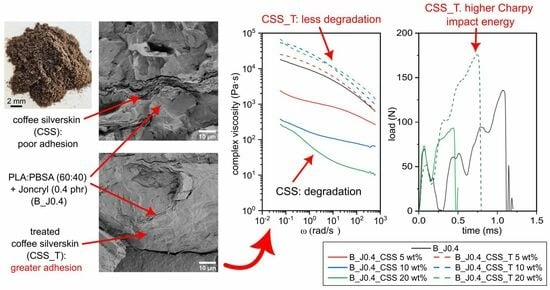
A Green Treatment Mitigates the Limitations of Coffee Silver Skin as a Filler for PLA/PBSA Compatibilized Biocomposites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of the PLA/PBSA/J Blends
2.1.1. Rheological and Microstructural Properties
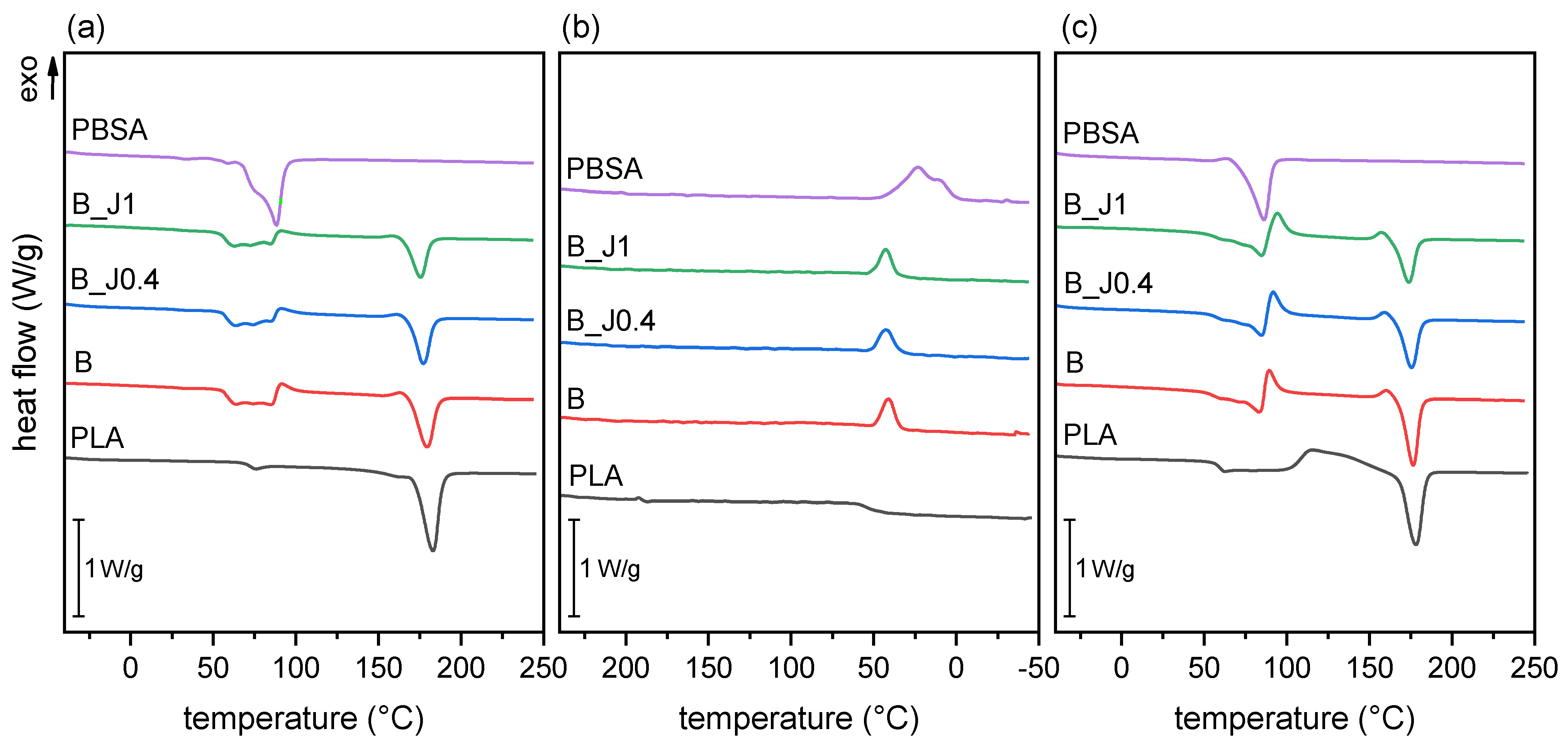
2.1.2. Thermal Properties
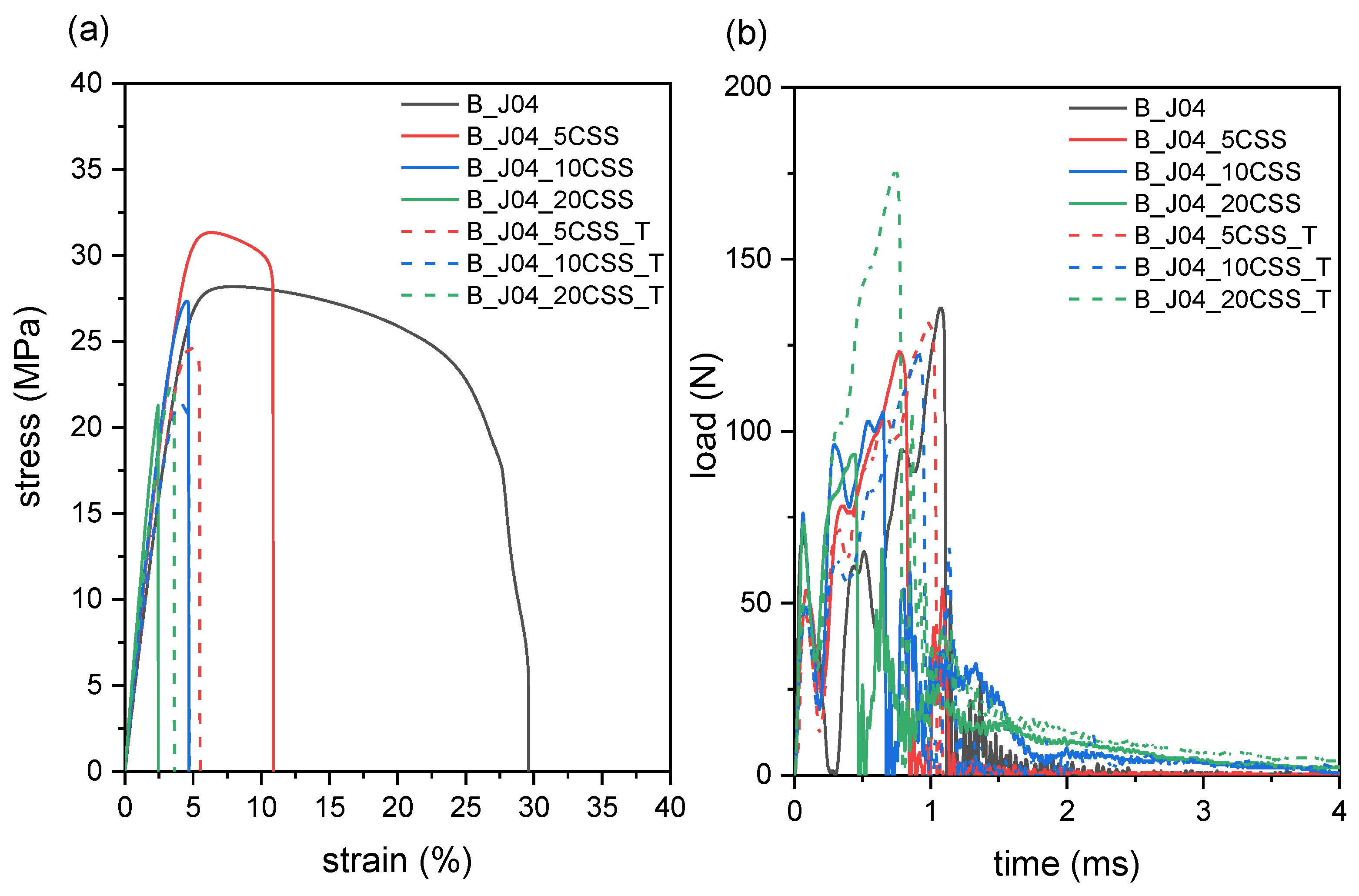
2.1.3. Mechanical Properties
2.2. Characterization of the PLA/PBSA/J/CSS Composites
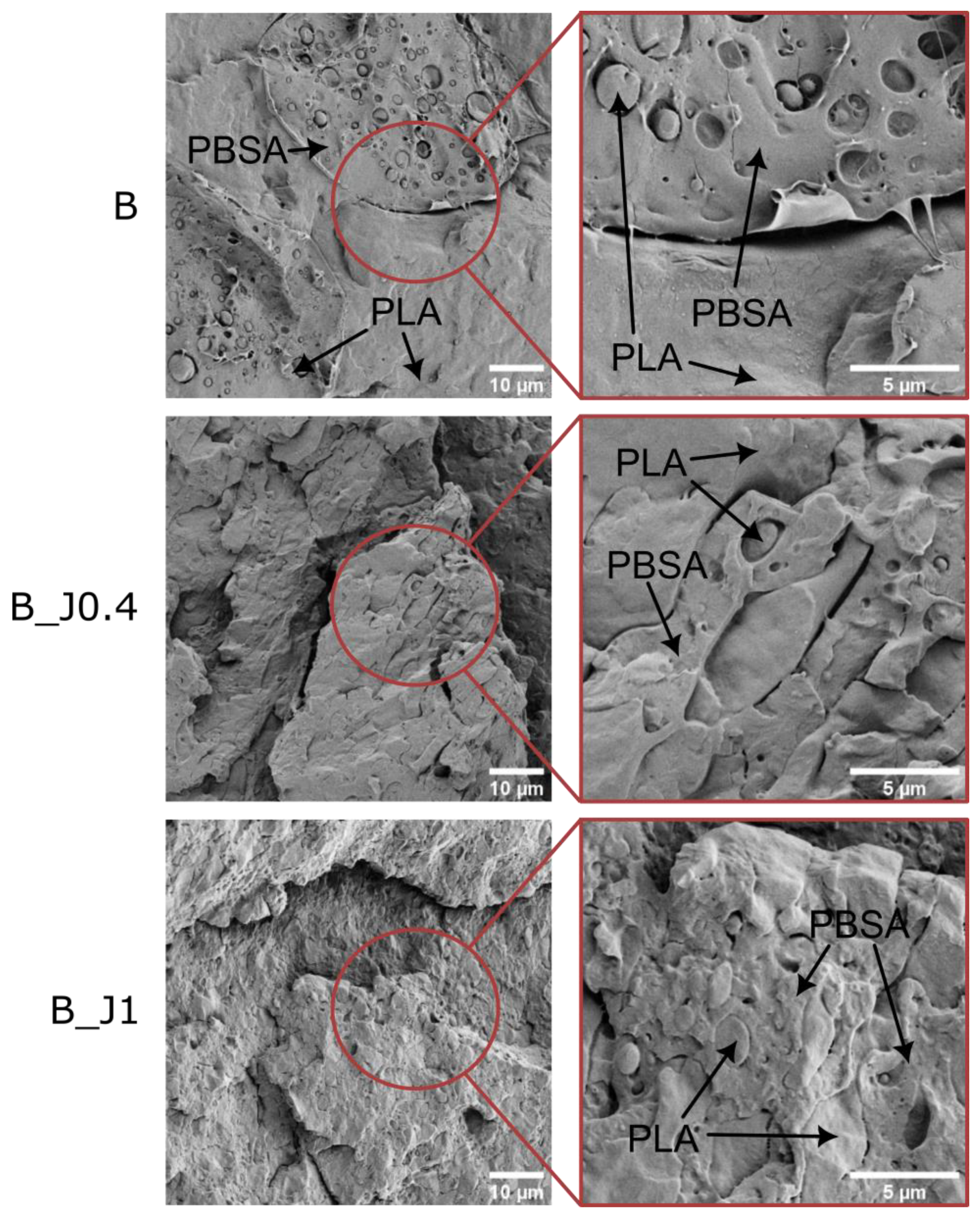
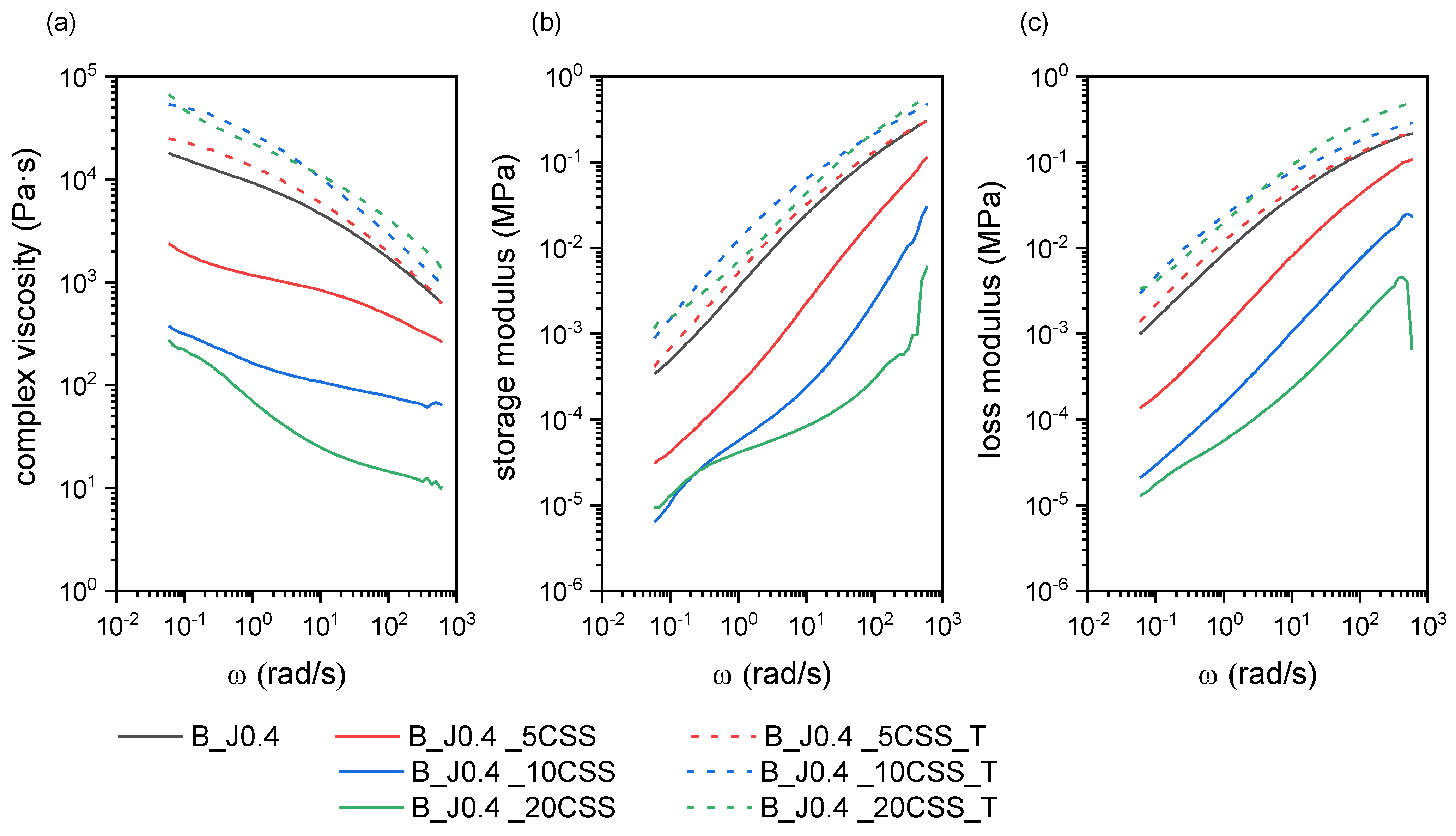
2.2.1. Rheological and Microstructural Properties
2.2.2. Thermal Properties
2.2.3. Mechanical Properties
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Sample Preparation
3.3. Characterization
3.3.1. Rheological Properties
3.3.2. Microstructural Properties
3.3.3. Thermal Properties
3.3.4. Mechanical and Thermomechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karan, H.; Funk, C.; Grabert, M.; Oey, M.; Hankamer, B. Green Bioplastics as Part of a Circular Bioeconomy. Trends Plant Sci. 2019, 24, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Bioplastics. Bioplastics: Facts and Figures; European Bioplastics: Berlin, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca, A.; Ramalho, E.; Gouveia, A.; Figueiredo, F.; Nunes, J. Life Cycle Assessment of PLA Products: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredi, G.; Dorigato, A. Recycling of bioplastic waste: A review. Adv. Ind. Eng. Polym. Res. 2021, 4, 159–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.M.; Qiu, S.; Yusuf, A.; Sun, J.; Zhai, Z.; Zhao, J.; Yin, G.Z. Recent advances in flame retardant and mechanical properties of polylactic acid: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 243, 125050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Ju, Z.; Tam, P.Y.; Hua, T.; Younas, M.W.; Kamrul, H.; Hu, H. Poly(lactic acid) fibers, yarns and fabrics: Manufacturing, properties and applications. Text. Res. J. 2020, 91, 1641–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiandra, E.F.; Shaw, L.; Starck, M.; McGurk, C.J.; Mahon, C.S. Designing biodegradable alternatives to commodity polymers. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 8085–8105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perego, G.; Cella, G.D.; Bastioli, C. Effect of molecular weight and crystallinity on poly(lactic acid) mechanical properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1996, 59, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fambri, L.; Dorigato, A.; Pegoretti, A. Role of Surface-Treated Silica Nanoparticles on the Thermo-Mechanical Behavior of Poly(Lactide). Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabedo, L.; Feijoo, J.L.; Villanueva, M.P.; Lagaron, J.M.; Gimenez, E. Optimization of Biodegradable Nanocomposites Based on aPLA/PCL Blends for Food Packaging Applications. Macromol. Symp. 2006, 233, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ma, W.; Gross, R.A.; McCarthy, S.P. Reactive compatibilization of biodegradable blends of poly(lactic acid) and poly(ε-caprolactone). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1998, 59, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perin, D.; Rigotti, D.; Fredi, G.; Papageorgiou, G.Z.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Dorigato, A. Innovative bio-based poly(lactic acid)/poly(alkylene furanoate) fiber blends for sustainable textile applications. J. Polym. Environ. 2021, 29, 3948–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredi, G.; Zonta, E.; Dussin, A.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Papageorgiou, G.Z.; Fambri, L.; Dorigato, A. Toughening effect of 2,5-furandicaboxylate polyesters on polylactide-based renewable fibers. Molecules 2023, 28, 4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredi, G.; Dorigato, A.; Dussin, A.; Xanthopoulou, E.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Botta, L.; Fiore, V.; Pegoretti, A. Compatibilization of polylactide/poly(ethylene furanoate) (PLA/PEF) blends for sustainable and bioderived packaging. Molecules 2022, 27, 6371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigotti, D.; Soccio, M.; Dorigato, A.; Gazzano, M.; Siracusa, V.; Fredi, G.; Lotti, N. Novel biobased polylactic acid/poly(pentamethylene 2,5-furanoate) blends for sustainable food packaging. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 13742–13750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliotta, L.; Vannozzi, A.; Cinelli, P.; Coltelli, M.B.; Lazzeri, A. Essential Work of Fracture and Evaluation of the Interfacial Adhesion of Plasticized PLA/PBSA Blends with the Addition of Wheat Bran By-Product. Polymers 2022, 14, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliotta, L.; Vannozzi, A.; Canesi, I.; Cinelli, P.; Coltelli, M.B.; Lazzeri, A. Poly(lactic acid) (PLA)/Poly(butylene succinate-co-adipate) (PBSA) Compatibilized Binary Biobased Blends: Melt Fluidity, Morphological, Thermo-Mechanical and Micromechanical Analysis. Polymers 2021, 13, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliotta, L.; Gigante, V.; Dal Pont, B.; Miketa, F.; Coltelli, M.