [48]. Before conducting weight-loss experiments and electrochemical experiments, X65 steel samples were subjected to surface preparation and coated with a CaCO3 layer through constant potential polarization on their surfaces for accelerated scaling. Through evaluating corrosion behavior of these samples, it can provide a better simulation for under-deposit corrosion under prolonged operational conditions in production pipelines. In this experiment, a three-electrode cathodic-polarization method was employed to accelerate scaling at scaling durations of 6 h.
The cathodic current was applied to the carbon steel electrode (relative to the saturated calomel electrode at −1.4 V). Ultimately, it induced the reduction in dissolved oxygen. As the pH near the working electrode increased, scale-forming ions in the solution formed deposits on the metal surface as follows:
OH− ions were generated near the cathode, causing an increase in pH value. Through the following chemical reaction, solid CaCO3 precipitated on the X65 steel electrode:
After pre-scaling operation, the obtained samples with pre-scaling time of 6 h were carefully rinsed with deionized water to remove any solution and impurities adhering to the surface. After rinsing with alcohol and drying with cold air, the samples were placed in an oven at 35 °C for 2 h, then taken out and placed in a dry vessel for later use. This is necessary to avoid long period exposure of the sample to air.
2.4. Weight-Loss Experiments
The weight-loss experiments were conducted under simulated on-site working conditions in a high-temperature and high-pressure autoclave. Three parallel samples were used for the weight-loss experiments, with two of them being calculated for the average corrosion rate after de-film process, and the other sample being washed and dried for characterization of product film. After the aforementioned pre-scaling treatment, three X65 steel samples with scales were suspended in a high-temperature and high-pressure autoclave. Before the corrosion experiment, 1.0 L of corrosive solution was placed into the autoclave (with a total volume of 1.5 L). Then, N2 gas with high purity was purged into the solution in the autoclave for 2 h to remove oxygen from the chamber. After that, CO2 saturated solution was obtained through another 2 h purging of CO2 gas. The heating was then applied to reach the specified temperature, and carbon dioxide was pumped in until it reached a pressure of 0.5 MPa. Pure N2 gas was then introduced until the total pressure reached 1 MPa. Timing started when the temperature and pressure inside the autoclave reached the designated conditions.
After soaking for 72 h, the X65 steel samples coated with scales were taken out from the autoclave. Any residual impurities on the surface were rinsed off with deionized water, then rinsed and dried with alcohol. One of the samples was placed in a vacuum oven at 35 °C for 2 h for characterization of the corrosion product film. The other two samples were acid-washed to remove the film, weighed three times, and average corrosion rate was calculated. The formula for calculating corrosion rate (in millimeters per year, mm/a) was as follows:
where CR was corrosion rate (mm/a), Δ was the weight-loss before and after corrosion experiment (g), S represented exposed surface area (cm2) and t represented the soaking time (h). The inhibition efficiency (IE) of corrosion inhibitor can be calculated as follows:
where was the corrosion rate of X65 steel in the solution with absence of corrosion inhibitor (mm/a) and was the corrosion rate of X65 steel in the solution with presence of corrosion inhibitor (mm/a).
2.5. Electrochemical Measurements
The in situ electrochemical measurements were conducted in a high-temperature and high-pressure autoclave [10,12]. The electrochemical samples were placed into the working electrode slot, and then sealed and fixed with a fluororubber O-ring (FKM) and a specialized electrochemical pressure cap. The samples coated with a pre-scaling layer were placed in the autoclave with corrosive solution for in situ electrochemical testing in the absence and presence of different corrosion inhibitors. Other operating conditions remained consistent with the weight-loss experiments. The in situ electrochemical measurements used a three-electrode measurement system, with X65 steel coated with scale as the working electrode, platinum wire as the reference electrode, and platinum foil as the auxiliary electrode. All of them are capable of withstanding high temperature and pressure environments, thus achieving in situ electrochemical measurements.
After the temperature and pressure reached the designated values, real-time monitoring of open circuit potential (OCP) began. Linear polarization resistance (LPR) and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) tests were performed at certain intervals during the experiment (12 h, 24 h, 48 h, 72 h). LPR measurement was performed by applying a potential ranging from −10 mV to 10 mV (vs. OCP) at a scanning rate of 0.25 mV/s. EIS was carried out at OCP with a frequency range from 105 to 10−2 Hz and an AC signal amplitude of ±10 mV. After 72 h soaking, the LPR and EIS measurements were completed, followed by Potentiodynamic Polarization Curve (PC) measurement. The scanning potential range was from −500 mV to +1200 mV (vs. OCP), with a scanning rate of 0.5 mV/s. In the linear polarization region, the corrosion current density can be calculated using the following formula:
where Rp is polarization resistance (Ω cm2) and B isthe constant, which can be calculated as follows:
ba and bk are the anodic and cathodic Tafel constants, respectively.
