Hypericin Ameliorates Depression-like Behaviors via Neurotrophin Signaling Pathway Mediating m6A Epitranscriptome Modification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Hypericin Relieve Depressive-like Behavior of UCMS Mice
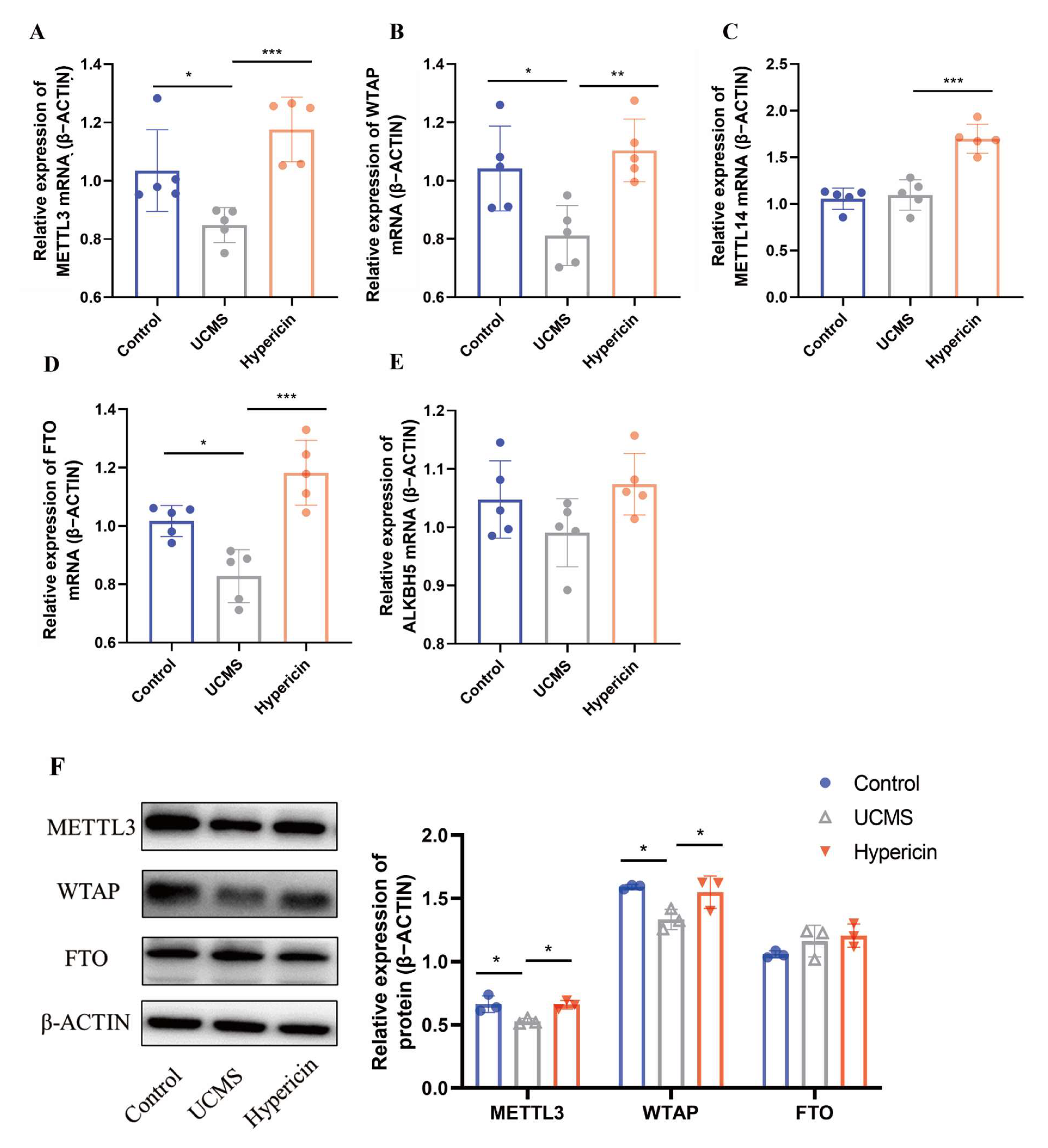
2.2. Hypericin Upregulated the Expression of METTL3 and WTAP
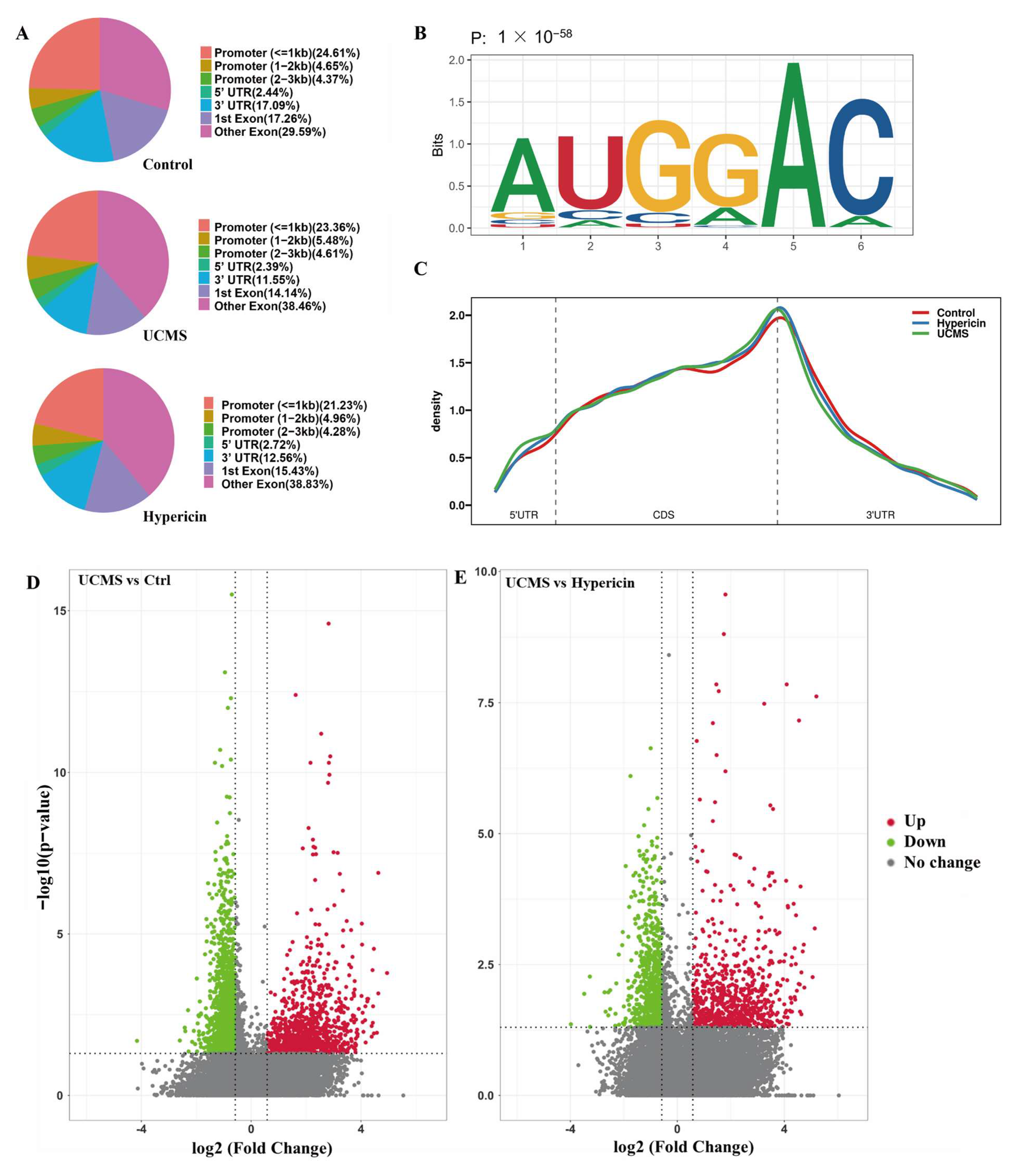
2.3. Hypericin-Treated Stabled m6A Methylation Levels of Hippocampus