-B.; Lazzeri, A. Tearing fracture of poly(lactic acid) (PLA)/poly(butylene succinate-co-adipate) (PBSA) cast extruded films: Effect of the PBSA content. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2023, 289, 109450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Han, Z.; Yan, X.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H. Rheological and mechanical properties, heat resistance and hydrolytic degradation of poly(butylene succinate-co-adipate)/stereocomplex polylactide blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2023, 140, e53884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, J.W. Characterization and processing of Biodegradable polymer blends of poly(lactic acid) with poly(butylene succinate adipate). Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 2005, 17, 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, T.; Yang, J.; Chen, F.; Fei, Y.; Zhong, M.; Kuang, T. Biomimetically Structured Poly(lactic acid)/Poly(butylene-adipate-co-terephthalate) Blends with Ultrahigh Strength and Toughness for Structural Application. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 4, 9351–9359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coiai, S.; Di Lorenzo, M.L.; Cinelli, P.; Righetti, M.C.; Passaglia, E. Binary Green Blends of Poly(lactic acid) with Poly(butylene adipate-co-butylene terephthalate) and Poly(butylene succinate-co-butylene adipate) and Their Nanocomposites. Polymers 2021, 13, 2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lascano, D.; Quiles-Carrillo, L.; Balart, R.; Boronat, T.; Montanes, N. Toughened Poly(Lactic Acid)-PLA Formulations by Binary Blends with Poly(Butylene Succinate-co-Adipate)-PBSA and Their Shape Memory Behaviour. Materials 2019, 12, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Pan, H.; Jia, S.; Wang, Z.; Tian, H.; Han, L.; Zhang, H. In-situ reaction compatibilization modification of poly(butylene succinate-co-terephthalate)/polylactide acid blend films by multifunctional epoxy compound. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 213, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palai, B.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. Synergistic effect of polylactic acid(PLA) and Poly(butylene succinate-co-adipate) (PBSA) based sustainable, reactive, super toughened eco-composite blown films for flexible packaging applications. Polym. Test. 2020, 83, 106130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojijo, V.; Ray, S.S.; Sadiku, R. Toughening of