2.6. Characterization of Corrosion Products
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM, EVO MA15 ZEISS, Tokyo, Japan) was used to observe the microstructure of the steel surface before and after layer removal. Additionally, the steel samples were sealed with epoxy resin and cut using a cutting machine after the epoxy layer had cured, in order to observe the cross-sectional morphology of corrosion product layers.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Corrosion and Inhibition Behavior by Weight-Loss Measurements
The corrosion rate and inhibition efficiency of X65 steel pre-scaling for 6 h in solutions with different corrosion inhibitors (50 mg/L) are shown in Figure 2. It can be seen that all the inhibitors provide corrosion inhibition for pre-scaled X65 steel, but their effectiveness varies significantly. The order of inhibitory effects for the four inhibitors is as follows: 1-CPN > BHQ > BPC > BQC. Among them, 1-CPN and BHQ have better corrosion inhibition effects, with corrosion inhibition rates reaching 80.22% and 80.15%, respectively. This indicates that the multi-benzene ring structure of 1-CPN plays a protective role in X65 steel after scaling, forming a protective film and producing a shielding effect to inhibit metal corrosion. At the same time, 1-CPN has a strong penetration ability and can effectively reach the metal substrate surface through the scale layer.
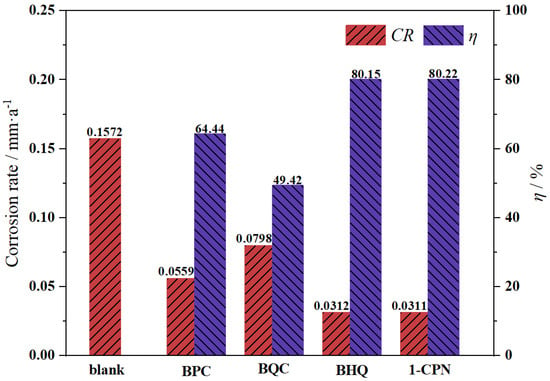
Figure 2.
Corrosion rate and inhibition efficiency of pre-scaled X65 steels after immersing in a solution environment at 40 °C, CO2 partial pressure of 0.5 MPa (total pressure of 1 MPa) for 72 h, with different corrosion inhibitors (50 mg/L).
3.2. Electrochemical Behavior of Corrosion Inhibitors to Scale-Coated X65 Steel
3.2.1. OCP Variations
After 6 h of pre-scaling treatment on X65 steel, in situ electrochemical testing was conducted, and the results of the open circuit potential (OCP) test are shown in Figure 3. It can be clearly observed that during the initial stage of corrosion, the OCP rapidly increases and then starts to stabilize with a slow upward trend around 18 h. The significant fluctuations in OCP during in situ monitoring often indicate major changes in corrosion product films. Therefore, it is evident that corrosion time has a significant impact on steady-state potential. Different protective films with a different protective performance are formed at different stages. Before the electrochemical test, a layer of product film (CaCO3) was deposited on the surface of X65 steel through an accelerated scaling process. However, CaCO3 does not provide ideal protection to the substrate and may also cause corrosion under the scale, accelerating corrosion behavior. Therefore, significant fluctuations in open circuit potential can be observed during the early stage of OCP testing. The presence of pre-scale (CaCO3 film) has a certain influence on the performance of corrosion inhibitors. Some corrosion inhibitors can only adhere to the scale layer, which reduces their effectiveness in inhibiting corrosion. Therefore, the penetrability of corrosion inhibitors through the scale layer is particularly important, as reflected by significant differences in open circuit potential (OCP) under different conditions of quaternary ammonium salts.
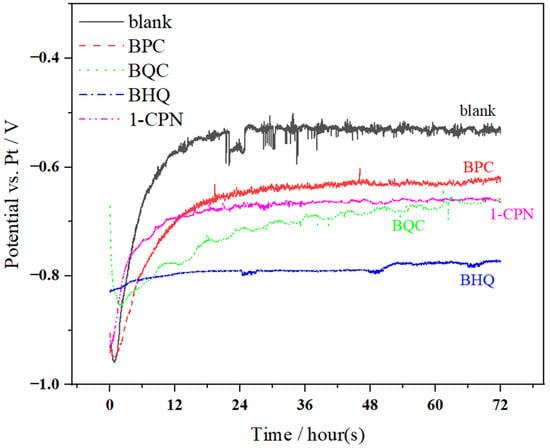
Figure 3.
The variation in OCP with time during a 72 h immersion process of X65 steel, pre-scaled for 6 h, at 40 °C and under different corrosion inhibitor conditions (50 mg/L) with a CO2 partial pressure of 0.5 MPa.
3.2.2. Linear Polarization Resistance
LPR tests were conducted at different time periods, and the results are shown in Figure 4. The electrochemical parameters are shown in Table 2. There was a significant difference in Rp under different corrosion inhibitor conditions, and the results with added inhibitors (50 mg/L) had higher Rp values than the blank. The relationship between Rp and corrosion current can be calculated using Formula (5), where B is a constant. A larger Rp value indicates a slower corrosion rate at this time. Therefore, the corrosion inhibition efficiency of different corrosion inhibitors is in the following order from high to low: 1-CPN > BHQ > BQC > BPC, which is consistent with the results of the weight-loss experiments. It is worth noting that the Rp value gradually decreases over time, indicating a relative weakening of the protective effect of corrosion product film during the 72 h immersion process. This may be because the CaCO3 product film generated during the pre-passivation process can provide a certain level of protection to the substrate in the early stages. However, as time goes on, some loosely attached product films formed via partial polarization will detach. At the same time, some corrosion inhibitors cannot penetrate through the scale layer and adhere to the surface product film. These ineffective corrosion inhibitors also detach and enter into the corrosive medium. Therefore, the Rp value tends to decrease with increasing time.
