Experimental and Machine-Learning-Assisted Design of Pharmaceutically Acceptable Deep Eutectic Solvents for the Solubility Improvement of Non-Selective COX Inhibitors Ibuprofen and Ketoprofen
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
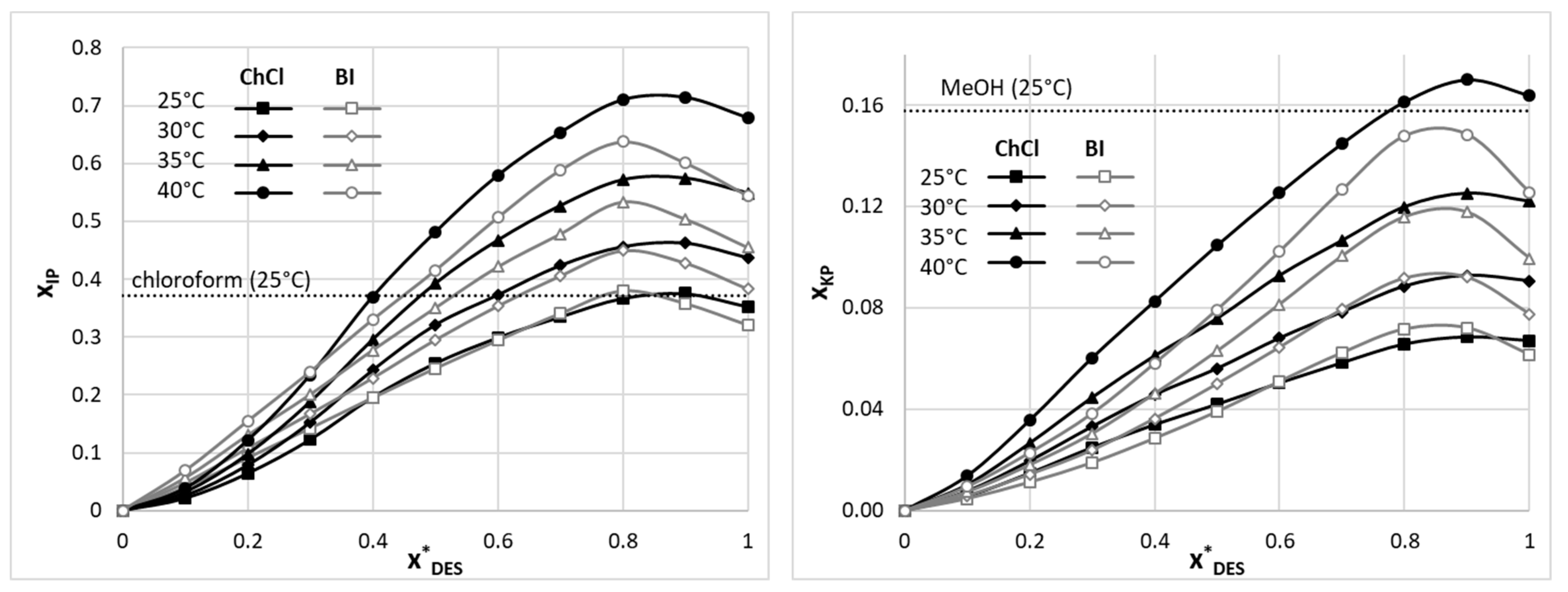
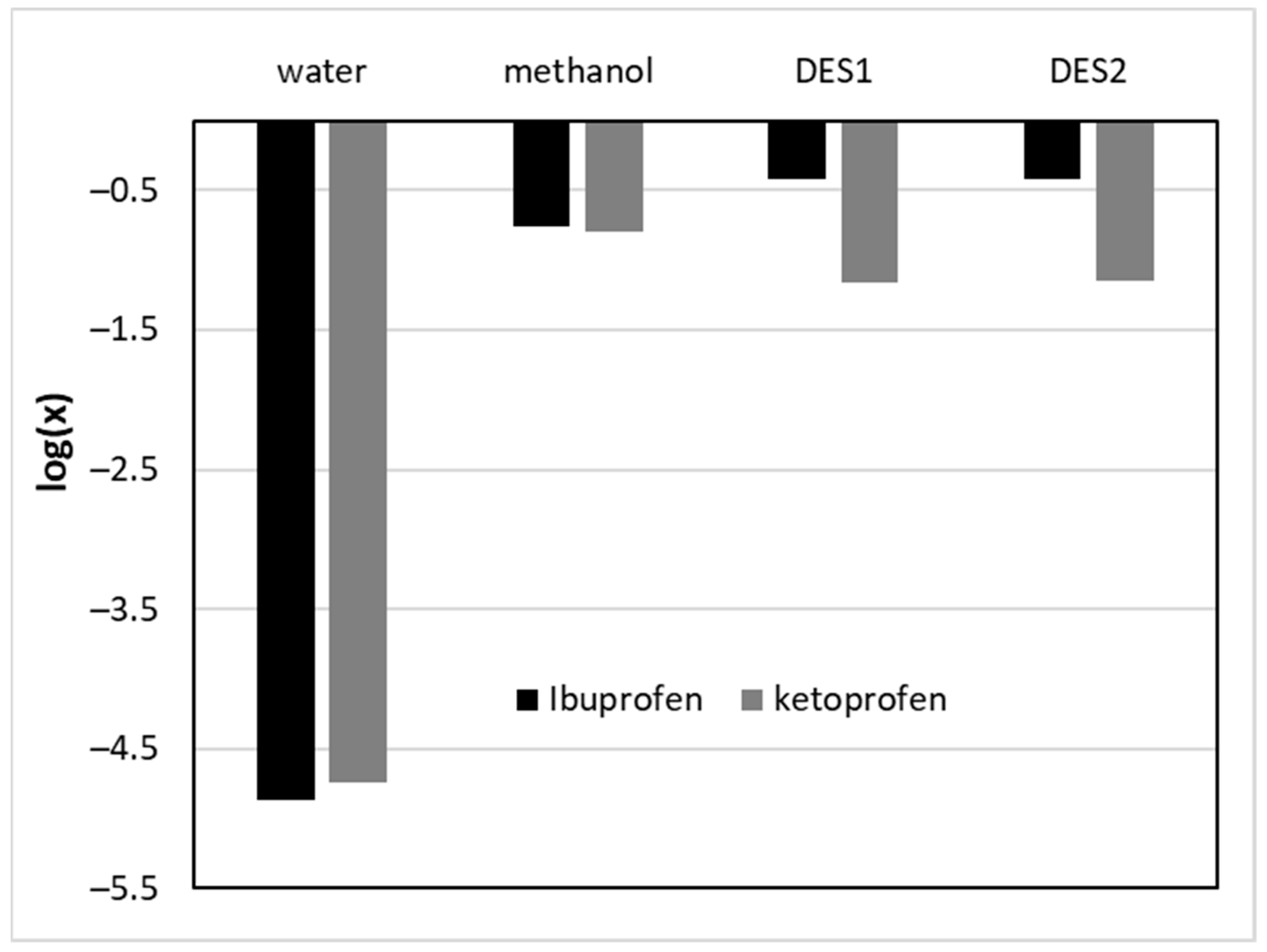
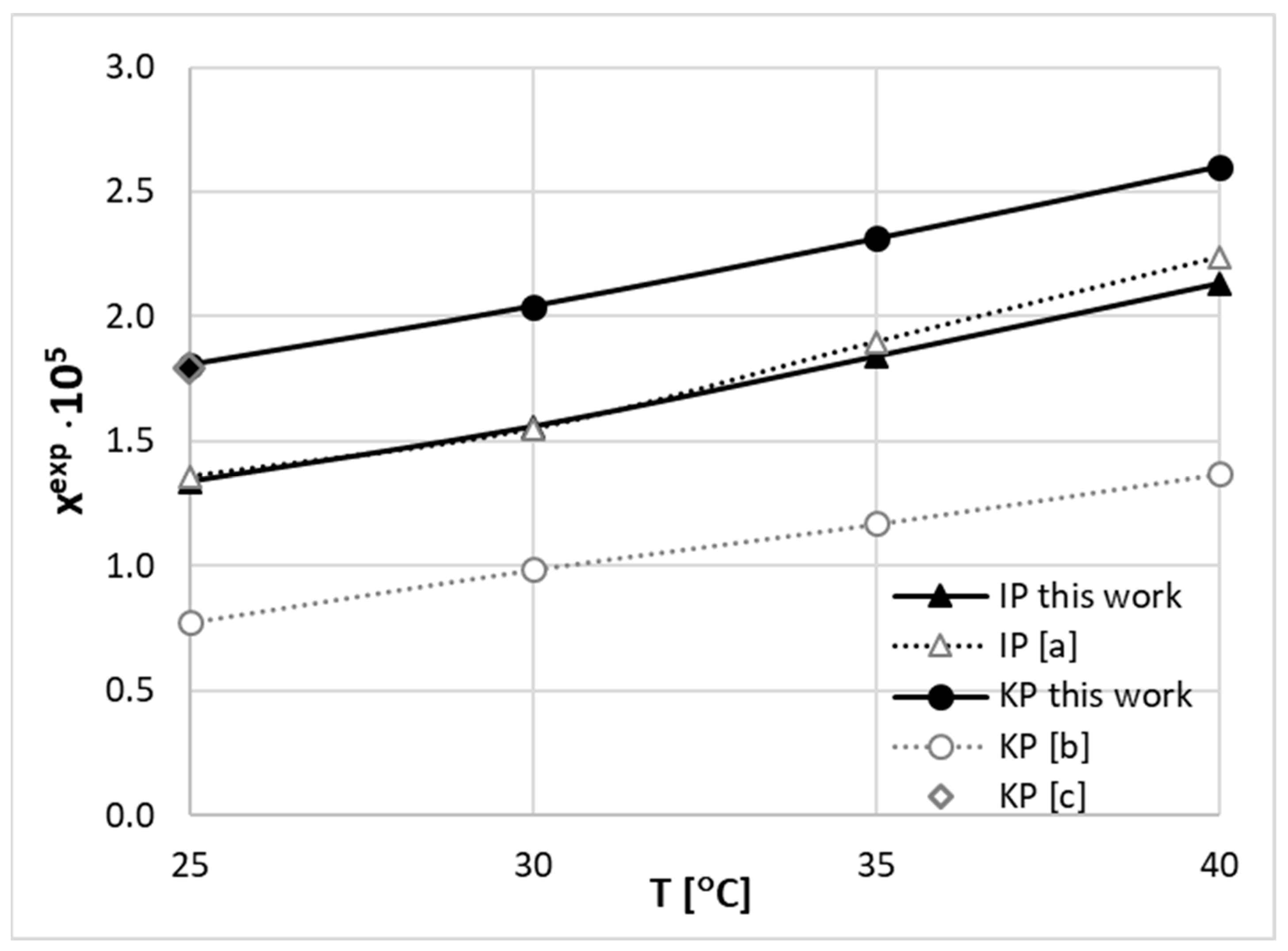
2.1. Solubility of IP and KP in DESs
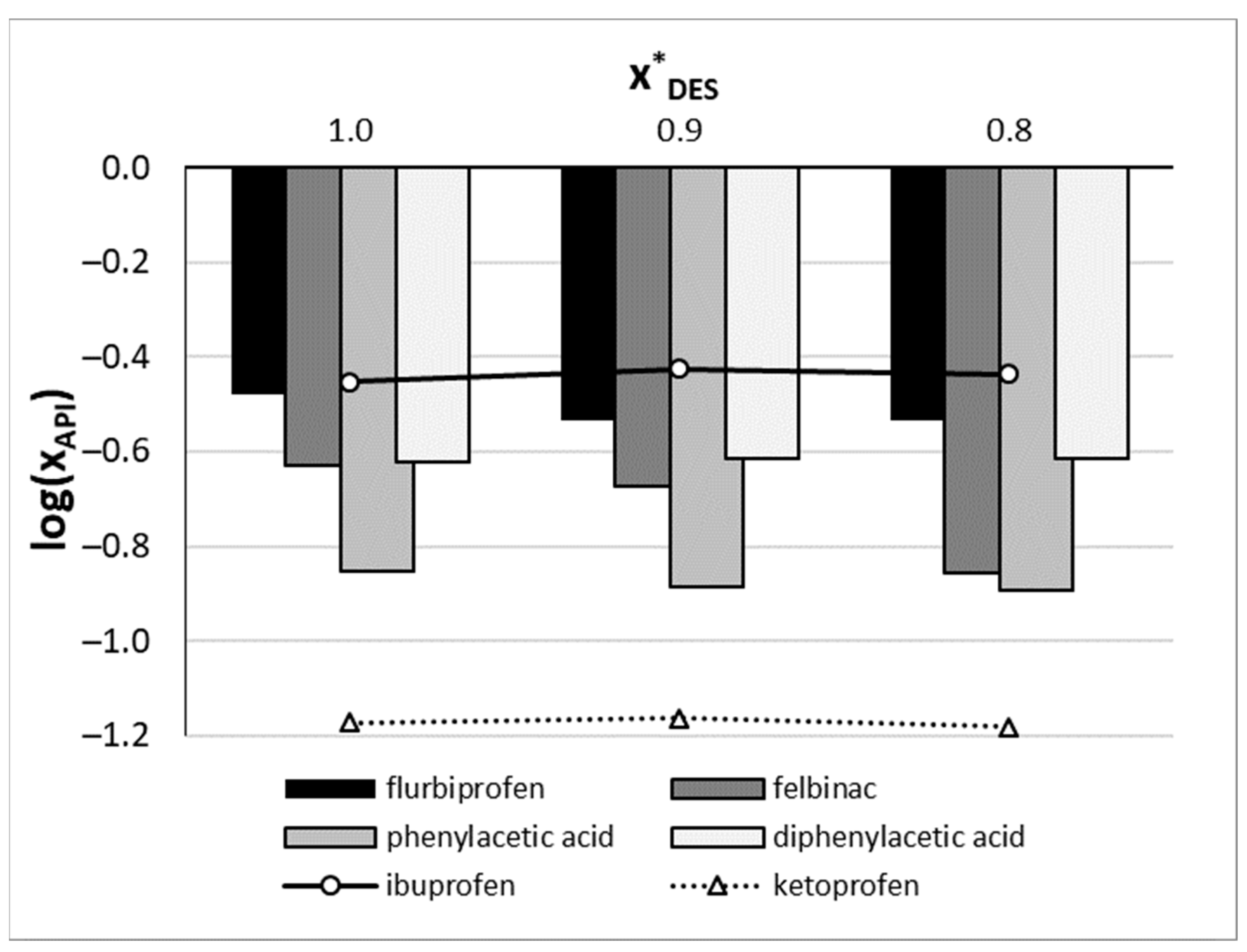
2.2. Solubility Dataset
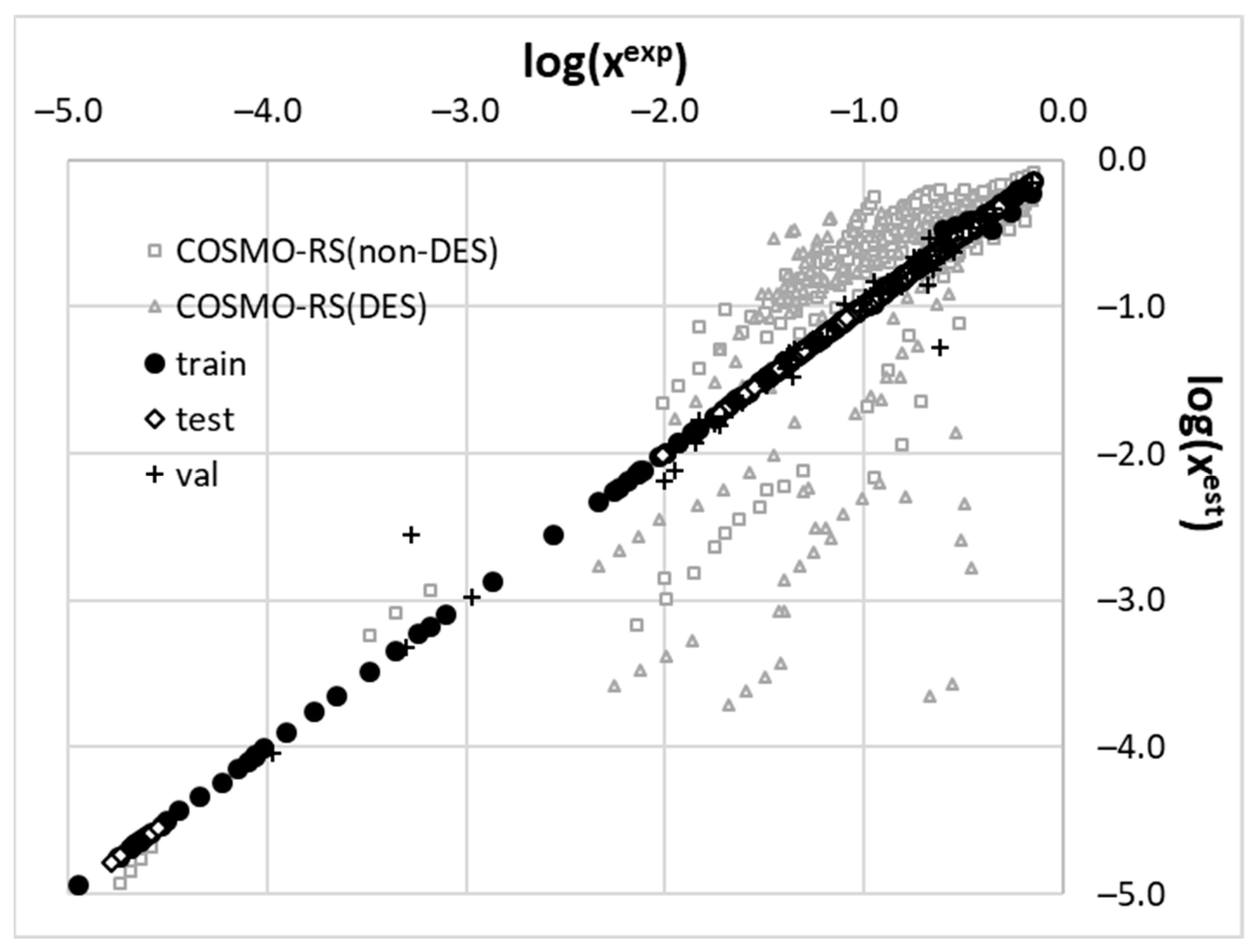
2.3. Machine Learning Model
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of the Calibration Curves
3.3. Sample Preparation and Solubility Measurements
3.4. Machine Learning Protocol
3.5. Molecular Descriptors
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moses, V.S.; Bertone, A.L. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Vet. Clin. N. Am.-Equine Pract. 2002, 18, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vane, J.R.; Botting, R.M. Mechanism of Action of Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs. Am. J. Med. 1998, 104, 2S–8S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanim, A.M.; Girgis, A.S.; Kariuki, B.M.; Samir, N.; Said, M.F.; Abdelnaser, A.; Nasr, S.; Bekheit, M.S.; Abdelhameed, M.F.; Almalki, A.J.; et al. Design and synthesis of ibuprofen-quinoline conjugates as potential anti-inflammatory and analgesic drug candidates. Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 119, 105557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maleškić Kapo, S.; Rakanović-Todić, M.; Burnazović-Ristić, L.; Kusturica, J.; Kulo Ćesić, A.; Ademović, E.; Loga-Zec, S.; Sarač-Hadžihalilović, A.; Aganović-Mušinović, I. Analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of diclofenac and ketoprofen patches in two different rat models of acute inflammation. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2023, 35, 102394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Han, Q.; Zhang, H.; Yan, Y. Evaluation of the binding interactions of p-acetylaminophenol, aspirin, ibuprofen and aminopyrine with norfloxacin from the view of antipyretic and anti-inflammatory. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 312, 113397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabré, F.; Fernández, M.F.; Calvo, L.; Ferrer, X.; García, M.L.; Mauleón, D. Analgesic, Antiinflammatory, and Antipyretic Effects of S(+)-Ketoprofen In Vivo. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1998, 38, 3S–10S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, S.S.; Girgis, A.S.; Honkanadavar, H.H.; George, R.F.; Srour, A.M. Synthesis of new ibuprofen hybrid conjugates as potential anti-inflammatory and analgesic agents. Future Med. Chem. 2020, 12, 1369–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinosa-Cano, E.; Aguilar, M.R.; Portilla, Y.; Barber, D.F.; Román, J.S. Anti-Inflammatory Polymeric Nanoparticles Based on Ketoprofen and Dexamethasone. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Næsdal, J.; Brown, K. NSAID-associated adverse effects and acid control aids to prevent them: A review of current treatment options. Drug Saf. 2006, 29, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Fan, J.; Liu, B.; Wang, L.; Peng, X. Ibuprofen-derived fluorescence inhibitor of COX-2 for breast cancer imaging, prevention and treatment. Dye. Pigment 2021, 190, 109326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Chávez, M.M.; Pineda-Urbina, K.; Pérez, D.J.; Obledo-Benicio, F.; Flores-Parra, A.; Gómez-Sandoval, Z.; Ramos-Organillo, Á. Organotin(IV) compounds derived from ibuprofen and cinnamic acids, an alternative into design of anti-inflammatory by the cyclooxygenases (COX-1 and COX-2) pathway. J. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 862, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levoin, N.; Chrétien, F.; Lapicque, F.; Chapleur, Y. Synthesis and Biological Testing of Acyl-CoA–Ketoprofen Conjugates as Selective Irreversible Inhibitors of COX-2. