Structural and Functional Changes in Soybean Protein via Remote Plasma Treatments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
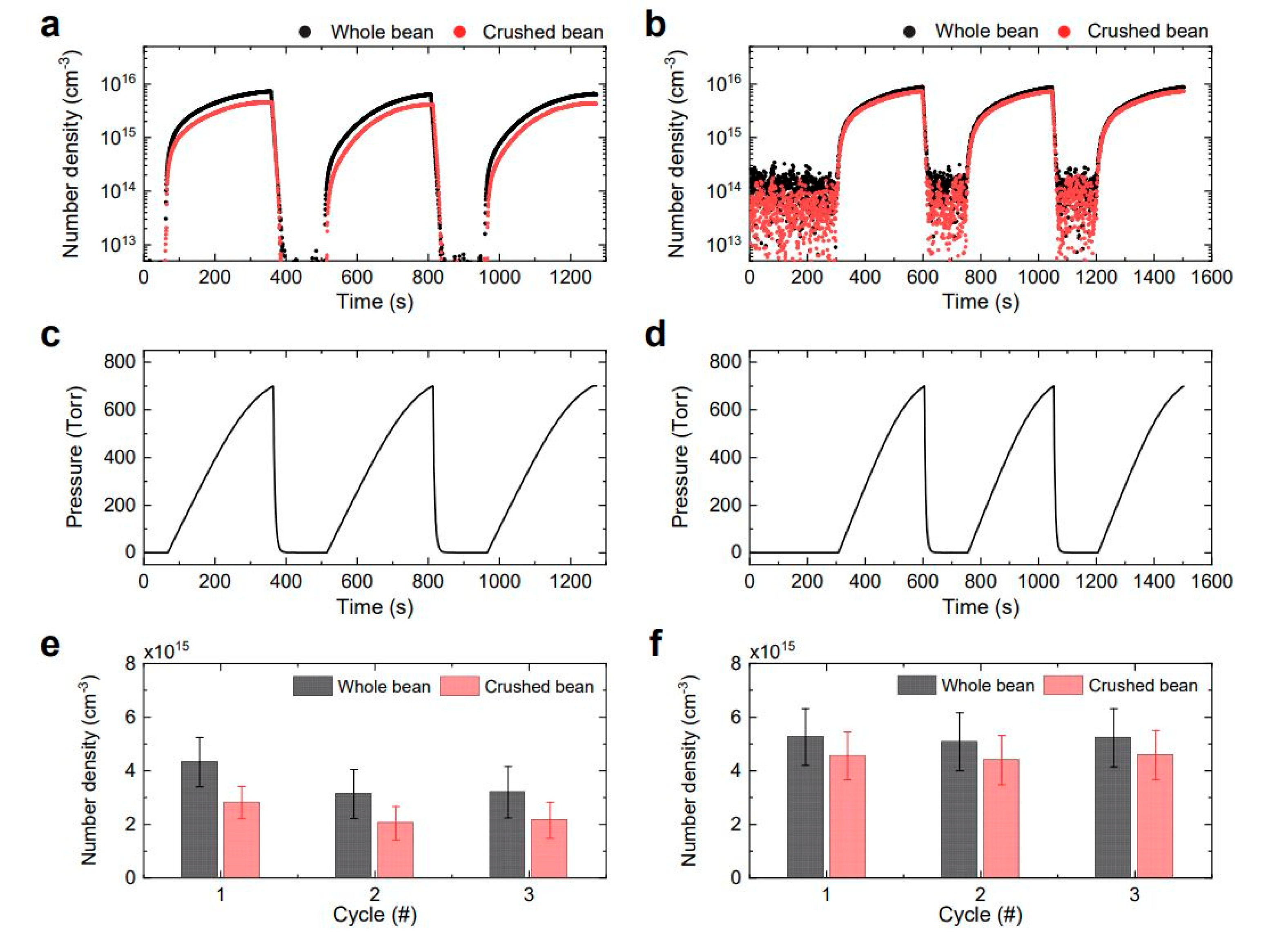
2.1. Ozone and NO2 Concentrations in the Pressure-Swing Reactor
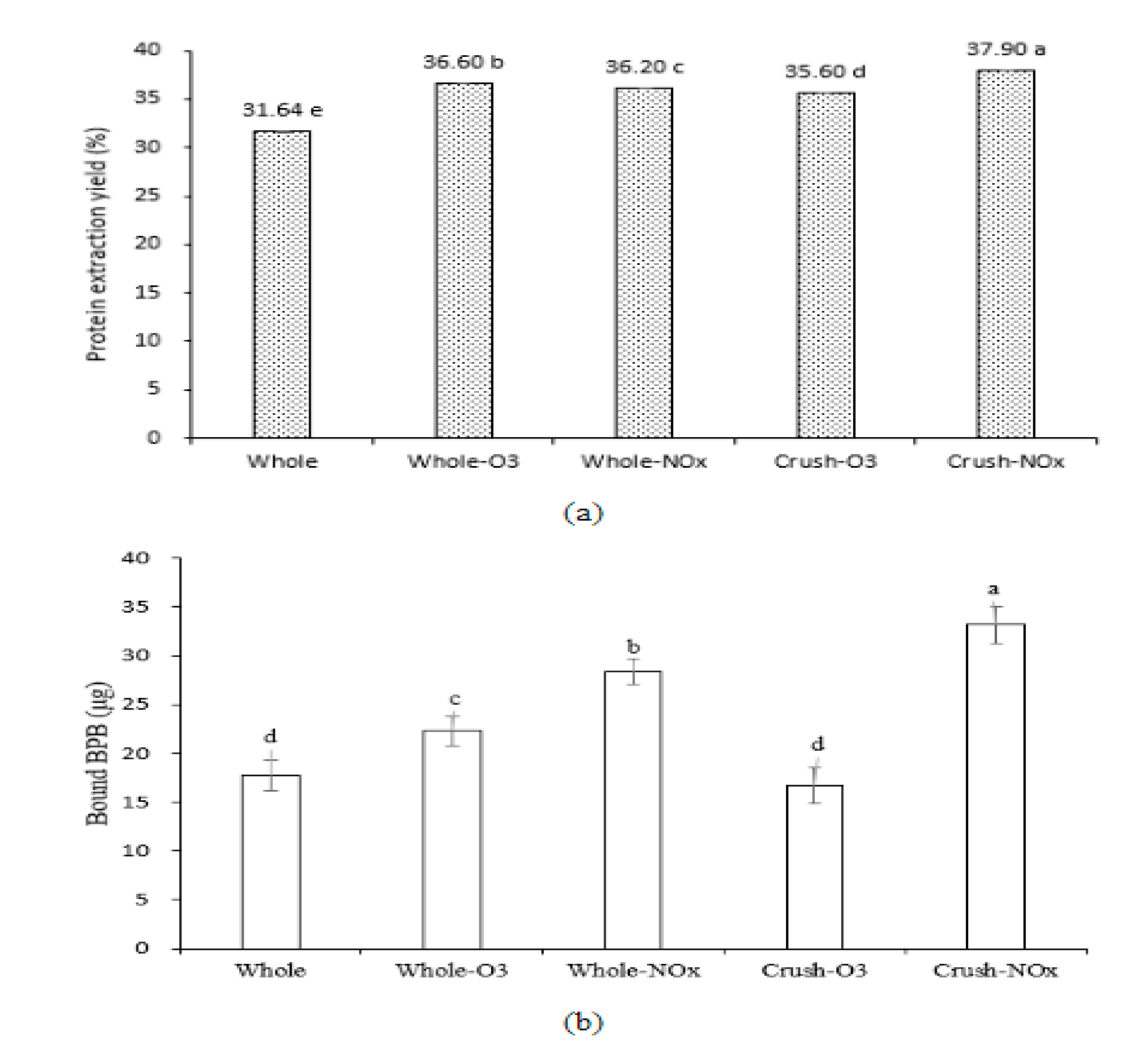
2.2. Functional Properties
2.3. Structural Properties
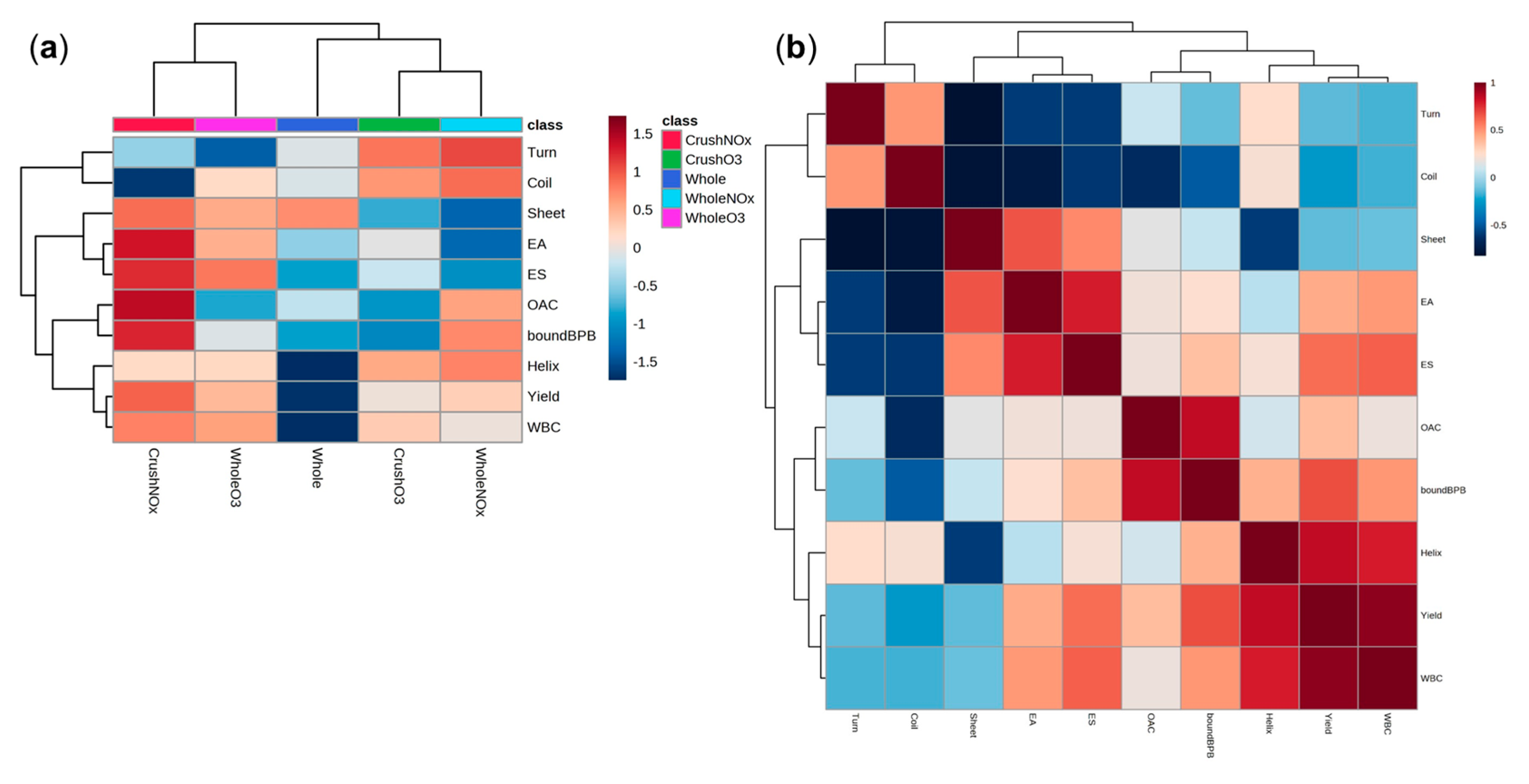
2.4. Heatmap and Correlation Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Samples
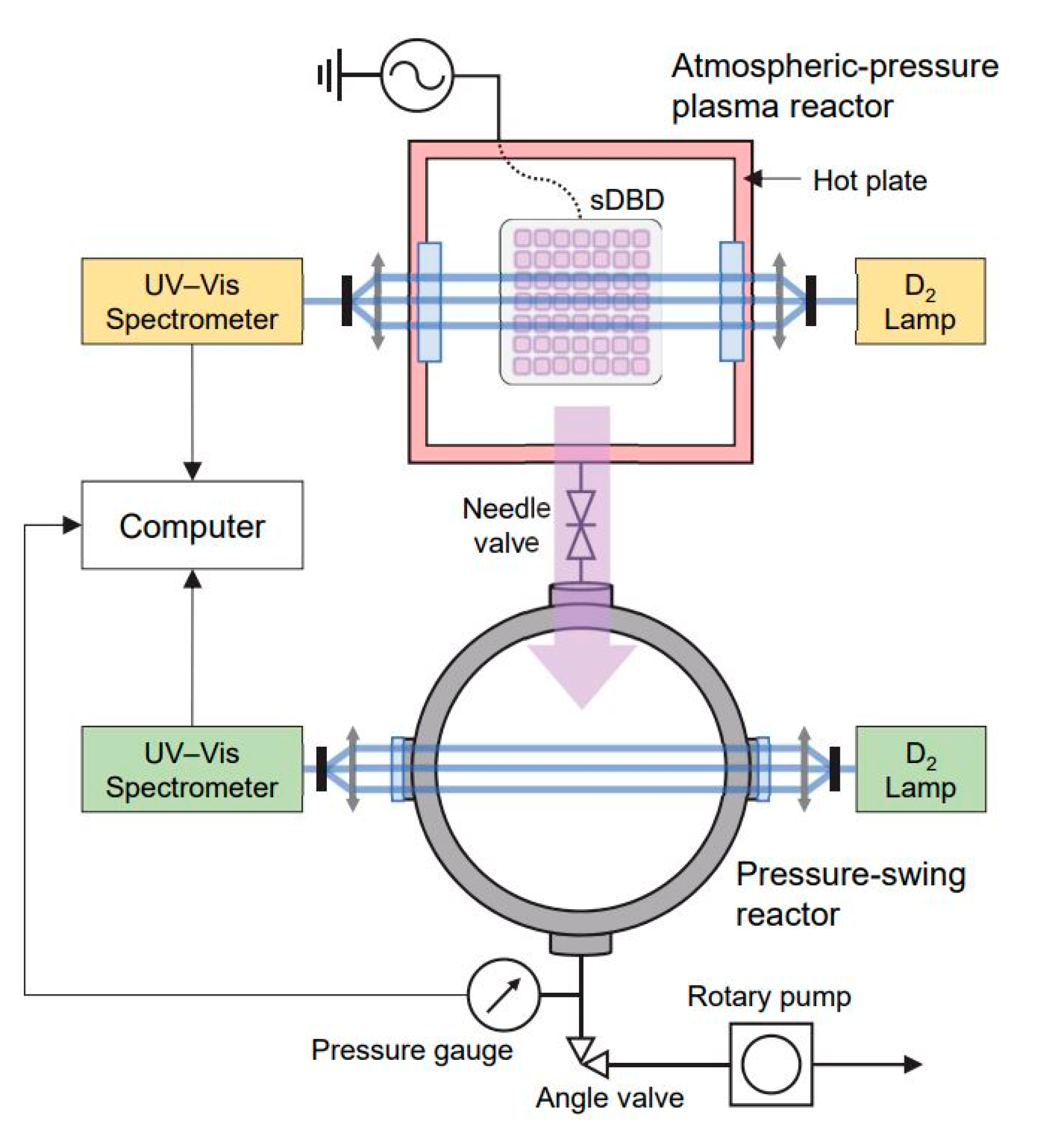
3.2. Experimental Setup for Remote Plasma Treatments
3.3. Protein Extraction
3.4. Functional Properties
3.4.1. Water Binding Capacity and Oil Absorption Capacity
3.4.2. Emulsifying Activity and Emulsion Stability
3.5. Structural Properties
3.5.1. Secondary Structure
3.5.2. Surface Hydrophobicity
3.6. Statistical Analyses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Cabanos, C.; Matsuoka, Y.; Maruyama, N. Soybean Proteins/Peptides: A Review on their Importance, Biosynthesis, Vacuolar Sorting, and Accumulation in Seeds. Peptides 2021, 143, 170598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.P.; Xu, Y.T.; Li, X.T.; Tang, C.H. Improving the Emulsification of Soy β-Conglycinin by Alcohol-Induced Aggregation. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 98, 105307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barać, M.B.; Stanojević, S.P.; Jovanović, S.T.; Pešić, M.B. Soy Protein Modification: A Review. Acta Period. Technol. 2004, 35, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Ding, X.; Dai, C.; Ma, H. Changes in the Structure and Dissociation of Soybean Protein Isolate Induced by Ultrasound-Assisted Acid Pretreatment. Food Chem. 2017, 232, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.; Lamsal, B.P.; Stepien, V.; Johnson, L.A.; Murphy, P.A. Functionality of Soy Protein Produced by Enzyme-Assisted Extraction. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2006, 83, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Dutta, S.; Lamsal, B.P. High-Power Sonication-Assisted Extraction of Soy Protein from Defatted Soy Meals: Influence of Important Process Parameters. J. Food Process Eng. 2021, 44, e13720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, N.N.; Schlüter, O.K.; Cullen, P.J. Cold plasma in Food and Agriculture. In Plasma in Agriculture; Ohta, T., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 209–221. [Google Scholar]
- Sharafodin, H.; Soltanizadeh, N. Potential Application of DBD Plasma Technique for Modifying Structural and Physicochemical Properties of Soy Protein Isolate. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 122, 107077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Lamsal, B.P. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction and Modification of Plant-Based Proteins: Impact on Physicochemical, Functional, and Nutritional Properties. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 1457–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, M.Y.; Lee, S.J.; Min, S.C. Mandarin Preservation by Microwave-Powered Cold Plasma Treatment. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 39, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, F.; Bao, Y.; Ahmed, Z.; Huang, J.Y. Effect of High Voltage Atmospheric Cold Plasma on Extraction of Fenugreek Galactomannan and its Physicochemical Properties. Food Res. Int. 2020, 138, 109776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzegorzewski, F.; Rohn, S.; Kroh, L.W.; Geyer, M.; Schlüter, O. Surface Morphology and Chemical Composition of Lamb’s Lettuce (Valerianella