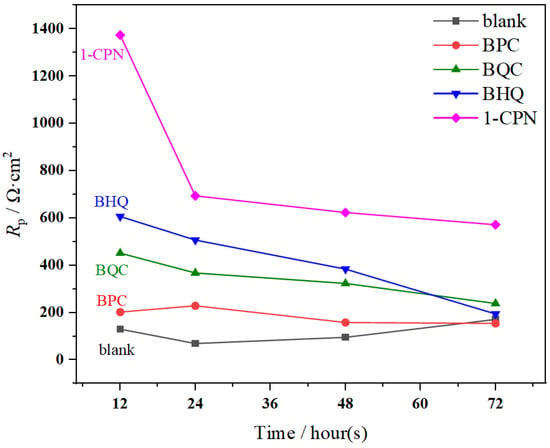
Figure 4.
The Rp values of X65 steel after pre-scaling for 6 h during immersion at 40 °C, with a CO2 partial pressure of 0.5 MPa, under various corrosion inhibitor conditions (50 mg/L).

Table 2.
The electrochemical parameters of the LPR for X65 steel with different corrosion inhibitors (50 mg/L) for samples of 6 h pre-scaling.
3.2.3. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
The in situ electrochemical tests were conducted on X65 steel after pre-scaling for 6 h. The Nyquist and Bode plots of the electrochemical impedance spectra obtained under different corrosion inhibitors (50 mg/L) are shown in Figure 5. The electrical circuit diagram used for fitting the EIS spectra is shown in Figure 6, where Rs represents solution resistance, CPEdl represents double layer capacitance, and n is the coefficient. When n = 1, CPEdl represents pure capacitance with capacitance Y−1. When n = 0, it represents the resistance as Y−1. When 0 < n < 1, it is non-ideal capacitance. When n = 0.5, it is Warburg impedance. Rct represents charge transfer resistance, L stands for inductance, and Rf represents the film resistance of corrosion products. The fitted electrochemical parameters are presented in Table 3.
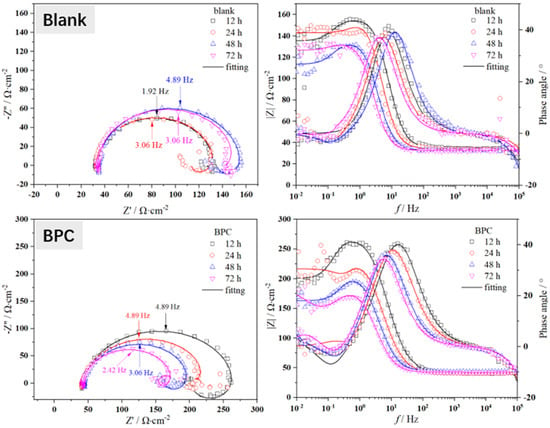
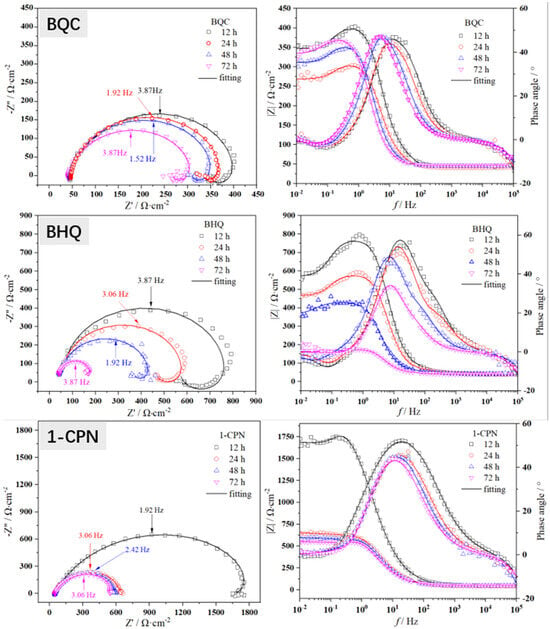
Figure 5.
The EIS spectra during a 72 h immersion process of X65 steel, pre-scaled for 6 h, at 40 °C and under a CO2 partial pressure of 0.5 MPa with different corrosion inhibitor conditions (50 mg/L).
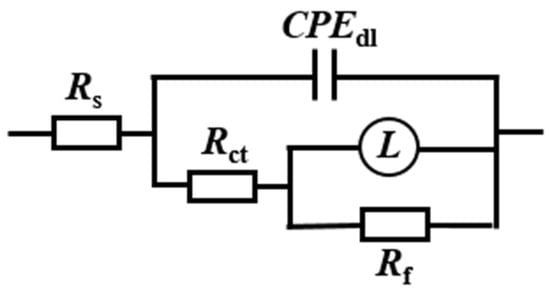
Figure 6.
Equivalent circuit diagram.

Table 3.
Electrochemical parameters obtained from fitting of EIS spectrum.