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2002, 10, 753–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knych, H.K.; McKemie, D.S.; Kass, P.H.; Stanley, S.D.; Blea, J. Ketoprofen in horses: Metabolism, pharmacokinetics, and effects on inflammatory biomarkers. Drug Test. Anal. 2024, 16, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaebler, A.J.; Schoretsanitis, G.; Ben Omar, N.; Haen, E.; Endres, K.; Hiemke, C.; Paulzen, M. Metamizole but not ibuprofen reduces the plasma concentration of sertraline: Implications for the concurrent treatment of pain and depression/anxiety disorders. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 87, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, S.; Mishra, M.; Salemi, M.R.; Phinney, B.S.; Newens, J.L.; Gomes, A.V. Gender-specific changes in energy metabolism and protein degradation as major pathways affected in livers of mice treated with ibuprofen. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettiol, A.; Marconi, E.; Vannacci, A.; Simonetti, M.; Magni, A.; Cricelli, C.; Lapi, F. Effectiveness of ibuprofen plus paracetamol combination on persistence of acute musculoskeletal disorders in primary care patients. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2021, 43, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iolascon, G.; Giménez, S.; Mogyorósi, D. A review of aceclofenac: Analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects on musculoskeletal disorders. J. Pain Res. 2021, 14, 3651–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, M.; Gürses, D.; Tükenmez, G. The effectiveness and safety of ibuprofen and acetylsalicylic acid in acute rheumatic fever. Pediatr. Int. 2022, 64, e15133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzeni, F.; Masala, I.F.; Bagnasco, M.; Lanata, L.; Mantelli, F.; Sarzi-Puttini, P. Comparison of Efficacy of Ketoprofen and Ibuprofen in Treating Pain in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pain Ther. 2021, 10, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.M.; Ismail, N.I.K.; Nasra, M.M.A.; El-Kamel, A.H. Repurposing ibuprofen-loaded microemulsion for the management of Alzheimer’s disease: Evidence of potential intranasal brain targeting. Drug Deliv. 2021, 28, 1188–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Tripathi, P.; Singh, S. Neuroinflammatory responses in Parkinson’s disease: Relevance of Ibuprofen in therapeutics. Inflammopharmacology 2021, 29, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, L.S.; Nóbrega, C.; Tavino, S.; Brinkhaus, M.; Matos, C.; Tomé, S.; Moreira, R.; Henriques, D.; Kaspar, B.K.; Pereira De Almeida, L. Ibuprofen enhances synaptic function and neural progenitors proliferation markers and improves neuropathology and motor coordination in Machado–Joseph disease models. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2019, 28, 3691–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varrassi, G.; Pergolizzi, J.V.; Dowling, P.; Paladini, A. Ibuprofen Safety at the Golden Anniversary: Are all NSAIDs the Same? A Narrative Review. Adv. Ther. 2020, 37, 61–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoubek, M.E.; Lucena, M.I.; Andrade, R.J.; Stephens, C. Systematic review: Ibuprofen-induced liver injury. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 51, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibraimi, Q.; Driton Selmani, D.; Arjeta Shabani, D. The safety of ketoprofen usage in different age. Int. J. Med. Healthc. 2023, 8, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Cumhur Cure, M.; Kucuk, A.; Cure, E. NSAIDs may increase the risk of thrombosis and acute renal failure in patients with COVID-19 infection. Therapie 2020, 75, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schjerning, A.M.; McGettigan, P.; Gislason, G. Cardiovascular effects and safety of (non-aspirin) NSAIDs. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, F.; Jouyban, A.; Acree, W.E. Pharmaceuticals solubility is still nowadays widely studied everywhere. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 23, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savjani, K.T.; Gajjar, A.K.; Savjani, J.K. Drug Solubility: Importance and Enhancement Techniques. ISRN Pharm. 