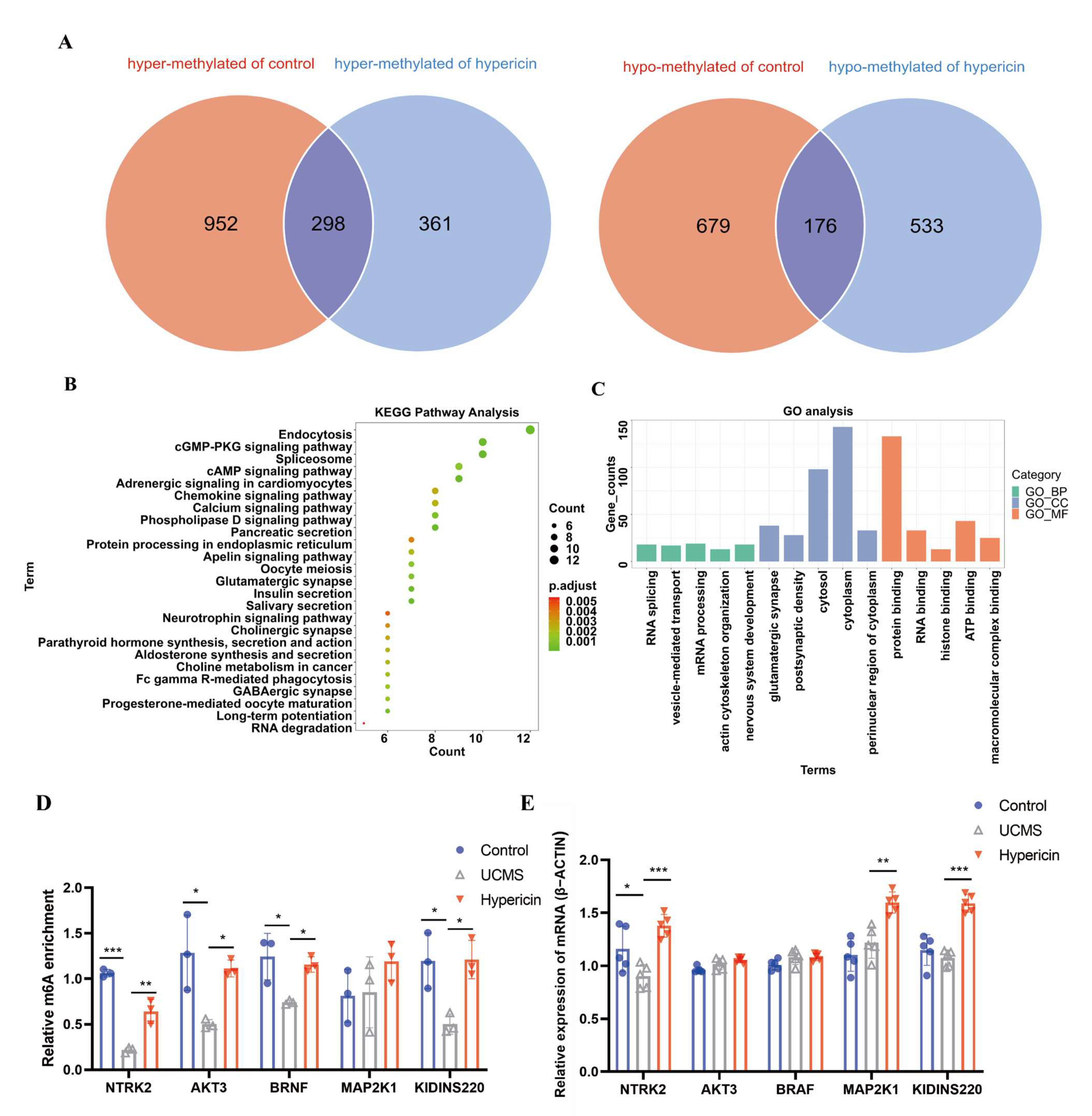
2.4. Hypericin-Treated Regulated mRNA Expression of Hippocampus in UCMS Mice
2.5. Validation of Results Candidate Genes and DMPs
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress Model and Treatments
5.2. Behavioral Tests
5.2.1. Sucrose Preference Test (SPT)
5.2.2. Forced Swimming Test (FST)
5.2.3. Tail Suspension Test (TST)
5.2.4. Open Field Test (OFT)
5.3. Tissue Isolation and mRNA Sequencing
5.4. MeRIP Sequencing
5.4.1. Library Construction
5.4.2. Data Analysis
5.4.3. Differential Peaks Identification and Functional Analysis
5.5. qRT-PCR and MeRIP-qPCR
5.6. Western Blot Analysis
5.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- WHO. Depression. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/depression (accessed on 19 November 2022).
