Untreated Opuntia ficus indica for the Efficient Adsorption of Ni(II), Pb(II), Cu(II) and Cd(II) Ions from Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
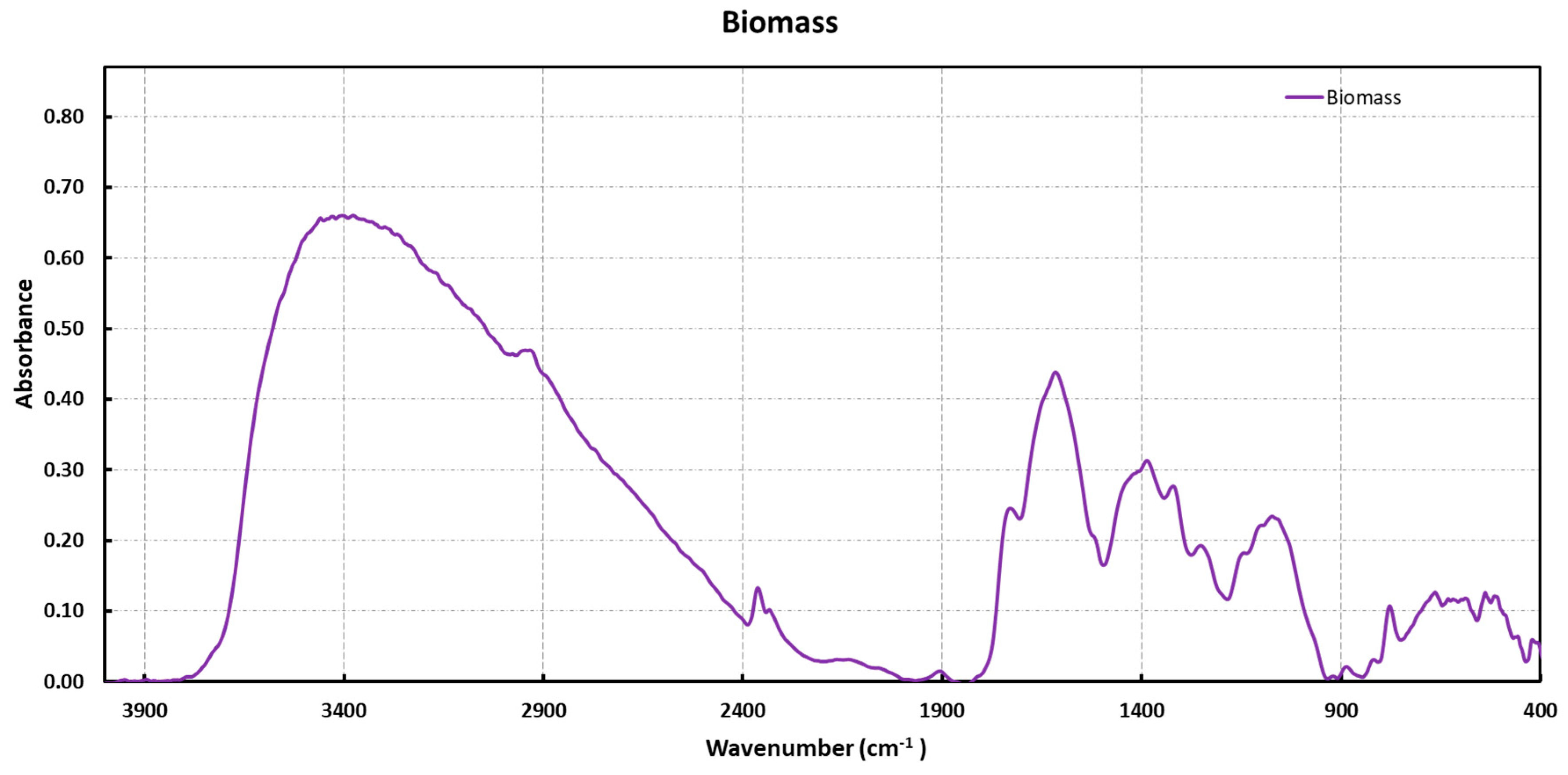
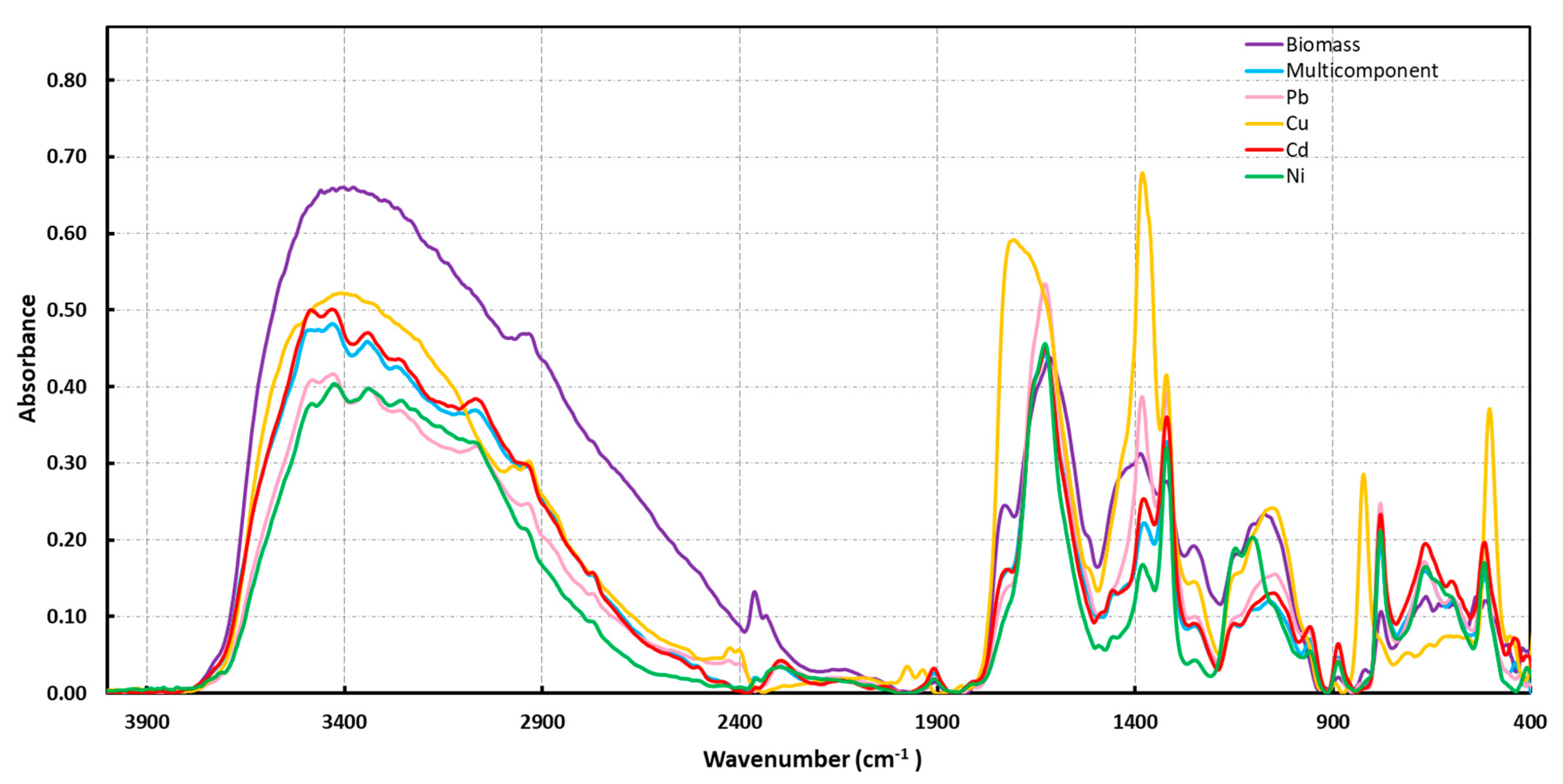
2.1. Biomass Characterization
2.2. Adsorption Studies
2.3. Kinetic Studies
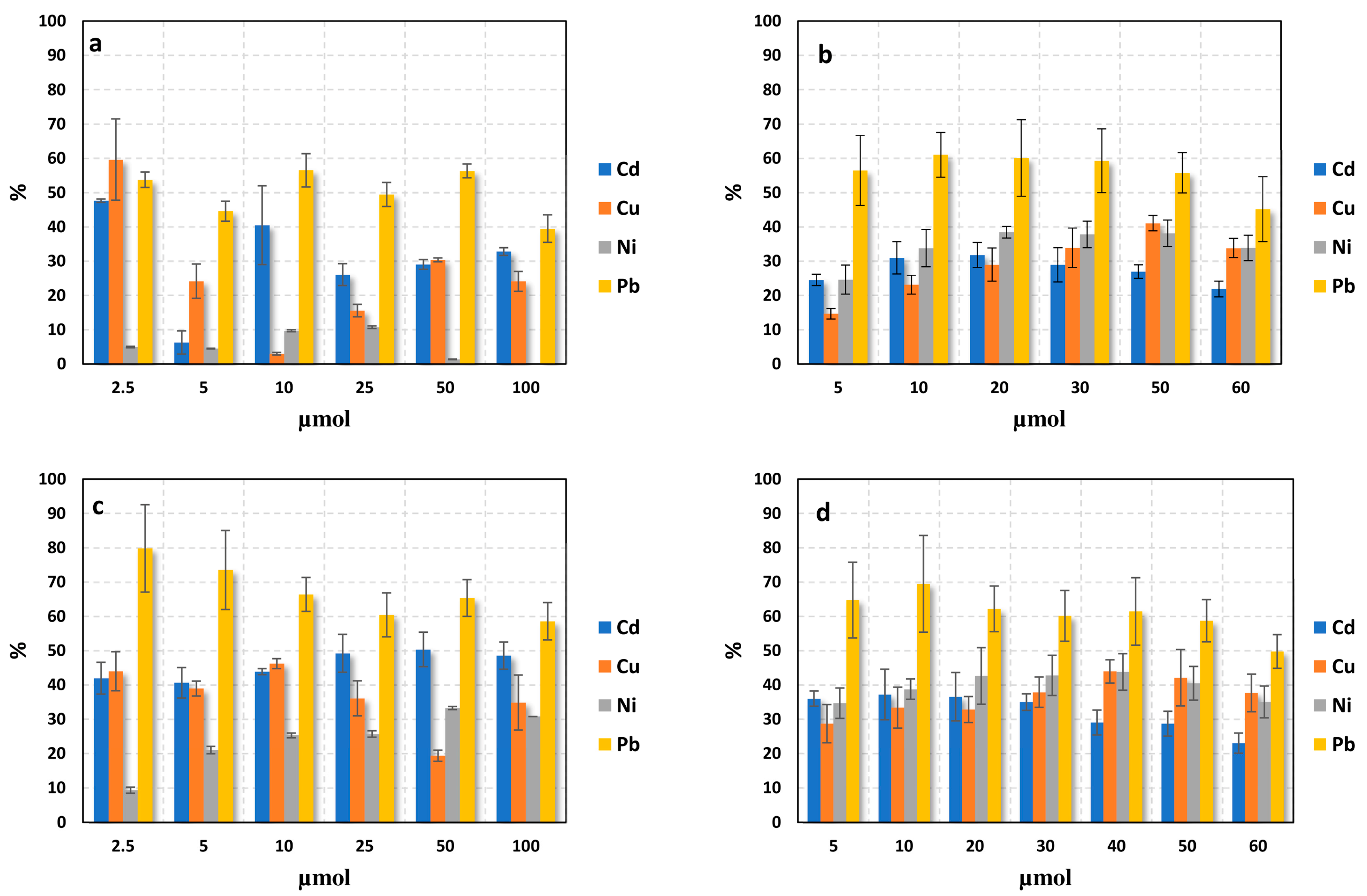
2.4. Adsorption Efficiency in Single- and Multi-Component Solutions
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Sample Preparation
3.3. Lewis’s Basic Sites Determination
3.4. Infrared Measurements
3.5. NMR Analysis
3.6. ICP-MS Measurements
3.7. Adsorptions Studies
3.8. Equilibrium Isotherm Models
- qeq = the equilibrium adsorbate loading on the biomass (mgadsorbate/gbiomass);
- Ceq = the equilibrium concentration of the adsorbate (mgadsorbate/L);
- Qmax = the ultimate capacity (mgadsorbate/gbiomass);
- b = the relative energy (intensity) of adsorption (L/mg), also known as the binding constant.
- qeq = the equilibrium adsorbate loading on the biomass (mgadsorbate/gbiomass);
- Ceq = the equilibrium concentration of the adsorbate (mgadsorbate/L);
- Kf = the Freundlich adsorption constant;
- n = the Freundlich exponent.
- Ceq = the equilibrium concentration of the adsorbate (mgadsorbate/L);
- Ci = the initial amount of ions used in the experimental approach (mg/L);
- Qm = the amount of ions that cover the layer of biomass (mgadsorbate/gbiomass);
- Qeq = the amount of ions trapped by the biomass (mgadsorbate/gbiomass);
- B = the affinity constant between the ionic species and the biomass.