locusta) after Exposure to a Low-Pressure Oxygen Plasma. Food Chem. 2010, 122, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumdas, R.; Trimukhe, A.; Deshmukh, R.R.; Annapure, U.S. Functional and Rheological Properties of Cold Plasma Treated Rice Starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 1723–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavakoli Lahijani, A.; Shahidi, F.; Habibian, M.; Koocheki, A.; Shokrollahi Yancheshmeh, B. Effect of Atmospheric NonThermal Plasma on Physicochemical, Morphology and Functional Properties of Sunn Pest (Eurygaster integriceps)-Damaged Wheat Flour. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 10, 2631–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifian, A.; Soltanizadeh, N.; Abbaszadeh, R. Effects of Dielectric Barrier Discharge Plasma on the Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Myofibrillar Proteins. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg Technol. 2019, 54, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Maximiuk, L.; Fenn, D.; Nickerson, M.T.; Hou, A. Development of a Method for Determining Oil Absorption Capacity in Pulse Flours and Protein Materials. Cereal Chem. 2020, 97, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, N.N.; Kaur, S.; Tiwari, B.K.; Kaur, A.; Singh, N.; Cullen, P.J. Atmospheric Pressure Cold Plasma (ACP) Treatment of Wheat Flour. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 44, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bußler, S.; Steins, V.; Ehlbeck, J.; Schlüter, O. Impact of Thermal Treatment Versus Cold Atmospheric Plasma Processing on the Techno-Functional Protein Properties from Pisum sativum ‘Salamanca’. J. Food Eng. 2015, 167, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Park, P.S.W.; Rhee, K.C. Functional