As shown in Figure 5, the electrochemical behavior of X65 steel under different corrosion inhibitors exhibits certain differences. However, in the test results, the Nyquist plots obtained under different corrosion inhibitor conditions have very similar shapes, showing a large semicircle in the high-frequency region and an inductive behavior in the low-frequency region [12,13,14]. This indicates that the electrochemical kinetics on the surface of X65 steel are identical. From the Nyquist plot, it can be observed that the semicircle at high frequencies represents the charging and discharging relaxation process on the electrode surface, while the semicircle at low frequencies corresponds to the adsorption of corrosion products on the anode and their coverage on the metal substrate. The appearance of inductance in the low-frequency region is attributed to the presence of a composite layer consisting of ferrous carbonate and calcium carbonate on the metal surface. The low-frequency induction loop indicates the active dissolution of X65 steel substrate in CO2 media, with a continuous adsorption of hydrogen ions and other surface substances. Moreover, there is a negative correlation between these surface substances’ coverage degree on the metal surface and potential.
The difference in charge transfer resistance (Rct) can be visually observed in the Nyquist plot shown in Figure 5. It is generally believed that Rct is inversely proportional to the corrosion rate, meaning that a higher Rct corresponds to a lower corrosion rate. The fitted values of Rct can be seen in Table 3, where the Rct value for the blank group is usually around 100 Ω·cm2. However, after adding corrosion inhibitors, there is an increase in Rct. For example, under the condition of using a 1-CPN inhibitor, Rct even reaches about six times that of the blank. This indicates that the corrosion inhibitor can penetrate through the pre-existing scale layer and adsorb on the substrate, but there are significant differences in penetration ability among different corrosion inhibitors. For example, under the conditions of BPC corrosion inhibitor, the Rct value only increases by less than two times compared to the blank. It is worth noting that under the same conditions, the EIS impedance arc radius decreases with time, which means that the protective effect of the corrosion product film decreases. Generally speaking, it is believed that with increasing time, the protective effect of the corrosion product film will gradually increase. The main reason for this phenomenon in this article is that a CaCO3 protective film is formed during the pre-scaling process. It is commonly believed that FeCO3 has a better protection effect than CaCO3. At the same time, the deposition of CaCO3 during the pre-scaling process also has a certain influence on ferrous carbonate sedimentation. Therefore, with the increase in immersion time, some loose CaCO3 will fall off, which will also take away some FeCO3 attached to the CaCO3 layer. The detachment of scale and the inability of newly formed products to effectively deposit on X65 steel matrix result in changes in Rp and EIS, as mentioned in the article. However, some corrosion inhibitors can still penetrate through the gaps between calcium carbonate scales and act on the matrix. Rf represents the film resistance value of the product film, and its size reflects the protective nature of the product film. At the same time, with the addition of corrosion inhibitors, CPEdl values gradually decrease, indicating a reduction in dielectric constant at the X65 sample corrosion interface. Quaternary ammonium salt molecules have larger sizes and smaller dielectric constants, which can further inhibit corrosion by adsorbing on X65 steel surface.
3.2.4. Polarization Curves
PC measurements were conducted in the final stage of in situ electrochemical testing. The polarization curve test results under different corrosion inhibitors conditions (50 mg/L) are shown in Figure 7. The electrochemical parameters obtained from fitting the PC data are presented in Table 4, indicating differences in PC under different corrosion inhibitor conditions. In the weight-loss experiment, the corrosion rates from smallest to largest were as follows: 1-CPN < BHQ < BQC < BPC < blank. Correspondingly, the corrosion current density (icorr) values obtained from fitting the polarization curves were 0.018 mA/cm2, 0.098 mA/cm2, 0.070 mA/cm2, 0.323 mA/cm2, and 0.531 mA/cm2, respectively. The greater the current density, the more severe the tendency for corrosion. Based on OCP analysis, the results indicate that after adding corrosion inhibitors, the relative negative shift in corrosion potential was observed, compared to the blank solution without any additives. Under different conditions of using various types of inhibitors, PC showed consistent trends where increasing potentials resulted in a continuous increase in anodic currents without clear signs of passivation phenomena. The main behavior of anodic processes was active dissolution until reaching higher potentials values. At high potentials, a significant increase in currents was observed due to the rapid deposition of corrosive products on metal surfaces. Literature reports suggest that if |∆Ecorr| exceeds 85 mV, it indicates either a cathodic or anodic-type inhibitor. While if |∆Ecorr| falls below 85 mV, it suggests a mixed-type inhibitor. These four quaternary ammonium salts belong to mixed-type inhibitors that are primarily cathode inhibitive in nature.
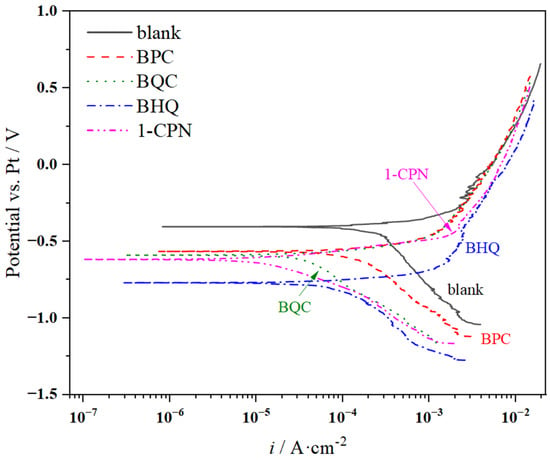
Figure 7.
PC comparison of X65 steel under different corrosion inhibitor addition (50 mg/L) after pre-scaling for 6 h.

Table 4.