- Abdoli, N.; Salari, N.; Darvishi, N.; Jafarpour, S.; Solaymani, M.; Mohammadi, M.; Shohaimi, S. The global prevalence of major depressive disorder (MDD) among the elderly: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 132, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, V.; Nestler, E.J. Linking molecules to mood: New insight into the biology of depression. Am. J. Psychiatry 2010, 167, 1305–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dell’Osso, L.; Carmassi, C.; Mucci, F.; Marazziti, D. Depression, Serotonin and Tryptophan. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latendresse, G.; Elmore, C.; Deneris, A. Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors as First-Line Antidepressant Therapy for Perinatal Depression. J. Midwifery Women’s Health 2017, 62, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moncrieff, J.; Cooper, R.E.; Stockmann, T.; Amendola, S.; Hengartner, M.P.; Horowitz, M.A. The serotonin theory of depression: A systematic umbrella review of the evidence. Mol. Psychiatry 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bale, T.L. Epigenetic and transgenerational reprogramming of brain development. Nat. Rev. Neuroscience 2015, 16, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binder, E.B. Dissecting the molecular mechanisms of gene x environment interactions: Implications for diagnosis and treatment of stress-related psychiatric disorders. Eur. J. Psychotraumatol. 2017, 8, 1412745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, C.J.; Nestler, E.J. Progress in Epigenetics of Depression. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2018, 157, 41–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Shi, H.; Ye, P.; Li, L.; Qu, Q.; Sun, G.; Sun, G.; Lu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Yang, C.G.; et al. m(6)A RNA Methylation Regulates the Self-Renewal and Tumorigenesis of Glioblastoma Stem Cells. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 2622–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Wang, Q. The Progression of N6-methyladenosine Study and Its Role in Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livneh, I.; Moshitch-Moshkovitz, S.; Amariglio, N.; Rechavi, G.; Dominissini, D. The m(6)A epitranscriptome: Transcriptome plasticity in brain development and function. Nat. Rev. Neuroscience 2020, 21, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, G.; Li, H.B.; Yin, Z.; Flavell, R.A. Recent advances in dynamic m6A RNA modification. Open Biol. 2016, 6, 160003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Hsu, P.J.; Chen, Y.S.; Yang, Y.G. Dynamic transcriptomic m(6)A decoration: Writers, erasers, readers and functions in RNA metabolism. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Xiu, J.; Zhu, C.; Meng, K.; Li, C.; Han, R.; Du, T.; Li, L.; Xu, L.; Liu, R.; et al. Fat mass and obesity-associated protein regulates RNA methylation associated with depression-like behavior in mice. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Yu, C.; Guo, M.; Zheng, X.; Ali, S.; Huang, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Huang, Y.; Qie, S.; et al. Down-Regulation of m6A mRNA Methylation Is Involved in Dopaminergic Neuronal Death. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 2355–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Yang, L.; Wei, W. Role of Fto on CaMKII/CREB signaling pathway of hippocampus in depressive-like behaviors induced by chronic restraint stress mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2021, 406, 113227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Li, Q.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Liu, H.; Xuan, A. Mettl3-mediated m(6) A modification of Lrp2 facilitates neurogenesis through Ythdc2 and elicits antidepressant-like effects. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2022, 36, e22392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.F.; Han, Q.Q.; Chen, F.F.; Shen, T.T.; Li, Y.H.; Cao, Y.; Chen, J.G.; Wang, F. Erasing m(6)A-dependent transcription signature of stress-sensitive genes triggers antidepressant actions. Neurobiol. Stress 2021, 15, 100390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelton, R.C.; Keller, M.B.; Gelenberg, A.; Dunner, D.L.; Hirschfeld, R.; Thase, M.E.; Russell, J.; Lydiard, R.B.; Crits-Cristoph, P.; Gallop, R.; et al. Effectiveness of St John’s wort in major depression: A randomized controlled trial. Jama 2001, 285, 1978–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hamdaoui, Y.; Zheng, F.; Fritz, N.; Ye, L.; Tran, M.A.; Schwickert, K.; Schirmeister, T.; Braeuning, A.; Lichtenstein, D.; Hellmich, U.A.; et al. Analysis of hyperforin (St. John’s wort) action at TRPC6 channel leads to the development of a new class of antidepressant drugs. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 5070–5085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.; Zhang, F.; Hu, R.; Wang, L. METTL3 Promotes Endothelium-Mesenchymal Transition of Pulmonary Artery Endothelial Cells by Regulating TRPC6/Calcineurin/NFAT Signaling Pathways. Evid. -Based Complement. Altern. Med. Ecam 2023, 2023, 8269356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Han, B.; Ju, M.; Chen, B.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; et al. N(6)-Methyladenosine Modification of Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase Messenger RNA in Circular RNA STAG1-Regulated Astrocyte Dysfunction and Depressive-like Behaviors. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 88, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, J.; Wang, B.; Wang, T.; Zhou, T. Mechanism of METTL3-mediated m6A modification in depression-induced cognitive deficits. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Psychiatr. Genet. 2022, 189, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Ma, L.; Zhang, H.; Cao, Y.; Wang, C.; Hou, N.; Huang, N.; von Deneen, K.M.; Zhao, C.; Shi, Y.; et al. Fto Deficiency Reduces Anxiety- and Depression-Like Behaviors in Mice via Alterations in Gut Microbiota. Theranostics 2019, 9, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overduin, J.; Collet, T.H.; Medic, N.; Henning, E.; Keogh, J.M.; Forsyth, F.; Stephenson, C.; Kanning, M.W.; Ruijschop, R.; Farooqi, I.S.; et al. Failure of sucrose replacement with the non-nutritive sweetener erythritol to alter GLP-1 or PYY release or test meal size in lean or obese people. Appetite 2016, 107, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q.; Cao, P.; Ren, X.; Fang, A.; Liao, H.; Liu, L. Obesity and the onset of depressive symptoms among middle-aged and older adults in China: Evidence from the CHARLS. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patten, S.B.; Williams, J.V.; Lavorato, D.H.; Brown, L.; McLaren, L.; Eliasziw, M. Major depression, antidepressant medication and the risk of obesity. Psychother. Psychosom. 2009, 78, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Paz-Filho, G.; Mastronardi, C.; Licinio, J.; Wong, M.L. Is increased antidepressant exposure a contributory factor to the obesity pandemic? Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 6, e759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boiko, A.S.; Pozhidaev, I.V.; Paderina, D.Z.; Bocharova, A.V.; Mednova, I.A.; Fedorenko, O.Y.; Kornetova, E.G.; Loonen, A.J.M.; Semke, A.V.; Bokhan, N.A.; et al. Search for Possible Associations of FTO Gene Polymorphic Variants with Metabolic Syndrome, Obesity and Body Mass Index in Schizophrenia Patients. Pharm. Pers. Med. 2021, 14, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizaki, K.; Asai, M.; Hara, T. High-Fat Diet Enhances Working Memory in the Y-Maze Test in Male C57BL/6J Mice with Less Anxiety in the Elevated Plus Maze Test. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batalla, A.; Homberg, J.R.; Lipina, T.V.; Sescousse, G.; Luijten, M.; Ivanova, S.A.; Schellekens, A.F.A.; Loonen, A.J.M. The role of the habenula in the transition from reward to misery in substance use and mood disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 80, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du Preez, A.; Onorato, D.; Eiben, I.; Musaelyan, K.; Egeland, M.; Zunszain, P.A.; Fernandes, C.; Thuret, S.; Pariante, C.M. Chronic stress followed by social isolation promotes depressive-like behaviour, alters microglial and astrocyte biology and reduces hippocampal neurogenesis in male mice. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 91, 24–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loonen, A.J.; Ivanova, S.A. Circuits Regulating Pleasure and Happiness: The Evolution of the Amygdalar-Hippocampal-Habenular Connectivity in Vertebrates. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loonen, A.J.M.; Ivanova, S.A. Circuits regulating pleasure and happiness—Focus on potential biomarkers for circuitry including the habenuloid complex. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2022, 34, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, M.; Eggert, C.; Kaplick, P.M.; Eder, M.; Röh, S.; Tietze, L.; Namendorf, C.; Arloth, J.; Weber, P.; Rex-Haffner, M.; et al. The Role of m(6)A/m-RNA Methylation in Stress Response Regulation. Neuron 2018, 99, 389–403.e389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, M.; Xie, D.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Ma, D.; Li, W.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, Y.G.; et al. METTL3-mediated N(6)-methyladenosine mRNA modification enhances long-term memory consolidation. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 1050–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichardt, L.F. Neurotrophin-regulated signalling pathways. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2006, 361, 1545–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, N.; Kuruvilla, R. Neurotrophin signaling endosomes: Biogenesis, regulation, and functions. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2016, 39, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewin, G.R.; Barde, Y.A. Physiology of the neurotrophins. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1996, 19, 289–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofroniew, M.V.; Howe, C.L.; Mobley, W.C. Nerve growth factor signaling, neuroprotection, and neural repair. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 24, 1217–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guclu, E.; Inan, S.Y.; Vural, H.C. The Sirtuin 2 Inhibitor AK-7 Leads to an Antidepressant-Like Effect in Mice via Upregulation of CREB1, BDNF, and NTRK2 Pathways. Molecular neurobiology 2022, 59, 7036–7044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhasz, G.; Dunham, J.S.; McKie, S.; Thomas, E.; Downey, D.; Chase, D.; Lloyd-Williams, K.; Toth, Z.G.; Platt, H.; Mekli, K.; et al. The CREB1-BDNF-NTRK2 pathway in depression: Multiple gene-cognition-environment interactions. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 69, 762–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, P.B.; Bettio, L.E.B.; Neis, V.B.; Moretti, M.; Kaufmann, F.N.; Tavares, M.K.; Werle, I.; Dalsenter, Y.; Platt, N.; Rosado, A.F.; et al. Antidepressant-like effect of guanosine involves activation of AMPA receptor and BDNF/TrkB signaling. Purinergic Signal. 