Properties of Proteolytic Enzyme Modified Soy Protein Isolate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1990, 38, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, S.; Annapure, U.S. Recent Trends in the Application of Cold Plasma for the Modification of Plant Proteins—A Review. Future Foods 2022, 5, 100119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, F.; Nayak, G.; Bruggeman, P.; Annor, G.; Ismail, B.P. Impact of Plasma Reactive Species on the Structure and Functionality of Pea Protein Isolate. Food Chem. 2022, 371, 131135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segat, A.; Misra, N.N.; Fabbro, A.; Buchini, F.; Lippe, G.; Cullen, P.J.; Innocente, N. Effects of Ozone Processing on Chemical, Structural and Functional Properties of Whey Protein Isolate. Food Res. Int. 2014, 66, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataratnam, H.; Sarangapani, C.; Cahill, O.; Ryan, C.B. Effect of Cold Plasma Treatment on the Antigenicity of Peanut Allergen Ara h 1. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 52, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Nasiru, M.M.; Wang, Y.; Fu, L. Atmospheric Cold Plasma Treatment of Soybean Protein Isolate: Insights into the Structural, Physicochemical, and Allergenic Characteristics. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Hatab, S.; Yan, J.; Miao, W.; Nyaisaba, B.M.; Piao, X.; Zheng, B.; Deng, S. Changes in Biochemical Properties and Activity of Trypsin-Like Protease (Litopenaeus vannamei) Treated by Atmospheric Cold Plasma (ACP). Foods 2022, 11, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; He, L.; Ma, S.; Wu, W.; Yang, H.; Sun, X.; Peng, A.; Wang, L.; Jin, G.; Zhang, J.; et al. Effect of Irradiation Modification on Conformation and Gelation Properties of Pork Myofibrillar and Sarcoplasmic Protein. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 84, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehr, H.M.; Koocheki, A. Effect of Atmospheric Cold Plasma on Structure, Interfacial and Emulsifying Properties of Grass Pea (Lathyrus sativus L.) Protein Isolate. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 106, 105899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Jo, K.; Jeong, H.G.; Yong, H.I.; Choi, Y.S.; Kim, D.; Jung, S. Freezing-Then-Aging Treatment Improved the Protein Digestibility of Beef in an In Vitro Infant Digestion Model. Food Chem. 2021, 350, 129224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Park, S.; Choe, W.; Yong, H.I.; Jo, C.; Kim, K. Plasma-Functionalized Solution: A Potent Antimicrobial Agent for Biomedical Applications from Antibacterial Therapeutics to Biomaterial Surface Engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 43470–43477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Choe, W.; Jo, C. Interplay Among Ozone and Nitrogen Oxides in Air Plasmas: Rapid Change in Plasma Chemistry. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 352, 1014–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, S.H.; Shin, K.O.; Han, K.S. Studies on the Characteristics of Concentrated Soy Protein. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 52, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Ko, J.Y.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, S.K.; Park, H.Y.; Sim, E.Y.; Oh, S.K.; Woo, K.S. Quality and Antioxidant Characteristics of Commercially Available Mixed Grains in Korea. Korean J. Food Nutr. 2017, 30, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.J.Y.; Humbert, E.S.; Sosulski, F.W. Certain Functional Properties of Sunflower Meal Products. J. Food Sci. 1974, 39, 368–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.J.; Park, J.R. The Effect of Protein Extraction pH on the Functional Properties of Sesame Protein Concentrates. J. Korean Soc. Food Nutr. 1995, 24, 619–624. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, S.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Mehmood, W.; Zhong, M.; Zhang, C.; Blecker, C. Effects of Low Voltage Electrostatic Field Thawing on the Changes in Physicochemical Properties of Myofibrillar Proteins of Bovine Longissimus dorsi Muscle. J. Food Eng. 2019, 261, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Chong, J.; Zhou, G.; de Lima Morais, D.A.; Chang, L.; Barrette, M.; Gauthier, C.; Jacques, P.É.; Li, S.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalyst 5.0: Narrowing the Gap Between Raw Spectra and Functional Insights. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W388–W396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.; Soufan, O.; Li, C.; Caraus, I.; Li, S.; Bourque, G.; Wishart, D.S.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalyst 4.0: Towards More Transparent and Integrative Metabolomics Analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W486–W494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Water Binding Capacity | Oil Absorption Capacity | Emulsifying Activity | Emulsion Stability | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Whole | 190.88 ± 1.11 d | 246.23 ± 1.21 c | 46.50 ± 1.00 bc | 47.33 ± 0.76 c |
| Whole-O3 | 204.43 ± 1.87 ab | 239.23 ± 0.91 d | 47.67 ± 0.76 ab | 49.50 ± 0.87 ab |
| Whole-NOx | 200.93 ± 1.52 c | 256.67 ± 1.50 b | 45.50 ± 0.50 c | 47.17 ± 1.04 c |
| Crush-O3 | 202.57 ± 1.39 bc | 237.60 ± 0.61 d | 47.00 ± 0.00 b | 48.17 ± 0.58 bc |