2012, 2012, 195727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coltescu, A.R.; Butnariu, M.; Sarac, I. The importance of solubility for new drug molecules. Biomed. Pharmacol. J. 2020, 13, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xia, M.; Dai, W.; Zhu, B.; Mei, X. Improving the dissolution behaviors and bioavailability of abiraterone acetate via multicomponent crystal forms. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 614, 121460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalam, M.A.; Alshamsan, A.; Alkholief, M.; Alsarra, I.A.; Ali, R.; Haq, N.; Anwer, M.K.; Shakeel, F. Solubility Measurement and Various Solubility Parameters of Glipizide in Different Neat Solvents. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 1708–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-S.; Kim, C.-M.; Jo, A.-N.; Kim, J.-E. Studies on Preformulation and Formulation of JIN-001 Liquisolid Tablet with Enhanced Solubility. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khadka, P.; Ro, J.; Kim, H.; Kim, I.; Kim, J.T.; Kim, H.; Cho, J.M.; Yun, G.; Lee, J. Pharmaceutical particle technologies: An approach to improve drug solubility, dissolution and bioavailability. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 9, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.E. Prodrug Approaches for Enhancing the Bioavailability of Drugs with Low Solubility. Chem. Biodivers. 2009, 6, 2071–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, T.; Mehta, C.H.; Nayak, U.Y. Multiple approaches for achieving drug solubility: An in silico perspective. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 1206–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Shi, C.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, C.; Sun, C.C.; Mao, S. Designing micellar Nanocarriers with improved drug loading and stability based on solubility parameter. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 816–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipinski, C.A. Drug-like properties and the causes of poor solubility and poor permeability. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2000, 44, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, F.L.O.; Marques, M.B.D.F.; Kato, K.C.; Carneiro, G. Nanonization techniques to overcome poor water-solubility with drugs. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2020, 15, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Baidya, A.T.K.; Mathew, A.T.; Yadav, A.K.; Kumar, R. Structural modification aimed for improving solubility of lead compounds in early phase drug discovery. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2022, 56, 116614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, C.A.S.; Avdeef, A. Perspectives in solubility measurement and interpretation. ADMET DMPK 2019, 7, 88–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, S.; Dang, L.; Liu, C.; Wei, H. On the measurement of solubility. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2013, 17, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boobier, S.; Hose, D.R.J.; Blacker, A.J.; Nguyen, B.N. Machine learning with physicochemical relationships: Solubility prediction in organic solvents and water. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovrić, M.; Pavlović, K.; Žuvela, P.; Spataru, A.; Lučić, B.; Kern, R.; Wong, M.W. Machine learning in prediction of intrinsic aqueous solubility of drug-like compounds: Generalization, complexity, or predictive ability? J. Chemom. 2021, 35, e3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalani, D.V.; Nutan, B.; Kumar, A.; Singh Chandel, A.K. Bioavailability Enhancement Techniques for Poorly Aqueous Soluble Drugs and Therapeutics. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manallack, D.T.; Yuriev, E.; Chalmers, D.K. The influence and manipulation of acid/base properties in drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2018, 27, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merisko-Liversidge, E.; Liversidge, G.G. Nanosizing for oral and parenteral drug delivery: A perspective on formulating poorly-water soluble compounds using wet media milling technology. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewster, M.E.; Loftsson, T. Cyclodextrins as pharmaceutical solubilizers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 645–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korn, C.; Balbach, S. Compound selection for development—Is salt formation the ultimate answer? Experiences with an extended concept of the “100mg approach”. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 57, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seedher, N.; Kanojia, M. Co-solvent solubilization of some poorly-soluble antidiabetic drugs. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2009, 14, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahnenkamp, I.; Graubner, G.; Gmehling, J. Measurement and prediction of solubilities of active pharmaceutical ingredients. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 388, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, M.H.; Smith, R.E.; Luchtefeld, R.; Boorem, A.J.; Lou, R.; Acree, W.E. Prediction of solubility of drugs and other compounds in organic solvents. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 1500–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, M.; Cronin, M.T.D.; Enoch, S.J.; Madden, J.C.; Roberts, D.W.; Dearden, J.C. In silico prediction of aqueous solubility: The solubility challenge. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2009, 49, 2572–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosca, E.M.; Bartolucci, R.; Magni, P. Application of artificial neural networks to predict the intrinsic solubility of drug-like molecules. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.; Jia, G.z. Prediction of aqueous solubility of compounds based on neural network. Mol. Phys. 2020, 118, e1600754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesolowski, M.; Suchacz, B. Artificial Neural Networks: Theoretical Background and Pharmaceutical Applications: A Review. J. AOAC Int. 2012, 95, 652–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agatonovic-Kustrin, S.; Beresford, R. Basic concepts of artificial neural network (ANN) modeling and its application in pharmaceutical research. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2000, 22, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenoir, D.; Schramm, K.W.; Lalah, J.O. Green Chemistry: Some important forerunners and current issues. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2020, 18, 100313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopach, M.; Leahy, D.; Manley, J. The green chemistry approach to pharma manufacturing. Innov. Pharm. Technol. 2012, 43, 72–75. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, J.; Manske, C.; Randl, S. Green chemistry and sustainability metrics in the pharmaceutical manufacturing sector. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2022, 33, 100562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.; Sharma, M.; Dubey, R.; Kumari, P.; Ranjan, V.; Pandey, J. Green synthesis interventions of pharmaceutical industries for sustainable development. Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 4, 100174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSimone, J.M. Practical approaches to green solvents. Science 2002, 297, 799–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häckl, K.; Kunz, W. Some aspects of green solvents. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2018, 21, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana-Mayor, Á.; Rodríguez-Ramos, R.; Herrera-Herrera, A.V.; Socas-Rodríguez, B.; Rodríguez-Delgado, M.Á. Deep eutectic solvents. The new generation of green solvents in analytical chemistry. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 134, 116108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanda, H.; Dai, Y.; Wilson, E.G.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Green solvents from ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents to natural deep eutectic solvents. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2018, 21, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruß, C.; König, B. Low melting mixtures in organic synthesis—An alternative to ionic liquids? Green Chem. 2012, 14, 2969–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, M.; Van Den Bruinhorst, A.; Kroon, M.C. Minireview. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2013, 11, 3074–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, K.A.; Sadeghi, R. Physicochemical properties of deep eutectic solvents: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 360, 119524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, A.; Craveiro, R.; Aroso, I.; Martins, M.; Reis, R.L.; Duarte, A.R.C. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents–Solvents for the 21st Century. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espino, M.; de los Ángeles Fernández, M.; Gomez, F.J.V.; Silva, M.F. Natural designer solvents for greening analytical chemistry. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 76, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Shi, M.; Zhang, P.; Tu, Z.; Hu, X.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y. Tuning the composition of deep eutectic solvents consisting of tetrabutylammonium chloride and n-decanoic acid for adjustable separation of ethylene and ethane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 298, 121680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Tao, X.; Jiang, S.; Gao, N.; Sun, Z. Tuning thermodynamic properties of deep eutectic solvents for achieving highly efficient photothermal sensor. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 308, 113163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomba, L.; Ribate, M.P.; Zaragoza, E.; Concha, J.; Garralaga, M.P.; Errazquin, D.; García, C.B.; Giner, B. Deep Eutectic Solvents: Are They Safe? Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Morais, P.; Gonçalves, F.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Ventura, S.P.M. Ecotoxicity of Cholinium-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 3398–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macário, I.P.E.; Jesus, F.; Pereira, J.L.; Ventura, S.P.M.; Gonçalves, A.M.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Gonçalves, F.J.M. Unraveling the ecotoxicity of deep eutectic solvents using the mixture toxicity theory. Chemosphere 2018, 212, 890–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nejrotti, S.; Antenucci, A.; Pontremoli, C.; Gontrani, L.; Barbero, N.; Carbone, M.; Bonomo, M. Critical Assessment of the Sustainability of Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Case Study on Six Choline Chloride-Based Mixtures. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 47449–47461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedro, S.N.; Freire, C.S.R.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Freire, M.G. Deep Eutectic Solvents and Pharmaceuticals. Encyclopedia 2021, 1, 942–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cysewski, P.; Jeliński, T.; Przybyłek, M. Experimental and Theoretical Insights into the Intermolecular Interactions in Saturated Systems of Dapsone in Conventional and Deep Eutectic Solvents. Molecules 2024, 29, 1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, N.R.; Spelbos, V.S.; Witkamp, G.J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Solubility and stability of some pharmaceuticals in natural deep eutectic solvents-based formulations. Molecules 2021, 26, 2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzo, G.C.; Pezzini, B.R.; Stulzer, H.K. Eutectic mixtures as an approach to enhance solubility, dissolution rate and oral bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 588, 119741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapre, S.; Palakurthi, S.S.; Jain, A.; Palakurthi, S. DES-igning the future of drug delivery: A journey from fundamentals to drug delivery applications. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 400, 124517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeliński, T.; Przybyłek, M.; Mianowana, M.; Misiak, K.; Cysewski, P. Deep Eutectic Solvents as Agents for Improving the Solubility of Edaravone: Experimental and Theoretical Considerations. Molecules 2024, 29, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, A.R.C.; Ferreira, A.S.D.; Barreiros, S.; Cabrita, E.; Reis, R.L.; Paiva, A. A comparison between pure active pharmaceutical ingredients and therapeutic deep eutectic solvents: Solubility and permeability studies. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 114, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.-H.; Augis, L.; Fourmentin, S.; Barratt, G.; Legrand, F.-X. Deep Eutectic Solvents for Innovative Pharmaceutical Formulations. In Deep Eutectic Solvents for Medicine, Gas Solubilization and Extraction of Natural Substances; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 41–102. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Yang, Q.; Yang, G. Deep eutectic solvents: Recent advances in fabrication approaches and pharmaceutical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 622, 121811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emami, S.; Shayanfar, A. Deep eutectic solvents for pharmaceutical formulation and drug delivery applications. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2020, 25, 779–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedro, S.N.; Freire, M.G.; Freire, C.S.R.; Silvestre, A.J.D. Deep eutectic solvents comprising active pharmaceutical ingredients in the development of drug delivery systems. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomba, L.; Garralaga, M.P.; Werner, Á.; Giner, B.; Baptista, P.M.; Sánchez-Romero, N. Ibuprofen solubility and cytotoxic study of deep eutectic solvents formed by xylitol, choline chloride and water. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 82, 104327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinet, Y.; Paccou, L.; Hédoux, A. Analysis of xylitol—Citric acid system forming deep eutectic solvent: Application for dissolving poorly water-soluble drugs. A combination of calorimetric and Raman investigations. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 318, 114317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roda, A.; Paiva, A.; Duarte, A.R.C. Therapeutic Liquid Formulations Based on Low Transition Temperature Mixtures for the Incorporation of Anti-Inflammatory Drugs. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, O.S.; Bowron, D.T.; Edler, K.J.; Hammond, S.; Edler, K.J.; Bowron, D.T. The Effect of Water upon Deep Eutectic Solvent Nanostructure: An Unusual Transition from Ionic Mixture to Aqueous Solution. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 9782–9785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriele, F.; Chiarini, M.; Germani, R.; Tiecco, M.; Spreti, N. Effect of water addition on choline chloride/glycol deep eutectic solvents: Characterization of their structural and physicochemical properties. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 291, 111301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracin, S.; Rasmuson, Å.C. Solubility of Phenylacetic Acid, p -Hydroxyphenylacetic Acid, p -Aminophenylacetic Acid, p -Hydroxybenzoic Acid, and Ibuprofen in Pure Solvents. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2002, 47, 1379–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzón, L.C.; Martínez, F. Temperature dependence of solubility for ibuprofen in some organic and aqueous solvents. J. Solution Chem. 2004, 33, 1379–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, R.; Verma, V.; Sadeghi, M.; Rasmuson, Å.C. Ketoprofen Solubility in Pure Organic Solvents Using In Situ FTIR and UV–Vis and Analysis of Solution Thermodynamics. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2021, 25, 2403–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Song, Z.; Wang, J.; Dong, Y.; Wu, M. Solubilities of Ibuprofen in Different Pure Solvents. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2010, 55, 5283–5285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, D.P.; Manrique, Y.J.; Martínez, F. Thermodynamic study of the solubility of ibuprofen and naproxen in some ethanol+propylene glycol mixtures. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2007, 262, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, J.; Manrique, F. Solubility of Ibuprofen in Some Ethanol + Water Cosolvent Mixtures at Several Temperatures. Lat. Am. J. Pharm. 2007, 26, 344–354. [Google Scholar]