2021, 17, 285–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Wong, M.L.; Licinio, J. Sequence variations of ABCB1, SLC6A2, SLC6A3, SLC6A4, CREB1, CRHR1 and NTRK2: Association with major depression and antidepressant response in Mexican-Americans. Mol. Psychiatry 2009, 14, 1105–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, D.E.; Müller, H.K.; Elfving, B.; Eskelund, A.; Joca, S.R.; Wegener, G. Antidepressant-like effect induced by P2X7 receptor blockade in FSL rats is associated with BDNF signalling activation. J. Psychopharmacol. 2019, 33, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Shen, S.; Ji, Y.T.; Li, X.Y.; Zhang, L.S.; Wang, X.D. Melatonin Augments the Effects of Fluoxetine on Depression-Like Behavior and Hippocampal BDNF-TrkB Signaling. Neurosci. Bull. 2018, 34, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.; Shan, J.; Wang, S.; Chang, L.; Pu, Y.; Wang, X.; Tan, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Hashimoto, K. Rapid-acting and long-lasting antidepressant-like action of (R)-ketamine in Nrf2 knock-out mice: A role of TrkB signaling. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2021, 271, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Guo, C.; Li, M.; Yang, L.; Liu, P.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Guo, X.; Cao, S.; Dong, Y.; et al. Hypothalamus-habenula potentiation encodes chronic stress experience and drives depression onset. Neuron 2022, 110, 1400–1415.e1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Cui, Y.; Sang, K.; Dong, Y.; Ni, Z.; Ma, S.; Hu, H. Ketamine blocks bursting in the lateral habenula to rapidly relieve depression. Nature 2018, 554, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyer, C.; Kranaster, L.; Sartorius, A.; Hellweg, R.; Gass, P. Long-term course of brain-derived neurotrophic factor serum levels in a patient treated with deep brain stimulation of the lateral habenula. Neuropsychobiology 2012, 65, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Abdourahman, A.; Tamm, J.A.; Pehrson, A.L.; Sánchez, C.; Gulinello, M. Reversal of age-associated cognitive deficits is accompanied by increased plasticity-related gene expression after chronic antidepressant administration in middle-aged mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2015, 135, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palazzo, E.; Luongo, L.; Guida, F.; Marabese, I.; Romano, R.; Iannotta, M.; Rossi, F.; D’Aniello, A.; Stella, L.; Marmo, F.; et al. D-Aspartate drinking solution alleviates pain and cognitive impairment in neuropathic mice. Amino Acids 2016, 48, 1553–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obach, R.S. Inhibition of human cytochrome P450 enzymes by constituents of St. John’s Wort, an herbal preparation used in the treatment of depression. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000, 294, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Butterweck, V.; Böckers, T.; Korte, B.; Wittkowski, W.; Winterhoff, H. Long-term effects of St. John’s wort and hypericin on monoamine levels in rat hypothalamus and hippocampus. Brain Res. 2002, 930, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assadi, A.; Zarrindast, M.R.; Jouyban, A.; Samini, M. Comparing of the effects of hypericin and synthetic antidepressants on the expression of morphine-induced conditioned place preference. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. IJPR 2011, 10, 916–926. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Zhao, T.; Zhao, S.; Chen, J.; Dou, T.; Ge, G.; Wang, C.; Sun, H.; Liu, K.; Meng, Q.; et al. Substrate-dependent Inhibition of Hypericin on Human Carboxylesterase 2: Implications for Herb-drug Combination. Curr. Drug Metab. 2022, 23, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Chen, Y.; Han, X.; Zhu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y. The protective effect of hypericin on postpartum depression rat model by inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome activation and regulating glucocorticoid metabolism. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 105, 108560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ali, T.; He, K.; Liu, Z.; Shah, F.A.; Ren, Q.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, A.; Li, S. Ibrutinib alleviates LPS-induced neuroinflammation and synaptic defects in a mouse model of depression. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 92, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodburn, S.C.; Bollinger, J.L.; Wohleb, E.S. The semantics of microglia activation: Neuroinflammation, homeostasis, and stress. J. Neuroinflammation 2021, 18, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, N.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, S.; Sun, J.; Ye, M.; Gao, H.; Pu, K.; Wu, M.; Wang, Q.; Zhai, Q. Therapeutic targeting of STING-TBK1-IRF3 signalling ameliorates chronic stress induced depression-like behaviours by modulating neuroinflammation and microglia phagocytosis. Neurobiol. Dis. 2022, 169, 105739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Xie, Z.; Shi, J.; Ou, R.; Wu, H.; Shi, H.; Huang, F.; Wu, X. Hippocampal mRNA expression profiling in mice exposed to chronic unpredictable mild stress. Brain Res. Bull. 2020, 162, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Meng, J.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Y. A novel algorithm for calling mRNA m6A peaks by modeling biological variances in MeRIP-seq data. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, i378–i385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


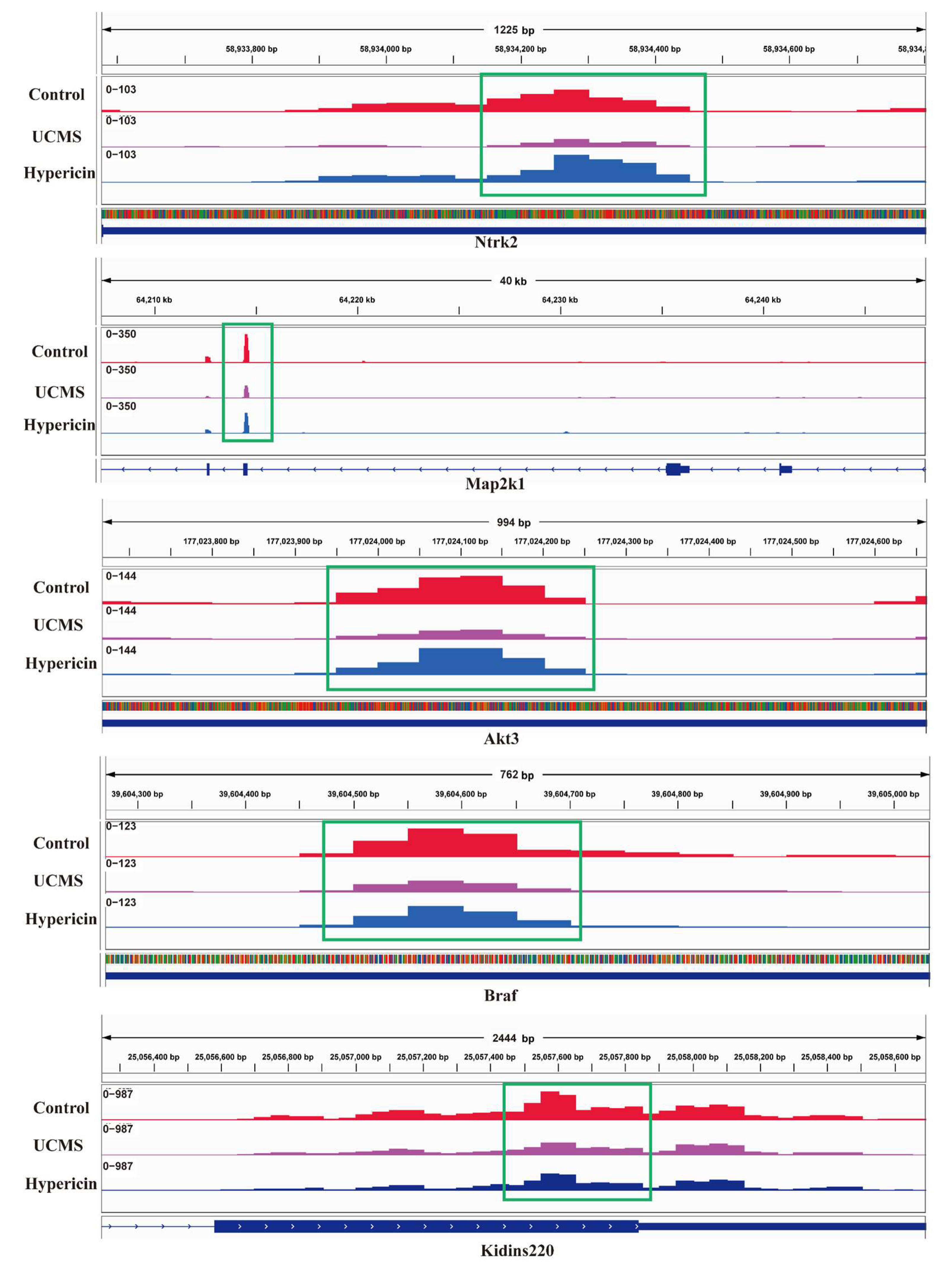
| Genes | Peak Start | Peak End | UCMS vs. Control | UCMS vs. Hypericin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-Value | log2FC | p-Value | log2FC | |||
| NTRK2 | 58,933,914 | 58,934,464 | 8.71 × 10−3 | −0.868 | 5.00 × 10−2 | −0.644 |
| MAP2K1 | 64,214,536 | 64,240,811 | 1.32 × 10−5 | −1.36 | 2.45 × 10−3 | −0.806 |
| AKT3 | 177,024,015 | 177,024,315 | 3.16 × 10−2 | −1.12 | 4.68 × 10−2 | −1.14 |
| BRAF | 39,604,527 | 39,604,777 | 1.15 × 10−2 | −1.16 | 1.62 × 10−4 | −1.72 |
| KIDINS220 | 25,056,695 | 25,058,240 | 8.51 × 10−4 | −0.914 | 8.91 × 10−3 | −0.645 |
| Genes | Description | UCMS vs. Control | UCMS vs. Hypericin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-Value | log2FC | p-Value | log2FC | ||
| Sort1 | Sortilin 1 | 0.04426 | 0.14 | 0.04656 | 0.24 |
| Camk4 | Calcium/calmodulin dependent protein kinase IV | 0.00635 | −0.27 | 0.04506 | −0.24 |
| Arhgdig | Rho GDP dissociation inhibitor gamma | 0.02523 | −0.24 | 0.02066 | −0.36 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lei, C.; Li, N.; Chen, J.; Wang, Q. Hypericin Ameliorates Depression-like Behaviors via Neurotrophin Signaling Pathway Mediating m6A Epitranscriptome Modification. Molecules 2023, 28, 3859. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093859
Lei C, Li N, Chen J, Wang Q. Hypericin Ameliorates Depression-like Behaviors via Neurotrophin Signaling Pathway Mediating m6A Epitranscriptome Modification. Molecules. 2023; 28(9):3859. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093859
Chicago/Turabian StyleLei, Chunguang, Ningning Li, Jianhua Chen, and Qingzhong Wang. 2023. "Hypericin Ameliorates Depression-like Behaviors via Neurotrophin Signaling Pathway Mediating m6A Epitranscriptome Modification" Molecules 28, no. 9: 3859. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093859
APA StyleLei, C., Li, N., Chen, J., & Wang, Q. (2023). Hypericin Ameliorates Depression-like Behaviors via Neurotrophin Signaling Pathway Mediating m6A Epitranscriptome Modification. Molecules, 28(9), 3859. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093859