| Crush-NOx | 205.50 ± 1.53 a | 267.67 ± 0.55 a | 48.67 ± 0.29 a | 50.00 ± 0.00 a |
| α-Helix | β-Sheet | β-Turn | Random Coil | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Whole | 11.43 ± 0.40 c | 36.13 ± 0.76 b | 17.93 ± 0.55 b | 34.50 ± 1.21 d |
| Whole-O3 | 17.97 ± 0.60 b | 33.23 ± 1.36 c | 12.43 ± 1.17 d | 36.37 ± 0.76 c |
| Whole-NOx | 20.47 ± 0.51 a | 13.50 ± 0.17 e | 25.00 ± 0.36 a | 41.03 ± 0.15 a |
| Crush-O3 | 19.47 ± 0.85 a | 17.70 ± 0.53 d | 23.40 ± 1.40 a | 39.43 ± 0.21 b |
| Crush-NOx | 17.93 ± 1.12 b | 39.47 ± 0.64 a | 16.20 ± 0.56 c | 26.40 ± 0.53 e |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H.-J.; Bae, J.H.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.; Jung, S.; Jo, C.; Lee, J.Y.; Seo, J.H.; Park, S. Structural and Functional Changes in Soybean Protein via Remote Plasma Treatments. Molecules 2023, 28, 3882. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093882
Kim H-J, Bae JH, Lee S, Kim J, Jung S, Jo C, Lee JY, Seo JH, Park S. Structural and Functional Changes in Soybean Protein via Remote Plasma Treatments. Molecules. 2023; 28(9):3882. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093882
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Hyun-Joo, Jin Hee Bae, Seonmin Lee, Jinwoo Kim, Samooel Jung, Cheorun Jo, Jin Young Lee, Jung Hyun Seo, and Sanghoo Park. 2023. "Structural and Functional Changes in Soybean Protein via Remote Plasma Treatments" Molecules 28, no. 9: 3882. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093882
APA StyleKim, H.-J., Bae, J. H., Lee, S., Kim, J., Jung, S., Jo, C., Lee, J. Y., Seo, J. H., & Park, S. (2023). Structural and Functional Changes in Soybean Protein via Remote Plasma Treatments. Molecules, 28(9), 3882. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093882