The electrochemical parameters of the PC for X65 steel with different corrosion inhibitors (50 mg/L) for samples of 6 h pre-scaling.
3.3. Surface Morphologies of Samples via SEM
3.3.1. Surface Morphologies of X65 Steel Samples after Corrosion Experiments
As for X65 steel samples coated with CaCO3 through 6 h of pre-scaling, they were taken into the autoclave for corrosion experiments. The surface morphologies of X65 steel with different corrosion inhibitors for 72 h immersion are shown in Figure 8. It can be observed that different corrosion inhibitors have a significant impact on the surface morphology of the samples. Figure 8a shows the surface of the blank sample after 6 h of scale formation, which exhibits severe corrosion with a large amount of porous and loose corrosion products covering the surface. These are commonly mixed corrosion products consisting of calcium carbonate scale and FeCO3 corrosion product scale [49]. After adding the corrosion inhibitor, the surface of the specimen shows varying degrees of corrosion. When BPC is added, the surface of the corrosion product film becomes denser and roughness decreases. However, when BQC and BHQ inhibitors are added, a large amount of flocculent corrosion product film covers the surface, increasing coverage and reducing pore size compared to blank samples. When 1-CPN is added as an inhibitor as shown in Figure 8c, the corrosion product is significantly reduced, with fewer corrosion products and a denser protective film on the substrate.
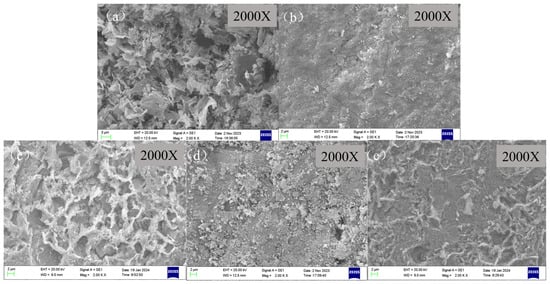
Figure 8.
SEM images of the corroded surface before product removal and after immersing scale-coated X65 steel in different corrosion inhibitors (50 mg/L) at a temperature of 40 °C and CO2 partial pressure of 0.5 MPa (total pressure of 1 MPa) for 72 h: (a) Blank, (b) BPC, (c) BQC, (d) BHQ and (e) 1-CPN.
The surface morphology after removing the corrosion product film of scale-coated X65 steel samples is shown in Figure 9. It can be seen that after film removal, the loose and porous surface corrosion product film on the blank sample without adding any corrosion inhibitor was effectively removed, revealing a clear surface morphology of the substrate after corrosion. There were large corrosive pits and holes all over, indicating uniform corrosion on the metal. The surface of the samples with corrosion inhibitors added after product layer removal changed from flocculent to cellular and exhibited numerous grooves, indicating that the addition of corrosion inhibitors inhibited the corrosion of X65 steel. This resulted in corrosive ions entering the metal substrate surface through scale layers and causing localized corrosion. However, BPC and BQC have limited protective effects on metals as their penetration ability is insufficient to form a uniform protective film. However, the corrosion inhibitors BHQ and 1-CPN exhibit excellent corrosion inhibition performance, with minimal adsorption on the scale surface and almost complete penetration through the scale to reach the metal surface underneath, protecting the metal [50]. After removing the corrosion product film, the sample surface is smooth and even, indicating effective corrosion inhibition, which is consistent with weight-loss and electrochemical results.
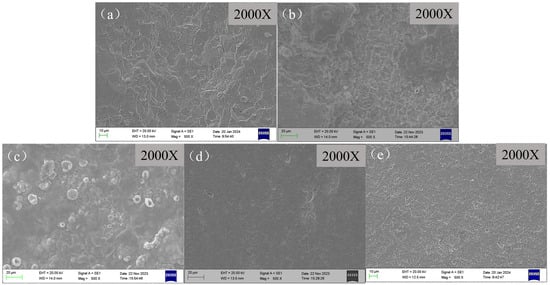
Figure 9.
SEM images of the X65 steel surface after removing the layer, which were immersion for 72 h at 40 °C and CO2 partial pressure of 0.5 MPa (total pressure of 1 MPa), with different corrosion inhibitors added (50 mg/L): (a) Blank, (b) BPC, (c) BQC, (d) BHQ and (e) 1-CPN.
3.3.2. Cross-Sectional Morphologies of Scale-Coated Samples after Corrosion Experiments
The cross-sectional morphologies of scale-coated X65 steel samples after being soaked in various corrosion inhibitor solutions for 72 h are shown in Figure 10. It indicates that there exists a layer of corrosion product film on the surface of the corroded samples. In the absence of a corrosion inhibitor, this layer of corrosion product film exhibits a loose attachment to the matrix surface and can be easily cleared off. After adding the corrosion inhibitor, it chelates with the scale layer to form a thicker corrosion product film, which makes it difficult for calcium carbonate scale to detach from the metal substrate. This provides isolation protection and reduces the contact between corrosive media and X65 steel, thereby lowering the corrosion rate. However, different corrosion inhibitors have varying abilities to penetrate the scale layer and provide uniform protection to the substrate. BPC, BQC and BHQ exhibit less than optimal corrosion inhibition effects, resulting in localized corrosion on the surface of X65 steel and an insufficient surface smoothness of the substrate. When using inhibitor 1-CPN, the corrosion product film is dense and evenly distributed on the substrate surface, effectively protecting it and significantly reducing its corrosion rate.