biodegradable polylactide/poly(butylene succinate-co-adipate) blends via in situ reactive compatibilization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 4266–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredi, G.; Dorigato, A. Compatibilization of biopolymer blends: A review. Adv. Ind. Eng. Polym. Res. 2023; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigato, A.; Fredi, G. Effect of nanofillers addition on the compatibilization of polymer blends. Adv. Ind. Eng. Polym. Res. 2023; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, M.A.; Abir, N.; Anannya, F.R.; Nabi Khan, A.; Rahman, A.; Jamine, N. Coir fiber as thermal insulator and its performance as reinforcing material in biocomposite production. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahdan, D.; Rosli, N.A.; Chen, R.S.; Ahmad, S.; Gan, S. Strategies for strengthening toughened poly(lactic acid) blend via natural reinforcement with enhanced biodegradability: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 251, 126214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruz-Cruz, M.A.; Herrera-Franco, P.J.; Flores-Johnson, E.A.; Moreno-Chulim, M.V.; Galera-Manzano, L.M.; Valadez-González, A. Thermal and mechanical properties of PLA-based multiscale cellulosic biocomposites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 18, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, R.A.; Sapuan, S.M.; Harussani, M.M.; Hakimi, M.; Haziq, M.Z.M.; Atikah, M.S.N.; Asyraf, M.R.M.; Ishak, M.R.; Razman, M.R.; Nurazzi, N.M.; et al. Polylactic Acid (PLA) Biocomposite: Processing, Additive Manufacturing and Advanced Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowman, A.C.; Picard, M.C.; Lim, L.-T.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A.K. Fruit Waste Valorization for Biodegradable Biocomposite Applications: A Review. BioResources 2019, 14, 10047–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siakeng, R.; Jawaid, M.; Ariffin, H.; Sapuan, S.M.; Asim, M.; Saba, N. Natural fiber reinforced polylactic acid composites: A review. Polym. Compos. 2018, 40, 446–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motaung, T.E.; Linganiso, L.Z. Critical review on agrowaste cellulose applications for biopolymers. Int. J. Plast. Technol. 2018, 22, 185–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, V.; Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M. Sustainable Green Composites: Value Addition to Agricultural Residues and Perennial Grasses. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narita, Y.; Inouye, K. Review on utilization and composition of coffee silverskin. Food Res. Int. 2014, 61, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolasco, A.; Squillante, J.; Velotto, S.; D’Auria, G.; Ferranti, P.; Mamone, G.; Errico, M.E.; Avolio, R.; Castaldo, R.; Cirillo, T.; et al. Valorization of coffee industry wastes: Comprehensive physicochemical characterization of coffee silverskin and multipurpose recycling applications. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 370, 133520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nzekoue, F.K.; Borsetta, G.; Navarini, L.; Abouelenein, D.; Xiao, J.; Sagratini, G.; Vittori, S.; Caprioli, G.; Angeloni, S. Coffee silverskin: Characterization of B-vitamins, macronutrients, minerals and phytosterols. Food Chem. 2022, 372, 131188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Weldon, R.; Lynam, J.G. Hydrothermal carbonization of coffee silverskins. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 36, 102145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbero-López, A.; Monzó-Beltrán, J.; Virjamo, V.; Akkanen, J.; Haapala, A. Revalorization of coffee silverskin as a potential feedstock for antifungal chemicals in wood preservation. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2020, 152, 105011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Pozo, C.; Bartroli, J.; Alier, S.; Puy, N.; Fabregas, E. Production of antioxidants and other value-added compounds from coffee silverskin via pyrolysis under a biorefinery approach. Waste Manag. 2020, 109, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, G.; Passos, C.P.; Ferreira, P.; Coimbra, M.A.; Goncalves, I. Coffee By-Products and Their Suitability for Developing Active Food Packaging Materials. Foods 2021, 10, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Varela, J.D.; Medina, D.I. Revalorization of Coffee Residues: Advances in the Development of Eco-Friendly Biobased Potential Food Packaging. Polymers 2023, 15, 2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barone, J.R. Lignocellulosic Fiber-Reinforced Keratin Polymer Composites. J. Polym. Environ. 2009, 17, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigante, V.; Seggiani, M.; Cinelli, P.; Signori, F.; Vania, A.; Navarini, L.; Amato, G.; Lazzeri, A. Utilization of coffee silverskin in the production of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) biopolymer-based thermoplastic biocomposites for food contact applications. Compos. Part. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 140, 106172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarasini, F.; Tirillò, J.; Zuorro, A.; Maffei, G.; Lavecchia, R.; Puglia, D.; Dominici, F.; Luzi, F.; Valente, T.; Torre, L. Recycling coffee silverskin in sustainable composites based on a poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)/poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) matrix. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 118, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarasini, F.; Luzi, F.; Dominici, F.; Maffei, G.; Iannone, A.; Zuorro, A.; Lavecchia, R.; Torre, L.; Carbonell-Verdu, A.; Balart, R.; et al. Effect of Different Compatibilizers on Sustainable Composites Based on a PHBV/PBAT Matrix Filled with Coffee Silverskin. Polymers 2018, 10, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghazvini, A.K.A.; Ormondroyd, G.; Curling, S.; Saccani, A.; Sisti, L. An investigation on the possible use of coffee silverskin in PLA/PBS composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, 52264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrinbakhsh, N.; Wang, T.; Rodriguez-Uribe, A.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A.K. Characterization of Wastes and Coproducts from the Coffee Industry for Composite Material Production. BioResources 2016, 11, 7637–7653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahyaee, N.; Javadi, A.; Garmabi, H.; Khaki, A. Effect of Two-Step Chain Extension using Joncryl and PMDA on the Rheological Properties of Poly (lactic acid). Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2019, 305, 1900423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojijo, V.; Sinha Ray, S.; Sadiku, R. Role of specific interfacial area in controlling properties of immiscible blends of biodegradable polylactide and poly[(butylene succinate)-co-adipate]. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 6690–6701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, T.; Wang, T.T. Melting Point Depression and Kinetic Effects of Cooling on Crystallization in Poly(viny1idene fluoride)-Poly (methyl methacrylate) Mixtures. Macromolecules 1975, 8, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imre, B.; Pukánszky, B. Compatibilization in bio-based and biodegradable polymer blends. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 1215–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Inventory of Effective Food Contact Substance (FCS) Notifications. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/food-ingredients-packaging/food-ingredient-and-packaging-inventories (accessed on 5 November 2023).
