Targeted Delivery of Arctigenin Using Sialic Acid Conjugate-Modified Liposomes for the Treatment of Breast Cancer
Abstract
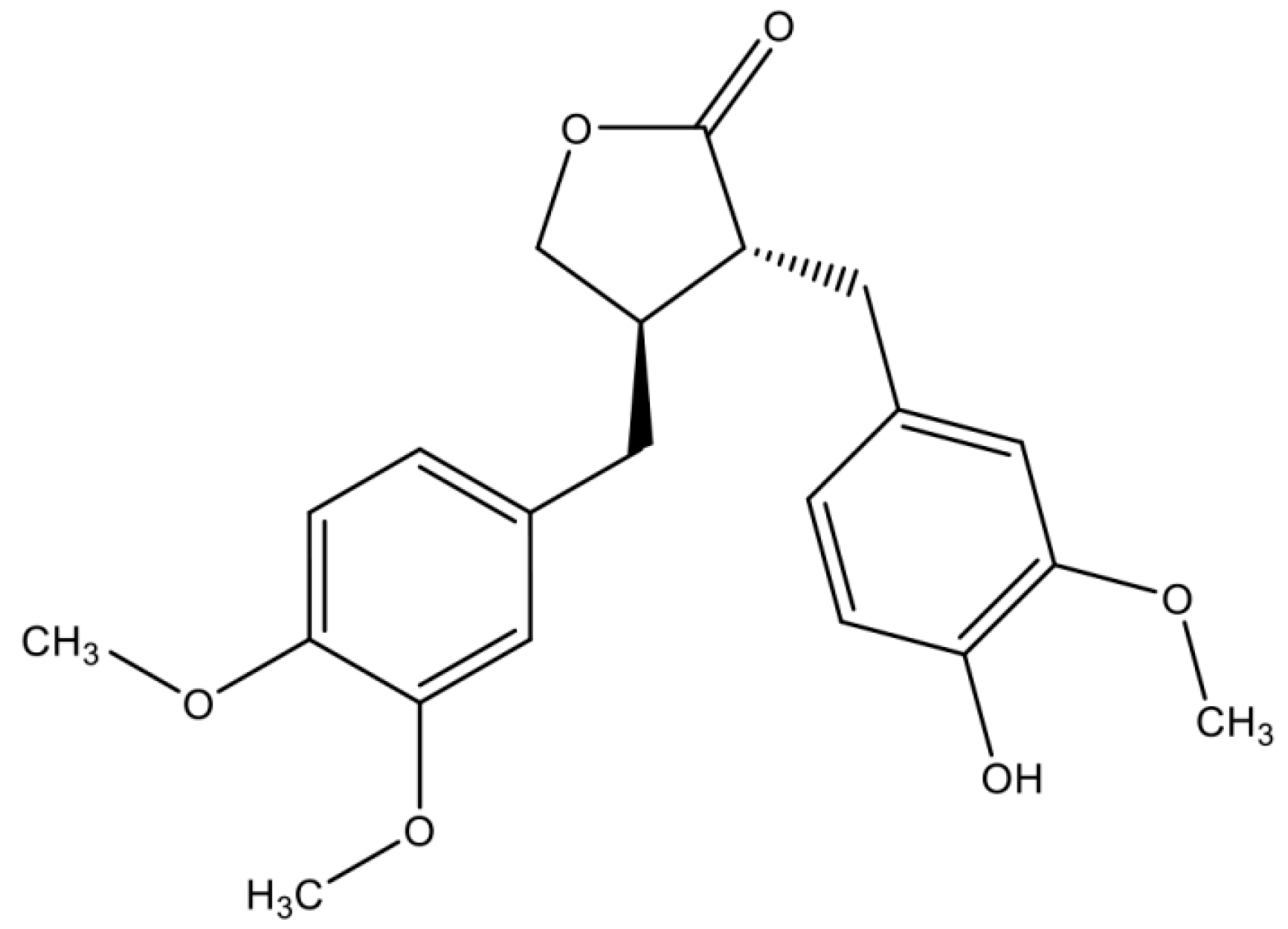
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Preparation and Formulation Optimization of ATG@Lip
2.1.1. Preparation Method
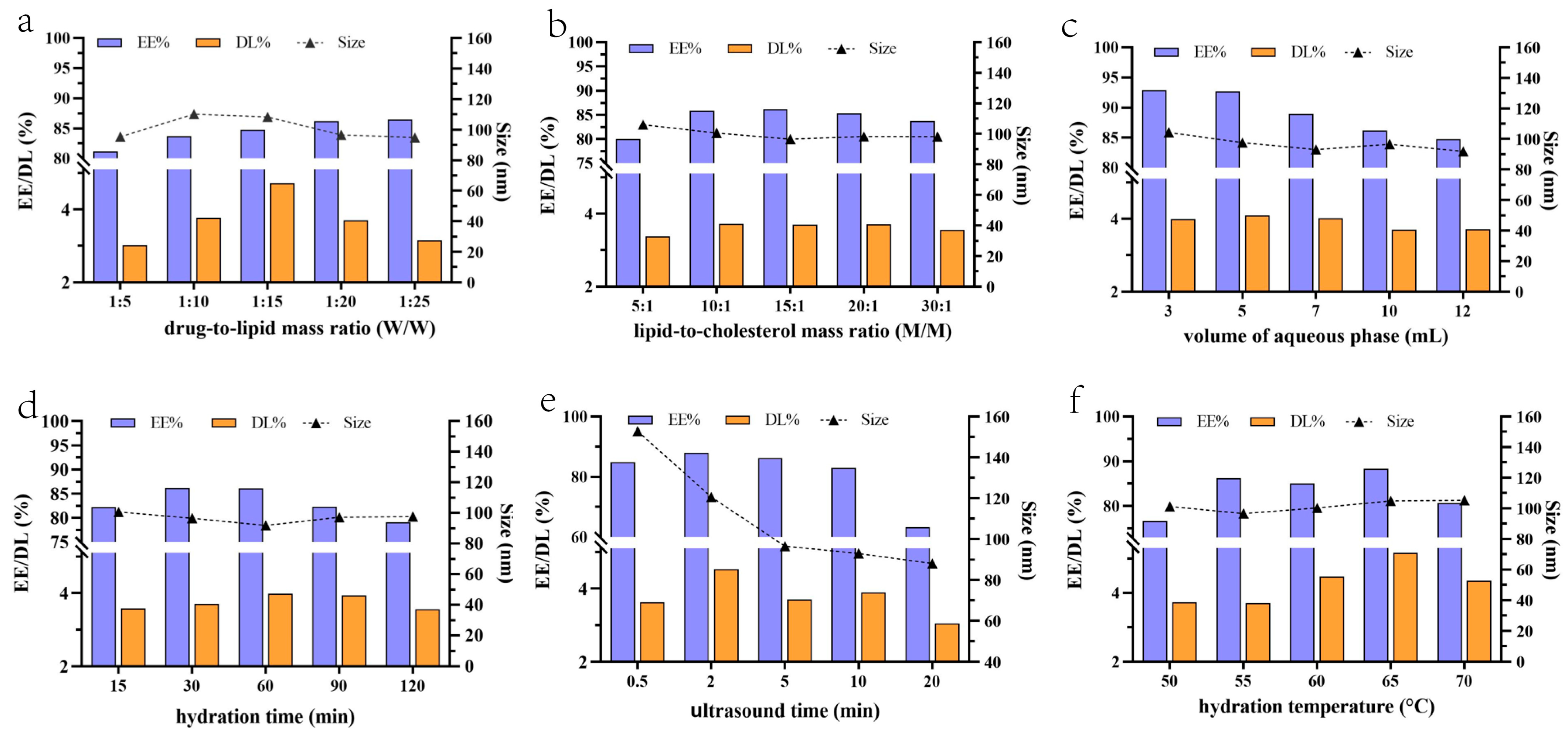
2.1.2. Optimization of Prescription by Single-Factor Experiments
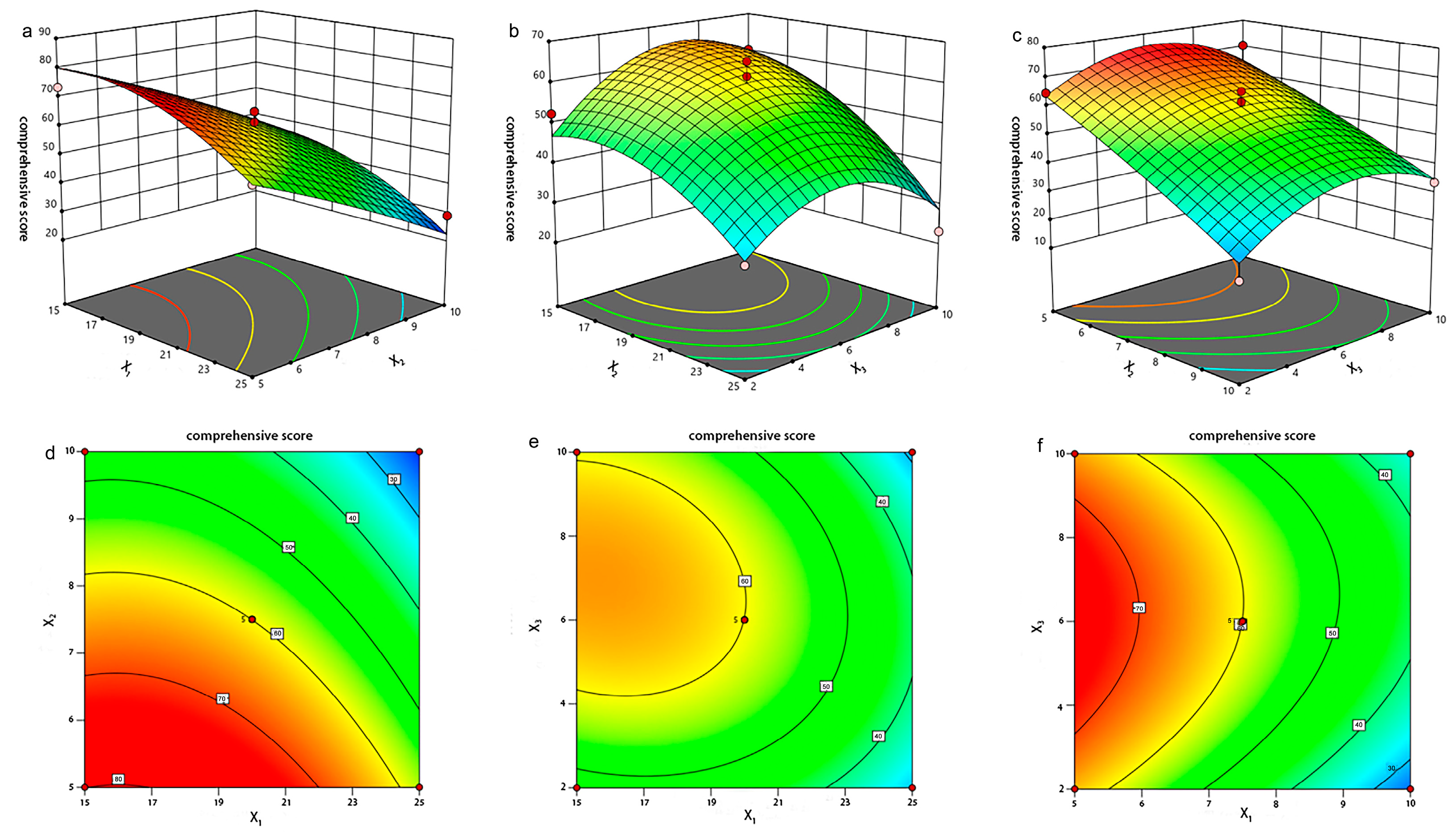
2.1.3. Optimization of Prescription by Box–Behnken Design
2.2. SA-ODA Toxicity Assay and ATG@SA-Lip Preparation
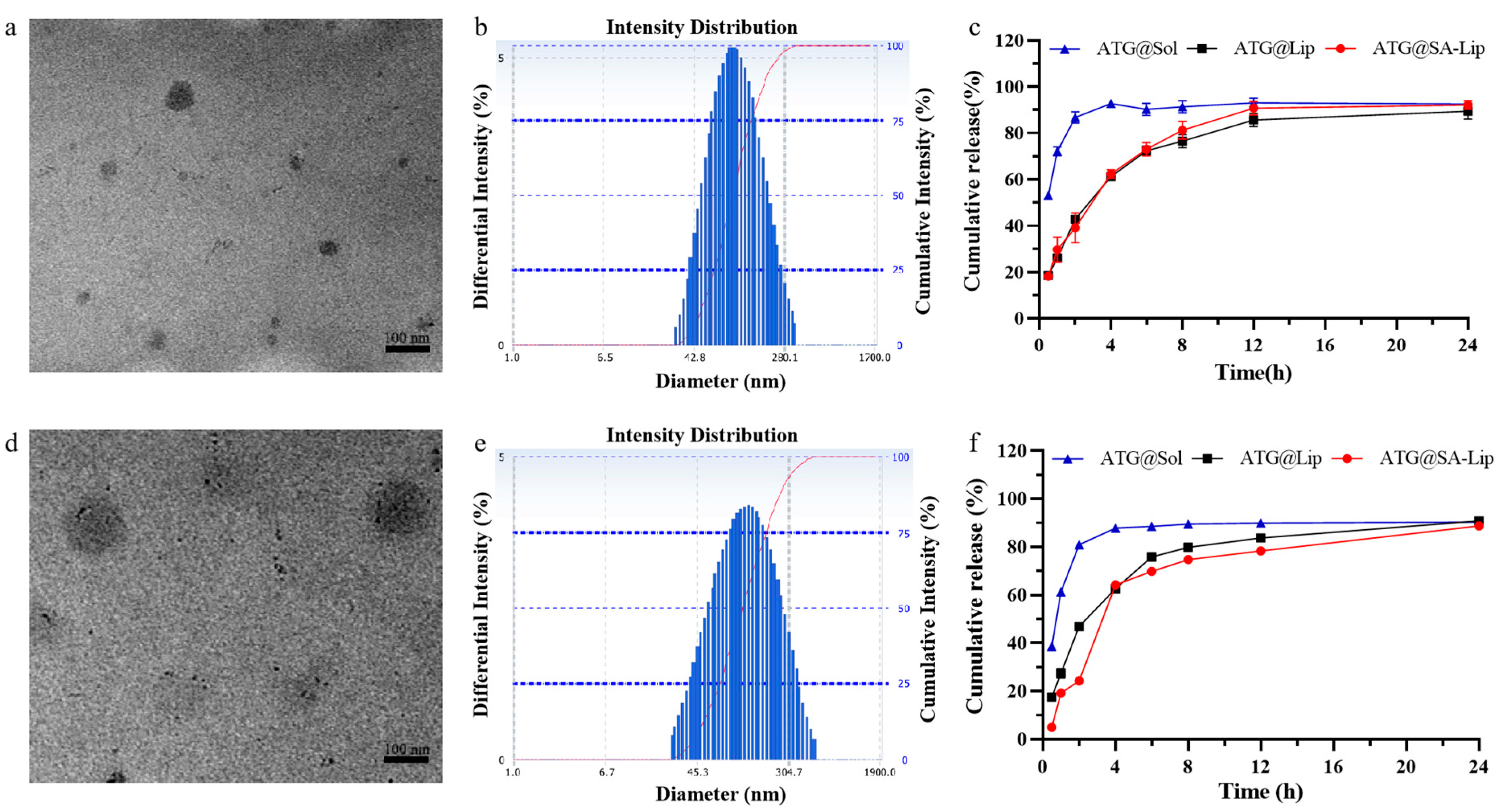
2.3. Characterization of Nanoliposomes
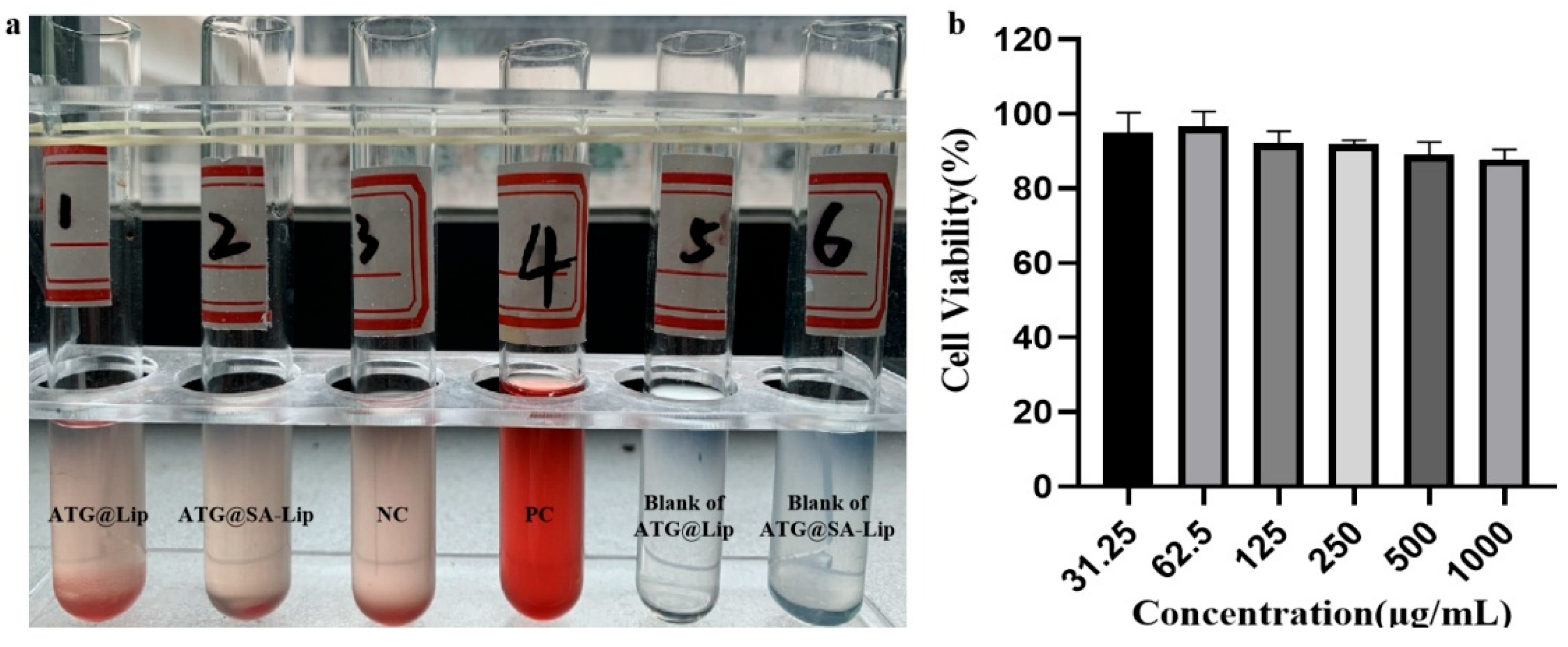
2.4. Evaluation of Biosafety
2.5. Cellular Uptake of ATG@Lip and ATG@SA-Lip
2.6. Cytotoxicity Studies of ATG@Lip and ATG@SA-Lip
2.7. Evaluation of Antitumor Activity and Toxicity In Vivo
2.8. Serum Biochemistry in Mice
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Cell Cultures and Animal Model
3.3. Preparation and Optimization of Nanoliposome and SA-Functionalized Nanoliposome Formulation
3.4. Characterization of Nanoliposomes
3.5. Evaluation of Cytotoxicity with CCK-8
3.6. Evaluation of Biosafety
3.7. Colony-Forming Experiment
3.8. Cellular Uptake of ATG@Lip and ATG@SA-Lip
3.9. Antitumor Activity and Toxicity Evaluation
3.10. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Xiang, C.; Feng, C.; Fan, C.; Liu, M.; Lu, H.; Su, H.; Zhou, Y.; Qi, Q.; et al. Identification of phosphodiesterase-4 as the therapeutic target of arctigenin in alleviating psoriatic skin inflammation. J. Adv. Res. 2021, 33, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Yang, M.; Zuo, Z. Overview of the anti-inflammatory effects, pharmacokinetic properties and clinical efficacies of arctigenin and arctiin from Arctium lappa L. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 787–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Lee, K.; Deng, Y.; Ma, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Wei, C.; Yang, S.; Wang, T.; Wong, N.J.; et al. Arctigenin attenuates diabetic kidney disease through the activation of PP2A in podocytes. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Fan, Q.; Cai, T.; Huang, W.; Xie, X.; Wen, Y.; Shi, Z. Molecular mechanisms of the action of Arctigenin in cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabgah, A.G.; Suksatan, W.; Achmad, M.H.; Bokov, D.O.; Abdelbasset, W.K.; Ezzatifar, F.; Hemmati, S.; Mohammadi, H.; Soleimani, D.; Jadidi-Niaragh, F.; et al. Arctigenin, an antitumor agent; a cutting-edge topic and up-to-the-minute approach in cancer treatment. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 909, 174419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Zhao, L.; Guo, X.; Fang, R.; Zhang, H.; Dong, G.; Fu, J.; Yan, F.; Zhang, J.; Ning, Z.; et al. Arctigenin Attenuates Breast Cancer Progression through Decreasing GM-CSF/TSLP/STAT3/β-Catenin Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.; Wang, F.; Luo, H.; Liu, H. Arctigenin inhibits human breast cancer cell proliferation, migratory and invasive abilities and epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting 4EBP1. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 21, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Liu, J.; Hong, W.; Fei, X.; Liu, R. Arctigenin Inhibits Glioblastoma Proliferation through the AKT/mTOR Pathway and Induces Autophagy. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 3542613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Tan, Y.J.; Lu, Z.Z.; Li, B.B.; Sun, C.H.; Li, T.; Zhao, L.L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, G.M.; Yao, J.C.; et al. Arctigenin Inhibits Liver Cancer Tumorigenesis by Inhibiting Gankyrin Expression via C/EBPα and PPARα. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naoe, A.; Tsuchiya, T.; Kondo, Y.; Uga, N.; Watanabe, S.; Yasui, T.; Hara, F.; Suzuki, T. Arctigenin induces apoptosis in human hepatoblastoma cells. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2019, 35, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, S.; Lv, C.; Tao, Y.; Miao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Sun, D.; Yun, X.; Xia, Y.; Wei, Z.; et al. Arctigenin disrupts NLRP3 inflammasome assembly in colonic macrophages via downregulating fatty acid oxidation to prevent colitis-associated cancer. Cancer Lett. 2020, 491, 162–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Ge, L.; Liu, T.