5-Oxo-ETE/OXER1: A Link between Tumor Cells and Macrophages Leading to Regulation of Migration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Soluble Factors Secreted by Cancer Cells Attract M1 and M2 Macrophages
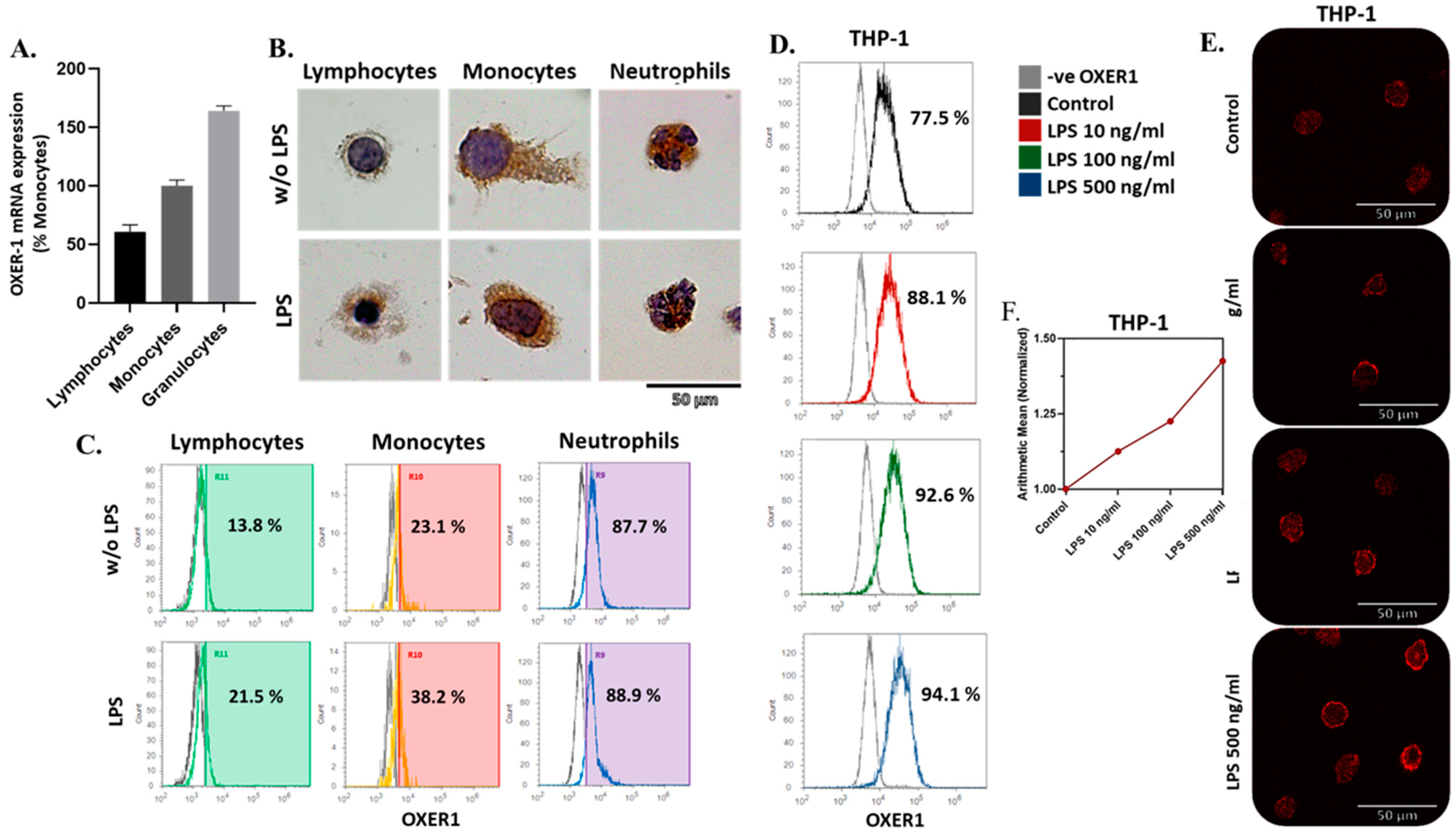
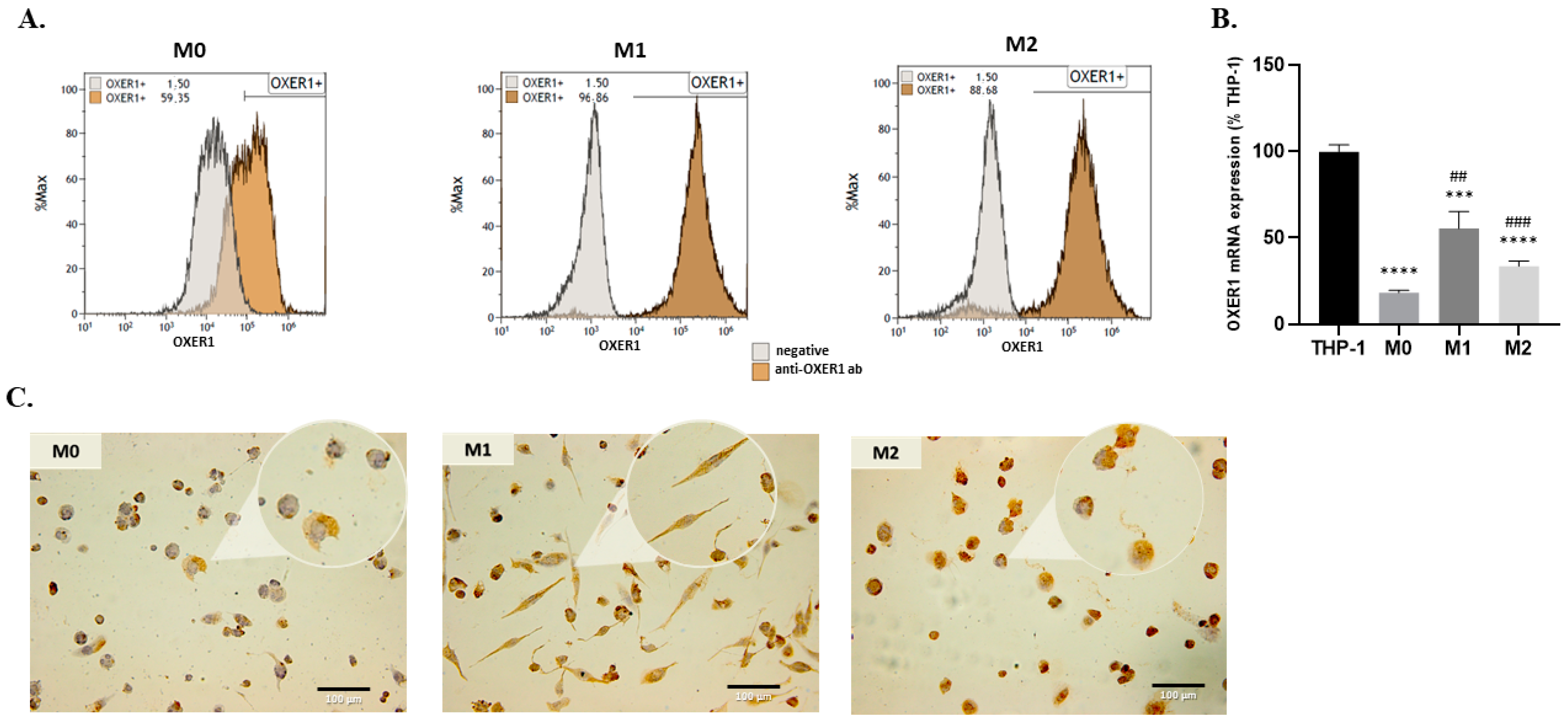
2.2. Expression of OXER1 by Macrophages during Their Differentiation
2.3. Effect of OXER1 Activation on THP1 Differentiation
2.4. Effect of OXER1 Activation on the Expression of Humoral Mediators
2.5. Differentiated Macrophages Express a Functional OXER1 Receptor
2.5.1. Ca2+ Release from Intracellular Sources
2.5.2. Gαi Mediated cAMP Modifications
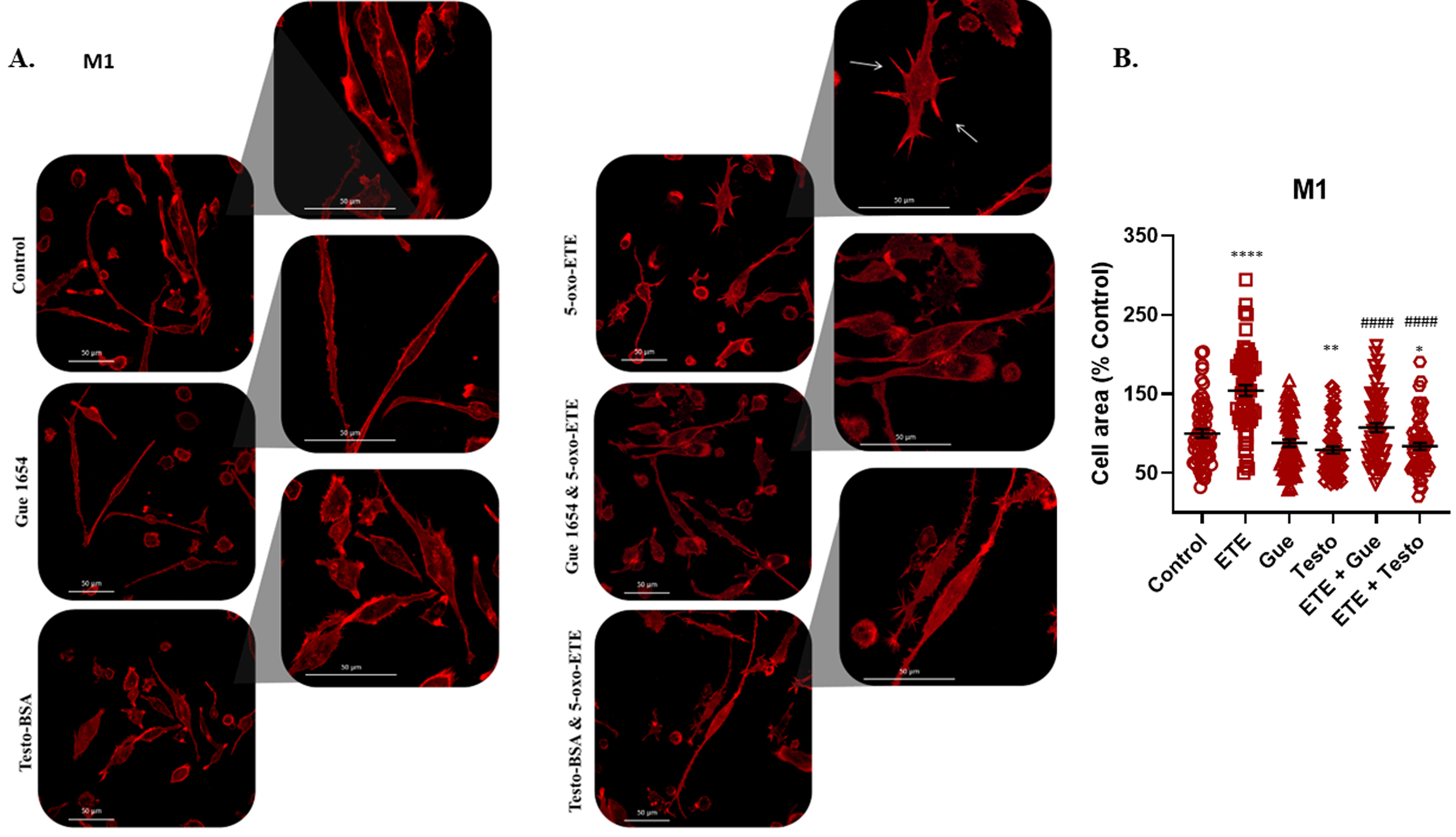
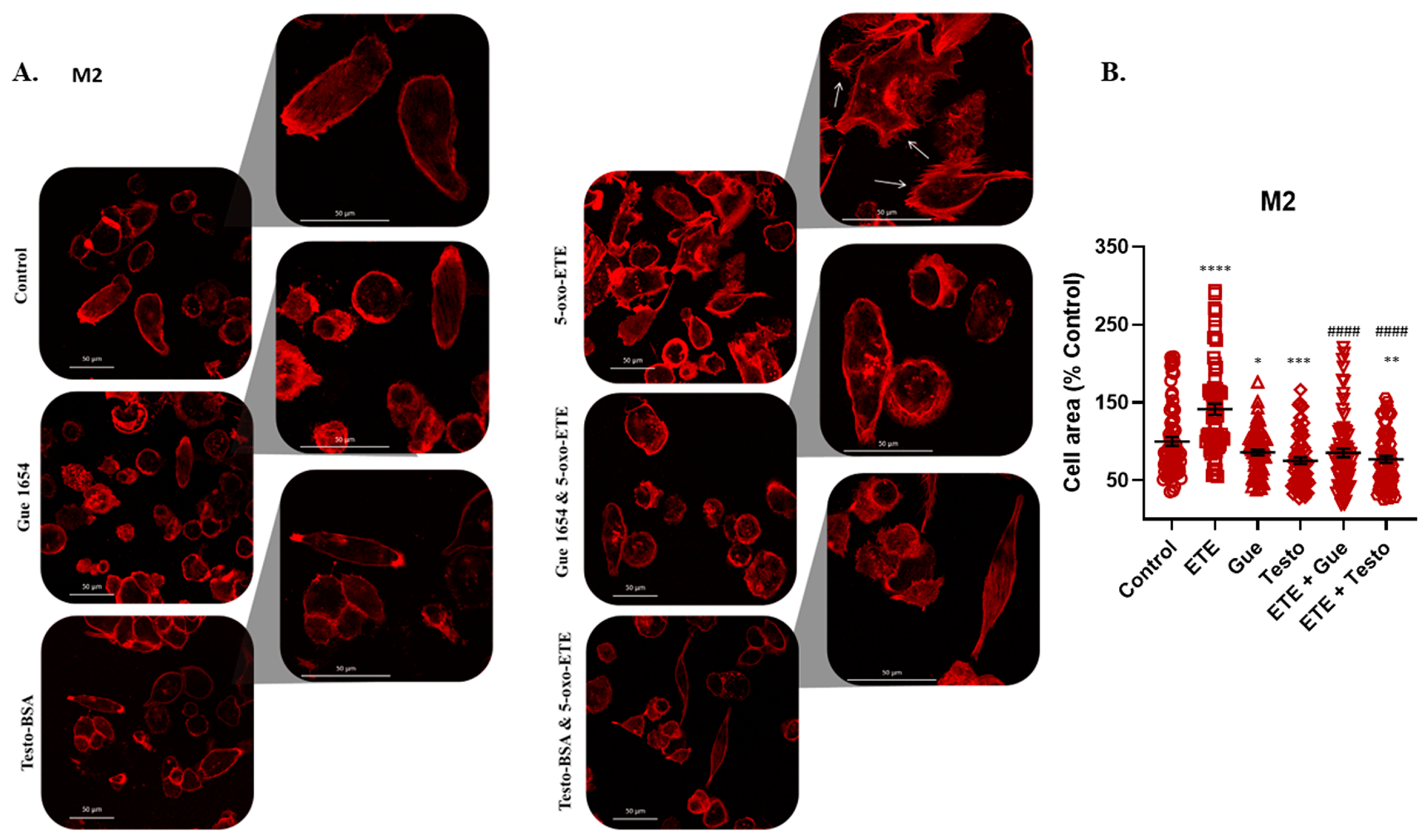
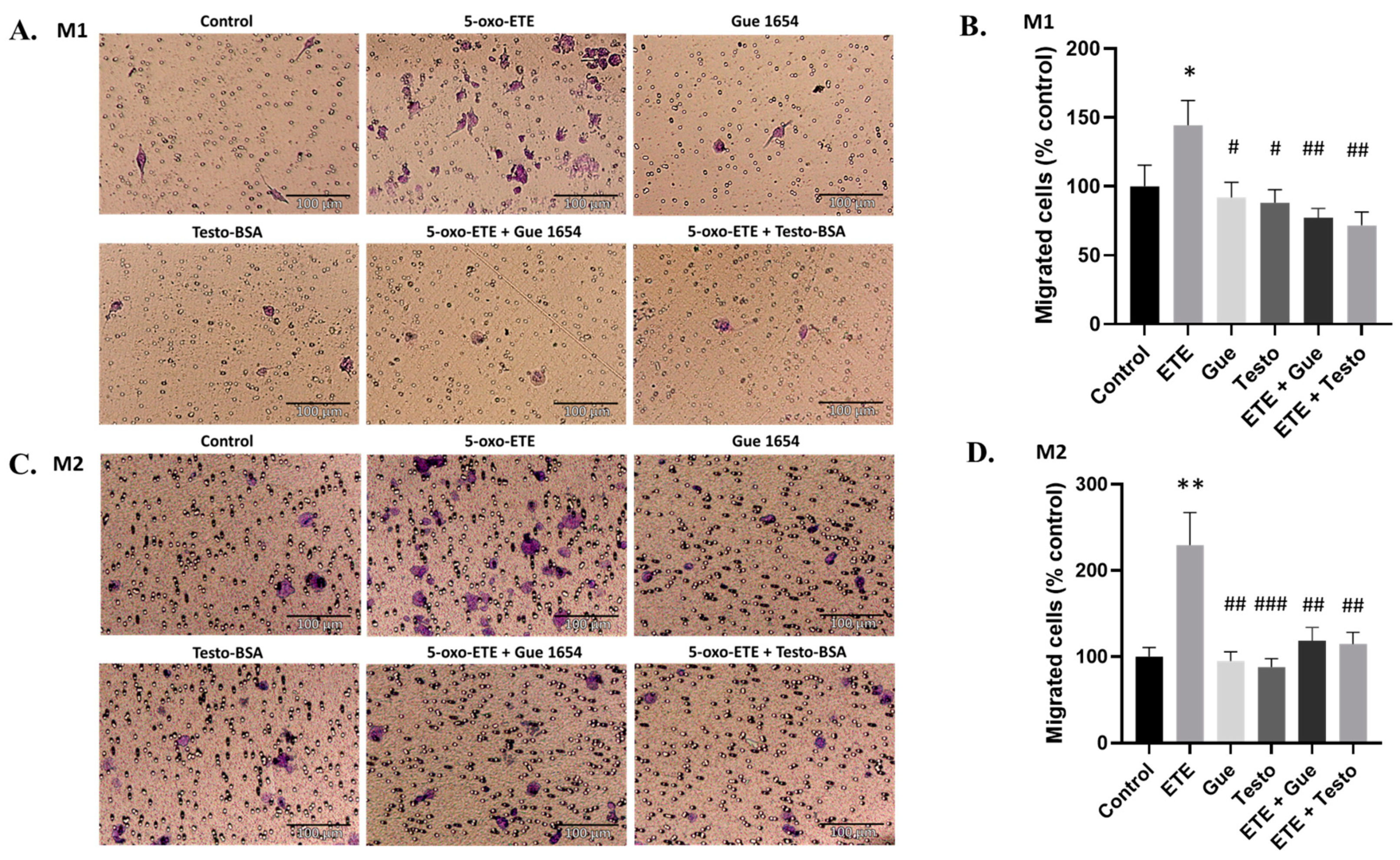
2.6. OXER1-Related Migration of Macrophages
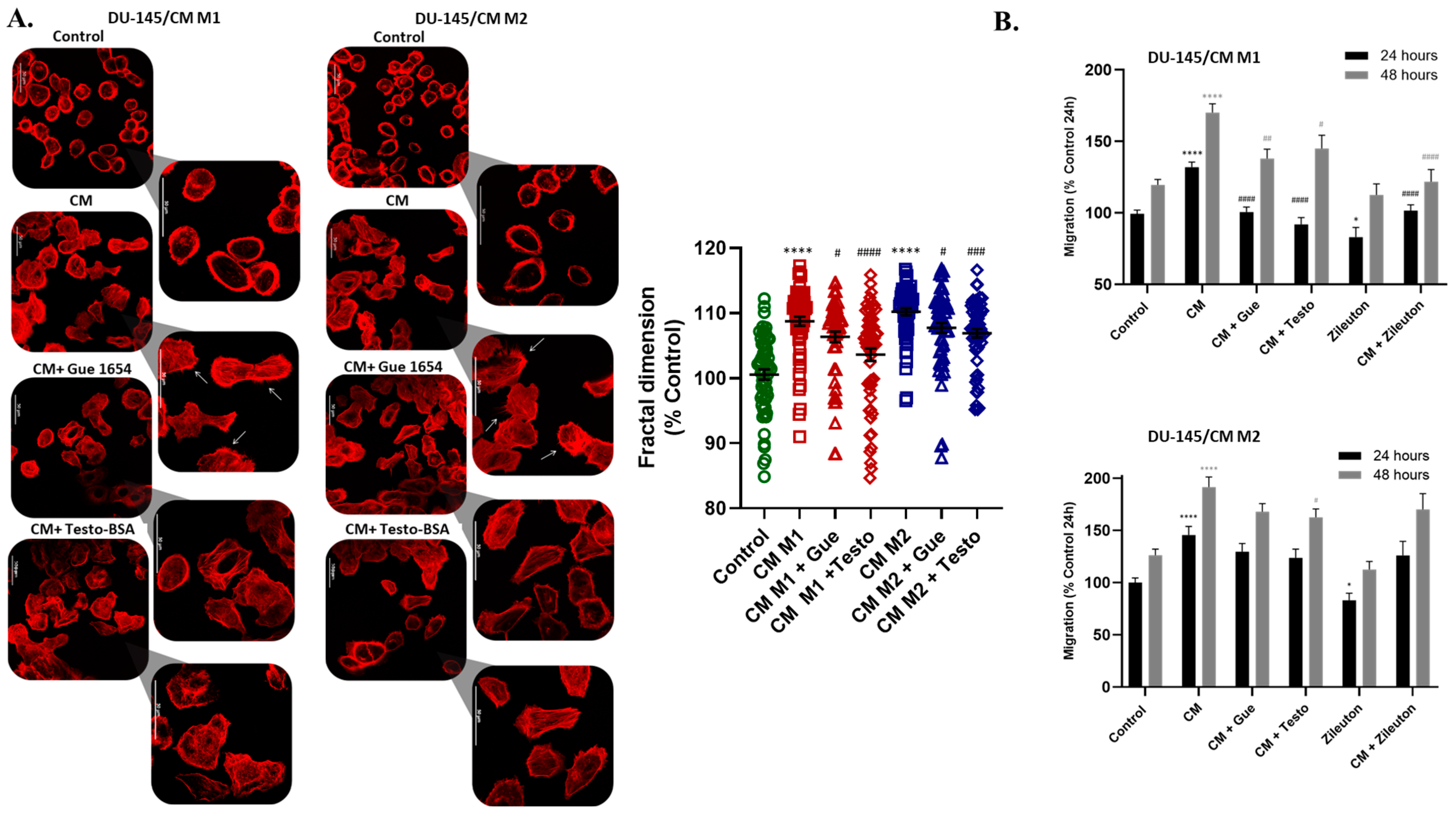
2.7. Reciprocal Attraction of Epithelial Cancer Cells by Macrophages, through 5-oxo-ETE/OXER1
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Cultures and Materials
4.2. WBC Isolation
4.3. THP-1 Differentiation to Macrophage-Like Cells
4.4. Conditioned Medium Derived from Differentiated Monocytes
4.5. Immunocytochemistry (ICC)
4.6. Calcium Changes
4.7. Actin Cytoskeleton Visualization
4.8. Immunofluorescence (IF) for Flow Cytometry (FACS) or Confocal Microscopy
4.9. Migration Assays
4.10. cAMP Assay
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barriga, V.; Kuol, N.; Nurgali, K.; Apostolopoulos, V. The Complex Interaction between the Tumor Micro-Environment and Immune Checkpoints in Breast Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; He, L.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, P.; Liang, S. Targeting tumor-associated macrophages for cancer treatment. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolopoulos, V.; Pietersz, G.A.; Loveland, B.E.; Sandrin, M.S.; McKenzie, I.F. Oxidative/reductive conjugation of mannan to antigen selects for T1 or T2 immune responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 10128–10132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bied, M.; Ho, W.W.; Ginhoux, F.; Bleriot, C. Roles of macrophages in tumor development: A spatiotemporal perspective. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2023, 20, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Yue, J.; Ruan, Y.; Han, Y.; Zhi, Y.; Lu, J.; Liu, M.; Xu, X.; Wang, J.; Gu, Q.; et al. Single-cell dissection of cervical cancer reveals key subsets of the tumor immune microenvironment. EMBO J. 2023, 42, e110757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T. Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Tumor Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 583084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyle, D.; Kitamura, T. Targeting Macrophage-Recruiting Chemokines as a Novel Therapeutic Strategy to Prevent the Progression of Solid Tumors. Front Immunol. 2018, 9, 2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brana, I.; Calles, A.; LoRusso, P.M.; Yee, L.K.; Puchalski, T.A.; Seetharam, S.; Zhong, B.; de Boer, C.J.; Tabernero, J.; Calvo, E. Carlumab, an anti-C-C chemokine ligand 2 monoclonal antibody, in combination with four chemotherapy regimens for the treatment of patients with solid tumors: An open-label, multicenter phase 1b study. Target. Oncol. 2015, 10, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calle, Y.; Burns, S.; Thrasher, A.J.; Jones, G.E. The leukocyte podosome. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 85, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Skrzypczynska, K.M.; Fang, Q.; Zhang, W.; O’Brien, S.A.; He, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Kim, A.; et al. Single-Cell Analyses Inform Mechanisms of Myeloid-Targeted Therapies in Colon Cancer. Cell 2020, 181, 442–459.e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyvianaki, K.; Gebhart, V.; Peroulis, N.; Panagiotopoulou, C.; Kiagiadaki, F.; Pediaditakis, I.; Aivaliotis, M.; Moustou, E.; Tzardi, M.; Notas, G.; et al. Antagonizing effects of membrane-acting androgens on the eicosanoid receptor OXER1 in prostate cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyvianaki, K.; Drosou, I.; Notas, G.; Castanas, E.; Kampa, M. Enhanced OXER1 expression is indispensable for human cancer cell migration. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 584, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosoi, T.; Koguchi, Y.; Sugikawa, E.; Chikada, A.; Ogawa, K.; Tsuda, N.; Suto, N.; Tsunoda, S.; Taniguchi, T.; Ohnuki, T. Identification of a novel human eicosanoid receptor coupled to G(i/o). J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 31459–31465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, W.S.; MacLeod, R.J.; Gravel, S.; Gravelle, F.; Bhakar, A. Metabolism and biologic effects of 5-oxoeicosanoids on human neutrophils. J. Immunol. 1996, 156, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panagiotopoulos, A.A.; Kalyvianaki, K.; Serifoglou, B.; Konstantinou, E.; Notas, G.; Castanas, E.; Kampa, M. OXER1 mediates testosterone-induced calcium responses in prostate cancer cells. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2022, 539, 111487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Flaherty, J.T.; Taylor, J.S.; Thomas, M.J. Receptors for the 5-oxo class of eicosanoids in neutrophils. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 32535–32541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Grant, G.E.; Rokach, J.; Powel, W.S. 5-Oxo-ETE and the OXE receptor. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2009, 89, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, W.S.; Rokach, J. Biochemistry, biology and chemistry of the 5-lipoxygenase product 5-oxo-ETE. Prog. Lipid Res. 2005, 44, 154–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.E.; Holden, S.; Tenaillon, L.; Bhatia, U.; Seuwen, K.; Tranter, P.; Turner, J.; Kettle, R.; Bouhelal, R.; Charlton, S.; et al. Expression and characterization of a 5-oxo-6E,8Z,11Z,14Z-eicosatetraenoic acid receptor highly expressed on human eosinophils and neutrophils. Mol. Pharmacol. 2003, 63, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, S.; Kadowaki, S.; Haga, T.; Takaesu, H.; Mitaku, S. Identification of G protein-coupled receptor genes from the human genome sequence. FEBS Lett. 2002, 520, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyvianaki, K.; Panagiotopoulos, A.A.; Malamos, P.; Moustou, E.; Tzardi, M.; Stathopoulos, E.N.; Ioannidis, G.S.; Marias, K.; Notas, G.; Theodoropoulos, P.A.; et