3.9. Kinetic Studies
3.10. Kinetic Modelling
3.11. Adsorption Efficiency
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Kumar, V.; Parihar, R.D.; Sharma, A.; Bakshi, P.; Sidhu, G.P.S.; Bali, A.S.; Karaouzas, I.; Bhardwaj, R.; Thukral, A.K.; Gyasi-Agyei, Y.; et al. Global evaluation of heavy metal content in surface water bodies: A meta-analysis using heavy metal pollution indices and multivariate statistical analyses. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wang, H.; Liao, X.; Xiao, R.; Liu, K.; Bai, J.; Li, B.; He, Q. Heavy metal pollution in coastal wetlands: A systematic review of studies globally over the past three decades. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Luo, P.; Zha, X.; Xu, C.; Kang, S.; Zhou, M.; Nover, D.; Wang, Y. Overview assessment of risk evaluation and treatment technologies for heavy metal pollution of water and soil. J.Clean. Prod. 2022, 379, 134043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punia, P.; Bharti, M.K.; Dhar, R.; Thakur, P.; Thakur, A. Recent advances in detection and removal of heavy metals from contaminated water. ChemBioEng Rev. 2022, 9, 351–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.F.; Kumar, P.S.; Rozbu, M.R.; Chowdhury, A.T.; Nuzhat, S.; Rafa, N.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Chyuan Ong, H.; Mofijur, M. Heavy metal toxicity, sources, and remediation techniques for contaminated water and soil. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 25, 102114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbera, M.; Gurnari, G. Wastewater Treatment and Reuse in the Food Industry; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, W.S.; Cheun, J.Y.; Kumar, P.S.; Mubashir, M.; Majeed, Z.; Banat, F.; Ho, S.H.; Show, P.L. A review on conventional and novel materials towards heavy metal adsorption in wastewater treatment application. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 296, 126589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, S.; Priya, T.A.K.; Khoo, K.S.; Hoang, T.K.; Ng, H.S.; Munawaroh, H.S.H.; Karaman, C.; Orooji, Y.; Show, P.L. A critical review on various remediation approaches for heavy metal contaminants removal from contaminated soils. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ethaib, S.; Zubaidi, S.L.; Al-Ansari, N. Evaluation water scarcity based on GIS estimation and climate-change effects: A case study of Thi-Qar Governorate, Iraq. Cogent Eng. 2022, 9, 2075301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Pal, D.B.; Mohammad, A.; Alhazmi, A.; Haque, S.; Yoon, T.; Gupta, V.K. Biological remediation technologies for dyes and heavy metals in wastewater treatment: New insight. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 343, 126154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olawale, S.A. Biosorption of heavy metals from aqueous solutions: An insight and review. Arch. Ind. Eng. 2021, 3, 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Antunes, E.; Vuppaladadiyam, A.K.; Kumar, R.; Vuppaladadiyam, V.S.; Sarmah, A.; Islam, M.A.; Dada, T. A circular economy approach for phosphorus removal using algae biochar. Clean. Circ. Bioeconomy 2022, 1, 100005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgarahy, A.M.; Elwakeel, K.Z.; Mohammad, S.H.; Elshoubaky, G.A. A critical review of biosorption of dyes, heavy metals and metalloids from wastewater as an efficient and green process. Cleaner Eng. Technol. 2021, 4, 100209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordóñez, J.I.; Cortés, S.; Maluenda, P.; Soto, I. Biosorption of Heavy Metals with Algae: Critical Review of Its Application in Real Effluents. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, E.M.; Elshaarawy, R.F.; Mahmoud, S.A.; El-Moselhy, K.M. New ulva lactuca algae based chitosan bio-composites for bioremediation of Cd (II) ions. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2021, 6, 223–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obey, G.; Adelaide, M.; Ramaraj, R. Biochar derived from non-customized matamba fruit shell as an adsorbent for wastewater treatment. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2022, 7, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manohara, H.M.; Nayak, S.S.; Franklin, G.; Nataraj, S.K.; Mondal, D. Progress in marine derived renewable functional materials and biochar for sustainable water purification. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 8305–8331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeła, M.; Skuza, M. Towards a circular economy: Analysis of the use of biowaste as biosorbent for the removal of heavy metals. Energies 2021, 14, 5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Alvarado, P.M.; Orozco-Crespo, E.; Verduga-Alcívar, D.A.; Diéguez-Santana, K.; Ruiz-Cedeño, S.D.M.; Sablón-Cossío, N. Prospective of the circular economy in a banana agri-food chain. Tec Empresarial 2023, 17, 34–52. [Google Scholar]