- Moustafa, H.; Guizani, C.; Dufresne, A. Sustainable biodegradable coffee grounds filler and its effect on the hydrophobicity, mechanical and thermal properties of biodegradable PBAT composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 134, 44498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panthapulakkal, S.; Sain, M. Agro-residue reinforced high-density polyethylene composites: Fiber characterization and analysis of composite properties. Compos. Part. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2007, 38, 1445–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garlotta, D. A Literature Review of Poly(Lactic Acid). J. Polym. Environ. 2001, 9, 63–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample | First Heating Scan | Cooling Scan | Second Heating Scan | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tg,PLA (°C) | Tm,PLA (°C) | ΔHm,PLA (J/g) | ΔHcc,PLA (J/g) | χc,PLA (%) | Tm,PBSA (°C) | ΔHm,PBSA (J/g) | Tc,PBSA (°C) | ΔHc,PBSA (J/g) | Tg,PLA (°C) | Tm,PLA (°C) | ΔHm,PLA (J/g) | Tm,PBSA (°C) | ΔHm,PBSA (J/g) | |
| PLA | 68.4 | 181.9 | 59.1 | 0 | 63.0 | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | 55.9 | 177.1 | 48.6 | n.a. | n.a. |
| B | 54.8 | 178.5 | 32.1 | 2.8 | 45.0 | n.d. | n.d. | 40.6 | 15.6 | 55.2 | 175.2 | 36.5 | n.d. | n.d. |
| B_J0.4 | 57.2 | 176.2 | 30.0 | 7.3 | 40.4 | n.d. | n.d. | 42.6 | 15.0 | 57.1 | 174.5 | 27.7 | n.d. | n.d. |
| B_J1 | 56.6 | 174.7 | 23.8 | 2.5 | 36.4 | n.d. | n.d. | 42.3 | 14.6 | 56.8 | 173.0 | 25.8 | n.d. | n.d. |
| PBSA | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | 88.8 | 63.2 | 23.2 | 47.2 | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | 85.3 | 46.1 |
| Sample | Tensile Test | Charpy Test | Vicat Test | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E (GPa) | σmax (MPa) | εb (%) | Fmax (N) | Etot,sp (kJ/m2) | VST (°C) | |
| B | 2.0 ± 0.1 | 29.6 ± 0.9 | 9 ± 2 | 99 ± 13 | 3.2 ± 0.5 | 123 ± 8 |
| B_0.4J | 1.9 ± 0.1 | 29.4 ± 1.1 | 28 ± 16 | 144 ± 12 | 5.1 ± 0.8 | 106 ± 2 |
| B_1J | 1.8 ± 0.1 | 28.6 ± 1.3 | 23 ± 14 | 181 ± 7 | 7.6 ± 0.8 | 82 ± 4 |
| Sample | Tonset (°C) | TD,PLA (°C) | TD,CSS (°C) | TD,PBSA (°C) | mr,700 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B_J0.4 | 341 | 351 | - | 379 | 0.0 |
| B_J0.4_5CSS | 300 | 315 | - | 369 | 1.3 |
| B_J0.4_10CSS | 284 | 299 | - | 379 | 5.9 |
| B_ J0.4_20CSS | 276 | 287 | - | 371 | 8.8 |
| B_ J0.4_5CSS_T | 341 | 355 | - | 388 | 3.1 |
| B_J0.4_10CSS_T | 338 | 349 | - | 383 | 5.0 |
| B_J0.4_20CSS_T | 320 | 338 | - | 390 | 7.8 |
