A NIR-Fluorochrome for Live Cell Dual Emission and Lifetime Tracking from the First Plasma Membrane Interaction to Subcellular and Extracellular Locales
Abstract
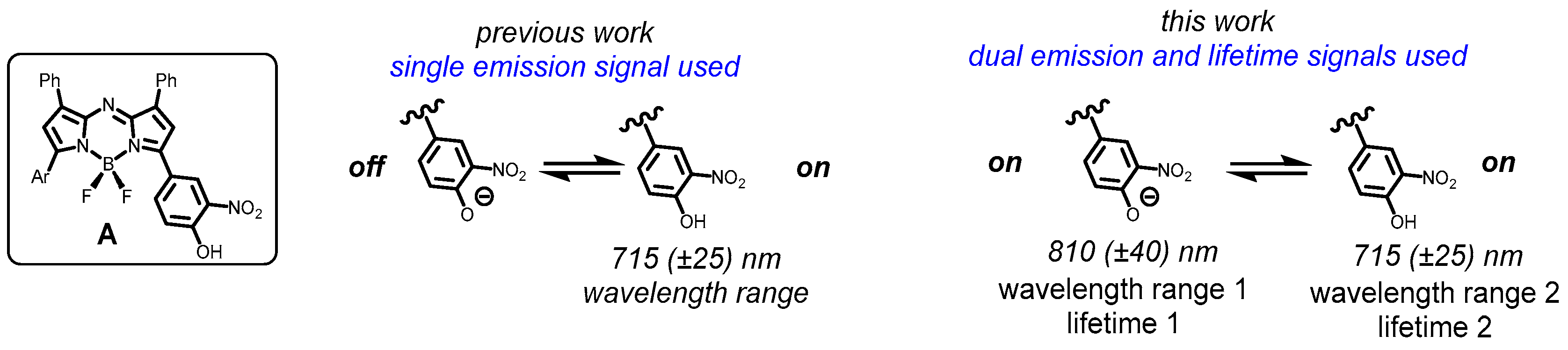
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
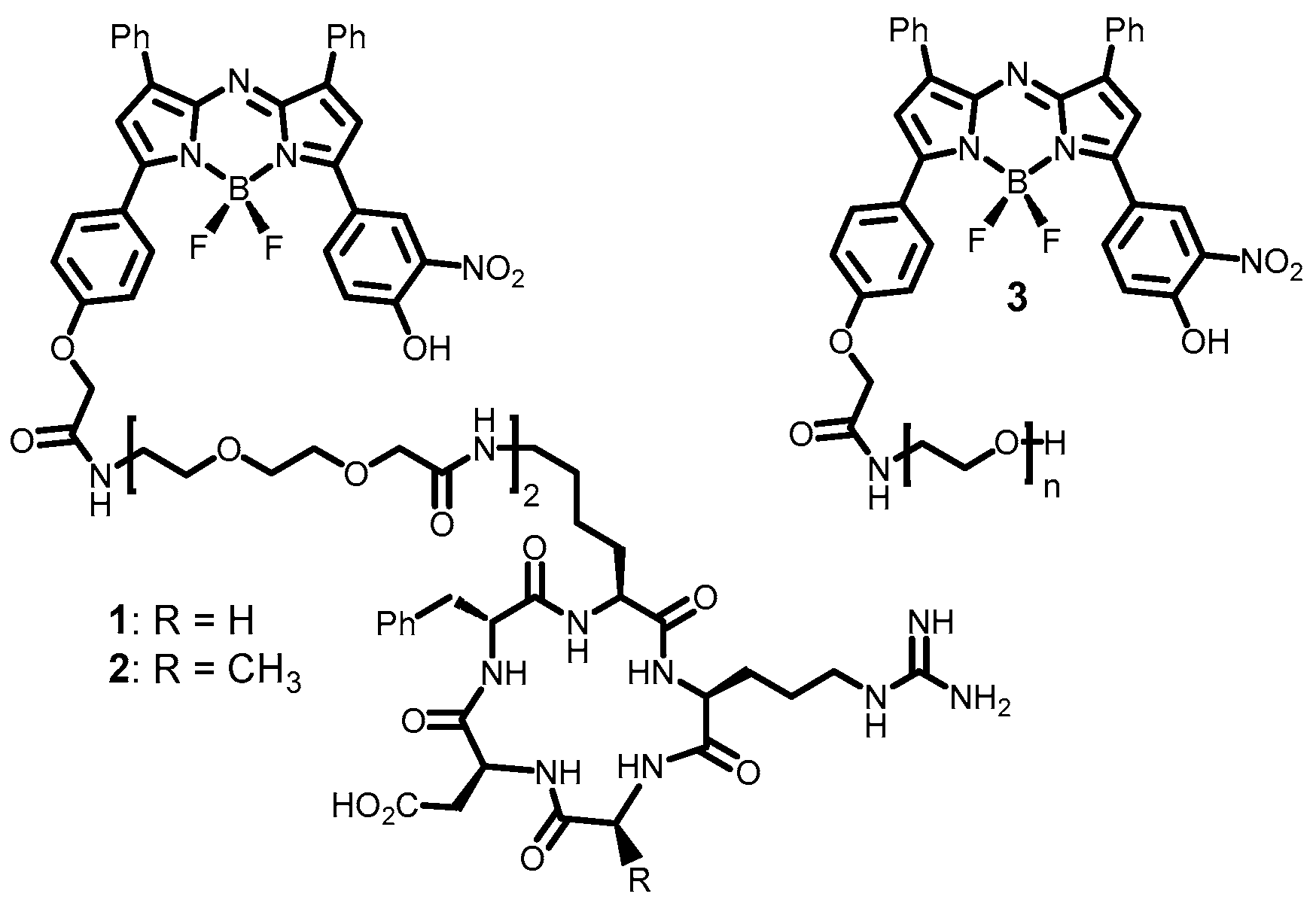
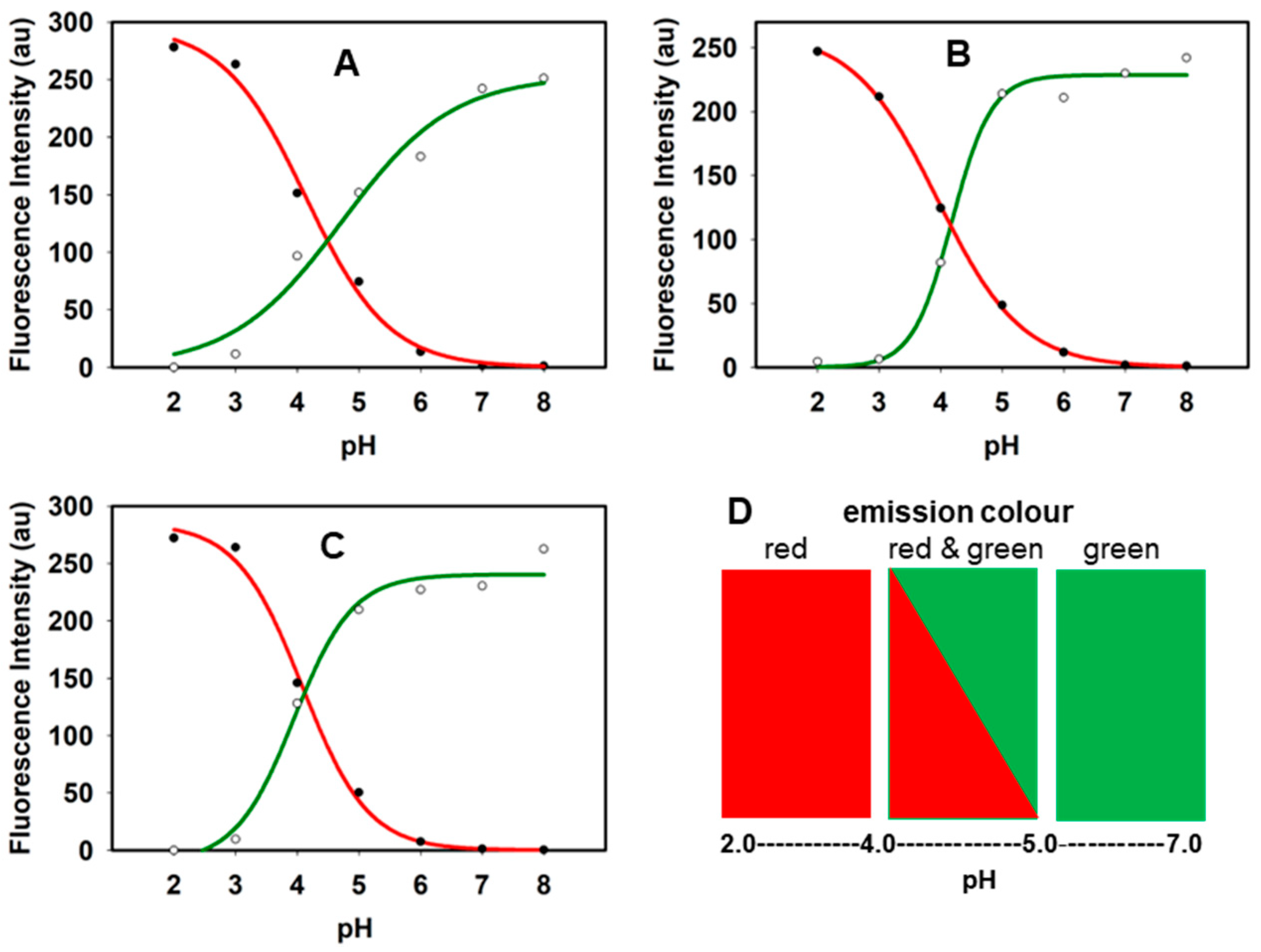
2.1. Fluorophores and Photophysical Characterizations
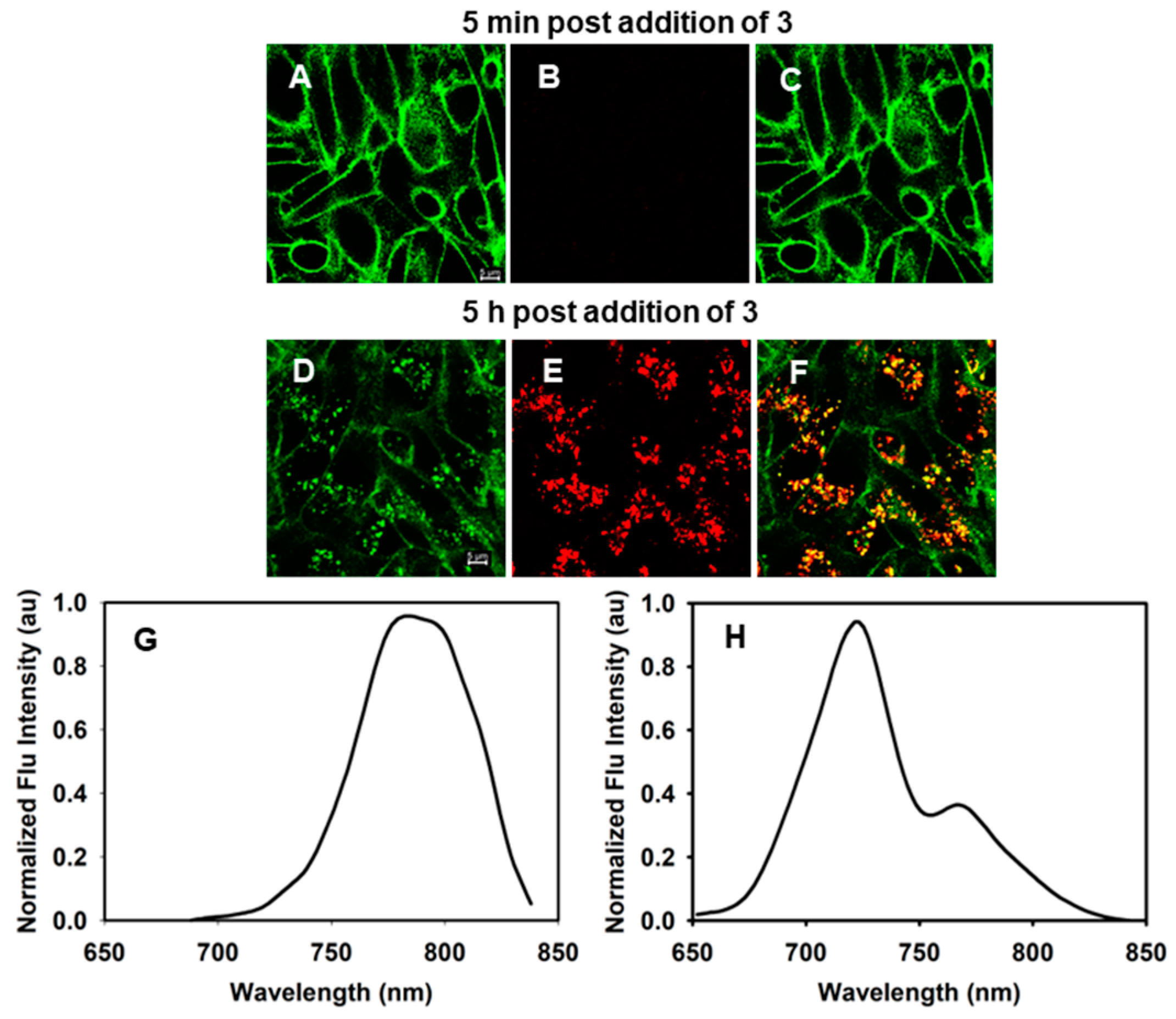
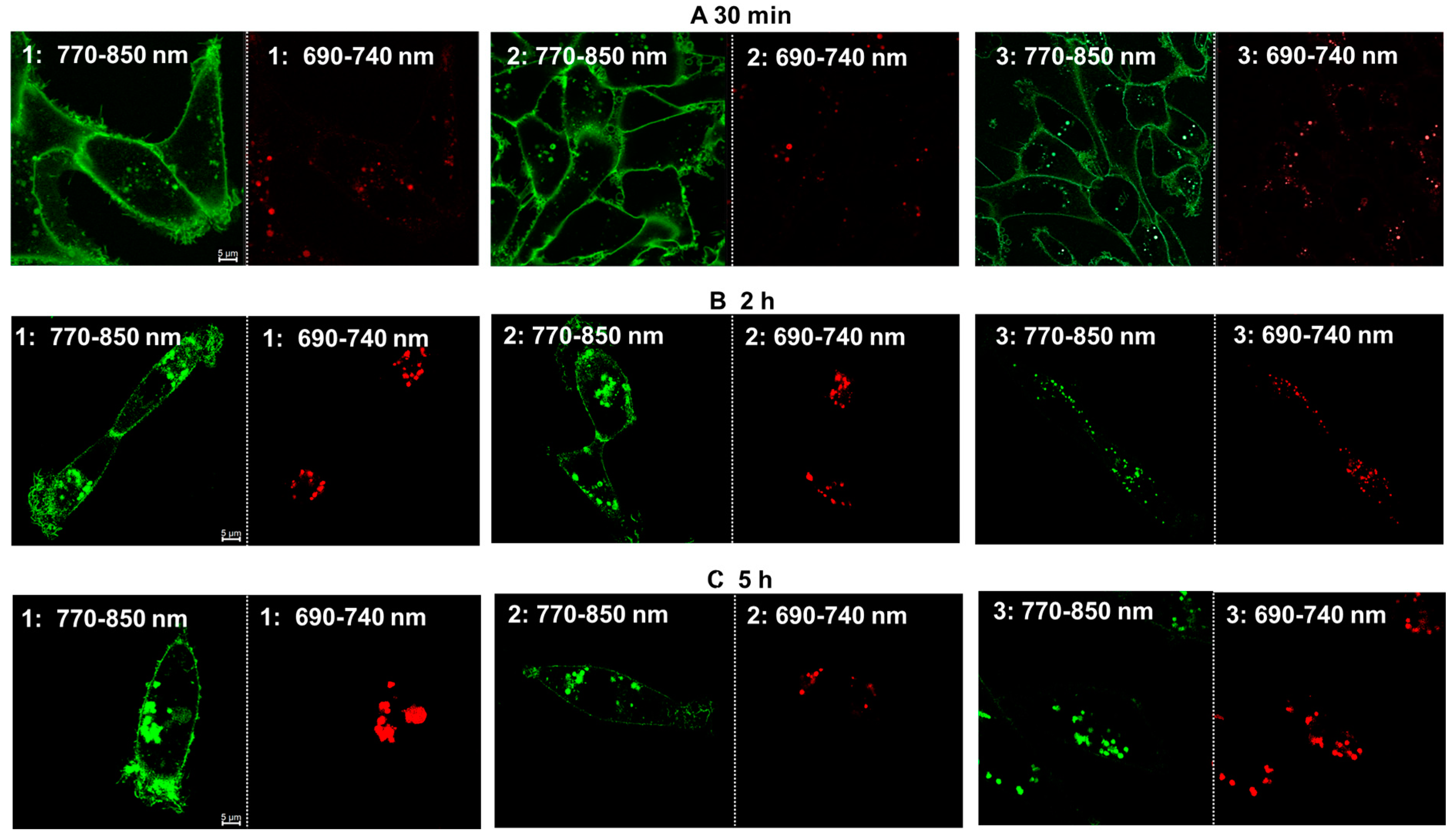
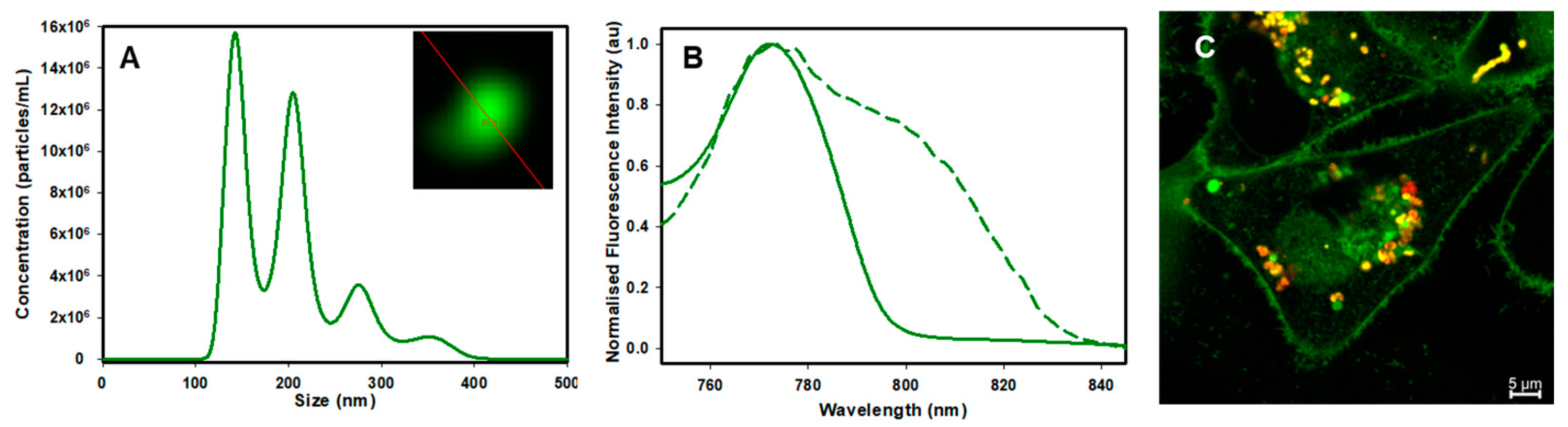
2.2. Live Cell Microscopy
2.3. Image Analysis
2.4. Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy
3. Experimental
3.1. General
3.2. Synthesis and Characterization
3.3. Spectroscopic pH Analysis
3.4. Cell Culture and Live Cell Confocal and FLIM Microscopy
3.5. EV Isolation
3.6. ImageJ Protocol for Color Subtraction
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hickey, S.M.; Ung, B.; Bader, C.; Brooks, R.; Lazniewska, J.; Johnson, I.R.D.; Sorvina, A.; Logan, J.; Martini, C.; Moore, C.R.; et al. Fluorescence microscopy—An outline of hardware, biological handling, and fluorophore considerations. Cells 2022, 11, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renz, M. Fluorescence microscopy a historical and technical perspective. Cytom. J. Int. Soc. Anal. Cytol. 2013, 83, 767–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, A. Recent advances in the standardization of fluorescence microscopy for quantitative image analysis. Biophys. Rev. 2022, 14, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, K.M.; Palmer, A.E. Advances in fluorescence labeling strategies for dynamic cellular imaging. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014, 10, 512–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Murfin, L.C.; Wu, L.; Lewis, S.E.; James, T.D. Fluorescent small organic probes for biosensing. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 3406–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Huy, B.; Thangadurai, D.T.; Sharipov, M.; Ngoc Nghia, N.; Van Cuong, N.; Lee, Y.-I. Recent advances in turn off-on fluorescence sensing strategies for sensitive biochemical analysis—A mechanistic approach. Microchem. J. 2022, 179, 107511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killoran, J.; O’Shea, D.F. Impact of a conformationally restricted receptor on the BF2 chelated azadipyrromethene fluorosensing platform. Chem. Commun. 2006, 14, 1503–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Ouyang, Q.; Werthmann, G.C.; Thompson, H.M.; Morrow, E.M. Live-cell microscopy and fluorescence-based measurement of luminal pH in intracellular organelles. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 5, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Qu, D.-H. A Single-fluorophore multicolor molecular sensor that visually identifies organic anions including phosphates. CCS Chem. 2023, 6, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, J.R.; Castruita-De Leon, G.; Turlakov, G.; Arias, E.; Moggio, I.; Montemayor, S.M.; Torres, R.; Ledezma, R.; Ziolo, R.F.; Gonzalez-Torres, J. Dual emission of meso-phenyleneethynylene-BODIPY oligomers: Synthesis, photophysics, and theoretical optoelectronic study. Chemistry 2021, 27, 2493–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.X.; Niu, L.Y.; Shao, N.; Yang, Q.Z. BODIPY-based fluorescent probe for dual-channel detection of nitric oxide and glutathione: Visualization of cross-talk in living cells. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 4301–4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhai, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Qin, Y.; Jiang, D. A near-infrared fluorescent aza-bodipy probe for dual-wavelength detection of hydrogen peroxide in living cells. Analyst 2016, 141, 2380–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtin, N.; Wu, D.; Cahill, R.; Sarkar, A.; Aonghusa, P.M.; Zhuk, S.; Barberio, M.; Al-Taher, M.; Marescaux, J.; Diana, M.; et al. Dual color imaging from a single BF2-azadipyrromethene fluorophore demonstrated in vivo for lymph node identification. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 18, 1541–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, M.; Junker, A.K.R.; Sørensen, T.J.; Laursen, B.W. Fluorescence pH probes based on photoinduced electron transfer quenching of long fluorescence lifetime triangulenium dyes. ChemPhotoChem 2019, 3, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xiao, Y.; Xie, Z.; Sun, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Huang, R. 2-Hydroxybenzophenone derivatives: ESIPT fluorophores based on switchable intramolecular hydrogen bonds and excitation energy-dependent emission. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 766179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Durán-Sampedro, G.; Fitzgerald, S.; Garre, M.; O’Shea, D.F. Double click macrocyclization with Sondheimer diyne of aza-dipyrrins for B–Free bioorthogonal imaging. Chem. Commun. 2023, 59, 1951–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonkaya, O.; Soylukan, C.; Pamuk Algi, M.; Algi, F. Aza-BODIPY-based fluorescent and colorimetric sensors and probes. Curr. Org. Synth. 2023, 20, 20–60. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.; Han, X.; Hu, W.; Bai, H.; Peng, B.; Ji, L.; Fan, Q.; Li, L.; Huang, W. Bioapplications of small molecule Aza-BODIPY: From rational structural design to in vivo investigations. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 7533–7567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.; O’Shea, D.F. Azadipyrromethenes: From traditional dye chemistry to leading edge applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 3846–3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Cheung, S.; Devocelle, M.; Zhang, L.J.; Chen, Z.L.; O’Shea, D.F. Synthesis and assessment of a maleimide functionalized BF2 azadipyrromethene near-infrared fluorochrome. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 16667–16670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; O’Shea, D.F. Fluorogenic NIR-probes based on 1,2,4,5-tetrazine substituted BF2-azadipyrromethenes. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 10804–10807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Daly, H.C.; Conroy, E.; Li, B.; Gallagher, W.M.; Cahill, R.A.; O’Shea, D.F. PEGylated BF2-Azadipyrromethene (NIR-AZA) fluorophores, for intraoperative imaging. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 161, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pino, Y.C.; Aguilera, J.A.; Garcia-Gonzalez, V.; Alatorre-Meda, M.; Rodriguez-Velazquez, E.; Espinoza, K.A.; Frayde-Gomez, H.; Rivero, I.A. Synthesis of Aza-BODIPYs, their differential binding for Cu(II), and results of bioimaging as fluorescent dyes of Langerhans β-cells. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 42752–42762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Liao, L.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Wu, F. Near-infrared fluorescent Aza-BODIPY dyes: Rational structural design and biomedical imaging. J. Lumin. 2023, 263, 120099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pewklang, T.; Chansaenpak, K.; Lai, R.Y.; Noisa, P.; Kamkaew, A. Aza-BODIPY probe for selective visualization of cyclooxygenase-2 in cancer cells. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 13372–13377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, A.; Gallagher, J.F.; Müller-Bunz, H.; Wolowska, J.; McInnes, E.J.L.; O’Shea, D.F. Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II) and Zn(II) complexes of tetraphenylazadipyrromethene. Dalton Trans. 