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, L. The therapeutic potential of arctigenin against multiple human diseases: A mechanistic review. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2023, 110, 154647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Scheuer, C.; Feng, D.; Menger, M.D.; Laschke, M.W. Inhibition of angiogenesis: A novel antitumor mechanism of the herbal compound arctigenin. Anticancer Drugs 2013, 24, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mottaghi, S.; Abbaszadeh, H. A comprehensive mechanistic insight into the dietary and estrogenic lignans, arctigenin and sesamin as potential anticarcinogenic and anticancer agents. Current status, challenges, and future perspectives. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 7301–7318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.G.; Lee, K.S.; Nam, K.S. Arctigenin-mediated cell death of SK-BR-3 cells is caused by HER2 inhibition and autophagy-linked apoptosis. Pharmacol. Rep. 2021, 73, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Shen, X.B.; Yuan, P.C.; Shao, T.L.; Wang, G.D.; Liu, X.P. Arctigenin inhibits proliferation of ER-positive breast cancer cells through cell cycle arrest mediated by GSK3-dependent cyclin D1 degradation. Life Sci. 2020, 256, 117983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medras, Z.J.H.; Mostafa, Y.M.; Ahmed, A.A.M.; El-Sayed, N.M. Arctigenin improves neuropathy via ameliorating apoptosis and modulating autophagy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2023, 29, 3068–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Lina, L.; Xu, L.; Yang, Z.; Qian, Z.; Zhou, J.; Suoni, L. Arctigenin enhances the sensitivity of cisplatin resistant colorectal cancer cell by activating autophagy. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 520, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraya, Y.S.; Wong, K.K.; Yaacob, N.S. The Immunomodulatory Potential of Selected Bioactive Plant-Based Compounds in Breast Cancer: A Review. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 770–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahednezhad, F.; Saadat, M.; Valizadeh, H.; Zakeri-Milani, P.; Baradaran, B. Liposome and immune system interplay: Challenges and potentials. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2019, 305, 194–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Dhawan, V.; Holm, R.; Nagarsenker, M.S.; Perrie, Y. Liposomes: Advancements and innovation in the manufacturing process. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 154–155, 102–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, D.; Cavaco-Paulo, A.; Nogueira, E. Design of liposomes as drug delivery system for therapeutic applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 601, 120571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steichen, S.D.; Caldorera-Moore, M.; Peppas, N.A. A review of current nanoparticle and targeting moieties for the delivery of cancer therapeutics. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. Off. J. Eur. Fed. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 48, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Du, C.; Guo, N.; Teng, Y.; Meng, X.; Sun, H.; Li, S.; Yu, P.; Galons, H. Composition design and medical application of liposomes. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 164, 640–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Fan, Z.; Yan, X.-Y.; Gao, X.; Lai, X.-X.; Song, Y.-Z.; Liu, X.-R.; Deng, Y.-H. Sialic acid binding receptors-impressive targets for tumor treatment. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2021, 56, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Schauer, R.; Kamerling, J.P. Exploration of the Sialic Acid World. Adv. Carbohydr. Chem. Biochem. 2018, 75, 1–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Yang, G.; Guan, F. Biological Functions and Analytical Strategies of Sialic Acids in Tumor. Cells 2020, 9, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanczak, M.A.; Siddiqui, S.S.; Trefny, M.P.; Thommen, D.S.; Boligan, K.F.; von Gunten, S.; Tzankov, A.; Tietze, L.; Lardinois, D.; Heinzelmann-Schwarz, V.; et al. Self-associated molecular patterns mediate cancer immune evasion by engaging Siglecs on T cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 4912–4923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, O.M.; Läubli, H. Sialic acids in cancer biology and immunity. Glycobiology 2016, 26, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkal, A.A.; Brewer, R.E.; Markovic, M.; Kowarsky, M.; Barkal, S.A.; Zaro, B.W.; Krishnan, V.; Hatakeyama, J.; Dorigo, O.; Barkal, L.J.; et al. CD24 signalling through macrophage Siglec-10 is a target for cancer immunotherapy. Nature 2019, 572, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Houtum, E.J.H.; Büll, C.; Cornelissen, L.A.M.; Adema, G.J. Siglec Signaling in the Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 790317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondioli, L.; Ruozi, B.; Belletti, D.; Forni, F.; Vandelli, M.A.; Tosi, G. Sialic acid as a potential approach for the protection and targeting of nanocarriers. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2011, 8, 921–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Qiu, Q.; Liu, M.; Liu, X.; Hu, L.; Luo, X.; Lai, C.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, H.; Gao, X.; et al. Sialic acid-conjugate modified liposomes targeting neutrophils for improved tumour therapy. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 2189–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.H.; Min, K.H.; Wang, Z.; Kim, J.; Jacobson, O.; Huang, P.; Zhu, G.; Liu, Y.; Yung, B.; Niu, G.; et al. Development of Sialic Acid-coated Nanoparticles for Targeting Cancer and Efficient Evasion of the Immune System. Theranostics 2017, 7, 962–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- She, Z.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Song, Y.; Cheng, X.; Huang, Z.; Deng, Y. The anticancer efficacy of pixantrone-loaded liposomes decorated with sialic acid-octadecylamine conjugate. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 5216–5225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.S.; Zheng, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.B.; Yu, B.; Zheng, W.; Yang, F.; Chen, T. Sialic acid surface decoration enhances cellular uptake and apoptosis-inducing activity of selenium nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 83, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najaf Najafi, M.; Arianmehr, A.; Sani, A.M. Preparation of Barije (Ferula gummosa) Essential Oil-Loaded Liposomes and Evaluation of Physical and Antibacterial Effect on Escherichia coli O157:H7. J. Food Prot. 2020, 83, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T.; Wang, C.; Huang, Z.; Luo, X.; Deng, Y. A review on phospholipids and their main applications in drug delivery systems. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 10, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Yu, C.; Lei, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, J. A novel chitosan-urea encapsulated material for persulfate slow-release to degrade organic pollutants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 426, 128083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H.; Wang, L.; Huang, G. Liposome encapsulated of temozolomide for the treatment of glioma tumor: Preparation, characterization and evaluation. Drug Discov. Ther. 2015, 9, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Huang, H.; Sullivan, M.O.; Kiick, K.L. Controlled Delivery of Vancomycin from Collagen-tethered Peptide Vehicles for the Treatment of Wound Infections. Mol. Pharm. 2023, 20, 1696–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grammer, J.B.; Kortüm, F.A.; Wolburg, H.; Lüdtke, R.; Schmidt, K.H.; Thiel, H.J.; Pleyer, U. Impregnation of collagen corneal shields with liposomes: Uptake and release of hydrophilic and lipophilic marker substances. Curr. Eye Res. 1996, 15, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grohganz, H.; Tho, I.; Brandl, M. Development and in vitro evaluation of a liposome based implant formulation for the decapeptide cetrorelix. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. Off. J. Arbeitsgemeinschaft Pharm. Verfahrenstechnik E.V 2005, 59, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ding, Z.; Lv, S.; Liu, J.; Pan, J.; Yu, Y.; Gao, J.; Huang, X. Development of tLyP-1 functionalized nanoliposomes with tunable internal water phase for glioma targeting. J. Liposome Res. 2023, 33, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vodovozova, E.L.; Moiseeva, E.V.; Grechko, G.K.; Gayenko, G.P.; Nifant’ev, N.E.; Bovin, N.V.; Molotkovsky, J.G. Antitumour activity of cytotoxic liposomes equipped with selectin ligand SiaLe(X), in a mouse mammary adenocarcinoma model. Eur. J. Cancer 2000, 36, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Gao, X.; Li, X.; Qiu, Q.; Li, C.; Yan, N.; Li, J.; Liu, M.; Tang, X.; Liu, X.; et al. Persistent immune response: Twice tumor exfoliation induced by sialic acid–modified vincristine sulfate liposomes. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 631, 122467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.-Y.; Li, X.-W.; Li, J.-J.; Shi, S.-L.; Zhang, T. Preparation of sialic acid-modified chlorogenic acid liposomes and its antitumor activity in vitro. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2020, 51, 6178–6187. [Google Scholar]
- Ethier, J.L.; Desautels, D.; Templeton, A.; Shah, P.S.; Amir, E. Prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res. 2017, 19, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Huang, P.; Jin, W.; Li, C.; Yang, J.; Wan, H.; He, Y. Optimization of Extraction or Purification Process of Multiple Components from Natural Products: Entropy Weight Method Combined with Plackett-Burman Design and Central Composite Design. Molecules 2021, 26, 5572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Pei, X. A new method of bid evaluation for renovation projects: Based on unascertained measure theory and entropy weight. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0271534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Dong, Z.; Tao, D.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z. The acidic tumor microenvironment: A target for smart cancer nano-theranostics. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2017, 5, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornaguera, C.; Solans, C. Methods for the In Vitro Characterization of Nanomedicines—Biological Component Interaction. J. Pers. Med. 2017, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Incubation Time (h) | ATG@Lip | ATG@SA-Lip | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size (nm) | PDI | Size (nm) | PDI | |
| 0 | 97.4 (±2.1) | 0.258 | 101.1 (±3.7) | 0.253 |
| 3 | 89.8 (±3.0) | 0.269 | 99.4 (±4.9) | 0.181 |
| 6 | 86.6 (±4.3) | 0.286 | 88.5 (±2.7) | 0.269 |
| 12 | 92.0 (±4.1) | 0.250 | 92.0 (±4.1) | 0.250 |
| 24 | 88.7 (±5.4) | 0.268 | 86.4 (±3.0) | 0.271 |
| 48 | 88.7 (±0.3) | 0.247 | 92.6 (±4.2) | 0.257 |