- Liguori, G.; Gaglio, R.; Greco, G.; Gentile, C.; Settanni, L.; Inglese, P. Effect of Opuntia ficus-indica mucilage edible coating on quality, nutraceutical, and sensorial parameters of minimally processed cactus pear fruits. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Es-Sbata, I.; Castro, R.; Carmona-Jiménez, Y.; Zouhair, R.; Durán-Guerrero, E. Influence of different bacteria Inocula and temperature levels on the chemical composition and antioxidant activity of prickly pear vinegar produced by surface culture. Foods 2022, 11, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, P.M.G.; de Souza, I.F.A.C.; Costa, M.C.V.V.; Santos, A.D.F.S.; Coelho, L.C.B.B. Opuntia sp. cactus: Biological characteristics, cultivation and applications. Adv. Res. 2016, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, E.Y.; Ezzat, M.I.; El Hefnawy, H.M.; Abdel-Sattar, E. An overview and update on the chemical composition and potential health benefits of Opuntia ficus-indica (L.) Miller. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sáenz, C.; Sepúlveda, E.; Matsuhiro, B. Opuntia spp mucilage’s: A functional component with industrial perspectives. J. Arid Environ. 2004, 57, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, M.T.F.; Ambrosio, E.; de Almeida, C.A.; de Souza Freitas, T.K.F.; Santos, L.B.; de Cinque Almeida, V.; Garcia, J.C. The use of a natural coagulant (Opuntia ficus-indica) in the removal for organic materials of textile effluents. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 5261–5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majdoub, H.; Roudesli, S.; Picton, L.; Le Cerf, D.; Muller, G.; Grisel, M. Prickly pear nopals pectin from Opuntia ficus-indica physico-chemical study in dilute and semi-dilute solutions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2001, 46, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otálora, M.C.; Wilches-Torres, A.; Gómez Castaño, J.A. Spray-Drying Microencapsulation of Pink Guava (Psidium guajava) Carotenoids Using Mucilage from Opuntia ficus-indica Cladodes and Aloe Vera Leaves as Encapsulating Materials. Polymers 2022, 14, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, E.S.; Awad, O.M.; El-Sayed, M.M. The mucilage of Opuntia ficus indica. Carbohydr. Res. 1970, 15, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobel, P.; Cavelier, J.; Andrade, J.L. Mucilage in cacti: Its apoplastic capacitance, associated solutes, and influence on tissue water relations. J. Exp. Bot. 1992, 43, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldo, S.; Gianguzza, A.; Pettignano, A.; Piazzese, D.; Sammartano, S. Complex formation of copper (II) and cadmium (II) with pectin and polygalacturonic acid in aqueous solution. An ISE-H and ISE-Me 2 Electrochemical Study. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 6722–6737. [Google Scholar]
- Cataldo, S.; Gianguzza, A.; Merli, M.; Muratore, N.; Piazzese, D.; Turco Liveri, M.L. Experimental and robust modeling approach for lead (II) uptake by alginate gel beads: Influence of the ionic strength and medium composition. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2014, 434, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzese, D.; Cataldo, S.; Muratore, N. Voltammetric Investigation on Uranyl Sorption by Alginate Based Material. Influence of Hydrolysis and pH Dependence. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2015, 10, 7423–7439. [Google Scholar]
- Indelicato, S.; Bongiorno, D.; Ceraulo, L. Recent approaches for chemical speciation and analysis by electrospray ionization (esi) mass spectrometry. Front. Chem. 2021, 8, 625945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nharingo, T.; Moyo, M. Application of Opuntia ficus-indica in bioremediation of wastewaters. A critical review. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 166, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, H.; Abdedayem, A.; Hamidi, I.; Najjar, S.S.; Ouederni, A. Biosorption of lead heavy metal on prickly pear cactus biomaterial: Kinetic, thermodynamic and regeneration studies. Cellul. Chem. Technol. 2021, 55, 919–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Trujillo, A.K.I.; Mussali-Galante, P.; de Hoces, M.C.; Blázquez-García, G.; Saldarriaga-Noreña, H.A.; Rodríguez-Solís, A.; Tovar-Sánchez, E.; Sánchez-Salinas, E.; Ortiz-Hernández, L. Biosorption of heavy metals on Opuntia fuliginosa and Agave angustifolia fibers for their elimination from water. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Solano, S.V.; Rodríguez-González, F.; Martínez-Velarde, R.; Morales-García, S.S.; Jonathan, M.P. Removal of heavy metals present in water from the Yautepec River Morelos México, using Opuntia ficus-indica mucilage. Environ. Adv. 2022, 7, 100160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, M.; Kumar, R.; Neogi, S. Activated biochar derived from Opuntia ficus-indica for the efficient adsorption of malachite green dye, Cu+2 and Ni+2 from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 392, 122441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Yang, N.; Li, Y.; Ren, B.; Ding, X.; Bian, H.; Yao, X. Total concentrations and sources of heavy metal pollution in global river and lake water bodies from 1972 to 2017. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 22, e00925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayin, F.; Akar, S.T.; Akar, T.; Celik, S.; Gedikbey, T. Chitosan immobilization and Fe3O4 functionalization of olive pomace: An eco–friendly and recyclable Pb2+ biosorbent. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 269, 118266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Drinking Water Standards and Health Advisories; Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; EPA 822-R-09-011. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S.Y.; Show, P.L.; Lau, B.F.; Chang, J.S.; Ling, T.C. New prospects for modified algae in heavy metal adsorption. Trends Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1255–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiano, F.; Ciofalo, M.; Cacciola, S.O.; Ramirez, S. Metal ion adsorption by Phomopsis sp. biomaterial in laboratory experiments and real wastewater treatments. Water Res. 2005, 39, 2273–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Córdova, B.M.; Venâncio, T.; Olivera, M.; Huamani-Palomino, R.G.; Valderrama, A.C. Xanthation of alginate for heavy metal ions removal. Characterization of xanthate-modified alginates and its metal derivatives. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 169, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvarengan, P.; Kubicki, J.D.; Guégan, J.P.; Châtellier, X. Complexation of carboxyl groups in bacterial lipopolysaccharides: Interactions of H+, Mg2+, Ca2+, Cd2+, and UO22+ with Kdo and galacturonate molecules via quantum mechanical calculations and NMR spectroscopy. Chem. Geol. 2010, 273, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jastrzab, R.; Nowak, M.; Skrobanska, M.; Zabiszak, M. Complexation copper (II) or magnesium ions with d-glucuronic acid–potentiometric, spectral and theoretical studies. J. Coord. Chem. 2016, 69, 2174–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiana, S.; Erre, L.; Micera, G.; Piu, P.; Gessa, C. Coordination of transition-metal ions by polygalacturonic acid: A spectroscopic study. Inorg. Chim. Acta 1980, 46, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Shao, S.; Zhou, J.; Yu, X. Synthesis And Characterization Of Chitosan-Cu(Ⅱ) Complexes. Acta Polym. Sin. 2000, 1, 297–300. [Google Scholar]
- Cotton, F.A.; Wilkinson, G.; Murillo, C.A.; Bochmann, M. Advanced Inorganic Chemistry, 6th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999; ISBN 978-0-471-19957-1. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sayed, G.O.; Dessouki, H.A.; Ibrahiem, S.S. Removal of Zn (II), Cd (II) and Mn(II) from aqueous solution by adsorption on maize stalks. Malays J. Anal. Sci. 2011, 15, 8–21. [Google Scholar]
- Riaz, M.; Nadeem, R.; Hanif, M.A.; Ansari, T.M. Pb (II) biosorption from hazardous aqueous streams using Gossypium hirsutum (Cotton) waste biomass. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.; Ng, J.; McKay, G. Kinetics of pollutants sorption by biosorbents: Review. Separ. Purif. Method. 2000, 29, 189–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, M.; Santos, M.J.; Abrao, T.; Rodriguez, J.; Rigol, A. Modeling competitive metal sorption in a mineral soil. Geoderma 2009, 149, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouki, S.K.; Kavannagh, M. Treatment of metal-contaminated waste waters by use of natural zeolites. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 39, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miretzky, P.; Munoz, C.; Carrillo-Chavez, A. Experimental binding of lead to a low cost on biosorbent: Nopal (Opuntia streptacantha). Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 1211–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onditi, M.; Adelodun, A.A.; Changamu, E.O.; Ngila, J.C. Removal of Pb2+ and Cd2+ from drinking water using polysaccharide extract isolated from cactus pads (Opuntia ficus indica). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 43913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Q.; Jiang, Y.Q.; Nan, H.Y.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, J.N. Unraveling sorption of nickel from aqueous solution by KMnO4 and KOH-modified peanut shell biochar: Implicit mechanism. Chemosphere 2019, 214, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodromou, M.; Pashalidis, I. Copper (II) removal from aqueous solutions by adsorption on non-treated and chemically modified Cactus fibres. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 68, 2497–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barka, N.; Ouzaouit, K.; Abdennouri, M.; El Makhfouk, M. Dried prickly pear Cactus (Opuntia ficus-indica) cladodes as a low-cost and eco-friendly biosorbent for dyes removal from aqueous solutions. J. Taiwan. Inst. Chem. Eng. 2013, 44, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, U.; Kozinski, J.A.; Khan, M.A.; Athar, M. Biosorption of heavy metal ions using wheat based biosorbents—A review of the recent literature. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 5043–5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastopoulos, I.; Massas, I.; Constantinos, E. Use of residues and by-products of the olive-oil production chain for the removal of pollutants from environmental media: A review of batch biosorption approaches. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2015, 50, 677–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Pathania, D.; Sharma, S. Adsorptive remediation of Cu (II) and Ni (II) by microwave assisted H3PO4 activated carbon. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S2836–S2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lin, J.; Chen, H.; Wang, W.; Yang, Y. Comparative Study of Biochar Modified with Different Functional Groups for Efficient Removal of Pb (II) and Ni (II). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Chen, H.; Xi, J.; Yao, D.; Zhou, Z.; Tian, Y.; Lu, X. Biochars with excellent Pb(II) adsorption property produced from fresh and dehydrated banana peels via hydrothermal carbonization. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 232, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, I.N.; Oommen, C. Removal of heavy metals by biosorption using freshwater alga Spirogyra hyaline. J. Environ. Biol. 2012, 33, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Klimmek, S.; Stan, H.J.; Wilke, A.; Bunke, G.; Buchholz, R. Comparative analysis of the biosorption of cadmium, lead, nickel and zinc by algae. Environ. Sci Technol. 2011, 35, 4283–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vianna, L.N.L.; Andrade, M.C.; Vicoli, J.R. Screening of waste biomass from Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Aspergillus oryzae and Bacillus lentus fermentations for removal of Cu, Zn and Cd by biosorption. World J. Microb. Biotechnol. 2000, 16, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selatnia, A.; Boukazoula, A.; Kechid, N.; Bakhti, M.Z.; Chergui, A.; Kerchich, Y. Biosorption of lead (II) from aqueous solution by a bacterial dead Streptomyces rimosus biomass. Biochem. Eng. J. 2004, 19, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selatnia, A.; Madani, A.; Bakhti, M.Z.; Kertous, L.; Mansouri, Y.; Yous, R. Biosorption of Ni2+ from aqueous solution by a NaOH-treated bacterial dead Streptomyces rimosus biomass. Miner. Eng. 2004, 17, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babel, S.; Kurniawan, T.A. Low-cost adsorbents for heavy metals uptake from contaminated water: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. B 2003, 97, 219–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.K.; Singh, A.K.; Sharma, A. Studies on the uptake of lead and zinc by lignin obtained from black liquor—A paper industry waste material. Environ. Technol. 1994, 15, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nharingo, T.; Zivurawa, M.T.; Guyo, U. Exploring the use of cactus Opuntia ficus indica in the biocoagulation–flocculation of Pb (II) ions from wastewaters. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 3791–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barka, N.; Abdennouri, M.; El Makhfouk, M.; Qourzal, S. Biosorption characteristics of cadmium and lead onto eco-friendly dried cactus (Opuntia ficus indica) cladodes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, K.; Palanivelu, K.; Velan, M. Biosorption of copper (II) and cobalt (II) from aqueous solutions by crab shell particles. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1411–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nharingo, T.; Shoniwa, V.; Hunga, O.; Shumba, M. Exploring the biosorption of Methylene Blue dye onto acid treated sugarcane bagasse. Int. J. Curr. Res. 2013, 5, 2169–2175. [Google Scholar]
- Mahamadi, C.; Nharingo, T. Modelling the kinetics and equilibrium properties of cadmium biosorption by river green alga and water hyacinth weed. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2007, 89, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voudrias, E.; Fytianos, F.; Bozani, E. Sorption–desorption isotherms of dyes from aqueous solutions and wastewaters with different sorbent materials. Glob. Nest. Int. J. 2002, 4, 75–83. [Google Scholar]