al. Membrane androgen receptors (OXER1, GPRC6A AND ZIP9) in prostate and breast cancer: A comparative study of their expression. Steroids 2019, 142, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sozzani, S.; Zhou, D.; Locati, M.; Bernasconi, S.; Luini, W.; Mantovani, A.; O’Flaherty, J.T. Stimulating properties of 5-oxo-eicosanoids for human monocytes: Synergism with monocyte chemotactic protein-1 and -3. J. Immunol. 1996, 157, 4664–4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, W.S.; Gravel, S.; MacLeod, R.J.; Mills, E.; Hashefi, M. Stimulation of human neutrophils by 5-oxo-6,8,11,14-eicosatetraenoic acid by a mechanism independent of the leukotriene B4 receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 9280–9286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilbert, M.; Ferland, C.; Bosse, M.; Flamand, N.; Lavigne, S.; Laviolette, M. 5-Oxo-6,8,11,14-eicosatetraenoic acid induces important eosinophil transmigration through basement membrane components: Comparison of normal and asthmatic eosinophils. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1999, 21, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enyedi, B.; Kala, S.; Nikolich-Zugich, T.; Niethammer, P. Tissue damage detection by osmotic surveillance. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 15, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katikaneni, A.; Jelcic, M.; Gerlach, G.F.; Ma, Y.; Overholtzer, M.; Niethammer, P. Lipid peroxidation regulates long-range wound detection through 5-lipoxygenase in zebrafish. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020, 22, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masi, M.; Garattini, E.; Bolis, M.; Di Marino, D.; Maraccani, L.; Morelli, E.; Grolla, A.A.; Fagiani, F.; Corsini, E.; Travelli, C.; et al. OXER1 and RACK1-associated pathway: A promising drug target for breast cancer progression. Oncogenesis 2020, 9, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotopoulos, A.A.; Kalyvianaki, K.; Notas, G.; Pirintsos, S.A.; Castanas, E.; Kampa, M. New Antagonists of the Membrane Androgen Receptor OXER1 from the ZINC Natural Product Database. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 29664–29674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotopoulos, A.A.; Konstantinou, E.; Pirintsos, S.A.; Castanas, E.; Kampa, M. Mining the ZINC database of natural products for specific, testosterone-like, OXER1 antagonists. Steroids 2023, 199, 109309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blattermann, S.; Peters, L.; Ottersbach, P.A.; Bock, A.; Konya, V.; Weaver, C.D.; Gonzalez, A.; Schroder, R.; Tyagi, R.; Luschnig, P.; et al. A biased ligand for OXE-R uncouples Galpha and Gbetagamma signaling within a heterotrimer. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2012, 8, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossette, C.; Miller, L.A.; Ye, Q.; Chourey, S.; Reddy, C.N.; Rokach, J.; Powell, W.S. Targeting the OXE receptor with a selective antagonist inhibits allergen-induced pulmonary inflammation in non-human primates. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 322–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akira, S. Toll-like receptor signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 38105–38108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweet, M.J.; Hume, D.A. Endotoxin signal transduction in macrophages. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1996, 60, 8–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, N.O.; Varvara, A.O.; Nikita, G.N.; Veronika, A.M.; Andrey, V.G.; Elena, B.R.; Dongwei, Z.; Dimitry, A.C. Monocyte differentiation and macrophage polarization. Vessel. Plus 2019, 3, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Hosoi, T.; Sugikawa, E.; Chikada, A.; Koguchi, Y.; Ohnuki, T. TG1019/OXE, a Galpha(i/o)-protein-coupled receptor, mediates 5-oxo-eicosatetraenoic acid-induced chemotaxis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 334, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konya, V.; Blattermann, S.; Jandl, K.; Platzer, W.; Ottersbach, P.A.; Marsche, G.; Gutschow, M.; Kostenis, E.; Heinemann, A. A biased non-Galphai OXE-R antagonist demonstrates that Galphai protein subunit is not directly involved in neutrophil, eosinophil, and monocyte activation by 5-oxo-ETE. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 4774–4782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werz, O.; Gerstmeier, J.; Libreros, S.; De la Rosa, X.; Werner, M.; Norris, P.C.; Chiang, N.; Serhan, C.N. Human macrophages differentially produce specific resolvin or leukotriene signals that depend on bacterial pathogenicity. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarczyk, R.B.; Tuli, N.Y.; Hanly, E.K.; Rahoma, G.B.; Maniyar, R.; Mittelman, A.; Geliebter, J.; Tiwari, R.K. Macrophage inflammatory factors promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 24272–24282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnewies, M.; Roberts, E.W.; Kersten, K.; Chan, V.; Fearon, D.F.; Merad, M.; Coussens, L.M.; Gabrilovich, D.I.; Ostrand-Rosenberg, S.; Hedrick, C.C.; et al. Understanding the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) for effective therapy. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.W.; Pittet, M.J.; Fukumura, D.; Jain, R.K. The local microenvironment matters in preclinical basic and translational studies of cancer immunology and immunotherapy. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 701–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, W.S.; Rokach, J. The eosinophil chemoattractant 5-oxo-ETE and the OXE receptor. Prog. Lipid Res. 2013, 52, 651–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, W.S.; Rokach, J. Targeting the OXE receptor as a potential novel therapy for asthma. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 179, 113930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruger, A.; Oldenburg, M.; Chebrolu, C.; Beisser, D.; Kolter, J.; Sigmund, A.M.; Steinmann, J.; Schafer, S.; Hochrein, H.; Rahmann, S.; et al. Human TLR8 senses UR/URR motifs in bacterial and mitochondrial RNA. EMBO Rep. 2015, 16, 1656–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linder, S.; Hufner, K.; Wintergerst, U.; Aepfelbacher, M. Microtubule-dependent formation of podosomal adhesion structures in primary human macrophages. J. Cell Sci. 2000, 113 Pt 23, 4165–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, M.F.; Sahai, E. The actin cytoskeleton in cancer cell motility. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2009, 26, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slany, A.; Bileck, A.; Kreutz, D.; Mayer, R.L.; Muqaku, B.; Gerner, C. Contribution of Human Fibroblasts and Endothelial Cells to the Hallmarks of Inflammation as Determined by Proteome Profiling. Mol. Cell Proteomics 2016, 15, 1982–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.K.; Sica, A.; Lewis, C.E. Plasticity of macrophage function during tumor progression: Regulation by distinct molecular mechanisms. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 2011–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.B.; Yeh, E.S.; Soloff, A.C. Tumor-associated macrophages: Unwitting accomplices in breast cancer malignancy. NPJ Breast Cancer 2016, 2, 15025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massague, J. TGFbeta in Cancer. Cell 2008, 134, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seoane, J.; Gomis, R.R. TGF-beta Family Signaling in Tumor Suppression and Cancer Progression. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2017, 9, a022277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, I.H.; Song, H.O.; Ryu, J.S. IL-6 produced by prostate epithelial cells stimulated with Trichomonas vaginalis promotes proliferation of prostate cancer cells by inducing M2 polarization of THP-1-derived macrophages. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Cao, J.; Zu, X. Tumor-associated macrophages: An important player in breast cancer progression. Thorac. Cancer 2022, 13, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coussens, L.M.; Tinkle, C.L.; Hanahan, D.; Werb, Z. MMP-9 supplied by bone marrow-derived cells contributes to skin carcinogenesis. Cell 2000, 103, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, E.W.; Graham, A.E.; Re, N.A.; Carr, I.M.; Robinson, J.I.; Mackie, S.L.; Morgan, A.W. Standardized protocols for differentiation of THP-1 cells to macrophages with distinct M(IFNgamma+LPS), M(IL-4) and