| Title 1 | Normal | NC | Positive | ATG Solution | ATG@Lip | ATG@SA-Lip |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HGB | 150.0 (±3.0) | 143.0 (±5.6) | 140.7 (±6.0) * | 148.7 (±3.8) | 150.7 (±4.6) | 149.7 (±2.1) |
| RBC | >7.90 | >7.90 | >7.90 | >7.90 | >7.90 | >7.90 |
| WBC | 7.42 (±0.7) △ | 145.8 (±28.9) * | 62.1 (±3.9) *△ | 61.0 (±17.1) △ | 114.9 (±13.0) * | 81.1 (±17.9) *△ |
| PLT | 885.3 (±9.7) | 716.3 (±47.4) | 879.0 (±70.7) △ | 793.5 (±58.7) | 878.5 (±102.5) | 815.3 (±43.8) |
| Mono# | 0.08 (±0.03) △ | 18.5 (±7.2) * | 8.54 (±9.55) | 0.47 (±0.30) △ | 9.26 (±8.28) | 9.05 (±2.71) |
| Bas# | 0.03 (±0.04) | 0.07 (±0.05) | 0.05 (±0.04) | 0.01 (±0.01) △ | 0.08 (±0.03) | 0.05 (±0.02) |
| Eos# | 0.11 (±0.03) △ | 3.14 (±1.00) * | 0.49 (±0.23) △ | 0.87 (±0.51) △ | 2.18 (±0.64) * | 1.68 (±0.90) *△ |
| Neu# | 1.21 (±0.14) △ | 109.1 (±18.5) * | 48.6 (±36.4) *△ | 38.2 (±24.6) △ | 90.1 (±15.6) * | 58.4 (±11.8) *△ |
| Lym# | 5.99 (±0.66) △ | 15.0 (±2.6) * | 7.04 (±2.05) △ | 7.26 (±2.76) △ | 13.3 (±1.1) * | 11.9 (±2.57) * |
| NLR | 0.20 (±0.02) △ | 7.30 (±0.26) * | 6.24 (±3.46) *△ | 4.89 (±2.10) * | 6.79 (±1.16) * | 4.94 (±0.21) *△ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; He, Y.; Feng, M.; Huang, Y.; Wu, W.; Wang, J. Targeted Delivery of Arctigenin Using Sialic Acid Conjugate-Modified Liposomes for the Treatment of Breast Cancer. Molecules 2024, 29, 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010278
Liu S, He Y, Feng M, Huang Y, Wu W, Wang J. Targeted Delivery of Arctigenin Using Sialic Acid Conjugate-Modified Liposomes for the Treatment of Breast Cancer. Molecules. 2024; 29(1):278. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010278
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shunfang, Yaozhen He, Minding Feng, Yongtong Huang, Wenhao Wu, and Jiu Wang. 2024. "Targeted Delivery of Arctigenin Using Sialic Acid Conjugate-Modified Liposomes for the Treatment of Breast Cancer" Molecules 29, no. 1: 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010278
APA StyleLiu, S., He, Y., Feng, M., Huang, Y., Wu, W., & Wang, J. (2024). Targeted Delivery of Arctigenin Using Sialic Acid Conjugate-Modified Liposomes for the Treatment of Breast Cancer. Molecules, 29(1), 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010278