| CSS | 264 | - | 313 | - | 27.6 |
| CSS_T | 291 | - | 362 | - | 20.8 |
| Sample | Tensile Test | Charpy Test | Vicat Test | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E (GPa) | σmax (MPa) | εb (%) | Fmax (N) | Etot,sp (kJ/m2) | VST (°C) | |
| B_0.4J | 1.9 ± 0.1 | 29.4 ± 1.1 | 28.0 ± 16.0 | 144 ± 12 | 5.1 ± 0.8 | 105.6 ± 1.8 |
| B_0.4J_5CSS | 2.2 ± 0.1 | 31.4 ± 0.7 | 12.2 ± 3.9 | 124 ± 7 | 3.6 ± 0.7 | 85.2 ± 7.3 |
| B_0.4J_10CSS | 2.4 ± 0.1 | 27.2 ± 1.1 | 4.6 ± 0.4 | 105 ± 6 | 3.1 ± 0.2 | 85.8 ± 5.0 |
| B_0.4J_20CSS | 3.1 ± 0.1 | 21.6 ± 0.2 | 2.4 ± 0.1 | 85 ± 5 | 1.8 ± 0.2 | 95.8 ± 0.7 |
| B_0.4J_5CSS_T | 1.9 ± 0.1 | 25.3 ± 0.5 | 5.8 ± 1.7 | 106 ± 17 | 5.0 ± 0.9 | 88.6 ± 10.1 |
| B_0.4J_10CSS_T | 1.6 ± 0.2 | 20.8 ± 1.0 | 4.5 ± 0.2 | 110 ± 16 | 5.2 ± 1.0 | 92.7 ± 8.9 |
| B_0.4J_20CSS_T | 2.0 ± 0.1 | 19.4 ± 3.1 | 3.2 ± 0.5 | 144 ± 12 | 4.9 ± 0.6 | 94.5 ± 2.0 |
| Sample | PLA (wt%) | PBSA (wt%) | J (phr) | CSS (wt%) | State of CSS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | 60 | 40 | 0 | - | - |
| B_0.4J | 60 | 40 | 0.4 | - | - |
| B_1J | 60 | 40 | 1.0 | - | - |
| B_0.4J_CSS5 | 57 | 38 | 0.4 | 5 | As received |
| B_0.4J_CSS10 | 54 | 36 | 0.4 | 10 | As received |
| B_0.4J_CSS20 | 48 | 32 | 0.4 | 20 | As received |
| B_0.4J_CSS5_T | 57 | 38 | 0.4 | 5 | Treated |
| B_0.4J_CSS10_T | 54 | 36 | 0.4 | 10 | Treated |
| B_0.4J_CSS20_T | 48 | 32 | 0.4 | 20 | Treated |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perin, D.; Dorigato, A.; Bertoldi, E.; Fambri, L.; Fredi, G. A Green Treatment Mitigates the Limitations of Coffee Silver Skin as a Filler for PLA/PBSA Compatibilized Biocomposites. Molecules 2024, 29, 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010226
Perin D, Dorigato A, Bertoldi E, Fambri L, Fredi G. A Green Treatment Mitigates the Limitations of Coffee Silver Skin as a Filler for PLA/PBSA Compatibilized Biocomposites. Molecules. 2024; 29(1):226. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010226
Chicago/Turabian StylePerin, Davide, Andrea Dorigato, Erica Bertoldi, Luca Fambri, and Giulia Fredi. 2024. "A Green Treatment Mitigates the Limitations of Coffee Silver Skin as a Filler for PLA/PBSA Compatibilized Biocomposites" Molecules 29, no. 1: 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010226
APA StylePerin, D., Dorigato, A., Bertoldi, E., Fambri, L., & Fredi, G. (2024). A Green Treatment Mitigates the Limitations of Coffee Silver Skin as a Filler for PLA/PBSA Compatibilized Biocomposites. Molecules, 29(1), 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010226