- Domańska, U.; Pobudkowska, A.; Pelczarska, A.; Gierycz, P. p K a and Solubility of Drugs in Water, Ethanol, and 1-Octanol. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 8941–8947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippa, M.A.; Gasull, E.I. Ibuprofen solubility in pure organic solvents and aqueous mixtures of cosolvents: Interactions and thermodynamic parameters relating to the solvation process. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2013, 354, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stovall, D.M.; Givens, C.; Keown, S.; Hoover, K.R.; Rodriguez, E.; Acree, W.E.; Abraham, M.H. Solubility of crystalline nonelectrolyte solutes in organic solvents: Mathematical correlation of ibuprofen solubilities with the Abraham solvation parameter model. Phys. Chem. Liq. 2005, 43, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragón, D.M.; Rosas, J.E.; Martínez, F. Thermodynamic study of the solubility of ibuprofen in acetone and dichloromethane. Brazilian J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 46, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manrique, Y.J.; Pacheco, D.P.; Martínez, F. Thermodynamics of Mixing and Solvation of Ibuprofen and Naproxen in Propylene Glycol + Water Cosolvent Mixtures. J. Solution Chem. 2008, 37, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, D.M.; Muñoz, M.M.; Rodríguez, C.J.; Cárdenas, Z.J.; Martínez, F. Solubility and preferential solvation of some non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in methanol + water mixtures at 298.15 K. Phys. Chem. Liq. 2016, 54, 686–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Wang, J. Measurement and correlation for solubility of dexibuprofen in different solvents from 263.15 to 293.15K. Thermochim. Acta 2012, 540, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gantiva, M.; Yurquina, A.; Martínez, F. Solution Thermodynamics of Ketoprofen in Ethanol + Water Cosolvent Mixtures. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2010, 55, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gantiva, M.; Martínez, F. Thermodynamic analysis of the solubility of ketoprofen in some propylene glycol+water cosolvent mixtures. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2010, 293, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippa, M.A.; Melo, G.M.; Gasull, E.I. Ketoprofen solubility in organic solvents and aqueous co-solvent systems: Interactions and thermodynamic parameters of solvation. J. Pharm. Chem. Biol. Sci. 2015, 3, 440–453. [Google Scholar]
- Yalkowsky, S.H.; Valvani, S.C.; Roseman, T.J. Solubility and Partitioning VI: Octanol Solubility and Octanol–Water Partition Coefficients. J. Pharm. Sci. 1983, 72, 866–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouyban, A. Handbook of Solubility Data for Pharmaceuticals; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; ISBN 9781439804889. [Google Scholar]
- Kurkov, S.V.; Perlovich, G.L. Thermodynamic studies of Fenbufen, Diflunisal, and Flurbiprofen: Sublimation, solution and solvation of biphenyl substituted drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 357, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybyłek, M.; Recki, Ł.; Mroczyńska, K.; Jeliński, T.; Cysewski, P. Experimental and theoretical solubility advantage screening of bi-component solid curcumin formulations. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 50, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeliński, T.; Przybyłek, M.; Cysewski, P. Solubility advantage of sulfanilamide and sulfacetamide in natural deep eutectic systems: Experimental and theoretical investigations. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2019, 45, 1120–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeliński, T.; Stasiak, D.; Kosmalski, T.; Cysewski, P. Experimental and theoretical study on theobromine solubility enhancement in binary aqueous solutions and ternary designed solvents. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cysewski, P.; Jeliński, T.; Przybyłek, M. Application of COSMO-RS-DARE as a Tool for Testing Consistency of Solubility Data: Case of Coumarin in Neat Alcohols. Molecules 2022, 27, 5274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeliński, T.; Przybyłek, M.; Różalski, R.; Cysewski, P. Solubility of dapsone in deep eutectic solvents: Experimental analysis, molecular insights and machine learning predictions. Polym. Med. 2024; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cysewski, P.; Jeliński, T.; Przybyłek, M. Finding the Right Solvent: A Novel Screening Protocol for Identifying Environmentally Friendly and Cost-Effective Options for Benzenesulfonamide. Molecules 2023, 28, 5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiba, T.; Sano, S.; Yanase, T.; Ohta, T.; Koyama, M. Optuna: A Next-generation Hyperparameter Optimization Framework. In Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining 2019, Anchorage, AK, USA, 4–8 August 2019; pp. 2623–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klamt, A.; Schüürmann, G. COSMO: A new approach to dielectric screening in solvents with explicit expressions for the screening energy and its gradient. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1993, 2, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cysewski, P.; Przybyłek, M.; Jeliński, T. Predicting sulfanilamide solubility in the binary mixtures using a reference solvent approach. Polym. Med. 2024; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cysewski, P.; Przybyłek, M.; Jeliński, T. Intermolecular Interactions as a Measure of Dapsone Solubility in Neat Solvents and Binary Solvent Mixtures. Materials 2023, 16, 6336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybyłek, M.; Jeliński, T.; Mianowana, M.; Misiak, K.; Cysewski, P. Exploring the Solubility Limits of Edaravone in Neat Solvents and Binary Mixtures: Experimental and Machine Learning Study. Molecules 2023, 28, 6877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cysewski, P.; Jeliński, T.; Przybyłek, M. Intermolecular Interactions of Edaravone in Aqueous Solutions of Ethaline and Glyceline Inferred from Experiments and Quantum Chemistry Computations. Molecules 2023, 28, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acree, W.; Chickos, J.S. Phase Transition Enthalpy Measurements of Organic and Organometallic Compounds and Ionic Liquids. Sublimation, Vaporization, and Fusion Enthalpies from 1880 to 2015. Part 2. C11–C192. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 2017, 46, 013104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dassault Systèmes. COSMOtherm; Version 24.0.0; Biovia: San Diego, CA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Dassault Systèmes. COSMOconf; Version 24.0.0; Dassault Systèmes, Biovia: San Diego, CA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cysewski, P.; Jeliński, T.; Przybyłek, M.; Mai, A.; Kułak, J. Experimental and Machine-Learning-Assisted Design of Pharmaceutically Acceptable Deep Eutectic Solvents for the Solubility Improvement of Non-Selective COX Inhibitors Ibuprofen and Ketoprofen. Molecules 2024, 29, 2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29102296
Cysewski P, Jeliński T, Przybyłek M, Mai A, Kułak J. Experimental and Machine-Learning-Assisted Design of Pharmaceutically Acceptable Deep Eutectic Solvents for the Solubility Improvement of Non-Selective COX Inhibitors Ibuprofen and Ketoprofen. Molecules. 2024; 29(10):2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29102296
Chicago/Turabian StyleCysewski, Piotr, Tomasz Jeliński, Maciej Przybyłek, Anna Mai, and Julia Kułak. 2024. "Experimental and Machine-Learning-Assisted Design of Pharmaceutically Acceptable Deep Eutectic Solvents for the Solubility Improvement of Non-Selective COX Inhibitors Ibuprofen and Ketoprofen" Molecules 29, no. 10: 2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29102296
APA StyleCysewski, P., Jeliński, T., Przybyłek, M., Mai, A., & Kułak, J. (2024). Experimental and Machine-Learning-Assisted Design of Pharmaceutically Acceptable Deep Eutectic Solvents for the Solubility Improvement of Non-Selective COX Inhibitors Ibuprofen and Ketoprofen. Molecules, 29(10), 2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29102296