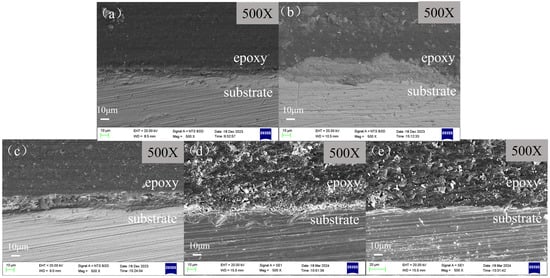
Figure 10.
Cross-sectional images of samples before product film removal after immersing scale-coated X65 steel in different corrosion inhibitors (50 mg/L) for 72 h at a temperature of 40 °C and CO2 partial pressure of 0.5 MPa (total pressure of 1 MPa): (a) Blank, (b) BPC, (c) BQC, (d) BHQ and (e) 1-CPN.
4. Conclusions
After 6 h of pre-scaling on X65 steel, the inhibition efficiencies of several corrosion inhibitors on under-deposit corrosion were compared using weight-loss and in situ electrochemical measurements. The conclusions are as follows:
- (1)
- Weight-loss experiments have shown that different corrosion inhibitors can effectively inhibit under-deposit corrosion. But there are different capabilities in inhibiting the under-deposit corrosion of X65 steels coated with CaCO3 layer. The inhibition efficiencies of the corrosion inhibitors from high to low are as follows: 1-CPN < BHQ < BQC < BPC.
- (2)
- The differences in electrochemical behavior under different corrosion inhibitor addition indicate different corrosion inhibition properties to the corrosion under-deposit layer. The pre-scaled CaCO3, which forms before corrosion occurs, provides adequate protection in the early stage. However, as immersion was prolonged, a decrease in Rp and Rct occurred, which inferred the increase in corrosion rate. Both EIS and PC results proved the best inhibition efficiency for 1-CPN.
- (3)
- The surface morphology of the sample in the absence of a corrosion inhibitor exhibits as a loose and porous layer, which can provide less protection to the substrate. However, in the presence of a different corrosion inhibitor, pre-scaled X65 steels exhibit varying degrees of corrosion. Under the action of corrosion inhibitors, the under-deposit corrosion is inhibited to varying degrees, with BHQ and 1-CPN showing the best inhibition effect to under-deposit corrosion. In the cross-sectional morphologies of BPC and BQC, it exhibited as uneven and the corrosion under the deposit was relatively severe. The corrosion product of 1-CPN covers the substrate surface as a thin and uniform layer. A slightly corroded surface can be observed after the product layer is removed.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.X.; Software, Z.L. and T.X.; Investigation, P.L.; Data curation, X.C.; Writing—original draft, H.L. and H.W.; Visualization, J.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in article.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Tianyi Xiewas employed by the company Gas Transmission Management Department, Southwest Oil & GasField Company. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Wang, X.; Melchers, R.E. Long-term under-deposit pitting corrosion of carbon steel pipes. Ocean. Eng. 2017, 133, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Brown, B.; Nesic, S.; Papavinasam, S.; Gould, D. Localized Corrosion of Mild Steel under Silica Deposits in Inhibited Aqueous CO2 Solutions. In Proceedings of the NACE CORROSION 2013, Orlando, FL, USA, 17–21 March 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kung, S.; Miller, N.; Eiyaakobi, F.; Moloney, J. Mitigation of Elemental Sulfur and Iron Sulfide Under-Deposit Corrosion. In Proceedings of the AMPP Annual Conference + Expo, Denver, CO, USA, 19–23 March 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kermani, M.B.; Morshed, A. Carbon dioxide corrosion in oil and gas production—A compendium. Corrosion 2003, 59, 659–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nešić, S. Key issues related to modelling of internal corrosion of oil and gas pipelines—A review. Corros. Sci. 2007, 49, 4308–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoori, H.; Young, D.; Brown, B.; Singer, M. Influence of calcium and magnesium ions on CO2 corrosion of carbon steel in oil and gas production systems-A review. J. Nat. Gas. Sci. Eng. 2018, 59, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoori, H.; Mirzaee, R.; Esmaeilzadeh, F.; Vojood, A.; Dowrani, A.S. Pitting corrosion failure analysis of a wet gas pipeline. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2017, 82, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, R.; Burkle, D.; Charpentier, T.; Thompson, H.; Neville, A. A review of iron carbonate (FeCO3) formation in the oil and gas industry. Corros. Sci. 2018, 142, 312–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, T.; Bandeira, M.; Moreira, R.M.; Mattos, O.R. New insights on the role of CO2 in the mechanism of carbon steel corrosion. Corros. Sci. 2017, 120, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiedong, R.; Yuan, L.; Qiang, W.; Liusi, Y.; Kaiyuan, Z.; Jiayi, T.; Hu, W.; Juan, X. The influence of Ca2+ on the growth mechanism of corrosion product film on N80 steel in CO2 corrosion environments. Corros. Sci. 2023, 218, 111168. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, T.C.; Bandeira, M.C.E.; Moreira, R.M.; Mattos, O.R. Discussion on “Electrochemistry of CO2 corrosion of mild steel: Effect of CO2 on iron dissolution reaction” by A. Kahyarian, B. Brown, S. Nesic, [Corros. Sci. 129 (2017) 146–151]. Corros. Sci. 2018, 133, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Wang, H.; Wei, Q.; Lu, Y.; Xiao, B.; Xie, J. Electrochemical behaviour of N80 steel in CO2 environment at high temperature and pressure conditions. Corros. Sci. 2021, 189, 109619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Pang, X.; Gao, K. The growth mechanism of CO2 corrosion product films. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Lu, X.; Wang, H. Synergistic effect between two quaternary ammonium salts and thiourea as corrosion inhibitors for X70 steels in CO2 saturated 3.5% NaCl solution. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2024, 19, 100443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.D.; Li, J.B.; Deng, C.Y.; Yang, L.; Lv, J.; Fu, L.P. Novel carbon dots as effective corrosion inhibitor for N80 steel in 1 M HCl and CO2-saturated 3.5 wt% NaCl solutions. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1250, 131897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, G. Efficient inhibition of mild steel corrosion in acidic medium by novel pyrimidine derivatives: Inhibitive effect evaluation and interface adsorption mechanism. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1291, 136005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaolin, Y.; Qiang, W.; Yuan, L.; Ming, D.; Hu, W.; Juan, X. The Synergistic Inhibition Effect between Imidazoline and 2-Mercaptoethanol on Carbon Steel Corrosion in CO2-saturated 3.5% NaCl solution. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2022, 17, 220556. [Google Scholar]
- El Basiony, N.M.; Elgendy, A.; El-Tabey, A.E.; Al-Sabagh, A.M.; Abd El-Hafez, G.M.; Abd El-raouf, M.; Migahed, M.A. Synthesis, characterization, experimental and theoretical calculations (DFT and MC) of ethoxylated aminothiazole as inhibitor for X65 steel corrosion in highly aggressive acidic media. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 297, 111940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Saha, S.K.; Kang, N.; Ganjoo, R.; Thakur, A.; Assad, H.; Kumar, A. Multidimensional analysis for corrosion inhibition by Isoxsuprine on mild steel in acidic environment: Experimental and computational approach. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 357, 119129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K.; Mehta, R.K.; Kumari, N.; Yadav, M.; Obot, I.B. Study on benzylidine derivatives as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in 15% HCl medium: Experimental & theoretical investigation. J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 2023, 183, 111632. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.J.; Yan, N.; Wang, Y.Q.; Mei, P.; Chen, W.; Lu, L.L.; Lai, L. Corrosion Inhibition Studies of 8-Hydroxyquinoline Derivatives for N80 Steel in a 1.0 M HCl Solution: Experimental, Computational Chemistry, and Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship Studies. Langmuir 2023, 39, 519–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Ansari, K.R.; Ali, I.H.; Alanazi, A.K.; Younas, M.; Lin, Y.H. Long chain imidazole derivative as a novel corrosion inhibitor for Q235 steel in 15 % HCl medium under hydrodynamic condition: Experimental and theoretical examinations. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2024, 313, 128798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, M.A.; Abdallah, M.; Awad, M.K.; Rezk, M. Three novel di-quaternary ammonium salts as corrosion inhibitors for API X65 steel pipeline in acidic solution. Part I: Experimental results. Corros. Sci. 2014, 81, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Ansari, K.R.; Chauhan, D.S.; Quraishi, M.A.; Lgaz, H.; Chung, I.M. Comprehensive investigation of steel corrosion inhibition at macro/micro level by ecofriendly green corrosion inhibitor in 15% HCl medium. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 560, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Thakur, A.; Sharma, M.K.; Kumar, A.; Jakhar, K.; Kumar, S.; Sihmar, A.; Dahiya, H.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, A.K.; et al. A convenient synthesis, electrochemical profiling, and morphological studies of a pyridine-based 1,3,4-oxadiazole hybrid: A promising study for corrosion mitigation of mild steel in strongly acidic environment. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 158, 111554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Hu, Y.; Han, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Nie, Z.; Wang, Y. Experimental and Theoretical Study on the Synergistic Inhibition Effect of Pyridine Derivatives and Sulfur-Containing Compounds on the Corrosion of Carbon Steel in CO2-Saturated 3.5 wt.% NaCl Solution. Molecules 2018, 23, 3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.R.; Lu, W.Q.; Yang, D.; Shen, J.J.; Gao, Z.S.; Zhang, S.Y.; Liao, Q.Q. Dithiocarbamate modified glucose as a novel eco-friendly corrosion inhibitor for copper in sodium chloride media. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2021, 22, 100488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.J.; Tan, B.C.; Zheng, X.W.; Chen, X.D.; Chen, J.D.; Li, W.P. Penetration into the inhibition performance of two piperazine derivatives as high-efficiency inhibitors for copper in sulfuric acid environment. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 356, 119015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouchane, M.; Dkhireche, N.; Rbaa, M.; Benhiba, F.; Ouakki, M.; Galai, M.; Lakhrissi, B.; Zarrouk, A.; Touhami, M.E. Insight into the corrosion inhibition performance of two quinoline-3-carboxylate derivatives as highly efficient inhibitors for mild steel in acidic medium: Experimental and theoretical evaluations. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 360, 119470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahya, S.; Kee, K.E.; Puad MJ, M.; Ismail, M.C. Evaluation on steel corrosion in water-based drilling fluids: Inhibitors and scale involvement. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 211, 110127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Yu, H.; Fu, Z.; Yue, P. Effect of Water-soluble Corrosion Inhibitor on Corrosion Behavior of Q235 Pipeline Steel for Construction. J. Chin. Soc. Corros. Prot. 2023, 43, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Ma, F.; Wu, Y.; Dong, Z. Optimization of Injection Technique of Corrosion Inhibitor in CO2-flooding Oil Recovery. J. Southw. Pet. Univ. (Sci. Tech. Ed.) 2020, 42, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Ying, L.; Wang, X.; Yang, F. Corrosion of X65 Pipeline Steel Under Deposit and Effect of Corrosion Inhibitor. J. Mater. Eng. 2016, 44, 100–108. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Xu, L.; Li, D.; Lu, M. Corrosion Inhibition Mechanism of Carbon Steel in O2/CO2 Coexisting Environment. J. Mater. Eng. 2017, 45, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Ying, L.; Yang, F.; Li, B.; Wang, X. Corrosion behavior of pipeline steel under deposit corrosion and the inhibition performance of organic phosphine inhibitor. Acta. Metal. Sin. 2016, 52, 320–330. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Z.; Wang, G.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, L.; Jiang, W.; Yi, R.; Cui, X.; Qiu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Y.; et al. Co-Evolution Law and Control Technology of Corrosion and Scaling in Water Injection Wells of a Middle East Carbonate Oilfield. In Proceedings of the International Petroleum Technology Conference, Bangkok, Thailand, 1–3 March 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, W.; Li, Q.; Zhang, D.; Yu, Y.; Cao, B.; Liu, Z. Under-deposit corrosion of tubing served for injection and production wells of CO2 flooding. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2021, 127, 105540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, J.L.A.; Barquera, S.S.; Perez, R. Effect of Wet Hydrogen Sulfide Environments on the Cracking Susceptibility of Medium Strength Microalloyed Pipeline Steels for Oil and Gas Transport. In Proceedings of the CORROSION 2003, San Diego, CA, USA, 16–20 March 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Sliem, M.H.; Fayyad, E.M.; Abdullah, A.M.; Younan, N.A.; Al-Qahtani, N.; Nabhan, F.F.; Arora, D. Monitoring of under deposit corrosion for the oil and gas industry: A review. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 204, 108752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standlee, S.; Efird, K.D.; Spiller, D. Under Deposit Corrosion from IRON sulfide. In Proceedings of the NACE CORROSION, Houston, TX, USA, 13–17 March 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kvarekvål, J.; Svenningsen, G. Effect of Iron Sulfide Deposits on Sour Corrosion of Carbon Steel. In Proceedings of the NACE CORROSION, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 6–10 March 2016; Volume 2, pp. 1513–1526. [Google Scholar]
- Vera, J.R.; Daniels, D.; Achour, M.H. Under Deposit Corrosion (UDC) in the Oil and Gas Industry: A Review of Mechanisms, Testing and Mitigation. In Proceedings of the Nace Corrosion, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 11–15 March 2012; Volume 4, pp. 3028–3040. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Yang, X.; Zeng, M.; Wang, H. Influence of CO2 partial pressure and flow rate on the corrosion behavior of N80 steel in 3.5% NaCl. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2023, 18, 100218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Chokshi, K.; Nesic, S. Iron Carbonate Scale Growth and the Effect of Inhibition in CO2 Corrosion of Mild Steel. In Proceedings of the NACE CORROSION, Houston, TX, USA, 3–7 April 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, J.E.; Park, N. Effect of Corrosion Inhibitor Active Components on the Growth of Iron Carbonate Scale under CO2 Conditions. In Proceedings of the NACE CORROSION, New Orleans, LA, USA, 16–20 March 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ciolkowski, M.; Neville, A.; Hu, X.; Mavredaki, E.; Sanders, L. Influence of Brine with Different Supersaturation Ratio on Corrosion Processes for Pipeline Material Carbon Steel X65, Scale Deposition and Performance of Combined Inhibitor. In Proceedings of the SPE International Oilfield Corrosion Conference and Exhibition, Aberdeen, UK, 28–29 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Shi, Y.; He, S.; Luo, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhai, K.; Duan, M.; Wang, H.; Xie, J. Study on the corrosion inhibition properties of some quinoline derivatives as acidizing corrosion inhibitors for steel. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2024, 19, 100547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stalker, R.; Graham, G.M.; Simpson, C. The Impact of Inorganic Scale Deposits and Their Removal on General CO2 Corrosion Rates and Corrosion Inhibitor Performance. In Proceedings of the SPE International Symposium on Oilfield Corrosion, Aberdeen, UK, 28 May 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Wei, Q.; Ren, X.; Wang, H.; Xie, J. Investigation of Scale Inhibition Mechanism by Electrochemical Quartz Crystal Microbalance. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2021, 16, 21057. [Google Scholar]
- He, S.; Zhao, H.; Tontiwachwuthikul, P.; Qiu, Y.; Luo, S.; Xia, X. Investigation on corrosion behavior and mechanism of carbon steel under CaCO3 deposit in CO2-flooding environment. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2022, 121, 103799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).