2009, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caulfield, C.; Wu, D.; Miller, I.S.; Byrne, A.T.; Mac Aonghusa, P.; Zhuk, S.; Cinelli, L.; Bannone, E.; Marescaux, J.; Gioux, S.; et al. BF2-Azadipyrromethene fluorophores for intraoperative vital structure identification. Molecules 2023, 28, 2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossi, M.; Morgunova, M.; Cheung, S.; Scholz, D.; Conroy, E.; Terrile, M.; Panarella, A.; Simpson, J.C.; Gallagher, W.M.; O’Shea, D.F. Lysosome triggered near-infrared fluorescence imaging of cellular trafficking processes in real time. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, S.; Wu, D.; Daly, H.C.; Busschaert, N.; Morgunova, M.; Simpson, J.C.; Scholz, D.; Gale, P.A.; O’Shea, D.F. Real-time recording of the cellular effects of the anion transporter prodigiosin. Chem 2018, 4, 879–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Daly, H.C.; Grossi, M.; Conroy, E.; Li, B.; Gallagher, W.M.; Elmes, R.; O’Shea, D.F. RGD conjugated cell uptake off to on responsive NIR-AZA fluorophores: Applications toward intraoperative fluorescence guided surgery. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 6944–6956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Nobuaki Tanaka, S.M.; Kawauchi, O.; Kodaira, K.; Nishikiori, H.; Kawai, Y. Absorption and fluorescence spectra of 9-anthrol and its chemical species in solution. Res. Chem. Intermed. 1997, 23, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, R.; Paudel, P.; Sharma, A.K.; Webb, S.; Ware, M. Evaluating the merit of a syringol derived fluorophore as a charge transfer probe for detection of serum albumins. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2022, 422, 113563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Li, C.; Pang, Z.; Chen, K.; Tan, Y.; Huang, Y.; Lu, Z. A new phenolate-ion-type two-photon near infrared fluorophore-based biosensor for high-performance detection of HNO. Chemistry 2020, 26, 12140–12144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Fei, B. Comprehensive review of surgical microscopes: Technology development and medical applications. J. Biomed. Opt. 2021, 26, 010901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caulfield, C.; Wu, D.; Garre, M.; O’Shea, D.F. Substituent directed cellular imaging in the 800–850 nm range with BF2-azadipyrromethene fluorophores. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 14963–14973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casey, J.R.; Grinstein, S.; Orlowski, J. Sensors and regulators of intracellular pH. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Li, H.; Xi, Y.; Hu, Q.; Liu, H.; Fan, J.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shui, W.; Lai, Y. Vesicle trafficking and vesicle fusion: Mechanisms, biological functions, and their implications for potential disease therapy. Mol. Biol. 2022, 3, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poteryaev, D.; Datta, S.; Ackema, K.; Zerial, M.; Spang, A. Identification of the switch in early-to-late endosome transition. Cell 2010, 141, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munan, S.; Yadav, R.; Pareek, N.; Samanta, A. Ratiometric fluorescent probes for pH mapping in cellular organelles. Analyst 2023, 148, 4242–4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hande, P.E.; Shelke, Y.G.; Datta, A.; Gharpure, S.J. Recent advances in small molecule-based intracellular pH probes. ChemBioChem 2022, 23, e202100448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montcourrier, P.; Silver, I.; Farnoud, R.; Bird, I.; Rochefort, H. Breast cancer cells have a high capacity to acidify extracellular milieu by a dual mechanism. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 1997, 15, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taherian, A.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Haas, T.A. Differences in integrin expression and signaling within human breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, Y.J.; Seo, E.B.; Jeong, A.J.; Lee, S.H.; Noh, K.H.; Lee, S.; Cho, C.H.; Lee, C.H.; Shin, H.M.; Kim, H.R.; et al. The acidic tumor microenvironment enhances PD-L1 expression via activation of STAT3 in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ralph, A.C.L.; Valadao, I.C.; Cardoso, E.C.; Martins, V.R.; Oliveira, L.M.S.; Bevilacqua, E.; Geraldo, M.V.; Jaeger, R.G.; Goldberg, G.S.; Freitas, V.M. Environmental control of mammary carcinoma cell expansion by acidification and spheroid formation in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montcourrier, P.; Mangeat, P.H.; Valembois, C.; Salazar, G.; Sahuquet, A.; Duperray, C.; Rochefort, H. Characterization of very acidic phagosomes in breast cancer cells and their association with invasion. J. Cell Sci. 1994, 107, 2381–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monopoli, M.P.; Zendrini, A.; Wu, D.; Cheung, S.; Sampedro, G.; Ffrench, B.; Nolan, J.; Piskareva, O.; Stalings, R.L.; Ducoli, S.; et al. Endogenous exosome labelling with an amphiphilic NIR-fluorescent probe. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 7219–7222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Met. 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolte, S.; Cordelières, F.P. A guided tour into subcellular colocalization analysis in light microscopy. J. Microsc. 2006, 224, 213–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, M.; Houhou, R.; Hniopek, J.; Bocklitz, T. Review of fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM) data analysis using machine learning. J. Exp. Theor. Anal. 2023, 1, 44–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitton, A.; Sambrano, J.; Valentino, S.; Houston, J.P. A review of new high-throughput methods designed for fluorescence lifetime sensing from cells and tissues. Front. Phys. 2021, 9, 648553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
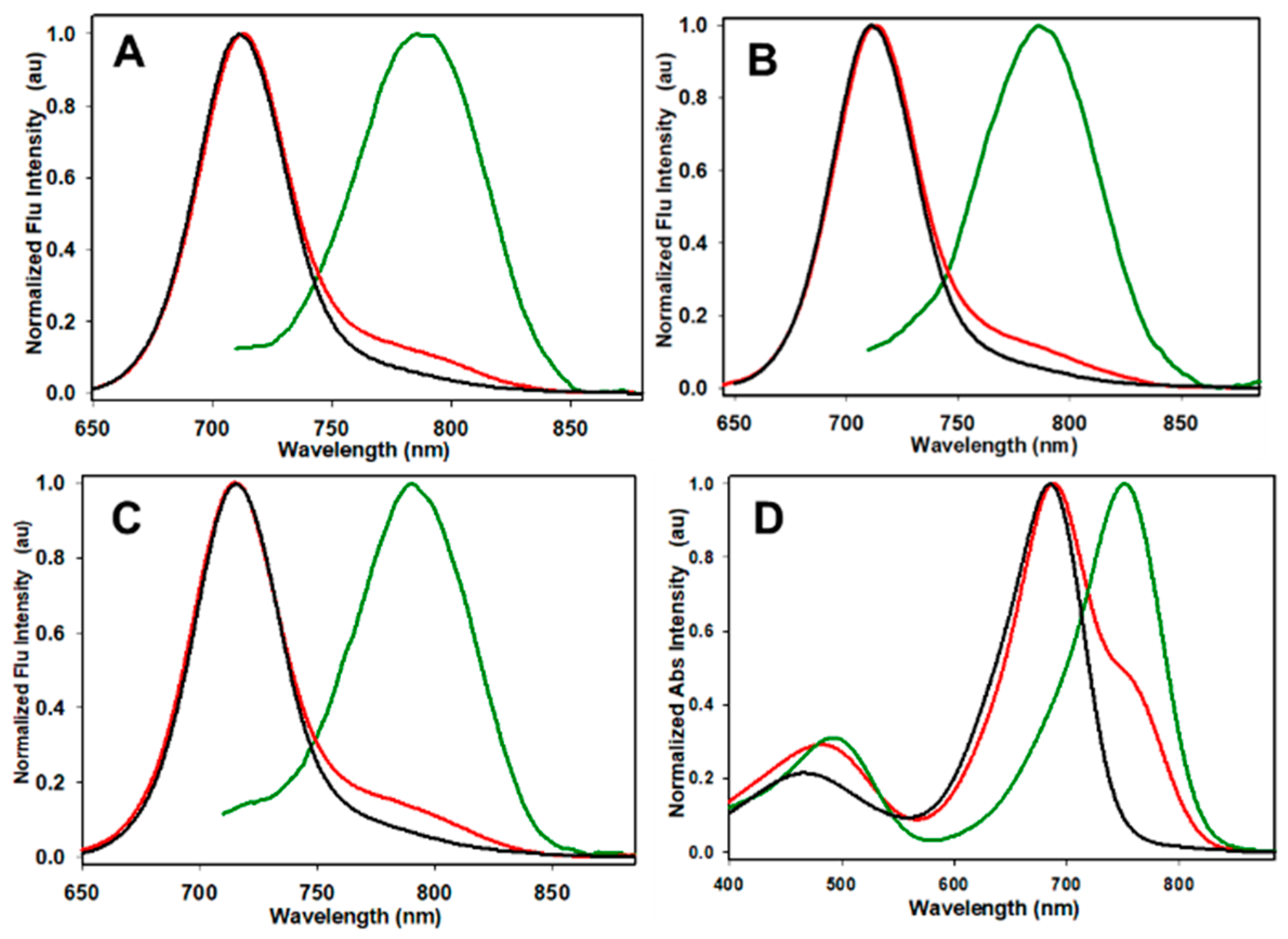