M(IL-10) phenotypes. J. Immunol. Methods 2020, 478, 112721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampa, M.; Theodoropoulou, K.; Mavromati, F.; Pelekanou, V.; Notas, G.; Lagoudaki, E.D.; Nifli, A.P.; Morel-Salmi, C.; Stathopoulos, E.N.; Vercauteren, J.; et al. Novel oligomeric proanthocyanidin derivatives interact with membrane androgen sites and induce regression of hormone-independent prostate cancer. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2011, 337, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngabire, D.; Niyonizigiye, I.; Patil, M.P.; Seong, Y.A.; Seo, Y.B.; Kim, G.D. M2 Macrophages Mediate the Resistance of Gastric Adenocarcinoma Cells to 5-Fluorouracil through the Expression of Integrin beta3, Focal Adhesion Kinase, and Cofilin. J. Immunol. Res. 2020, 2020, 1731457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalyvianaki, K.; Salampasi, E.M.; Katsoulieris, E.N.; Boukla, E.; Vogiatzoglou, A.P.; Notas, G.; Castanas, E.; Kampa, M. 5-Oxo-ETE/OXER1: A Link between Tumor Cells and Macrophages Leading to Regulation of Migration. Molecules 2024, 29, 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010224
Kalyvianaki K, Salampasi EM, Katsoulieris EN, Boukla E, Vogiatzoglou AP, Notas G, Castanas E, Kampa M. 5-Oxo-ETE/OXER1: A Link between Tumor Cells and Macrophages Leading to Regulation of Migration. Molecules. 2024; 29(1):224. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010224
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalyvianaki, Konstantina, Evangelia Maria Salampasi, Elias N. Katsoulieris, Eleni Boukla, Amalia P. Vogiatzoglou, George Notas, Elias Castanas, and Marilena Kampa. 2024. "5-Oxo-ETE/OXER1: A Link between Tumor Cells and Macrophages Leading to Regulation of Migration" Molecules 29, no. 1: 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010224
APA StyleKalyvianaki, K., Salampasi, E. M., Katsoulieris, E. N., Boukla, E., Vogiatzoglou, A. P., Notas, G., Castanas, E., & Kampa, M. (2024). 5-Oxo-ETE/OXER1: A Link between Tumor Cells and Macrophages Leading to Regulation of Migration. Molecules, 29(1), 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010224