- Farhan, A.M.; Al-Dujaili, A.H.; Awwad, A.M. Equilibrium and kinetic studies of cadmium (II) and lead (II) ions biosorption onto Ficus carcia leaves. Int. J. Ind. Chem. 2013, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldo, S.; Cavallaro, G.; Gianguzza, A.; Lazzara, G.; Pettignano, A.; Piazzese, D.; Villaescusa, I. Kinetic and equilibrium study for cadmium and copper removal from aqueous solutions by sorption onto mixed alginate/pectin gel beads. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 1252–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebadi, A.; Soltan Mohammadzadeh, J.S.; Khudiev, A. What is the correct form of BET isotherm for modeling liquid phase adsorption? Adsorption 2009, 15, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Metals | Langmuir * | BET * | Freundlich | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r2 | r2 | r2 | Kf | n | µmol | |
| Pb (pH 4.0) | 0.0273 | 0.039 | 0.9842 | 1.48 × 10−1 | 1.08 | 50 |
| Pb (pH 5.0) | 0.9826 | 0.622 | 0.9821 | 6.83 × 10−1 | 1.36 | 98 |
| Cd (pH 4.0) | 0.0904 | 0.588 | 0.9845 | 1.52 × 10−1 | 1.26 | 52 |
| Cd (pH 5.0) | 0.9975 | 0.001 | 0.9833 | 1.18 × 10−1 | 1.10 | 71 |
| Cd (pH 6.0) | 1 | 0.966 | 0.9537 | 1.87 × 10−2 | 0.87 | 22 |
| Ni (pH 4.0) | 0.9755 | 0.576 | 0.9928 | 2.11 × 10−3 | 0.76 | 16 |
| Ni (pH 5.0) | 0.8771 | 0.531 | 0.9818 | 9.74 × 10−3 | 0.80 | 52 |
| Ni (pH 6.0) | 0.9852 | 0.331 | 0.9863 | 1.16 × 10−2 | 0.77 | 31 |
| Cu (pH 4.0) | 0.7346 | 0.371 | 0.9237 | 7.61 × 10−2 | 1.12 | 18 |
| Cu (pH 5.0) | 0.0007 | 0.073 | 0.9808 | 8.58 × 10−2 | 1.07 | 101 |
| Contact Time (min) | Cd | Ni | Cu | Pb | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH4.0 | pH5.0 | pH6.0 | pH4.0 | pH5.0 | pH6.0 | pH4.0 | pH5.0 | pH4.0 | pH5.0 | |
| 30 | 82 ± 4 | 86 ± 6 | 86 ± 5 | 98 ± 1 | 82 ± 6 | 87 ± 3 | 82 ± 4 | 87 ± 3 | 90 ± 7 | 99 ± 8 |
| 60 | 82 ± 3 | 86 ± 9 | 85 ± 7 | 98 ± 5 | 82 ± 5 | 87 ± 4 | 83 ± 5 | 86 ± 2 | 90 ± 10 | 99 ± 6 |
| 1560 | 82 ± 1 | 93 ± 6 | 87 ± 9 | 98 ± 7 | 85 ± 5 | 88 ± 1 | 85 ± 2 | 87 ± 16 | 88 ± 5 | 98 ± 12 |
| Metals Ions | qeq (mg/g) | qeq (mmol/g) | k2 (g/mg min−1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu (pH 4.0) | 14.5 | 0.23 | 0.0023 | 0.9965 |
| Cu (pH 5.0) | 21.3 | 0.33 | 0.0035 | 0.9996 |
| Cd (pH 4.0) | 77.5 | 0.69 | 0.0350 | 1 |
| Cd (pH 5.0) | 32.7 | 0.29 | 0.0066 | 0.9772 |
| Cd (pH 6.0) | 60.2 | 0.54 | 0.0018 | 0.9996 |
| Ni (pH 4.0) | 17.7 | 0.30 | 0.0016 | 0.9975 |
| Ni (pH 5.0) | 9.0 | 0.15 | 0.0032 | 0.9995 |
| Ni (pH 6.0) | 18.9 | 0.32 | 0.1100 | 1 |
| Pb (pH 4.0) | 19.7 | 0.19 | 0.0021 | 0.9798 |
| Pb (pH 5.0) | 113.6 | 0.55 | 0.0092 | 1 |
| Cd | Ni | Cu | Pb | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH 4.0 | pH 5.0 | pH 6.0 | pH 4.0 | pH 5.0 | pH 6.0 | pH 4.0 | pH 5.0 | pH 6.0 | pH 4.0 | pH 5.0 | pH 6.0 |
| 82 ± 4 | 94 ± 5 | 87 ± 7 | 51 ± 4 | 43 ± 3 | 45 ± 3 | 48 ± 2 | 45 ± 3 | - | 103 ± 8 | 114 ± 11 | - |
| Adsorbent Material | Cd | Cu | Ni | Pb | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cactus | 44 | [58] | |||
| Raw fibres | 41 | [59] | |||
| Raw cladodes | 99 | [60] | |||
| Triticum eastivum | 52 | 17 | 87 | [61] | |
| Olive cake | 6 | 30 | [62] | ||
| Rice bran | 202 | [63] | |||
| Corn | 47–64 | 156–244 | [64] | ||
| Lignin | 80 | [65] | |||
| Banana peel | 315 | [65] | |||
| Ascophyllum nodosum | 115 | 70 | 50 | 204 | [66] |
| Vaucheria dichotoma | 31 | 22 | 145 | [67] | |
| Biochar modified | 49 | 44 | [38] | ||
| Phomopsis sp. | 26 | 25 | 6 | 179 | [44] |
| Bacillus lentus | 30 | 30 | [68] | ||
| Rizopus arrhizus | 19 | 104 | [69] | ||
| Streptomyces rimosus | 33 | 135 | [70] | ||
| Chitosan | 6 | 222 | 164 | 16 | [71] |
| Lignin | 1865 | [72] | |||
| Clinoptilolite | 70 | 62 | [55] | ||
| Chabazite | 137 | 175 | [55] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barbera, M.; Indelicato, S.; Bongiorno, D.; Censi, V.; Saiano, F.; Piazzese, D. Untreated Opuntia ficus indica for the Efficient Adsorption of Ni(II), Pb(II), Cu(II) and Cd(II) Ions from Water. Molecules 2023, 28, 3953. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093953
Barbera M, Indelicato S, Bongiorno D, Censi V, Saiano F, Piazzese D. Untreated Opuntia ficus indica for the Efficient Adsorption of Ni(II), Pb(II), Cu(II) and Cd(II) Ions from Water. Molecules. 2023; 28(9):3953. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093953
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarbera, Marcella, Serena Indelicato, David Bongiorno, Valentina Censi, Filippo Saiano, and Daniela Piazzese. 2023. "Untreated Opuntia ficus indica for the Efficient Adsorption of Ni(II), Pb(II), Cu(II) and Cd(II) Ions from Water" Molecules 28, no. 9: 3953. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093953
APA StyleBarbera, M., Indelicato, S., Bongiorno, D., Censi, V., Saiano, F., & Piazzese, D. (2023). Untreated Opuntia ficus indica for the Efficient Adsorption of Ni(II), Pb(II), Cu(II) and Cd(II) Ions from Water. Molecules, 28(9), 3953. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093953