| Fluorophore Conjugate | λmax abs/nm pH 7 (pH 4) | λmax flu/nm pH 7 a (pH 4 b) | pKa c |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 751 (694) | 792 (719) | 4.5 |
| 2 | 750 (688) | 783 (719) | 4.3 |
| 3 | 754 (692) | 787 (720) | 4.1 |
| Fluorophore Conjugate | Time (h) | Pearson’s Coefficient | M1 | M2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 0.7 (±0.06) | 0.78 (±0.03) | 0.96 (±0.02) |
| 1 | 5 | 0.75 (±0.05) | 0.76 (±0.09) | 0.98 (±0.01) |
| 2 | 2 | 0.6 (±0.02) | 0.59 (±0.04) | 0.96 (±0.01) |
| 2 | 5 | 0.65 (±0.09) | 0.68 (±0.1) | 0.93 (±0.03) |
| 3 | 2 | 0.52 (±0.09) | 0.53 (±0.11) | 0.78 (±0.05) |
| 3 | 5 | 0.69 (±0.03) | 0.73 (0.08) | 0.90 (±0.02) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Booth, E.; Garre, M.; Wu, D.; Daly, H.C.; O’Shea, D.F. A NIR-Fluorochrome for Live Cell Dual Emission and Lifetime Tracking from the First Plasma Membrane Interaction to Subcellular and Extracellular Locales. Molecules 2024, 29, 2474. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112474
Booth E, Garre M, Wu D, Daly HC, O’Shea DF. A NIR-Fluorochrome for Live Cell Dual Emission and Lifetime Tracking from the First Plasma Membrane Interaction to Subcellular and Extracellular Locales. Molecules. 2024; 29(11):2474. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112474
Chicago/Turabian StyleBooth, Eden, Massimiliano Garre, Dan Wu, Harrison C. Daly, and Donal F. O’Shea. 2024. "A NIR-Fluorochrome for Live Cell Dual Emission and Lifetime Tracking from the First Plasma Membrane Interaction to Subcellular and Extracellular Locales" Molecules 29, no. 11: 2474. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112474
APA StyleBooth, E., Garre, M., Wu, D., Daly, H. C., & O’Shea, D. F. (2024). A NIR-Fluorochrome for Live Cell Dual Emission and Lifetime Tracking from the First Plasma Membrane Interaction to Subcellular and Extracellular Locales. Molecules, 29(11), 2474. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112474





